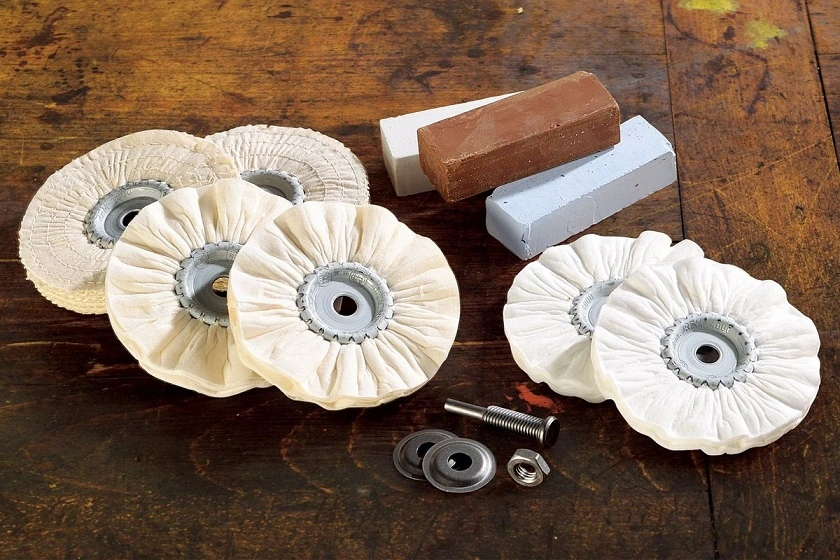

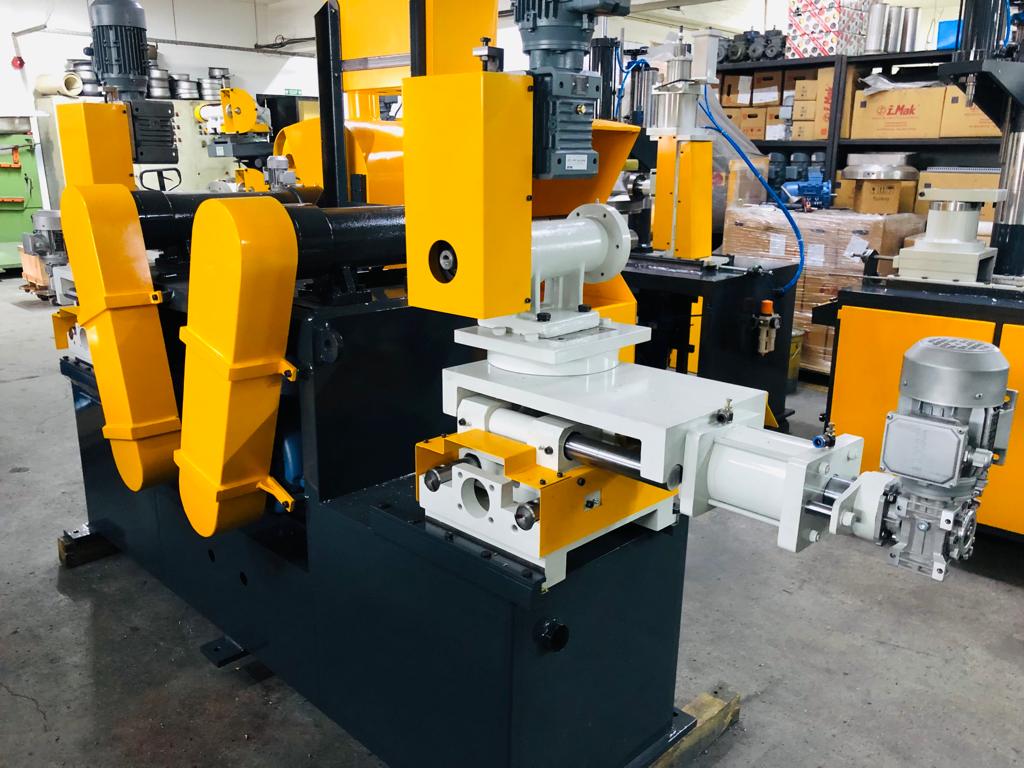
We manufacture a Deburring Aluminium Sheet to deburr the sheet metal edges of Aluminium and Stainless Steel. These machines are used in metalworking industries
When deburring aluminum sheets, there are several methods you can use to remove burrs and smooth out the edges. Here are some common techniques:
- Hand Deburring Tools: You can use handheld deburring tools like files, deburring knives, or deburring blocks to manually remove burrs from the edges of the aluminum sheet. These tools allow for precise control and are suitable for smaller or intricate areas.
- Sandpaper or Emery Cloth: Use fine-grit sandpaper or emery cloth to gently sand away the burrs and smooth out the edges of the aluminum sheet. Start with a coarser grit and gradually move to finer grits for a smoother finish.
- Deburring Wheels or Brushes: Attach a deburring wheel or brush to a rotary tool or bench-mounted deburring machine to remove burrs from the aluminum sheet. These tools work well for larger surfaces and can be more efficient for larger quantities of aluminum sheets.
- Vibratory or Tumbling Deburring: If you have multiple aluminum sheets to deburr, you can consider using a vibratory or tumbling deburring machine. These machines use abrasive media and tumbling action to remove burrs and produce a smoother finish. This method is suitable for batch processing and can save time and effort.
- Chemical Deburring: Chemical deburring involves the use of special chemicals to dissolve the burrs from the aluminum sheet. This method is often used for complex or hard-to-reach areas. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use appropriate safety measures when using chemical deburring solutions.
Remember to always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety glasses and gloves, when deburring aluminum sheets. Additionally, ensure proper ventilation when using chemical deburring methods.
It’s a good practice to test the deburring technique on a scrap or inconspicuous area of the aluminum sheet before working on the final piece to ensure the desired results.
Deburring Aluminium Sheet
Deburring aluminium sheet is an essential process in metalworking to remove sharp edges, burrs, and imperfections from the edges of aluminum sheets. These imperfections can arise from various metalworking processes, such as cutting, stamping, or forming. Deburring is crucial for several reasons:
Safety: Sharp edges and burrs on aluminum sheets pose a significant safety hazard, increasing the risk of cuts, lacerations, and other injuries. Removing these hazards enhances worker safety and reduces the risk of accidents.
Aesthetics: Rounded edges and a smooth surface improve the overall appearance of aluminum sheet components, making them more visually appealing and aesthetically pleasing. This is particularly important for products that will be visible in the final product, such as appliance panels or architectural components.
Functionality: Rounded edges can prevent snagging, tearing, or abrasion of materials that come into contact with the aluminum sheet. This is important for parts that need to move smoothly, such as conveyor belts, machinery components, or packaging materials.
Methods for Deburring Aluminium Sheet:
- Hand Deburring Tools:
For small aluminum sheets or in situations where access is limited, hand-held tools offer a convenient option. Common hand-held deburring tools include:
- Files: Files with varying coarseness levels can be used to remove burrs and smooth out rough edges.
- Deburring Knives: Knives with rounded blades are specifically designed to trim and remove burrs from aluminum sheets.
- Deburring Wheels: Deburring wheels with abrasive grit are effective for deburring aluminum sheets.
- Power Deburring Tools:
For larger aluminum sheets or high-volume production, power tools provide a more efficient and powerful solution. Examples include:
- Rotary Deburring Tools: These tools utilize rotating abrasive discs or belts to quickly remove burrs from aluminum sheets.
- Sanders: Sanders with appropriate abrasive belts can be used for deburring and surface finishing of aluminum sheets.
- Stationary Deburring Machines:
For high-precision deburring or deburring complex shapes, specialized stationary machines offer consistent and precise results. These machines may utilize rotating cutters, abrasive belts, or a combination of both.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Deburring Method:
- Sheet Size and Thickness: The size and thickness of the aluminum sheet will determine the tool’s capacity and suitability.
- Desired Level of Precision: The required level of precision will dictate whether a hand-held tool, a power tool, or a specialized machine is more appropriate.
- Accessibility of Edges: The accessibility of the edges will influence whether a handheld or stationary tool is more suitable.
- Production Volume: For high-volume production, a power tool or a specialized machine may be necessary.
- Cost Considerations: The cost of different deburring methods and tools should be evaluated based on production volume and desired precision.
Conclusion:
Deburring aluminium sheet is an essential step in metalworking to ensure the safety, aesthetics, and functionality of aluminum components. The choice of deburring method depends on factors such as sheet size, precision requirements, accessibility, production volume, and cost considerations. By effectively removing burrs and imperfections, deburring enhances the quality and safety of aluminum products across various industries.
Hand Deburring Tools
Hand deburring tools are manual tools designed to remove burrs and sharp edges from various materials, including metal, plastic, and wood. They offer precise control and are commonly used for small-scale or intricate deburring tasks. Here are some commonly used hand deburring tools:
- Deburring Knife: A deburring knife is a small, handheld tool with a sharp blade specifically designed for removing burrs. It allows for precise cutting and scraping of burrs from the edges of the material.
- Deburring File: Deburring files have fine teeth or abrasive surfaces that can be used to file down burrs and smooth out rough edges. They come in various shapes and sizes, including flat, half-round, round, and needle files, to suit different deburring requirements.
- Deburring Tool with Blades: These handheld tools feature interchangeable blades designed to remove burrs from different materials and contours. The blades are inserted into the tool and can be rotated or replaced as needed.
- Deburring Block or Stone: Deburring blocks or stones are typically made of abrasive materials, such as silicon carbide or aluminum oxide. They are used by rubbing the block or stone against the edges of the material to remove burrs and create a smooth surface.
- Countersink Tool: While primarily used for creating countersunk holes, countersink tools can also be used for deburring. They have a conical-shaped cutting edge that can be run along the edges of the material to remove burrs and chamfer the surface.
- Handheld Sanding or Emery Cloth: Sanding or emery cloth can be wrapped around a finger or held in hand to manually sand down burrs and smooth out edges. Different grits of sandpaper or emery cloth can be used depending on the level of deburring required.
- Wire Brush: Wire brushes with bristles made of stainless steel or brass can be used to remove burrs and clean the surface of the material. They are particularly useful for removing burrs from harder metals.
When using hand deburring tools, ensure you have a secure grip, work in a well-lit area, and wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as safety glasses and gloves. It’s recommended to start with a light touch and gradually increase pressure as needed to avoid damaging the material.
Sandpaper or Emery Cloth
Sandpaper and emery cloth are abrasive materials commonly used for deburring, sanding, and smoothing surfaces. They are available in various grits and can be used by hand or with a sanding block. Here’s how you can use sandpaper or emery cloth for deburring:
- Select the Right Grit: Sandpaper and emery cloth are available in different grit sizes, which determine the coarseness of the abrasive particles. For deburring, start with a coarser grit to remove the burrs and then gradually move to finer grits for a smoother finish. The specific grits to use depend on the material and the extent of the burrs.
- Secure the Material: Place the aluminum sheet or workpiece on a stable surface or secure it in a vise to prevent movement during the deburring process. This ensures stability and helps achieve even results.
- Wrap the Sandpaper or Emery Cloth: If using by hand, wrap the sandpaper or emery cloth around your fingers or a sanding block, ensuring it is taut but not overly tight. If using a sanding block, secure the abrasive material to the block using clips or adhesive.
- Apply Light Pressure: Hold the sandpaper or emery cloth firmly but apply light pressure while rubbing it along the burrs and edges of the aluminum sheet. Move in a back-and-forth or circular motion, following the contours of the material. Avoid excessive pressure that can cause gouging or uneven sanding.
- Check Progress: Regularly check the progress by running your fingers over the surface to feel for any remaining burrs. Inspect the area under good lighting to ensure all burrs have been removed and the surface is smooth.
- Gradually Progress to Finer Grits: As the burrs are removed, switch to progressively finer grits of sandpaper or emery cloth to refine the surface. This helps achieve a smoother finish and removes any scratches or marks left by coarser grits.
- Clean the Surface: After deburring, clean the aluminum sheet to remove any debris or abrasive particles. Use a clean cloth or compressed air to ensure the surface is free from residue.
Remember to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety glasses and a dust mask, to protect yourself from particles generated during the deburring process. Additionally, work in a well-ventilated area or consider using a dust collection system to minimize airborne dust.
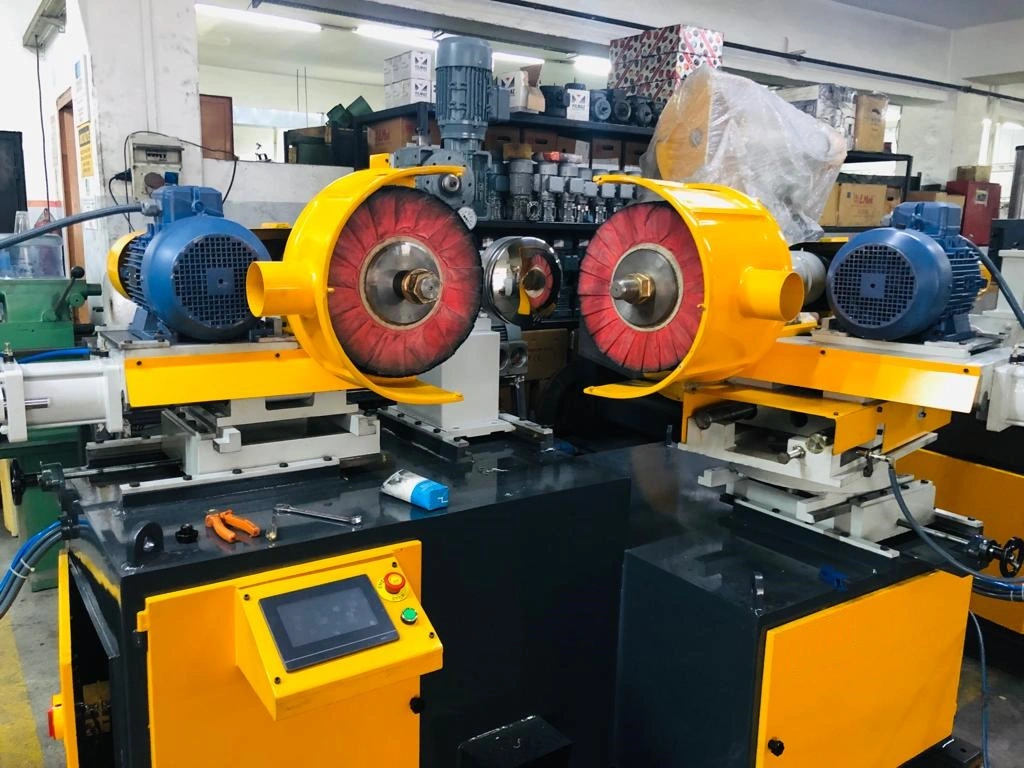
Deburring Wheels or Brushes
Deburring wheels and brushes are rotary tools designed to remove burrs, sharp edges, and other imperfections from various materials. They are commonly used in metalworking, woodworking, and fabrication industries. Here’s an overview of deburring wheels and brushes:
Deburring Wheels: Deburring wheels are typically made of abrasive materials such as bonded abrasive particles, non-woven nylon fibers, or wire bristles. They are attached to rotary tools such as bench grinders, angle grinders, or handheld rotary tools. Deburring wheels come in different shapes, sizes, and abrasive densities to suit various applications.
- Abrasive Wheels: These wheels are made of abrasive materials like aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, or diamond particles. They are effective for removing burrs, grinding, and smoothing edges. The coarseness of the abrasive determines the aggressiveness of the wheel.
- Non-Woven Wheels: Non-woven wheels are made of nylon fibers impregnated with abrasive particles. They are less aggressive than abrasive wheels and provide a more controlled deburring action. Non-woven wheels are suitable for finer deburring and blending operations.
- Wire Wheels: Wire wheels consist of wire bristles in various configurations such as crimped or twisted. They are used for aggressive deburring, cleaning, and rust removal. Wire wheels are available in different wire thicknesses and densities to suit the application.
Deburring Brushes: Deburring brushes are handheld or machine-mounted brushes with bristles made of various materials such as steel wire, stainless steel, or nylon. They are used for targeted deburring and surface conditioning. Deburring brushes come in different shapes, including cup brushes, wheel brushes, and end brushes.
- Wire Brushes: Wire brushes with steel or stainless steel bristles are effective for heavy-duty deburring, rust removal, and cleaning applications. They can be used on different materials, including metal, wood, or plastic.
- Nylon Brushes: Nylon brushes are gentler than wire brushes and are suitable for lighter deburring, cleaning, and surface conditioning tasks. They can be used on delicate materials like aluminum or plastic without causing damage.
When using deburring wheels or brushes, consider the following tips:
- Ensure the wheel or brush is securely mounted on the rotary tool or machine.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety glasses, gloves, and protective clothing.
- Keep a steady hand and maintain control over the tool to avoid unintended damage or injury.
- Use the appropriate wheel or brush for the material and type of deburring required.
- Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for operating speed, pressure, and technique.
- Regularly inspect and replace worn-out wheels or brushes to maintain optimal performance.
Note: It is important to consider the specific requirements of your deburring application and select the appropriate type of deburring wheel or brush accordingly.
Vibratory or Tumbling Deburring
Vibratory or tumbling deburring is a mass finishing process used to remove burrs, sharp edges, and surface imperfections from small to medium-sized parts in bulk. It involves placing the parts along with abrasive media and a deburring compound into a vibratory or tumbling machine. Here’s an overview of vibratory and tumbling deburring:
Vibratory Deburring:
- Process: Vibratory deburring involves placing the parts and abrasive media in a vibratory bowl or tub. The vibratory machine generates vibrations that cause the media and parts to rub against each other, effectively removing burrs and imparting a smooth finish.
- Media: Various types of abrasive media can be used in vibratory deburring, such as ceramic media, plastic media, or stainless steel media. The media selection depends on the material and desired level of deburring.
- Deburring Compound: A deburring compound, also known as a burnishing compound or soap, is often added to the vibratory machine. It enhances the deburring action by providing lubrication and aiding in the removal of burrs.
- Process Control: The duration of the vibratory deburring process can vary depending on the type and quantity of parts, the level of deburring required, and the condition of the media. The process can be monitored and controlled to achieve consistent results.
Tumbling Deburring:
- Process: Tumbling deburring involves placing the parts, abrasive media, and deburring compound into a rotating drum or barrel. The barrel tumbles the contents, causing the parts and media to interact and remove burrs and surface imperfections.
- Media: Similar to vibratory deburring, various types of abrasive media are used in tumbling deburring, including ceramic, plastic, or stainless steel media. The media choice depends on the material and desired deburring outcome.
- Deburring Compound: A deburring compound is often added to the tumbling process to enhance the deburring action and improve the overall surface finish.
- Process Control: Tumbling deburring time can be adjusted based on the part size, complexity, and deburring requirements. The speed of the barrel rotation and the amount of media and compound used can also be controlled to achieve desired results.
Advantages of Vibratory and Tumbling Deburring:
- Suitable for batch processing and deburring multiple parts simultaneously.
- Provides consistent and uniform deburring results.
- Can handle a variety of part shapes, sizes, and materials.
- Helps remove burrs in hard-to-reach areas.
- Can impart a smoother and polished finish on the parts.
Considerations:
- The selection of the appropriate abrasive media, deburring compound, and process parameters depends on the specific part requirements and desired finish.
- It is important to follow safety guidelines and wear appropriate PPE when working with vibratory or tumbling deburring machines.
- Regularly check the condition of the media, compound, and machine parts to maintain optimal performance and avoid contamination.
It’s recommended to consult with deburring equipment manufacturers or experts to determine the most suitable vibratory or tumbling deburring process for your specific parts and requirements.
Chemical Deburring
Chemical deburring is a process used to remove burrs and sharp edges from metal parts using chemical solutions. It is particularly useful for complex or hard-to-reach areas where traditional mechanical deburring methods may be challenging or ineffective. Here’s an overview of the chemical deburring process:
- Process Preparation: The metal parts to be deburred are thoroughly cleaned and prepared for the chemical deburring process. This involves removing any oils, grease, or contaminants from the parts to ensure optimal chemical interaction.
- Chemical Deburring Solution: A specially formulated chemical deburring solution is used for the process. The solution typically contains a combination of acids or alkaline compounds that selectively dissolve the burrs without significantly affecting the base metal.
- Immersion or Spray Method: The parts are either immersed in the chemical deburring solution or subjected to a spray application, depending on the size, complexity, and nature of the parts. Immersion involves placing the parts in a tank filled with the solution, while spray application involves applying the solution onto the parts using spray nozzles.
- Reaction Time: The parts are left in contact with the chemical deburring solution for a specific duration, allowing the solution to dissolve the burrs. The reaction time depends on factors such as the type and thickness of the burrs, the material of the parts, and the concentration of the deburring solution.
- Rinse and Neutralization: After the deburring process, the parts are thoroughly rinsed to remove any residual deburring solution. This is typically done using water or a neutralizing solution to ensure the complete removal of the deburring chemicals.
- Drying and Post-Treatment: Once rinsed, the parts are dried using appropriate methods such as air drying, hot air drying, or other drying techniques. Depending on the specific requirements, additional post-treatment steps may be carried out, such as surface conditioning, passivation, or protective coating application.
Advantages of Chemical Deburring:
- Effective for deburring complex or intricate parts with hard-to-reach areas.
- Consistent and uniform removal of burrs, even in challenging geometries.
- Can be applied to a wide range of metal materials.
- Minimizes the risk of damage or distortion to the parts, compared to mechanical methods.
- Can be automated for high-volume production.
Considerations:
- Chemical deburring requires careful handling of the deburring solution and adherence to safety protocols, including the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
- The selection of the deburring solution and process parameters should be based on the specific material and burr characteristics.
- Environmental considerations should be taken into account, including proper disposal or treatment of the used deburring solution.
It is recommended to consult with chemical deburring solution manufacturers or experts to ensure the appropriate selection and implementation of the chemical deburring process for your specific parts and requirements.
Deburring Tool for Metal
https://www.youtube.com/embed/mMRmnQuYgjE?feature=oembedDeburring Tool for Metal
Deburring tools are essential for removing burrs, sharp edges, and imperfections from metal components. These tools are crucial for maintaining the safety, functionality, and aesthetics of metal products across various industries.
Types of Deburring Tools for Metal:
- Hand-Held Deburring Tools: These tools provide portability and convenient deburring for smaller metal parts or in situations where access is limited. Common hand-held deburring tools include:
- Files: Files with varying coarseness levels are effective for removing burrs and smoothing out rough edges on metal.
- Deburring Knives: Knives with rounded blades are specifically designed to trim and remove burrs from metal edges.
- Deburring Wheels: Deburring wheels with abrasive grit are effective for deburring metal edges.
- Power Deburring Tools: These tools offer greater efficiency and power for deburring larger metal components or in high-volume production. Examples include:
- Rotary Deburring Tools: Utilize rotating abrasive discs or belts to quickly remove burrs from metal parts.
- Sanders: Sanders with appropriate abrasive belts can be used for deburring and surface finishing of metal components.
- Stationary Deburring Machines: For high-precision deburring or deburring complex shapes, specialized stationary machines offer consistent and precise results. These machines may utilize rotating cutters, abrasive belts, or a combination of both.
- Ultrasonic Deburring Systems: For precision deburring of delicate metal parts or complex geometries, ultrasonic deburring offers a gentle and effective method.
Choosing the Right Deburring Tool for Metal

The choice of deburring tool for metal depends on several factors, including:
- Size and shape of the metal part: The tool should be able to accommodate the size and shape of the part comfortably.
- Material of the metal part: The abrasive material used in the tool should be compatible with the material of the part.
- Desired level of precision: The tool should be able to achieve the desired level of precision for the application.
- Production volume: If high-volume production is required, a stationary machine may be more efficient.
- Safety features: The tool should incorporate adequate safety features to protect the operator from potential hazards.
Benefits of Using Deburring Tools for Metal:
- Improved safety: Deburring tools can reduce the risk of injuries to operators by removing sharp edges and burrs.
- Improved functionality: Rounded edges can prevent snagging and protect other components from damage.
- Enhanced aesthetics: A smooth, burr-free surface improves the overall appearance of metal products.
- Increased efficiency: Power deburring tools and stationary machines can significantly reduce deburring time.
Applications of Deburring Tools for Metal:
- Automotive industry: Deburring car bodies, engine components, and other automotive parts.
- Aerospace manufacturing: Deburring precision metal components for aircraft and spacecraft.
- Construction: Deburring metal components for buildings, bridges, and other structures.
- Electronics manufacturing: Deburring metal components for circuit boards, electronic devices, and other electronics.
- Consumer goods manufacturing: Deburring metal components for appliances, furniture, and other consumer products.
Deburring tools play an essential role in maintaining the quality and safety of metal components across various industries. By effectively removing burrs and imperfections, deburring enhances the functionality, aesthetics, and overall value of metal products.
Metal deburring, grinding, and rounding are common applications in metalworking processes aimed at smoothing rough edges, removing burrs, and achieving a uniform finish on metal parts. Here’s a brief overview of each:
- Deburring: This process involves removing sharp edges or burrs left on metal parts after machining, cutting, or forming operations. It improves safety, functionality, and aesthetics of the parts.
- Grinding: Grinding is used to achieve precise dimensional control and surface finish. It involves using abrasive wheels or belts to remove material from a workpiece, often to prepare surfaces for further finishing or to achieve specific tolerances.
- Rounding: Rounding, also known as edge rounding, is done to soften sharp edges or corners on metal parts. It improves part handling, reduces the risk of injury, and can be aesthetically pleasing.
These processes are essential in various industries such as automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and precision engineering, where metal parts must meet high standards of quality, safety, and performance.
- Deburring:
- Purpose: Deburring removes burrs, which are unwanted rough edges or protrusions on metal parts that result from machining, cutting, or forming processes.
- Methods: Deburring can be achieved through various methods such as manual deburring tools, abrasive stones, brushes, tumbling machines (vibratory or centrifugal), or chemical deburring solutions.
- Importance: Removing burrs improves the functional and aesthetic quality of metal parts. It also enhances safety by eliminating sharp edges that could cause injuries during handling or assembly.
- Grinding:
- Purpose: Grinding is used to achieve precise dimensional control, improve surface finish, and remove excess material from metal parts.
- Types: There are several types of grinding processes, including surface grinding, cylindrical grinding, centerless grinding, and internal grinding, each suited for specific part geometries and surface requirements.
- Equipment: Grinding machines use abrasive wheels (grinding wheels or belts) that rotate at high speeds to grind away material from the workpiece.
- Applications: Grinding is crucial for preparing surfaces for further finishing operations (such as polishing or plating), achieving tight tolerances, or removing defects like surface imperfections or weld seams.
- Rounding (Edge Rounding):
- Purpose: Rounding, or edge rounding, involves smoothing sharp edges or corners on metal parts.
- Methods: This can be done through mechanical methods like deburring tools with radius edges, vibratory or centrifugal tumbling processes with rounded media, or automated edge rounding machines.
- Benefits: Rounding improves part handling safety by reducing the risk of cuts or scratches. It also enhances the part’s appearance and can be critical for components that interact with other parts or personnel during assembly or use.
These processes are fundamental in metalworking industries where precision, quality, and safety are paramount. They ensure that metal parts meet exacting standards for functionality, durability, and aesthetics demanded by various applications, from automotive and aerospace to electronics and consumer goods manufacturing.
Deburring

Deburring is a critical process in metalworking that involves the removal of burrs, which are unwanted rough edges or protrusions on metal parts. These burrs typically occur as a result of machining, cutting, or forming operations such as drilling, milling, stamping, or punching.
Importance of Deburring:
- Safety: Removing burrs eliminates sharp edges that can cause injuries during handling or assembly of parts.
- Functionality: Deburring ensures that parts fit together properly without interference from protrusions or rough edges.
- Aesthetics: Smooth edges improve the appearance of parts and enhance overall product quality.
- Performance: Burrs can affect the performance of moving parts or components that require precise tolerances.
Methods of Deburring:
- Manual Deburring Tools: Hand tools such as files, deburring knives, scrapers, or abrasive pads are used to manually remove burrs from small or intricate parts.
- Abrasive Stones and Brushes: Rotary tools equipped with abrasive stones or brushes can be used to remove burrs from larger or more accessible surfaces.
- Tumbling Machines: Vibratory or centrifugal tumbling machines use abrasive media (such as ceramic or plastic pellets) to deburr multiple parts simultaneously. This method is effective for small to medium-sized parts with complex geometries.
- Chemical Deburring: Chemical solutions or processes can be employed to selectively dissolve burrs, particularly in internal passages or complex shapes where mechanical methods may be challenging.
Deburring Considerations:
- Material Type: Different metals (e.g., aluminum, steel, titanium) require specific deburring techniques due to variations in hardness and machinability.
- Part Geometry: Deburring methods are chosen based on the size, shape, and accessibility of the burrs and the part itself.
- Quality Control: Inspecting parts after deburring ensures that all burrs are removed and that the part meets required specifications.
Deburring is essential in industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, and precision engineering, where high-quality, safe, and functional metal components are crucial.
Grinding

Grinding is a machining process used to remove material from a workpiece to achieve desired dimensions and surface finish. It is a versatile process widely used in various industries for both roughing and finishing operations on metal and other materials.
Purpose of Grinding
- Dimensional Control: Grinding allows for precise control over the dimensions of a workpiece, achieving tight tolerances that are difficult to achieve through other machining processes.
- Surface Finish: By using abrasive grains bonded into wheels or belts, grinding can produce smooth surfaces with low roughness values, enhancing the appearance and functionality of the parts.
- Material Removal: Grinding efficiently removes excess material, such as weld beads, casting flash, or stock material from forgings or billets, preparing the workpiece for subsequent operations.
Types of Grinding Processes:
- Surface Grinding: Involves grinding flat surfaces to achieve a smooth finish. It is commonly used for finishing hardened steel, cast iron, and similar materials.
- Cylindrical Grinding: Used to grind the outside diameter of cylindrical workpieces. It is ideal for creating precise roundness and surface finishes on shafts, rods, and other cylindrical components.
- Centerless Grinding: A type of cylindrical grinding where the workpiece is supported between two wheels: the grinding wheel and a regulating wheel. It is used for high-volume production of cylindrical parts with consistent dimensional accuracy.
- Internal Grinding: Grinding the inside diameter of a workpiece. It is used to create precise bores or holes with a smooth surface finish.
Equipment and Tools:
- Grinding Machines: Include surface grinders, cylindrical grinders, centerless grinders, and internal grinders, each designed for specific grinding applications.
- Grinding Wheels: Made from abrasive grains bonded together in various shapes and sizes. Types include aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, and diamond, each suited to different materials and applications.
Applications of Grinding:
- Manufacturing: Grinding is essential in the production of precision components for automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and consumer electronics.
- Tool and Die Making: Used for sharpening cutting tools and dies to maintain sharp edges and precise dimensions.
- Repair and Maintenance: Grinding is also employed for repairing worn or damaged parts by restoring their original dimensions and surface finish.
Grinding is a fundamental machining process that plays a crucial role in achieving the required dimensional accuracy, surface quality, and overall performance of metal parts in modern manufacturing.
Rounding

Rounding, also known as edge rounding or radiusing, is a finishing process used to smooth sharp edges and corners on metal parts. This process is essential for improving safety, enhancing aesthetics, and ensuring proper functionality of the parts, especially in applications where handling and contact with personnel or other components are involved.
Purpose and Benefits of Rounding:
- Safety: Rounded edges reduce the risk of injuries during handling, assembly, or use by eliminating sharp points or edges that could cause cuts or abrasions.
- Aesthetics: Smooth, rounded edges enhance the appearance of metal parts, making them more visually appealing and professional in finished products.
- Functionality: Rounding can improve the performance of parts by reducing stress concentrations at corners, which can extend the service life of components subjected to cyclic loading or wear.
Methods of Rounding:
- Manual Methods: Hand tools such as files, deburring tools with radiused edges, or abrasive pads can be used for small-scale rounding operations on accessible edges and corners.
- Machine Rounding: Automated edge rounding machines or dedicated deburring machines equipped with specialized tools can efficiently round edges and corners of larger or complex-shaped parts.
- Tumbling Processes: Vibratory or centrifugal tumbling machines using abrasive media (e.g., ceramic or plastic pellets) can uniformly round edges of multiple parts simultaneously. This method is effective for small to medium-sized parts with consistent edge profiles.
Considerations for Rounding:
- Part Geometry: The shape and size of the part influence the choice of rounding method. Complex geometries may require specialized equipment or multiple processes to achieve uniform rounding.
- Material Compatibility: Different metals (e.g., aluminum, stainless steel, titanium) and alloys have varying hardness and machinability characteristics, which may affect the choice of rounding tools and methods.
- Surface Finish Requirements: Rounding should maintain or improve the overall surface finish of the part, ensuring it meets functional and aesthetic specifications.
Applications of Rounding:
- Consumer Products: Rounding is crucial in industries such as furniture manufacturing, where rounded edges on metal components improve safety and user comfort.
- Automotive and Aerospace: Parts like brackets, panels, and housings benefit from rounded edges to prevent injuries during assembly and maintenance operations.
- Medical Devices: Ensuring smooth, rounded edges on surgical instruments and equipment enhances patient safety and ease of handling.
Rounding plays a vital role in enhancing the usability, safety, and appearance of metal parts across various industries, contributing to overall product quality and customer satisfaction.
Surface finishing operations are essential processes applied to sheet metal parts to enhance their appearance, functionality, and durability. These operations involve the removal of imperfections, smoothing of surfaces, and application of protective coatings. The importance of surface finishing cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the performance, longevity, and aesthetic appeal of the final product.
- Key Objectives of Surface Finishing:
- Improve aesthetic appearance.
- Enhance corrosion resistance.
- Reduce friction and wear.
- Remove surface defects.
- Prepare surfaces for further processing.
Overview of Surface Finishing Techniques
Surface finishing techniques encompass a wide range of processes, each tailored to achieve specific results. The primary techniques include deburring, polishing, and buffing, each serving a unique purpose in the finishing workflow.
- Deburring: The process of removing burrs—tiny protrusions or unwanted materials—from the edges of sheet metal parts.
- Polishing: Involves smoothing and shining the surface to achieve a reflective finish.
- Buffing: A finishing process that further enhances the shine and smoothness of the surface.
Applications in Industry
Surface finishing operations are vital across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods. The demand for high-quality finishes in these sectors drives innovation and the development of advanced finishing techniques.
- Automotive: Enhancing the appearance and durability of car components.
- Aerospace: Ensuring precision and performance in aircraft parts.
- Electronics: Improving the aesthetic and functional quality of devices.
- Consumer Goods: Increasing the appeal and longevity of products.
Section 2: Deburring in Sheet Metal Parts

Definition and Types of Burrs
Deburring is the process of removing small, unwanted protrusions or burrs that form on the edges of sheet metal parts during manufacturing processes like cutting, drilling, and stamping. Burrs can negatively affect the performance, safety, and appearance of metal parts, making deburring a critical step in the production cycle.
- Types of Burrs:
- Poisson Burr: Caused by material deformation, often appears as a thin edge.
- Roll-Over Burr: Occurs when material is pushed over the edge of a part.
- Tear Burr: Created by tearing of material, resulting in irregular edges.
- Cut-Off Burr: Occurs at the end of the cutting process, often requiring specific removal techniques.
Methods of Burr Removal
The selection of a deburring method depends on factors such as the type of burr, material properties, and desired surface finish. Below are common deburring methods:
Manual Deburring
- Tools Used: Files, scrapers, abrasive pads, and brushes.
- Advantages:
- Cost-effective for small-scale production.
- Provides control over the finishing process.
- Disadvantages:
- Labor-intensive and time-consuming.
- Inconsistent results due to human error.
Mechanical Deburring
- Methods:
- Tumbling: Parts are placed in a tumbler with abrasive media that polishes the edges.
- Vibratory Finishing: Uses vibrations to agitate parts and media for deburring.
- Grinding: Utilizes rotating abrasive wheels to remove burrs.
- Advantages:
- Suitable for large-scale production.
- Consistent and repeatable results.
- Disadvantages:
- May require additional equipment and space.
- Potential for media contamination.
Thermal Deburring
- Process: Involves exposing parts to a controlled explosion of gas to burn away burrs.
- Advantages:
- Effective for hard-to-reach areas.
- Fast and efficient for complex parts.
- Disadvantages:
- High initial setup cost.
- Limited to specific materials.
Electrochemical Deburring
- Process: Involves the use of electrolytic solutions to dissolve burrs.
- Advantages:
- Precise and controlled removal.
- Minimal tool wear.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires careful handling of chemicals.
- High operational costs.
Tools and Equipment Used
- Manual Tools: Files, sandpaper, brushes.
- Mechanical Equipment: Tumblers, grinders, vibratory finishers.
- Advanced Equipment: Thermal deburring machines, electrochemical setups.
Challenges in Deburring
- Material Compatibility: Different materials require specific deburring techniques.
- Cost Considerations: Balancing cost and efficiency in high-volume production.
- Quality Control: Ensuring consistent results across batches.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Automotive Component Deburring
- Objective: Improve the precision and safety of automotive parts.
- Method Used: Mechanical deburring with vibratory finishing.
- Outcome: Enhanced safety and performance of components, reduced production time.
Case Study 2: Aerospace Part Deburring
- Objective: Achieve high precision and reliability in aircraft parts.
- Method Used: Electrochemical deburring for intricate components.
- Outcome: Improved accuracy and reliability, meeting industry standards.
Section 3: Polishing of Sheet Metal Parts

Definition and Purpose
Polishing is a surface finishing process aimed at smoothing and shining metal parts to achieve a reflective finish. It enhances the appearance and functionality of metal parts by removing scratches, pits, and other imperfections.
- Purpose of Polishing:
- Improve aesthetic appeal.
- Increase corrosion resistance.
- Enhance surface smoothness and reflectivity.
- Prepare surfaces for further coating or finishing processes.
Polishing Techniques
Various polishing techniques are employed based on the desired finish and application requirements.
Mechanical Polishing
- Process: Involves the use of abrasive materials to remove surface irregularities.
- Techniques:
- Belt Polishing: Uses abrasive belts for continuous polishing.
- Disk Polishing: Utilizes rotating disks with abrasive pads.
- Buffing Wheels: Employs rotating cloth wheels with polishing compounds.
- Advantages:
- Cost-effective and versatile.
- Suitable for various metals and shapes.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited precision for complex geometries.
- Requires skilled operators for optimal results.
Electropolishing
- Process: Involves the use of an electrolytic bath to dissolve the surface layer of metal, resulting in a smooth and shiny finish.
- Advantages:
- Superior surface finish and reflectivity.
- Removes microscopic imperfections.
- Enhances corrosion resistance.
- Disadvantages:
- High setup and operational costs.
- Limited to specific metals and applications.
Tools and Equipment Used
- Abrasive Belts and Disks: Used for mechanical polishing.
- Buffing Wheels and Compounds: For fine finishing.
- Electropolishing Equipment: Includes electrolytic baths and power supplies.
Comparison of Different Polishing Methods
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | Cost-effective, versatile | Limited precision for complex parts |
| Electropolishing | Superior finish, corrosion resistance | High cost, limited material compatibility |
Applications in Various Industries
- Automotive: Enhancing the appearance of exterior and interior components.
- Medical Devices: Ensuring the smoothness and biocompatibility of implants and tools.
- Aerospace: Improving the aerodynamics and aesthetics of aircraft parts.
- Consumer Electronics: Enhancing the visual appeal of devices and components.
Challenges and Solutions
- Surface Uniformity: Achieving consistent finishes across complex geometries.
- Material Constraints: Adapting techniques for various metals and alloys.
- Environmental Concerns: Managing waste and emissions from polishing processes.
Section 4: Buffing Process for Sheet Metal Parts

Definition and Difference from Polishing
Buffing is a surface finishing process that involves the use of soft cloth wheels and polishing compounds to achieve a high-gloss finish on metal surfaces. While similar to polishing, buffing focuses on enhancing the final appearance rather than removing significant surface imperfections.
- Difference from Polishing:
- Polishing: Involves removing surface material to smooth and refine.
- Buffing: Focuses on creating a high-gloss, reflective finish.
Buffing Techniques
Different buffing techniques are employed based on the desired finish and complexity of the parts.
Manual Buffing
- Process: Involves the use of hand-held buffing wheels and compounds.
- Advantages:
- Flexibility for small-scale production.
- Control over the finishing process.
- Disadvantages:
- Labor-intensive and time-consuming.
- Inconsistent results due to human error.
Automatic Buffing
- Process: Utilizes automated machines and robotic arms for buffing.
- Advantages:
- Suitable for large-scale production.
- Consistent and repeatable results.
- Disadvantages:
- High initial setup cost.
- Limited flexibility for intricate parts.
Buffing Compounds and Materials
Buffing compounds are essential for achieving desired finishes and vary based on the material and application.
- Types of Buffing Compounds:
- Tripoli: Used for initial cutting and smoothing.
- Rouge: Provides a high-gloss finish.
- White Diamond: Removes light scratches and enhances shine.
- Materials Used:
- Cloth Wheels: Made from cotton, flannel, or sisal.
- Buffing Pads: Available in various grades for different finishes.
Tools and Equipment Used
- Buffing Machines: Includes bench grinders and automated buffing stations.
- Buffing Wheels and Pads: Available in different sizes and materials.
- Polishing Compounds: Formulated for specific applications and finishes.
Applications in Various Industries
- Jewelry: Enhancing the luster and appeal of metal pieces.
- Automotive: Achieving high-gloss finishes on body panels and trim.
- Furniture: Polishing metal components for aesthetic appeal.
- Consumer Goods: Improving the appearance of household items and appliances.
Advantages and Limitations
- Advantages:
- Enhances aesthetic appeal and surface smoothness.
- Suitable for various metals and applications.
- Limitations:
- Limited material removal capability.
- Requires careful handling to avoid surface damage.
Section 5: Comparison of Deburring, Polishing, and Buffing
Differences in Techniques and Applications
| Process | Purpose | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Deburring | Remove burrs and imperfections | Manufacturing, machining |
| Polishing | Smooth and shine surfaces | Automotive, aerospace, electronics |
| Buffing | Enhance gloss and appearance | Jewelry, consumer goods, automotive |
Suitability for Different Types of Sheet Metal
- Deburring: Essential for parts with sharp edges and complex geometries.
- Polishing: Suitable for achieving reflective finishes on flat and contoured surfaces.
- Buffing: Ideal for enhancing the appearance of decorative and high-visibility parts.
Cost and Time Considerations
- Deburring: Cost-effective for high-volume production, but may require specialized equipment.
- Polishing: Balances cost with desired finish quality, may involve multiple steps.
- Buffing: Cost-effective for achieving high-gloss finishes, but may require additional polishing.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
- Deburring: Potential for media and chemical contamination, requires proper disposal.
- Polishing: Generates dust and waste, necessitating effective ventilation and filtration.
- Buffing: Involves the use of chemicals, requires protective equipment and safety measures.
Section 6: Advancements in Surface Finishing Technologies
Automation and Robotics
The integration of automation and robotics in surface finishing operations has revolutionized the industry, offering improved efficiency, precision, and consistency.
- Benefits of Automation:
- Reduced labor costs and human error.
- Enhanced precision and repeatability.
- Increased production speed and efficiency.
- Applications:
- Robotic deburring for intricate parts.
- Automated polishing systems for large components.
- Intelligent buffing machines with adaptive control.
Innovative Materials and Techniques
Advancements in materials and techniques continue to drive improvements in surface finishing processes.
- Innovative Materials:
- Advanced Abrasives: Developments in abrasive materials enhance cutting and polishing efficiency.
- Eco-Friendly Compounds: Formulations that reduce environmental impact and improve safety.
- New Techniques:
- Laser Deburring: Uses laser beams to remove burrs with precision.
- Nano-Polishing: Employs nanotechnology for superior surface finishes.
Impact of Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is reshaping surface finishing operations through the integration of smart technologies and data-driven approaches.
- Key Aspects of Industry 4.0:
- IoT Connectivity: Enables real-time monitoring and control of finishing processes.
- Data Analytics: Provides insights into process optimization and quality control.
- AI and Machine Learning: Enhances decision-making and process automation.
Case Studies on Modern Applications
Case Study 1: Automotive Industry
- Objective: Improve production efficiency and finish quality.
- Solution: Implementation of robotic polishing systems with IoT connectivity.
- Outcome: Increased production speed, reduced defects, and enhanced finish quality.
Case Study 2: Aerospace Industry
- Objective: Achieve high precision and consistency in aircraft parts.
- Solution: Integration of AI-driven deburring and polishing systems.
- Outcome: Improved accuracy, reduced waste, and compliance with industry standards.
Section 7: Best Practices and Quality Control
Quality Standards and Certifications
Adhering to quality standards and certifications ensures the reliability and performance of surface-finished parts.
- Key Standards:
- ISO 9001: Quality management systems for consistent product quality.
- ISO 14001: Environmental management standards for sustainable practices.
- NADCAP: Aerospace industry standards for process quality and control.
Inspection Techniques
Effective inspection techniques are crucial for maintaining the quality and consistency of finished parts.
- Visual Inspection: Identifying surface defects and irregularities.
- Dimensional Inspection: Measuring critical dimensions and tolerances.
- Surface Roughness Testing: Assessing surface smoothness and texture.
- Non-Destructive Testing: Evaluating structural integrity without damaging parts.
Process Optimization
Optimizing surface finishing processes enhances efficiency and reduces costs.
- Key Strategies:
- Lean Manufacturing: Minimizing waste and improving workflow.
- Continuous Improvement: Implementing feedback loops for process refinement.
- Process Automation: Utilizing technology for increased efficiency and precision.
Safety Measures and Precautions
Ensuring safety in surface finishing operations is paramount to protect workers and the environment.
- Safety Precautions:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Gloves, masks, goggles, and protective clothing.
- Ventilation and Filtration: Effective air quality management to reduce dust and fumes.
- Training and Education: Ongoing training programs for workers to ensure safe practices.
Section 8: Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
- Surface finishing operations, including deburring, polishing, and buffing, are essential for enhancing the appearance, functionality, and durability of sheet metal parts.
- Deburring removes burrs and imperfections, while polishing smooths and shines surfaces, and buffing enhances gloss and appearance.
- Advancements in technology, automation, and materials continue to drive improvements in surface finishing processes.
Future Trends in Surface Finishing
The future of surface finishing operations will be shaped by continued advancements in automation, materials, and sustainability.
- Emerging Trends:
- Green Technologies: Development of eco-friendly compounds and processes.
- Advanced Robotics: Increased use of robotics for precision and efficiency.
- Smart Manufacturing: Integration of IoT and AI for data-driven process optimization.
Final Thoughts
Surface finishing operations are a vital component of modern manufacturing, contributing to the quality and performance of sheet metal parts across various industries. By staying abreast of technological advancements and best practices, manufacturers can achieve superior finishes and meet the evolving demands of the market.
Types of Polishing

Polishing is primarily categorized into mechanical and chemical methods, each serving different purposes and achieving unique results.
1. Mechanical Polishing
Mechanical polishing involves using abrasive tools and materials to physically remove surface material and achieve a smooth, reflective finish.
a. Belt Polishing
- Process: Uses abrasive belts that continuously rotate around rollers to polish the surface of the metal.
- Applications: Ideal for flat surfaces and edges.
- Advantages: Cost-effective, easy to set up, and suitable for removing larger imperfections.
- Commonly Used Materials:
- Aluminum Oxide: A widely used abrasive for general-purpose polishing.
- Silicon Carbide: Suitable for hard metals and provides a fine finish.
b. Disk Polishing
- Process: Utilizes rotating disks with abrasive pads to polish surfaces.
- Applications: Suitable for curved and irregular surfaces.
- Advantages: Provides uniform pressure and can reach tight spots.
- Commonly Used Materials:
- Diamond Abrasives: Known for cutting efficiency and durability, especially on hard metals.
- Ceramic Abrasives: Used for rapid stock removal and fine finishes.
c. Buffing Wheels
- Process: Employs cloth wheels coated with polishing compounds to achieve a high-gloss finish.
- Applications: Suitable for finishing and enhancing shine on metal surfaces.
- Advantages: Produces a mirror-like finish, ideal for aesthetic applications.
- Commonly Used Materials:
- Cotton and Flannel Wheels: Provide softness and flexibility, allowing for smooth finishes.
- Sisal Wheels: Used for cutting and initial buffing stages due to their firmness.
d. Vibratory Polishing
- Process: Involves placing parts in a vibrating container filled with abrasive media and compounds.
- Applications: Ideal for small and complex parts that require even polishing.
- Advantages: Provides consistent finishes, handles large volumes, and reduces manual labor.
- Commonly Used Materials:
- Ceramic Media: Effective for heavy cutting and smoothing.
- Plastic Media: Used for delicate parts and achieving fine finishes.
2. Chemical and Electrochemical Polishing
Chemical and electrochemical polishing methods involve the use of chemical reactions to remove surface material and achieve a smooth finish.
a. Electropolishing
- Process: Uses an electrolytic bath to dissolve the surface layer of metal, smoothing and leveling the surface.
- Applications: Commonly used in industries requiring high precision and cleanliness, such as medical and food processing.
- Advantages: Removes microscopic burrs, enhances corrosion resistance, and improves surface reflectivity.
- Commonly Used Materials:
- Electrolytic Solutions: Acidic solutions containing phosphoric and sulfuric acids.
- Anodes and Cathodes: Typically made from stainless steel or titanium for durability.
b. Chemical Polishing
- Process: Involves submerging the metal in a chemical solution that selectively removes surface material.
- Applications: Suitable for intricate shapes and areas difficult to reach with mechanical methods.
- Advantages: Provides uniform finishes and is effective for complex geometries.
- Commonly Used Materials:
- Acidic Solutions: Mixtures of nitric, hydrochloric, and sulfuric acids tailored to specific metals.
- Additives: Agents that control the polishing rate and improve surface quality.
3. Abrasive Polishing
Abrasive polishing uses fine abrasive particles to refine the surface, removing minor scratches and achieving a high level of smoothness.
a. Sandblasting
- Process: Propels fine abrasive particles against the surface of the metal to remove contaminants and smoothen the surface.
- Applications: Suitable for preparing surfaces for painting or coating.
- Advantages: Fast and effective for large surfaces and tough residues.
- Commonly Used Materials:
- Silica Sand: Traditional abrasive for general-purpose sandblasting.
- Glass Beads: Provides a smoother finish and is less aggressive than sand.
- Garnet: Known for its hardness and sharpness, ideal for heavy-duty applications.
b. Lapping
- Process: Involves using a lapping plate and abrasive slurry to achieve a fine, flat surface finish.
- Applications: Used in precision applications requiring tight tolerances, such as in optics and semiconductor industries.
- Advantages: Produces extremely flat surfaces and fine finishes.
- Commonly Used Materials:
- Diamond Slurry: Provides precision and is used for hard materials.
- Aluminum Oxide Slurry: Suitable for softer materials and less abrasive applications.
c. Micro-Abrasive Blasting
- Process: Uses a controlled stream of micro-abrasive particles to remove fine surface layers.
- Applications: Ideal for delicate and detailed parts requiring precision.
- Advantages: Highly controlled process, reduces risk of surface damage.
- Commonly Used Materials:
- Aluminum Oxide Powder: Common for general applications and provides a good balance of cutting and polishing.
- Sodium Bicarbonate: Gentle abrasive for sensitive materials.
Materials Used in Polishing

The choice of materials used in polishing depends on the type of metal, desired finish, and specific polishing method. Below are commonly used materials and compounds in metal polishing:
1. Abrasive Materials
- Aluminum Oxide: A versatile and widely used abrasive for various metals, including steel and aluminum. It provides a good balance between cutting and finishing capabilities.
- Silicon Carbide: Known for its hardness and sharpness, it is used for polishing hard metals and achieving a smooth surface.
- Diamond Abrasives: Offers superior cutting efficiency and is ideal for polishing hard and brittle metals, such as tungsten and ceramics.
- Ceramic Abrasives: Used for heavy-duty applications, offering high material removal rates and durability.
2. Polishing Compounds
Polishing compounds are essential in achieving the desired finish and are formulated for specific metals and applications.
a. Tripoli Compound
- Description: A coarse compound used for initial cutting and smoothing of surfaces.
- Applications: Commonly used on softer metals like aluminum and brass to remove scratches and surface imperfections.
b. Rouge Compound
- Description: A fine polishing compound used for achieving a high-gloss finish.
- Applications: Ideal for polishing precious metals such as gold and silver, as well as achieving a mirror-like finish on stainless steel.
c. White Diamond Compound
- Description: A versatile compound used for polishing and refining surfaces.
- Applications: Suitable for use on plastics and metals, providing a bright finish and removing light scratches.
d. Green Chromium Oxide Compound
- Description: A compound containing chromium oxide, used for achieving a fine finish.
- Applications: Ideal for polishing stainless steel and other hard metals, providing a high level of smoothness and shine.
3. Polishing Pads and Wheels
Polishing pads and wheels come in various materials and are selected based on the desired finish and application requirements.
- Cotton Buffing Wheels: Soft and flexible, suitable for applying polishing compounds and achieving a smooth finish.
- Flannel Buffing Wheels: Provide a finer finish and are often used in the final buffing stage.
- Sisal Buffing Wheels: Firm and durable, used for cutting and initial buffing stages.
- Foam Polishing Pads: Used in conjunction with polishing compounds for fine finishing and detailing.
4. Chemical Solutions
Chemical solutions play a critical role in chemical and electrochemical polishing processes, providing the necessary reactions to achieve desired surface finishes.
- Electrolytic Solutions: Composed of acids like phosphoric and sulfuric acids, used in electropolishing to dissolve surface material and enhance smoothness.
- Chemical Polishing Solutions: Tailored mixtures of acids and additives designed for specific metals and applications, providing controlled material removal and surface refinement.
Conclusion
Polishing is a vital surface finishing process that enhances the appearance and functionality of metal parts. By understanding the various polishing methods and materials, manufacturers can achieve the desired finishes for different applications and industries. Whether through mechanical, chemical, or abrasive techniques, the choice of polishing materials and compounds plays a crucial role in achieving high-quality surface finishes.
Best Polishing Methods for Metal

Polishing metal surfaces is a critical step in many manufacturing processes, enhancing both the aesthetic appeal and functional properties of metal parts. The best polishing methods depend on various factors, including the type of metal, the desired finish, and specific application requirements. Below, we’ll explore some of the most effective polishing methods and their respective advantages, disadvantages, and suitable applications.
1. Mechanical Polishing
Mechanical polishing is one of the most commonly used methods due to its versatility and effectiveness in achieving smooth, shiny surfaces. This method involves using abrasive materials to physically remove surface imperfections.
a. Belt Polishing
Process: Belt polishing uses continuous abrasive belts to grind and polish metal surfaces. It is suitable for flat and slightly curved surfaces.
- Advantages:
- Cost-effective and suitable for high-volume production.
- Can handle a wide range of metals, including steel, aluminum, and brass.
- Efficient at removing larger surface imperfections.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited precision for intricate parts and complex geometries.
- May require additional finishing steps to achieve a mirror-like finish.
- Applications:
- Automotive parts such as body panels and bumpers.
- Large metal sheets and plates.
- Metal furniture components.
b. Disk Polishing
Process: Disk polishing involves rotating abrasive disks to smooth and shine metal surfaces. It is often used for smaller or more intricate parts.
- Advantages:
- Provides uniform pressure and consistent results.
- Suitable for complex shapes and small parts.
- Versatile for a range of metals and finishes.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires skilled operators to avoid over-polishing.
- Limited to flat and moderately curved surfaces.
- Applications:
- Jewelry and small metal components.
- Precision instruments and tools.
- Metal parts with intricate designs.
c. Vibratory Polishing
Process: Vibratory polishing involves placing metal parts in a vibrating container filled with abrasive media and compounds. The vibrations cause the media to polish the surfaces of the parts.
- Advantages:
- Ideal for large batches of small parts.
- Provides even polishing across surfaces.
- Reduces manual labor and operator fatigue.
- Disadvantages:
- Slower than other mechanical methods.
- Limited to smaller parts and components.
- Applications:
- Small automotive components.
- Hardware and fasteners.
- Jewelry and decorative items.
d. Buffing Wheels
Process: Buffing involves using cloth wheels and polishing compounds to achieve a high-gloss finish on metal surfaces. It is often used as a final finishing step.
- Advantages:
- Achieves a mirror-like, high-gloss finish.
- Suitable for a wide range of metals, including stainless steel and aluminum.
- Enhances the aesthetic appeal of metal surfaces.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited material removal capability.
- Requires careful handling to avoid surface damage.
- Applications:
- Automotive trim and decorative parts.
- Consumer electronics and appliances.
- Jewelry and luxury goods.
2. Chemical and Electrochemical Polishing
Chemical and electrochemical polishing methods use chemical reactions to smooth and refine metal surfaces, offering high precision and uniform finishes.
a. Electropolishing
Process: Electropolishing involves submerging metal parts in an electrolytic bath, where controlled electrical currents dissolve the surface layer of the metal, smoothing and leveling it.
- Advantages:
- Produces superior surface finishes with excellent reflectivity.
- Removes microscopic burrs and imperfections.
- Enhances corrosion resistance and passivation of metals.
- Disadvantages:
- High initial setup and operational costs.
- Limited to conductive materials like stainless steel, titanium, and aluminum.
- Applications:
- Medical devices and implants.
- Food processing equipment.
- Aerospace components.
b. Chemical Polishing
Process: Chemical polishing involves immersing metal parts in a chemical solution that selectively removes surface material, refining and smoothing the surface.
- Advantages:
- Uniform finishes on complex geometries.
- Suitable for delicate parts and thin-walled components.
- Reduces surface stress and improves fatigue resistance.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires precise control of chemical concentrations and temperature.
- Potential environmental and safety concerns with chemical handling.
- Applications:
- Intricate metal parts and components.
- Electronics and semiconductor industries.
- Decorative metal products.
3. Abrasive Polishing
Abrasive polishing methods involve using fine abrasive particles to achieve a smooth and refined surface finish, often used for precision applications.
a. Lapping
Process: Lapping uses a lapping plate and abrasive slurry to achieve flat, smooth surfaces with tight tolerances. It is often used for precision applications.
- Advantages:
- Achieves extremely flat and smooth surfaces.
- Suitable for high-precision parts and components.
- Provides tight tolerances and uniform finishes.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires specialized equipment and expertise.
- Limited to flat surfaces and precision applications.
- Applications:
- Optics and lenses.
- Semiconductor wafers.
- Precision mechanical components.
b. Micro-Abrasive Blasting
Process: Micro-abrasive blasting uses a controlled stream of micro-abrasive particles to remove fine surface layers and achieve precision finishes.
- Advantages:
- Highly controlled process for precision applications.
- Suitable for delicate and detailed parts.
- Minimizes surface damage and distortion.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited to small areas and precision applications.
- Requires specialized equipment and expertise.
- Applications:
- Aerospace and aviation components.
- Medical devices and instruments.
- Precision electronics and circuit boards.
Comparison of Polishing Methods
Here’s a table comparing the various polishing methods to highlight their advantages, disadvantages, and applications:
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Belt Polishing | Cost-effective, handles large surfaces | Limited precision, may require additional finishing | Automotive parts, large metal sheets |
| Disk Polishing | Uniform pressure, suitable for intricate parts | Skilled operation required, limited to flat surfaces | Jewelry, precision instruments, complex shapes |
| Vibratory Polishing | Even polishing, suitable for large batches | Slower process, limited to small parts | Small automotive components, hardware, jewelry |
| Buffing Wheels | Achieves high-gloss finish, enhances aesthetics | Limited material removal, requires careful handling | Automotive trim, consumer electronics, jewelry |
| Electropolishing | Superior finishes, removes microscopic burrs, enhances corrosion resistance | High setup costs, limited to conductive materials | Medical devices, food processing, aerospace components |
| Chemical Polishing | Uniform finishes on complex geometries, reduces surface stress | Precise control required, environmental concerns | Intricate parts, electronics, decorative products |
| Lapping | Extremely flat surfaces, tight tolerances | Requires specialized equipment, limited to flat surfaces | Optics, semiconductor wafers, precision components |
| Micro-Abrasive Blasting | Controlled process, suitable for delicate parts | Limited to small areas, requires specialized equipment | Aerospace components, medical devices, precision electronics |
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Polishing Method
Selecting the best polishing method for a specific application involves considering several key factors:
- Material Type: Different metals have varying properties, such as hardness and corrosion resistance, that affect their suitability for specific polishing methods. For example, stainless steel benefits from electropolishing due to its corrosion resistance, while softer metals like aluminum can be effectively polished using mechanical methods.
- Desired Finish: The intended appearance and surface quality of the finished product influence the choice of polishing method. For instance, a high-gloss finish may require buffing, while a matte finish could be achieved with abrasive blasting.
- Component Geometry: The shape and complexity of the metal parts play a crucial role in determining the most suitable polishing method. Intricate geometries may require chemical or electrochemical polishing for uniform finishes, while flat surfaces can be efficiently polished using mechanical methods.
- Production Volume: The scale of production impacts the choice of polishing method, with high-volume production benefiting from automated mechanical processes and small-batch or custom work requiring more manual techniques.
- Cost and Efficiency: The overall cost and efficiency of the polishing process, including equipment, labor, and materials, must be evaluated to determine the most cost-effective solution without compromising quality.
- Environmental and Safety Considerations: The environmental impact and safety of the polishing process, including waste management and operator safety, should be considered when selecting a method. Chemical processes may require special handling and disposal procedures, while mechanical methods can generate dust and noise.
Conclusion
Polishing is a vital process in the metalworking industry, significantly impacting the appearance and functionality of metal parts. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each polishing method, manufacturers can select the most appropriate technique to achieve the desired finish and meet specific application requirements. Whether through mechanical, chemical, or abrasive methods, the choice of polishing technique plays a critical role in producing high-quality, durable metal products.
What is Industrial Buffing?

Industrial buffing is a crucial process in the metal finishing industry, aimed at enhancing the appearance and functional properties of metal surfaces. It involves using buffing wheels and compounds to produce smooth, reflective finishes on various metal products. This section will explore the methods, materials, applications, and advancements in industrial buffing, providing a comprehensive understanding of this essential metalworking technique.
Industrial buffing is a surface finishing process used to achieve a high-gloss, mirror-like finish on metal surfaces. It involves using buffing wheels made from cloth, felt, or other materials, along with buffing compounds, to polish and smoothen the surface of metal parts. Buffing is often the final step in the finishing process, following grinding or polishing, to achieve the desired surface quality.
Objectives of Industrial Buffing
- Enhance Aesthetic Appeal: Buffing improves the visual appearance of metal parts by creating a reflective, glossy surface.
- Improve Surface Smoothness: The process removes fine scratches and imperfections, resulting in a smooth, even surface.
- Increase Corrosion Resistance: A polished surface can help reduce the risk of corrosion by minimizing surface irregularities where moisture could accumulate.
- Prepare for Further Coating: Buffing can prepare metal surfaces for additional coatings, such as paint or plating, by ensuring a smooth base.
Buffing Methods
Industrial buffing can be performed using various methods, each tailored to specific applications and desired finishes. Below are the primary methods used in industrial buffing:
1. Manual Buffing
Manual buffing involves skilled operators using hand-held buffing tools to polish metal surfaces. This method is often used for small-scale production or intricate parts requiring precise attention to detail.
- Advantages:
- Provides greater control over the buffing process.
- Suitable for complex shapes and detailed work.
- Allows for adjustments during the process to achieve the desired finish.
- Disadvantages:
- Labor-intensive and time-consuming.
- Inconsistent results due to human error.
- Limited to small production volumes.
- Applications:
- Jewelry and decorative items.
- Small automotive components.
- Custom metalwork.
2. Automated Buffing
Automated buffing employs machines and robotic systems to buff metal surfaces, offering consistent and efficient results for large-scale production.
- Advantages:
- High-speed production and consistent quality.
- Reduces labor costs and human error.
- Capable of handling large and complex parts.
- Disadvantages:
- High initial setup and equipment costs.
- Limited flexibility for intricate parts or custom finishes.
- Applications:
- Automotive parts and assemblies.
- Household appliances and electronics.
- Aerospace components.
3. Robotic Buffing
Robotic buffing utilizes robotic arms equipped with buffing tools to perform precise and efficient buffing operations, especially for complex geometries and large parts.
- Advantages:
- High precision and repeatability.
- Reduced human labor and increased safety.
- Capable of handling intricate and large-scale parts.
- Disadvantages:
- High capital investment for robotic systems.
- Requires programming and maintenance expertise.
- Applications:
- Aerospace and automotive industries.
- Large metal structures and equipment.
- High-volume production of standardized parts.
Buffing Compounds and Materials

The choice of buffing compounds and materials significantly influences the quality and efficiency of the buffing process. Various compounds are used based on the type of metal and desired finish.
Buffing Compounds
Buffing compounds are abrasive materials mixed with binders that help achieve the desired finish on metal surfaces. They come in different formulations, each suited for specific applications.
a. Tripoli Compound
- Description: A coarse compound used for initial cutting and smoothing of metal surfaces.
- Applications: Ideal for removing scratches and surface imperfections on softer metals like aluminum and brass.
b. Rouge Compound
- Description: A fine compound used to achieve a high-gloss, mirror-like finish.
- Applications: Suitable for polishing precious metals such as gold and silver, as well as stainless steel.
c. White Diamond Compound
- Description: A versatile compound used for polishing and refining metal surfaces.
- Applications: Effective on plastics and metals, providing a bright finish and removing light scratches.
d. Green Chromium Oxide Compound
- Description: A compound containing chromium oxide, used for achieving a fine finish.
- Applications: Ideal for polishing stainless steel and other hard metals, offering a high level of smoothness and shine.
Buffing Wheels and Materials
Buffing wheels are essential tools in the buffing process, available in various materials and configurations to suit different applications.
a. Cloth Buffing Wheels
- Description: Made from cotton or flannel, cloth wheels are soft and flexible, allowing for smooth finishes.
- Applications: Commonly used for applying buffing compounds and achieving a polished finish.
b. Sisal Buffing Wheels
- Description: Made from natural fibers, sisal wheels are firm and durable, making them suitable for initial cutting and buffing stages.
- Applications: Used for aggressive cutting and removing surface imperfections before finer buffing.
c. Felt Buffing Wheels
- Description: Dense and rigid, felt wheels are used for precision buffing and achieving high-gloss finishes.
- Applications: Ideal for detailed work and achieving mirror-like finishes on metals.
Applications of Industrial Buffing

Industrial buffing is used across various industries to enhance the appearance and functionality of metal parts. Here are some key applications:
1. Automotive Industry
- Applications:
- Buffing car body panels to achieve a smooth, glossy finish.
- Polishing chrome trim and accessories for enhanced aesthetic appeal.
- Smoothing engine components and parts for improved performance.
- Benefits:
- Improves the overall appearance and marketability of vehicles.
- Enhances corrosion resistance and durability of parts.
- Prepares surfaces for additional coatings or treatments.
2. Aerospace Industry
- Applications:
- Buffing aircraft components for improved aerodynamics and aesthetics.
- Polishing turbine blades and engine parts for enhanced performance.
- Smoothing fuselage and wing surfaces for reduced drag.
- Benefits:
- Increases the efficiency and reliability of aerospace components.
- Enhances safety and performance of aircraft.
- Meets stringent industry standards for quality and precision.
3. Jewelry and Decorative Products
- Applications:
- Buffing gold, silver, and platinum jewelry to achieve a high-gloss finish.
- Polishing decorative metal items such as sculptures and ornaments.
- Enhancing the appearance of metal art pieces and custom creations.
- Benefits:
- Improves the aesthetic appeal and value of jewelry and decorative items.
- Provides a luxurious and professional finish to products.
- Enhances the durability and wear resistance of metal pieces.
4. Electronics and Appliances
- Applications:
- Buffing metal casings and components for electronics and appliances.
- Polishing stainless steel surfaces for enhanced appearance and cleanliness.
- Smoothing metal parts for improved functionality and aesthetics.
- Benefits:
- Enhances the visual appeal and marketability of products.
- Improves the performance and longevity of electronic devices.
- Provides a polished and professional finish to consumer goods.
Advancements in Industrial Buffing

The field of industrial buffing has seen significant advancements in recent years, driven by technological innovations and industry demands for improved efficiency and quality. Here are some notable advancements:
1. Automation and Robotics
The integration of automation and robotics in industrial buffing processes has revolutionized the industry, offering improved precision, efficiency, and consistency.
- Benefits:
- Reduces labor costs and human error.
- Increases production speed and throughput.
- Provides consistent and repeatable results.
- Applications:
- Automated buffing systems for automotive and aerospace components.
- Robotic buffing for large and complex parts in various industries.
- Intelligent systems with adaptive control for customized finishes.
2. Innovative Materials and Compounds
Advancements in buffing materials and compounds have led to improved performance and environmental sustainability.
- Innovative Materials:
- Eco-Friendly Compounds: Formulations that reduce environmental impact and improve safety.
- Advanced Abrasives: Developments in abrasive materials enhance cutting and polishing efficiency.
- Applications:
- High-performance compounds for demanding industrial applications.
- Environmentally friendly solutions for sustainable manufacturing practices.
- Custom formulations for specific metals and finishes.
3. Industry 4.0 and Smart Technologies
Industry 4.0 is reshaping industrial buffing through the integration of smart technologies and data-driven approaches.
- Key Aspects:
- IoT Connectivity: Enables real-time monitoring and control of buffing processes.
- Data Analytics: Provides insights into process optimization and quality control.
- AI and Machine Learning: Enhances decision-making and process automation.
- Applications:
- Smart buffing systems for adaptive process control and optimization.
- Predictive maintenance and quality assurance through data-driven insights.
- Integration of IoT and AI for intelligent manufacturing solutions.
Challenges and Solutions in Industrial Buffing

Despite its advantages, industrial buffing also presents certain challenges that need to be addressed for optimal performance and quality. Here are some common challenges and their solutions:
1. Surface Uniformity
- Challenge: Achieving consistent finishes across complex geometries and large surfaces can be difficult, leading to variations in surface quality.
- Solution: Implementing automated and robotic systems ensures uniform pressure and consistent results, reducing variations in surface quality.
2. Material Compatibility
- Challenge: Different metals have varying properties, such as hardness and corrosion resistance, that affect their compatibility with specific buffing methods and materials.
- Solution: Selecting appropriate buffing compounds and materials for each metal type ensures optimal performance and finish quality.
3. Cost and Efficiency
- Challenge: Balancing cost and efficiency in high-volume production while maintaining quality can be challenging, especially with manual buffing processes.
- Solution: Investing in automated and robotic systems reduces labor costs and increases efficiency, allowing for cost-effective production without compromising quality.
4. Environmental and Safety Concerns
- Challenge: Managing waste and emissions from buffing processes, as well as ensuring operator safety, can be challenging, especially with chemical compounds and dust generation.
- Solution: Implementing effective ventilation and filtration systems, as well as using eco-friendly compounds, minimizes environmental impact and enhances safety.
Best Practices for Industrial Buffing
To achieve optimal results in industrial buffing, it is essential to follow best practices that ensure quality, efficiency, and safety. Here are some key best practices:
1. Quality Control and Inspection
Implementing robust quality control and inspection processes ensures the consistency and reliability of buffing results.
- Visual Inspection: Identifying surface defects and irregularities to ensure uniform finishes.
- Surface Roughness Testing: Assessing surface smoothness and texture to meet quality standards.
- Dimensional Inspection: Measuring critical dimensions and tolerances to ensure precision.
2. Process Optimization
Optimizing buffing processes enhances efficiency and reduces costs, ensuring high-quality results.
- Lean Manufacturing: Minimizing waste and improving workflow for efficient production.
- Continuous Improvement: Implementing feedback loops for process refinement and optimization.
- Process Automation: Utilizing technology for increased efficiency and precision.
3. Safety Measures and Precautions
Ensuring safety in industrial buffing operations is paramount to protect workers and the environment.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Providing gloves, masks, goggles, and protective clothing to ensure operator safety.
- Ventilation and Filtration: Implementing effective air quality management systems to reduce dust and fumes.
- Training and Education: Offering ongoing training programs for workers to ensure safe practices and awareness.
4. Maintenance and Upkeep
Regular maintenance and upkeep of buffing equipment and systems ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Routine Inspections: Conducting regular inspections and maintenance to identify and address equipment issues.
- Cleaning and Lubrication: Keeping buffing tools and equipment clean and lubricated for smooth operation.
- Calibration and Adjustments: Ensuring equipment is calibrated and adjusted for precise and consistent results.
Conclusion
Industrial buffing is a vital process in the metalworking industry, offering numerous benefits in terms of appearance, functionality, and durability. By understanding the methods, materials, applications, and advancements in buffing, manufacturers can achieve high-quality finishes and meet the evolving demands of the market. Whether through manual, automated, or robotic methods, the choice of buffing technique plays a critical role in producing superior metal products. By adhering to best practices and addressing challenges, the industry can continue to innovate and improve the efficiency and quality of industrial buffing operations.
Types of Deburring Machines

A deburring machine is an essential tool in metal fabrication, designed to remove burrs and other imperfections from metal parts. Burrs are unwanted projections of material that often occur during machining, cutting, or stamping processes. These imperfections can negatively affect the performance, safety, and appearance of metal parts, making deburring an important step in the manufacturing process.
Below, we’ll explore the various types of deburring machines, their working principles, applications, advantages, and considerations for selecting the right machine for your needs.
Deburring machines come in various types, each suited for specific applications and materials. Here are some of the most common types of deburring machines used in the industry:
1. Vibratory Deburring Machines
Description
Vibratory deburring machines use a vibrating bowl filled with abrasive media and parts to remove burrs. The vibrations cause the media to rub against the parts, effectively deburring and polishing them.
Working Principle
- Parts and abrasive media are placed inside a vibrating chamber.
- The vibrations cause the media to move in a circular motion, rubbing against the parts.
- The abrasive action of the media removes burrs and smooths the surface of the parts.
Applications
- Suitable for small to medium-sized parts.
- Ideal for batch processing of components.
- Used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
Advantages
- Effective for complex shapes and geometries.
- Can process multiple parts simultaneously.
- Provides a consistent and uniform finish.
Disadvantages
- Limited to smaller parts and components.
- May require longer processing times for heavy burrs.
2. Centrifugal Disc Deburring Machines
Description
Centrifugal disc deburring machines use a rotating disc to generate high-speed motion, creating a sliding movement of abrasive media against the parts.
Working Principle
- Parts and abrasive media are placed in a stationary container with a rotating disc at the bottom.
- The rotation creates a centrifugal force that causes the media to slide against the parts.
- The abrasive action removes burrs and smooths the surfaces.
Applications
- Suitable for small to medium-sized parts with intricate shapes.
- Used in industries such as jewelry, electronics, and precision engineering.
Advantages
- Provides fast and efficient deburring.
- Produces smooth and polished finishes.
- Suitable for delicate and intricate parts.
Disadvantages
- Limited to smaller parts and components.
- May not be suitable for large or heavy parts.
3. Tumbling Deburring Machines
Description
Tumbling deburring machines use a rotating barrel filled with abrasive media and parts. The rotation causes the media to tumble against the parts, removing burrs and smoothing surfaces.
Working Principle
- Parts and abrasive media are placed in a rotating barrel or drum.
- The rotation causes the media and parts to tumble against each other.
- The abrasive action of the media removes burrs and polishes the surfaces.
Applications
- Suitable for small to medium-sized parts.
- Commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods.
Advantages
- Cost-effective and simple to operate.
- Capable of processing large batches of parts.
- Provides consistent and uniform finishes.
Disadvantages
- Limited to smaller parts and components.
- May require longer processing times for heavy burrs.
4. Magnetic Deburring Machines
Description
Magnetic deburring machines use magnetic fields to agitate small steel pins or media, which in turn deburr and polish the surfaces of metal parts.
Working Principle
- Parts are placed in a chamber with small steel pins or media.
- Magnetic fields agitate the pins, causing them to move and interact with the parts.
- The mechanical action of the pins removes burrs and polishes surfaces.
Applications
- Suitable for small, delicate, and intricate parts.
- Commonly used in industries such as electronics, medical devices, and jewelry.
Advantages
- Gentle and precise deburring.
- Suitable for intricate and delicate parts.
- Can access hard-to-reach areas.
Disadvantages
- Limited to small parts and components.
- May require additional equipment for larger parts.
5. Brush Deburring Machines
Description
Brush deburring machines use rotating brushes made from abrasive materials to remove burrs and smooth surfaces.
Working Principle
- Parts are fed through the machine where rotating brushes make contact with the surfaces.
- The abrasive action of the brushes removes burrs and smooths the surfaces.
Applications
- Suitable for flat surfaces and edges.
- Used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and metal fabrication.
Advantages
- Effective for flat surfaces and edges.
- Provides consistent and uniform finishes.
- Can be integrated into production lines.
Disadvantages
- Limited to flat surfaces and edges.
- May not be suitable for complex shapes or intricate parts.
6. Thermal Deburring Machines
Description
Thermal deburring machines use controlled explosions of gas to burn away burrs from metal parts.
Working Principle
- Parts are placed in a chamber filled with a mixture of gases.
- The gases are ignited, creating a controlled explosion that burns away burrs.
Applications
- Suitable for complex and intricate parts.
- Commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and precision engineering.
Advantages
- Effective for hard-to-reach areas and complex shapes.
- Provides a clean and burr-free finish.
- Fast and efficient process.
Disadvantages
- High initial setup and operational costs.
- Limited to specific materials and applications.
7. Electrochemical Deburring Machines
Description
Electrochemical deburring machines use electrolytic solutions to dissolve burrs from metal parts.
Working Principle
- Parts are submerged in an electrolytic bath with an electric current applied.
- The current causes the burrs to dissolve, leaving a smooth surface.
Applications
- Suitable for precision and intricate parts.
- Used in industries such as aerospace, medical devices, and electronics.
Advantages
- Precise and controlled deburring.
- Minimal tool wear and surface damage.
- Suitable for intricate and delicate parts.
Disadvantages
- Requires careful handling of chemicals.
- High operational costs.
Selecting the Right Deburring Machine
Choosing the right deburring machine involves considering several factors, including the type of metal, the size and complexity of the parts, and the desired finish. Here are some key considerations for selecting the right deburring machine:
1. Type of Metal
Different metals have varying properties that affect their deburring requirements. Consider the hardness, ductility, and conductivity of the metal when selecting a deburring machine.
2. Size and Complexity of Parts
The size and complexity of the parts influence the choice of deburring machine. Consider the geometry, size, and intricacy of the parts to determine the most suitable machine.
3. Desired Finish
The desired finish and surface quality of the parts play a crucial role in selecting the right deburring machine. Consider the level of smoothness, precision, and appearance required for the finished parts.
4. Production Volume
The scale of production impacts the choice of deburring machine. Consider the production volume and batch size to determine whether manual or automated machines are more suitable.
5. Cost and Efficiency
Evaluate the overall cost and efficiency of the deburring process, including equipment, labor, and materials, to determine the most cost-effective solution without compromising quality.
6. Environmental and Safety Considerations
Consider the environmental impact and safety of the deburring process, including waste management and operator safety, when selecting a machine. Some machines may require special handling and disposal procedures for chemicals or emissions.
Advantages of Deburring Machines
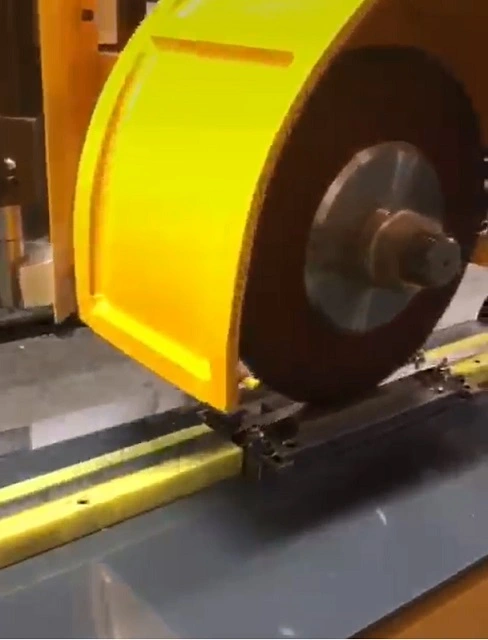

Deburring machines offer several advantages over manual deburring methods, making them essential tools in modern manufacturing processes. Here are some key advantages of using deburring machines:
1. Improved Efficiency and Productivity
Deburring machines automate the deburring process, significantly reducing the time and labor required compared to manual methods. This results in increased efficiency and productivity in manufacturing operations.
2. Consistent and Uniform Finishes
Deburring machines provide consistent and uniform finishes across batches, ensuring high-quality results with minimal variations in surface quality. This is particularly important for precision parts and components.
3. Reduced Labor Costs
Automated deburring machines reduce the need for manual labor, leading to lower labor costs and improved resource allocation in manufacturing operations.
4. Enhanced Safety
Deburring machines reduce the risk of operator injuries associated with manual deburring processes, such as cuts and abrasions. Additionally, automated machines minimize the exposure to hazardous materials and chemicals.
5. Versatility and Flexibility
Deburring machines offer versatility and flexibility in handling a wide range of parts and materials, making them suitable for various industries and applications.
6. Precision and Accuracy
Deburring machines provide precise and accurate deburring, ensuring high-quality finishes with minimal surface damage or tool wear.
Challenges and Solutions in Deburring

Despite their advantages, deburring machines also present certain challenges that need to be addressed for optimal performance and quality. Here are some common challenges and their solutions:
1. Material Compatibility
Challenge: Different materials require specific deburring techniques, which can impact the selection of deburring machines and abrasive media.
Solution: Select appropriate deburring machines and materials for each metal type to ensure optimal performance and finish quality.
2. Surface Uniformity
Challenge: Achieving consistent finishes across complex geometries and large surfaces can be difficult, leading to variations in surface quality.
Solution: Implement automated and robotic systems to ensure uniform pressure and consistent results, reducing variations in surface quality.
3. Cost and Efficiency
Challenge: Balancing cost and efficiency in high-volume production while maintaining quality can be challenging, especially with manual deburring processes.
Solution: Invest in automated and robotic systems to reduce labor costs and increase efficiency, allowing for cost-effective production without compromising quality.
4. Environmental and Safety Concerns
Challenge: Managing waste and emissions from deburring processes, as well as ensuring operator safety, can be challenging, especially with chemical compounds and dust generation.
Solution: Implement effective ventilation and filtration systems, as well as use eco-friendly compounds, to minimize environmental impact and enhance safety.
Best Practices for Using Deburring Machines

To achieve optimal results in deburring, it is essential to follow best practices that ensure quality, efficiency, and safety. Here are some key best practices for using deburring machines:
1. Quality Control and Inspection
Implement robust quality control and inspection processes to ensure the consistency and reliability of deburring results.
- Visual Inspection: Identify surface defects and irregularities to ensure uniform finishes.
- Surface Roughness Testing: Assess surface smoothness and texture to meet quality standards.
- Dimensional Inspection: Measure critical dimensions and tolerances to ensure precision.
2. Process Optimization
Optimize deburring processes to enhance efficiency and reduce costs, ensuring high-quality results.
- Lean Manufacturing: Minimize waste and improve workflow for efficient production.
- Continuous Improvement: Implement feedback loops for process refinement and optimization.
- Process Automation: Utilize technology for increased efficiency and precision.
3. Safety Measures and Precautions
Ensure safety in deburring operations to protect workers and the environment.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Provide gloves, masks, goggles, and protective clothing to ensure operator safety.
- Ventilation and Filtration: Implement effective air quality management systems to reduce dust and fumes.
- Training and Education: Offer ongoing training programs for workers to ensure safe practices and awareness.
4. Maintenance and Upkeep
Regular maintenance and upkeep of deburring equipment and systems ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Routine Inspections: Conduct regular inspections and maintenance to identify and address equipment issues.
- Cleaning and Lubrication: Keep deburring tools and equipment clean and lubricated for smooth operation.
- Calibration and Adjustments: Ensure equipment is calibrated and adjusted for precise and consistent results.
Conclusion
Deburring machines play a crucial role in the metalworking industry, providing efficient and effective solutions for removing burrs and imperfections from metal parts. By understanding the types, applications, and considerations for selecting deburring machines, manufacturers can achieve high-quality finishes and meet the evolving demands of the market. Whether through vibratory, centrifugal, tumbling, or advanced methods like thermal and electrochemical deburring, the choice of deburring machine plays a critical role in producing superior metal products. By adhering to best practices and addressing challenges, the industry can continue to innovate and improve the efficiency and quality of deburring operations.
If you have any further questions or need more detailed information on specific aspects of deburring machines, feel free to ask!
Best Deburring Techniques

Deburring is a crucial step in metalworking and manufacturing that involves removing burrs—unwanted protrusions or rough edges—resulting from machining, cutting, drilling, or stamping processes. The presence of burrs can negatively affect the performance, safety, and aesthetics of metal parts. Therefore, selecting the best deburring techniques is essential for achieving smooth, functional, and visually appealing products.
Below, we’ll explore the most effective deburring techniques, their applications, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for choosing the right method for specific needs.
1. Manual Deburring
Manual deburring involves using hand tools to remove burrs from metal parts. It is one of the oldest and most straightforward methods, offering flexibility and precision for small-scale or intricate tasks.
Tools Used
- Files: Metal files are used to manually scrape and smooth burrs off the edges of metal parts. Available in various shapes and sizes to match specific needs.
- Scrapers: Sharp, flat tools used for removing burrs from flat surfaces and edges.
- Abrasive Pads: Scouring pads that can be used to smooth out small imperfections and surface burrs.
- Rotary Tools: Dremel-like tools with small abrasive attachments for precise deburring of intricate areas.
Applications
- Suitable for small batches and custom jobs.
- Ideal for intricate and delicate parts where precision is critical.
- Commonly used in the aerospace, automotive, and jewelry industries.
Advantages
- Low initial investment and setup costs.
- Provides precise control over the deburring process.
- Flexibility to handle various part sizes and shapes.
Disadvantages
- Labor-intensive and time-consuming for large volumes.
- Inconsistent results due to human error.
- Limited efficiency for high-volume production.
Best Practices
- Ensure operators are well-trained and skilled in using manual tools.
- Use appropriate safety gear, such as gloves and goggles, to protect against metal filings.
- Regularly maintain and sharpen tools to ensure efficiency and precision.
2. Mechanical Deburring
Mechanical deburring involves using machines to automate the deburring process. This method is suitable for high-volume production and can handle various part sizes and shapes.
Types of Mechanical Deburring
a. Vibratory Deburring
- Process: Uses a vibrating container filled with abrasive media to deburr parts. The vibration causes the media to rub against the parts, removing burrs.
- Applications: Suitable for small to medium-sized parts with complex geometries.
- Advantages: Handles multiple parts simultaneously, consistent finishes, effective for complex shapes.
- Disadvantages: Limited to smaller parts, longer processing times for heavy burrs.
b. Tumbling Deburring
- Process: Uses a rotating barrel filled with abrasive media and parts. The rotation causes the media to tumble against the parts, removing burrs.
- Applications: Ideal for small parts and batch processing.
- Advantages: Cost-effective, simple operation, capable of processing large batches.
- Disadvantages: Limited to smaller parts, may require longer processing times for heavy burrs.
c. Brush Deburring
- Process: Involves using rotating brushes made from abrasive materials to remove burrs from flat surfaces and edges.
- Applications: Suitable for flat surfaces and edges, used in industries such as automotive and aerospace.
- Advantages: Consistent finishes, can be integrated into production lines, effective for flat surfaces.
- Disadvantages: Limited to flat surfaces, not suitable for intricate shapes.
Best Practices
- Choose the right abrasive media for the specific material and part geometry.
- Regularly monitor and maintain machinery to ensure optimal performance.
- Adjust processing times and media compositions based on part specifications and desired finishes.
3. Thermal Deburring
Thermal deburring is an advanced method that uses controlled explosions of gas to remove burrs from metal parts. It is particularly effective for complex and intricate parts.
Process
- Parts are placed in a chamber filled with a mixture of combustible gases, such as hydrogen and oxygen.
- The gases are ignited, creating a controlled explosion that burns away burrs.
Applications
- Suitable for intricate and complex parts with hard-to-reach areas.
- Commonly used in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Advantages
- Effective for hard-to-reach areas and complex shapes.
- Provides a clean and burr-free finish.
- Fast and efficient process for large volumes.
Disadvantages
- High initial setup and operational costs.
- Limited to specific materials that can withstand high temperatures.
- Requires careful handling and safety measures.
Best Practices
- Ensure the chamber and parts are properly sealed to prevent gas leaks.
- Conduct thorough safety checks and adhere to safety protocols to prevent accidents.
- Regularly maintain equipment to ensure consistent and safe operation.
4. Electrochemical Deburring
Electrochemical deburring uses electrolytic solutions to dissolve burrs from metal parts. This method is precise and effective for parts with complex geometries.
Process
- Parts are submerged in an electrolytic bath with an electric current applied.
- The current causes the burrs to dissolve, leaving a smooth surface.
Applications
- Suitable for precision parts and intricate geometries.
- Used in industries such as aerospace, medical devices, and electronics.
Advantages
- Precise and controlled deburring.
- Minimal tool wear and surface damage.
- Suitable for intricate and delicate parts.
Disadvantages
- Requires careful handling of chemicals and electrolytes.
- High operational costs and initial setup.
- Limited to conductive materials.
Best Practices
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to handle chemicals safely.
- Regularly test and maintain electrolyte solutions to ensure effective deburring.
- Optimize current levels and exposure times based on part specifications.
5. High-Pressure Water Jet Deburring
High-pressure water jet deburring uses water jets to remove burrs and clean metal surfaces. This technique is suitable for parts that are sensitive to heat and require precision deburring.
Process
- High-pressure water jets are directed at the metal parts, removing burrs through the force of the water.
- The process may involve rotating nozzles to reach all areas of the part.
Applications
- Suitable for heat-sensitive materials and precision components.
- Commonly used in the aerospace, automotive, and medical device industries.
Advantages
- No thermal distortion or material stress.
- Environmentally friendly, as it uses water instead of chemicals.
- Effective for precision and intricate parts.
Disadvantages
- High initial setup costs for equipment.
- Limited to parts that can withstand high water pressure.
- May require additional drying processes after deburring.
Best Practices
- Ensure proper pressure levels and nozzle configurations for effective deburring.
- Implement drying procedures to prevent corrosion or water damage.
- Regularly inspect and maintain equipment to ensure consistent performance.
6. Cryogenic Deburring
Cryogenic deburring uses extremely low temperatures to embrittle burrs, making them easier to remove. This method is effective for flexible or rubber-like materials that are difficult to deburr using traditional methods.
Process
- Parts are exposed to cryogenic temperatures using liquid nitrogen or similar substances.
- The low temperature makes the burrs brittle, allowing them to be easily removed by tumbling or blasting.
Applications
- Suitable for plastic, rubber, and flexible materials.
- Commonly used in the automotive, electronics, and medical device industries.
Advantages
- Effective for materials that are difficult to deburr using traditional methods.
- Minimal impact on the part’s structural integrity.
- Environmentally friendly, as it uses no chemicals.
Disadvantages
- Limited to materials that can withstand low temperatures.
- High setup and operational costs for cryogenic equipment.
- May require additional processes to remove residual cold materials.
Best Practices
- Ensure proper handling and safety measures when using cryogenic materials.
- Optimize exposure times and temperatures based on material specifications.
- Regularly maintain equipment to ensure efficient and safe operation.
Comparison of Deburring Techniques
Here’s a comparison table summarizing the advantages, disadvantages, and applications of each deburring technique:
| Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Deburring | Low cost, precise control, flexible for various shapes | Labor-intensive, inconsistent results, limited efficiency | Small batches, custom jobs, intricate parts |
| Vibratory Deburring | Consistent finishes, handles complex shapes, batch processing | Limited to smaller parts, longer processing times | Small to medium-sized parts, complex geometries |
| Tumbling Deburring | Cost-effective, simple operation, large batch processing | Limited to smaller parts, longer processing times | Small parts, batch processing |
| Brush Deburring | Consistent finishes, integrated into production lines | Limited to flat surfaces, not suitable for intricate shapes | Flat surfaces, edges, automotive and aerospace |
| Thermal Deburring | Effective for complex shapes, fast and efficient | High costs, limited to specific materials, safety concerns | Intricate parts, automotive, aerospace |
| Electrochemical Deburring | Precise deburring, minimal tool wear, suitable for intricate parts | Requires chemical handling, high costs, limited to conductive materials | Precision parts, aerospace, medical devices |
| High-Pressure Water Jet | No thermal distortion, environmentally friendly | High costs, limited to parts that can withstand water pressure | Heat-sensitive materials, precision components |
| Cryogenic Deburring | Effective for flexible materials, minimal impact on structural integrity | Limited to low-temperature materials, high costs | Plastic, rubber, flexible materials |
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Deburring Technique
Selecting the right deburring technique depends on several factors, including the type of material, part geometry, production volume, and desired finish. Here are some key considerations:
- Material Type: Different materials have varying properties that affect their deburring requirements. Consider the hardness, ductility, and thermal sensitivity of the material when choosing a deburring method.
- Part Geometry: The shape and complexity of the parts influence the choice of deburring technique. Intricate geometries may require advanced methods like electrochemical or thermal deburring for effective results.
- Production Volume: The scale of production impacts the choice of deburring technique, with high-volume production benefiting from automated methods and small-batch or custom work requiring manual techniques.
- Cost and Efficiency: Evaluate the overall cost and efficiency of the deburring process, including equipment, labor, and materials, to determine the most cost-effective solution without compromising quality.
- Environmental and Safety Considerations: Consider the environmental impact and safety of the deburring process, including waste management and operator safety. Some methods may require special handling and disposal procedures for chemicals or emissions.
- Desired Finish: The intended surface quality of the finished product influences the choice of deburring technique. For instance, precision parts with tight tolerances may benefit from electrochemical deburring, while simpler parts may be effectively deburred using mechanical methods.
Conclusion
Deburring is a vital process in manufacturing, significantly impacting the quality and functionality of metal parts. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each deburring technique, manufacturers can select the most appropriate method to achieve the desired finish and meet specific application requirements. Whether through manual, mechanical, thermal, or advanced methods, the choice of deburring technique plays a critical role in producing high-quality, durable metal products. By adhering to best practices and addressing challenges, the industry can continue to innovate and improve the efficiency and quality of deburring operations.
An Edge Trimming Machine is used in various industries to trim or cut excess material from the edges of products, ensuring precise dimensions and a clean finish. These machines are commonly found in sectors like packaging, metalworking, woodworking, textiles, and plastics.
Types of Edge Trimming Machines
- Paper and Packaging Industry
- Rotary Trimmers: Used for trimming excess paper or board in printing and packaging.
- Guillotine Cutters: Ensure clean, straight cuts for paper stacks.
- Metalworking Industry
- Shearing Machines: Used to trim metal sheets and plates.
- Slitting Machines: Cut wide metal rolls into narrower strips with precise edges.
- Woodworking Industry
- Edge Banding Machines: Trim and apply protective edging on wood panels.
- CNC Routers: Provide precise edge trimming with automation.
- Plastic and Rubber Industry
- Hot Knife Trimmers: Used for cutting plastic sheets or rubber edges smoothly.
- Laser Trimming Machines: Provide high-precision cutting for plastic components.
- Textile Industry
- Fabric Cutting Machines: Trim excess fabric edges for a uniform finish.
Key Features
- Automatic or Manual Operation
- Adjustable Cutting Blades
- Precision Control Systems
- Dust or Waste Collection Systems
- Safety Guards and Sensors
An edge trimming machine is used to remove excess material from the edges of a workpiece, ensuring precise dimensions and a clean finish. These machines are widely used in industries such as packaging, metalworking, woodworking, plastics, and textiles. Depending on the application, they can operate manually, semi-automatically, or fully automatically with CNC control. In the paper and packaging industry, edge trimming machines help achieve clean cuts on paper stacks, cardboard, and labels. In metalworking, they trim sheets, plates, and coils using shearing or slitting techniques.
Woodworking applications involve trimming edges of panels, often with edge banding machines that also apply protective edging. Plastic and rubber industries use hot knife trimmers or laser cutters for smooth and precise trimming. In textiles, fabric cutting machines ensure uniform edge finishing. Common features include adjustable cutting blades, precision control, waste collection systems, and safety mechanisms. Selecting the right machine depends on material type, thickness, production speed, and required precision.
Edge trimming machines play a crucial role in manufacturing and finishing processes across multiple industries by ensuring that materials have clean, uniform, and precisely cut edges. These machines are designed to remove excess material efficiently, improving both the functionality and aesthetics of the final product. Depending on the industry and application, edge trimming machines come in various forms, including manual, semi-automatic, and fully automated systems with CNC integration.
In the paper and packaging industry, edge trimming machines are used to cut excess paper, cardboard, or plastic film, ensuring that printed materials, cartons, and labels have clean and precise edges. High-speed rotary trimmers and guillotine cutters are commonly used to process large volumes of paper and packaging materials, helping to maintain consistency in shape and size. Many modern machines are equipped with sensors and computerized controls to enhance accuracy and minimize waste.
In metalworking, edge trimming machines play a vital role in cutting and finishing metal sheets, plates, and coils. Shearing machines are often used to trim excess material from metal sheets, while slitting machines cut wide metal rolls into narrower strips with extreme precision. Some advanced machines utilize laser or plasma cutting technology to achieve highly accurate edge finishes, particularly for applications requiring intricate designs or tight tolerances. These machines are essential in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction, where precise metal trimming affects the overall integrity of components.
The woodworking industry relies heavily on edge trimming machines to refine wooden panels, furniture components, and cabinetry. Edge banding machines not only trim the edges of wooden boards but also apply protective bands that enhance durability and aesthetics. CNC routers with specialized cutting heads are used for complex trimming operations, allowing for customized edge profiles. Proper edge trimming in woodworking ensures a smooth finish, eliminates splinters, and enhances the final appearance of wooden products.
In plastic and rubber processing, edge trimming is critical for achieving smooth and accurate edges on plastic sheets, molded parts, and rubber components. Hot knife trimmers use heat to cut through plastic and rubber materials, reducing rough edges and preventing fraying. Laser trimming machines provide even greater precision, making them ideal for applications where intricate designs or delicate materials are involved. Industries such as automotive manufacturing, medical device production, and consumer electronics frequently use these machines to ensure high-quality plastic and rubber components.
The textile industry also benefits from edge trimming machines, especially in fabric and garment production. Automated fabric cutting machines are used to trim excess material from textiles, ensuring that garments and fabric-based products maintain uniform dimensions. Some machines are equipped with ultrasonic or laser cutting technology, which helps prevent fraying and enhances durability. Proper edge trimming in textiles is crucial for maintaining fabric integrity and achieving professional-quality finishes in clothing, upholstery, and industrial fabric applications.
Across all these industries, edge trimming machines are designed with advanced features such as precision control systems, adjustable cutting blades, automated feed mechanisms, and waste collection systems. Many high-end models incorporate digital controls, allowing operators to adjust cutting parameters with high accuracy. Safety is also a major consideration, with modern machines equipped with protective guards, emergency stop mechanisms, and sensor-based safety features to prevent accidents.
The selection of an edge trimming machine depends on several factors, including the type of material being processed, the required level of precision, production speed, and specific industry requirements. For instance, a high-speed slitting machine would be ideal for metal processing, while a CNC-controlled edge banding machine would be better suited for woodworking applications. Understanding these factors helps manufacturers choose the most suitable machine for their operations, ultimately improving production efficiency, reducing material waste, and enhancing product quality.
Edge trimming machines continue to evolve with advancements in technology, offering greater precision, automation, and efficiency across different industries. The increasing demand for high-quality finishes, minimal material waste, and faster production times has driven the development of sophisticated edge trimming solutions that cater to diverse manufacturing needs. Modern machines integrate state-of-the-art features such as computer numerical control (CNC), real-time monitoring, and adaptive cutting mechanisms, allowing them to handle complex trimming tasks with minimal operator intervention.
In industrial settings, automation has significantly improved productivity by reducing manual labor and ensuring consistent trimming accuracy. Automated edge trimming machines, especially those equipped with CNC systems, can be programmed to handle different materials and cutting patterns with remarkable precision. These machines can adjust blade pressure, speed, and cutting depth dynamically, ensuring that each piece meets exact specifications. For instance, in metal processing plants, high-speed slitting machines with automatic alignment features enable the continuous trimming of metal coils, optimizing material utilization while maintaining quality. Similarly, in woodworking, CNC edge banding machines use robotic arms to apply adhesive strips and trim excess material with near-perfect accuracy, eliminating the inconsistencies associated with manual trimming.
Another important aspect of modern edge trimming machines is their integration with smart manufacturing technologies. Many machines now come with IoT (Internet of Things) connectivity, allowing operators to monitor performance, detect potential issues, and optimize processes in real time. Smart sensors embedded in these machines can track cutting precision, blade wear, and material feed rates, sending alerts when maintenance is required. This predictive maintenance capability helps reduce downtime and prolongs machine lifespan, making operations more cost-effective in the long run. Additionally, some advanced models use AI-driven algorithms to optimize cutting patterns, minimizing waste while maximizing efficiency.
Environmental sustainability is another driving factor in the evolution of edge trimming machines. Many industries are now focusing on reducing material waste, improving energy efficiency, and adopting eco-friendly trimming solutions. Modern trimming machines are designed to minimize scrap by using precise cutting mechanisms that optimize material utilization. For example, some paper trimming machines are equipped with automatic waste separation systems, ensuring that excess paper can be efficiently recycled. In plastic processing, laser trimming technology helps achieve clean edges without generating plastic dust or harmful residues, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional cutting methods. In metalworking, high-precision plasma and waterjet cutting machines reduce material wastage and eliminate the need for additional finishing processes, contributing to more sustainable manufacturing practices.
One of the most significant challenges in edge trimming operations is handling different material properties. Hard metals, flexible textiles, brittle plastics, and composite materials all require specialized trimming techniques to achieve clean and precise edges. Manufacturers address this challenge by developing versatile edge trimming machines capable of adapting to various materials. Multi-functional machines with interchangeable cutting heads allow industries to process different materials without needing multiple machines, reducing costs and increasing operational flexibility. For example, a hybrid trimming machine equipped with both rotary blades and laser cutting capabilities can handle both soft and hard materials seamlessly.
Another area of innovation in edge trimming technology is customization and modular design. Manufacturers can now configure machines based on specific production requirements, allowing businesses to scale their trimming operations as needed. Modular machines enable companies to integrate additional features such as dust extraction systems, automated feeding mechanisms, and real-time quality control cameras, improving overall efficiency and product quality. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for industries where product designs and material specifications frequently change, such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace engineering, and high-end furniture production.
As industries continue to demand higher precision, efficiency, and sustainability in their manufacturing processes, edge trimming machines will continue to advance. Future developments may include AI-powered quality control systems, fully autonomous trimming solutions, and enhanced eco-friendly cutting technologies that further reduce environmental impact. The increasing adoption of robotics and machine learning in manufacturing could lead to fully integrated edge trimming systems capable of making real-time adjustments based on material characteristics and production requirements.
Circular End Head Joggling Machine
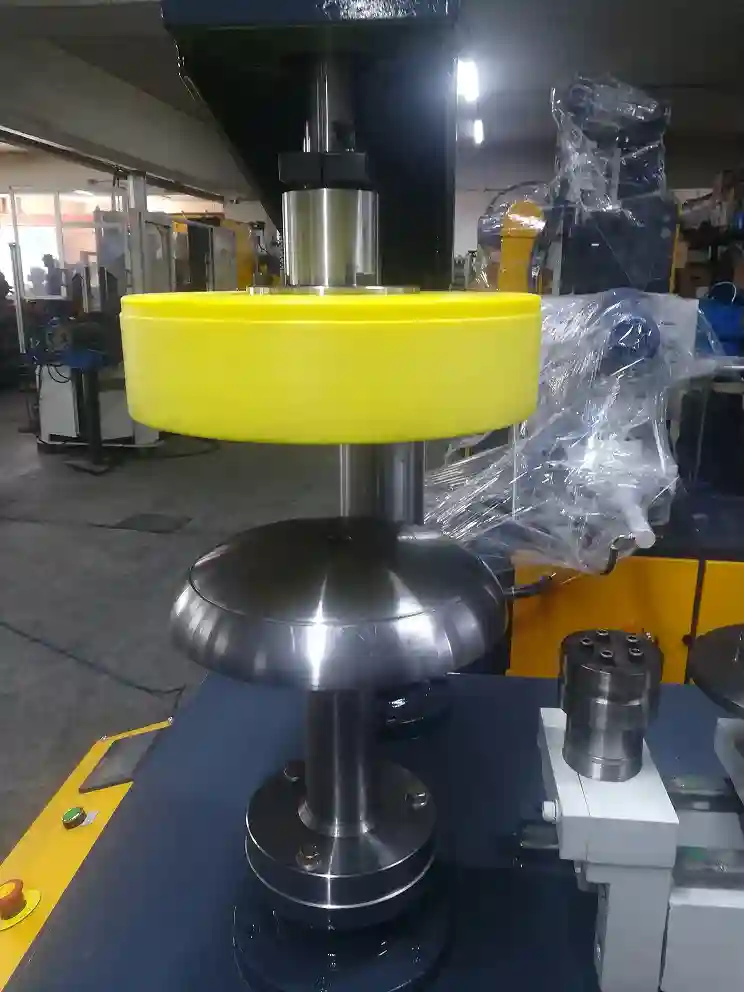

A Circular End Head Joggling Machine is a specialized piece of equipment used in metalworking, particularly in the fabrication of pressure vessels, storage tanks, and industrial pipelines. The machine is designed to create a joggled edge on circular metal end heads, which allows for a better fit and stronger welded joint when assembling cylindrical or conical sections. Joggling is a metal-forming process where a step or offset is introduced into the material, enabling overlapping joints that improve structural integrity and reduce welding gaps.
Working Principle
The Circular End Head Joggling Machine uses hydraulic or mechanical force to press a precisely controlled joggled edge into the metal workpiece. The process involves:
- Clamping the circular end head securely to prevent movement during forming.
- Applying controlled pressure using a forming die or roller to create a step in the metal without cracking or deforming it.
- Ensuring uniform depth and width of the joggled section to maintain consistency across multiple pieces.
- Final shaping and edge finishing to remove irregularities and improve assembly compatibility.
Key Features
- Hydraulic or Pneumatic Operation: Ensures precise and powerful forming.
- CNC or Manual Control: Advanced machines use CNC programming for repeatability and accuracy.
- Customizable Joggle Depth and Width: Adjustable settings to accommodate different material thicknesses.
- Heavy-Duty Frame and Clamping Mechanism: Prevents deformation during processing.
- Application for Various Metals: Works with stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, and other alloys used in industrial tanks and pressure vessels.
Applications
- Pressure Vessel Manufacturing: Ensures precise fitting of end caps with cylindrical shells.
- Storage Tanks and Silos: Used in industries like oil & gas, chemical processing, and food storage.
- Aerospace and Shipbuilding: Helps in creating strong joints for curved metal panels.
A Circular End Head Joggling Machine is used in metal fabrication to create joggled edges on circular end heads, ensuring better fitment and stronger welded joints in pressure vessels, storage tanks, and industrial pipelines. The joggling process involves forming a precise step or offset along the edge of the metal component, allowing it to overlap seamlessly with cylindrical or conical sections, reducing gaps and enhancing structural integrity. These machines operate using hydraulic or mechanical force to press the joggled edge into the material, maintaining uniformity without causing cracks or deformation. The process begins with securely clamping the circular end head to prevent movement, followed by applying controlled pressure using a forming die or roller to create the step. Modern machines often feature CNC control for precision and repeatability, enabling operators to set the exact depth and width of the joggled section based on material specifications.
Designed to handle materials like stainless steel, carbon steel, and aluminum, these machines are widely used in industries that require high-precision metal forming. Their applications extend to pressure vessel manufacturing, where end caps must fit precisely with cylindrical shells, and in storage tank production for industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and food storage. Aerospace and shipbuilding industries also utilize joggling machines to create strong overlapping joints for curved metal panels. Key features include hydraulic or pneumatic operation for consistent pressure, heavy-duty clamping mechanisms to maintain stability during processing, and customizable settings to accommodate different material thicknesses.
Advancements in machine technology have led to automation and integration with smart manufacturing systems, allowing for real-time monitoring, adaptive control, and improved efficiency. Some high-end joggling machines come equipped with IoT connectivity, enabling predictive maintenance and process optimization. As manufacturing demands continue to evolve, the role of joggling machines in ensuring high-quality, precision-formed components becomes increasingly important.
A Circular End Head Joggling Machine is a crucial tool in metal fabrication, designed to create precise joggled edges on circular end heads to improve assembly, welding quality, and structural integrity. This process is particularly important in industries such as pressure vessel manufacturing, storage tank production, aerospace, and shipbuilding, where a secure and seamless joint between curved metal components is essential. By forming a step or offset along the edge of the metal component, the joggling process allows one piece to overlap another, reducing welding gaps, improving strength, and ensuring a better overall fit. The machine operates using hydraulic or mechanical force, applying controlled pressure through a forming die or roller to shape the material without causing cracks or distortions. Modern machines often incorporate CNC technology to allow precise control over the depth and width of the joggled section, ensuring uniformity across multiple pieces and reducing manual adjustments.
The working process of a Circular End Head Joggling Machine starts with securing the metal workpiece in place using a heavy-duty clamping mechanism. This is crucial to prevent movement during the joggling operation and to ensure accuracy. Once the workpiece is held firmly, a hydraulic or pneumatic system applies pressure to the forming die, which presses the material to create the joggled profile. Depending on the machine’s design, this process may be performed in a single pass or multiple stages, gradually forming the desired step without overstressing the material. Many machines allow for adjustable joggle depth and width, accommodating different material thicknesses and application requirements. In industries where precision and consistency are critical, CNC-controlled joggling machines provide repeatable results, reducing human error and increasing efficiency.
The materials commonly processed with joggling machines include stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, and various alloys used in pressure vessels and industrial tanks. In pressure vessel manufacturing, the joggled edge ensures a tighter fit between the end cap and the cylindrical shell, minimizing the need for extensive welding and reducing the risk of defects such as leaks or weak joints. In the storage tank industry, particularly for oil, gas, and chemical processing, joggling enhances the assembly of large-diameter tanks, making construction more efficient and ensuring structural stability. Aerospace and shipbuilding applications also benefit from joggling technology, as it allows for lightweight, high-strength joints in curved metal structures, improving both performance and durability.
One of the key advantages of modern joggling machines is their ability to integrate with smart manufacturing technologies, including IoT-based monitoring systems that track machine performance, detect maintenance needs, and optimize production efficiency. Some high-end machines feature real-time process monitoring, adaptive pressure control, and automated tool adjustment, further reducing material waste and ensuring consistent quality. As manufacturing demands continue to evolve, innovations in joggling machine technology will likely focus on increased automation, improved material adaptability, and more energy-efficient operation. The ability to handle complex shapes and high-strength alloys with precision will be a major factor in the future development of these machines, making them an essential component of advanced metal fabrication.
Sheet Metal Curling Tool

A Sheet Metal Curling Tool is a specialized tool or machine used to form a curved or rolled edge on sheet metal. Curling is commonly applied to enhance structural strength, eliminate sharp edges, and improve the appearance of metal parts. This process is widely used in manufacturing industries such as automotive, aerospace, HVAC, and metal can production, where smooth, rolled edges are required for safety, functionality, and aesthetic purposes.
Curling can be performed manually using hand tools such as pliers and hammers for small-scale or custom applications, but industrial settings typically rely on mechanical or CNC curling machines for precision and efficiency. These machines use rollers or forming dies to gradually shape the metal edge into a uniform curl. The process involves clamping the sheet metal in place and passing it through progressively tighter rollers until the desired curl is achieved. Advanced machines offer programmable settings for different curl diameters, ensuring consistent results across multiple parts.
The main benefits of curling sheet metal include improved safety by eliminating sharp edges, increased rigidity by strengthening the metal’s edge, and enhanced assembly compatibility when curling is used to interlock parts. Different curl types exist based on application requirements, such as open curls for decorative purposes, closed curls for reinforcement, and interlocking curls for connecting components. Materials like aluminum, stainless steel, and mild steel can be curled, with factors such as material thickness and hardness influencing the required force and tool selection.
Modern curling machines integrate automation features such as servo-driven rollers and digital controls for precise adjustments, reducing manual labor and increasing production efficiency. These machines are commonly found in sheet metal fabrication shops and specialized manufacturing facilities producing ductwork, metal enclosures, and rolled-edge containers. As industries continue to seek improved manufacturing techniques, curling tools are evolving with advanced forming capabilities and better integration into automated production lines.
A Sheet Metal Curling Tool is designed to form a smooth, rounded edge on sheet metal, providing increased strength, improved safety, and enhanced aesthetics. This process is essential in industries such as automotive, aerospace, HVAC, and packaging, where sharp edges must be eliminated, and structural integrity is required. Curling is often used to create rolled edges for decorative purposes, reinforcement, or interlocking joints in assembled components. The process involves shaping the edge of a metal sheet into a circular form using mechanical force, with manual hand tools or specialized curling machines used depending on the application.
For small-scale or custom fabrication, manual curling tools such as pliers, mallets, or forming stakes can be used to gradually bend the metal edge into shape. However, in industrial manufacturing, mechanical and CNC curling machines offer greater precision, consistency, and efficiency. These machines operate by clamping the sheet metal securely and passing it through a series of rollers or dies, progressively bending the edge into a curl. Advanced models allow for adjustable curl diameters and shapes, ensuring that each piece meets exact specifications without excessive manual adjustments. Materials such as aluminum, stainless steel, and mild steel are commonly curled, with the required force and tool selection depending on factors like thickness and hardness.
The advantages of using a curling tool extend beyond aesthetics. By rolling the edge, the metal gains additional rigidity, making the final product more durable. The rounded edge also enhances safety by removing sharp, exposed metal, reducing the risk of injury during handling and assembly. Different types of curls can be produced, including open curls for lightweight applications, closed curls for reinforced edges, and interlocking curls for structural connections. This versatility makes curling an essential process in sheet metal fabrication, particularly in products such as ductwork, enclosures, storage containers, and industrial components.
As manufacturing technology advances, modern curling machines incorporate automation features such as servo-driven rollers, programmable digital controls, and real-time process monitoring. These innovations improve accuracy, reduce material waste, and integrate seamlessly into automated production lines. With industries demanding higher efficiency and precision in sheet metal processing, curling tools continue to evolve, offering more adaptable and intelligent solutions for various fabrication needs. Would you like recommendations on specific curling machines, insights into optimizing the curling process for your application, or guidance on selecting the right tool for different materials and thicknesses?
A Sheet Metal Curling Tool is an essential device used to form a smooth, rounded edge on sheet metal, enhancing both structural integrity and safety while also improving the aesthetics of the finished product. This process is widely used in industries such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace, HVAC ductwork, packaging, and metal can production, where sharp edges need to be eliminated and additional reinforcement is required. The curling process involves bending the outer edge of a metal sheet into a circular form, which not only makes it safer to handle but also strengthens the material by redistributing stress along the curved edge. The choice of curling method depends on the application, material type, and production scale, with both manual and automated tools available to achieve the desired results.
In small-scale operations or custom metalworking, manual tools such as pliers, hammers, and forming stakes are commonly used to create curled edges through gradual shaping. These tools require skill and precision, making them ideal for artisanal or specialized fabrication tasks. For higher efficiency and consistency, mechanical curling machines are employed, utilizing rollers or forming dies to shape the metal edge into a uniform curl. These machines operate by securing the sheet metal in place and gradually bending the edge as it moves through progressively tighter rollers. Advanced curling machines are equipped with CNC controls, allowing operators to program specific curl diameters, shapes, and tolerances for repeatable accuracy in mass production.
Curling offers multiple benefits beyond aesthetics and safety. By rolling the edge of a sheet metal component, the material becomes more rigid and durable, reducing the risk of deformation under stress. This makes curled edges particularly valuable in structural applications where additional reinforcement is needed. Different curling techniques are used based on functional requirements, such as open curls for decorative applications, closed curls for added strength, and interlocking curls that enable secure joining of multiple parts without welding. The ability to customize curl profiles makes these tools versatile in a wide range of manufacturing processes, from producing storage containers and enclosures to fabricating components for aircraft and industrial machinery.
The materials commonly used in curling operations include aluminum, stainless steel, mild steel, and other alloys, each requiring different force levels and tooling considerations. Thicker or harder materials may require hydraulic or servo-driven curling machines, which apply greater pressure with precision control. In contrast, thinner metals can be processed using simpler mechanical rollers or hand tools. The choice of equipment depends on production volume, material specifications, and the complexity of the required curl profile.
Technological advancements in sheet metal fabrication have led to the development of highly automated curling machines that integrate digital monitoring, adaptive force control, and smart automation. Modern machines equipped with servo-driven rollers can dynamically adjust pressure and speed based on material characteristics, ensuring consistent curl formation while reducing waste. Some high-end models also feature real-time quality monitoring systems that detect irregularities and make automatic corrections, further improving efficiency and product quality. As industries continue to demand faster, more precise manufacturing processes, the role of curling machines is evolving to meet these needs, providing enhanced automation, greater material adaptability, and energy-efficient operation.
As sheet metal processing continues to advance, curling tools and machines will play a critical role in improving product durability, safety, and functionality across multiple industries. Whether for small-scale workshops or high-volume manufacturing plants, selecting the right curling tool is essential for optimizing production efficiency and ensuring high-quality results. Would you like recommendations on specific curling machine models, guidance on selecting the right tool for different materials and thicknesses, or insights into advanced automation technologies for curling operations?
Border Crimping Machine
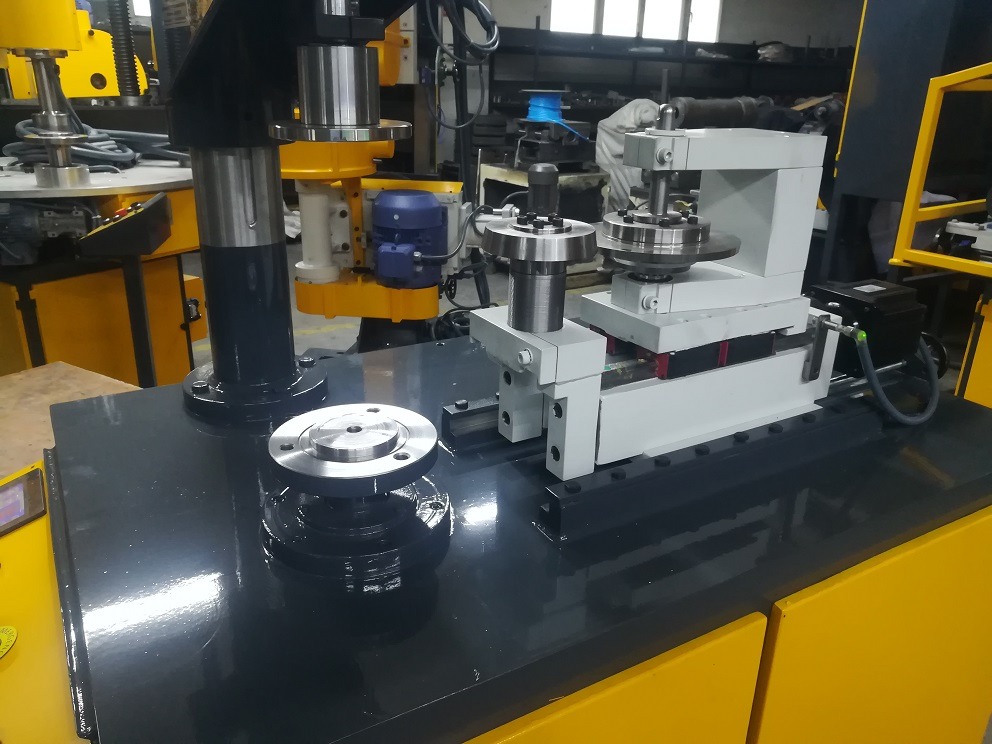

A Border Crimping Machine is a specialized tool used primarily in the textile and fabric industries to fold, crimp, and finish the edges of fabric or other materials. This process, known as crimping, creates a strong, durable edge by compressing and folding the material’s borders, preventing fraying, unraveling, and wear. Border crimping is commonly applied in the production of garments, home textiles, industrial fabrics, and packaging materials, where the edges of the fabric need to be reinforced or aesthetically finished. The machine is typically used for items such as curtains, upholstery, bags, and carpets, where a neat, durable border is necessary for both appearance and function.
The working principle of a border crimping machine involves feeding the fabric through a set of rollers or dies that apply pressure to the edges, creating a crimped, folded effect. The crimping process can be adjusted for various materials, including cotton, polyester, nylon, and blends. The machine typically features adjustable settings to control the depth of the crimp, the size of the fold, and the material feed rate, ensuring precise edge finishing.
Border crimping machines come in both manual and automated versions. Manual crimping machines are typically used in smaller operations or for custom work, where individual pieces are processed by hand or foot pedal. Automated crimping machines are used in larger-scale operations where high-volume production is required. These machines are often integrated with computerized controls to ensure consistent results and optimize production speed. Some advanced models are capable of handling multiple materials at once, adjusting their settings automatically based on the fabric type or thickness.
The benefits of using a border crimping machine include increased production speed, reduced labor costs, and enhanced quality of the finished product. The crimped edges are not only stronger but also provide a more polished, professional look, which is particularly important in the fashion, home textiles, and upholstery industries. Crimping can also improve the durability of products by reinforcing the edges, reducing the likelihood of wear and tear during use.
Modern border crimping machines often come with features like automatic tension control, digital displays, and programmable settings that allow operators to fine-tune the crimping process for different materials and production needs. Some models also include safety features to prevent accidents during operation, including automatic shutoffs or safety guards. Additionally, the machines may incorporate waste management systems that collect and remove any offcuts or excess material, further improving the overall efficiency of the production line.
In industries such as home textiles, upholstery, and automotive, where fabric edges need to withstand stress and regular handling, border crimping plays a crucial role in ensuring that the final product maintains its structural integrity and appearance over time. As the demand for high-quality, durable, and visually appealing fabric products increases, the importance of border crimping machines continues to grow, helping manufacturers meet these expectations efficiently.
A Border Crimping Machine is essential in industries like textiles and fabric production, where it is used to create reinforced, finished edges on materials to prevent fraying and improve both strength and appearance. The process involves feeding fabric through a set of rollers or dies that apply pressure, folding and crimping the edges to create a durable, professional finish. This is especially valuable for items like curtains, upholstery, bags, and carpets, where the edges need to be neat, strong, and resistant to wear. The machine can be adjusted to accommodate different materials like cotton, polyester, nylon, or mixed fabric blends, allowing manufacturers to produce high-quality, consistent results across a variety of textiles.
Border crimping machines range from manual to automated versions. Manual machines are typically used in smaller operations or for custom, low-volume production, where each piece is crimped individually, either by hand or using a foot pedal. In larger-scale production, automated machines are commonly used to handle higher volumes of fabric, ensuring that each piece is crimped precisely and efficiently. These machines often feature advanced controls, allowing operators to adjust the crimping depth, fold size, and feed rate based on the material and desired outcome. Some modern machines also offer digital controls, enabling manufacturers to fine-tune settings for consistent quality and faster turnaround times. Automated machines can even adjust the crimping parameters automatically, depending on the fabric’s thickness or type, improving both speed and accuracy.
The benefits of using a border crimping machine are numerous. It not only increases production speed but also reduces labor costs and improves the overall quality of the finished products. Crimping the edges of fabric strengthens them, making the final product more durable and less likely to unravel over time. This is especially crucial in products that experience frequent handling or wear, like upholstery or automotive textiles. Additionally, the crimped edge offers a more polished, professional look, which is important in industries where presentation matters, such as fashion, interior design, and home textiles. The crimping process also ensures that fabric edges remain intact under stress, extending the product’s lifespan.
Modern machines incorporate additional features, such as automatic tension control, safety features like automatic shutoffs, and waste management systems to improve the efficiency of the production process. With digital displays and programmable settings, these machines allow manufacturers to maintain high levels of consistency while adapting to various fabric types and production demands. This technology also reduces material waste, as the machines are designed to ensure that the crimping process is applied precisely and without excess, improving the overall sustainability of fabric production.
As industries continue to demand higher quality and more durable fabric products, border crimping machines play an increasingly critical role. Whether in small, specialized workshops or large-scale manufacturing facilities, these machines are invaluable for ensuring high-quality, long-lasting fabric edges, improving both the aesthetics and durability of a wide range of products.
The versatility of Border Crimping Machines continues to enhance manufacturing processes across various sectors, particularly where fabric integrity and aesthetics are key considerations. These machines allow for the consistent application of crimped edges, which is essential for producing high-quality textiles that are both durable and visually appealing. In addition to the obvious benefits of improving strength and safety, crimped edges also contribute to reducing material waste, as they ensure that fabric is efficiently processed with minimal offcuts. This is especially important for industries focusing on sustainability and cost-efficiency.
In high-demand environments, such as large-scale textile mills or mass production facilities, the ability to quickly and accurately crimp fabric edges helps maintain a smooth and uninterrupted workflow. With automated Border Crimping Machines, manufacturers can easily scale their operations to meet growing demand, allowing them to maintain high output rates without compromising on quality. These machines are particularly valuable when dealing with fabrics that are prone to fraying or curling, as crimping ensures a neat and secure finish, preventing such issues from affecting the overall product.
The application of border crimping technology is not limited to textiles alone. It extends to other sectors, including automotive, packaging, and even military applications, where the need for durable, finished edges is crucial. For example, in the automotive industry, where fabric is often used for seat covers and interior upholstery, crimped edges are essential to provide a clean, professional look while ensuring that the material can withstand wear and tear over time. Similarly, in packaging, where materials like canvas or synthetic fabrics are used, crimped edges prevent fabric degradation and enhance the packaging’s structural integrity.
As technological advancements continue to shape the textile industry, Border Crimping Machines are evolving as well. Future models may integrate more sophisticated automation and artificial intelligence, enabling machines to make real-time adjustments based on fabric composition or environmental conditions. This will further optimize the crimping process, allowing for even more precise control over material handling and edge finishing. The continued development of smart machines, which communicate with other parts of the production line, could also streamline operations and enhance efficiency in industries relying on fabric processing.
In addition, as manufacturers focus more on energy-efficient processes, modern Border Crimping Machines are being designed with sustainability in mind. Innovations in energy consumption and material handling reduce environmental impacts, making the machines not only faster and more accurate but also greener and more eco-friendly. This aligns with the growing trend of adopting sustainable practices in production lines, where reducing carbon footprints and improving resource efficiency are prioritized.
With their wide range of applications, ability to improve production efficiency, and constant technological innovations, Border Crimping Machines will remain a cornerstone of textile and fabric manufacturing, ensuring that products meet the highest standards of durability, appearance, and functionality. Whether you’re operating in high-volume production or specialized, low-volume applications, investing in a high-quality crimping machine offers substantial long-term benefits.
Sheet Metal Edge Deburring Machine
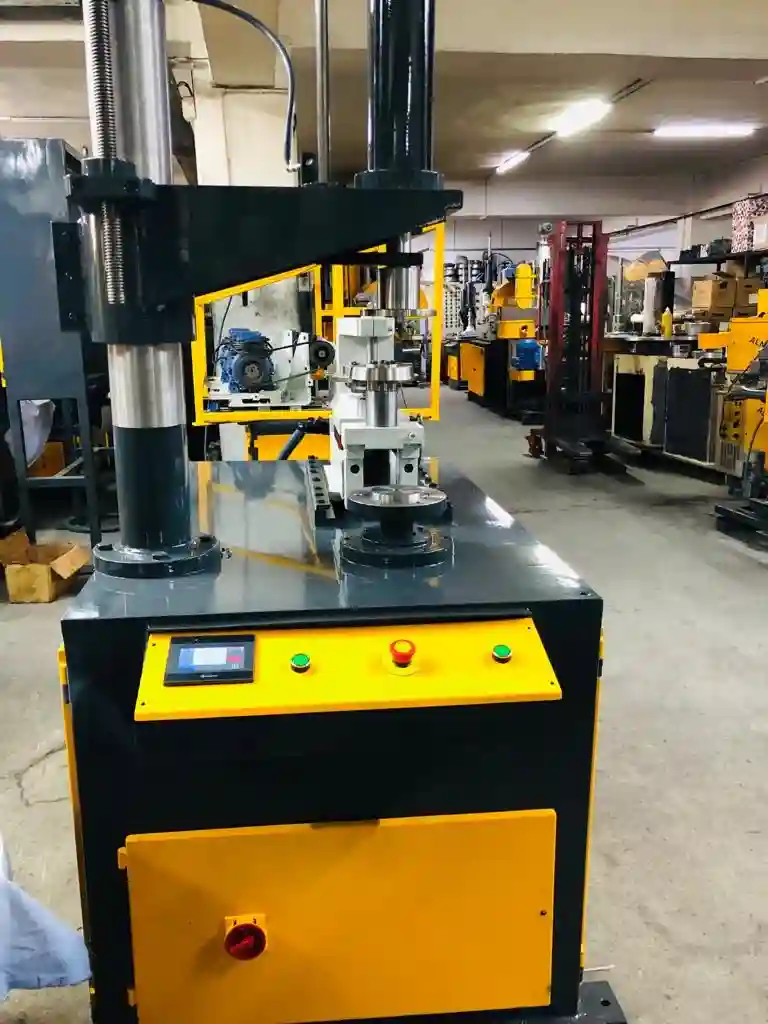

A Sheet Metal Edge Deburring Machine is designed to remove sharp edges, burrs, and other imperfections from sheet metal after cutting, stamping, or laser cutting processes. Burrs are the small, raised edges or material fragments left on the surface of metal after it has been cut or machined. These burrs can be hazardous, affecting the safety of workers, the functionality of the finished product, and the quality of subsequent manufacturing processes, such as assembly, painting, or welding. A deburring machine smooths the edges, ensuring that the metal is safe to handle and ready for further processing or use.
The operation of a sheet metal edge deburring machine typically involves feeding the metal sheet through a set of rotating abrasive tools, such as brushes, rotary wheels, or sanding belts, which remove the burrs and smooth out the edges. The machine works by applying controlled pressure to the metal, either using mechanical rollers or a combination of abrasives that carefully smooth out the edges without damaging the rest of the material. Advanced models often feature automated systems for adjusting the speed, pressure, and abrasive type based on the material and thickness of the metal, ensuring uniform deburring results.
There are several types of deburring machines, including dry, wet, and vibratory systems. In dry deburring machines, the metal is passed through abrasive wheels or brushes without the use of liquids, making them ideal for faster processing. Wet deburring machines use a combination of water or coolant along with abrasives to remove burrs more effectively, especially for tougher materials. These systems help cool down the metal and prevent excessive wear on the deburring tools. Vibratory deburring uses a machine to agitate metal parts in a vibrating tub filled with abrasive media, which can deburr and finish the edges simultaneously.
The benefits of using a sheet metal edge deburring machine are numerous. First and foremost, these machines improve worker safety by removing sharp edges that can cause cuts and injuries. They also improve the aesthetic quality of the metal by creating smooth, clean edges that enhance the final product’s appearance. Furthermore, deburring ensures better fit and alignment during assembly, as sharp edges or burrs can hinder the joining of metal parts during welding, riveting, or bolting. Additionally, deburring reduces the risk of damage to other components that come into contact with the metal edges, such as seals, gaskets, or other precision parts.
As industries continue to demand higher-quality products, the use of automated deburring machines has increased, allowing manufacturers to improve the speed and efficiency of their production lines. These machines not only save time but also reduce labor costs, as the deburring process is performed with little manual intervention. Many modern sheet metal deburring machines feature CNC controls, allowing for precise adjustments to be made quickly and easily. This is particularly beneficial for manufacturers producing high-precision components or working with different metal materials, as the machine settings can be fine-tuned to optimize the deburring process for each specific application.
Some advanced models of deburring machines include features such as brushes with variable speeds, suction systems for dust and debris removal, and automated feeders to handle large quantities of parts without requiring constant manual loading. Additionally, some machines are designed for easy integration into existing automated production lines, further streamlining the manufacturing process. The ability to adjust the pressure and abrasive materials based on the metal’s hardness, thickness, and specific requirements allows manufacturers to achieve optimal deburring results without damaging the workpieces.
A sheet metal edge deburring machine is an essential tool for industries that rely on sheet metal components, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and general manufacturing. By providing consistent, high-quality edge finishing, deburring machines improve the overall product quality, reduce manufacturing defects, and enhance safety. With ongoing advancements in automation and technology, the capabilities of these machines continue to grow, offering even greater precision, efficiency, and adaptability for diverse applications. Would you like to explore specific models or features of deburring machines suited for your production needs?
A Sheet Metal Edge Deburring Machine is crucial for removing burrs, sharp edges, and imperfections left on sheet metal during cutting, stamping, or laser processes. Burrs can pose serious risks to both safety and functionality, potentially causing injury to workers, damaging equipment, and impacting the quality of further processes like assembly, welding, or painting. The deburring process ensures that the metal is smooth and safe to handle while preparing it for additional processing or final use. These machines typically use abrasive tools such as brushes, sanding belts, or rotary wheels to apply controlled pressure to the metal, effectively smoothing the edges without damaging the rest of the material.
In some machines, abrasives are mounted on rotating drums or brushes that are applied directly to the edges of the metal as it moves through the system. This helps to gently remove the burrs while leaving the metal sheet’s surface intact. Deburring machines can be equipped with adjustable settings, allowing operators to control variables such as the speed of the abrasives, the pressure applied, and the type of abrasive material used, depending on the specific characteristics of the metal and the desired finish. The process ensures a consistent, uniform result, which is essential in industries that require high-quality and precise metal parts.
There are different types of deburring machines available, depending on the material and requirements of the operation. Some machines operate in a dry system, where abrasive tools work without the use of coolant, offering a faster deburring process, while others are wet, using coolant or water combined with abrasives to keep the metal cool during the operation. Wet deburring is particularly useful for tougher materials, as it minimizes heat buildup, which can distort the metal or wear down the tools more quickly. In contrast, vibratory deburring machines use vibration to agitate the metal parts with abrasive media inside a vibrating container, offering a gentler deburring process suitable for smaller or more delicate parts.
The main advantages of using a deburring machine go beyond just enhancing the appearance of the metal. By removing sharp edges, these machines reduce the risk of injury to workers handling the material, which is essential in any industrial environment. They also improve the performance of the final product, as burrs and sharp edges can interfere with the fitting and alignment of metal parts during assembly, welding, or machining. In addition, deburring ensures a cleaner surface for processes like painting or coating, as burrs can interfere with the adhesion of paints or finishes.
Deburring machines are particularly beneficial in high-volume production environments, where maintaining consistency, speed, and quality is critical. Automation in these machines allows for faster and more precise operations, reducing the need for manual labor and enhancing the efficiency of the production line. Many modern deburring machines feature CNC controls, which enable operators to program the machine to handle different materials and thicknesses automatically. This reduces setup times and increases flexibility in processing various metal types and configurations.
Additionally, advanced models are designed to be integrated seamlessly into existing production systems, improving the overall flow of operations and reducing bottlenecks. Some deburring machines come equipped with features like dust extraction systems to capture and remove any debris created during the process, maintaining a clean and safe work environment. This integration also helps optimize material handling by automating the feeding of metal sheets, which further streamlines the production process.
For industries that demand precision and high-quality results, deburring machines offer an essential solution. Whether in automotive manufacturing, aerospace, electronics, or general fabrication, these machines enhance product durability, improve safety, and reduce defects that could affect the final product’s performance. With ongoing advancements in technology, these machines continue to evolve, becoming more efficient, customizable, and integrated into automated production lines, further boosting the capabilities of manufacturers. The result is faster production cycles, fewer defects, and higher-quality metal parts that meet the demands of modern industry.
As manufacturing processes continue to advance, Sheet Metal Edge Deburring Machines are evolving to meet the increasing demands for higher precision, faster production, and more complex applications. The need for high-quality, burr-free metal parts is critical in many industries where metal components must meet strict standards for safety, performance, and appearance. Industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical device manufacturing rely heavily on these machines to ensure that components are not only free of burrs but also meet exacting tolerances and surface finish requirements.
Some of the newer advancements in deburring technology focus on automating the entire process from start to finish. Automated feeding systems allow sheet metal to be processed continuously without the need for manual handling, reducing labor costs and minimizing the risk of errors. These systems can handle sheets of various sizes and thicknesses, adapting to the needs of the production line without requiring frequent adjustments. Additionally, robotic arms and automated tool changers are increasingly being integrated into deburring machines, enabling more flexibility in processing different metal types and geometries. The use of robotics also allows for greater precision and repeatability, ensuring that each part undergoes the exact same deburring process, resulting in a uniform finish.
As the demand for energy-efficient and eco-friendly solutions increases, manufacturers are also focusing on designing deburring machines that reduce energy consumption and improve sustainability. Innovations such as low-energy motors, recyclable abrasive materials, and closed-loop systems for coolant or water usage help reduce the environmental impact of metalworking operations. These improvements not only lower operating costs but also support green manufacturing initiatives by reducing waste and the consumption of resources.
Another area of improvement is in the machine’s dust and debris management systems. In industrial settings, fine metal particles can become airborne during the deburring process, leading to both health risks for workers and contamination of the manufacturing environment. To combat this, modern deburring machines often come equipped with high-efficiency vacuum systems or filtered dust collection units that capture and contain metal dust, ensuring cleaner air and a safer workplace. In addition to health benefits, this approach also reduces the need for additional cleaning and maintenance, lowering overall costs.
Moreover, with the rise of Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing, deburring machines are becoming more connected. These machines are now equipped with sensors and software that provide real-time data on the deburring process, such as the condition of the abrasive tools, the wear on parts, and the overall efficiency of the machine. This data can be monitored remotely, allowing for predictive maintenance, reducing downtime, and preventing equipment failure before it happens. Machine operators can be alerted to issues like abrasive wear or material buildup, allowing for quick intervention and minimizing disruption to the production schedule.
The integration of AI and machine learning is another trend that is starting to impact deburring technology. By analyzing production data, these systems can learn to optimize deburring parameters for different metal types and part geometries. This not only improves the quality of the deburring process but also enhances overall process efficiency. AI-powered systems can also predict and recommend adjustments to improve material yield and minimize waste, further enhancing productivity.
As manufacturers continue to push for higher production rates, enhanced safety, and greater precision, the role of Sheet Metal Edge Deburring Machines becomes increasingly vital. With advancements in automation, energy efficiency, and smart technology, these machines are helping manufacturers meet the growing demand for high-quality, burr-free metal parts, while also reducing costs and environmental impact. Whether it’s a small workshop looking for precise, low-volume deburring or a large-scale operation requiring continuous, high-speed processing, these machines are integral to achieving the desired results in today’s competitive manufacturing landscape.
CNC Flanging Machine
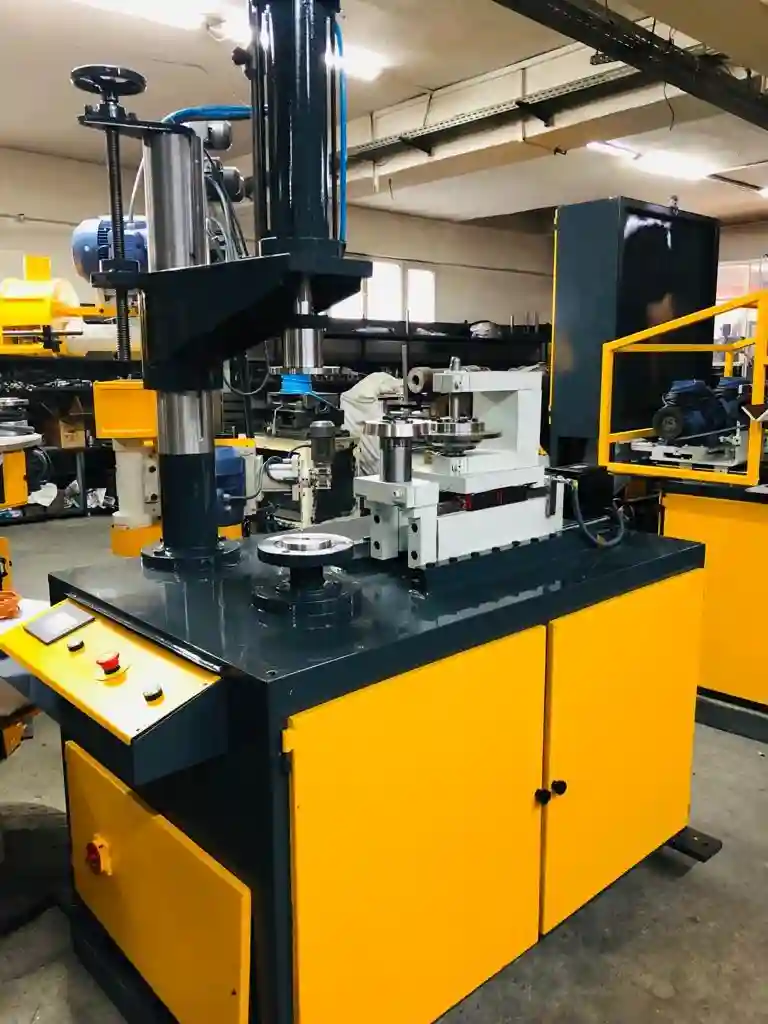

A CNC Flanging Machine is a precision tool used in metalworking to create flanges on sheet metal, pipes, or other metal components with high accuracy and repeatability. Flanging is a process that involves bending or forming the edges of a workpiece to create a raised lip or rim, which is often used for reinforcement, joining, or sealing purposes in industries such as aerospace, automotive, HVAC, and heavy manufacturing. The CNC (Computer Numerical Control) aspect of the machine allows for automated, programmable control of the flanging process, ensuring uniform results while significantly reducing manual labor and errors.
The operation of a CNC Flanging Machine typically involves clamping the metal workpiece securely in place before a rotating tool or forming die applies controlled force to bend the material into the desired flange shape. The CNC system allows operators to program specific dimensions, angles, and radii, ensuring precise and consistent flanging for each part. The machine can be adjusted to work with various metal thicknesses and materials, including aluminum, stainless steel, and carbon steel, making it highly versatile for different applications.
Compared to manual or semi-automatic flanging methods, CNC flanging offers significant advantages in terms of speed, efficiency, and precision. The automation of the process eliminates inconsistencies caused by human error and ensures that each flange is formed to exact specifications. Additionally, CNC-controlled machines can handle complex designs and custom flange shapes that would be difficult to achieve using traditional methods. This capability is particularly beneficial for industries that require high-precision components, such as aerospace, where even minor deviations in flange dimensions can affect performance and safety.
Many modern CNC Flanging Machines are equipped with advanced software interfaces that allow operators to input designs directly from CAD files, streamlining the production process and reducing setup times. Some machines also include real-time monitoring systems that track tool wear, material deformation, and process parameters, providing instant feedback to optimize performance and reduce material waste. Additionally, safety features such as automatic shutdown systems, overload protection, and enclosed work areas help minimize risks during operation.
Another key benefit of CNC flanging technology is its ability to work with a wide range of flange types, including straight flanges, curved flanges, and custom-formed flanges. This versatility makes it an essential tool in manufacturing sectors where sheet metal parts must be joined or reinforced efficiently. In applications such as automotive manufacturing, flanged edges are commonly used in exhaust systems, fuel tanks, and structural components, while in HVAC systems, flanges help create secure duct connections. In aerospace and shipbuilding, precision flanging is critical for ensuring airtight and structurally sound assemblies.
With the increasing demand for automation and smart manufacturing, CNC Flanging Machines are continually evolving to incorporate AI-driven optimizations, predictive maintenance capabilities, and seamless integration with other CNC machining processes. These advancements help manufacturers achieve greater productivity, reduce production costs, and improve overall product quality. As industries continue to move toward fully automated production lines, the role of CNC flanging machines in ensuring high-speed, high-accuracy metal forming will become even more vital.
The continued development of CNC Flanging Machines is driving efficiency and precision across multiple industries, particularly in metal fabrication and manufacturing environments that require consistent, high-quality flange formation. One of the key advantages of these machines is their ability to process a variety of materials, from lightweight aluminum and stainless steel to heavy-duty carbon steel and alloys. This flexibility makes CNC flanging indispensable in industries such as aerospace, shipbuilding, and heavy machinery, where different metal grades are used for structural integrity, durability, and performance.
Modern CNC Flanging Machines are equipped with multi-axis control systems, allowing for the formation of highly complex flange geometries. Unlike traditional single-axis machines that only bend metal in a linear fashion, multi-axis CNC machines can create intricate curves, variable-radius bends, and compound flanges that meet the strict requirements of specialized applications. This is particularly beneficial in the automotive sector, where flanged components must meet precise tolerances for parts like exhaust systems, fuel tanks, and body panels. In HVAC and ductwork manufacturing, CNC flanging ensures that connections between air ducts and ventilation systems are airtight and secure, improving energy efficiency and system performance.
The integration of smart automation in CNC Flanging Machines further enhances their efficiency. Many machines now come with real-time monitoring and adaptive control systems that adjust parameters such as pressure, feed rate, and tooling position based on material properties and processing conditions. These systems help prevent defects such as material thinning, cracking, or warping, ensuring that every flange meets strict industry standards. Additionally, touchscreen interfaces and user-friendly programming software allow operators to quickly modify settings, reducing setup time and minimizing errors.
Another key advancement in CNC flanging is the incorporation of robotic loading and unloading systems, which enable fully automated production lines. In high-volume manufacturing environments, these robotic systems eliminate the need for manual handling, reducing labor costs while increasing production speed and consistency. Some machines also feature automatic tool changers, allowing for seamless transitions between different flange sizes and shapes without operator intervention.
From a sustainability standpoint, modern CNC Flanging Machines are designed to minimize material waste and optimize energy usage. Features such as servo-controlled forming mechanisms and high-efficiency hydraulic or electric drive systems reduce power consumption while maintaining high-speed operation. This focus on sustainability is especially important in industries where reducing scrap material and improving production efficiency translate directly into cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Looking toward the future, the role of CNC Flanging Machines will continue to expand as manufacturers seek higher levels of precision, automation, and integration with digital manufacturing ecosystems. With advancements in AI-driven process optimization, predictive maintenance, and remote monitoring, these machines will become even more intelligent and adaptive, reducing downtime and further improving productivity. As Industry 4.0 technologies become more widespread, CNC flanging systems will seamlessly integrate with IoT-connected production lines, allowing for real-time data exchange and process optimization across entire manufacturing facilities.
Ultimately, CNC Flanging Machines remain a critical asset for modern fabrication, offering unmatched speed, accuracy, and flexibility in metal forming. Their ability to produce precise, durable, and functionally optimized flanges makes them indispensable in industries where component reliability and structural integrity are paramount. Whether in aerospace, automotive, HVAC, or heavy industry, CNC flanging continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible in high-performance metal manufacturing.
As CNC Flanging Machines continue to evolve, manufacturers are pushing for even greater precision, automation, and efficiency to meet the demands of high-performance industries. One of the most significant trends in the development of these machines is the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to enhance production capabilities. AI-driven systems can analyze vast amounts of data collected during the flanging process, learning from previous operations to optimize settings such as forming pressure, speed, and tool positioning. This reduces defects, minimizes waste, and improves overall efficiency by adapting to different materials and thicknesses in real time.
Another major advancement is the incorporation of predictive maintenance technology, which allows CNC Flanging Machines to detect signs of wear in critical components such as forming dies, hydraulic systems, and drive motors before failures occur. Sensors embedded within the machine monitor vibration levels, temperature fluctuations, and cycle counts, transmitting real-time data to maintenance teams. This proactive approach significantly reduces unexpected downtime and helps manufacturers maintain high levels of productivity without costly disruptions.
The integration of collaborative robotics (cobots) is also transforming CNC flanging operations. Cobots work alongside human operators, assisting in material handling, positioning, and post-processing tasks. Unlike traditional industrial robots, cobots are equipped with advanced safety features such as force sensors and vision systems, allowing them to operate safely in shared workspaces. This innovation is particularly beneficial for small and medium-sized manufacturers looking to enhance automation without investing in complex robotic cells.
One of the most critical challenges in flanging operations is maintaining dimensional accuracy across large production runs. To address this, modern CNC Flanging Machines are designed with active compensation systems that automatically adjust forming parameters to account for variations in material properties, thickness inconsistencies, and machine wear. This ensures that every flange meets strict tolerances, reducing the need for secondary finishing processes such as trimming or reworking.
Material innovation is another area where CNC flanging technology is advancing. With the increasing use of high-strength and lightweight alloys in industries like aerospace and electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing, flanging machines must be capable of forming materials that are more resistant to deformation while maintaining their structural integrity. New forming techniques, such as incremental flanging and multi-stage forming, allow manufacturers to create complex flanges in materials that would otherwise crack or warp under conventional forming pressures.
Another key development is the seamless integration of CNC Flanging Machines into fully automated production lines. With advancements in digital manufacturing, these machines are now connected to Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platforms, enabling real-time process monitoring, remote diagnostics, and cloud-based analytics. This connectivity allows manufacturers to track production efficiency, predict maintenance needs, and make data-driven decisions to optimize workflows.
The future of CNC flanging will also see the rise of hybrid manufacturing techniques, combining traditional flanging with additive manufacturing (3D printing) to create highly engineered metal components. In aerospace and medical industries, for example, parts can be initially shaped using additive manufacturing and then finished using CNC flanging to achieve the necessary precision and strength.
With all these advancements, CNC Flanging Machines are becoming smarter, more versatile, and more energy-efficient, reinforcing their importance in modern fabrication. As industries continue to push for higher performance, tighter tolerances, and increased automation, these machines will remain at the forefront of high-precision metal forming, helping manufacturers meet the demands of next-generation engineering and production.
Edge Flanging Machine

An Edge Flanging Machine is a specialized metal forming tool used to bend or fold the edges of sheet metal to create a flange. This process is essential in a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, HVAC, shipbuilding, and general fabrication, where precise edge forming is necessary for assembly, reinforcement, and sealing purposes. Unlike standard flanging machines that work on various parts of a metal sheet, an edge flanging machine focuses specifically on shaping the edges of a workpiece, ensuring uniformity, strength, and accuracy.
These machines can handle different materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, carbon steel, and high-strength alloys, depending on the application requirements. The primary goal of edge flanging is to prepare the metal for welding, riveting, bolting, or sealing, improving the overall durability and functionality of the component.
How Edge Flanging Machines Work
Edge flanging machines operate by using a controlled force to bend the edges of the metal sheet at a predefined angle. The process usually involves the following steps:
- Clamping the Metal Sheet: The workpiece is secured to prevent movement during the flanging process.
- Positioning the Flanging Tool: The machine aligns the flanging tool to the sheet’s edge.
- Forming the Flange: The tool applies force to gradually bend the metal edge to the required angle, which can range from small lip bends to fully closed hems.
- Finishing and Quality Control: The formed edge is inspected to ensure it meets the desired specifications and consistency.
Edge flanging can be performed using different forming techniques, including roller flanging, press flanging, and incremental bending, depending on the complexity and precision required. Some machines use servo-driven rollers to gradually shape the flange, while others rely on hydraulic or mechanical presses for high-force bending.
Types of Edge Flanging Machines
- Manual Edge Flanging Machines – Used for small-scale production and custom fabrications where operators control the forming process manually.
- Semi-Automatic Edge Flanging Machines – Feature automated feeding and forming mechanisms but still require some operator input.
- CNC Edge Flanging Machines – Fully automated, programmable machines that provide high-speed, high-precision edge flanging with minimal operator intervention.
Advantages of Edge Flanging Machines
- Improved Strength & Structural Integrity: Flanged edges increase the rigidity of metal sheets, reducing deformation risks.
- Enhanced Assembly & Joint Strength: Properly flanged edges improve welding, bolting, or adhesive bonding performance.
- Reduced Material Waste: Modern machines optimize the forming process to minimize scrap.
- Consistency & Accuracy: CNC-controlled machines ensure repeatable and uniform flanging, eliminating human errors.
- Increased Production Speed: Automated systems allow for high-volume manufacturing, reducing processing times.
Applications of Edge Flanging Machines
- Automotive Industry: Used for forming panel edges, door frames, and structural reinforcements.
- Aerospace Manufacturing: Creates precise, lightweight, and durable flanges for aircraft components.
- HVAC & Ductwork: Ensures air-tight connections in sheet metal ducts and ventilation systems.
- Shipbuilding & Heavy Industry: Strengthens metal plates and structural components for ships and large machinery.
With the increasing demand for precision and automation in metal fabrication, edge flanging machines are continuously evolving. Advanced models now feature AI-driven process control, real-time monitoring, and Industry 4.0 connectivity, ensuring high efficiency and quality in modern manufacturing environments.
As edge flanging machines continue to advance, they are becoming even more precise, efficient, and versatile, meeting the evolving demands of modern manufacturing. With the integration of automation, AI-driven optimization, and real-time monitoring, these machines are now capable of producing high-quality flanged edges with minimal human intervention, reducing both production time and costs.
Technological Advancements in Edge Flanging Machines
One of the most significant advancements is the introduction of servo-driven flanging systems, which allow for more precise control over the bending process. Unlike traditional hydraulic or pneumatic systems, servo-driven machines offer higher accuracy, better energy efficiency, and reduced maintenance requirements. These systems can dynamically adjust forming forces based on material thickness and hardness, ensuring consistent results across different workpieces.
Another innovation is multi-axis control, which enables machines to form complex flanges with varying angles and radii. This is particularly useful in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and shipbuilding, where parts often require non-standard flanges with precise tolerances. Multi-axis systems can handle curved, tapered, and asymmetric flanging operations with ease, expanding the range of possible applications.
Edge Flanging & Industry 4.0 Integration
With the rise of smart manufacturing, modern edge flanging machines are now equipped with IoT (Internet of Things) connectivity, enabling real-time data collection and process monitoring. Sensors embedded in the machine continuously track forming forces, tool wear, and workpiece alignment, providing feedback to optimize operations. This data-driven approach enhances quality control by identifying potential defects before they occur, reducing scrap rates and increasing efficiency.
Additionally, manufacturers are integrating predictive maintenance capabilities, which analyze machine performance and usage patterns to anticipate mechanical failures before they happen. This reduces unexpected downtime and extends the lifespan of critical components, leading to higher overall productivity.
High-Speed Automation & Robotics
Automation is playing an increasingly important role in edge flanging. Robotic loading and unloading systems are now being used to streamline production, especially in high-volume manufacturing environments. By reducing manual handling, these systems improve workplace safety, enhance consistency, and allow for 24/7 operation. Some advanced setups even feature automated tool changers, which enable seamless transitions between different flange sizes and shapes without stopping production.
Sustainability & Energy Efficiency
In response to global sustainability goals, many modern edge flanging machines are now designed with eco-friendly features, such as:
- Energy-efficient servo motors that reduce power consumption.
- Recyclable tool materials that minimize waste.
- Optimized material utilization software, which maximizes sheet metal usage, reducing scrap.
By implementing these innovations, manufacturers can significantly lower their carbon footprint while improving cost-effectiveness.
Future Trends & Applications
Looking ahead, edge flanging machines will continue to evolve, integrating AI-powered process optimization, adaptive forming techniques, and even hybrid manufacturing methods that combine flanging with laser cutting or additive manufacturing (3D printing). These advancements will enable manufacturers to create more complex, lightweight, and high-strength components, catering to industries such as electric vehicle (EV) production, space exploration, and renewable energy infrastructure.
With these technological improvements, edge flanging machines remain an indispensable tool in precision metalworking, offering unmatched efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability for modern fabrication needs.
Automatic Forming Machine

An Automatic Forming Machine is a highly advanced and efficient system designed to shape metal, plastic, or composite materials into precise forms with minimal human intervention. These machines are widely used in automotive, aerospace, HVAC, construction, packaging, and electronics industries, where speed, accuracy, and consistency are critical in the manufacturing process.
Unlike traditional forming methods that rely on manual adjustments, automatic forming machines integrate CNC (Computer Numerical Control), servo-driven systems, and AI-driven process optimization to achieve high-speed production while maintaining precision. They can handle a variety of operations, such as bending, flanging, stamping, deep drawing, roll forming, and hydroforming, depending on the application and material requirements.
How Automatic Forming Machines Work
Automatic forming machines use programmable control systems to execute forming operations with high precision. The process generally involves:
- Material Feeding: The raw material (sheet metal, plastic sheets, or wire) is automatically fed into the machine. Some models include coil feeding systems for continuous production.
- Positioning & Clamping: The material is accurately positioned and secured to ensure stability during the forming process.
- Shaping/Forming Process: The machine applies force through dies, rollers, hydraulic presses, or electromagnetic forming systems to shape the material according to programmed specifications.
- Quality Control & Adjustments: Sensors and vision systems monitor the process in real-time, ensuring that the formed parts meet design tolerances.
- Automated Ejection or Transfer: The finished part is either ejected or transferred to the next production stage without manual handling.
Types of Automatic Forming Machines
- CNC Sheet Metal Forming Machines – Used in automotive and aerospace industries for precision forming of metal panels, enclosures, and components.
- Roll Forming Machines – Continuously shape metal sheets into profiles such as roofing sheets, structural beams, and tubing.
- Deep Drawing Machines – Used for creating complex 3D shapes like fuel tanks, cookware, and automotive parts.
- Hydraulic Forming Machines – Use high-pressure hydraulic systems for applications requiring deep and precise material deformation.
- Thermoforming Machines – Common in packaging and medical device manufacturing, these machines heat plastic sheets and mold them into desired shapes.
- Wire Forming Machines – Used for producing springs, brackets, and custom wire shapes for electrical and mechanical applications.
Advantages of Automatic Forming Machines
- High Production Speed & Efficiency – Significantly reduces cycle times, increasing throughput.
- Precision & Consistency – CNC and AI-controlled systems ensure tight tolerances and repeatable results.
- Reduced Labor Costs – Automation minimizes the need for manual intervention.
- Versatility – Can handle various materials and complex geometries.
- Waste Reduction – Optimized forming processes improve material utilization.
- Enhanced Safety – Reduces operator fatigue and exposure to high-pressure forming forces.
Integration with Industry 4.0 & Future Trends
Modern automatic forming machines are equipped with IoT connectivity, allowing for real-time data monitoring, predictive maintenance, and remote control. AI-powered software can analyze forming parameters and adjust processes to optimize material usage and minimize defects. The future of automatic forming machines will likely include AI-driven quality inspection, hybrid forming technologies (combining laser cutting & forming), and sustainable energy-efficient designs to further improve productivity and reduce environmental impact.
With continuous advancements in smart automation, AI, and adaptive forming techniques, automatic forming machines will remain a cornerstone of high-precision manufacturing, meeting the growing demands for speed, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness in modern industries.
As Automatic Forming Machines continue to evolve, they are becoming more intelligent, adaptive, and capable of handling an increasingly diverse range of materials and applications. These machines are now integral to high-precision industries, where consistency, efficiency, and adaptability are essential for meeting modern production demands.
Advanced Features of Modern Automatic Forming Machines
1. AI-Driven Process Optimization
One of the most significant advancements in automatic forming technology is the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms. These systems analyze production data in real time to:
- Optimize forming parameters, such as pressure, speed, and temperature.
- Detect material variations and adjust forming techniques accordingly.
- Predict defects before they occur, minimizing scrap and rework.
By continuously learning from previous operations, AI-powered forming machines reduce errors, increase material efficiency, and improve overall productivity.
2. Smart Sensors & Real-Time Monitoring
Modern machines are equipped with IoT-enabled smart sensors that collect and transmit real-time data on:
- Forming force and tool wear
- Material thickness and consistency
- Temperature fluctuations in the forming process
- Cycle times and overall efficiency
This data is analyzed by cloud-based manufacturing systems, allowing for remote monitoring and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and unexpected failures.
3. Robotics & Automation in Material Handling
Advanced automatic forming machines now integrate with robotic arms and automated material handling systems. These collaborative robots (cobots):
- Load and unload materials without human intervention.
- Position workpieces with extreme precision, improving forming accuracy.
- Work alongside operators safely, increasing productivity in high-volume manufacturing environments.
Some machines also feature automated tool changers, allowing them to switch between different dies, forming heads, and processes without stopping production.
4. Hybrid Manufacturing Capabilities
To further expand their capabilities, some automatic forming machines are being integrated with other manufacturing processes, such as:
- Laser cutting & punching – Allows for precision cutting before or after forming.
- 3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing) – Enables hybrid metal forming with customized designs.
- Incremental Sheet Forming (ISF) – A flexible approach for producing low-volume, complex geometries.
This multi-functional approach allows manufacturers to complete multiple fabrication steps in a single operation, reducing the need for secondary processing.
5. Energy Efficiency & Sustainable Manufacturing
With increasing focus on green manufacturing, automatic forming machines are now designed with energy-efficient motors, regenerative braking systems, and optimized forming cycles to:
- Reduce power consumption, lowering operational costs.
- Minimize material waste, making production more sustainable.
- Utilize eco-friendly forming techniques, such as electromagnetic or hydroforming, which consume less energy compared to traditional press forming.
Future Trends in Automatic Forming Machines
The next generation of forming machines will likely incorporate:
- AI-powered self-correcting systems, which adjust forming operations dynamically based on real-time feedback.
- Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) interfaces, allowing operators to simulate forming processes before actual production.
- Fully autonomous forming lines, where machines communicate with each other to optimize production without human intervention.
- Advanced materials processing, including forming of next-gen lightweight alloys, composites, and ultra-high-strength steels for industries like electric vehicles, aerospace, and renewable energy.
Conclusion
Automatic forming machines are transforming manufacturing by delivering high-speed, high-precision, and fully automated forming solutions. Their ability to adapt to new materials, integrate with smart factory systems, and reduce costs makes them a key technology in modern Industry 4.0 production environments. As advancements continue, these machines will play an even greater role in high-precision, sustainable, and efficient manufacturing across multiple industries.
How to Smooth Sheet Metal Edges
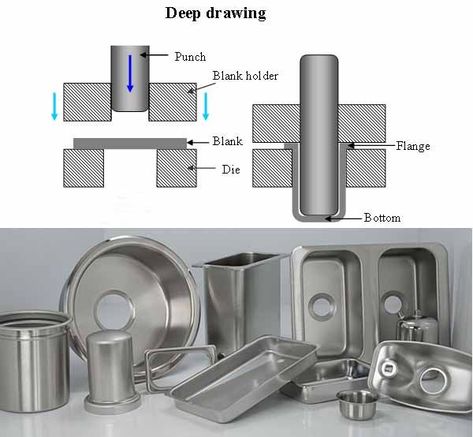
Smoothing sheet metal edges is essential to improve safety, aesthetics, and functionality in metalworking projects. Rough or sharp edges can cause injuries, hinder assembly, or lead to premature wear. There are several methods to smooth sheet metal edges, depending on the material type, thickness, and desired finish.
Manual Methods for Smoothing Sheet Metal Edges
These methods are suitable for small-scale or custom projects where precision is needed without specialized machinery.
1. Sanding Blocks or Sandpaper
- Use medium-grit sandpaper (80-120 grit) to remove burrs and sharp edges.
- Follow up with fine-grit sandpaper (220-400 grit) for a smoother finish.
- Move in a consistent, even motion along the edge to prevent uneven wear.
2. Hand Files
- Use a bastard file (coarse-cut) to remove large burrs.
- Switch to a second-cut or fine file to refine the edge.
- Always file in one direction, avoiding a back-and-forth motion.
3. Deburring Tool
- A rotary deburring tool with a sharp, angled blade can remove burrs efficiently.
- Ideal for curved or complex shapes where sanding or filing is difficult.
- Use light pressure to prevent removing too much material.
4. Scouring Pads or Steel Wool
- For softer metals like aluminum or copper, scouring pads can smooth edges without excessive material removal.
- Works well for achieving a polished finish after initial deburring.
Power Tool Methods for Smoothing Sheet Metal Edges
For larger-scale projects or thick sheet metal, power tools can make the process faster and more consistent.
1. Angle Grinder with Flap Disc
- Use a 120-grit flap disc for aggressive material removal.
- Move the grinder along the edge with light pressure to avoid overheating.
- Ideal for steel, stainless steel, and thick metal sheets.
2. Bench Grinder or Belt Sander
- A fine-grit belt (120-220 grit) removes burrs quickly and evenly.
- Keep the metal moving to prevent overheating and discoloration.
- Works well for large sheets or repetitive tasks.
3. Dremel Rotary Tool
- A sanding drum or grinding bit can deburr small or intricate edges.
- Best for detailed work, tight corners, or decorative edges.
- Use at moderate speed to avoid excessive material loss.
Chemical & Specialized Techniques
For ultra-smooth finishes or mass production, specialized techniques can be used.
1. Electrochemical Deburring
- Uses electrical current and electrolyte solution to dissolve sharp edges.
- Common in precision machining and aerospace industries.
2. Tumbling & Vibratory Finishing
- Small parts are placed in a tumbling or vibratory machine with abrasive media.
- Effective for large batches of small metal parts.
Final Finishing
After smoothing, apply:
- Metal polish for shine and rust prevention.
- Protective coatings (clear coat, paint, or anodizing) to prevent corrosion.
Safety Tips
- Wear cut-resistant gloves to protect hands.
- Use eye protection to avoid metal dust or debris.
- Work in a well-ventilated area when using power tools.
By selecting the right method based on material type and project scale, you can achieve smooth, safe, and professional-looking metal edges efficiently.
Smoothing sheet metal edges is a crucial step to enhance safety, improve aesthetics, and ensure proper functionality in metalworking projects. Rough or sharp edges can cause injuries, interfere with assembly, and lead to premature wear or corrosion. Various methods are available, ranging from manual techniques to power tools and specialized processes, depending on the material type, thickness, and required finish.
Manual methods are suitable for small-scale work and detailed finishing. Using sandpaper or sanding blocks with medium grit (80-120) can effectively remove burrs, while fine grit (220-400) provides a smoother edge. Hand files, particularly bastard files for coarse cutting and second-cut files for refining, offer precise control. Filing should be done in a single direction for consistency. A deburring tool with a rotary blade is an efficient choice for curved or intricate edges, as it removes sharp edges with minimal effort. For softer metals like aluminum or copper, scouring pads or steel wool can gently smooth out irregularities and prepare the surface for polishing.
Power tools significantly speed up the process for larger projects or thicker metal sheets. An angle grinder equipped with a 120-grit flap disc removes burrs quickly while maintaining control over the material. When using a bench grinder or belt sander, applying steady pressure and keeping the metal moving prevents overheating and uneven surfaces. A Dremel rotary tool with a sanding drum or grinding bit is ideal for intricate designs, corners, or small-scale work requiring precision. These tools provide efficient and consistent results, reducing the time needed to finish metal edges.
For high-volume manufacturing or applications requiring ultra-smooth edges, specialized techniques such as electrochemical deburring and vibratory finishing are effective. Electrochemical deburring uses an electrical current combined with an electrolyte solution to dissolve sharp edges with high precision, commonly used in aerospace and precision machining. Tumbling or vibratory finishing involves placing small metal parts in a machine with abrasive media to automatically smooth the edges, making it an excellent choice for batch processing.
After smoothing the edges, applying a protective finish enhances durability and prevents oxidation or corrosion. Metal polish can improve shine, while clear coatings, paint, or anodizing add a protective barrier against environmental factors. Safety precautions should always be followed, including wearing cut-resistant gloves to protect hands, eye protection to shield against metal debris, and ensuring proper ventilation when using power tools.
By selecting the appropriate method based on project requirements, material type, and production scale, it is possible to achieve smooth, professional-quality edges that enhance both the appearance and performance of the final product.
Achieving perfectly smooth sheet metal edges not only enhances safety but also improves the overall quality and functionality of fabricated parts. Whether for industrial applications, custom manufacturing, or artistic metalwork, ensuring well-finished edges prevents injuries, facilitates better assembly, and reduces wear on adjoining components. The choice of smoothing method depends on factors such as metal type, thickness, and production scale, with options ranging from manual techniques to advanced automated systems.
For precision work or smaller projects, manual methods provide excellent control. Sanding with progressively finer grits of sandpaper is one of the simplest ways to refine rough edges, while hand files allow for targeted smoothing, especially for complex shapes. A bastard file is effective for heavy material removal, whereas a second-cut or fine file is ideal for refining and finishing. Using a deburring tool with a sharp, rotating blade offers a quick and efficient way to remove burrs, particularly for curved or intricate edges. Scouring pads or steel wool can be used as a final step to further smooth the surface, especially for softer metals such as aluminum or brass.
For more demanding projects requiring efficiency and consistency, power tools significantly enhance the smoothing process. An angle grinder equipped with a flap disc offers rapid burr removal and is especially effective on thick metal sheets. A bench grinder or belt sander provides a more controlled finish for straight edges and repetitive tasks, ensuring uniformity across multiple pieces. A Dremel rotary tool, fitted with a sanding drum or grinding bit, is ideal for detailed work, allowing for precision edge finishing in small or intricate areas. These power tools not only save time but also ensure a high-quality finish when used with steady hands and the right level of pressure.
In large-scale production environments, advanced techniques such as electrochemical deburring and vibratory finishing are utilized. Electrochemical deburring, which uses a controlled electrical current and electrolyte solution, is highly precise and effective for delicate components that require minimal mechanical stress. Vibratory finishing involves placing multiple metal parts in a machine filled with abrasive media, which continuously polishes and smooths the edges in a consistent manner. These methods are particularly beneficial for mass production, where efficiency and uniformity are critical.
Beyond the smoothing process, applying a final protective treatment enhances both appearance and longevity. Polishing compounds can give the metal a refined shine, while protective coatings such as paint, clear lacquer, or anodizing safeguard against corrosion and wear. Adhering to safety precautions is crucial throughout the smoothing process. Wearing cut-resistant gloves prevents hand injuries, eye protection shields against flying metal particles, and proper ventilation is necessary when using power tools to manage dust and fumes.
With continued advancements in metalworking technology, new automated deburring and edge-finishing solutions are emerging, further improving efficiency and precision. AI-driven process monitoring, CNC-integrated deburring stations, and robotic smoothing systems are being adopted in high-tech industries, ensuring that metal edges meet exacting quality standards with minimal manual intervention. By selecting the most suitable method based on project needs, manufacturers and craftsmen alike can achieve smooth, flawless edges that contribute to superior product quality and long-term durability.
Choosing the best metal deburring tool depends on the specific needs of your project, such as the type of metal, the size and shape of the workpiece, the scale of production, and the desired finish. Here are some of the top deburring tools available, categorized by their use case:
1. Manual Deburring Tools
These are ideal for smaller batches, intricate workpieces, or situations where precision is key.
Rotary Deburring Tool
- Best for: Light to medium deburring, small or intricate parts.
- Example:RUKO Rotary Deburring Tool
- Features: Offers interchangeable blades for different edge profiles and is easy to use on curved and hard-to-reach areas. It’s a hand-held, ergonomic tool that’s perfect for small to medium-sized projects.
- Pros: Great for precision work, easy to control, and comfortable to use for long periods.
- Cons: Manual operation, so it can be slower for large volumes.
Deburring Blades (Handheld)
- Best for: Removing burrs from edges of metal parts.
- Example:Proxxon 28500 Deburring Tool
- Features: Interchangeable high-quality steel blades that effectively remove burrs from inside or outside edges of metal parts.
- Pros: Affordable, easy to use, and portable for tight spaces.
- Cons: Requires manual effort and can be slow for high-volume work.
Manual File
- Best for: Larger burrs and rough edges, especially on thin metals.
- Example:Nicholson 5-Button File Set
- Features: Flat, round, or half-round files that come in various shapes and coarseness to suit different applications.
- Pros: Versatile and great for detailed manual work.
- Cons: Requires skill and can be time-consuming for larger jobs.
2. Electric & Pneumatic Deburring Tools
Electric and pneumatic deburring tools are more efficient for high-volume production and larger workpieces. They can remove burrs quickly and are designed for use in industrial environments.
Electric Deburring Tool
- Best for: General-purpose deburring and high-volume work.
- Example:Makita 9403 Belt Sander
- Features: Powerful sander with a continuous belt for fast and smooth deburring of edges on large metal sheets.
- Pros: Efficient and reliable, especially for finishing large pieces quickly.
- Cons: Not as precise as rotary tools for smaller parts or delicate operations.
Pneumatic Deburring Tool
- Best for: Heavy-duty deburring in high-production environments.
- Example:Chicago Pneumatic CP7262 Pneumatic Deburring Tool
- Features: Uses air power to drive a high-speed rotary deburring head that can quickly remove burrs from metal surfaces.
- Pros: High efficiency, reduces fatigue, and works well in industrial environments where power tools are required.
- Cons: Needs an air compressor, making it less portable and requiring more setup.
3. Power Tools for Deburring
For large-scale applications and fast results, power tools are a great option. These tools can be fitted with different attachments or abrasives to optimize the deburring process.
Angle Grinder
- Best for: Large-scale deburring on thicker metals or industrial applications.
- Example:Makita GA7021 Angle Grinder
- Features: Heavy-duty grinder with a variety of attachments like wire wheels or flap discs for deburring.
- Pros: Fast and powerful for removing large burrs on thick materials.
- Cons: Can be too aggressive for delicate or thin metals, creating a risk of damaging the workpiece.
Dremel Rotary Tool
- Best for: Detailed deburring on intricate parts or small projects.
- Example:Dremel 4000 Rotary Tool
- Features: Precision control with various attachments such as sanding drums, grinding wheels, and deburring bits.
- Pros: Excellent for small, precise work in tight areas.
- Cons: Limited power for larger industrial tasks.
4. Deburring Machines
In high-production settings, deburring machines provide automated and consistent results. These machines are suitable for handling large batches of parts and can work at high speed.
Vibratory Finishing Machine
- Best for: High-volume, batch deburring and polishing.
- Example:Mass Finishing Vibratory Deburring Machine
- Features: Parts are placed in a vibrating bowl filled with abrasive media to smooth edges and surfaces.
- Pros: Ideal for batch processing, requires little manual effort.
- Cons: Takes longer for larger pieces, and may not work for highly detailed work.
CNC Deburring Machine
- Best for: Precision deburring for parts with complex geometries or tight tolerances.
- Example:Timesavers 1100 Series Deburring Machine
- Features: Uses CNC-controlled abrasive belts and brushes to achieve consistent and precise deburring on a variety of materials.
- Pros: Highly efficient, precise, and ideal for mass production.
- Cons: High cost and typically used for industrial-scale applications.
5. Specialized Tools
For certain materials or complex applications, specialized deburring tools are designed for optimal results.
Electrochemical Deburring Tool
- Best for: Precision deburring of delicate or intricate parts, especially in the aerospace or automotive industries.
- Example:R&R Electrochemical Deburring System
- Features: Uses a controlled electrochemical process to remove burrs from internal passages and complex geometries.
- Pros: Ideal for highly precise deburring without applying mechanical stress.
- Cons: Expensive and used primarily in specialized industries.
Tumbling & Polishing Machines
- Best for: Smoothing edges of small metal parts in high-volume production.
- Example:LJMU Vibratory Finishing Machine
- Features: Uses abrasive media in a vibrating or rotating barrel to smooth edges and finish parts in bulk.
- Pros: Great for high-volume applications with consistent, smooth results.
- Cons: Less precise than manual methods.
Conclusion
When selecting the best metal deburring tool, consider the size of your project, material type, and whether you are working on small, detailed items or large, industrial components. For smaller, detailed jobs, rotary tools, hand files, or manual deburring blades are sufficient. For high-volume or industrial work, pneumatic, electric tools, or automated machines like vibratory finishing machines will improve efficiency and consistency. Investing in the right deburring tool based on your needs will ensure cleaner, safer, and more professional metal edges.
When selecting the best metal deburring tool, it’s important to assess factors such as project scale, the type of metal you’re working with, and whether you need precision for small parts or speed for large-scale applications. For small, intricate jobs or occasional use, manual deburring tools like handheld deburring blades or rotary tools are ideal. These tools are easy to use and allow for high precision, making them great for detailed work or smaller batches. Rotary deburring tools, in particular, are effective for removing sharp edges, especially in hard-to-reach areas. These tools offer replaceable blades for different profiles, making them versatile for various applications.
For larger tasks or heavy-duty deburring, electric and pneumatic tools are great choices. Pneumatic deburring tools, driven by air pressure, are perfect for industrial environments and can handle more aggressive burr removal. These tools are faster and more efficient than manual options, making them well-suited for high-volume production. However, they require an air compressor, which limits portability but enhances performance in large-scale settings. Electric deburring tools, on the other hand, provide more control for medium-duty applications and can be used effectively in a variety of metalworking situations. They work well for deburring edges, especially when combined with abrasive attachments like sanding drums or wire wheels.
Power tools such as angle grinders and Dremel rotary tools offer a fast, efficient way to deburr metal. Angle grinders, equipped with a variety of attachments, can quickly remove large burrs from thicker materials, while Dremel tools are great for small, intricate parts where precision is crucial. Both tools are more aggressive than manual options, so they may not be ideal for delicate metals or tight areas. Nevertheless, they are indispensable for larger projects where speed is necessary.
For mass production or high-volume deburring, automated machines like vibratory finishing machines and CNC deburring machines are excellent choices. Vibratory finishing machines, which use abrasive media to smooth edges by vibrating parts in a bowl or drum, are perfect for batch processing and can handle hundreds or even thousands of pieces simultaneously. These machines are highly efficient, providing consistent results with minimal manual labor, but they are better suited for simpler geometries rather than highly detailed or intricate parts. CNC deburring machines are ideal for parts with complex shapes or precise edge finishes. These machines use computer-controlled abrasive belts or brushes to remove burrs, offering unparalleled consistency and precision. However, their high cost makes them best suited for large-scale industrial environments.
Specialized tools such as electrochemical deburring systems are perfect for particularly delicate parts or those with complex internal features. This method uses electrical current and electrolyte solutions to gently remove burrs from the metal without applying mechanical force, which is especially beneficial for parts that could be damaged by traditional methods. Though effective, electrochemical deburring is generally used in industries that require the highest levels of precision, such as aerospace or medical device manufacturing.
Tumbling and polishing machines are also commonly used for deburring small metal parts in bulk. These machines work by tumbling parts in a rotating drum or bowl filled with abrasive media. The parts are continuously smoothed and polished as they collide with the media. This method is ideal for high-volume production runs, as it ensures consistent deburring with minimal labor involvement, but it may not work well for larger or more complex parts that need precise finishing.
Ultimately, the best deburring tool depends on the specific demands of the project. For smaller jobs requiring fine control, manual deburring tools are effective and affordable. For larger-scale production, pneumatic or electric tools provide the speed and efficiency needed to handle high volumes. Automated systems such as vibratory finishers or CNC machines are the go-to choice for industries requiring high precision and large batch processing. By understanding the scope and needs of your project, you can select the right tool that provides the best balance of efficiency, cost, and finish quality.
To further refine your deburring process, it’s important to consider the material being worked with. Different metals have varying hardness and properties, which can influence the type of deburring tool needed. For example, soft metals like aluminum or copper are easier to deburr using manual tools such as rotary deburring tools or hand files, but they may require finer abrasives or softer materials to avoid damaging the surface. On the other hand, harder metals like stainless steel or titanium require more robust tools, such as pneumatic deburring machines or angle grinders with specialized abrasive discs designed for harder materials. These tools can effectively handle the tougher surfaces, ensuring efficient burr removal without causing unnecessary wear on the tool itself.
When working with delicate parts, especially those with complex geometries or intricate features, precision is key. Tools like the Dremel rotary tool with various attachments or even specialized grinding heads provide detailed control and allow for meticulous deburring of small areas without compromising the part’s integrity. Additionally, for parts with internal passages or inaccessible spots, electrochemical deburring can be the best solution, as it uses an electrolyte solution and electrical current to gently dissolve burrs in hard-to-reach areas, leaving the surrounding surface unaffected.
The scale of your operation also influences the type of deburring tool that will offer the best return on investment. For small to medium-sized shops or one-off projects, manual and electric tools might suffice, as they are more affordable and flexible. However, in high-volume production environments, investing in automated solutions like vibratory finishing machines or CNC deburring systems can dramatically increase productivity while ensuring uniform quality across large batches. These machines are designed to operate at high speeds and are particularly beneficial when dealing with repetitive deburring tasks, reducing manual labor and minimizing the potential for human error.
Maintenance of your deburring tools is essential to ensure they continue performing at their best over time. Regularly checking and replacing worn blades, sanding drums, or abrasives will help maintain their effectiveness and avoid inefficient or inconsistent results. Additionally, proper cleaning and storage are important for prolonging the life of tools, especially for pneumatic or electric machines that rely on moving parts. Keeping tools well-maintained also contributes to a safer working environment by reducing the chances of malfunction or injury during operation.
For those working in specialized industries, such as automotive, aerospace, or medical device manufacturing, ensuring that deburring methods meet industry standards is critical. These industries often require deburring tools that offer not only precision but also consistency in finish, as well as the ability to process parts without introducing defects or contaminating sensitive materials. For instance, using a deburring tool with adjustable speeds and pressures may be necessary to ensure that parts are deburred without affecting the mechanical properties or dimensions.
In addition to choosing the right tools for your project, ensuring proper safety practices is key. Many deburring tools, especially power tools like grinders and pneumatic machines, produce sharp debris, sparks, or intense noise levels. Wearing personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety goggles, gloves, ear protection, and protective clothing, is critical to minimize the risk of injury. Furthermore, adequate ventilation should be ensured, especially when working with power tools or when performing operations that generate heat or fumes. Regularly inspecting the workspace for potential hazards and keeping the area clean of metal debris will also help create a safer working environment.
Overall, selecting the best deburring tool involves a combination of understanding your project needs, the materials you’re working with, and the scale of production. Whether you’re working on a small, detailed project or a large batch of parts, there are tools available to help achieve smooth, burr-free metal edges quickly and efficiently. With the right tool in hand, you can ensure that your metalworking projects meet the highest standards of quality, safety, and precision.
As you continue to refine your deburring process, it’s important to explore additional techniques and advancements that can further enhance the overall quality of your work and streamline production. One emerging area in deburring technology is the use of automation and robotics. In larger industrial settings, robots can be integrated with deburring tools, such as CNC systems or robotic arms with sanding heads. These robotic systems can perform consistent deburring tasks on complex parts, greatly improving efficiency and reducing human error. This is particularly useful for high-precision applications, such as in the aerospace, automotive, or electronics industries, where consistent quality is paramount.
Another key development in deburring technology is the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. AI systems can monitor the deburring process in real time, adjusting tool parameters such as speed, pressure, and angle to optimize performance based on the material being processed. This adaptive approach helps minimize material waste, reduces the risk of over-deburring or under-deburring, and improves the overall consistency of the finish. Some CNC deburring machines now incorporate AI to predict tool wear and adjust operational parameters automatically, ensuring long-term, consistent results without the need for frequent manual adjustments.
For businesses aiming to improve their sustainability practices, some modern deburring machines offer features that reduce energy consumption and minimize material waste. For example, some systems utilize water-based coolants or eco-friendly abrasive materials to reduce environmental impact. Additionally, certain vibratory finishing machines can use reusable media that extends the life of the abrasives, further decreasing the need for new materials and reducing the overall cost of consumables.
In addition to technological advancements, the development of specialized abrasives and coatings for deburring has also seen significant progress. For instance, ceramic abrasives have gained popularity due to their durability and ability to maintain sharp cutting edges over extended use. These abrasives are particularly useful for deburring harder metals like stainless steel and titanium, as they provide a smoother, more consistent finish compared to traditional abrasives. Similarly, coated abrasives, such as those with a diamond or CBN (cubic boron nitride) coating, are increasingly used in industries requiring extremely high precision and toughness. These abrasives can withstand the demands of harder materials while delivering an ultra-fine surface finish.
Additionally, integrating deburring into the broader manufacturing process can help streamline workflows and reduce production times. For example, by incorporating deburring as part of an in-line process on CNC machines or during robotic assembly, the need for additional manual deburring steps is reduced, allowing for faster turnaround times and fewer errors. This integration can be particularly useful for industries like automotive manufacturing, where large quantities of parts are produced and efficiency is critical to meeting tight deadlines and quality standards.
When considering the environmental impact of deburring operations, it’s also worth exploring dust collection and fume extraction systems. Power tools like grinders, sanders, and CNC deburring machines can generate a significant amount of airborne dust and debris, which can pose both health and environmental risks. Investing in effective dust collection systems ensures cleaner air in the workspace and reduces the potential for respiratory issues among workers. These systems can also help keep the work area cleaner, reducing maintenance costs and extending the life of tools and machinery.
For businesses with diverse production needs, flexibility in deburring tools is a significant advantage. Tools with interchangeable heads, blades, or attachments allow workers to quickly switch between different types of deburring tasks, accommodating various metal thicknesses, shapes, and sizes. This versatility ensures that the deburring process can be adapted to different projects without the need for purchasing additional specialized tools.
Lastly, it’s important to keep in mind the long-term cost-effectiveness of the deburring tools you select. While some high-end machines may seem expensive upfront, their efficiency, speed, and consistency can lead to cost savings in the long run by reducing labor costs, minimizing material waste, and preventing defects. Businesses should also consider the lifespan of tools and consumables. High-quality abrasives, for instance, may cost more initially but will last longer, offering better overall value compared to cheaper alternatives.
By staying informed about advancements in deburring technology and understanding the best tools for your specific applications, you can optimize your workflow, improve quality, and increase overall productivity. Whether you are a hobbyist working on small projects or an industrial manufacturer producing large volumes of parts, there is a wide range of deburring solutions available to meet your needs. Combining the right tools with efficient processes and continuous learning will help ensure that your metalworking projects achieve the best possible results.
Deburring Tool for Sheet Metal

When it comes to deburring sheet metal, selecting the right tool depends on the material type, thickness, the size of the part, and the desired finish. Sheet metal, being relatively thin and flexible, requires precision in the deburring process to avoid damaging the material or compromising its integrity. Here’s a detailed look at some of the best deburring tools for sheet metal:
1. Manual Deburring Tools
For smaller jobs, or when precision is key, manual deburring tools can be highly effective. They provide the control needed for delicate work and allow for fine adjustments.
Handheld Rotary Deburring Tools
- Best for: Small to medium-sized parts, especially for edge finishing and fine burr removal.
- Example:RUKO Rotary Deburring Tool
- Features: These tools often come with replaceable, sharp blades for different edge profiles (e.g., round, straight), ideal for removing burrs on both inside and outside edges.
- Pros: Allows for control, ergonomic, and easy to use.
- Cons: Manual operation, so not suitable for high-volume work.
Manual Deburring Blades
- Best for: Removing burrs from straight, simple edges.
- Example:Proxxon 28500 Deburring Tool
- Features: This tool uses replaceable, high-quality steel blades to remove burrs from sheet metal edges with minimal effort. It’s especially useful for cleaning up sharp, thin edges that could be dangerous.
- Pros: Inexpensive, portable, and offers high control.
- Cons: Labor-intensive for larger jobs.
Files and Hand Scrapers
- Best for: Precision deburring, especially on thicker sheet metal or parts requiring a finer finish.
- Example:Nicholson Hand Files
- Features: These hand tools come in a variety of shapes, including flat, round, and half-round files, making them versatile for different metalworking tasks.
- Pros: Offers excellent control and is effective for specific burr removal, especially on sharp or tight edges.
- Cons: Time-consuming for large batches or high-volume work.
2. Power Deburring Tools
For higher efficiency, power tools can be used for faster and more consistent burr removal, especially on larger sheet metal pieces or when working with high-volume production.
Pneumatic (Air-Powered) Deburring Tools
- Best for: High-volume, industrial use with the need for rapid burr removal.
- Example:Chicago Pneumatic CP7262 Pneumatic Deburring Tool
- Features: Pneumatic deburring tools are powered by compressed air, offering greater power and speed. These tools come with rotating deburring heads and are highly effective for removing burrs from sheet metal quickly and efficiently.
- Pros: Fast, powerful, and effective for large batches.
- Cons: Requires an air compressor and is less portable.
Electric Deburring Tools
- Best for: Medium-duty applications and where more control is needed than with pneumatic tools.
- Example:Makita 9403 Belt Sander
- Features: A belt sander equipped with abrasive cloth can effectively smooth and remove burrs from sheet metal edges. Electric tools are versatile and suitable for both thin and thicker materials.
- Pros: Ideal for smoothing large, flat sheet metal surfaces quickly.
- Cons: Can be too aggressive for finer, more intricate work.
Angle Grinder with Deburring Disc
- Best for: Heavy-duty deburring, particularly for thicker or more rigid sheet metal.
- Example:Makita GA7021 Angle Grinder
- Features: With the right deburring disc or flap wheel attachment, angle grinders can quickly remove burrs and smooth rough edges on sheet metal. These are ideal for working on large surfaces or heavy-duty projects.
- Pros: High power and efficiency, suitable for high-production environments.
- Cons: Requires care to avoid over-smoothing or damage to the edges.
3. Specialized Machines
For automated deburring or handling large quantities of parts, industrial machines designed for deburring sheet metal can be extremely beneficial. These machines are used in high-production environments where speed and consistency are crucial.
Vibratory Finishing Machines
- Best for: Batch processing of small parts.
- Example:Mass Finishing Vibratory Deburring Machine
- Features: These machines use abrasive media in a vibrating bowl to remove burrs from multiple sheet metal parts simultaneously. Ideal for cleaning up edges on small to medium-sized parts.
- Pros: Excellent for high-volume processing, consistent finish.
- Cons: Requires enough part size and quantity to justify its use.
CNC Deburring Machines
- Best for: High precision deburring of sheet metal with intricate shapes or fine details.
- Example:Timesavers 1100 Series CNC Deburring Machine
- Features: CNC-controlled machines use abrasive belts and brushes to automatically deburr sheet metal parts with high precision. These machines are perfect for ensuring consistent edge finishes across large batches of parts.
- Pros: Fast, precise, and ideal for high-volume production.
- Cons: Expensive and requires significant space and setup.
Brush Deburring Machines
- Best for: Removing burrs from the edges of sheet metal without compromising the part’s shape.
- Example:BRUSH CNC Deburring Machine
- Features: These machines use rotating brushes to sweep away burrs from the edges of sheet metal, offering a smoother and less aggressive finish than other types of automated systems.
- Pros: Ideal for fine burr removal and more delicate materials.
- Cons: May not be as effective on thicker materials or very stubborn burrs.
4. Specialty Deburring Techniques
For complex geometries or when traditional deburring tools are insufficient, specialty techniques such as electrochemical deburring or laser deburring can be employed.
Electrochemical Deburring
- Best for: Intricate or complex parts, especially those with internal features that are difficult to reach.
- Example:R&R Electrochemical Deburring System
- Features: Electrochemical deburring uses an electrolyte solution and electrical current to remove burrs from sheet metal in a non-mechanical, stress-free manner. This is particularly useful for parts with internal passageways or fine details.
- Pros: High precision with minimal mechanical stress.
- Cons: Expensive and best suited for high-precision industries such as aerospace.
Laser Deburring
- Best for: Precision deburring of sheet metal, especially for very fine burrs or delicate materials.
- Example:Trumpf Laser Deburring System
- Features: Laser systems use high-powered light beams to vaporize burrs from metal edges without physical contact. This is an excellent solution for thin sheet metals, particularly for extremely fine burrs.
- Pros: Very precise, no contact with the material, minimal wear on parts.
- Cons: Expensive and generally used in industries that require high-precision deburring, like electronics and medical devices.
Conclusion
When selecting the best deburring tool for sheet metal, consider the scale of your operation, the thickness and type of material you’re working with, and the level of precision required. For small, detailed jobs, manual tools like rotary deburring tools or hand files provide excellent control. For high-volume production, pneumatic or electric deburring tools, such as angle grinders or belt sanders, offer faster and more efficient solutions. If you’re dealing with large batches of parts or need high precision, investing in automated solutions like vibratory finishers or CNC deburring machines will help streamline your workflow and maintain consistent quality. With the right tool for the job, you can ensure smooth, clean edges that are safe and ready for further processing or assembly.
Choosing the right deburring tool for sheet metal largely depends on the specific demands of the task at hand. For smaller jobs or those requiring precision, manual tools such as handheld rotary deburring tools and files are effective choices. These tools allow for meticulous control, making them ideal for detailed work, such as removing burrs from edges or holes. While they can be time-consuming for larger quantities, they are cost-effective and provide a high level of accuracy, especially for jobs that require finesse.
In contrast, for larger or higher-volume tasks, power tools like pneumatic or electric deburring tools provide increased speed and efficiency. Pneumatic tools, which run on compressed air, are particularly useful in industrial settings where high production volumes are common. They tend to be faster than manual tools and can handle more aggressive deburring tasks, such as removing burrs from thicker sheet metal or large batches of parts. These tools are often equipped with rotating heads and various abrasives that can tackle burrs on both internal and external edges.
Electric deburring tools, while similar in function to pneumatic tools, tend to offer more control. These tools are often more convenient for medium-duty tasks and can handle a range of materials, from thin sheet metal to thicker pieces. They are especially useful when precision is needed, such as when deburring small, intricate parts or finishing surfaces after cutting.
For even larger production environments, automated systems like vibratory finishing machines or CNC deburring machines are often the best solution. Vibratory machines are ideal for bulk processing, allowing parts to be deburred in large quantities. These machines use abrasive media and a vibrating bowl to smooth edges and remove burrs without the need for manual labor. CNC deburring machines, on the other hand, offer high precision and can automate the deburring process for parts with complex shapes or features, ensuring consistency and reducing human error.
Specialized deburring techniques like electrochemical deburring or laser deburring offer even more precision, particularly for parts with intricate designs or those requiring delicate handling. Electrochemical deburring uses a chemical process to remove burrs without physically touching the material, making it ideal for parts with delicate internal features or complex geometries. Laser deburring, which utilizes a laser beam to vaporize burrs, offers another precise solution, especially for very thin or fine materials where minimal physical contact is required.
While the type of tool is important, so too is the choice of abrasives and attachments. Using the right abrasives, such as ceramic or diamond-coated tools, can enhance the deburring process by ensuring a consistent finish while also increasing the lifespan of the tool itself. The abrasives should be chosen based on the hardness of the material and the level of burr removal required. For softer metals like aluminum, finer abrasives are often sufficient, while harder metals like stainless steel may require more aggressive abrasives to effectively remove burrs without damaging the surface.
In addition to the tools themselves, it’s important to consider the safety measures needed during the deburring process. Many deburring tools, especially power tools, can create flying debris or produce high levels of noise. Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as goggles, gloves, and hearing protection, is crucial to minimize the risk of injury. Furthermore, ensuring proper ventilation and dust collection systems is essential, especially when working with power tools that can generate metal dust or fumes, which can be harmful to both workers and the environment.
The choice of deburring tool for sheet metal will ultimately depend on the specific needs of the project—whether that’s fine precision for a small, detailed part or speed and efficiency for mass production. The key is to select the right tool for the job that will not only provide the desired finish but also ensure productivity, cost-efficiency, and safety throughout the process. Whether you’re working on a small project, a medium-scale job, or a large industrial task, there are tools available to suit every level of operation and material type.
As the industry continues to evolve, there are several additional factors to consider when selecting a deburring tool for sheet metal, especially when aiming for increased efficiency and improved quality. One such factor is the level of automation integrated into deburring equipment. For high-volume production environments, automation can significantly reduce manual labor, improve precision, and ensure consistency across large batches of parts. Automated systems like robotic deburring cells, CNC machines with deburring attachments, and in-line automated deburring stations are increasingly popular. These systems allow for precise, repeatable results without the need for human intervention, which can improve throughput and reduce error rates.
Another important consideration is the flexibility and adaptability of the deburring system. Sheet metal comes in various thicknesses, alloys, and shapes, and the deburring tool needs to be versatile enough to handle these variations. Many modern deburring machines offer adjustable settings, such as variable speeds, pressure controls, and customizable abrasive types, to adapt to different materials and part configurations. This adaptability ensures that the deburring process is optimized for each unique piece, whether it’s a delicate, thin sheet of aluminum or a thicker steel part.
The environmental impact of deburring operations is also gaining increasing attention. Manufacturers are exploring ways to reduce waste, energy consumption, and the use of harmful chemicals in the deburring process. Eco-friendly abrasives, such as those made from recycled materials, are becoming more common, as are water-based coolants and cleaning agents that minimize the environmental footprint. Additionally, the development of dust extraction and filtration systems helps maintain a clean and safe workspace while reducing the release of hazardous materials into the air.
Maintenance and tool longevity are also critical factors to consider. Regular maintenance of deburring equipment ensures that tools operate efficiently and produce consistent results over time. This includes routine inspection, cleaning, and replacement of worn-out parts such as abrasives, blades, and brushes. Some modern deburring machines even feature built-in diagnostic tools that monitor the condition of key components, alerting operators when it’s time for maintenance or when tool wear might affect performance. This proactive approach to maintenance can help prevent unexpected breakdowns, minimize downtime, and extend the life of the equipment.
Training is another essential component of effective deburring, especially in environments where operators handle complex machinery. Ensuring that workers are properly trained on how to operate the tools, handle materials safely, and troubleshoot issues can improve both the quality of the deburring process and the safety of the workplace. Some deburring machines, especially automated systems, may require more technical expertise to operate effectively. Therefore, investing in training programs can be an essential step in achieving the best possible results while maintaining a safe and productive working environment.
Finally, cost-effectiveness remains a major consideration when choosing deburring tools, especially for small businesses or shops operating on a budget. While advanced machinery can offer high precision and productivity, the upfront costs can be significant. For smaller operations, manual and semi-automated tools may offer a more cost-effective solution without sacrificing quality. In many cases, operators can start with more affordable options and scale up as production demands increase or as specific requirements evolve.
In conclusion, when selecting the best deburring tools for sheet metal, it is essential to assess not only the material and size of the parts but also factors like speed, precision, automation, environmental impact, and long-term cost-effectiveness. Advances in automation, abrasives, and tool design continue to provide businesses with more efficient and sustainable ways to improve the deburring process. Whether you’re working in a small workshop or a large-scale industrial environment, there’s a wide array of deburring tools and techniques that can help you achieve smooth, clean, and burr-free metal edges, ensuring that your sheet metal parts are ready for further processing or assembly.
Sheet Metal Grinding Machine
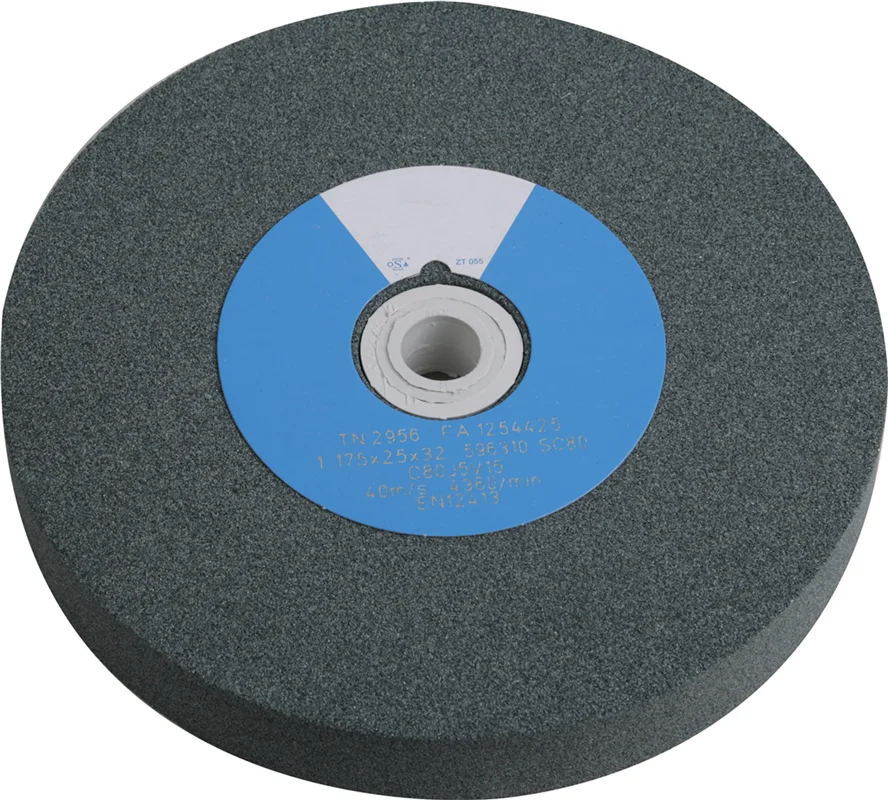

A sheet metal grinding machine is designed to smooth, refine, and deburr metal surfaces by using abrasives. These machines are essential in industries where metal surfaces need to be finished with high precision, such as in automotive, aerospace, and general manufacturing. Grinding is typically used to remove sharp edges, improve surface finish, or shape metal parts to specific dimensions. There are various types of sheet metal grinding machines, each suited for different tasks and production volumes.
Types of Sheet Metal Grinding Machines:
- Belt Grinders
- Description: Belt grinders are widely used for sheet metal grinding, where an abrasive belt rotates at high speed to grind the surface of the metal. These machines are effective for both rough grinding and polishing.
- Applications: Suitable for deburring, removing rust or scale, and polishing metal surfaces. They can handle a variety of materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, and carbon steel.
- Advantages: Offers excellent material removal rate and can handle large surfaces. Belt grinders are also relatively easy to control and can be used on curved or flat parts.
- Example: Belt Grinding Machines by Kalamazoo Industries – These machines offer versatile grinding options for different materials and have adjustable belts for various applications.
- Surface Grinders
- Description: Surface grinding machines use a rotating grinding wheel to remove material from a flat metal surface, producing a smooth and precise finish. The part is typically placed on a flat surface, and the grinding wheel is moved over the part.
- Applications: Used for finishing large, flat metal surfaces with high precision. Ideal for creating smooth, uniform finishes and accurate dimensions.
- Advantages: Provides an extremely flat, smooth finish and is ideal for high-precision applications. The operation is highly controllable, allowing for tight tolerance finishing.
- Example: Okamoto Surface Grinders – Known for their precision and efficiency, these machines are ideal for high-quality surface finishes.
- Disc Grinders (Angle Grinders)
- Description: Disc grinders, or angle grinders, are portable, handheld devices with a rotating disc covered in abrasive material. These machines are versatile and can be used for both grinding and polishing sheet metal.
- Applications: Used for heavy-duty deburring, cleaning, rust removal, and shaping sheet metal edges. Ideal for smaller-scale work or when flexibility is required.
- Advantages: Portable and versatile; they can be used in various industrial applications for quick material removal. The variety of discs available also makes them useful for different surface finishes.
- Example: Makita GA7021 Angle Grinder – This grinder offers high power for tackling tough metal surfaces, including grinding and finishing sheet metal.
- Cylindrical Grinders
- Description: Cylindrical grinding machines are used to grind the outer surfaces of cylindrical parts, typically between two centers or in a chuck. These machines are less common for sheet metal but can be used for parts with cylindrical shapes.
- Applications: Used for precision grinding of cylindrical sheet metal parts, such as shafts or tubes, where both diameter and surface finish are crucial.
- Advantages: High precision and ability to handle both small and large cylindrical parts.
- Example: Studer Cylindrical Grinders – Known for their precision in cylindrical grinding, especially for high-quality applications.
- Bench Grinders
- Description: Bench grinders are stationary machines mounted on a workbench and are typically used for smaller parts or manual grinding operations. They consist of two rotating grinding wheels and are commonly used for fine polishing or sharpening tools.
- Applications: Ideal for light grinding tasks such as deburring, polishing, or sharpening small metal parts. Often used in smaller workshops or as an auxiliary tool for general metalworking.
- Advantages: Compact and easy to use for small parts or light grinding tasks. Economical and versatile for a variety of workshop applications.
- Example: JET JBG-8A Bench Grinder – A reliable bench grinder for fine-tuning metal surfaces and deburring smaller sheet metal parts.
Grinding Methods for Sheet Metal:
- Deburring and Edge Refining: Grinding machines are highly effective in removing sharp edges or burrs left over after processes such as punching, cutting, or laser cutting. This is a crucial step to ensure safety, improve the metal’s aesthetic appearance, and prepare the part for further operations such as welding or coating.
- Surface Finishing: Grinding can also be used for achieving a smooth surface finish, often required in industries where the visual appeal of the product is important. Fine grinding and polishing allow for a more uniform surface that is free from marks, scratches, or defects.
- Material Removal: Grinding is also used when significant amounts of material need to be removed from a sheet metal part, such as when preparing a part for a different machining operation or removing excess material.
Key Features to Look for in Sheet Metal Grinding Machines:
- Adjustable Speed Control: Adjustable speed settings are essential for controlling the intensity of the grinding process, especially when working with different types of metals or varying thicknesses of sheet metal.
- Dust Collection System: Grinding produces a significant amount of dust and metal particles, which can be hazardous. Machines with built-in dust collection systems help maintain a clean working environment and improve operator safety.
- Versatility of Abrasive Materials: The ability to use different types of abrasives, such as ceramic, aluminum oxide, or silicon carbide, gives operators flexibility when grinding different types of metals.
- Ergonomics and Safety: Safety features like motor overload protection, adjustable safety shields, and ergonomic handles can improve the safety and ease of use for operators. Additionally, vibration reduction systems can enhance comfort during prolonged usage.
Maintenance Considerations for Grinding Machines:
Maintaining a sheet metal grinding machine is essential for ensuring that it operates efficiently and extends its lifespan. Some key maintenance practices include:
- Regular Inspection of Grinding Wheels: Check the grinding wheels for wear and damage, as they can affect the machine’s performance and the quality of the finish.
- Lubrication: Ensure that the machine’s moving parts, such as the grinding head or belt, are properly lubricated to prevent excessive wear and ensure smooth operation.
- Cleaning: Clean the grinding machine regularly to remove metal shavings, dust, and debris that accumulate during the grinding process. This helps prevent clogging of dust collection systems and ensures optimal performance.
- Wheel Dressing: Periodically dressing the grinding wheel helps maintain its effectiveness by restoring its sharpness and removing any clogged abrasive material.
Conclusion:
A sheet metal grinding machine is a critical tool in metalworking processes, providing essential functions like deburring, surface finishing, and material removal. The choice of machine depends on the specific requirements of the project, such as the size of the workpiece, the material being processed, and the type of finish needed. Whether you choose a manual tool like a bench grinder for small-scale work or an industrial belt grinder for large-scale production, proper machine selection, maintenance, and safety precautions will help ensure efficient and high-quality results in sheet metal grinding operations.
When selecting a sheet metal grinding machine, it’s essential to understand the specific requirements of your application. Grinding is not just about removing material; it’s about achieving the desired surface finish, smooth edges, and maintaining precise tolerances. Depending on the scale of your operation, whether it’s a small workshop or a large-scale industrial environment, there are different machines and tools designed for various types of grinding, deburring, and polishing tasks.
The process of grinding sheet metal is widely used to refine surfaces, remove burrs, and achieve specific geometries. For smaller-scale operations, tools like handheld angle grinders or bench grinders are often sufficient for light tasks, such as polishing edges or removing small amounts of material. These machines are particularly effective for deburring metal parts after cutting, punching, or laser cutting. For tasks requiring a finer finish or higher precision, more advanced machines like belt grinders or surface grinders are commonly used.
Belt grinders are a go-to choice for many industrial operations. Their abrasive belts can quickly and effectively smooth surfaces, remove excess material, and refine edges on both flat and curved sheet metal parts. These machines are efficient for medium to high-volume tasks, especially in industries like automotive manufacturing or metal fabrication, where a smooth surface is crucial for both aesthetic and functional reasons. The flexibility of belt grinders also allows for easy adjustments to accommodate different types of metals and varying thicknesses, making them a versatile addition to any workshop.
Surface grinders, on the other hand, are ideal for applications that require a high level of precision. These machines use rotating grinding wheels to precisely grind flat surfaces, producing a smooth and uniform finish. They are excellent for creating a perfect finish on large sheet metal surfaces or for parts that require tight tolerances. These grinders are typically found in precision engineering environments, where accuracy and surface quality are paramount.
For heavy-duty grinding tasks, where aggressive material removal is necessary, angle grinders or disc grinders can be highly effective. These machines are more versatile and portable than larger grinding machines and are suitable for cleaning, deburring, and rough grinding on sheet metal. With a variety of grinding discs and abrasives available, angle grinders can handle a wide range of materials and provide flexibility in grinding applications.
The performance of any grinding machine depends largely on the abrasives used. Selecting the right abrasive material is crucial, as different metals and applications require different types of abrasives to achieve the desired finish. For instance, aluminum oxide abrasives are commonly used for general grinding, while silicon carbide abrasives are ideal for working with harder metals like stainless steel. The hardness of the material, the type of finish needed, and the amount of material removal all play a role in choosing the correct abrasive.
Another important consideration when selecting a grinding machine is the presence of safety features. Sheet metal grinding can generate dust and sparks, which can pose safety risks. Machines with built-in dust collection systems are a great way to reduce airborne particles and improve the overall cleanliness of the work area. Additionally, operators should always use personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, and hearing protection, to ensure their safety while operating the machines.
Beyond safety, machine maintenance is also critical for consistent performance. Regular cleaning, inspection, and maintenance of grinding wheels, belts, and other moving parts are necessary to keep the equipment in optimal condition. Worn-out or damaged grinding wheels can affect the quality of the finish and may lead to poor performance or safety hazards. Proper lubrication and calibration of machines help ensure that they run smoothly and effectively.
In industrial settings where production volumes are high, automated grinding solutions such as CNC grinders or robotic grinding systems are becoming increasingly popular. These systems can automate the grinding process, offering consistent, repeatable results and reducing the need for manual labor. CNC grinders, in particular, provide high precision and allow for the processing of complex geometries with minimal operator intervention. For high-volume operations, robotic systems can handle the repetitive nature of grinding tasks, freeing up human labor for more complex or value-added activities.
Choosing the right sheet metal grinding machine comes down to balancing the needs of the specific job with the available equipment and budget. For smaller operations or more straightforward tasks, manual tools or entry-level machines may be sufficient. For more complex or high-volume production, investing in higher-end machines that offer greater precision, automation, and efficiency may be necessary. Ultimately, the key to success lies in selecting the right equipment, maintaining it properly, and ensuring safe and effective use.
In addition to the basic functionality and types of grinding machines, it’s essential to consider the broader aspects of sheet metal grinding, including the operational environment, material handling, and overall workflow integration. In high-volume or industrial settings, the choice of grinding machine can significantly impact not only the quality of the finished product but also the efficiency of the entire production process.
One important factor is material handling. In large-scale operations, managing the flow of parts into and out of grinding stations can become a challenge. Automated systems, such as conveyor belts or robotic arms, can help streamline this process by feeding parts into grinding machines and removing finished products for the next stage of production. Integrating these systems into a factory’s workflow can reduce labor costs, minimize human error, and ensure consistent part orientation, which is crucial for high-precision grinding tasks.
Another consideration is surface finish quality. While deburring and removing excess material are essential steps in metal processing, the desired surface finish is often just as important. Many industries require specific surface finishes, such as smooth, polished, or textured surfaces, depending on the product’s final use. Surface grinders are commonly used to achieve highly polished finishes, while belt grinders can be used for more uniform and rougher finishes. Machines equipped with adjustable speed settings and various abrasive options can allow for finer control over the surface finish, meeting the specific requirements for different applications.
Moreover, the efficiency of the grinding process plays a crucial role in maintaining a competitive edge in the marketplace. While grinding is an effective method for finishing metal parts, it is also relatively slow compared to some other processes like laser cutting or water jetting. As a result, optimizing grinding processes for speed and efficiency is important. For example, using high-performance abrasives or adopting more advanced grinding machines with faster material removal rates can reduce processing time and improve overall productivity.
Energy consumption is another factor that has become more important in modern metalworking operations. Energy-efficient machines not only reduce operating costs but also contribute to more sustainable manufacturing practices. Manufacturers are increasingly investing in machines that offer energy-saving features, such as variable-speed motors, optimized grinding cycles, and better heat management. Additionally, reducing the amount of energy used by the grinding machine can help minimize the environmental impact of the operation, particularly when dealing with energy-intensive processes.
When it comes to quality control, it is important to have systems in place to monitor the grinding process and ensure that the finished parts meet the required specifications. Some advanced grinding machines come equipped with sensors and integrated measurement systems that monitor the size, shape, and finish of parts during the grinding process. These machines can automatically adjust settings to maintain consistency, reducing the need for manual inspection and rework. This level of automation ensures that each part meets tight tolerances and minimizes waste.
For manufacturers handling sheet metal parts with complex shapes or non-standard geometries, there are grinding machines available that can handle intricate designs. CNC grinding machines and robotic grinding systems are capable of working with parts that would be difficult or time-consuming to grind manually. These advanced machines can be programmed to follow precise paths and contours, ensuring that even the most complex parts receive a consistent and uniform finish.
Cost considerations are always present when selecting any machinery. While automated and high-precision grinding machines offer advanced features, they come with a significant upfront investment. Smaller operations or those with less frequent grinding needs might opt for more economical, manual tools or semi-automated machines. However, these machines may have higher operating costs in terms of labor and time. For larger operations or those seeking to streamline production, investing in automated systems may be more cost-effective in the long run, as they can significantly reduce labor costs and improve overall throughput.
In addition, the cost of abrasives is an ongoing factor that should be considered in any grinding operation. Different materials, such as grinding wheels, belts, or discs, wear down over time and need to be replaced. The type of abrasive selected can impact both the cost and the quality of the finished product. High-quality abrasives can provide a superior finish and a longer lifespan but may come with a higher initial cost. Balancing abrasive quality and cost-effectiveness is crucial for maintaining profitability in grinding operations.
Lastly, training and skill development for operators are vital to ensure that grinding machines are used efficiently and safely. Operators need to understand how to set up and adjust the machines correctly, select the appropriate abrasives, and troubleshoot issues as they arise. For advanced grinding systems, such as CNC grinders or robotic cells, operators must be trained in programming and monitoring machine performance. Investing in operator training not only helps prevent costly mistakes but also contributes to the overall success of the grinding operation.
In conclusion, the selection and optimization of sheet metal grinding machines go far beyond simply choosing the right tool for the job. Factors such as material handling, surface finish requirements, efficiency, energy consumption, and automation play significant roles in ensuring that the grinding process is as effective, productive, and cost-efficient as possible. Whether operating in a small-scale workshop or a high-volume industrial setting, integrating the right grinding technology, combined with a strong focus on quality control, maintenance, and operator training, will lead to more consistent results and better overall performance in sheet metal processing.
Power deburring tools for metal are essential for finishing processes where sharp edges, burrs, or imperfections are removed from metal parts. Burrs are often created during machining operations such as cutting, drilling, milling, or grinding, and they can cause problems in assembly, aesthetics, and even function if left unaddressed. Power deburring tools are designed to automate and improve the efficiency of deburring, offering a cleaner, smoother surface finish while reducing manual labor. There are various types of power deburring tools available, each suited to different metalworking applications.
Types of Power Deburring Tools:
- Rotary Deburring Tools (Handheld Electric Deburring Tools)
- Description: These tools are often hand-held, electric-powered devices with rotating attachments like brushes, abrasive discs, or rotary burrs. The tool spins the abrasive element at high speed to remove burrs or smooth edges.
- Applications: Commonly used for small to medium-sized metal parts in a variety of industries such as automotive, aerospace, and general manufacturing. They can be used on both flat and curved surfaces.
- Advantages: Versatile, portable, and effective for a wide range of deburring tasks. They provide a high degree of control and are ideal for operators to handle intricate areas or delicate parts.
- Examples:
- Makita GD0601 – A lightweight rotary tool for precise deburring applications.
- Bosch GGS 28 C Professional – Known for its ergonomic design and strong performance for deburring small workpieces.
- Pneumatic Deburring Tools
- Description: Pneumatic deburring tools are powered by compressed air and are typically used for high-volume production. They operate similarly to electric tools, but they often offer greater torque and are lighter, reducing operator fatigue.
- Applications: Pneumatic tools are frequently used in industrial environments where high-speed, continuous deburring is necessary. They are ideal for larger production lines or environments requiring a higher level of efficiency.
- Advantages: Light and easy to maneuver, pneumatic deburring tools are ideal for extended use in industrial applications. They also offer more power compared to electric models, especially in environments where high torque is needed.
- Examples:
- Dynabrade 52800 – A versatile, high-quality pneumatic tool for deburring, sanding, and polishing.
- Ingersoll Rand 3101G – Known for its durability and high performance in deburring and surface finishing.
- Angle Grinders with Deburring Attachments
- Description: Angle grinders, typically used for cutting or grinding tasks, can also be fitted with specialized deburring attachments such as flap discs, wire brushes, or grinding wheels. These attachments allow angle grinders to effectively remove burrs and smooth metal surfaces.
- Applications: Ideal for heavy-duty deburring of larger metal pieces or for operations requiring a more aggressive material removal process.
- Advantages: Angle grinders are versatile and widely available, making them cost-effective for many deburring tasks. They are particularly useful for tough metals or when large quantities of material need to be removed quickly.
- Examples:
- Makita GA7021 Angle Grinder – Known for its durability and ease of use, ideal for aggressive deburring tasks.
- DeWalt D28402K – A high-performance grinder with various accessories for deburring and polishing.
- Deburring and Polishing Machines
- Description: These are more advanced, industrial-scale machines designed to automate the deburring process. They use rotating abrasive brushes, belts, or drums to finish parts and are often integrated into production lines for continuous deburring operations.
- Applications: Used in high-volume manufacturing environments where consistent results and high throughput are required. These machines are suitable for deburring large batches of parts with minimal operator involvement.
- Advantages: These machines can automate the deburring process, resulting in more uniform and consistent finishes with significantly reduced labor costs. They are ideal for factories with high production needs.
- Examples:
- Timesavers 1200 Series – Offers a high degree of automation and versatility for metal deburring, polishing, and surface finishing.
- Belt Grinders by Kalamazoo – Designed for deburring, edge finishing, and sanding in larger volumes.
- CNC Deburring Machines
- Description: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) deburring machines are highly automated systems that can precisely control the deburring process for both flat and intricate parts. These machines use automated tools to deburr the edges of metal parts with very tight tolerances.
- Applications: Typically used for high-precision applications, where parts require exact dimensions and consistent deburring results. Often used in aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries.
- Advantages: CNC machines offer unparalleled precision, making them ideal for parts with complex geometries and tight tolerances. They can operate without human intervention, improving efficiency and reducing human error.
- Examples:
- Abrasive Waterjet Deburring Systems by OMAX – Combining waterjets with abrasives, these systems automate deburring for complex geometries.
- Geibel & Hotz CNC Deburring Systems – These machines are designed for precise, high-quality deburring of intricate metal parts.
- Robotic Deburring Systems
- Description: Robotic deburring systems use robotic arms equipped with specialized deburring tools, such as brushes or grinding wheels, to remove burrs from metal parts. These systems are programmable, allowing for automated deburring of parts with varying shapes and sizes.
- Applications: Used in large-scale manufacturing environments, robotic deburring systems are often employed when high-speed, high-precision deburring is required. They are suitable for parts with complex or irregular shapes.
- Advantages: Robots can perform deburring tasks with high consistency, precision, and speed. These systems can be integrated with other parts of a manufacturing line for fully automated production.
- Examples:
- Fanuc Robotic Deburring Solutions – These systems integrate robotics with deburring tools to create highly automated and efficient deburring stations.
- ABB Robotics for Deburring – ABB offers robotic systems that can handle a wide range of deburring and surface finishing tasks.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Power Deburring Tool for Metal:
- Material Type: The type of metal being processed (such as aluminum, steel, stainless steel, etc.) will impact the choice of deburring tool. Some tools are more suitable for soft metals, while others are designed to handle tougher, harder metals.
- Part Size and Complexity: The size and shape of the part being deburred will determine whether a manual or automated solution is needed. For smaller, more intricate parts, hand-held tools or precision robotic systems may be necessary. For larger parts, more industrial solutions such as belt grinders or CNC deburring machines are preferred.
- Speed and Efficiency: For high-volume production, tools that offer faster deburring rates (such as pneumatic or automated systems) are more desirable. However, for smaller batches or more delicate work, slower, more controlled tools may be more appropriate.
- Safety Features: Safety is a major concern when working with power tools. Ensure that the tool comes with proper safety features such as guards, dust collection systems, and emergency shut-off mechanisms.
- Ease of Use and Maintenance: Tools that are easy to set up, operate, and maintain will improve productivity. Look for machines that allow for quick changes in abrasive attachments and offer clear instructions for maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Cost and Return on Investment (ROI): While automated systems like CNC machines and robotic arms offer high precision and throughput, they come with higher upfront costs. For smaller operations or limited budgets, investing in manual or pneumatic tools may offer a better ROI.
In conclusion, power deburring tools for metal offer a wide range of solutions to address the burr removal and surface finishing needs of metalworking operations. Whether you’re working with small, intricate parts or large, heavy-duty materials, the right tool can make the difference in achieving clean, precise finishes while improving the efficiency and consistency of your production process. From handheld electric tools to advanced robotic systems, the choice of deburring tool should be tailored to the specific requirements of your project, ensuring both quality and cost-effectiveness.
Power deburring tools for metal are essential for ensuring that metal parts are free from sharp edges, burrs, and other imperfections that can affect both the functionality and appearance of a part. These tools use various power sources, including electric, pneumatic, and robotic systems, to automate or enhance the deburring process, saving time and improving precision compared to manual methods.
The main function of power deburring tools is to remove unwanted burrs formed during manufacturing processes such as cutting, drilling, milling, and grinding. These burrs, if left untreated, can cause issues such as difficulty in assembly, interference with moving parts, or even safety hazards. Deburring is not just a cosmetic process; it also contributes to the overall performance and durability of the part. By ensuring a smooth and uniform edge, power deburring tools help to prevent potential mechanical failures caused by stress concentrations at sharp edges.
Handheld rotary deburring tools are commonly used in small to medium-sized operations. These tools are versatile and easy to maneuver, making them ideal for manual deburring of various metal parts. With rotating abrasive attachments such as brushes, grinding wheels, or rotary burrs, these tools can remove burrs from both flat and contoured surfaces. Electric-powered tools are especially useful for lighter deburring tasks, providing the operator with more control over the process. Pneumatic versions of these tools, powered by compressed air, are typically lighter and provide more torque, which is beneficial for handling tougher materials or larger volumes of deburring work.
For more aggressive deburring or situations requiring high material removal rates, angle grinders or belt sanders can be used. These power tools are often outfitted with specialized deburring attachments, such as flap discs or wire brushes. While angle grinders are commonly used for heavy-duty tasks like grinding and cutting, when equipped with the right attachments, they can be very effective for deburring applications as well. They are particularly useful for rough deburring of large or thick metal parts. However, due to their higher power output, they should be used with care to avoid over-removal of material, which could alter the part’s dimensions or shape.
When dealing with high volumes of parts or intricate shapes, automated systems such as robotic deburring machines or CNC deburring machines can be employed. These systems are capable of performing the deburring process without human intervention, providing highly consistent results with tight tolerances. Robotic deburring systems, which use robotic arms fitted with various deburring tools, are particularly useful for parts with complex geometries. These systems can be programmed to follow specific paths and contours, ensuring that every part receives uniform deburring treatment. CNC deburring machines, on the other hand, use computer-controlled settings to remove burrs with extreme precision, making them suitable for parts that require both deburring and finishing in one step.
For large-scale manufacturing or situations where high throughput is required, deburring machines that use rotating abrasive brushes, drums, or belts can be integrated into production lines. These machines are ideal for continuous deburring operations, offering high efficiency and automation. The workpieces are fed into the machine, where they are processed quickly and consistently, providing a uniform finish on large quantities of parts. These machines can be equipped with adjustable settings to accommodate various materials and part sizes, making them adaptable to a wide range of production environments.
In addition to choosing the right tool for the deburring process, it’s also essential to consider the abrasives being used. Different metals and materials require different abrasive types to achieve optimal results. For example, aluminum and softer metals often require abrasives with a finer grit to avoid damage to the surface, while harder materials such as stainless steel or titanium may require coarser abrasives to effectively remove burrs. The choice of abrasive is critical for ensuring both the quality of the finish and the longevity of the deburring tool itself.
Another key consideration is the safety and ergonomics of power deburring tools. Because the deburring process can generate heat, sparks, and metal dust, it’s important for operators to wear appropriate protective gear, including gloves, goggles, ear protection, and respirators. Tools with safety features like dust collection systems or guards can help improve operator safety by reducing exposure to harmful debris and minimizing the risk of accidents. Additionally, the ergonomic design of the tool should allow for comfortable handling, reducing operator fatigue during long deburring sessions.
Maintenance is also crucial to ensure that power deburring tools perform effectively over time. Regular inspection and replacement of worn parts, such as grinding wheels, abrasive discs, or brushes, are necessary to maintain optimal performance. Keeping the machine clean and properly lubricated can also extend its lifespan and prevent downtime caused by mechanical failures.
Ultimately, the selection of a power deburring tool depends on factors such as the scale of production, the materials being processed, the complexity of the parts, and the desired finish. Smaller operations may benefit from handheld or pneumatic tools, which offer flexibility and ease of use. For larger-scale operations or when precise deburring is required, automated solutions such as robotic systems or CNC machines are more appropriate. By selecting the right tool for the job and incorporating best practices for safety and maintenance, manufacturers can ensure that their metal parts are deburred efficiently, consistently, and safely.
As manufacturing processes evolve, the demands for precision and speed continue to grow. This has led to the development of more advanced power deburring tools that not only improve the quality of metal finishes but also help streamline the production process. The latest advancements in power deburring tools are geared toward increasing efficiency, automation, and safety while reducing costs.
One notable trend in the industry is the integration of robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) into deburring systems. Robotic deburring systems, equipped with advanced sensors and AI algorithms, are capable of detecting burrs and imperfections on parts in real-time. These systems can adjust their movements and tool settings dynamically to accommodate different shapes and sizes of parts, ensuring consistent and high-quality results without manual intervention. Additionally, the use of AI allows for predictive maintenance, meaning that the system can identify potential issues before they occur and notify operators to perform necessary repairs or adjustments. This results in less downtime, fewer defects, and a more efficient deburring process.
Increased automation is also seen in the form of automated material handling systems that work in conjunction with deburring machines. These systems are designed to feed parts into deburring machines automatically and remove them once the process is complete. With the integration of conveyors, robotic arms, and vision systems, these automated handling solutions improve the flow of parts through the production process and reduce the need for manual labor. In turn, this minimizes human error and increases the overall throughput of the manufacturing process.
Another significant development is the use of abrasive belt grinders in combination with advanced abrasive materials. These grinders are often used in high-volume applications where speed and consistency are critical. Abrasive belts are available in a range of materials, including silicon carbide, aluminum oxide, and zirconia, which are selected based on the metal type and deburring requirements. These belts are designed to wear evenly, providing a consistent finish while minimizing the risk of overheating or material damage. Some newer belt grinders also feature adjustable speed settings, allowing operators to fine-tune the speed based on the hardness of the material and the nature of the burrs being removed.
For particularly hard metals, such as stainless steel, titanium, or hardened alloys, specialized power deburring tools have been developed. These tools are often equipped with more durable abrasives, such as ceramic or diamond-coated grinding heads, that can withstand the challenges posed by these tough materials. Tools like these offer better material removal rates and longer tool life, ensuring that deburring operations remain efficient even in demanding environments.
A growing concern in metalworking industries is the impact of deburring processes on the environment. The use of power deburring tools can produce a significant amount of dust and debris, which, if not properly controlled, can create hazardous conditions for workers and contribute to environmental pollution. To address this, modern power deburring tools are increasingly equipped with dust extraction systems. These systems help collect metal dust, chips, and debris as they are produced, preventing them from becoming airborne and reducing the risk of respiratory issues for operators. Dust extraction also helps to keep the work area cleaner, which can improve overall visibility and safety.
In addition to dust collection, noise reduction technologies are becoming more prevalent in power deburring tools. Many industrial-grade tools generate significant noise during operation, which can contribute to hearing loss for workers over time. Manufacturers are responding to this concern by designing quieter tools and incorporating sound-dampening materials into their construction. For example, pneumatic tools are being developed with mufflers and vibration-dampening features to minimize the noise level during use, helping to create a safer and more comfortable working environment.
The growing focus on sustainability in manufacturing has also led to innovations in energy efficiency. Modern power deburring tools are designed to consume less energy while maintaining high levels of performance. For example, variable-speed motors and energy-efficient drive systems are being implemented to reduce power consumption without sacrificing effectiveness. This is especially important in high-volume manufacturing, where energy costs can quickly add up. The push toward sustainable practices is also prompting manufacturers to develop tools that use recyclable or eco-friendly abrasives, further minimizing the environmental impact of the deburring process.
Customization and adaptability are other key trends that are gaining traction in the field of power deburring tools. In today’s fast-paced manufacturing environment, many companies work with a wide variety of parts that have different shapes, sizes, and material compositions. This variability can present challenges for deburring, as each type of part may require a different approach or tool configuration. To address this, many power deburring tools are now designed with greater flexibility, allowing them to be easily adjusted or customized for different applications. For example, modular deburring machines can be fitted with different heads, brushes, or abrasives to accommodate various part types, giving manufacturers the ability to process a wide range of components without needing to invest in multiple specialized machines.
Moreover, the integration of digital technologies is revolutionizing the way deburring is performed. Tools are becoming increasingly connected to smart systems that allow for real-time monitoring of performance. These systems provide valuable data on machine utilization, tool wear, and part quality, helping operators identify areas for improvement. The use of digital feedback systems enables more accurate adjustments to the deburring process, leading to improved part quality and more efficient use of resources. Additionally, cloud-based software allows manufacturers to track maintenance schedules, manage parts inventory, and monitor production metrics from a central location, providing greater visibility into the deburring operation and overall manufacturing process.
For businesses looking to improve their deburring process without overhauling their entire system, attachment-based solutions are an effective option. These tools allow existing machines, such as drills, lathes, or mills, to be converted into deburring tools with the addition of simple attachments or accessories. This makes power deburring more accessible to smaller shops or businesses that may not have the budget for a full-scale deburring machine. These attachments can be fitted with various abrasive discs, brushes, or grinding stones to achieve the desired finish, providing a cost-effective solution for businesses that need to perform deburring without investing in additional machinery.
In conclusion, power deburring tools for metal have come a long way in terms of efficiency, precision, and safety. As industries continue to prioritize automation, sustainability, and customization, manufacturers are increasingly turning to advanced tools that offer greater flexibility and integration with other systems. Whether through robotic arms, automated conveyors, or energy-efficient systems, the future of deburring lies in highly adaptable, smart, and sustainable solutions that deliver consistent results while meeting the evolving needs of the modern manufacturing environment. As technology continues to advance, the power deburring tools of tomorrow will no doubt become even more versatile, intelligent, and capable of handling increasingly complex metalworking challenges.
Deburring Aluminium Sheet

Deburring aluminum sheets is an essential step in the manufacturing process, as aluminum can produce sharp edges, burrs, and rough surfaces after cutting, punching, or milling. These imperfections not only affect the appearance of the material but can also impact its functionality, safety, and ease of assembly. Proper deburring ensures smoother edges, reduces the risk of injuries, and prepares the material for further processing or assembly.
Aluminum, being a soft metal, requires careful handling during the deburring process. If not deburred properly, the burrs can interfere with other processes, such as welding, coating, or further machining. Deburring aluminum sheets is typically done using a variety of methods and tools, depending on factors like part size, volume, and required finish. Below are some common methods for deburring aluminum sheets.
Methods of Deburring Aluminum Sheet:
1. Manual Deburring: Manual deburring involves using handheld tools to remove burrs from aluminum sheets. This process is typically used for small volumes, intricate parts, or when a high level of precision is required.
- Hand Files: One of the most basic manual methods for deburring aluminum is using hand files. These tools allow the operator to carefully shave off burrs and smooth out edges. Files are ideal for light deburring or for parts with small burrs that need to be cleaned up in tight areas.
- Deburring Blades: Deburring blades or scrapers are also commonly used to manually remove burrs. These blades are particularly useful for softer burrs and can be very effective for edge finishing.
- Wire Brushes: A wire brush attached to a handheld grinder or electric tool can be used to remove light burrs. The wire bristles help dislodge small burrs and provide a smoother finish.
2. Rotary Tools (Electric or Pneumatic): Electric or pneumatic rotary tools are popular for deburring aluminum sheets. These tools feature rotating abrasive attachments, which can quickly remove burrs from both flat and contoured surfaces. Common rotary tools include:
- Rotary Deburring Tools: These are lightweight, handheld tools that are equipped with various abrasive heads, such as rotary burrs, abrasive brushes, or sanding discs. The rotating action of the tool helps remove burrs efficiently without damaging the aluminum surface. Pneumatic versions offer more torque and are often preferred in industrial settings.
- Flap Discs and Sanding Wheels: Mounted on an angle grinder or rotary tool, flap discs and sanding wheels provide an efficient way to remove burrs from aluminum sheets. The flaps of the sanding discs help ensure a consistent surface finish without excessive material removal.
3. Vibratory Deburring (Tumbling): For small aluminum parts or high-volume production, vibratory deburring is an effective method. In this process, parts are placed in a vibrating bowl or tumbler along with abrasive media (such as ceramic or plastic chips). The vibrations cause the parts to rub against each other and the abrasive media, effectively removing burrs and smoothing edges.
- Benefits: Vibratory deburring is ideal for batch processing and provides consistent results. It is particularly effective for small, delicate parts that may be difficult to handle manually or with handheld power tools.
- Considerations: While vibratory deburring is efficient for small parts, it may not be suitable for larger sheets or complex geometries. The process also requires careful control of time and abrasive media to avoid over-polishing or damaging the material.
4. Abrasive Belt Sanders: Abrasive belt sanders are another common method for deburring aluminum sheets. The sanding belts are made from abrasive materials such as aluminum oxide or silicon carbide and are used to grind away burrs along the edges of the sheet.
- Wide Belt Sanders: These machines are typically used for high-volume operations and can handle larger sheets of aluminum. They provide an even, consistent deburring action across the entire surface of the material. Adjustable feed speeds and belt tension settings allow for customization based on the type of aluminum and the desired finish.
- Handheld Belt Sanders: For smaller jobs or manual control, handheld belt sanders can be used to deburr aluminum sheets. These are particularly effective for deburring edges or removing burrs in areas that are difficult to reach with larger machines.
5. CNC Deburring Machines: For high-precision applications or large volumes, CNC deburring machines can be used to automate the process. These machines use computer-controlled tools to precisely remove burrs from aluminum sheets. CNC deburring machines can be set up to handle both flat and complex shapes, ensuring consistent quality and reducing labor time.
- Robotic Deburring: In some industrial settings, robotic arms fitted with deburring tools are used for automated deburring. These robots can follow pre-programmed paths to deburr sheets of aluminum with high precision. Robotic deburring systems can also incorporate vision systems to detect burrs, ensuring that no imperfection is missed.
6. Laser Deburring: Laser deburring is a non-contact process that uses high-energy laser beams to precisely remove burrs from aluminum sheets. This method works by vaporizing the burrs with a focused laser beam, leaving behind smooth edges without physical contact with the material.
- Benefits: Laser deburring is extremely precise and works well for parts with very tight tolerances. It also reduces the risk of surface contamination or damage to the aluminum sheet.
- Considerations: The cost of laser deburring equipment is relatively high, which can make it less suitable for smaller-scale operations. Additionally, it may not be as effective for larger burrs or thicker material.
7. Waterjet Deburring: Waterjet deburring uses a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive particles to remove burrs from aluminum sheets. The waterjet’s pressure and abrasive particles effectively cut away burrs without damaging the underlying material. This method is ideal for parts with intricate geometries or delicate features, where traditional mechanical deburring methods may be too aggressive.
- Benefits: Waterjet deburring is a clean, precise method that doesn’t require physical contact with the material, reducing the risk of damage. It also works well with a wide range of materials, including aluminum.
- Considerations: Waterjet deburring requires significant water and power resources, and the process can be slower than other methods. However, it is effective for parts that require high precision and intricate details.
8. Chemical Deburring: Chemical deburring is a process that involves the use of specialized chemicals to dissolve burrs on aluminum sheets. This method is primarily used for delicate parts or when deburring by mechanical means is impractical.
- Benefits: Chemical deburring can be highly effective at removing burrs from hard-to-reach areas and is particularly useful for parts with complex shapes or intricate features.
- Considerations: The chemicals used in the process must be carefully selected to avoid damaging the material. Chemical deburring also requires strict safety protocols, as the chemicals can be hazardous if not handled correctly.
Considerations for Deburring Aluminum Sheets:
- Surface Finish: Aluminum sheets are often used in applications where the appearance of the part is important. The deburring process should leave a smooth, consistent surface without introducing additional imperfections. Some deburring methods, such as vibratory deburring or abrasive belt sanding, can also provide additional polishing and smoothness to the material.
- Burr Size and Type: The size and type of burrs on the aluminum sheet will influence the choice of deburring method. Larger burrs may require more aggressive methods, such as grinding or abrasive belt sanding, while smaller burrs can often be removed with rotary tools or chemical methods.
- Material Thickness: Thicker aluminum sheets may require more heavy-duty deburring methods, such as abrasive belt sanders or CNC machines, as these can handle the greater material removal required. For thinner sheets, manual or rotary tools may be sufficient.
- Production Volume: For high-volume production, automated deburring systems like CNC deburring machines, robotic systems, or vibratory tumblers are ideal. These systems are capable of processing large batches of parts quickly and consistently. For smaller quantities, manual or handheld deburring tools may be more cost-effective.
In conclusion, deburring aluminum sheets is a crucial step in the metalworking process, ensuring that aluminum parts are free of sharp edges and burrs that could cause problems in assembly, functionality, or safety. The choice of deburring method depends on factors such as part size, volume, burr size, and finish requirements. Whether using manual tools for smaller jobs or advanced robotic systems for high-volume production, proper deburring ensures that aluminum sheets meet the desired standards of quality and performance.
Deburring aluminum sheets is a crucial process in the manufacturing industry, as it ensures that aluminum parts are free from sharp edges, burrs, and rough surfaces that can affect both the functionality and appearance of the material. When aluminum sheets are cut, punched, or machined, burrs are created along the edges of the part. These burrs can cause problems such as difficulty in assembly, mechanical failure, and safety risks. The deburring process helps to remove these imperfections and prepare the material for further processing, assembly, or use.
There are several methods to deburr aluminum sheets, and the choice of method depends on factors such as part size, production volume, and the severity of the burrs. For small or intricate parts, manual deburring using hand files, deburring blades, or wire brushes may be effective. These methods allow operators to carefully remove burrs from edges or small areas that require precision. While effective, manual deburring can be time-consuming and labor-intensive, especially for large quantities of parts.
Rotary tools, such as electric or pneumatic deburring tools, are commonly used to remove burrs from aluminum sheets. These tools have rotating abrasive attachments, such as rotary burrs, brushes, or sanding discs, that effectively remove burrs and smooth out edges. Electric rotary tools are commonly used in small to medium-scale operations, while pneumatic tools are more powerful and are often used in industrial settings where higher torque is needed for tougher burrs or larger volumes.
For high-volume production, vibratory deburring is an effective method. This technique involves placing aluminum parts into a vibrating bowl or tumbler along with abrasive media. The vibration causes the parts to rub against each other and the media, removing burrs and providing a smooth finish. Vibratory deburring is particularly effective for small parts and provides consistent results, though it may not be suitable for larger or more complex geometries.
Abrasive belt sanders are another method for deburring aluminum sheets, particularly when a smooth, consistent finish is required. These sanders use abrasive belts to grind away burrs and smooth out edges. Wide belt sanders are used for larger sheets or high-volume production, while handheld belt sanders can be used for smaller parts or more intricate tasks. Abrasive belt sanders offer high material removal rates and can be adjusted to accommodate different materials and thicknesses.
In more advanced applications, CNC deburring machines and robotic systems are used to automate the deburring process. These systems are programmed to precisely remove burrs from aluminum sheets with high accuracy. CNC deburring machines are ideal for parts that require tight tolerances or intricate geometries, while robotic deburring systems use robotic arms to handle parts and apply deburring tools where needed. These automated systems offer high precision and can significantly reduce labor costs by streamlining the deburring process.
Laser deburring is another advanced method that uses a focused laser beam to remove burrs from aluminum sheets. The laser vaporizes the burrs, leaving behind smooth, burr-free edges. This method is highly precise and works well for parts with tight tolerances. However, it is a costly option and may not be suitable for large-scale production due to its relatively slower processing speed.
Waterjet deburring uses a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive particles to remove burrs from aluminum sheets. This non-contact process is ideal for delicate parts or those with complex geometries, as the waterjet can remove burrs without damaging the material. Waterjet deburring is also versatile, as it can handle a wide range of materials, including aluminum. However, it requires significant resources and is slower than other methods.
For situations where mechanical deburring is impractical, chemical deburring may be used. This method involves applying specialized chemicals to dissolve the burrs on aluminum parts. Chemical deburring is particularly useful for small parts or those with intricate features that are difficult to deburr mechanically. However, it requires careful handling of chemicals and safety protocols to avoid damage to the material or exposure to harmful substances.
Choosing the right deburring method for aluminum sheets depends on various factors, including the type and size of the burrs, part geometry, production volume, and the desired surface finish. For high-volume production, automated systems such as CNC machines or robotic deburring tools can offer efficiency and consistency. For smaller batches or parts with intricate features, manual deburring or rotary tools may be more appropriate. Abrasive belt sanders and vibratory deburring are effective for handling a wide range of part sizes and burr sizes, while laser and waterjet deburring offer high precision for more complex or delicate parts.
Additionally, when deburring aluminum sheets, it is important to consider the surface finish. Burrs and rough edges not only affect the aesthetics of the part but can also impact its performance, especially in applications where parts need to fit together or withstand mechanical stress. Deburring methods should leave behind a smooth, uniform edge that is free of any defects. Furthermore, deburring should be done carefully to avoid removing too much material, which can alter the part’s dimensions or cause other issues down the line.
In industrial settings, safety is also a key concern. Deburring aluminum sheets can generate metal dust, chips, and sparks, which pose safety risks. Operators should wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves, safety goggles, and ear protection, to reduce the risk of injury. Using tools with built-in safety features, such as guards or dust extraction systems, can help mitigate these risks and create a safer work environment.
Overall, deburring aluminum sheets is an essential part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that aluminum parts are free from burrs, sharp edges, and rough surfaces. The right deburring method depends on the specific requirements of the part, including its size, material, and finish. With the right tools and techniques, manufacturers can ensure that aluminum parts are of high quality, function properly, and meet safety standards.
Deburring aluminum sheets, like any metalworking process, is critical for maintaining product quality, improving safety, and ensuring that parts can be further processed without complications. Given aluminum’s tendency to form burrs and rough edges during cutting, milling, punching, or shearing, removing these imperfections is essential for both aesthetic appeal and functional performance.
One of the key aspects of deburring aluminum sheets is selecting the right tool for the task. While manual tools can work for small batches or intricate parts, larger-scale operations typically demand automated systems that can process a significant number of parts efficiently. Even in high-volume production, it’s essential to monitor the deburring process to ensure that parts meet precise specifications without excessive wear on the tooling or part deformation.
For larger aluminum sheets, it’s important to understand that excessive pressure during deburring can lead to deformation, especially in softer grades of aluminum. Therefore, it’s critical to adjust the tooling and speed settings appropriately to avoid compressing or bending the sheet. The use of variable-speed systems on machines like abrasive belt sanders or CNC deburring machines can help prevent these issues, giving operators more control over the process and allowing for smoother, burr-free edges without sacrificing part integrity.
When deburring aluminum, ensuring a consistent surface finish is a priority. Some methods, like rotary tools or abrasive belt sanders, not only remove burrs but can also provide a polished or brushed finish to the material’s edges. This is especially important in industries where the appearance of the final product is just as important as its functionality, such as in automotive or consumer electronics. The finish must not only be free of burrs but also uniform to ensure that parts fit together properly, reducing the likelihood of assembly issues.
Another important consideration when deburring aluminum sheets is the type of burrs present. Burrs can vary significantly depending on the cutting or shaping process used, with some being sharp and brittle, while others may be more resistant to removal. For example, burrs produced by shearing often have a harder, more embedded nature than those formed during stamping or laser cutting. In such cases, a combination of methods may be needed to effectively remove burrs without damaging the part. This could involve using abrasives for rough burrs followed by polishing to refine the surface.
Deburring aluminum also has environmental and operational considerations. During traditional deburring methods, metal chips, dust, and particles are often created. Aluminum dust, in particular, can pose a risk to health and safety if not properly controlled. Modern deburring equipment comes with integrated dust extraction systems to ensure that the debris is safely removed from the work environment. These systems help reduce airborne contaminants, improving air quality and reducing the potential for respiratory issues among workers.
The environmental impact of deburring also extends to energy consumption. Deburring machines and tools, particularly those that are automated, can require significant power input. However, with advances in energy-efficient motor technologies and smarter equipment design, new deburring machines are being built to reduce energy usage without compromising on performance. This is an important consideration for manufacturers looking to reduce operational costs while maintaining an environmentally conscious approach to production.
In industries like aerospace and automotive manufacturing, where aluminum is commonly used due to its lightweight properties, deburring is essential for ensuring that parts meet strict standards for precision and performance. Even the smallest burrs can cause problems in these applications, where precise fits and tolerances are often required. In such cases, advanced deburring technologies like robotic systems, CNC machines, and laser deburring may be utilized to guarantee that each part is consistently deburred to the highest standard.
In addition to the technical aspects of deburring, operators should be trained to recognize when a deburring process is complete. Over-deburring, where too much material is removed, can cause dimensional changes to the part, leading to potential fitment issues during assembly. As a result, knowing how to strike the right balance between effective burr removal and preserving part integrity is an important skill for deburring operators.
Another consideration in deburring aluminum sheets is the type of aluminum being processed. Aluminum alloys come in many different grades, each with its own set of characteristics. For example, 3003 aluminum is more easily deburred than harder grades like 7075 aluminum, which require more specialized tools and techniques. Understanding the material properties and adjusting deburring parameters accordingly can ensure that the process is both efficient and effective.
The role of automation in deburring continues to grow. As demand for faster production cycles and higher part quality increases, automated deburring systems are becoming more popular. These systems can be programmed to detect burrs and imperfections in real-time and adjust the deburring process accordingly. For instance, some robotic systems are equipped with vision systems to identify burrs on parts, automatically guiding the deburring tool to remove them. This reduces the need for manual inspection, minimizes the risk of errors, and speeds up production times.
Another promising development is the use of additive manufacturing technologies to assist in the deburring process. In some cases, 3D-printed tools or customized parts can be used alongside traditional deburring methods to improve precision or access hard-to-reach areas. The adaptability of additive manufacturing has enabled the creation of specialized deburring tools that perfectly match the contours of the parts being worked on, which can lead to better results and greater efficiency.
Finally, manufacturers must also consider the cost-effectiveness of deburring methods. While automated systems and advanced tools offer significant advantages in terms of speed and consistency, they come with higher upfront costs. For businesses with lower production volumes, a combination of manual deburring and less costly machinery may be more appropriate. However, for high-volume operations where consistency, speed, and precision are paramount, investing in more advanced deburring technology may provide long-term savings by reducing labor costs and improving throughput.
In conclusion, deburring aluminum sheets is a multifaceted process that requires careful consideration of the material, part geometry, and production requirements. From manual methods for small-scale operations to high-precision automated systems for large-volume manufacturing, there are a variety of tools and techniques available to ensure a burr-free finish. By selecting the right deburring method, considering environmental and safety factors, and continuously improving the process, manufacturers can ensure that their aluminum parts are ready for further processing, assembly, or use, meeting the necessary quality standards.
Aluminum Deburring Tool

An aluminum deburring tool is a specialized tool designed to remove burrs, sharp edges, and imperfections from aluminum parts or sheets after cutting, milling, punching, or other machining processes. Burrs are rough, unwanted edges that form on the material when it’s cut or shaped, and they can pose safety hazards, interfere with assembly, and affect the overall quality of the product. Deburring tools are essential for ensuring smooth, burr-free edges that enhance both the functionality and aesthetic quality of aluminum parts.
Aluminum is a relatively soft and lightweight metal, but it can still produce burrs that require careful removal, especially in high-precision applications like automotive, aerospace, or electronics manufacturing. There are several types of deburring tools available, each suited for different needs, whether for small-scale manual work or large-scale automated production.
Types of Aluminum Deburring Tools
- Handheld Deburring Tools: These tools are simple and effective for small jobs, repairs, or intricate parts. They’re typically used manually to remove burrs from edges, corners, and hard-to-reach spots.
- Deburring Blades: These are one of the most common handheld tools for removing burrs from aluminum. Deburring blades feature sharp edges that scrape away the burrs without damaging the material underneath. They are ideal for smaller burrs or for accessing areas that are difficult to reach with other tools.
- Files and Rasps: Hand files, especially needle files, are useful for finer deburring tasks. They are available in a range of shapes (flat, round, half-round, etc.) and can be used to smooth edges and remove light burrs from aluminum. The coarse nature of rasps makes them suitable for tougher burrs.
- Rotary Hand Tools: Handheld rotary tools, such as those from brands like Dremel, can be fitted with abrasive discs, sanding tips, or rotary burrs designed specifically for deburring. These tools are effective for more aggressive deburring and can work on a variety of surface shapes, including contoured and irregular parts.
- Power Deburring Tools: Power tools provide greater efficiency and are often used for high-volume production or when larger, tougher burrs need to be removed. These tools can operate either electrically or pneumatically.
- Pneumatic Deburring Tools: Pneumatic (air-powered) deburring tools are widely used in industrial applications. These tools are lightweight and provide strong torque, making them ideal for quickly and efficiently removing burrs from aluminum parts. They often come with interchangeable heads like abrasive brushes, flap discs, or sanding belts for various deburring tasks.
- Electric Deburring Tools: Electric deburring tools offer more control than pneumatic ones and are often used for precision work. They provide consistent speed and torque, which helps in maintaining a uniform finish across the entire surface. Many electric deburring tools can be fitted with different types of abrasives or attachments, allowing for versatility in removing burrs and polishing the material.
- Rotary Deburring Tools: Rotary deburring tools are available in both manual and power-assisted versions and are designed for faster, more efficient deburring. They typically feature rotating abrasive tips, brushes, or discs that remove burrs from metal surfaces by grinding them away.
- Rotary Burrs: These are cutting tools with fluted heads that are used with rotary hand tools, such as grinders or drills, to efficiently remove burrs from aluminum. Rotary burrs come in different shapes, sizes, and materials, with carbide burrs being especially effective for aluminum because of their hardness and durability.
- Flap Discs and Abrasive Wheels: Mounted on angle grinders or rotary tools, flap discs and abrasive wheels can be used for more aggressive deburring tasks. The discs or wheels feature multiple layers of abrasive material that wear down as they’re used, providing a consistent and efficient method for removing burrs from aluminum sheets or parts.
- Vibratory Deburring Machines: Vibratory deburring uses abrasive media (such as ceramic, plastic, or steel media) in a vibrating bowl or barrel to smooth out rough edges and remove burrs from aluminum parts. This process is ideal for high-volume deburring, particularly for small, intricate parts that may be difficult to deburr manually.
- Vibratory Tumblers: These machines allow parts to be tumbled with abrasive media, gently deburring them while providing a smooth finish. The process is typically used for batch processing and is particularly suitable for small parts with consistent burrs. The media size and type can be customized to meet the specific needs of the aluminum parts being deburred.
- CNC Deburring Machines: For high-precision deburring tasks, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) deburring machines are used in automated manufacturing processes. These machines use rotary tools or abrasive heads that are controlled by computer programming to remove burrs from aluminum sheets or parts with high accuracy.
- Robotic Deburring: Robotic systems equipped with deburring tools are capable of detecting burrs on parts and automatically removing them based on pre-programmed instructions. These systems provide consistent results and can handle complex part geometries or large volumes with minimal human intervention.
- CNC Routers or Grinders: CNC routers or grinders can be fitted with deburring heads to remove burrs from aluminum parts. These systems offer high precision, allowing manufacturers to maintain tight tolerances while deburring parts at scale.
- Abrasive Belt Sanders: Abrasive belt sanders are another popular method for deburring aluminum sheets. The sandpaper belts are designed to remove burrs and smooth edges without damaging the underlying material. These machines can be used in a variety of configurations, from handheld models to larger, more industrial-sized units.
- Wide-Belt Sanders: These are used for deburring larger aluminum sheets and parts. The sanding belts can be adjusted for different speeds and pressures, making them versatile for various applications. They are effective for smoothing the edges of parts and removing both small and larger burrs efficiently.
- Handheld Belt Sanders: These are more portable options for smaller jobs. They are commonly used to remove burrs from edges or perform light finishing work on aluminum parts that may require a more hands-on approach.
- Chemical Deburring: Chemical deburring is a non-mechanical method that involves using chemical solutions to dissolve burrs from aluminum parts. This method is effective for intricate parts or those with complex geometries where traditional mechanical deburring might be challenging.
- Chemical Solutions: Specialized chemical solutions are applied to aluminum parts, and the burrs are chemically removed in a controlled manner. Chemical deburring is generally slower and can be costly compared to other methods, but it’s highly effective for delicate parts with intricate shapes or fine features.
- Laser Deburring: Laser deburring uses a focused laser beam to remove burrs from aluminum parts. This high-precision method is effective for removing small, delicate burrs without physically touching the part, reducing the risk of damage. Laser deburring is often used in high-precision industries such as aerospace and electronics.
- Benefits: Laser deburring provides a highly controlled and precise method for burr removal. It is ideal for parts with fine features, intricate geometries, or tight tolerances. It also leaves behind a clean, smooth edge with minimal or no thermal damage to the part.
Considerations When Choosing a Deburring Tool
- Type of Burr: The size, location, and material of the burr play a significant role in determining which deburring tool is best suited for the task. Large, hard burrs may require more aggressive methods, while smaller burrs can be removed with lighter tools.
- Production Volume: For high-volume production, automated systems such as CNC deburring machines, robotic deburring, or vibratory tumblers are ideal for consistent and efficient results. For lower volumes, manual tools or handheld power tools may be more appropriate.
- Material Type: While aluminum is a relatively soft material, different alloys may require different deburring approaches. Softer alloys may be easier to deburr manually, while harder alloys may require more specialized tools or methods.
- Edge Quality: The desired edge finish is an important consideration. Some methods, like abrasive belt sanding or laser deburring, also polish the surface, while others may leave a rougher finish that requires further refinement.
- Safety: Deburring tools can generate metal chips, dust, and debris. It’s essential to ensure the proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, and hearing protection, depending on the tool and the environment.
In conclusion, selecting the right aluminum deburring tool depends on various factors, including the size and type of burrs, production volume, and the finish required. Whether using manual tools for small jobs or automated systems for large-scale manufacturing, a suitable deburring tool will ensure smooth, safe, and high-quality aluminum parts.
Aluminum deburring tools are essential for removing burrs, sharp edges, and imperfections that are created during the cutting, machining, or shaping of aluminum parts. Burrs are the unwanted, rough edges that form when aluminum is cut, sheared, or stamped, and they can affect the functionality, appearance, and safety of the part. The process of deburring involves the removal of these imperfections to ensure that the aluminum parts are smooth, precise, and safe for further processing or assembly.
For small-scale jobs or intricate work, manual deburring tools such as deburring blades, files, and hand-held tools are commonly used. Deburring blades are typically used for removing small burrs along edges, while hand files, especially needle files, can be used for finer deburring tasks. These tools are versatile and allow operators to control the amount of material removed, ensuring precision and smooth edges. However, manual deburring can be labor-intensive and time-consuming, particularly for larger volumes of parts or tougher burrs.
Power deburring tools, including pneumatic and electric tools, provide more efficient and consistent burr removal, especially for high-volume or industrial applications. Pneumatic tools are often lighter and offer strong torque, making them ideal for fast deburring without causing excessive wear on the material. Electric tools provide greater control and are often preferred for more delicate or precise deburring tasks. These tools can be equipped with various attachments like abrasive brushes, sanding discs, and rotary burrs, allowing them to handle different types of burrs and surface finishes.
Rotary deburring tools, including rotary burrs, flap discs, and abrasive wheels, are widely used to remove burrs from aluminum parts quickly. These tools are designed to be used with rotary tools like drills, grinders, or angle grinders, which rotate at high speeds to remove material effectively. Rotary burrs, made of durable materials like carbide, are particularly effective at removing tough burrs and can be used to deburr both external and internal surfaces. Flap discs and abrasive wheels are available in various grits and can be used to smooth and finish edges while removing burrs.
For larger-scale operations, vibratory deburring is an efficient and cost-effective method. This involves placing parts into a vibratory bowl along with abrasive media. The vibration causes the parts to rub against each other and the media, which helps remove burrs and smooth out edges. Vibratory deburring is ideal for small, intricate parts or high-volume production and ensures consistent results without damaging the parts. It is a non-contact process, which makes it particularly useful for delicate parts or those with complex shapes.
In high-precision manufacturing environments, CNC deburring machines and robotic systems are often employed. These machines use computer-controlled tools to remove burrs from parts with high accuracy. CNC deburring machines can be equipped with various deburring heads, including rotary tools or abrasive pads, and can be programmed to remove burrs from parts with complex geometries or tight tolerances. Robotic deburring systems, equipped with advanced vision systems and AI, can autonomously detect and remove burrs from parts, reducing human labor and increasing production efficiency.
Laser deburring is another cutting-edge method for removing burrs from aluminum. This technique uses a focused laser beam to precisely vaporize burrs without physically touching the part. Laser deburring offers high precision and is ideal for parts with tight tolerances, intricate geometries, or those requiring a smooth, polished finish. However, it is more expensive than other methods and may not be suitable for all production environments due to its relatively slow processing speed.
Chemical deburring is an alternative method where chemical solutions are used to dissolve burrs from aluminum parts. This method is often used for parts with intricate features or complex geometries that may be difficult to deburr mechanically. The chemicals break down the burrs, leaving behind a smooth, clean surface. While effective, chemical deburring requires careful handling of chemicals and may not be suitable for all aluminum alloys.
Abrasive belt sanders are another popular choice for deburring aluminum, especially when a smooth and consistent finish is required. Abrasive belt sanders can remove burrs and rough edges from larger sheets of aluminum, providing a smooth finish that is ideal for parts that will be painted or coated. These machines can be fitted with different grades of abrasive belts to achieve the desired level of material removal and surface finish.
When choosing a deburring method for aluminum, several factors must be considered, including the type and size of the burrs, the material being worked on, the volume of parts, and the desired finish. High-precision methods like CNC deburring or laser deburring are ideal for parts that require tight tolerances or intricate features, while vibratory deburring or abrasive belt sanders are better suited for high-volume, less-precise applications. Manual tools and rotary tools are effective for smaller jobs or parts that require delicate handling.
Safety is another key consideration when using deburring tools, as the process can generate metal dust, chips, and sparks. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, and ear protection, should be worn to reduce the risk of injury. Additionally, dust extraction systems should be used with pneumatic and rotary tools to ensure a clean and safe working environment.
In summary, aluminum deburring tools are essential for producing high-quality, burr-free aluminum parts. Whether using manual tools for small-scale operations, power tools for larger jobs, or automated systems for high-precision manufacturing, the right deburring tool can help improve part quality, reduce safety risks, and increase production efficiency. By choosing the appropriate deburring method for the task at hand, manufacturers can ensure smooth, safe, and high-performing aluminum parts.
Round Deburring Tool

A round deburring tool is a specialized hand tool used to remove burrs, sharp edges, and imperfections from the edges of metal parts, especially in applications where a smooth, rounded edge is desired. Burrs are created during cutting, machining, or shaping processes and can affect the functionality, appearance, and safety of the part. Round deburring tools are designed specifically to address these issues by smoothing or rounding off edges, which is particularly useful when working with materials like aluminum, steel, copper, and other metals.
These tools are commonly used in industries like manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and general metalworking, where parts need to meet precise tolerances and have smooth edges to prevent sharp edges from causing injuries or interfering with assembly.
Features of Round Deburring Tools:
- Round Cutting Blade: The defining feature of a round deburring tool is its round cutting blade or rotary head. This blade is designed to smoothly remove burrs from the edges of a metal part without damaging the surface. The round shape allows for efficient cutting along the edges, ensuring that the burrs are removed uniformly and that the edge is rounded rather than sharp or jagged.
- Ergonomic Handle: Most round deburring tools are equipped with ergonomic handles to ensure comfort and control during use. The handle is usually designed to allow for a firm grip, which is important for applying the right amount of pressure while working on the metal part. Some handles are also designed to reduce vibrations during use, further enhancing operator comfort.
- Adjustable Blades: Many round deburring tools feature adjustable or replaceable blades, allowing users to switch out blades as they wear down or for different deburring tasks. Some tools even allow for the angle of the blade to be adjusted to suit different edge geometries.
- Versatility: Round deburring tools are versatile and can be used on a variety of materials, including ferrous and non-ferrous metals. This makes them suitable for applications in different industries, including electronics, automotive, and metal fabrication.
Types of Round Deburring Tools:
- Manual Round Deburring Tools: These are typically handheld tools that operate by rotating a round cutting blade along the edge of a part to remove burrs. These tools are simple to use and are often employed in low to medium-volume applications. The user manually guides the tool along the edge, providing control over the amount of material removed.
- Rotary Round Deburring Tools: For faster or higher-volume deburring, rotary round deburring tools are available. These tools use a motor to rotate the deburring head, which helps speed up the deburring process. The motorized action ensures a consistent and smooth finish and is especially useful for applications where a high level of precision and efficiency is required.
- Double-Ended Round Deburring Tools: These tools have two ends, each with a different blade configuration. One end typically has a blade designed for fine burr removal, while the other is designed for heavier burrs. This dual functionality makes them suitable for a range of deburring tasks on different types of metal parts.
- Adjustable Round Deburring Tools: Some round deburring tools feature adjustable settings, allowing the operator to modify the depth of the blade or the angle at which it cuts. This feature provides more flexibility and precision, particularly when deburring parts with complex shapes or varying thicknesses.
How Round Deburring Tools Work:
Round deburring tools are generally used in a rotating or scraping motion to effectively remove burrs from metal edges. The round blade or head of the tool makes contact with the burr and removes it by cutting away the excess material. The design of the tool ensures that the edge is not only deburred but also rounded, which is crucial for certain applications where sharp edges are undesirable.
- Manual Operation: For manual round deburring tools, the user applies pressure as they move the tool along the edge of the part. The cutting blade rotates or scrapes along the metal, shaving off burrs and leaving a smooth, rounded edge. The operator controls the amount of pressure to ensure an even cut, preventing over-deburring or damage to the part.
- Motorized Operation: In motorized round deburring tools, the rotation of the cutting blade is powered by an electric or pneumatic motor, which helps remove burrs quickly and consistently. These tools are especially useful for high-volume production environments, where fast and uniform burr removal is essential.
Advantages of Round Deburring Tools:
- Efficient Burr Removal: Round deburring tools are specifically designed to remove burrs from the edges of parts, providing a cleaner, smoother finish than other manual methods, such as using files or sandpaper.
- Precision: Round deburring tools allow for precise control over the deburring process, making them ideal for parts that need to meet tight tolerances or specific edge requirements. The round blade ensures that the edge is not only smooth but also rounded, which can be necessary for safety or design purposes.
- Ease of Use: Most round deburring tools are straightforward to use, even for those with limited experience in metalworking. The ergonomic handle design helps reduce operator fatigue, while the simple motion of using the tool makes it easy to achieve the desired results.
- Versatility: These tools can be used on a wide range of metals and alloys, including aluminum, stainless steel, copper, and brass. This versatility makes them a great choice for many different applications, from small repairs to large-scale manufacturing.
- Improved Safety: Burrs can be dangerous, especially in industries like automotive and aerospace, where sharp edges can cause injuries during assembly or handling. By removing these burrs, round deburring tools help improve safety for workers and prevent accidents.
- Improved Product Quality: Deburring edges ensures that parts fit together properly and reduces the risk of mechanical failure. This can enhance the overall quality of the finished product, making it more reliable and durable.
Common Applications:
- Automotive Industry: Round deburring tools are used to remove burrs from metal components like engine parts, body panels, and structural elements, ensuring smooth edges that fit together properly during assembly.
- Aerospace Industry: Deburring is essential in the aerospace industry to ensure that metal parts meet strict tolerance requirements. Round deburring tools are often used to smooth the edges of components used in aircraft, spacecraft, and related machinery.
- Electronics Manufacturing: When working with metal parts for electronics, smooth edges are crucial to ensure that parts fit together without causing damage or interference. Round deburring tools are used to ensure clean edges for connectors, housings, and other components.
- Metalworking and Fabrication: In general metalworking, round deburring tools are used on a variety of parts, from structural beams to custom-made components. These tools help improve the aesthetic quality and functional performance of the parts.
In conclusion, round deburring tools are essential for ensuring clean, smooth, and safe edges on aluminum and other metal parts. Whether manually operated or powered by electricity or air, these tools provide an effective solution for removing burrs and sharp edges, improving both the functionality and appearance of the metal parts.
Round deburring tools are used to remove burrs, sharp edges, and imperfections from the edges of metal parts, particularly when a smooth, rounded edge is needed. Burrs are the unwanted rough edges that form during cutting, machining, or shaping of metal parts. These burrs can affect the performance, safety, and aesthetic quality of the part. Round deburring tools are specifically designed to smooth or round off edges, making them safer for handling, assembly, and further processing.
These tools are typically used in industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and general metalworking, where parts must meet high standards of precision and safety. The primary feature of a round deburring tool is its round cutting blade or rotary head, which is designed to work efficiently along the edges of metal parts, ensuring uniform removal of burrs without damaging the part itself. The tool’s rounded edge helps in smoothing the burrs while also rounding off sharp edges, which is particularly beneficial when sharpness could interfere with the function or safety of the final product.
Round deburring tools come in various types, including manual handheld tools, rotary tools, and motorized versions. Manual tools are the most straightforward and commonly used for smaller jobs or intricate parts that require careful control. They typically consist of a handle with a rotating blade at the end, which is applied to the burr to scrape or shave it off. The user can guide the tool along the edge, applying the necessary pressure to achieve a smooth finish. These tools are simple to use and provide precise control over the amount of material being removed.
For higher efficiency or higher-volume work, rotary round deburring tools are powered by motors that rotate the deburring head. These tools offer faster and more consistent burr removal compared to manual tools, making them ideal for industrial settings where time and consistency are crucial. The motorized action allows for smoother operation, reducing the effort required from the operator while increasing the speed of the deburring process.
Motorized deburring tools can be powered either electrically or pneumatically, with pneumatic tools often being preferred in industrial settings because they are lightweight and can deliver strong torque without producing excessive heat. Electric models, on the other hand, provide more precise control over speed and power, making them useful for delicate parts or jobs that require a high degree of accuracy.
Adjustable round deburring tools are another type, which allows users to change the angle of the blade or adjust the cutting depth. This feature makes the tool more versatile and capable of handling various deburring tasks on parts with different thicknesses or edge geometries. Some models are equipped with double-ended blades, each designed for a different type of burr, further enhancing their functionality and making them suitable for a range of applications.
These tools are not only used to remove burrs but also to ensure that edges are rounded to avoid sharpness, which is important in many industries. For example, in the automotive industry, sharp edges on parts can cause injuries during assembly or increase the likelihood of malfunctioning when the parts are joined together. In aerospace, ensuring smooth, rounded edges is essential for the integrity and safety of components. Similarly, in electronics manufacturing, burr-free edges are necessary to ensure proper fit and function of connectors and housings.
One of the significant advantages of using round deburring tools is their ability to provide precise and consistent results. Burrs can vary in size and shape depending on the cutting process, and the tool’s design ensures that the burrs are evenly removed while leaving the underlying material intact. This helps ensure that parts are not only free of burrs but also have a smooth, rounded edge that is ideal for fitting, assembly, or further processing.
Round deburring tools also improve the overall safety and quality of the finished product. Sharp burrs can cause cuts, scratches, or other injuries during handling, and they can also lead to poor part fitment, which may result in the failure of the part in its intended application. By removing burrs and rounding off edges, these tools enhance the safety of the parts and ensure that they will perform as expected without causing damage to other components or the end user.
In terms of versatility, round deburring tools are suitable for various metals and alloys, including aluminum, steel, brass, copper, and more. This versatility makes them valuable tools in multiple industries where metal parts are shaped, cut, or machined. Whether for small-scale manual work or large-volume production, these tools can be used to achieve consistent and high-quality results.
In addition to improving safety and performance, using a round deburring tool can help reduce the time spent on manual filing, sanding, or polishing. It provides an efficient and precise solution for burr removal and edge rounding, allowing operators to focus on other important aspects of the production process.
In conclusion, round deburring tools are crucial for ensuring smooth, burr-free, and safe metal parts. Whether using manual, motorized, or adjustable versions, these tools help improve part quality, reduce the risk of injury, and enhance the overall functionality of the final product. They are essential in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and metalworking, where precision and safety are paramount.
Round deburring tools are indispensable in many metalworking applications, providing a precise and efficient way to remove burrs, sharp edges, and other imperfections from metal parts. The need for such tools becomes especially crucial when the edges of metal parts need to be rounded or smoothed for safety, aesthetics, or functionality. For example, sharp edges on metal parts can cause injuries during handling, create difficulties during assembly, or prevent parts from fitting properly together. Round deburring tools address these issues by ensuring a smooth, rounded finish, making parts safer to handle and improving the overall quality of the product.
Manual round deburring tools, often simple and easy to use, are the most common for small-scale applications or delicate parts. These tools offer operators the flexibility to control the pressure applied to the edge of the part, allowing for more accurate deburring and rounding. As the operator moves the tool along the edge, the round blade rotates or scrapes off the burr, leaving behind a clean, smooth surface. These tools are widely used in settings where the volume of work is low or when parts require fine, detailed deburring work.
For higher-volume operations, or when more consistent and faster results are needed, motorized round deburring tools are an excellent choice. These power-driven tools can remove burrs much more quickly than manual tools, reducing the time and effort required for deburring. In industries where mass production is common, motorized tools help improve efficiency and ensure uniform results across large batches of parts. The motorized tools are available in both electric and pneumatic versions, each offering unique advantages depending on the work environment. Pneumatic tools, for instance, are often lighter and provide a high level of torque, while electric tools offer precise control over speed and power, making them ideal for delicate deburring tasks that require accuracy.
Some round deburring tools also feature adjustable blades or cutting heads, allowing the user to modify the tool to suit different part geometries or specific burr removal needs. This level of customization ensures that the tool can be adapted for a wide range of applications, from parts with simple straight edges to those with more complex, curved, or contoured surfaces. Adjustable tools are especially useful in precision industries, such as aerospace or automotive manufacturing, where parts with varying thicknesses and edge profiles are common.
The versatility of round deburring tools extends beyond the types of parts they can handle; they also work well with a broad range of materials, including aluminum, stainless steel, copper, and other alloys. The ability to deburr different materials means these tools are widely applicable in many industries, including metal fabrication, electronics, construction, and more.
In addition to their functional benefits, round deburring tools also contribute to improving part appearance. Sharp edges or burrs can create a rough, unfinished look, making the part less aesthetically appealing. By smoothing out these imperfections, round deburring tools help achieve a polished finish, enhancing the part’s overall visual quality. This is especially important in industries like consumer electronics or automotive, where appearance can be as critical as function.
Another key advantage is the safety improvements that come from using round deburring tools. Burrs and sharp edges are not just an aesthetic concern; they pose a safety hazard during both the production process and the use of the final product. For example, in the automotive industry, burrs can cause cuts or scratches during assembly or handling, while in aerospace, sharp edges can lead to mechanical failures if parts don’t fit together properly. Round deburring tools reduce these risks by removing sharp edges and rounding off the corners of metal parts, making them safer for workers and users alike.
Round deburring tools also enhance the overall quality control of the production process. When parts are deburred correctly, they fit together more easily and are less prone to wear and tear during use. Burrs and sharp edges can interfere with the mechanical properties of a part, leading to problems like poor assembly, reduced part durability, and even part failure. Proper deburring ensures that these issues are minimized, resulting in a more reliable and functional product.
The ease of use and low learning curve of round deburring tools make them accessible to a wide range of operators. Even individuals without extensive experience in metalworking can quickly learn to use these tools effectively, which helps streamline operations and reduce the need for extensive training. Additionally, the simplicity of these tools makes them ideal for smaller workshops or operations with limited resources, where high-end automated systems might not be feasible.
As industries continue to prioritize safety, quality, and efficiency, round deburring tools will remain an essential part of the metalworking process. Whether used for high-precision deburring in industries like aerospace or automotive, or for general-purpose applications in manufacturing and fabrication, round deburring tools provide the ideal solution for achieving smooth, safe, and high-quality metal parts.
External Deburring Tool for Metal Pipe
An external deburring tool for metal pipes is a specialized tool designed to remove burrs, sharp edges, and imperfections from the outer surface of metal pipes, which are commonly created during the cutting, machining, or manufacturing processes. Burrs and rough edges on metal pipes can affect their fit, function, and safety during handling, welding, and assembly. The external deburring tool ensures that the pipe edges are smooth and free from defects, improving both the performance and safety of the final product.
These tools are commonly used in industries such as plumbing, HVAC, oil and gas, construction, and general metalworking, where pipes and tubing need to be deburred to meet safety and quality standards. The external deburring tool works by removing the rough edges, also known as burrs, from the exterior of the pipe, which might be left behind after cutting or machining operations.
Features of External Deburring Tools for Metal Pipes:
- Rotary or Fixed Cutting Blades: Most external deburring tools for metal pipes are equipped with rotary or fixed cutting blades that can scrape, shave, or cut off burrs from the outer surface of the pipe. The rotary blades are often designed to follow the pipe’s contour as the tool is moved along the pipe, providing an even and consistent deburring effect.
- Adjustable Blade Depth: Some external deburring tools feature adjustable blades that allow the operator to modify the depth of the cut. This ensures that the burrs are fully removed without over-deburring or damaging the pipe’s surface. Adjustable tools provide more flexibility and control, especially when working with pipes of varying sizes or wall thicknesses.
- Ergonomic Handle Design: Many external deburring tools come with ergonomic handles to provide a comfortable and secure grip. This design helps operators maintain control over the tool and reduces hand fatigue, especially when working on large quantities of pipes.
- Compatibility with Various Pipe Sizes: External deburring tools are typically designed to handle pipes of various diameters, making them versatile for different applications. Many tools can be adjusted or have interchangeable components to fit pipes with different outer diameters, making them suitable for a wide range of pipe sizes.
- Durable Construction: Since metal pipes can be made from a variety of materials such as steel, stainless steel, copper, aluminum, and PVC, external deburring tools are built with durable materials that can withstand the wear and tear of working with different metals and alloys. High-quality materials such as hardened steel are commonly used in the construction of the cutting blades and tool body to ensure longevity.
- Portable and Lightweight: Many external deburring tools are lightweight and portable, making them easy to use on job sites or in the field. Their compact design allows for easy storage and transportation, which is especially beneficial for workers who need to carry the tool between various locations.
Types of External Deburring Tools for Metal Pipes:
- Manual External Deburring Tools: These are handheld tools that require the operator to apply manual force to remove burrs from the pipe. They typically feature a rotating blade or scraper that cuts off the burrs as the tool is moved around the outer surface of the pipe. Manual tools are often used for smaller jobs or when working on low volumes of pipe.
- Pneumatic External Deburring Tools: Pneumatic tools are powered by compressed air and are ideal for high-volume deburring operations. They offer increased speed and efficiency compared to manual tools and can be used continuously without requiring much physical effort from the operator. Pneumatic tools are often used in industrial settings or on larger production lines.
- Electric External Deburring Tools: Electric deburring tools provide a motorized solution for removing burrs from the outer edges of metal pipes. These tools offer more consistent power and control compared to manual tools, making them suitable for larger projects or when precise deburring is required. Electric tools are often used in workshops and production environments where multiple pipes need to be deburred quickly and uniformly.
- Combination Tools: Some external deburring tools combine deburring with other features, such as chamfering, polishing, or surface finishing. These multi-functional tools are ideal for operations that require multiple processes to be performed on the same pipe, helping to save time and reduce the number of tools needed for the job.
How External Deburring Tools Work:
External deburring tools work by using a rotating blade or cutting head to remove the burrs from the outer surface of the pipe. The tool is typically moved along the pipe’s edge, allowing the blade to scrape or cut off the burrs, leaving the surface smooth and rounded. The blade may be a rotary blade or a fixed blade, depending on the tool design. In some cases, the tool is designed to adjust its blade depth or angle to accommodate different pipe sizes or burr sizes.
Manual tools require the operator to physically move the tool around the pipe while applying the appropriate amount of pressure to remove the burrs. For motorized tools (pneumatic or electric), the operator simply guides the tool along the pipe while the motor rotates the blade at a consistent speed, making the process faster and more efficient.
Advantages of External Deburring Tools:
- Improved Safety: Burrs on the edges of pipes can be sharp and pose a risk of cuts or injuries during handling, transport, and installation. By removing burrs with an external deburring tool, the pipe edges are made smoother and safer to work with.
- Enhanced Pipe Fitment: Burrs can interfere with the proper fit of pipes during welding or assembly. Deburring ensures that pipes fit together correctly, helping to create tight, secure connections and reducing the risk of leaks or mechanical failure.
- Increased Productivity: External deburring tools, particularly pneumatic and electric models, can significantly speed up the deburring process, making them ideal for high-volume production environments. With faster burr removal, production timelines are shortened, and more parts can be processed in less time.
- Improved Pipe Aesthetics: Burrs and rough edges can make metal pipes look unfinished, which may be undesirable in applications where appearance matters. Deburring tools ensure that the pipes have a clean, professional appearance by smoothing the edges.
- Longer Tool Life: The use of high-quality external deburring tools with durable cutting blades ensures that they can withstand the rigors of deburring metal pipes, providing a longer tool life and fewer replacements. Proper maintenance, such as blade sharpening or replacement, can further extend the lifespan of the tool.
- Versatility: Many external deburring tools are compatible with various pipe sizes, making them versatile for use in different applications, from plumbing and construction to industrial piping systems.
Common Applications:
- Plumbing: External deburring tools are essential for preparing pipes for installation in plumbing systems. They ensure that the pipes fit together properly and are safe to handle, preventing issues like leaks and injuries.
- HVAC Systems: When installing air conditioning and heating systems, external deburring tools help prepare metal pipes and ducts for proper connection and assembly, ensuring a smooth flow of air and efficient system performance.
- Oil and Gas Industry: In the oil and gas sector, external deburring tools are used on pipes that need to meet stringent quality standards. Burr-free edges ensure that pipes can withstand the pressures and stresses encountered during operation.
- Construction: For various construction applications involving metal piping, deburring tools help prepare pipes for welding and installation, ensuring a precise fit and smooth surface for secure connections.
- Industrial Manufacturing: External deburring tools are used to prepare pipes for further processing, such as coating, welding, or assembly. Removing burrs improves the performance and durability of the finished pipes.
In conclusion, external deburring tools are critical for ensuring the safety, functionality, and quality of metal pipes. By removing burrs and sharp edges, these tools help ensure that pipes fit together properly, are safe to handle, and meet industry standards for performance and appearance. Whether used manually, pneumatically, or electrically, external deburring tools are essential for industries that work with metal pipes, ensuring efficient, high-quality results.
External deburring tools for metal pipes are crucial for ensuring that pipes are free from burrs and sharp edges that could cause issues during handling, installation, or further processing. These tools are designed to smooth out the rough edges left on the outer surface of metal pipes after cutting, machining, or manufacturing. Burrs can interfere with the fit of pipes, cause injury to workers, and affect the quality of the final assembly, which is why deburring is an essential step in the metalworking process.
The tools are equipped with cutting blades, typically rotary or fixed, that are used to scrape or shave off the burrs from the pipe’s outer surface. This process not only ensures that the pipe edges are smooth but also helps round off sharp corners that could otherwise cause safety hazards or damage to other parts. The design of these tools makes them versatile for use on various pipe sizes and materials, such as steel, copper, aluminum, and stainless steel. Whether the pipe is small and thin-walled or large and thick, external deburring tools are capable of removing burrs effectively and uniformly.
The effectiveness of external deburring tools also depends on the type of blade or cutting mechanism used. In some cases, the tool will feature an adjustable blade depth or angle, allowing the user to control how much material is removed based on the size and type of burr. This ensures that the burrs are fully eliminated without over-deburring or damaging the pipe. The adjustable settings also make the tools adaptable for a variety of pipe geometries, including those with curved or angled edges.
Pneumatic and electric external deburring tools are often preferred in industrial settings because they provide more consistent results and greater efficiency compared to manual tools. Pneumatic tools are powered by compressed air, offering a lightweight and high-torque solution for deburring, which is ideal for high-volume work environments. Electric tools, on the other hand, offer precise speed and power control, making them suitable for more delicate or high-precision tasks. The motorized nature of these tools means that operators can deburr pipes quickly and consistently, reducing manual effort and increasing productivity.
For applications where portability is important, many external deburring tools are designed to be lightweight and compact, allowing them to be easily carried between job sites. This is particularly useful in industries like plumbing, HVAC, and construction, where pipes must often be deburred on-site. Even in larger industrial environments, portability can help streamline the process by allowing workers to bring the deburring tool to the pipes instead of having to transport the pipes to a fixed station.
Manual external deburring tools remain a popular choice for smaller tasks or when a more hands-on approach is needed. These tools typically require the operator to manually rotate the tool around the pipe’s edge, applying the necessary pressure to remove burrs. While slower than motorized options, manual deburring tools offer excellent control and precision, making them ideal for intricate jobs or when working with smaller quantities of pipes.
One of the most significant advantages of using external deburring tools is the safety they provide. Burrs and sharp edges on metal pipes pose risks such as cuts, abrasions, or punctures during handling, welding, and assembly. By removing these hazards with a deburring tool, workers are less likely to suffer injuries, which improves overall safety on the job. Moreover, deburring also ensures that pipes fit together more securely, preventing issues like misalignment or leaks that can occur when sharp edges interfere with the fitting process.
Beyond safety, deburring tools also contribute to the aesthetic quality of the finished pipes. Burrs on the edges of pipes can create an unsightly appearance and lead to imperfections in the final product. Removing these burrs improves the pipe’s visual appeal, ensuring a clean and professional finish. This is especially important in industries where the appearance of metal parts plays a role in customer satisfaction or product quality, such as in the automotive or consumer electronics sectors.
The overall quality of the finished pipe is also enhanced by deburring. Burrs can cause wear and tear over time, particularly when pipes are subject to pressure, friction, or vibration during operation. By removing burrs, the pipe’s structural integrity is maintained, reducing the risk of failure or damage. Additionally, burrs can affect the performance of the pipe in certain applications. For example, in the oil and gas industry, burrs on the edges of pipes can cause problems with sealing and leak prevention. Proper deburring ensures that pipes will function as intended in these critical applications.
Using an external deburring tool also helps to ensure that the deburring process is done consistently and uniformly. Manual methods like filing or sanding can be time-consuming and result in inconsistent results, whereas external deburring tools remove burrs quickly and evenly. This consistency is particularly important in mass production or high-precision industries, where uniformity is crucial to product quality and performance.
In summary, external deburring tools are indispensable for ensuring that metal pipes are safe, functional, and high-quality. Whether used manually or powered by air or electricity, these tools effectively remove burrs and sharp edges from metal pipes, improving their fit, appearance, and safety. From small-scale plumbing projects to large-scale industrial applications, external deburring tools are essential in ensuring that pipes meet the necessary standards for quality, performance, and safety.
External deburring tools are indispensable in industries that deal with metal pipes, as they ensure the final product is safe, durable, and functional. Removing burrs and sharp edges is not only a matter of aesthetics but also plays a crucial role in the performance and safety of the pipes. Burrs left on the pipe edges can cause several issues, such as difficulty in joining pipes, poor fitting during welding or assembly, and even failure to meet industry standards for pressure containment. By using an external deburring tool, manufacturers and workers can avoid these problems and improve both the safety and functionality of the pipes they produce.
One additional advantage of using external deburring tools is the time and cost savings in the long term. By ensuring that the pipes are free from imperfections and ready for installation or further processing, deburring helps reduce the need for rework or repairs. Pipes with sharp edges may require additional attention during the assembly process, slowing down production and increasing labor costs. Proper deburring also minimizes the risk of damage during transport or installation, leading to fewer returns and replacements.
For large-scale operations, investing in motorized external deburring tools, such as pneumatic or electric models, can significantly boost efficiency. These tools reduce the labor time required to remove burrs compared to manual tools, allowing workers to focus on other tasks. In high-volume environments where thousands of pipes need to be processed, these motorized tools can handle the workload, delivering consistent, high-quality results with minimal downtime. Moreover, many of these tools are designed for easy maintenance, allowing for long-term reliability and performance.
In some industries, especially those with stringent regulations or safety standards, deburring is not just a quality enhancement but a compliance requirement. For example, the aerospace, automotive, and oil and gas industries often require metal pipes to meet specific tolerances for deburring and finishing. Using external deburring tools ensures that the pipes conform to these standards, preventing costly compliance issues or delays in production. This is particularly important in industries where even the smallest defect can lead to serious consequences, such as in pressure-sensitive systems or critical infrastructure components.
External deburring tools are also versatile enough to be used on various pipe materials, which is important given the range of metals commonly used in pipe manufacturing. For example, steel, copper, and aluminum each present unique challenges when deburring due to differences in hardness, malleability, and composition. High-quality external deburring tools are engineered to handle these materials efficiently, ensuring that burrs are removed without damaging the pipe surface.
Furthermore, deburring tools can be paired with other pipe preparation equipment, such as chamfering tools, to provide a complete solution for finishing metal pipes. Chamfering tools, which bevel the edges of pipes, can help improve the fitment of pipes, particularly when welding or assembling sections of pipe. By combining deburring and chamfering processes, manufacturers can produce pipes that are ready for immediate installation, reducing delays in the production line and enhancing the overall workflow.
Another advantage is the environmental impact. By using high-efficiency deburring tools, the amount of waste material produced during the deburring process can be minimized. Properly finished pipes also lead to fewer failures and repairs down the line, reducing the need for new materials and minimizing the environmental footprint of manufacturing. Some modern deburring tools are designed to minimize the release of metal dust or shavings, further contributing to a cleaner work environment and safer practices.
Moreover, the adaptability of external deburring tools is another key factor in their widespread use. Many tools can be adjusted to accommodate pipes with different diameters, wall thicknesses, or geometries. Some models come with interchangeable heads or attachments, allowing the user to switch between different deburring methods, such as scraping, cutting, or polishing. This flexibility makes the tools suitable for a wide range of pipe sizes and production requirements.
The ease of use is another reason why external deburring tools are so popular in both manual and industrial applications. For workers with minimal experience in metalworking, the straightforward operation of these tools makes them easy to integrate into the workflow without extensive training. While motorized models may require some operator knowledge for optimal performance, the overall design of deburring tools focuses on simplicity and efficiency, allowing them to be used effectively across different levels of skill and expertise.
Finally, external deburring tools help to maintain the integrity of the pipes. Pipes with burrs or rough edges are more prone to corrosion, especially when exposed to harsh environments or chemicals. By ensuring a smooth and even surface, deburring tools help protect the metal from premature wear and degradation. This extends the life of the pipes, reduces maintenance costs, and helps avoid unexpected failures that could result in costly repairs or downtime in industries where pipe failure could have catastrophic consequences.
In conclusion, external deburring tools are an essential part of metal pipe fabrication, offering a variety of benefits, from improving safety and quality to enhancing productivity and ensuring compliance with industry standards. Whether used for small-scale, manual tasks or large-volume, motorized operations, these tools provide the precision, efficiency, and versatility required to meet the demands of modern manufacturing. With the right deburring tool, manufacturers can produce pipes that are safe, durable, and ready for installation, improving both the bottom line and the performance of the final product.
Metal Deburring Tool

A metal deburring tool is an essential tool used to remove burrs, sharp edges, and rough surfaces from metal parts that result from manufacturing processes such as cutting, machining, stamping, or casting. Burrs are unwanted projections or rough spots left on the edge of a metal part, and they can be dangerous, affect the part’s fit, and lead to safety concerns. Deburring tools are used to smooth out these imperfections, ensuring a clean and safe edge on metal parts, improving both their functionality and appearance.
Metal deburring tools come in various types, including manual, electric, pneumatic, and handheld models. The type of tool chosen depends on the size of the metal part, the volume of parts to be deburred, and the specific needs of the application. Some common types of metal deburring tools include:
Manual Deburring Tools
Manual deburring tools are typically hand-held devices that allow the operator to manually scrape or shave off burrs from metal parts. They are often used for smaller parts or for situations where precise control is needed. These tools can come in various designs, such as rotary blades, scraping tools, or hand files.
- Rotary Blade Deburring Tools: These tools use rotating blades to remove burrs as they are guided along the edge of the metal. They are commonly used for straight or slightly curved edges.
- Scraping Deburring Tools: These tools have sharp, fixed blades that are used to manually scrape the burrs off. They are effective for cleaning up rough edges on small parts or precise areas.
Manual tools are favored for their portability and low cost, making them ideal for small-scale projects, maintenance, and repair jobs.
Electric and Pneumatic Deburring Tools
Electric and pneumatic deburring tools are motorized and powered by electricity or compressed air, respectively. These tools are more efficient than manual tools and are ideal for high-volume operations, as they can remove burrs more quickly and consistently. They are commonly used in industrial settings where large quantities of parts need to be deburred.
- Electric Deburring Tools: These tools are powered by electricity and are suitable for various applications. They are available in both handheld and bench-mounted versions. Electric deburring tools can be fitted with different types of blades or brushes and are often used for precision deburring of metal parts.
- Pneumatic Deburring Tools: These tools are powered by compressed air and are commonly used in heavy-duty, industrial environments. They are often preferred for their high torque and ability to maintain continuous operation without overheating. Pneumatic deburring tools are effective for removing burrs from large quantities of metal parts in manufacturing settings.
Both electric and pneumatic tools offer significant speed advantages over manual tools and are well-suited for larger-scale manufacturing environments.
Types of Deburring Blades and Attachments
Deburring tools often use interchangeable blades or attachments to suit different types of burrs or materials. Some of the most common blades or attachments include:
- Rotary Blades: These blades are used in rotary deburring tools and are ideal for removing burrs from edges and holes.
- Brushes: Brushes, often made from nylon or steel, are used for polishing and deburring sensitive or delicate parts. They are commonly used when a smooth finish is required without removing too much material.
- Scrapers: Scrapers are used for manually scraping off burrs from the surface of a metal part, especially in situations where precision is required.
The choice of blade or attachment depends on the material of the metal, the size of the burrs, and the desired finish.
Benefits of Using a Metal Deburring Tool
- Improved Safety: Burrs and sharp edges on metal parts can pose significant risks to workers, leading to cuts, scratches, and other injuries during handling and installation. Using a deburring tool eliminates these hazards, ensuring a safer working environment.
- Better Fit and Function: Burrs can interfere with the proper fit of metal parts during assembly or welding. Removing burrs ensures that parts fit together more accurately, which is crucial for maintaining the quality and performance of the final product.
- Enhanced Appearance: Burrs can make metal parts look unfinished or rough. Deburring tools smooth out the edges, resulting in a cleaner and more professional-looking finish. This is especially important for parts that are visible in the final product.
- Increased Durability: Burrs left on the edges of metal parts can cause premature wear or corrosion, especially when exposed to harsh conditions or frequent use. Deburring ensures that the parts have a smooth surface that is less prone to damage and corrosion, extending their lifespan.
- Improved Performance: In some applications, burrs can affect the performance of metal parts. For example, in fluid systems, burrs can disrupt the flow of liquids or gases, leading to inefficiency or damage. By removing burrs, deburring tools help maintain the functionality of the parts.
- Cost-Effective: While purchasing a deburring tool represents an initial investment, the long-term benefits often outweigh the cost. By preventing damage, reducing the need for repairs, and increasing the speed of production, deburring tools can improve the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process.
How to Choose the Right Metal Deburring Tool
When selecting a metal deburring tool, several factors should be considered:
- Type of Metal: Different metals require different deburring techniques. For example, softer metals like aluminum may need gentler tools, while harder metals like stainless steel require more robust deburring tools. Some tools are designed specifically for certain materials, so it’s important to choose one that is compatible with the metal you’re working with.
- Size and Shape of the Part: The size and shape of the part being deburred will affect the type of tool you need. Smaller parts or those with intricate shapes may benefit from manual or handheld tools, while larger parts or high-volume production will benefit from electric or pneumatic tools.
- Burr Size and Type: The size and type of burr will also influence the choice of deburring tool. Some burrs are small and fine, while others are larger and more jagged. A tool with adjustable speed or various attachments may be necessary to handle different burr sizes and types.
- Volume of Parts: For large-scale manufacturing or high-volume production, pneumatic or electric deburring tools are often the best choice due to their speed and consistency. For smaller, more detailed jobs, manual tools may be sufficient.
- Budget and Maintenance: Manual tools are more affordable but require more labor and time, whereas electric and pneumatic tools are more expensive upfront but can save money in the long run due to their efficiency. It’s also essential to consider maintenance costs, as some tools require regular maintenance or replacement parts.
Popular Metal Deburring Tools
- Deburring Scissors: These tools are designed for quickly trimming and deburring thin metal parts. They have special blades that allow them to cut through metal and remove burrs effectively.
- Rotary Deburring Tools: These are often powered tools with rotating blades that efficiently deburr edges and holes on metal parts. These tools are versatile and can be used for various metal types and burr sizes.
- Manual Hand Deburring Tools: These are small, portable tools that are useful for light deburring tasks. They can come with different blades, such as scrapers, files, or rotary tools, and are ideal for manual deburring of small parts.
- Pneumatic or Electric Burr Removers: These tools are powered by compressed air or electricity, providing high torque and fast rotation speeds. They are used in industrial environments where large volumes of parts need to be deburred quickly and efficiently.
- Wire Brushes: Wire brushes can be used for cleaning and deburring metal surfaces, particularly for polishing the edges and providing a smoother finish without removing too much material.
In conclusion, a metal deburring tool is an indispensable tool for improving the safety, performance, and appearance of metal parts. Whether manual or motorized, deburring tools are available in various designs to suit different needs and applications. By selecting the right tool for the job, manufacturers can ensure high-quality, burr-free parts that are safer, more functional, and more aesthetically pleasing.
A metal deburring tool is designed to remove burrs, sharp edges, and rough surfaces left on metal parts after manufacturing processes such as cutting, machining, or casting. Burrs can create several problems, such as impairing the fit of parts, causing safety hazards, and affecting the overall quality of the finished product. Deburring tools are essential for ensuring the metal edges are smooth, safe, and ready for further processing or installation. These tools come in various forms, including manual, electric, and pneumatic versions, each suited to different types of tasks and applications.
Manual deburring tools are hand-held and often consist of rotary blades, scrapers, or hand files. These tools are commonly used for small jobs or in situations where precise control is needed. They are portable and inexpensive, making them suitable for low-volume tasks or repairs. On the other hand, motorized deburring tools, which can be powered by electricity or compressed air, are more efficient and better suited for high-volume or industrial applications. These tools allow for faster and more consistent deburring, reducing labor time and increasing productivity.
Electric deburring tools are powered by electricity and typically feature a rotating motor that drives a blade or abrasive head. These tools can come in handheld or bench-mounted designs and are used for precision deburring in environments where fine edges are required. Pneumatic deburring tools, which are powered by compressed air, are favored for their ability to work continuously without overheating, making them ideal for large-scale manufacturing. These tools offer high torque and speed, making them effective for deburring larger or thicker metal parts.
Deburring tools may use various blades, attachments, or abrasives depending on the metal and the type of burrs being removed. Rotary blades are used for edges, while scrapers are effective for finer burrs. Brushes, such as those made from steel or nylon, are often used for polishing or removing delicate burrs. The choice of attachment or blade depends on the material of the metal being deburred, the size of the burr, and the desired finish.
One of the key benefits of using a metal deburring tool is improved safety. Burrs and sharp edges on metal parts can pose serious injury risks to workers during handling or installation. By removing these burrs, deburring tools eliminate these hazards, reducing the likelihood of cuts or abrasions. Additionally, deburring ensures that metal parts fit together more precisely, improving the quality of welds, joints, and assemblies, and contributing to the durability and performance of the final product.
Using deburring tools also contributes to better aesthetic results. Burrs and rough edges can make metal parts appear unfinished, while deburring tools provide a smooth and professional-looking finish. This is particularly important in industries like automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods, where the appearance of metal parts can be crucial to customer satisfaction. Furthermore, deburring helps prevent future issues such as corrosion or wear. Burrs and rough edges can act as stress concentrators, leading to premature failure or wear. By smoothing these edges, deburring tools help enhance the longevity and reliability of the parts.
Deburring tools can also improve the performance of metal parts. In applications where precise fits are necessary, burrs can interfere with the proper assembly of parts, leading to misalignments, leaks, or other functional issues. By ensuring smooth, uniform edges, deburring tools help maintain the integrity of assemblies and improve their overall functionality. For example, in piping systems, burrs can disrupt the flow of fluids, affecting the efficiency of the system. Deburring ensures that the parts fit together tightly, reducing the likelihood of leaks and improving the system’s performance.
When selecting a deburring tool, it’s essential to consider factors such as the type of metal, the size of the parts, and the level of burr removal required. Softer metals, such as aluminum, may require less aggressive tools, while harder metals, like stainless steel, may need more robust tools with higher cutting power. Similarly, small or intricate parts may require manual tools for precise work, while larger or high-volume operations benefit from electric or pneumatic tools that can handle greater workloads efficiently. The size and type of the burr, whether fine or large, will also influence the type of blade or attachment used with the tool.
Another key consideration when choosing a deburring tool is the desired finish. Some applications may require a high degree of precision and smoothness, while others may simply need to remove larger burrs. For example, tools that use abrasive discs or polishing brushes can be used to create a smooth, satin finish, while more aggressive cutting blades may be used to remove larger burrs quickly.
Deburring tools also contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing waste and improving the lifespan of parts. By removing burrs at an early stage in the manufacturing process, these tools help avoid the need for rework or repairs, leading to less material waste and fewer defective products. Additionally, deburring reduces the chances of pipe or part failures, which can lead to costly replacements or additional repairs in industries such as plumbing, HVAC, and automotive manufacturing. Proper deburring also ensures that parts are ready for assembly or installation without further modifications, improving overall production efficiency.
In industrial and high-volume settings, pneumatic or electric deburring tools offer several advantages over manual tools. They are faster, allowing for more parts to be processed in less time, and provide consistent results with minimal human error. Pneumatic tools, in particular, are well-suited for environments where tools must operate for extended periods, as they are less likely to overheat compared to electric models. For precision tasks, some deburring tools come with adjustable speeds or settings, giving the operator full control over how much material is removed.
Regardless of the type of deburring tool used, regular maintenance is necessary to ensure optimal performance. Over time, the blades or abrasive heads can become worn or dull, affecting the quality of the deburring process. Replacing worn parts and cleaning the tool regularly helps maintain its effectiveness and prolongs its lifespan.
In conclusion, a metal deburring tool is a critical piece of equipment for any metalworking or manufacturing operation. Whether used for small repairs or large-scale industrial processes, deburring tools ensure that metal parts are safe, functional, and aesthetically pleasing. By selecting the right tool for the job and maintaining it properly, manufacturers can improve safety, enhance part quality, reduce costs, and increase production efficiency.
An industrial deburring machine is a specialized piece of equipment designed to automate the process of removing burrs, sharp edges, and surface imperfections from metal parts. Burrs are the unwanted raised edges or material left on a metal part after machining processes such as cutting, grinding, or stamping. These burrs can create safety hazards, interfere with part assembly, and negatively impact the performance and appearance of the final product. An industrial deburring machine is typically used in high-volume manufacturing settings to quickly and efficiently remove these burrs from large quantities of metal parts.
Industrial deburring machines are available in various designs and configurations to accommodate different types of parts and manufacturing processes. The choice of deburring machine depends on factors such as the type of material being worked on, the complexity of the part, the volume of parts being processed, and the required level of burr removal.
One common type of industrial deburring machine is the rotary brush deburring machine. This machine uses rotating brushes, usually made of nylon or steel, to remove burrs from the surface of metal parts. The parts are fed through the machine, and the brushes are carefully positioned to contact the edges and surfaces of the parts, scrubbing away the burrs. Rotary brush deburring machines are effective for parts with intricate shapes, such as stamped or machined components, and can be used for both external and internal deburring.
Another popular type is the vibratory deburring machine, which uses vibrational motion to agitate the parts along with abrasive media (such as ceramic or plastic chips). As the parts tumble and vibrate inside the machine, the abrasive media helps remove the burrs from the edges and surfaces. This type of deburring machine is particularly effective for small, delicate parts and is often used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. The vibratory deburring process is ideal for parts that require a gentle yet consistent deburring action, and it is often used when a smooth, polished finish is desired.
For larger or more rugged metal parts, belt grinding deburring machines are commonly used. These machines use abrasive belts to grind down burrs and smooth out rough edges. Belt grinding machines are ideal for heavier-duty applications, where parts are subjected to more aggressive machining processes, and more significant burrs need to be removed. These machines can be adjusted to control the speed and pressure applied to the parts, allowing for precise control over the deburring process.
Disc deburring machines use rotating discs, often equipped with abrasive pads, to remove burrs from parts. These machines are typically used for flat or large parts and are highly effective for uniform deburring across a large surface area. They can also be used in combination with other finishing processes, such as polishing or grinding, to achieve a high-quality surface finish.
An abrasive flow deburring machine is another type of equipment used in industries where precision is paramount. This machine uses an abrasive slurry that flows over the metal part, removing burrs and smoothening rough edges. Abrasive flow deburring is especially effective for parts with tight tolerances or hard-to-reach areas, such as holes, internal passages, or intricate designs.
Wet deburring machines are used when a cooling or lubricating effect is required during the deburring process. These machines use water or a specialized coolant solution in combination with abrasives to reduce friction and heat generation during the deburring process. Wet deburring is especially useful for heat-sensitive materials or when excessive heat buildup could lead to warping or other issues.
Industrial deburring machines offer several advantages over manual deburring methods, particularly in high-volume or high-precision manufacturing environments. One of the most significant benefits is increased efficiency. Deburring machines can process large numbers of parts in a fraction of the time it would take to manually deburr each piece, significantly improving throughput and reducing labor costs.
Another advantage is the consistency that these machines provide. Unlike manual deburring, which can vary depending on the operator’s skill and attention to detail, industrial deburring machines deliver uniform results with consistent burr removal across all parts. This consistency is particularly important in industries where high standards of quality and performance are required, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing.
Additionally, industrial deburring machines help ensure safety. Burrs and sharp edges on metal parts can be hazardous to workers during handling and assembly. By automating the deburring process, these machines reduce the likelihood of injuries caused by handling sharp-edged parts and create a safer working environment.
Industrial deburring machines also contribute to improved part quality. By removing burrs and sharp edges, these machines prevent issues such as poor fitment, misalignment, or functional problems that could arise during assembly or use. In some cases, deburring can improve the performance of the parts themselves, particularly in fluid or gas systems where burrs can disrupt flow and create leaks or inefficiencies.
The use of industrial deburring machines also provides cost savings over time. While there is an initial investment required for purchasing and setting up the equipment, the increased productivity, reduced labor costs, and improved part quality result in significant long-term savings. Moreover, deburring machines help reduce the need for rework or repairs, as burrs are eliminated at the early stages of production.
When selecting an industrial deburring machine, several factors must be taken into account, including the type of material being processed, the size and complexity of the parts, the volume of parts to be deburred, and the desired level of finish. Additionally, some machines may be equipped with features such as adjustable speed settings, programmable controls, or filtration systems to improve the performance and longevity of the machine.
In conclusion, an industrial deburring machine is an essential tool in modern manufacturing that helps automate and streamline the burr removal process. These machines offer significant advantages in terms of efficiency, consistency, safety, and part quality. With a wide range of deburring options available, manufacturers can select the appropriate machine for their specific needs, whether for small parts or large-scale production. As industries continue to demand higher levels of precision and quality, industrial deburring machines will remain a critical component in the production of metal parts and assemblies.
An industrial deburring machine is designed to automate the process of removing burrs, sharp edges, and surface imperfections from metal parts after manufacturing processes like cutting, stamping, and machining. Burrs are unwanted, rough edges that can form when metal parts are cut or shaped, creating potential safety hazards and negatively impacting the fit, appearance, and performance of the parts. These burrs need to be removed for parts to meet quality standards and ensure smooth, functional assemblies. Industrial deburring machines are designed to address these challenges in high-volume manufacturing settings where precision and efficiency are critical.
The key benefit of an industrial deburring machine is its ability to process large quantities of parts quickly and consistently. These machines can handle the repetitive task of deburring metal parts, reducing the need for manual labor and cutting down on production time. For businesses that produce large volumes of parts, this level of automation significantly improves efficiency and throughput. Moreover, industrial deburring machines provide greater consistency in results compared to manual methods, reducing the variability that can occur with human operators.
Industrial deburring machines come in various forms, each tailored to specific types of parts or deburring processes. For example, rotary brush deburring machines use rotating brushes to remove burrs from the edges of metal parts. These machines are particularly effective for delicate parts or components with intricate shapes. The brushes, which may be made of materials like steel or nylon, scrub away burrs from both flat and curved surfaces. As the parts move through the machine, they come into contact with the brushes, which efficiently remove the burrs without damaging the underlying material. This process is particularly useful for parts that require more gentle deburring, such as stamped metal components or machined parts with thin edges.
For smaller parts or those requiring a more delicate touch, vibratory deburring machines are commonly used. These machines use vibrational energy to agitate metal parts along with abrasive media, such as ceramic or plastic chips. The vibration causes the parts to tumble inside the machine, with the abrasive media rubbing against the burrs and gently removing them. Vibratory deburring is effective for parts that may be too small or delicate for more aggressive methods. This process also allows for a smooth, uniform finish, making it ideal for parts that require a high level of surface quality. These machines are often used in industries like automotive, electronics, and aerospace, where small components with tight tolerances are common.
Belt grinding deburring machines are another popular choice for industrial deburring. These machines use abrasive belts to grind down burrs and smooth rough edges. Belt grinding machines are ideal for larger or more rugged parts that require more aggressive burr removal. The abrasive belts are adjustable to provide varying levels of pressure and speed, which allows operators to control the intensity of the deburring process. This type of machine is particularly useful for heavy-duty applications, such as removing burrs from thick metal parts or large sheets of material.
In addition to rotary, vibratory, and belt grinding machines, disc deburring machines are also widely used in industrial applications. These machines feature rotating discs equipped with abrasive pads that remove burrs from the edges of metal parts. They are especially effective for deburring flat parts and large surfaces, providing a consistent, uniform finish. Disc deburring machines are often used for applications that require a high-quality finish over a broad surface area, such as deburring the edges of metal plates or large stamped components.
Abrasive flow deburring machines are another specialized option for removing burrs, particularly in parts with hard-to-reach areas, such as internal passages or intricate designs. These machines use an abrasive slurry that flows over the part, gently removing burrs from difficult-to-reach surfaces. The abrasive flow process is especially effective for parts that require high precision and tight tolerances, such as those found in the medical device, aerospace, and automotive industries.
Some industrial deburring machines are designed for wet deburring, where water or a special coolant solution is used in conjunction with abrasives to reduce friction and heat buildup during the deburring process. Wet deburring is particularly useful for heat-sensitive materials, such as aluminum, that may warp or deform if excessive heat is generated. The use of a coolant also helps to extend the life of the abrasive tools and reduces the potential for dust and debris, which can create a cleaner, safer working environment.
The automation of deburring with industrial machines offers several advantages over manual deburring methods. The most significant benefit is the efficiency it brings to the manufacturing process. Automated deburring machines can work continuously without the need for rest, unlike manual labor, which can slow down due to fatigue or inconsistencies. This allows manufacturers to process large batches of parts with minimal downtime, maximizing production capacity. Additionally, deburring machines are more consistent than manual methods, ensuring that each part is deburred to the same high standard without the variability that can occur when an operator manually removes burrs. This consistency is critical for industries where high-quality standards must be met, such as in the production of medical devices, aerospace components, or high-performance automotive parts.
Another key advantage of industrial deburring machines is the improved safety they provide. Burrs and sharp edges on metal parts pose significant risks to workers who handle the parts during assembly or further processing. Automated deburring reduces the need for manual handling of sharp-edged parts and eliminates the need for operators to use handheld tools for deburring, reducing the likelihood of cuts or injuries. Moreover, by ensuring a smooth edge, deburring machines create a safer working environment overall.
Industrial deburring machines also help to improve part quality by ensuring that burrs and rough edges are consistently removed. Removing burrs not only improves the appearance of the parts but also enhances their functionality. Burrs can interfere with part assembly, cause misalignment, or lead to functional issues, particularly in fluid systems where burrs can disrupt the flow of liquids or gases. By deburring metal parts before they are assembled or used, these machines help maintain the integrity and performance of the final product.
In addition, the use of industrial deburring machines can lead to cost savings for manufacturers. While the initial investment in automated deburring equipment may be significant, the long-term savings from increased productivity, reduced labor costs, and decreased scrap or rework can outweigh the costs. Automated deburring also reduces the need for manual labor and the possibility of human error, which can lead to costly mistakes and delays in production.
Selecting the right industrial deburring machine depends on several factors, such as the type of material being processed, the size and complexity of the parts, and the desired level of burr removal. Manufacturers need to consider the characteristics of the metal parts they are working with, including whether they are soft or hard metals, as well as the types of burrs present (e.g., fine burrs, heavy burrs, or those in hard-to-reach areas). Different machines may be better suited for different materials and part shapes, so it’s important to choose the most appropriate equipment for each application. Additionally, considerations such as the volume of parts to be deburred, the need for precision, and the required surface finish must be taken into account when making a selection.
In conclusion, industrial deburring machines play a vital role in modern manufacturing, enabling companies to efficiently and consistently remove burrs and sharp edges from metal parts. These machines provide numerous benefits, including improved safety, enhanced part quality, increased efficiency, and long-term cost savings. By automating the deburring process, manufacturers can achieve higher productivity and meet the stringent quality standards required in industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing.
Industrial deburring machines are essential tools in modern manufacturing processes, especially in industries that work with metal parts. These machines are designed to automate the removal of burrs, sharp edges, and other surface imperfections that can form during the machining, cutting, or shaping of metal components. Burrs are small, raised areas of metal that are often left on parts after they have been cut, stamped, or machined. These burrs can interfere with the proper fit and function of metal parts, compromise safety, and negatively impact the overall quality of the finished product.
One of the primary benefits of industrial deburring machines is their ability to handle high volumes of parts with consistent, reliable results. When manufacturers produce large quantities of metal parts, manually deburring each piece would be time-consuming, inefficient, and prone to human error. Automated deburring machines eliminate the need for manual labor, allowing manufacturers to process more parts in less time while maintaining a high level of quality.
In addition to speed and consistency, industrial deburring machines offer improved safety for workers. Sharp edges and burrs on metal parts can pose significant risks during handling, assembly, or further processing. By removing these hazardous features, deburring machines reduce the likelihood of accidents, such as cuts or punctures, and create a safer work environment. The machines can also be programmed to handle parts without the need for direct human interaction, minimizing exposure to sharp-edged materials.
Industrial deburring machines also contribute to enhanced part quality. Burrs and sharp edges can affect the performance and appearance of metal components, especially in precision industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics. Burrs can cause misalignments, leaks, or other functional issues when parts are assembled, and they can also lead to poor surface finishes. Deburring machines remove these imperfections, ensuring that parts fit together properly, function correctly, and meet the required specifications.
The versatility of industrial deburring machines is another advantage. Different types of deburring machines are available to handle various materials, part shapes, and burr types. For example, rotary brush deburring machines are effective for deburring parts with delicate features or intricate shapes, while belt grinding machines are better suited for more aggressive burr removal on thicker, harder materials. Vibratory deburring machines, on the other hand, are ideal for smaller parts or delicate components that require a more gentle deburring process.
Another key advantage is the ability to improve surface finishes. Some deburring machines can provide a polished or smooth finish in addition to burr removal. This is important in industries where appearance and surface quality are critical, such as in the production of consumer goods or high-end machinery. For example, a vibratory deburring machine can provide a satin finish on small metal parts, making them ready for assembly or use without the need for additional polishing steps.
In addition to improving the quality and safety of metal parts, industrial deburring machines also offer cost savings in the long run. While the initial investment in automated equipment can be high, the reduced labor costs, increased productivity, and improved part quality quickly offset this expense. Manufacturers can also reduce the costs associated with rework and scrap by ensuring that burrs are removed early in the production process. This proactive approach helps prevent defects and ensures that the finished parts are ready for use or assembly without the need for further modifications.
Choosing the right industrial deburring machine for a specific application depends on several factors, including the type of metal, the size and complexity of the parts, the volume of production, and the required finish. Manufacturers must consider these variables to ensure that the machine is well-suited to the tasks at hand. Some machines, for example, may be more effective for softer materials like aluminum, while others are better for harder metals like stainless steel. Similarly, some deburring machines are better suited for larger parts, while others are more effective for smaller, more intricate components.
In some cases, the type of burr removal required also influences the choice of equipment. Some deburring machines are designed to remove heavy burrs quickly, while others are optimized for finer burrs or those in hard-to-reach areas. For instance, abrasive flow deburring machines use a slurry to flow over the part, gently removing burrs from internal passages or small, delicate areas that might be difficult to reach with other tools.
Overall, industrial deburring machines play a crucial role in modern manufacturing, offering a range of benefits, including faster production times, improved safety, enhanced part quality, and long-term cost savings. By automating the deburring process, these machines allow manufacturers to produce high-quality, burr-free metal parts in a more efficient and consistent manner. As industries continue to demand higher standards of precision and quality, the role of industrial deburring machines in the manufacturing process will continue to grow.
Sheet Metal Edge Rounding

Sheet metal edge rounding is a process used to smooth and round the sharp edges of metal sheets after they have been cut, stamped, or formed. This process is particularly important in industries where safety, part functionality, and quality are paramount, such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and metal fabrication. Sharp edges on metal parts can be hazardous during handling, cause injuries, and impact the fit and finish of components during assembly. Edge rounding helps eliminate these issues by creating smooth, rounded edges that are safer to handle and more suitable for further processing.
There are several methods used to round the edges of sheet metal, each chosen based on the type of material, the desired radius, and the level of automation required. Below are some of the most common techniques:
- Mechanical Edge Rounding: This involves using various mechanical tools or machines that physically round the edges of sheet metal. Common tools include edge rounding machines, deburring tools, and specialized machines with rotary brushes or grinding heads. Mechanical edge rounding is typically used for parts that have been cut with shears or lasers, which often leave sharp edges. The machines apply abrasive action to smooth the sharp corners and edges, providing a consistent and uniform radius across all parts. Some machines are designed for both deburring and edge rounding, offering versatility for different metalworking needs.
- Rollers or Rotary Tools: Some machines use rollers or rotary tools with abrasive materials to round the edges of sheet metal. The metal sheet is fed through the rollers, which apply pressure to the edges while simultaneously polishing them. This technique is particularly effective for parts with a large surface area, such as panels or metal sheets used in construction. It helps create a uniform edge radius and is suitable for high-volume production.
- Flap Wheels: Flap wheels, which consist of overlapping abrasives attached to a wheel or drum, are often used for edge rounding. When the flap wheel is applied to the sharp edges of sheet metal, the abrasives remove burrs and smooth out rough edges, rounding the corners. This method is useful for creating a smooth, polished finish while rounding the edges of various sheet metal thicknesses.
- CNC Machines: For highly precise edge rounding, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines can be programmed to precisely round the edges of metal sheets. These machines use rotating tools, such as milling heads or grinders, to remove material from the edges. CNC edge rounding allows for high levels of accuracy and is typically used for parts that require tight tolerances or complex geometries. It is particularly useful in industries like aerospace or electronics, where precision is essential.
- Laser or Plasma Cutting with Edge Rounding: Laser cutting or plasma cutting can be paired with edge rounding techniques to provide a smooth, rounded edge directly after the part is cut. Some cutting systems are equipped with automated edge rounding features, allowing the laser or plasma cutter to leave smooth, rounded edges without the need for additional processing. This technique is typically used for thinner sheets of metal or when a high degree of automation is required.
- Abrasive Blasting: Abrasive blasting, also known as sandblasting, can be used to smooth and round the edges of sheet metal. Fine abrasive particles are propelled at high velocity toward the metal edges, removing burrs and smoothing the surface. While this technique is effective for removing surface imperfections and rounding edges, it is typically used for parts that require additional surface finishing, such as cleaning or polishing.
- Manual Edge Rounding Tools: In some smaller-scale operations, or for more intricate parts, manual edge rounding tools can be used. These tools are hand-held and allow operators to manually round the edges of sheet metal. They typically consist of abrasive wheels, sanding pads, or hand files. Manual tools are best for small batches or custom parts but are not as efficient or consistent as automated methods.
Edge rounding serves several important functions. The most obvious is safety: sharp edges can lead to cuts or injuries, particularly during the handling of parts, assembly, or installation. By rounding the edges, manufacturers reduce the risk of worker accidents and create a safer working environment. Additionally, rounded edges contribute to better part fit and appearance, which are crucial for industries where part assembly and aesthetics are important.
In automotive applications, for example, sheet metal parts with rounded edges are easier to handle and fit more effectively into assemblies, improving the overall quality of the vehicle. Similarly, in the aerospace industry, rounded edges ensure that parts function optimally, particularly in areas where aerodynamics and material integrity are critical. Rounding edges also improves the strength and durability of parts, as sharp corners can be stress concentrators, leading to the potential for cracking or failure under pressure or fatigue.
Edge rounding also enhances the paintability of metal parts. Sharp edges can cause coatings like paint or powder coating to peel or wear away more quickly. By rounding the edges, manufacturers create a smoother surface that holds paint or other finishes better, contributing to the longevity and appearance of the part.
While edge rounding is beneficial, it does add an additional step to the manufacturing process, and in high-volume production environments, it is important to choose an efficient and cost-effective method. Automated machines like CNC edge rounding machines or rotary deburring tools can help streamline this process by handling large quantities of parts with minimal manual labor, improving consistency and reducing production time.
In conclusion, sheet metal edge rounding is a crucial process in metal fabrication that improves the safety, quality, and functionality of metal parts. Whether through mechanical, CNC, or abrasive techniques, rounding the edges of sheet metal parts reduces the risks associated with sharp edges and enhances the performance of the parts in their final applications. By choosing the appropriate edge rounding method based on the material, volume, and precision required, manufacturers can achieve high-quality results efficiently, ensuring that their products meet the necessary standards for performance, safety, and aesthetics.
Sheet metal edge rounding is a critical step in many manufacturing processes that helps to smooth sharp edges left after cutting, stamping, or forming. The removal of these sharp edges is necessary for both safety and functionality, as sharp edges can cause injuries during handling and affect the performance and appearance of the final product. By rounding the edges, manufacturers create a safer environment for workers and improve the overall quality of the metal components.
Edge rounding is particularly important in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and metal fabrication, where the sharpness of the edges could interfere with the proper fit and function of the parts. In addition, sharp edges can cause parts to wear or corrode more quickly, leading to reduced product lifespan. Rounding the edges reduces wear and tear, improving the part’s durability and resistance to stress or fatigue.
There are various methods used for edge rounding depending on the size, complexity, and material of the metal parts. One of the most common methods is mechanical edge rounding, where specialized machines use abrasive tools to round off the sharp edges. These machines work by applying an abrasive action to the metal’s edges, effectively smoothing out the sharp corners and creating a uniform radius. Machines can be equipped with rotary brushes, grinding heads, or sanders that handle different levels of burrs and sharpness. The type of abrasive used in the process, such as grinding wheels, sanding belts, or polishing pads, depends on the desired finish and material being processed.
Another method of edge rounding is through the use of rollers or rotary tools. These machines apply pressure to the edges of the sheet metal, simultaneously polishing and rounding the corners. This is often done in high-volume production environments where a smooth and uniform edge radius is necessary. The rollers can be adjusted to different pressures and speeds to cater to various material thicknesses and burr sizes. This method is ideal for larger parts or sheets that require mass production.
Flap wheels are also commonly used for edge rounding. These wheels consist of layered abrasives attached to a rotating wheel or drum, which gently smooths and rounds the sharp edges of sheet metal. Flap wheels are effective for both light deburring and edge rounding, providing a uniform, smooth finish. The abrasive materials used in flap wheels vary, but they are generally softer than traditional grinding wheels, making them ideal for more delicate tasks where precision is important.
CNC machines are another effective solution for precise edge rounding. These machines are capable of performing highly accurate, automated edge rounding by using rotating tools like milling heads or grinders. CNC machines are particularly useful when working with parts that require tight tolerances or complex shapes, such as aerospace components or high-precision electronic parts. The CNC machine can be programmed to round the edges to a specific radius, ensuring consistency and minimizing human error. This is particularly valuable for industries where precision and repeatability are critical.
Laser cutting systems can also be adapted for edge rounding, often in combination with deburring or cutting processes. Laser or plasma cutting machines can be equipped with automated features that round off the edges immediately after the part is cut. This method is effective for thinner sheets of metal and is often employed in industries where speed and automation are essential. Some laser systems have the capability to cut and round edges simultaneously, allowing manufacturers to produce parts with clean, smooth edges in a single operation.
Abrasive blasting, or sandblasting, is another technique that can be used for edge rounding, especially when parts require additional surface finishing. In this process, abrasive particles are propelled at high speed against the metal’s edges, effectively smoothing and rounding sharp corners. While abrasive blasting is often used for cleaning or polishing metal surfaces, it can also be used to round edges, particularly when dealing with parts that require a more textured or rustic finish.
Manual edge rounding tools, such as hand-held rotary tools or files, are still in use for smaller-scale or more customized work. These tools are ideal for low-volume production, custom parts, or parts with unique geometries. While these tools are less efficient than automated machines, they allow operators to carefully round edges on smaller batches or in tight spaces where larger machines may not be suitable.
The benefits of sheet metal edge rounding extend beyond safety. Rounded edges enhance the aesthetic appearance of metal parts by eliminating rough, jagged edges that could detract from the overall quality. Additionally, parts with rounded edges are easier to assemble and fit together, as sharp edges can cause misalignments during assembly or damage other components. Rounded edges also improve the ability of parts to undergo additional processes, such as welding or coating, without issues like poor adhesion or uneven seams.
In industries where aesthetics and performance are important, such as automotive or electronics, edge rounding is an essential step. For example, in automotive manufacturing, sheet metal parts like car body panels or frames require smooth, rounded edges to ensure proper assembly, minimize wear and tear, and contribute to the vehicle’s overall safety. Similarly, in electronics, edge rounding of metal parts ensures that components fit together more easily, reducing the risk of damage during assembly and improving the overall functionality of the product.
In summary, sheet metal edge rounding is a vital step in the manufacturing process that serves multiple purposes: improving safety by eliminating sharp edges, enhancing part quality and durability, and ensuring proper fit and functionality during assembly. Whether using mechanical, CNC, laser, or abrasive techniques, manufacturers have a variety of methods at their disposal to achieve smooth, rounded edges that meet the required specifications. The choice of method depends on factors such as part size, material type, production volume, and precision requirements, but in all cases, the goal is to create high-quality, burr-free, and safely handled components.
A metal edge rounding machine is a specialized tool designed to round off the sharp edges of metal parts after they have been cut, stamped, or formed. This process is essential for improving safety, part fit, and surface finish, as sharp edges can cause injuries during handling and interfere with the functionality or aesthetics of metal components. Metal edge rounding machines are widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and general manufacturing, where sharp edges are a common byproduct of cutting or machining metal parts.
The machine works by using various mechanical processes such as grinding, polishing, or abrasive action to smooth and round the edges of the metal. These machines can process different types of metals, including steel, aluminum, stainless steel, and other alloys, depending on the material type, thickness, and hardness.
Types of Metal Edge Rounding Machines:
- Rotary Brush Machines: Rotary brush machines use abrasive brushes or wheels that rotate around the edges of metal parts to smooth out sharp corners and create a rounded profile. These machines are particularly effective for parts that have been laser cut, stamped, or sheared. The brushes can be adjusted to apply different levels of pressure and abrasiveness, allowing for varying degrees of edge rounding. Rotary brush machines are often used for lightweight and medium-duty metal parts, providing a quick and efficient way to round edges.
- Belt Grinding Machines: Belt grinding machines use abrasive belts that are powered by motors to grind and round the edges of metal parts. These machines typically feature a belt that moves continuously over the metal part, smoothing the edges and rounding off sharp corners. Belt grinders are suitable for thicker metals and are often used in high-volume production environments. The machine’s speed, belt type, and grit size can be adjusted to achieve the desired edge radius and surface finish.
- CNC Edge Rounding Machines: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) edge rounding machines are highly precise tools used for edge rounding of metal parts that require tight tolerances and complex geometries. These machines use rotating tools, such as milling heads or grinding wheels, to remove material from the edges of metal parts. CNC machines can be programmed to round edges to specific radii, making them ideal for industries where precision is essential, such as aerospace or medical device manufacturing. They can handle both small and large batches, providing consistent and accurate results across all parts.
- Rotary Deburring and Edge Rounding Machines: Some machines combine deburring and edge rounding capabilities in one unit. These systems use rotating brushes or abrasive tools to remove burrs and round sharp edges in a single step. Rotary deburring and edge rounding machines are particularly useful when parts have rough edges after cutting and require both burr removal and edge smoothing. These machines offer high efficiency and versatility, making them ideal for mass production.
- Vibratory Deburring Machines: Vibratory deburring machines use a vibrating chamber filled with abrasive media to round the edges of metal parts. As the parts vibrate within the chamber, the abrasive media wears away the sharp edges, creating a smooth, rounded profile. While vibratory deburring machines are typically used for smaller or delicate parts, they can also be used for edge rounding. These machines are ideal for achieving a uniform finish on large quantities of small or intricate parts.
Key Features of Metal Edge Rounding Machines:
- Adjustable Settings: Many edge rounding machines offer adjustable settings that allow operators to control the pressure, speed, and abrasiveness of the tools used. This flexibility ensures that the machine can handle different types of metal and varying thicknesses, as well as produce different edge radii to meet specific requirements.
- Automation: In high-volume production environments, automated metal edge rounding machines are beneficial. These machines can handle a large number of parts without the need for manual intervention, improving productivity and consistency. Automated systems can be integrated with other stages of production, such as cutting, stamping, or forming, to streamline the manufacturing process.
- Safety Features: Metal edge rounding machines often include safety features to protect operators from injury during operation. These can include enclosures, automatic shut-off systems, and safety guards that prevent accidental contact with moving parts.
- Customization: Some edge rounding machines are customizable to handle different part shapes and sizes. This is particularly important in industries like aerospace, where parts may have complex geometries. Customizable machines can be configured with different abrasive tools or attachments to handle various edge profiles and materials.
Applications of Metal Edge Rounding Machines:
- Automotive Manufacturing: Rounding the edges of metal parts used in vehicle bodies, chassis, or engine components is crucial for improving assembly processes and enhancing safety. Rounded edges also contribute to the overall finish of the vehicle, improving aesthetics and reducing the risk of corrosion.
- Aerospace Industry: In aerospace manufacturing, edge rounding is essential for ensuring that parts fit together precisely and safely. Rounded edges reduce the potential for stress concentration, which could lead to material failure under load.
- Metal Fabrication and Construction: Sheet metal parts used in construction often require edge rounding to ensure smooth, safe edges. This is especially important for parts that are handled frequently, as sharp edges can cause injuries or damage to other materials.
- Electronics Manufacturing: In the production of electronic components, such as heat sinks, casings, or metal housings, edge rounding ensures that parts fit together without interference and that sharp edges do not damage sensitive components during assembly.
In conclusion, metal edge rounding machines are vital tools for ensuring safety, improving part quality, and enhancing the performance of metal components in a wide range of industries. By automating the edge rounding process, manufacturers can achieve consistent results, reduce manual labor, and ensure that parts are safe to handle and assemble. Whether for high-volume production or precision applications, these machines play a key role in creating high-quality, burr-free metal parts that meet the necessary standards for function and safety.
Metal edge rounding machines are essential tools in modern manufacturing, particularly when it comes to ensuring that the sharp edges left after cutting, punching, or stamping metal parts are safely rounded off. The primary goal of these machines is to improve the overall safety, quality, and performance of the metal parts by removing the dangerous and rough edges that could cause injuries or negatively affect the final product. These machines are used in a wide range of industries, from automotive to aerospace, electronics, and general metal fabrication, where sharp edges are common byproducts of various metalworking processes.
In most cases, metal parts are cut, stamped, or sheared to shape, leaving behind jagged or sharp edges that can be problematic. These sharp edges not only pose a risk to operators but can also affect the integrity of the parts during further processing or assembly. For example, sharp edges may cause misalignments when parts are being assembled or can damage other components that come into contact with them. Rounding the edges of these parts makes them safer to handle, improves the overall fit and finish, and often reduces the likelihood of damage or wear over time.
Metal edge rounding machines typically use different types of mechanical processes, such as grinding, polishing, and abrasive actions, to achieve the desired edge profile. The most common method involves applying abrasive materials to the edges of the metal, which gradually removes the sharp points and smooths out the corners. This process can be done manually or through automated systems, depending on the specific needs of the production process.
One of the main advantages of automated metal edge rounding machines is the ability to process large quantities of parts in a short amount of time. This is particularly beneficial in high-volume manufacturing settings, where efficiency and consistency are key. These machines can be equipped with adjustable settings that allow operators to control the pressure, speed, and abrasiveness, making it possible to fine-tune the edge rounding process to suit different materials and thicknesses. This flexibility ensures that a wide variety of metal parts can be processed with a high degree of precision, regardless of the part’s size, shape, or material.
The automation of edge rounding processes also helps improve consistency across large production runs. By using CNC-controlled machines or robotic systems, manufacturers can achieve precise, repeatable results without the need for manual intervention. This ensures that every part has a uniform, rounded edge, which is crucial for industries where tight tolerances and high-quality finishes are essential.
Additionally, the rounded edges of metal parts are not just about safety. A smooth, rounded edge often contributes to the overall aesthetic quality of the part. In industries like automotive and aerospace, where appearance is important, edge rounding helps to achieve a sleek, polished look. Furthermore, rounded edges can make it easier to apply coatings, such as paint or powder coatings, because sharp edges can cause coatings to peel or wear away more easily. Rounded edges provide a smoother surface that helps finishes adhere better and last longer.
In terms of performance, rounded edges are beneficial because sharp edges can create stress concentrators in metal parts. Stress concentrators are areas where stress is more likely to build up, leading to a higher risk of cracks or failures. By rounding the edges, stress is more evenly distributed, reducing the chances of material failure and enhancing the overall durability of the part. This is especially important in applications like aerospace, where even the smallest structural issues can have significant consequences.
Edge rounding is also important for ensuring that parts fit together properly during assembly. Sharp edges can interfere with the assembly process, making it harder for parts to align correctly or causing them to become damaged during handling. By rounding the edges, parts can be assembled more easily, which speeds up the overall production process and reduces the risk of damage or delays.
The versatility of metal edge rounding machines is another key factor in their widespread use. These machines can process a wide range of metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and other alloys, making them suitable for various industries. Additionally, many edge rounding machines can be used to process parts of different sizes and shapes, from large metal sheets to smaller, more intricate components. Whether the parts are flat, curved, or have irregular geometries, the machine can be adjusted to handle different types of edges and achieve the desired result.
Another significant advantage of using metal edge rounding machines is the potential for reducing labor costs. Automated machines require less manual intervention, which means fewer operators are needed to oversee the process. This not only reduces labor costs but also minimizes the likelihood of human error, ensuring that every part is processed accurately and consistently.
In addition to the mechanical processes, some advanced machines incorporate integrated features such as dust collection systems to maintain a clean working environment. This is especially important when dealing with abrasive materials, as they can generate dust and debris during the rounding process. A good dust collection system helps keep the workspace clean and ensures the safety of workers.
In conclusion, metal edge rounding machines play an essential role in improving the safety, quality, and performance of metal parts across various industries. By rounding off sharp edges, these machines help prevent injuries, improve part fit and function, and contribute to a more professional finish. The ability to automate the process, achieve consistent results, and reduce labor costs makes these machines invaluable in high-volume production settings. Whether it’s in automotive manufacturing, aerospace, electronics, or metal fabrication, edge rounding machines provide a reliable solution for enhancing the overall quality and durability of metal components.
EMS Metalworking Machinery
We design, manufacture and assembly metalworking machinery such as:
- Hydraulic transfer press
- Glass mosaic press
- Hydraulic deep drawing press
- Casting press
- Hydraulic cold forming press
- Hydroforming press
- Composite press
- Silicone rubber moulding press
- Brake pad press
- Melamine press
- SMC & BMC Press
- Labrotaroy press
- Edge cutting trimming machine
- Edge curling machine
- Trimming beading machine
- Trimming joggling machine
- Cookware production line
- Pipe bending machine
- Profile bending machine
- Bandsaw for metal
- Cylindrical welding machine
- Horizontal pres and cookware
- Kitchenware, hotelware
- Bakeware and cuttlery production machinery
as a complete line as well as an individual machine such as:
- Edge cutting trimming beading machines
- Polishing and grinding machines for pot and pans
- Hydraulic drawing presses
- Circle blanking machines
- Riveting machine
- Hole punching machines
- Press feeding machine
You can check our machinery at work at: EMS Metalworking Machinery – YouTube
Applications:
- Beading and ribbing
- Flanging
- Trimming
- Curling
- Lock-seaming
- Ribbing
- Flange-punching
