
We manufacture laboratory press types for sample production, sample testing, and small size particle manufacturing. Price for Sale directly from the manufacturer.
A laboratory press, also known as a hydraulic laboratory press or a laboratory hydraulic press, is a specialized piece of equipment used in scientific research and material testing laboratories. It is designed to apply controlled pressure to various samples or materials for research, analysis, and experimentation. Here are key details about laboratory presses:
1. Pressure Application:
- The primary function of a laboratory press is to apply pressure to samples or materials. This pressure can range from a few tons to several tons, depending on the specific model and application.
2. Hydraulic System:
- Laboratory presses are typically hydraulic, meaning they use hydraulic fluid to generate and control the pressure. Hydraulic systems allow for precise and uniform pressure application.
3. Pressure Control:
- Laboratory presses feature pressure control mechanisms, such as pressure gauges and controls, to adjust and monitor the applied pressure accurately.
4. Heating Capability:
- Some laboratory presses are equipped with heating elements to apply both pressure and heat simultaneously. This is especially useful for applications such as sample molding and polymer research.
5. Sample Containers:
- Laboratory presses often include containers or molds in which the samples or materials are placed. These containers can be customized to suit various research needs.
6. Sample Preparation:
- Researchers prepare their samples or materials according to the experimental requirements and place them in the press for testing or analysis.
7. Material Testing:
- Laboratory presses are commonly used for material testing, including compression tests, tensile tests, and other mechanical property evaluations. They can assess the strength, deformation, and behavior of materials under controlled pressure conditions.
8. Research Applications:
- Laboratory presses find applications in a wide range of scientific fields, including materials science, chemistry, geology, and engineering. They are used for research, development, and quality control purposes.
9. Sample Consolidation:
- In geology and soil science, laboratory presses are used to consolidate soil or rock samples into specified sizes and shapes for testing and analysis.
10. Sample Preparation for Spectroscopy: – Laboratory presses are used to prepare thin pellet samples for spectroscopic analysis, such as X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy.
11. Powder Compaction: – They are used for compacting powdered materials into tablets or pellets for pharmaceutical, chemical, and materials research.
12. Particle Size Analysis: – In particle size analysis, laboratory presses can be used to prepare solid samples for sieving or laser diffraction measurements.
13. Quality Control: – Laboratory presses are used for quality control in various industries to ensure that materials and products meet specified standards and requirements.
14. Safety Features: – Safety features, such as emergency stop buttons and safety guards, are typically incorporated into laboratory presses to protect operators during experiments.
15. Customization: – Some laboratory presses are highly customizable, allowing researchers to adapt them for specific research needs and applications.
Laboratory presses are valuable tools for scientists and researchers who need to apply controlled pressure to samples or materials as part of their investigations. They play a critical role in advancing research, quality control, and materials characterization in a wide range of scientific disciplines.
Laboratory Press
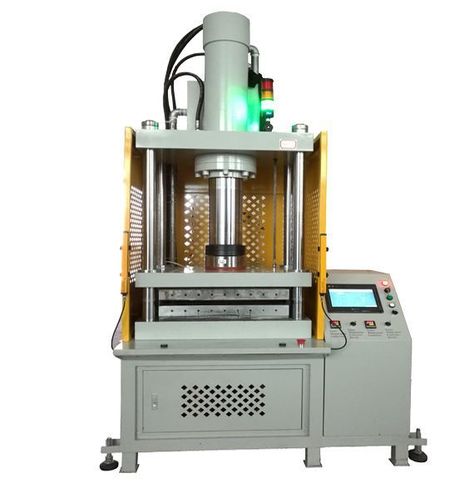

Laboratory presses play a crucial role in the development and testing of materials in scientific and industrial fields. These machines are designed to generate controlled pressure, typically ranging from a few pounds per square inch (PSI) to several tons, depending on the specific model and application. Laboratory presses are used for a variety of processes, such as molding, compression, laminating, or pelletizing materials for testing purposes.
The primary goal of laboratory presses is to reproduce consistent, repeatable results that are essential for material testing, research, and development. They are vital in laboratories where precision and accuracy are of utmost importance, such as those found in research institutions, universities, and commercial industries.
Some of the most common laboratory presses include those used in the plastics, polymer, pharmaceutical, and electronics industries. These machines can range from small benchtop models suitable for light-duty tasks to more robust, floor-standing versions that handle high-pressure applications. They typically come with features such as precise temperature control, programmable settings, and various safety features to ensure accurate, efficient operation.
Laboratory presses are often customized to meet the specific needs of the user, with manufacturers offering various options for pressure capacities, heating elements, platens, and control systems. The advancements in laboratory press technology have made it easier for operators to achieve exact results, while automation has reduced the need for manual labor in many cases.
In short, laboratory presses are indispensable in many research and development environments. Their flexibility, ease of use, and precision make them ideal tools for a wide range of applications.
Types of Laboratory Presses
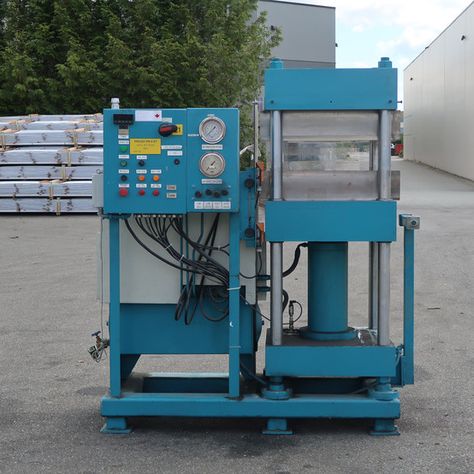

Understanding the different types of laboratory presses is essential for selecting the right machine for specific applications. Here, we will explore the four primary types: manual, hydraulic, pneumatic, and electric presses.
2.1. Manual Presses
Manual presses are typically operated by hand, using a lever or screw mechanism to generate pressure. These presses are suitable for smaller applications where the required force is relatively low. While not as powerful as hydraulic or pneumatic presses, manual presses offer precision and are ideal for tasks that do not require high levels of force. They are also affordable, easy to maintain, and do not require external power sources, making them ideal for small-scale operations or educational environments.
Key features:
- Simple, robust design
- Ideal for low-force applications
- No need for external power
- Cost-effective and portable
2.2. Hydraulic Presses
Hydraulic laboratory presses use hydraulic cylinders to generate force. These presses are known for their ability to produce high levels of pressure, making them suitable for applications that require more significant force, such as molding polymers or testing materials. Hydraulic presses offer precise control over the applied pressure and can be automated or manually operated, depending on the model. The hydraulic system enables the press to exert force evenly and consistently, making it ideal for industries like plastics, rubber, and pharmaceuticals.
Key features:
- Capable of producing high pressure
- Suitable for a variety of materials
- Consistent and even force distribution
- Available in both manual and automated versions
2.3. Pneumatic Presses
Pneumatic laboratory presses use compressed air to generate force, offering a more efficient solution for applications that require lower pressure. These presses are typically faster than hydraulic presses, making them ideal for operations where speed and efficiency are critical. However, they are limited in the amount of force they can produce, which is why they are best suited for light-duty tasks, such as laminating or small-scale compression.
Key features:
- Fast and efficient operation
- Best for lower-pressure applications
- Clean, requiring minimal maintenance
- Ideal for high-cycle processes
2.4. Electric Presses
Electric laboratory presses are powered by electric motors, offering a highly efficient and clean alternative to hydraulic and pneumatic presses. Electric presses are known for their precision and ease of use, as they allow operators to control the pressure and speed with high accuracy. They are also quieter and require less maintenance than other types of presses, making them an attractive option for laboratories that prioritize a clean, quiet working environment.
Key features:
- High precision and control
- Quiet operation
- Low maintenance
- Ideal for precision testing and small-scale manufacturing
2.5. Comparison of Different Types
When comparing the various types of laboratory presses, it is important to consider the specific needs of the application. Manual presses are ideal for simple, low-force tasks, while hydraulic presses offer higher pressure capabilities and are suitable for more demanding applications. Pneumatic presses provide speed and efficiency, while electric presses offer precision and cleanliness.
- Cost: Manual presses tend to be the most affordable, while hydraulic and electric presses can be more expensive.
- Pressure Capacity: Hydraulic presses offer the highest pressure capacity, followed by pneumatic and electric presses.
- Maintenance: Electric presses require the least maintenance, while hydraulic systems may require more upkeep due to fluid handling.
- Precision: Electric presses offer the highest level of control and precision, while manual presses may be less exact.
Components and Technical Features
Laboratory presses consist of several key components that determine their performance and functionality. These components vary slightly depending on the type of press but share common features that enhance their operation.
3.1. Frame Design
The frame of a laboratory press provides structural support and helps distribute force evenly during operation. Most laboratory presses have a steel or cast-iron frame designed to withstand high levels of pressure without bending or warping. The frame design can also determine the footprint of the machine, with benchtop presses having smaller, more compact frames for use in confined spaces.
3.2. Pressure Systems
The pressure system of a laboratory press is its core component. In hydraulic presses, the system consists of a hydraulic cylinder filled with fluid that generates force when pressure is applied. Pneumatic presses use compressed air to create pressure, while manual presses rely on mechanical force applied by a hand-operated lever or screw.
3.3. Heating Elements and Temperature Control
Many laboratory presses include integrated heating elements, which allow materials to be processed under controlled temperatures. Heating platens are essential for applications like laminating or molding polymers, where heat is necessary to activate the material. Temperature control systems ensure that the press operates within the desired temperature range, providing precise control over heating parameters.
3.4. Control Panels and Monitoring Systems
Modern laboratory presses come equipped with digital control panels that allow operators to set pressure, temperature, and cycle time parameters with high precision. These control systems often include monitoring features that provide real-time feedback on the press’s performance, ensuring accurate and consistent results.
3.5. Customizable Features
Many laboratory presses offer customizable features to meet the specific needs of the user. These features can include interchangeable platens, programmable cycles, and additional safety mechanisms to enhance the machine’s versatility.
Applications of Laboratory Presses

Laboratory presses are used across various industries and research fields due to their ability to apply precise pressure and temperature. Below are some of the key applications:
4.1. Scientific Research
In academic and research laboratories, presses are used for material testing and sample preparation. They help in the development of new materials, ensuring uniformity and consistency in the samples produced for further analysis. Polymers, ceramics, and composite materials are frequently tested in these settings.
4.2. Material Testing
In material science and engineering, laboratory presses are indispensable tools for testing the properties of materials under controlled conditions such as high pressure and temperature. Laboratory presses are used to prepare specimens for tensile, compression, and bending tests, ensuring the materials meet industry standards. Some common materials tested include plastics, rubber, metals, and composites.
Laboratory presses are particularly essential in the development of new materials where precise control over pressure and temperature is required to study how these variables affect the mechanical properties of a material. This information is crucial for industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction, where the materials used must meet rigorous performance standards.
4.3. Pharmaceutical Applications
The pharmaceutical industry makes extensive use of laboratory presses, particularly in the production of tablets. Tablet presses are used to compress powders into uniform tablets with precise dosage control. These presses allow for the accurate control of both the force applied and the shape of the tablets, ensuring consistency in drug formulation.
Additionally, laboratory presses are used in drug research and development to study the effects of compression on different formulations and to create sample batches for clinical trials. This is a critical step in pharmaceutical R&D as it helps to ensure that the final product will be effective and safe for patients.
4.4. Polymer and Plastics Industry
In the polymer and plastics industry, laboratory presses are employed for compression molding, a process that involves shaping materials by applying heat and pressure in a mold. This technique is widely used to produce high-strength plastic components and composite materials.
Presses are also used in testing polymer samples for properties like tensile strength, elasticity, and thermal stability. By simulating real-world conditions, these tests help manufacturers assess the performance of their materials and adjust their formulations to achieve the desired properties.
4.5. Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing
In the electronics and semiconductor industries, laboratory presses are utilized in several critical applications. These include the lamination of circuit boards, encapsulation of electronic components, and wafer bonding. The high precision and control offered by laboratory presses are essential for ensuring that the delicate electronic components are not damaged during the manufacturing process.
The pressure and temperature parameters can be finely tuned to match the specific needs of the application, making laboratory presses a key tool in the production of high-performance electronic devices.
4.6. Other Specialized Applications
Laboratory presses find uses in other specialized fields such as:
- Forensic Science: Used for the analysis of evidence, like creating casts of impressions found at crime scenes.
- Environmental Science: Presses are used in the preparation of samples for environmental testing, such as creating thin films for spectroscopic analysis.
- Food Science: Used to compress food samples for texture analysis, and in packaging tests to determine the strength of different materials.
Each of these applications requires the precision and versatility that laboratory presses provide, further underscoring their value across multiple industries.
Advantages of Laboratory Presses
Laboratory presses are indispensable due to their precision, versatility, and efficiency. Here are some of the most significant advantages they offer:
5.1. Precision and Control
One of the main advantages of laboratory presses is the high degree of precision they offer. Whether testing materials or manufacturing small parts, laboratory presses allow for precise control over parameters such as pressure, temperature, and duration. This ensures consistent and reliable results, which is critical in research and development environments.
Modern presses are equipped with advanced digital control systems that allow users to fine-tune the settings, monitor the process in real-time, and make adjustments as needed. This level of control is crucial in industries such as pharmaceuticals and electronics, where even the slightest variations can have significant consequences.
5.2. Versatility Across Multiple Industries
Laboratory presses are versatile machines used in various industries, from pharmaceuticals to electronics to polymers. Their ability to handle different materials and processes makes them valuable in both research laboratories and industrial production lines.
The adaptability of laboratory presses is enhanced by the availability of different models—manual, hydraulic, pneumatic, and electric—and the ability to customize the machine for specific applications. Whether creating a small batch of products or conducting large-scale material testing, laboratory presses can meet a wide range of needs.
5.3. Ease of Use and Safety Features
Most modern laboratory presses are designed with user-friendly interfaces that make them easy to operate. This is particularly important in environments where operators may not be highly specialized. Many presses are equipped with touch-screen control panels, pre-programmable cycles, and safety features such as overload protection, emergency stop buttons, and automatic shut-offs.
Safety is paramount when working with high-pressure and high-temperature equipment. Therefore, laboratory presses are typically designed to meet stringent safety standards, ensuring the well-being of the operators. Features such as transparent safety shields, automatic locking mechanisms, and temperature sensors help prevent accidents.
5.4. Compact Design for Laboratory Use
Most laboratory presses are designed with compactness in mind, making them suitable for use in laboratories with limited space. Benchtop models are especially popular in academic and research settings where the machine’s footprint needs to be small, yet capable of delivering reliable results. Even larger, floor-standing models are typically designed to fit within standard laboratory layouts without requiring major adjustments to the space.
This makes laboratory presses a practical choice for environments where space is at a premium, while still offering the full range of capabilities needed for precise material testing or small-scale production.
Buying Considerations and Specifications
Choosing the right laboratory press for your needs involves careful consideration of several factors. The machine must meet the specific requirements of your application, both in terms of performance and operational costs. Below are some key considerations to keep in mind:
6.1. Factors to Consider When Choosing a Laboratory Press
Several key factors should be considered when purchasing a laboratory press:
- Pressure Capacity: Determine the maximum pressure required for your application. This will influence whether you need a manual, hydraulic, pneumatic, or electric press.
- Heating Elements: Some applications require heat in addition to pressure. Be sure to check whether the press offers the necessary heating capabilities and if the temperature control is precise enough for your needs.
- Size and Footprint: Ensure the press fits within your laboratory’s available space. Benchtop presses are suitable for smaller spaces, while floor-standing models are better for more demanding applications.
- Automation: Depending on your needs, an automated press might save time and improve consistency by reducing the need for manual operation.
- Durability and Build Quality: Laboratory presses are an investment, so it’s essential to select a machine made from high-quality materials that can withstand constant use.
6.2. Standard Industry Specifications
Laboratory presses typically come with standard industry specifications that help ensure reliability and performance. These include:
- Pressure Ratings: Measured in tons or PSI, this indicates the maximum force the press can generate.
- Platen Size: Refers to the size of the heated or non-heated plates used for compression. Larger platens allow for bigger samples or multiple tests to be conducted simultaneously.
- Cycle Time: The time it takes for the press to complete a single cycle, including pressure application and, where applicable, heating and cooling.
- Safety Standards: Most presses adhere to international safety standards such as CE marking or ISO certifications, which ensure the equipment is safe for operation.
6.3. Cost, Maintenance, and Warranty Options
The cost of a laboratory press will vary depending on the type, size, and features. Manual presses tend to be the most affordable, while hydraulic and electric presses are more expensive due to their advanced systems. However, the initial cost should be weighed against the machine’s long-term benefits, such as precision, durability, and ease of use.
Maintenance is another factor to consider. Some types of presses, particularly hydraulic ones, may require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance, such as fluid replacement or system calibration. Be sure to ask about maintenance schedules and support services when purchasing a press.
Lastly, consider the warranty options available. A good warranty will cover repairs and replacement parts for a specified period, ensuring peace of mind and protecting your investment.
6.4. Importance of Manufacturer Reputation
When buying a laboratory press, it’s crucial to purchase from a reputable manufacturer. Well-established manufacturers not only produce high-quality equipment but also offer reliable customer service and technical support. This ensures that your press will perform as expected and that any issues will be addressed promptly.
Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in your industry and those who offer comprehensive warranties and service packages. Reading customer reviews and requesting references from the manufacturer can also help you make an informed decision.
Introduction to EMS Metalworking Machinery

7.1. Company Overview and History
EMS Metalworking Machinery is a leading manufacturer of high-quality laboratory presses. Founded several decades ago, the company has grown into a global supplier of cutting-edge metalworking and laboratory equipment. Known for its innovative engineering and commitment to quality, EMS serves a wide range of industries including pharmaceuticals, polymers, electronics, and research institutions.
EMS’s reputation is built on its dedication to producing reliable, durable, and precise machinery. Their presses are designed to meet the specific needs of their clients, from small research laboratories to large-scale industrial manufacturers.
7.2. Specialization in Laboratory Press Manufacturing
Over the years, EMS has become a specialist in manufacturing laboratory presses. Their product lineup includes hydraulic, pneumatic, and electric models, all of which are customizable to meet specific customer requirements. EMS presses are known for their accuracy, ease of use, and robust construction, making them a top choice for organizations that require high-performance equipment.
The company invests heavily in research and development to stay ahead of the latest technological trends. This enables them to offer laboratory presses with state-of-the-art features such as digital control systems, automated processes, and advanced safety mechanisms.
7.3. Product Range and Customization Options
EMS offers a comprehensive range of laboratory presses, from benchtop models suitable for small laboratories to large, industrial-scale presses. Each press is built with high-grade materials and precision engineering to ensure consistent performance.
One of EMS’s key strengths is its ability to customize presses to meet the specific needs of its customers. Whether you need a press with additional heating elements, higher pressure capacity, or specialized safety features, EMS can design a solution tailored to your application.
7.4. Quality Control and Certifications
EMS Metalworking Machinery takes pride in its rigorous quality control process. Each machine is thoroughly tested to ensure it meets the highest industry standards before being shipped to the customer. The company is ISO 9001 certified, which demonstrates its commitment to quality management systems and continuous improvement.
Additionally, EMS laboratory presses are CE-marked, ensuring compliance with European safety standards. This gives customers confidence that they are purchasing equipment that is not only high-performing but also safe and reliable.
7.5. Global Market Presence and Clientele
EMS has a strong global market presence, with customers in over 50 countries. The company’s laboratory presses are used by top research institutions, pharmaceutical companies, and manufacturers around the world. EMS’s commitment to customer satisfaction has helped it build long-lasting relationships with its clients, many of whom return to EMS for additional equipment as their needs evolve.
The company’s international sales team works closely with clients to ensure they receive the right press for their application, providing technical support and advice throughout the purchasing process. EMS’s after-sales service is also highly regarded, offering ongoing support for maintenance, repairs, and upgrades.
Conclusion
In conclusion, laboratory presses are essential tools for a wide range of applications across industries such as pharmaceuticals, materials testing, electronics, and polymer manufacturing. Their precision, versatility, and ease of use make them invaluable in both research and industrial settings.
When selecting a laboratory press, it is important to consider factors such as pressure capacity, heating requirements, size, automation options, and manufacturer reputation. Investing in a high-quality press from a trusted manufacturer ensures reliable performance, durability, and peace of mind.
EMS Metalworking Machinery stands out as a leading manufacturer of laboratory presses, offering a comprehensive range of customizable models to meet the specific needs of its customers. With a focus on innovation, quality, and customer service, EMS has established itself as a global leader in the metalworking and laboratory press market. Their commitment to producing reliable, high-performance machinery makes them the ideal choice for any organization seeking top-quality laboratory presses.
Introduction to Laboratory Presses
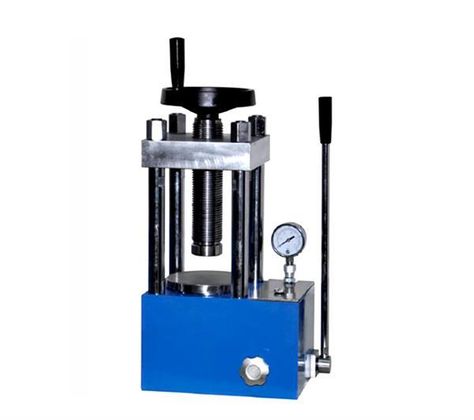

Laboratory presses are specialized machines designed to apply controlled pressure and sometimes heat to various materials in a laboratory setting. These presses are essential tools for a range of industries, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, electronics, and polymers. By applying pressure, laboratory presses enable researchers and technicians to create samples, conduct material tests, or form products in a consistent and precise manner.
Laboratory presses come in a variety of types, each suited for specific applications. From manual to hydraulic, pneumatic, and electric, the selection of a press depends on the intended use, pressure requirements, temperature control, and budget constraints. The technology behind these machines has evolved considerably over the years, with modern presses offering advanced digital controls, safety features, and enhanced customization options.
The importance of laboratory presses extends to material testing, where accurate and repeatable pressure application is critical for determining the physical properties of materials. Moreover, in production settings, laboratory presses are used for small-batch manufacturing, making them indispensable tools for quality control and R&D.
Manual Laboratory Presses

2.1. Definition and Basic Operation
Manual laboratory presses are the most basic type of press, operated by hand using either a lever, screw, or toggle mechanism to generate pressure. These presses are widely used in educational settings, small laboratories, and for low-pressure applications. Due to their simplicity, manual presses require no external power source and can be used in remote or resource-limited environments.
2.2. Key Components
Manual presses generally consist of:
- Frame: The structure that holds the components together and bears the load during pressing.
- Pressure Mechanism: A lever or screw that converts manual force into pressure.
- Platen: The surface on which materials are placed during pressing, often removable or interchangeable.
- Pressure Gauge: A dial that measures the force being applied (for certain models).
2.3. Applications of Manual Presses
Manual presses are typically used for smaller tasks such as:
- Sample Preparation: Creating specimens for material testing.
- Tablet Pressing: In pharmaceutical labs to create small batches of tablets.
- Material Testing: Limited force applications for polymers or light materials.
2.4. Advantages and Disadvantages
Manual presses have several advantages:
- Low Cost: One of the most affordable types of presses.
- Simplicity: Easy to use with minimal training.
- Portability: Due to their size and lack of dependence on external power.
However, they also have limitations:
- Limited Pressure: Unsuitable for high-pressure applications.
- Operator Fatigue: Prolonged use can lead to physical strain.
2.5. Manual Press Variants
There are several subtypes of manual presses, each suited to specific applications:
- Hand-Operated Presses: The simplest version, where pressure is applied using a hand-operated lever.
- Screw Presses: A screw mechanism provides more control over pressure application.
- Toggle Presses: Utilize a toggle mechanism to apply pressure, offering a balance between ease of use and force generation.
Hydraulic Laboratory Presses
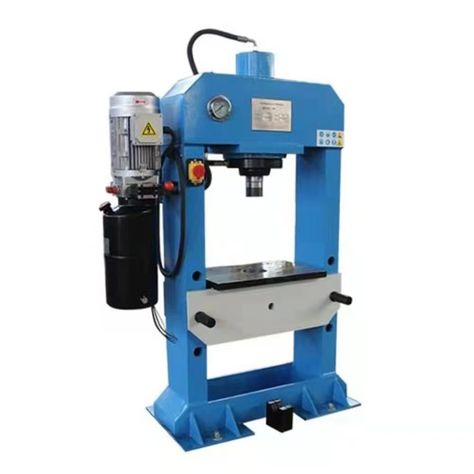

3.1. Definition and How They Work
Hydraulic laboratory presses use a hydraulic cylinder filled with oil to generate force. By compressing the oil in a confined space, hydraulic presses can produce very high levels of pressure, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications such as compression molding, material testing, and forming parts.
3.2. Components of a Hydraulic Press
- Hydraulic Cylinder: The main component that creates pressure through fluid compression.
- Pump: Responsible for moving the hydraulic fluid into the cylinder.
- Pressure Gauge: Displays the pressure being exerted by the press.
- Control Valve: Regulates the flow of hydraulic fluid, allowing the operator to control the pressure and release.
3.3. Types of Hydraulic Presses
There are several types of hydraulic presses used in laboratory settings:
- Single-Action Hydraulic Presses: These presses apply pressure in one direction and are commonly used in forming or compression applications.
- Double-Action Hydraulic Presses: These presses apply pressure in both upward and downward directions, increasing efficiency and versatility.
- Four-Post Hydraulic Presses: A robust design where four posts guide the platen, allowing for even pressure distribution across large surfaces.
3.4. Applications in Material Testing, Molding, and R&D
Hydraulic presses are versatile and used in a variety of fields, including:
- Compression Molding: Forming composite materials and polymers by applying heat and pressure.
- Material Testing: Testing materials for strength, durability, and other properties under high pressure.
- R&D: Developing new materials and testing their behavior under different conditions.
3.5. Advantages and Disadvantages of Hydraulic Presses
Advantages:
- High Pressure: Capable of generating extremely high force.
- Precision: Offers precise control over the pressure applied.
- Durability: Hydraulic systems are robust and long-lasting.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: More expensive than manual presses.
- Maintenance: Hydraulic systems require regular maintenance, including oil changes and seal replacements.
Pneumatic Laboratory Presses

4.1. Understanding Pneumatic Presses and Mechanisms
Pneumatic laboratory presses operate using compressed air to generate force. These presses are faster than hydraulic models and are suited for light to medium-duty applications. Pneumatic systems are highly efficient in terms of speed and can handle high-cycle processes with ease.
4.2. Key Components of Pneumatic Presses
- Air Cylinder: Uses compressed air to generate force.
- Compressor: Supplies the press with compressed air.
- Regulator: Controls the pressure within the system.
- Control System: Allows the operator to adjust the air pressure and force applied.
4.3. Applications in Industrial Labs
Pneumatic presses are ideal for tasks such as:
- Laminating: Used in the electronics industry to laminate circuit boards and other components.
- Pelletizing: Compressing powders into pellets for pharmaceutical or industrial use.
- Light Molding: Suitable for molding small parts or materials that don’t require high-pressure applications.
4.4. Advantages of Pneumatic Presses
- Speed: Faster than hydraulic presses, making them suitable for high-cycle processes.
- Efficiency: Low energy consumption and minimal waste.
- Easy to Operate: Pneumatic systems require less maintenance than hydraulic systems and are easier to control.
4.5. Disadvantages (Force Limitations, Maintenance)
- Limited Force: Cannot generate as much pressure as hydraulic presses.
- Air Supply Dependency: Requires a consistent supply of compressed air, adding operational costs.
Electric Laboratory Presses

5.1. Electric vs. Other Press Types
Electric laboratory presses use electric motors to generate force, providing a cleaner and quieter alternative to hydraulic and pneumatic systems. Electric presses offer precise control over pressure and are ideal for environments where accuracy and repeatability are crucial.
5.2. How Electric Presses Operate
Electric presses work by converting electrical energy into mechanical force. Motors drive the press, which can be finely controlled using digital systems. This allows for high precision in pressure application, making electric presses a preferred choice for sensitive applications.
5.3. Features and Advantages of Electric Presses (Precision, Quietness)
- Precision: Electric presses allow for very fine adjustments in pressure and cycle time, offering a high level of control.
- Quiet Operation: Since they do not rely on compressed air or fluid, electric presses operate with minimal noise.
- Low Maintenance: Electric presses have fewer moving parts than hydraulic or pneumatic models, reducing the need for regular maintenance.
5.4. Common Applications (Semiconductors, Electronics)
Electric presses are commonly used in industries such as:
- Semiconductors: Bonding and packaging semiconductor materials.
- Electronics: Laminating, encapsulating, and forming parts for electronic devices.
- Medical Devices: Used in the manufacturing of precision medical components.
5.5. Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Energy Efficient: Consumes less energy compared to hydraulic systems.
- Clean and Environmentally Friendly: No fluids or compressed air required.
- Long Lifespan: Due to fewer moving parts, electric presses tend to last longer.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Force: Not suitable for heavy-duty applications that require very high pressure.
- Cost: Higher initial cost compared to manual or pneumatic presses.
Specialized Laboratory Presses

6.1. Hot Presses
Hot presses are designed to apply both pressure and heat to a material, making them ideal for processes like bonding, molding, and laminating. These presses are used in industries that work with thermoplastics, composites, and adhesives.
Key components of hot presses include:
- Heated Platens: Used to apply heat uniformly across the material.
- Temperature Control Systems: Allows the operator to set precise temperature ranges.
6.2. Cold Presses
Cold presses, on the other hand, are used when temperature is not a critical factor in the pressing process. They are commonly used in applications such as material testing or bonding processes where heat could potentially damage the material.
6.3. Vacuum Presses
Vacuum presses remove air from the press chamber before pressure is applied, making them ideal for applications where air bubbles or contamination would affect the quality of the material. These presses are often used in composite material manufacturing and laminating.
6.4. Hybrid Presses (Hydraulic-Electric, Pneumatic-Electric)
Hybrid presses combine elements of different types of presses to offer the best of both worlds. For example, a hydraulic-electric press may use hydraulic power for high pressure but an electric control system for precision.
6.5. Applications of Specialized Presses (R&D, Composite Materials)
Specialized presses are often used in research and development, where precise control over multiple parameters (pressure, temperature, vacuum) is needed to create new materials or study specific properties.
Comparative Analysis of Press Types
7.1. Pressure Capacity
- Manual Presses: Low pressure, typically up to a few tons.
- Hydraulic Presses: High pressure, suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Pneumatic Presses: Moderate pressure, but limited compared to hydraulic presses.
- Electric Presses: Moderate pressure, ideal for precision applications.
7.2. Speed and Efficiency
- Pneumatic Presses: Fastest, best for high-cycle applications.
- Hydraulic Presses: Slower but more powerful.
- Electric Presses: Offer a balance of speed and precision.
7.3. Temperature Control Capabilities
- Hot Presses: Equipped with heating elements for applications requiring heat.
- Cold Presses: Suitable for processes where temperature control is not needed.
7.4. Size and Space Requirements
- Manual Presses: Typically the most compact.
- Hydraulic Presses: Larger and more space-consuming.
- Electric and Pneumatic Presses: Mid-range in terms of size.
7.5. Precision and Customization Options
- Electric Presses: Offer the highest level of precision.
- Hydraulic and Pneumatic Presses: Can be customized for various applications but may offer less precision than electric models.
7.6. Maintenance and Costs
- Hydraulic Presses: Require more maintenance due to fluid systems.
- Electric Presses: Low maintenance, but higher upfront costs.
- Manual Presses: Low cost and minimal maintenance.
Emerging Trends in Laboratory Press Technology
8.1. Automation and Digital Control
Automation is becoming increasingly common in laboratory presses, with systems that allow for the automatic control of pressure, temperature, and cycle times. This reduces operator error and improves consistency in production.
8.2. Advanced Materials Pressing
With the development of new materials such as composites and nanomaterials, laboratory presses are evolving to meet the demands of these new materials. Presses with enhanced temperature control, vacuum capabilities, and ultra-precision settings are becoming more prevalent.
8.3. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
There is growing demand for laboratory presses that are energy efficient and environmentally friendly. Electric presses, in particular, are favored for their lower energy consumption and cleaner operation.
8.4. Impact of Industry 4.0 on Laboratory Presses
The integration of digital technologies, IoT (Internet of Things), and smart controls is transforming the way laboratory presses operate. Advanced data collection, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance are some of the trends shaping the future of laboratory presses.
Conclusion
Laboratory presses come in many forms, each designed to meet specific industrial and research needs. From manual and hydraulic presses to pneumatic, electric, and specialized models, the range of available presses offers something for every type of laboratory. Understanding the differences in pressure capacity, speed, precision, and cost is key to selecting the right press for the job.
The future of laboratory presses is moving towards greater automation, precision, and energy efficiency, with manufacturers developing presses that are increasingly capable of handling complex and advanced materials. These innovations are pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved in both research and industrial settings.
As technology continues to evolve, laboratory presses will remain an indispensable tool for material testing, manufacturing, and scientific research, contributing to advancements across multiple industries.
Introduction to Laboratory Press Components

Laboratory presses are sophisticated machines designed to apply controlled pressure (and sometimes heat) to materials for various purposes such as molding, forming, and testing. While different types of laboratory presses serve a wide range of applications, from pharmaceuticals to material science, they all share several core components that work together to ensure the desired results.
The efficiency and functionality of a laboratory press depend significantly on its components. The components form the foundation of the press’s operation, whether it’s a manual press used for low-pressure applications or a hydraulic press designed for heavy-duty tasks. Understanding these components and their roles is critical for selecting and maintaining a laboratory press that will meet the specific demands of a laboratory or industrial environment.
Broadly, laboratory presses consist of structural parts like frames and platens, pressure generation systems (hydraulic, pneumatic, or mechanical), control mechanisms (manual or electronic), heating and cooling elements, safety features, and customizable parts such as interchangeable dies or platens.
In this comprehensive overview, we will explore each of these essential components, their construction, variations, and functions. By the end of this section, you will have a clear understanding of how these components work together to ensure precision, reliability, and safety in laboratory presses.
Frame and Structural Components
2.1. Types of Frames
The frame is the backbone of any laboratory press. It holds the press together, bears the brunt of the force applied during operation, and ensures that pressure is evenly distributed across the working area. There are several types of frames commonly used in laboratory presses, each with specific strengths and weaknesses:
- C-Frame: The C-frame design features a single open side, which allows for easy access to the working area. These presses are compact and space-efficient but may have limited capacity for high-pressure applications because of the uneven force distribution.
- H-Frame: H-frames are sturdier and more stable than C-frames, with a symmetrical structure that distributes force more evenly. They are better suited for heavy-duty applications but take up more space.
- Four-Post Frame: A four-post design provides the ultimate stability and uniform pressure application. The posts guide the platen, ensuring minimal deflection and even force distribution. These are often used in high-precision or high-pressure applications.
2.2. Material Considerations for Frames
The material from which the frame is constructed significantly affects its durability, weight, and performance. Common materials used for frames include:
- Steel: Steel frames are durable and strong, making them ideal for high-pressure applications. Steel frames can be treated with rust-resistant coatings to improve longevity.
- Cast Iron: Cast iron frames are often used in smaller, lighter presses. Cast iron provides excellent compressive strength but can be brittle under extreme pressure.
- Aluminum: In some cases, lightweight presses use aluminum frames, though these are generally limited to low-pressure or mobile units due to aluminum’s lower strength.
2.3. Frame Stability and Stress Distribution
The frame’s design directly impacts the stability and ability to distribute stress during pressing operations. H-frames and four-post frames excel in maintaining stability and distributing pressure evenly across the material, reducing the risk of deformation or damage to the sample.
2.4. Role of the Bed and Base Plates
The bed or base plate is where the lower platen and the material being pressed rest. Base plates must be rigid and durable to ensure they can withstand the forces applied without warping. Base plates may also include slots or grooves for the installation of dies or fixtures used in specific pressing applications.
Press Platens

3.1. Definition and Importance of Platens
Platens are the flat, usually metallic surfaces between which materials are compressed in a laboratory press. They are crucial for delivering consistent pressure across the material, ensuring uniformity in the pressed material’s thickness and structure.
3.2. Types of Platens
Different applications require different platen designs. Common types of platens include:
- Heated Platens: Often used in presses designed for compression molding, laminating, or material testing, heated platens allow materials to be worked under controlled temperature conditions. This is critical for thermoplastics, polymers, and certain composites.
- Cold Platens: These are standard platens with no built-in heating elements. They are ideal for applications where temperature control is unnecessary or where materials may be sensitive to heat.
- Customizable Platens: In specialized applications, platens can be customized to accommodate specific shapes, sizes, or surface textures to better grip or compress unique materials.
3.3. Material Composition of Platens
The material used for constructing platens plays a critical role in their performance:
- Steel Platens: Durable and capable of withstanding high temperatures and pressures, steel is often used for heavy-duty and high-temperature applications.
- Aluminum Platens: These are lighter and provide adequate strength for lower-pressure applications but may deform or degrade at higher temperatures or pressures.
- Ceramic-Coated Platens: Some presses use platens with a ceramic coating to provide excellent temperature stability and resistance to chemical corrosion.
3.4. Uniform Pressure Distribution and Surface Flatness
Ensuring uniform pressure distribution is critical for achieving consistent results in pressing applications. Platens must have extremely flat surfaces, as even small imperfections can result in uneven pressure distribution, which can affect the quality of the pressed material. High-quality platens are machined to be flat within micrometer tolerances.
3.5. Removable and Interchangeable Platens
Many presses allow for the platens to be removed and replaced with different designs, depending on the specific material or application. Interchangeable platens are particularly valuable in research and development settings, where flexibility and customization are key.
Pressure Generation Systems

4.1. Mechanical Pressure Systems (Levers, Screws)
Mechanical pressure systems rely on manual force, often applied via levers, screws, or toggle mechanisms, to generate pressure. While these systems are limited in the amount of force they can generate, they offer simplicity, portability, and ease of use, making them ideal for small-scale, low-pressure applications.
- Lever Mechanisms: In a simple manual press, a lever system multiplies the operator’s force to apply pressure to the material.
- Screw Mechanisms: Screw presses use a rotating screw to generate downward force on the material, offering more precise control than a lever system.
These systems are best suited for tasks such as sample preparation, small-scale compression, or educational purposes, where high pressure is not required.
4.2. Hydraulic Systems (Pumps, Cylinders, Fluid Circuits)
Hydraulic pressure systems use fluid (typically oil) to generate high levels of force. Hydraulic systems are widely used in laboratory presses for heavy-duty applications such as molding, material testing, and high-pressure forming.
- Hydraulic Pump: The pump is responsible for pressurizing the hydraulic fluid and delivering it to the cylinder.
- Hydraulic Cylinder: The cylinder converts the fluid pressure into mechanical force. The cylinder size and fluid pressure determine the total force the press can exert.
- Fluid Circuit: Hydraulic presses use a closed fluid circuit, consisting of hoses, valves, and reservoirs, to manage the flow and pressure of the hydraulic fluid.
Hydraulic systems provide excellent force multiplication and precision, making them ideal for high-pressure tasks. However, they require regular maintenance (such as fluid changes) and are generally more expensive than pneumatic or mechanical systems.
4.3. Pneumatic Systems (Air Cylinders, Compressors, Regulators)
Pneumatic systems use compressed air to generate pressure. They are well-suited for moderate-pressure applications and high-cycle processes, such as laminating, pelletizing, or light-duty molding.
- Compressor: The compressor supplies the press with the compressed air needed to generate force.
- Air Cylinder: Similar to a hydraulic cylinder, the air cylinder converts compressed air into mechanical force.
- Regulator: The regulator controls the air pressure supplied to the press, allowing for precise adjustments to the applied force.
Pneumatic systems are fast, efficient, and require less maintenance than hydraulic systems. However, they are limited in the amount of force they can generate compared to hydraulic presses.
4.4. Electric Pressure Systems (Electric Motors, Servo Systems)
Electric pressure systems use electric motors and sometimes servo systems to generate force. These systems are typically found in high-precision applications where the force and speed need to be finely controlled.
- Electric Motor: The motor drives the press’s mechanical components, providing precise control over the force and speed of the pressing operation.
- Servo Systems: Servo systems provide even greater control by allowing for exact positioning and feedback, making electric presses highly precise.
Electric systems are clean, quiet, and require minimal maintenance. They are ideal for applications such as electronics manufacturing, medical device assembly, and research and development.
4.5. Pressure Control Mechanisms (Manual, Digital)
Each pressure system (mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, electric) requires a means of controlling and regulating the force applied. In manual systems, this control is often achieved through mechanical adjustments such as handwheels or dials. In more advanced systems, digital controllers allow operators to set exact pressure values, which can be maintained automatically throughout the pressing cycle.
Control Systems
5.1. Manual Controls (Levers, Dials, Hand-Wheels)
In basic laboratory presses, control systems are entirely manual. Operators adjust force, speed, and cycle time by manipulating levers, dials, or hand-wheels. While these systems offer simplicity, they lack the precision and repeatability of more advanced electronic controls. Manual controls are typically found in mechanical or manual presses, where high precision is not a priority.
5.2. Electronic Control Panels (Touchscreens, Keypads)
Electronic control panels are more sophisticated than manual controls, offering digital interfaces such as touchscreens or keypads. These panels allow operators to input precise parameters for pressure, temperature, and cycle time. Additionally, electronic control panels often include preset programs for commonly used applications, reducing the risk of operator error.
- Touchscreen Controls: A modern feature in many high-end presses, touchscreens offer a user-friendly interface that makes it easy to set and monitor press parameters.
- Keypad Controls: Older or more basic electronic presses may use keypads for input. These are often paired with digital displays that show the current settings.
5.3. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Automation
In automated laboratory presses, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are used to control the entire pressing process. PLCs allow for a high level of automation, including the ability to set and monitor multiple parameters simultaneously.
- Automated Press Cycles: PLCs enable presses to perform fully automated cycles, reducing the need for operator intervention and ensuring consistent results.
- Remote Monitoring: In some systems, PLCs can be connected to remote monitoring systems, allowing operators to control and monitor the press from a distance, enhancing safety and convenience.
5.4. Feedback Systems (Sensors, Gauges)
Feedback systems are critical for ensuring that the press is operating within the desired parameters. Common feedback devices include:
- Pressure Sensors: These measure the force being applied in real time, allowing for adjustments to be made if the pressure deviates from the set value.
- Temperature Sensors: In presses with heating elements, temperature sensors ensure that the platens remain at the desired temperature.
- Load Cells: These devices measure the actual force being applied to the material, providing real-time data that can be used to adjust the pressure.
5.5. Safety Mechanisms Integrated into Control Systems
Many presses include safety mechanisms within their control systems to prevent accidents or equipment damage. Common features include:
- Overload Protection: Automatically shuts off the press if the pressure exceeds a preset limit.
- Emergency Stop Buttons: Allow operators to halt the press immediately in the event of an emergency.
These systems ensure that presses are safe to operate, even in high-pressure environments.
Heating Elements and Temperature Control

6.1. Importance of Heat in Pressing Operations
For certain materials, especially plastics, polymers, and composites, heat is necessary to soften or activate the material during pressing. Laboratory presses that are used for these applications often include integrated heating elements in their platens.
6.2. Types of Heating Elements (Electric, Infrared, Induction)
The heating elements in laboratory presses come in various forms, depending on the specific application:
- Electric Heaters: The most common type of heating element, electric heaters use resistance wires to generate heat.
- Infrared Heaters: These heaters provide more localized heat, ideal for applications that require rapid heating of specific areas.
- Induction Heaters: Used for high-precision applications, induction heating elements provide fast, even heat without direct contact with the material.
6.3. Temperature Sensors and Thermocouples
To ensure precise temperature control, most laboratory presses include sensors such as thermocouples, which monitor the temperature of the platens in real time. These sensors are often linked to the control system, allowing for automatic adjustments if the temperature deviates from the set value.
6.4. Programmable Heating and Cooling Cycles
Advanced presses allow operators to program specific heating and cooling cycles, making it easy to create consistent, repeatable processes. These cycles may include:
- Ramp-Up Times: Gradually increasing the temperature over time to avoid thermal shock.
- Hold Times: Maintaining a specific temperature for a set period to ensure that the material is evenly heated.
- Cooling Cycles: Some presses include cooling elements to bring the material back to room temperature after pressing.
6.5. Heat Dissipation and Insulation Strategies
Managing heat dissipation is critical in presses that operate at high temperatures. To prevent heat loss and ensure safety, many presses are equipped with insulation around the platens and heating elements. Additionally, heat shields or guards may be used to protect operators from accidental burns.
Pressure Gauges and Monitoring Devices
7.1. Types of Pressure Gauges (Analog, Digital)
Pressure gauges are essential for monitoring the force being applied during pressing. These gauges come in two primary forms:
- Analog Gauges: Traditional pressure gauges that use a mechanical dial to display the force being applied. These are simple and reliable but may not offer the precision required for certain applications.
- Digital Gauges: More modern presses use digital pressure gauges, which offer greater precision and are often easier to read. Digital gauges are typically integrated into the press’s control system, allowing for real-time feedback.
7.2. Load Cells and Pressure Transducers
For high-precision applications, load cells and pressure transducers are used to measure the actual force applied to the material. These devices provide more accurate readings than traditional pressure gauges and can be used to control the press automatically.
7.3. Real-Time Monitoring and Data Logging
Many modern laboratory presses are equipped with systems that allow for real-time monitoring of pressure, temperature, and other parameters. This data can be logged for later analysis, which is particularly useful in research and development settings where documenting the process is critical.
7.4. Alarms and Safety Cutoffs
To prevent equipment damage or operator injury, many presses include alarms that sound if the pressure or temperature exceeds a safe limit. In some cases, the press will automatically shut off if these limits are reached, ensuring safe operation.
7.5. Calibration and Maintenance of Monitoring Devices
To ensure accuracy, pressure gauges and monitoring devices must be regularly calibrated. Calibration typically involves comparing the gauge readings to a known standard and adjusting the device if necessary. Regular maintenance of these devices is essential for ensuring that the press continues to operate within safe and accurate parameters.
Safety Components
8.1. Safety Shields and Guards
Safety is a critical consideration in any laboratory press. Many presses include safety shields or guards that prevent operators from coming into contact with moving parts or hot surfaces during operation. These shields may be made of transparent materials, such as tempered glass or polycarbonate, to allow operators to view the pressing process while remaining protected.
8.2. Emergency Stop Systems
In the event of an emergency, presses are equipped with emergency stop systems that allow the operator to halt the machine immediately. These stop systems are typically large, easily accessible buttons or levers located near the control panel.
8.3. Overload Protection Devices
Overloading a press can cause serious damage to the machine and endanger the operator. To prevent this, many presses include overload protection devices that automatically stop the press if the applied force exceeds the machine’s rated capacity. These devices are critical in preventing damage to both the press and the material being worked.
8.4. Pressure Relief Valves
Hydraulic presses are often equipped with pressure relief valves to release excess fluid pressure in the system. These valves prevent dangerous over-pressurization, which could result in system failure or rupture.
8.5. Operator Safety Standards and Certifications
Laboratory presses must adhere to strict safety standards to ensure they are safe to operate. These standards are often set by regulatory bodies such as CE (Conformité Européenne) marking in Europe or ISO certifications internationally. Manufacturers must meet these standards and provide documentation to prove compliance, ensuring their presses are built to the highest safety standards.
Customizable and Auxiliary Components
9.1. Interchangeable Platens and Dies
Many presses offer interchangeable platens and dies to accommodate different applications. For example, a press may include flat platens for general pressing tasks but can be equipped with custom-shaped dies for forming specific materials. Interchangeable components allow for greater flexibility and make it easier to adapt a press for various uses.
9.2. Vacuum Chambers
Some laboratory presses are equipped with vacuum chambers, which remove air from the pressing area before pressure is applied. This is particularly useful in applications such as composite material manufacturing, where air bubbles can compromise the integrity of the final product.
9.3. Automatic Ejection Systems
In some presses, automatic ejection systems are used to remove the material from the press after the cycle is complete. This is especially useful in high-cycle environments where manual removal would be too time-consuming or labor-intensive.
9.4. Sensors and Automation for Precision Pressing
For high-precision applications, presses may be equipped with additional sensors that monitor parameters such as pressure, temperature, and displacement. These sensors can feed data to an automated control system, ensuring that the press operates within tight tolerances and producing consistent results.
9.5. Cooling Systems and Water Circulation Units
Certain materials, particularly thermoplastics and composites, require controlled cooling after pressing. Some presses are equipped with cooling systems, such as water circulation units, to bring the material back to room temperature quickly and evenly.
Conclusion and Summary of Key Components
In conclusion, the components of a laboratory press are the foundation upon which its performance, efficiency, and safety are built. From the frame and pressure systems to the control mechanisms, platens, and safety features, each component plays a critical role in ensuring that the press operates reliably and consistently.
Choosing the right components for a laboratory press depends on the intended application, as different types of presses and components are better suited for specific tasks. For instance, hydraulic systems are ideal for high-pressure applications, while electric presses offer precision for delicate materials. Likewise, heated platens are essential for thermoplastic molding, while cold platens are sufficient for simpler tasks.
In the future, we can expect laboratory press components to become even more advanced, with greater emphasis on automation, real-time monitoring, and energy efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, laboratory presses will remain an indispensable tool in research, development, and production across numerous industries.
Introduction to Laboratory Presses and Their Applications

Laboratory presses are vital tools used to apply controlled pressure (and sometimes heat) to materials, enabling research, testing, and manufacturing in a variety of fields. These versatile machines can be found in laboratories across numerous industries, ranging from pharmaceuticals and polymers to aerospace and electronics. Laboratory presses are engineered to replicate real-world conditions, allowing researchers and engineers to understand how materials behave under pressure and to develop new products and materials based on precise data.
Laboratory presses are available in various types, including manual, hydraulic, pneumatic, and electric presses, each designed for specific applications. The controlled pressure that these presses apply allows users to manipulate materials in a way that ensures repeatability and accuracy—critical for scientific research and product development. Many modern laboratory presses also feature additional functionalities, such as heating elements for temperature control, programmable cycles, and real-time monitoring of force and other parameters, further enhancing their usefulness across applications.
Laboratory presses are used in a range of testing processes, including mechanical, thermal, and durability tests. They support industries such as pharmaceuticals for drug development, electronics for the manufacturing of circuit boards, and aerospace for the creation of lightweight composites. As technology evolves, so too do the applications of laboratory presses, especially with the growing demand for automation, sustainability, and advanced materials testing.
In this section, we will explore the various applications of laboratory presses in detail, focusing on how they support research, development, manufacturing, and quality control across different industries.
Scientific Research Applications

Laboratory presses play a significant role in scientific research, particularly in fields like material science, chemistry, and earth sciences. In research laboratories, these presses are used to prepare samples for analysis, simulate real-world conditions, and explore the mechanical and thermal properties of materials under controlled pressure and temperature conditions.
2.1. Material Science Research
In material science, laboratory presses are crucial for creating and testing new materials. Researchers use presses to explore the behavior of materials under stress, including how they deform, fracture, or compress under various pressure levels. Laboratory presses are also used to mold materials into specific shapes for further testing or application in real-world scenarios. The ability to control pressure precisely is essential when testing composite materials, ceramics, metals, or nanomaterials, all of which have diverse applications in industries ranging from construction to electronics.
2.2. Polymers and Plastics Development
Polymers and plastics are often tested using laboratory presses to evaluate their behavior under different conditions. Researchers use presses to perform compression molding, which involves applying heat and pressure to polymer samples to form a specific shape. This process helps researchers understand how new polymers will behave in real-world applications, such as in automotive parts, medical devices, or consumer goods.
Laboratory presses are also used to produce films, laminates, and plastic sheets for testing their mechanical and thermal properties. In R&D laboratories, scientists can experiment with polymer blends and composites, creating innovative materials with specific properties like flexibility, strength, or heat resistance.
2.3. Composite Materials Research
Composite materials, made by combining two or more different materials to create a superior product, are widely studied in academic and industrial research settings. Laboratory presses are used to create and test these composites by applying high pressure and heat to bond the materials together. Researchers often focus on creating composites with specific mechanical properties, such as strength-to-weight ratio or heat resistance, which are valuable in industries like aerospace, automotive, and construction.
In research laboratories, the ability to precisely control both the pressure and temperature is critical for ensuring that composite materials exhibit consistent properties. Presses allow researchers to replicate real-world conditions in a controlled environment, ensuring that the materials can withstand the stress and conditions of their intended application.
2.4. Geoscience and Earth Materials
In geosciences, laboratory presses are used to simulate the high-pressure and high-temperature conditions found deep within the Earth. These conditions are important for understanding processes like mineral formation, rock deformation, and tectonic activity. Geoscientists use laboratory presses to study the properties of rocks, minerals, and other earth materials by replicating the conditions of deep-earth environments.
For example, high-pressure presses can be used to replicate the forces experienced by materials in the Earth’s crust or mantle, helping researchers better understand the processes that lead to the formation of mountains, earthquakes, and volcanic activity. These presses are also valuable in paleontology for studying fossilized materials under controlled pressure conditions.
Material Testing Applications

Material testing is one of the most critical applications of laboratory presses across various industries. Laboratory presses are used to apply controlled pressure to test a material’s strength, durability, hardness, and thermal properties. These tests help ensure that materials meet the necessary quality and safety standards before they are used in production or consumer products.
3.1. Mechanical Testing (Compression, Tensile, Shear, etc.)
Laboratory presses are commonly used to perform mechanical tests on materials, including compression, tensile, and shear tests. In compression testing, materials are subjected to a controlled compressive force to determine their behavior under load. Compression tests are widely used to evaluate the strength and stiffness of materials like metals, plastics, and composites.
- Tensile Testing: Tensile testing involves stretching a material until it fractures. Laboratory presses are used to apply a steady force to the material, measuring how much stress it can withstand before breaking. This is particularly important for materials used in construction, automotive, and aerospace applications, where strength and durability are crucial.
- Shear Testing: Shear tests involve applying force parallel to a material’s surface to evaluate its shear strength. This type of testing is essential for materials used in joints, rivets, or any application where the material will experience forces in different directions.
Laboratory presses provide the controlled environment necessary for these mechanical tests, ensuring that the results are repeatable and accurate.
3.2. Thermal Testing (DSC, TGA)
Thermal testing helps determine how materials respond to changes in temperature. Laboratory presses, equipped with heating elements, are used to apply controlled heat while compressing materials, simulating real-world conditions in which materials are exposed to both heat and mechanical stress. Two common types of thermal testing are:
- Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC): DSC measures the heat flow into or out of a material as it is heated or cooled. Laboratory presses can be equipped with thermal control systems to compress materials while recording changes in thermal properties.
- Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA): TGA measures the weight change of a material as it is subjected to heat. Laboratory presses with integrated heating elements are used to compress materials and assess their thermal stability or decomposition rates.
Thermal testing is especially important in industries where materials will be exposed to high temperatures, such as in aerospace, automotive, or electronics applications.
3.3. Hardness and Durability Tests
Hardness testing involves applying force to a material to determine how resistant it is to indentation, scratching, or abrasion. Laboratory presses are used in hardness tests like Rockwell, Brinell, or Vickers hardness tests, where controlled pressure is applied using a specific indenter shape and force.
Durability testing evaluates a material’s ability to withstand repeated loading or stress over time. Laboratory presses are used to simulate real-world conditions by applying repeated compressive or tensile forces to materials, helping determine their long-term performance in applications such as construction materials, automotive parts, and consumer goods.
3.4. Wear and Tear Tests
Wear and tear tests help manufacturers understand how materials will behave over time when subjected to friction, impact, or environmental stressors. Laboratory presses are used to apply controlled pressure and friction to materials to simulate real-world wear conditions. These tests are especially valuable for industries like automotive and aerospace, where materials are expected to endure extreme conditions over long periods.
Laboratory presses used in wear testing may be equipped with specialized platens that simulate abrasive surfaces, and the results of these tests can be used to improve the durability of products like tires, brakes, and engine components.
3.5. Fatigue Testing
Fatigue testing involves applying repeated or cyclical loads to a material to evaluate how it performs under long-term stress. Laboratory presses can simulate the repeated application of force over time, providing insights into how materials will perform in real-world applications. Fatigue testing is crucial for industries like construction, transportation, and aerospace, where materials must withstand constant loading and unloading cycles.
By subjecting materials to controlled cycles of compression or tension, laboratory presses help engineers and scientists understand when and how materials will fail due to fatigue. This information is critical for improving the design and safety of products that experience repeated stress, such as bridges, buildings, and aircraft components.
Pharmaceutical Applications
In the pharmaceutical industry, laboratory presses are essential tools for drug development, formulation, and quality control. From tablet pressing to the creation of drug delivery systems, laboratory presses ensure that pharmaceutical products meet stringent quality and safety standards.
4.1. Tablet Compression and Formulation
One of the most critical applications of laboratory presses in the pharmaceutical industry is tablet compression. Tablets are created by compressing powders into a solid form using a tablet press. Laboratory-scale tablet presses are used during the development phase to create sample batches for testing, enabling researchers to fine-tune formulations and ensure the correct dosage of active ingredients.
Laboratory presses allow pharmaceutical companies to simulate the conditions of large-scale tablet production, helping to identify potential issues with powder flow, compression, and tablet hardness before scaling up production. Additionally, presses are used to test different excipient formulations, ensuring that tablets have the necessary properties, such as disintegration time and dissolution rate, to be effective in delivering the drug.
4.2. Granulation and Pelletizing
In addition to tablet pressing, laboratory presses are used in the granulation and pelletizing processes. Granulation involves forming small particles (granules) from powders to improve flowability and compressibility. This process is essential in ensuring consistent tablet production. Pelletizing involves compressing powders into small, uniform spheres or pellets that can be used in various drug delivery systems, such as capsules or modified-release formulations.
Laboratory presses provide the controlled environment necessary for developing and optimizing granulation and pelletizing processes. Researchers use these presses to test different formulations and processing conditions, ensuring that the final product meets the desired specifications.
4.3. Drug Development and R&D Testing
Laboratory presses play an important role in the early stages of drug development and research. Researchers use presses to compress active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients into tablets for initial testing. This allows them to evaluate how the drug will perform in vivo, including its dissolution rate, bioavailability, and stability.
Presses are also used to create samples for clinical trials, ensuring that the drug meets all regulatory requirements before moving into large-scale production. This is especially important in the development of new drug formulations, where laboratory presses provide the precision and control needed to create consistent, high-quality samples.
4.4. Medical Device Manufacturing
In addition to pharmaceuticals, laboratory presses are used in the manufacturing of medical devices. Many medical devices, such as implants, catheters, and drug delivery systems, are made from polymers that require controlled pressure and heat during the manufacturing process.
Laboratory presses are used to form and bond these materials, ensuring that the devices meet strict quality and safety standards. For example, polymeric materials used in medical implants must be strong, biocompatible, and able to withstand the mechanical stresses of the human body. Laboratory presses are used to test and refine these materials during the development process.
Polymers and Plastics Industry Applications

The polymers and plastics industry relies heavily on laboratory presses for both product development and quality control. Laboratory presses are used to mold, shape, and test plastic materials, helping manufacturers create high-performance products for a variety of applications.
5.1. Compression Molding of Thermoplastics
Compression molding is a common process used to create plastic parts by applying heat and pressure to a polymer material in a mold. Laboratory presses are used for small-scale compression molding, allowing researchers and manufacturers to develop and test new thermoplastic materials before moving into full-scale production.
In a laboratory setting, researchers can experiment with different polymer blends, additives, and processing conditions to create materials with specific properties, such as impact resistance, heat tolerance, or flexibility. Laboratory presses provide the controlled environment necessary for these experiments, ensuring that the results are repeatable and accurate.
5.2. Film Casting and Lamination
Laboratory presses are used to create plastic films and laminates for testing and product development. Films are created by applying pressure and heat to a polymer material, which is then stretched into a thin sheet. Laminates are formed by pressing multiple layers of material together, creating a composite with improved strength, flexibility, or barrier properties.
Film casting and lamination processes are used in a variety of industries, including packaging, automotive, and electronics. Laboratory presses allow manufacturers to develop and test new materials with specific properties, such as moisture resistance, UV protection, or transparency, ensuring that they meet the needs of their intended application.
5.3. R&D for Plastic Materials
The development of new plastic materials requires extensive research and testing. Laboratory presses are essential tools in this process, allowing researchers to compress, mold, and test plastic samples under controlled conditions. These presses are used to create prototype materials for testing mechanical properties, such as tensile strength, flexibility, and heat resistance.
Laboratory presses are also used to test the performance of plastic materials under real-world conditions. For example, researchers can simulate the effects of long-term exposure to heat, moisture, or UV light, helping them develop materials that are more durable and better suited to specific applications.
5.4. Quality Control and Batch Testing
In the production of plastic materials, quality control is essential to ensure that the final product meets industry standards and customer specifications. Laboratory presses are used to perform batch testing, where small samples of material are compressed and tested to ensure consistency and quality.
Presses are used to measure properties like density, hardness, and flexibility, helping manufacturers identify any potential issues before full-scale production begins. By using laboratory presses for batch testing, manufacturers can ensure that their plastic products meet all necessary requirements, reducing the risk of defects or failures in the final product.
Electronics and Semiconductor Applications
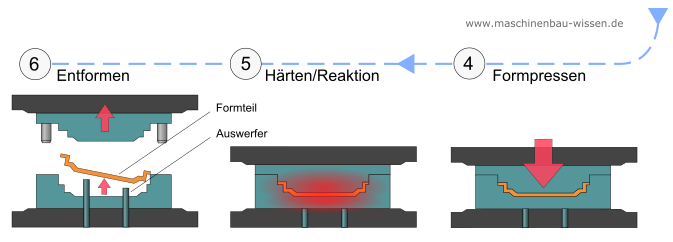
The electronics and semiconductor industries rely on laboratory presses for precision manufacturing and quality control. From creating printed circuit boards (PCBs) to encapsulating delicate components, laboratory presses play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and performance of electronic devices.
6.1. PCB Lamination and Bonding
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the foundation of modern electronics, and laboratory presses are used in the PCB manufacturing process to laminate multiple layers of material together. This lamination process involves applying pressure and heat to bond the layers, creating a solid and durable PCB that can support the electrical components of the device.
Laboratory presses are also used to bond flexible PCBs, which are used in applications like smartphones, wearables, and medical devices. The ability to control pressure and temperature precisely ensures that the bonding process is consistent and reliable, reducing the risk of defects in the final product.
6.2. Encapsulation of Components
Many electronic components, such as integrated circuits (ICs), sensors, and chips, need to be protected from environmental factors like moisture, dust, and heat. Laboratory presses are used to encapsulate these components in protective materials, ensuring that they remain functional and reliable in various conditions.
Encapsulation involves compressing a protective material, such as epoxy or silicone, around the component. Laboratory presses provide the controlled environment necessary to ensure that the encapsulation material is applied evenly and consistently, protecting the component without damaging it.
6.3. Wafer Bonding and Packaging
In semiconductor manufacturing, wafer bonding is a critical process that involves bonding two or more silicon wafers together to create complex electronic devices. Laboratory presses are used to apply the precise pressure and temperature needed to bond these wafers without damaging the delicate electronic structures within.
In addition to wafer bonding, laboratory presses are used in the packaging of semiconductor devices. Packaging involves encasing the semiconductor chip in a protective material that shields it from environmental factors and provides a way to connect the chip to the external circuitry.
6.4. Flexible Electronics and Sensors
Flexible electronics, such as bendable displays, sensors, and wearable devices, are becoming increasingly popular in the consumer electronics market. Laboratory presses are used in the development and production of these flexible electronics by bonding, laminating, and encapsulating the various layers of material.
Flexible electronics require materials that can withstand repeated bending and flexing without losing their functionality. Laboratory presses allow researchers and manufacturers to test these materials under real-world conditions, ensuring that they are durable and reliable in their intended applications.
Automotive and Aerospace Applications
The automotive and aerospace industries rely heavily on laboratory presses for the development and testing of high-performance materials, such as composites, polymers, and metals. These industries demand materials that are strong, lightweight, and capable of withstanding extreme conditions, making laboratory presses essential for both research and quality control.
7.1. Composite Materials for Lightweight Structures
Composite materials, which combine multiple materials to create a product with superior properties, are widely used in both the automotive and aerospace industries. Laboratory presses are used to create and test these composites by applying controlled pressure and heat to bond the materials together.
In the automotive industry, composites are used to create lightweight components that improve fuel efficiency without sacrificing strength. In the aerospace industry, composites are used in aircraft structures to reduce weight and improve performance. Laboratory presses allow manufacturers to develop and test these materials, ensuring that they meet the necessary performance standards.
7.2. Development of High-Performance Materials
High-performance materials, such as carbon fiber, ceramics, and metal alloys, are critical for the automotive and aerospace industries. These materials need to withstand extreme temperatures, pressures, and mechanical stresses, making laboratory presses an essential tool for their development.
Researchers use laboratory presses to simulate the conditions that these materials will face in real-world applications, helping them refine the materials and improve their performance. This is particularly important in the aerospace industry, where materials must meet strict safety and performance standards to ensure the safety of passengers and crew.
7.3. Testing of Structural Components
Laboratory presses are also used to test the structural components of vehicles and aircraft. For example, presses can simulate the forces experienced by an aircraft’s wings during flight or the impact forces on a car’s chassis during a collision. These tests help engineers understand how the materials and components will behave under stress, allowing them to design safer and more efficient vehicles.
7.4. Simulation of Extreme Conditions
Both the automotive and aerospace industries require materials that can perform in extreme conditions, such as high temperatures, high pressures, and exposure to chemicals or radiation. Laboratory presses are used to simulate these conditions in a controlled environment, helping manufacturers develop materials that can withstand the rigors of space travel, high-speed flight, or harsh operating environments.
Other Specialized Industrial Applications
Laboratory presses are used in a wide range of specialized industrial applications beyond the fields of pharmaceuticals, plastics, electronics, and aerospace. These presses support industries as diverse as forensic science, energy, food science, medical devices, and environmental science, each requiring precise control over pressure and temperature for testing and manufacturing.
8.1. Forensic Science Applications
In forensic science, laboratory presses are used to create casts of impressions, such as shoe prints, tire tracks, or tool marks. These casts are used to analyze the evidence collected from crime scenes, helping forensic scientists identify suspects or reconstruct events. Laboratory presses provide the controlled pressure needed to create accurate and detailed casts of these impressions.
Laboratory presses are also used in forensic laboratories to prepare samples for analysis. For example, bone or tissue samples may be compressed into thin sections for microscopic examination, allowing forensic scientists to identify traces of chemicals, drugs, or other substances.
8.2. Energy Sector (Fuel Cells, Batteries)
The energy sector relies on laboratory presses for the development and testing of advanced energy storage systems, such as fuel cells, batteries, and supercapacitors. Laboratory presses are used to compress and assemble the layers of materials needed for these devices, ensuring that they are both efficient and durable.
In the development of fuel cells, for example, laboratory presses are used to apply controlled pressure to the proton exchange membrane (PEM) and electrode layers, ensuring that they are properly bonded and will perform reliably in real-world conditions. Similarly, in battery manufacturing, laboratory presses are used to assemble the electrodes and separators, ensuring that the battery will function as intended.
8.3. Food Science and Packaging Testing
In the food industry, laboratory presses are used to test the strength, durability, and barrier properties of packaging materials. For example, presses are used to compress and test plastic films, paperboard, or metal foils used in food packaging to ensure that they will protect the product during transportation and storage.
Laboratory presses are also used in food science research to analyze the texture and compressibility of food products. For example, researchers may use a press to measure the firmness of fruits or vegetables or to test the structural integrity of baked goods. These tests help food manufacturers improve the quality and consistency of their products.
8.4. Medical and Dental Materials
In the medical and dental fields, laboratory presses are used to develop and test materials used in implants, prosthetics, and dental restorations. These materials need to be strong, biocompatible, and capable of withstanding the mechanical stresses of the human body.
Laboratory presses are used to form and test these materials, ensuring that they meet the necessary performance and safety standards. For example, laboratory presses are used to compress and shape dental ceramics, ensuring that they are strong enough to withstand the forces of biting and chewing. Similarly, presses are used to form medical-grade polymers used in implants and prosthetics.
8.5. Environmental Science and Waste Management
In environmental science, laboratory presses are used to prepare samples for analysis, such as compressing soil, sediment, or waste materials into thin sections for examination. These samples are used to study the environmental impact of human activity, assess the quality of natural resources, or monitor pollution levels.
Laboratory presses are also used in waste management to test the compressibility and durability of materials used in waste containment, such as liners or covers for landfills. These tests help ensure that the materials will perform effectively in containing waste and preventing environmental contamination.
Future Trends in Laboratory Press Applications
As technology continues to evolve, laboratory presses are becoming more advanced, with new features and capabilities that are transforming the way they are used in research and industry. In this section, we will explore some of the emerging trends in laboratory press applications.
9.1. Automation and Smart Presses
One of the most significant trends in laboratory presses is the increasing use of automation. Automated laboratory presses are capable of performing complex tasks with minimal operator intervention, improving efficiency and consistency in testing and manufacturing processes.
Smart presses, equipped with sensors, data logging, and real-time feedback systems, allow users to monitor and adjust press parameters remotely. This level of control and automation is particularly valuable in industries like pharmaceuticals, electronics, and materials science, where precision and repeatability are critical.
9.2. Advanced Material Testing
With the development of new materials, such as nanomaterials, graphene, and advanced composites, laboratory presses are evolving to meet the demands of these cutting-edge fields. Presses are now being designed with greater precision, higher pressure capacities, and more advanced temperature control systems, allowing researchers to test these materials under extreme conditions.
For example, laboratory presses are being used to study the behavior of graphene under high pressure and temperature, helping researchers understand its potential applications in electronics, energy storage, and other fields.
9.3. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
As industries increasingly focus on sustainability and reducing their environmental impact, laboratory presses are being developed with energy efficiency in mind. Electric presses, which are more energy-efficient than hydraulic or pneumatic models, are becoming more popular in laboratories and manufacturing facilities.
In addition, presses are being designed to use fewer materials, reduce waste, and operate more efficiently, helping industries minimize their carbon footprint and reduce their reliance on non-renewable resources.
9.4. Integration with Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0, the integration of digital technologies into manufacturing processes, is transforming the way laboratory presses are used in industrial settings. Laboratory presses equipped with digital controls, sensors, and data analytics are becoming an integral part of smart factories, where they can be monitored and controlled in real time.
This integration allows for greater flexibility, precision, and efficiency in testing and manufacturing processes, helping industries adapt to changing demands and improve the quality of their products.
Conclusion
Laboratory presses are essential tools across a wide range of industries, from pharmaceuticals and electronics to aerospace and energy. These versatile machines allow researchers, engineers, and manufacturers to test materials, develop new products, and ensure the quality and safety of their processes.
The applications of laboratory presses are vast and diverse, ranging from tablet compression in pharmaceuticals to wafer bonding in semiconductor manufacturing. Laboratory presses are also used in scientific research, material testing, and quality control, helping industries create better products and advance technological innovation.
As laboratory presses continue to evolve, with new features like automation, real-time monitoring, and advanced material testing capabilities, their role in industry will only grow. The future of laboratory presses lies in their ability to adapt to the demands of modern manufacturing, sustainability, and advanced materials, making them indispensable tools for research, development, and production in the 21st century.
A laboratory press is a device used in laboratories to compress or mold materials into desired shapes. It is a versatile tool that can be used for a wide variety of applications, including:
- Creating pellets from powdered materials
- Compacting samples for spectroscopy or other analytical techniques
- Forming tablets for pharmaceutical or cosmetic applications
- Testing the strength and properties of materials
- Laminating materials together
Laboratory presses typically consist of a frame that houses a hydraulic or mechanical press mechanism. The material to be compressed is placed between two platens, and the press is activated to apply pressure. The amount of pressure can be controlled by adjusting the settings of the press.
There are two main types of laboratory presses:
- Hydraulic presses use hydraulic fluid to apply pressure. They are generally more powerful than mechanical presses and can be used to compress a wider range of materials.
- Mechanical presses use gears or levers to apply pressure. They are generally less powerful than hydraulic presses but are simpler to operate and maintain.
Laboratory presses are available in a variety of sizes and capacities to accommodate different applications. They are typically benchtop instruments, but larger models are also available for industrial applications.
Here are some of the benefits of using a laboratory press:
- Versatility: Laboratory presses can be used for a wide variety of applications.
- Accuracy: Laboratory presses can apply precise amounts of pressure, which is important for many applications.
- Reproducibility: Laboratory presses can produce consistent results, which is important for research and development.
- Safety: Laboratory presses are equipped with safety features to protect the operator.
Here are some of the applications of laboratory presses:
- Pharmaceutical industry: Laboratory presses are used to create tablets, capsules, and other dosage forms.
- Cosmetics industry: Laboratory presses are used to create compacts, powders, and other cosmetic products.
- Materials science: Laboratory presses are used to test the strength and properties of materials.
- Metallurgy: Laboratory presses are used to compact metal powders into forms that can be further processed.
- Geology: Laboratory presses are used to create thin sections of rocks and minerals for microscopy.
Laboratory presses are an essential tool for scientists, engineers, and technicians in a variety of industries. They are versatile, accurate, and safe, making them an ideal choice for a wide range of applications.
Hydraulic Laboratory Press

A hydraulic laboratory press is a versatile and powerful tool used in a variety of applications, such as compacting powders, forming tablets, and testing materials. It consists of a frame that houses a hydraulic cylinder and a piston, which is used to apply force to the material being compressed.
Key components of a hydraulic laboratory press:
- Frame: The frame provides the structural support for the press and houses the hydraulic cylinder and piston. It is typically made of steel or aluminum and is designed to withstand the high pressures generated by the press.
- Hydraulic cylinder: The hydraulic cylinder is the heart of the press and is responsible for generating the force that compresses the material. It consists of a cylinder filled with hydraulic fluid and a piston that moves back and forth within the cylinder.
- Piston: The piston is the moving part of the hydraulic cylinder and is responsible for applying force to the material being compressed. It is typically made of steel or aluminum and has a flat or spherical surface that comes into contact with the material.
- Valves: Valves control the flow of hydraulic fluid into and out of the hydraulic cylinder. They are responsible for adjusting the pressure and speed of the press.
- Controls: Controls allow the operator to set the desired pressure, speed, and cycle time for the press. They typically include a pressure gauge, a timer, and a switch to activate the press.
Applications of hydraulic laboratory presses:
- Compacting powders: Hydraulic presses are commonly used to compact powders into pellets, tablets, or other shapes. This is a common technique used in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries.
- Forming tablets: Tablets are an important form of medication and are typically made by compressing powdered ingredients into a solid form. Hydraulic presses are used to compress powders at high pressures to ensure that the tablets are strong and durable.
- Testing materials: Hydraulic presses are also used to test the properties of materials, such as their strength, ductility, and toughness. This is done by compressing a sample of the material to a specific pressure and measuring the resulting deformation.
- Laminating materials: Hydraulic presses can be used to laminate materials together, such as plastics, metals, and ceramics. This is a common technique used in the manufacturing of various products.
Advantages of hydraulic laboratory presses:
- High pressure: Hydraulic presses can generate very high pressures, which makes them ideal for applications that require compaction or forming of materials.
- Power: Hydraulic presses are very powerful and can handle a wide range of materials, including hard and brittle materials.
- Controllability: Hydraulic presses are very controllable and can be precisely adjusted to the desired pressure and speed.
- Versatility: Hydraulic presses are versatile and can be used for a wide variety of applications.
Disadvantages of hydraulic laboratory presses:
- Complexity: Hydraulic presses are more complex than mechanical presses and require more maintenance.
- Cost: Hydraulic presses are typically more expensive than mechanical presses.
- Safety: Hydraulic presses can be dangerous if not used properly, and operators must be trained and follow safety procedures.
Overall, hydraulic laboratory presses are powerful, versatile, and controllable tools that are used in a wide variety of applications. Their ability to generate high pressures makes them ideal for compacting and forming materials, while their controllability allows them to be used for a wide range of tasks. However, their complexity, cost, and safety considerations need to be carefully weighed before selecting a hydraulic laboratory press for a particular application.
Mechanical Laboratory Press

A mechanical laboratory press is a versatile and reliable tool used in various applications, such as compacting powders, forming tablets, and testing materials. It utilizes mechanical force to apply pressure to the material being compressed, typically employing gears or levers to achieve the desired force.
Key Components of a Mechanical Laboratory Press:
- Frame: The sturdy frame provides the structural support for the press, housing the mechanical components and ensuring stability during operation. It is typically constructed from durable materials like steel or aluminum.
- Platens: Platens are the flat surfaces that come into direct contact with the material being pressed. They are typically made of hardened steel or other wear-resistant materials to withstand the high pressures and prevent damage.
- Mechanical Drive System: The mechanical drive system is responsible for generating the force that compresses the material. It consists of gears, levers, or other mechanical components that transfer force from the input source to the platens.
- Adjustment Mechanisms: Adjustment mechanisms allow for precise control of the pressing force and platen positioning. These mechanisms can include hand cranks, calibrated dials, or digital controls.
- Safety Features: Mechanical laboratory presses are equipped with safety features to protect the operator from potential hazards, such as safety guards, emergency stop buttons, and overload protection systems.
Applications of Mechanical Laboratory Presses:
- Compacting Powders: Mechanical presses are commonly used to compact powders into pellets, tablets, or other shapes. This is a common technique used in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries.
- Forming Tablets: Tablets are an important form of medication and are typically made by compressing powdered ingredients into a solid form. Mechanical presses are used to compress powders at moderate pressures to ensure that the tablets are strong and durable.
- Testing Materials: Mechanical presses are also used to test the properties of materials, such as their strength, ductility, and hardness. This is done by compressing a sample of the material to a specific force and measuring the resulting deformation.
- Laminating Materials: Mechanical presses can be used to laminate materials together, such as plastics, metals, and composites. This is a common technique used in the manufacturing of various products.
Advantages of Mechanical Laboratory Presses:
- Simplicity: Mechanical presses are relatively simple in design and operation, making them easy to maintain and troubleshoot.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Mechanical presses are typically less expensive than hydraulic presses, making them a more economical option for many applications.
- Durability: Mechanical presses are built to withstand demanding conditions and can provide years of reliable service.
- Safety: Mechanical presses generally offer a lower risk of operational hazards compared to hydraulic presses.
Disadvantages of Mechanical Laboratory Presses:
- Limited Pressure Range: Mechanical presses typically have a lower maximum pressure range compared to hydraulic presses.
- Manual Operation: Some mechanical presses require manual operation, which can be time-consuming and less efficient for high-volume applications.
- Precision Control: Mechanical presses may have less precise control over pressure and speed compared to some hydraulic presses.
In summary, mechanical laboratory presses offer a balance of simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and durability, making them suitable for various applications in laboratories and manufacturing settings. Their suitability depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as the desired pressure range, production volume, and precision control needs.
Application Areas

Laboratory presses find application in a variety of scientific and industrial fields where controlled pressure is essential for research, experimentation, and quality control. Here are some of the key application areas for laboratory presses:
- Materials Science and Research:
- Testing the mechanical properties of materials, including compression and tensile strength measurements.
- Conducting studies on material behavior under different pressure conditions.
- Research on material deformation and stress analysis.
- Chemistry and Chemical Research:
- Pressing powders into pellets or tablets for spectroscopic analysis, such as X-ray diffraction (XRD) or Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy.
- Sample preparation for chemical analysis and quality control.
- Geology and Soil Science:
- Consolidating soil or rock samples into standardized shapes and sizes for laboratory testing.
- Studying the mechanical properties and behavior of geological materials under various pressures.
- Pharmaceuticals and Drug Development:
- Compacting pharmaceutical powders into tablets for dosage uniformity and dissolution testing.
- Research on the compression behavior of pharmaceutical formulations.
- Material Quality Control:
- Ensuring the quality and consistency of materials in manufacturing processes, such as ceramics, polymers, and metals.
- Assessing the durability and performance of materials used in construction and engineering.
- Sample Preparation for Spectroscopy:
- Preparing thin pellet samples for X-ray spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and other spectroscopic techniques.
- Particle Size Analysis:
- Preparing solid samples for particle size analysis methods like sieving, laser diffraction, and sedimentation.
- Biomedical and Life Sciences:
- Studying the mechanical properties of biological tissues and biomaterials.
- Sample preparation for research on tissue engineering and drug delivery systems.
- Quality Control in Manufacturing:
- Ensuring the consistency and quality of manufactured products by testing materials and components under controlled pressure conditions.
- Aerospace and Automotive:
- Evaluating the structural integrity of materials and components used in aerospace and automotive industries.
- Research on materials for lightweighting and fuel efficiency.
- Energy and Renewable Resources:
- Research on the behavior of materials under high pressure for applications in energy generation, including geothermal and hydrocarbon extraction.
- Testing materials used in renewable energy technologies such as solar cells and batteries.
- Educational and Training:
- Laboratory presses are used in educational institutions for hands-on learning and experiments in physics, materials science, and engineering programs.
- Custom Research Projects:
- Laboratory presses can be adapted for custom research projects and specialized applications, making them versatile tools in research and development.
Laboratory presses are essential equipment in various fields, providing researchers and engineers with the means to study material behavior, conduct experiments, and ensure the quality and reliability of materials and products in diverse applications.
EMS Metalworking Machinery: Your Trusted Partner in Precision Metalworking

EMS Metalworking Machinery is a leading manufacturer of high-quality metalworking equipment, dedicated to providing innovative solutions that meet the evolving needs of industries worldwide. With a rich history of excellence and a commitment to technological advancement, we have earned a reputation for delivering cutting-edge machinery that ensures precision, efficiency, and durability.
Our Product Range:
- CNC Spinning Lathes: From precision bench lathes to heavy-duty industrial models, our lathes offer unmatched accuracy and performance for a wide range of applications, including machining shafts, gears, and other cylindrical components.
- Trimming Beading Machine: Our trimming beading machines are designed to provide exceptional cutting capabilities and versatility, enabling you to create complex shapes and intricate details with ease. Whether you need a horizontal or vertical trimming machine, we have the perfect solution for your needs.
- Hydraulic Deep Drawing Press Machines: Our hydraulic deep drawing press machines are built to deliver precise and powerful drawing operations, ensuring clean holes and exceptional surface finishes. We offer a comprehensive range to suit various applications.
- Grinding Machines: Our grinding machines are engineered for precision and efficiency, allowing you to achieve the highest levels of surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Whether you need a surface grinder, cylindrical grinder, or tool grinder, we have the equipment to meet your specific requirements.
- Sawing Machines: Our sawing machines are designed for fast and accurate cutting of metals, providing clean cuts and minimal burrs. From band saws to circular saws, we offer a variety of options to suit different materials and cutting needs.
- Custom Machinery: In addition to our standard product line, we also specialize in custom machinery fabrication. Our experienced engineers can work with you to design and build tailored solutions that meet your unique requirements and optimize your production processes.
Why Choose EMS Metalworking Machinery:
- Quality: Our machines are crafted with the highest quality materials and components, ensuring long-lasting performance and reliability.
- Precision: We are committed to delivering machinery that meets the most stringent tolerances and standards, ensuring exceptional accuracy in your metalworking operations.
- Innovation: We continuously invest in research and development to stay at the forefront of technological advancements, offering innovative solutions that enhance your productivity and efficiency.
- Customer Support: Our dedicated team of experts is always available to provide comprehensive support, from machine selection and installation to maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Customization: We understand that every business has unique needs, and we offer flexible customization options to tailor our machines to your specific requirements.
At EMS Metalworking Machinery, we are more than just a supplier of equipment; we are your trusted partner in metalworking success. By choosing EMS, you can be confident in the quality, reliability, and performance of your machinery, enabling you to achieve your business goals and stay ahead of the competition.
Laboratory presses

Laboratory presses are essential tools used across a wide range of industries and scientific disciplines. These presses apply controlled pressure (and often heat) to materials, enabling users to carry out material testing, compression, molding, laminating, and other processes under specific conditions. Laboratory presses serve a variety of functions in research, development, and production environments, including pharmaceuticals, electronics, material sciences, and engineering.
As technology advances, laboratory presses have become more sophisticated, offering enhanced precision, control, and safety. They provide critical support in scientific research by helping researchers and manufacturers understand the physical properties of materials under different stress conditions, such as pressure, heat, or mechanical force. The ability to control these variables in a laboratory setting allows for accurate simulations of real-world conditions, making laboratory presses indispensable tools for product development and material testing.
From early, manually-operated presses to today’s automated, programmable models, the evolution of laboratory presses reflects the increasing demand for precision and efficiency. Early presses were relatively simple devices that relied on manual force, but modern versions incorporate hydraulic, pneumatic, or electric systems to generate force, often coupled with digital control systems for precise pressure and temperature regulation.
This comprehensive exploration of laboratory press advantages will outline their numerous benefits, detailing how they improve efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness in various applications, supporting industries in creating high-quality products, advancing research, and ensuring safety.
Precision and Control
One of the greatest advantages of laboratory presses is their ability to provide high levels of precision and control. This is crucial in laboratory and industrial environments where consistency and accuracy are paramount.
2.1. Importance of Precision in Laboratory Applications
In scientific research and product development, precise pressure and temperature application is critical for producing reliable and repeatable results. Laboratory presses allow for fine-tuned control over the amount of force applied to a material, ensuring that every test or production cycle is consistent. This precision is especially important in industries like pharmaceuticals, where even slight variations in tablet compression could result in altered dosage effectiveness.
2.2. Advanced Pressure and Temperature Control Systems
Modern laboratory presses come equipped with advanced control systems that allow users to set precise parameters for both pressure and temperature. These systems often include digital interfaces that display real-time data, making it easier for operators to monitor and adjust settings during the process. Many presses also offer programmable cycles, enabling researchers to replicate specific conditions repeatedly, which is essential for long-term testing or production runs.
The integration of servo motors or hydraulic actuators into laboratory presses enhances their ability to maintain constant pressure throughout the pressing cycle. Additionally, the availability of fine-grain adjustments (such as adjusting pressure in small increments) provides even greater control over the experiment or process.
2.3. Digital Interfaces for Enhanced Accuracy
The shift from mechanical to digital interfaces in laboratory presses has greatly improved accuracy and ease of use. Digital touchscreens and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) allow users to enter precise values for pressure, temperature, and timing, reducing the risk of human error. Many presses also offer pre-programmed settings for common applications, allowing operators to quickly configure the press for their specific task.
Digital control systems often include real-time feedback mechanisms that monitor pressure and temperature throughout the pressing cycle. This enables operators to identify and correct issues before they affect the outcome, ensuring consistent results every time.
2.4. Consistency and Repeatability in Experimental Results
Laboratory presses play a vital role in ensuring repeatability—the ability to replicate the same results across multiple tests or production cycles. This is particularly important in fields like material science, where researchers need to understand how materials behave under specific conditions. With a laboratory press, scientists can precisely control variables such as pressure and heat, ensuring that each experiment is conducted under identical conditions.
In industrial settings, this repeatability is equally important. Manufacturers rely on laboratory presses to produce consistent results, whether they are creating batches of pharmaceuticals or testing the durability of new materials. By ensuring that each cycle of the press is consistent, manufacturers can maintain high-quality standards and minimize defects.
Versatility Across Multiple Applications
Laboratory presses are incredibly versatile machines, designed to adapt to a variety of applications across multiple industries. This versatility is one of their key advantages, as it enables users to employ the same piece of equipment for different purposes, reducing the need for multiple specialized machines.
3.1. Adaptability to Various Industries
One of the reasons laboratory presses are so widely used is their adaptability. From pharmaceuticals to aerospace, these machines serve diverse industries. For example:
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Laboratory presses are used to compress powders into tablets, ensuring uniformity and proper dosage.
- Material Science: Researchers use presses to explore the mechanical properties of materials like polymers, metals, and composites under various conditions.
- Electronics: Presses are utilized in the creation of laminated circuit boards and for encapsulating delicate electronic components.
- Automotive and Aerospace: Laboratory presses are used to create lightweight composite materials and simulate the extreme conditions that materials will face in these industries.
3.2. Supporting Different Materials
Another significant advantage of laboratory presses is their ability to handle a wide range of materials. Whether working with fragile biological samples, polymers, metals, ceramics, or composites, these presses can be adjusted to suit the material’s unique properties. This makes them essential tools for researchers and manufacturers who work with multiple materials or are developing new materials.
For instance, laboratory presses are widely used in the plastics industry to test thermoplastics and create samples for durability and flexibility testing. In metallurgy, they are used to compress metal powders into solid parts, and in composite material research, they help create new blends with improved properties for industries like construction and aviation.
3.3. Flexibility in Research and Development
In research and development (R&D) environments, flexibility is a key asset. Laboratory presses allow researchers to conduct a variety of experiments, from compression molding to laminating and sample preparation, all on the same machine. The ability to control pressure and temperature precisely also makes it easier for researchers to develop and test new materials under realistic conditions.
The modular nature of many laboratory presses means they can be customized to fit specific R&D needs. Whether it’s integrating vacuum capabilities for materials that require a low-oxygen environment or adding heating platens for experiments with polymers, laboratory presses can be tailored to support specific research projects.
3.4. Customization Options for Specialized Applications
Many laboratory presses offer customization options that enhance their versatility. These options include interchangeable platens, specialized dies, or attachments that allow the press to perform unique functions. For example:
- Heated Platens: Often used in applications where materials need to be processed at high temperatures, such as in the molding of thermoplastic materials.
- Vacuum Chambers: For pressing materials that are sensitive to air or require the removal of bubbles during compression.
- Custom Dies and Attachments: In industries like pharmaceuticals, custom dies are used to create tablets of specific shapes and sizes.
This adaptability allows laboratory presses to meet the needs of diverse applications while maintaining high levels of performance.
Time and Cost Efficiency
Another key advantage of laboratory presses is the time and cost efficiency they bring to the table, especially in environments that require quick, repeatable processes with minimal downtime. Laboratory presses help businesses and researchers optimize their workflow, reduce errors, and lower operational costs.
4.1. Reduction in Labor and Human Error Through Automation
Many modern laboratory presses are designed to be automated, significantly reducing the need for manual operation. Automation not only speeds up the pressing process but also minimizes human error, ensuring that pressure, temperature, and cycle times are applied consistently across tests or production runs.
Automated presses allow operators to set parameters and walk away while the machine completes the pressing cycle, freeing up valuable labor resources for other tasks. This automation also enables multi-tasking in a laboratory or production environment, improving overall efficiency.
By reducing the need for constant supervision, laboratory presses also help companies save on labor costs. With automated systems, one operator can manage multiple presses simultaneously, increasing productivity without sacrificing quality.
4.2. Fast Testing and Production Cycles
Laboratory presses offer fast cycle times, which is particularly beneficial in industrial settings where time is money. In production environments, the ability to complete pressing cycles quickly and efficiently allows manufacturers to produce more in less time. This is especially important in industries such as pharmaceuticals, where tablets must be compressed quickly and consistently to meet demand.
Even in research environments, where testing may be more exploratory, fast cycle times are an advantage. Laboratory presses that can quickly generate results allow researchers to run multiple experiments in a shorter period, speeding up the pace of innovation and development.
4.3. Cost Savings in Research and Quality Control
The cost savings associated with laboratory presses extend beyond labor reductions. By providing consistent and reliable results, these machines help reduce the cost of failed experiments, defective products, or low-quality batches in manufacturing. For example, in pharmaceutical production, laboratory presses help ensure that each tablet contains the correct dosage, preventing costly recalls due to dosage errors.
In material testing, laboratory presses provide highly accurate data on material properties, reducing the risk of product failure once materials are used in real-world applications. This kind of precision helps manufacturers maintain high quality without the need for expensive reworks or product recalls.
4.4. Lower Maintenance and Operational Costs
Laboratory presses are designed to be durable and low-maintenance. Many models are built with high-quality materials such as steel, cast iron, or aluminum, ensuring that they can withstand constant use without frequent breakdowns. Additionally, the simplicity of the hydraulic, pneumatic, or electric systems used in these presses means that they require minimal maintenance over their lifespan.
When maintenance is required, many laboratory presses are designed for easy access, making it simple to replace worn parts or service the machine. This reduces downtime, allowing the press to return to operation quickly and minimizing the overall cost of ownership.
Enhanced Safety Features
Safety is a paramount concern in laboratory environments, especially when working with machines that generate high pressure and, in some cases, high temperatures. Laboratory presses are equipped with a range of safety features designed to protect operators and ensure that processes are conducted safely and efficiently.
5.1. Safety Protocols and Design Features
Laboratory presses are designed with operator safety in mind. Many presses feature built-in safety protocols that prevent the machine from operating if conditions are unsafe. For example, hydraulic presses may include pressure relief valves that release excess pressure if it exceeds the machine’s capacity, preventing mechanical failure or damage.
Other presses are designed to prevent operation unless all safety mechanisms are engaged. For instance, safety shields or guards may need to be in place before the press can start a cycle, ensuring that operators are not exposed to moving parts or hazardous conditions.
5.2. Operator Protection Systems (Shields, Emergency Stops)
Most modern laboratory presses come equipped with operator protection systems such as safety shields, which prevent operators from coming into contact with the machine’s moving parts during operation. These shields are often transparent, allowing operators to monitor the process without putting themselves at risk.
Many presses also feature emergency stop buttons, which allow operators to halt the pressing process immediately in case of an emergency. These buttons are typically located in easily accessible areas, ensuring that they can be reached quickly in the event of a problem.
5.3. Overload and Pressure Relief Systems
To protect both the machine and the operator, many laboratory presses are equipped with overload protection systems. These systems monitor the pressure applied during the pressing cycle and automatically stop the machine if the pressure exceeds safe limits. This not only prevents damage to the press but also ensures that the material being worked on is not over-pressed, which could lead to defects or failures in the final product.
In hydraulic presses, pressure relief valves play a critical role in maintaining safety. These valves release excess fluid pressure from the system, preventing dangerous over-pressurization that could damage the machine or create unsafe working conditions.
5.4. Adherence to International Safety Standards
Many laboratory presses are designed to meet international safety standards such as CE (Conformité Européenne) marking or ISO (International Organization for Standardization) certifications. These certifications indicate that the press has been tested and verified to meet specific safety requirements, providing operators with peace of mind that the machine is safe to use.
Presses that adhere to these standards are less likely to experience mechanical failures or cause injuries, making them a safer investment for laboratories and industrial facilities.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
With increasing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency, laboratory presses are being designed to minimize their environmental impact while still delivering high levels of performance. This focus on efficiency benefits both the environment and the bottom line by reducing energy consumption and waste.
6.1. Energy-Efficient Models (Electric Presses)
Many modern laboratory presses, particularly electric presses, are designed to be energy efficient. Unlike hydraulic or pneumatic presses, which may require a continuous supply of power to maintain pressure, electric presses only use energy when the press is actively moving. This makes them more energy-efficient, especially in laboratories or industrial settings where presses may be used intermittently.
Electric presses also tend to have fewer moving parts than hydraulic or pneumatic models, reducing the energy required to operate them. In addition to lower energy consumption, this also means that electric presses produce less heat and noise, contributing to a more comfortable and sustainable working environment.
6.2. Reducing Waste in Production and Testing
Laboratory presses are often used in quality control and testing applications, where precision is critical to reducing waste. By providing accurate, repeatable results, laboratory presses help manufacturers minimize the amount of material wasted due to errors or defects. This not only reduces costs but also contributes to more sustainable production processes.
For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, laboratory presses ensure that tablets are produced with the correct dosage and weight, reducing the need to discard defective batches. In material testing, presses help manufacturers select the most suitable materials for their products, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and reducing the need for rework or replacement.
6.3. Lower Environmental Impact Compared to Traditional Methods
In many cases, laboratory presses provide a greener alternative to traditional manufacturing and testing methods. For example, presses can often compress materials without the need for additional binders or chemicals, reducing the environmental impact of the process. Similarly, laboratory presses used in material testing can simulate real-world conditions without the need for large-scale production runs, allowing companies to test materials more sustainably.
Hydraulic and pneumatic presses can also be optimized for energy efficiency through the use of variable-speed pumps and energy-efficient compressors. These components help reduce the amount of energy required to operate the press, lowering its overall environmental impact.
6.4. Long-Term Sustainability in Research and Industry
As industries continue to focus on sustainability, laboratory presses are likely to play an even greater role in reducing waste, energy consumption, and the environmental impact of manufacturing processes. Advances in press technology, such as the integration of smart systems that optimize energy use or the development of more sustainable materials for press construction, will further enhance the long-term sustainability of these machines.
In research environments, laboratory presses help drive innovation by enabling the development of new, more sustainable materials. For example, researchers are using laboratory presses to develop bio-based plastics, lightweight composites, and other materials that reduce the reliance on fossil fuels and other non-renewable resources.
Compact Design and Space Utilization

In laboratory environments, where space is often limited, the compact design of many laboratory presses is a significant advantage. These presses are designed to fit seamlessly into small workspaces without sacrificing performance, making them ideal for both small research labs and larger industrial facilities.
7.1. Space-Saving Designs for Laboratory Use
Many laboratory presses are designed with a small footprint, allowing them to fit comfortably on benchtops or in tight spaces. This is particularly important in laboratories where space is at a premium and multiple pieces of equipment may need to be accommodated in a single area.
Benchtop presses are especially popular in research and development settings. These compact machines are designed to deliver the same precision and control as larger presses but in a smaller, more space-efficient package. They are often used for testing small batches of materials or for developing new products in early-stage research.
7.2. Benchtop Presses vs. Full-Scale Industrial Presses
While benchtop presses are ideal for small-scale testing and research, full-scale industrial presses are available for larger applications where higher pressure and larger materials need to be processed. However, even full-scale presses are often designed to maximize space efficiency, with vertical designs or modular configurations that make them easier to fit into existing production environments.
Manufacturers can choose the size and type of press that best fits their needs, ensuring that they are making the most of their available space without compromising on functionality.
7.3. Mobility and Portability in Small Laboratories
In smaller laboratories, the portability of laboratory presses can be a key advantage. Many benchtop models are designed to be lightweight and easy to move, allowing them to be relocated as needed to different areas of the laboratory. This flexibility is particularly useful in dynamic research environments where equipment needs to be frequently reconfigured to accommodate new experiments or workflows.
Portable laboratory presses are also useful for fieldwork or remote testing, where researchers may need to compress samples or conduct tests in situ.
7.4. Multi-Functionality in Limited Spaces
Another advantage of laboratory presses in small or crowded workspaces is their multi-functionality. Many presses are designed to handle a variety of tasks, from compression molding to material testing, allowing users to perform multiple functions on a single machine. This versatility reduces the need for additional equipment, further optimizing space utilization in laboratories or production facilities.
Customization and Advanced Features
One of the key advantages of laboratory presses is their customizability. Many presses offer a wide range of customization options, from interchangeable platens to programmable control systems, allowing users to tailor the machine to their specific needs.
8.1. Customizable Platens, Dies, and Attachments
A major advantage of laboratory presses is the ability to customize the platens, dies, and attachments used in the pressing process. This flexibility allows users to adapt the press for different materials, applications, or testing scenarios. For example:
- Interchangeable Platens: Presses can be equipped with different types of platens, such as heated or cold platens, depending on the application. Heated platens are used in processes like compression molding or laminating, where heat is required to soften or bond materials. Cold platens, on the other hand, are ideal for applications that do not require heat.
- Specialized Dies: In industries like pharmaceuticals, custom dies can be used to create tablets of specific shapes and sizes. In material science, different dies may be used to test how materials deform under pressure.
- Attachments: Additional attachments, such as vacuum systems or automatic ejection systems, can be added to laboratory presses to support specific processes or enhance productivity.
8.2. Programmable Cycles and Automated Processes
Many laboratory presses feature programmable cycles that allow users to automate the pressing process. This is particularly useful in production environments, where consistency and efficiency are key. By programming the press to follow a specific cycle, users can ensure that each batch of material is processed under identical conditions, reducing the risk of defects or errors.
Automated laboratory presses also allow for more complex processes to be carried out with minimal operator intervention. For example, in compression molding, the press can be programmed to apply pressure and heat for a specific duration, then automatically cool and release the material. This level of automation not only improves productivity but also ensures repeatable results.
8.3. Integration with Industry 4.0 and Smart Technologies
With the rise of Industry 4.0, laboratory presses are becoming more integrated with smart technologies. Many modern presses are equipped with sensors and data logging capabilities that allow users to monitor the pressing process in real time. These systems can provide valuable insights into how materials behave under pressure, helping researchers optimize their processes and improve product quality.
Smart laboratory presses can also be connected to cloud-based systems or Internet of Things (IoT) networks, enabling remote monitoring and control. This is particularly useful in large production facilities, where operators may need to monitor multiple presses from a central location.
8.4. Compatibility with Emerging Materials and Techniques
As industries continue to develop new materials and techniques, laboratory presses are evolving to keep pace. For example, researchers are using laboratory presses to test advanced materials like graphene, nanomaterials, and bio-based polymers. These materials often require specialized processes, such as ultra-high pressure or precise temperature control, which modern laboratory presses can provide.
In fields like biotechnology and medicine, laboratory presses are being used to develop new drug delivery systems, biodegradable materials, and other innovations that require highly controlled processing environments. The ability to customize laboratory presses for these emerging applications ensures that they remain relevant as new materials and technologies emerge.
Long-Term Reliability and Durability
Laboratory presses are built to last. High-quality construction, reliable components, and minimal maintenance requirements make them a sound investment for laboratories and industrial facilities alike.
9.1. High-Quality Construction Materials (Steel, Cast Iron, Aluminum)
Laboratory presses are typically constructed from high-quality materials such as steel, cast iron, or aluminum, which provide durability and resistance to wear and tear. Steel frames, for example, are known for their strength and ability to withstand high pressures without warping or degrading over time. Cast iron is another popular material for laboratory presses, offering excellent compressive strength and durability.
These high-quality construction materials ensure that laboratory presses can handle heavy use over extended periods, making them suitable for both small-scale laboratory testing and large-scale industrial production.
9.2. Longevity and Consistent Performance Over Time
One of the key advantages of laboratory presses is their longevity. Many presses are designed to operate for years, if not decades, with minimal downtime or performance degradation. This reliability is essential in industries where consistent performance is critical, such as pharmaceuticals, material science, and electronics.
Laboratory presses are engineered to provide consistent pressure and temperature control over time, ensuring that each batch or test is processed under the same conditions. This level of consistency helps businesses maintain high quality standards, reducing the risk of defects or failures.
9.3. Low Maintenance Requirements and Support Systems
Many laboratory presses require minimal maintenance compared to other types of industrial equipment. This is particularly true for electric presses, which have fewer moving parts and require less frequent servicing than hydraulic or pneumatic models. When maintenance is required, it is often straightforward and can be completed quickly, reducing downtime and keeping the press operational.
Manufacturers of laboratory presses typically offer support systems such as warranties, maintenance plans, and customer service to ensure that presses continue to operate efficiently throughout their lifespan. This level of support further enhances the long-term reliability of laboratory presses, making them a sound investment for laboratories and industrial facilities.
9.4. Warranty and Service Support from Manufacturers
Most laboratory press manufacturers offer comprehensive warranties and service support, which further enhances the reliability of their products. These warranties typically cover repairs, replacement parts, and maintenance services for a specified period, ensuring that the press remains in optimal working condition.
Manufacturers often provide technical support and training to help operators get the most out of their laboratory presses. This ensures that users are familiar with the machine’s features and can perform routine maintenance tasks to extend the press’s lifespan.
Conclusion: The Growing Importance of Laboratory Presses
Laboratory presses offer numerous advantages across a wide range of industries, from pharmaceuticals and materials science to electronics and aerospace. Their precision, versatility, safety features, and cost-efficiency make them essential tools for research, development, and production processes.
The ability of laboratory presses to provide consistent, repeatable results is critical in fields where accuracy is paramount. Whether used for testing new materials, producing pharmaceuticals, or developing electronics, laboratory presses deliver the precision and control needed to ensure high-quality results.
As industries continue to evolve and new materials and technologies emerge, laboratory presses will remain a key asset. The integration of smart technologies, automation, and energy-efficient systems ensures that laboratory presses will continue to meet the demands of modern research and production environments.
For businesses and research institutions looking to invest in equipment that will provide long-term reliability, versatility, and performance, laboratory presses are a clear choice. Their ability to adapt to different applications, provide energy-efficient solutions, and deliver consistent results makes them an invaluable asset in today’s fast-paced, innovation-driven world.
Precision and Control
Precision and control are at the core of what makes laboratory presses essential in modern research, development, and manufacturing. The need for fine-tuned pressure, temperature, and timing is paramount in industries like pharmaceuticals, material sciences, and electronics, where even minor deviations can result in failed experiments, defective products, or suboptimal results. The precision provided by laboratory presses ensures the repeatability and accuracy of the pressing process.
2.1. Importance of Precision in High-Stakes Applications
In industries such as medical device manufacturing and drug development, precision is non-negotiable. Consider the example of a pharmaceutical company developing new medications. During the tablet compression process, the active ingredients must be distributed evenly, and the tablets must have uniform hardness, size, and dissolution rates. Even a slight deviation in the pressure applied during compression could lead to dosage discrepancies, potentially causing ineffective or even dangerous products. Laboratory presses equipped with precise pressure controls help ensure that the tablets meet strict regulatory standards and that each tablet in a batch is identical in composition and performance.
In material science, precision becomes even more critical when researchers are experimenting with advanced composites, polymers, or nanomaterials. These materials are often designed for high-performance applications like aerospace or automotive components, where slight differences in material composition or structure can compromise safety and performance. For instance, a lab developing carbon fiber composites must apply exact pressure and heat levels during the compression molding process to ensure that the material’s fiber alignment and bonding strength are consistent. Any irregularity could weaken the composite, resulting in structural failure in its application.
2.2. Advanced Pressure and Temperature Control Systems
Most modern laboratory presses, especially hydraulic and electric models, come with highly advanced control systems. These control systems allow for minute adjustments in pressure, ensuring precision that can go down to fractions of a percent. Digital pressure gauges and load cells are often integrated into these systems, providing real-time feedback on the exact pressure being applied at any moment. This is particularly important in quality control and research settings where minor variations could lead to skewed data or product defects.
For example, in ceramics manufacturing, high levels of precision are required during the pressing and sintering process. Laboratory presses with advanced control systems allow for exact pressure application, ensuring uniform compaction of ceramic powders before they are fired. This prevents defects such as cracks or inconsistencies in the finished product, which could weaken the ceramic material.
Temperature control is another critical factor in presses used in research and production. Laboratory presses with built-in heating elements allow for the precise control of temperature alongside pressure, which is essential for applications like thermoforming plastics or vulcanizing rubber. The ability to accurately control both pressure and heat ensures that materials behave consistently under controlled conditions, leading to better material properties and higher-quality products.
2.3. Digital Interfaces for Enhanced Accuracy
The advent of digital interfaces on laboratory presses has significantly improved the accuracy with which operators can control the pressing process. Earlier versions of laboratory presses relied on manual adjustments and mechanical dials, which introduced a greater margin for error. Today, many laboratory presses are equipped with touchscreen controls or digital keypads that allow operators to set precise parameters such as pressure, temperature, and cycle duration.
These digital interfaces also often include programmable logic controllers (PLCs), which enable users to save specific pressing profiles and recall them later for repeatability. This is particularly useful in industrial settings where a consistent manufacturing process is essential to meeting production quotas and maintaining quality control. For example, in a facility producing flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs), a laboratory press can be programmed to apply exact pressures and temperatures for laminating the multiple layers of the PCB together. Once the parameters are set and tested, operators can recall the same profile for future production runs, ensuring consistency across batches.
Furthermore, many digital interfaces include data logging capabilities, which record the parameters of each press cycle. This data can be invaluable for researchers and manufacturers who need to analyze the relationship between pressure, temperature, and material properties. In industries like semiconductors, where material properties must meet precise specifications, this capability allows for ongoing optimization of the production process based on real-time data.
2.4. Consistency and Repeatability in Experimental Results
One of the defining advantages of laboratory presses is their ability to provide consistent and repeatable results. In scientific research, repeatability is one of the pillars of credibility. When results can be consistently replicated, it adds validity to the research and leads to reliable outcomes. The ability of laboratory presses to precisely control pressure, temperature, and timing ensures that the same conditions can be applied repeatedly, making it easier to replicate experimental results.
For instance, in the development of polymer blends, laboratory presses allow researchers to apply the same pressure and temperature conditions across multiple samples, enabling them to determine how slight variations in the polymer composition affect the final properties of the material. This repeatability is essential for drawing accurate conclusions and for scaling up production from the laboratory to full-scale manufacturing.
In addition, repeatability is crucial in batch production processes. Whether the press is being used to create small batches of tablets in a pharmaceutical lab or to laminate composite materials in an aerospace factory, consistent results are necessary to ensure product quality. Laboratory presses that can repeat the same cycle hundreds or thousands of times without deviation help companies maintain strict quality control standards, reducing waste and preventing costly production errors.
Versatility Across Multiple Applications
Versatility is one of the primary reasons laboratory presses are so widely used in research and manufacturing environments. Whether used for pressing powders into tablets, molding composite materials, laminating layers of polymers, or testing the mechanical properties of metals, laboratory presses can be adapted to a wide range of applications. Their flexibility makes them a valuable asset across industries such as pharmaceuticals, electronics, aerospace, and automotive manufacturing.
3.1. Adaptability to Various Industries
The versatility of laboratory presses makes them indispensable in numerous fields. Let’s take a closer look at how they are used in some of the key industries:
- Pharmaceutical Industry: In pharmaceutical R&D and production, laboratory presses are used to compress powders into tablets, ensuring that each tablet has the correct dosage and meets regulatory standards for size, hardness, and dissolution rate. This process is critical for quality control, as uniformity in tablet production is essential for patient safety. Additionally, presses are used to prepare samples for testing new drug formulations, as well as for granulation and pelletization processes in drug development.
- Material Science: Laboratory presses are widely used in material science research for sample preparation and testing. For example, presses are used to mold polymer samples, prepare metal powders for sintering, or create composite materials for testing their mechanical properties. This versatility allows scientists to conduct a wide range of experiments with a single press, enabling them to study materials under different pressures and temperatures.
- Electronics and Semiconductor Industry: In electronics manufacturing, laboratory presses are used in the production of printed circuit boards (PCBs), wafer bonding, and component encapsulation. Presses help bond layers of material together to form flexible PCBs, laminate sensitive electronics, or apply protective coatings to semiconductors. The precision and control offered by laboratory presses ensure that electronic components are manufactured with the necessary structural integrity and performance characteristics.
- Automotive and Aerospace: In the automotive and aerospace industries, laboratory presses are used to develop and test composite materials. These industries increasingly rely on composites such as carbon fiber to reduce weight without compromising strength. Laboratory presses are essential in the testing and production of these materials, allowing engineers to study their performance under high pressures and extreme conditions, such as heat or stress. Presses are also used in the molding of interior and exterior components in automotive manufacturing, where precise pressure and temperature control are essential for ensuring the integrity of the finished parts.
3.2. Supporting Different Materials
One of the most significant advantages of laboratory presses is their ability to work with a wide variety of materials. From soft biological tissues to rigid metals and everything in between, laboratory presses can be adapted to suit the unique requirements of different materials. The following are just a few examples of the types of materials laboratory presses are commonly used with:
- Polymers and Plastics: In industries such as plastics manufacturing and research, laboratory presses are used to test thermoplastics and create samples for durability testing. These presses can be configured to handle the heat-sensitive nature of some polymers, while also applying the necessary pressure to shape or test the material. In polymer science, presses are often used to prepare samples for tensile or compression testing to determine the material’s mechanical properties.
- Composites: The use of composite materials is growing in industries like automotive, aerospace, and construction. These materials often combine the strengths of different substances, such as polymers and fibers, to create lightweight yet strong structures. Laboratory presses allow researchers and manufacturers to test different combinations of materials under controlled pressure and temperature conditions, ensuring that the final composite material performs as expected.
- Metals and Ceramics: Laboratory presses are also widely used in metallurgy and ceramics research. Metal powders are often compressed into solid parts using a press before being sintered, while ceramics are pressed into shape before being fired. The precision and consistency of laboratory presses help ensure that these materials are formed correctly, preventing defects and ensuring uniformity.
In addition to handling these standard materials, laboratory presses are also used with biomaterials in medical research, semiconductor materials in electronics, and adhesives in the production of laminated products.
3.3. Flexibility in Research and Development
One of the key reasons laboratory presses are so valuable in R&D environments is their flexibility. Because laboratory presses can be used for a wide range of applications, they are often the only piece of equipment needed for researchers working on multiple projects. For example, a laboratory press in a university materials science department might be used for compression molding of plastics, sample preparation for metals testing, and even tablet compression in pharmaceutical research.
This flexibility also allows researchers to experiment with new materials and processes. Whether they are developing a new polymer blend for industrial use or testing the performance of a biodegradable plastic, researchers can rely on the laboratory press to provide the controlled pressure and temperature conditions needed to carry out their experiments.
In the field of nanotechnology, laboratory presses are being used to test nanocomposites and nanomaterials. These materials require extremely precise pressure and temperature controls during testing to ensure that their unique properties are maintained. Laboratory presses with servo motors and digital controls are ideal for these experiments, offering the fine-tuned control necessary to study nanomaterials’ behavior under different conditions.
3.4. Customization Options for Specialized Applications
The customization of laboratory presses is another factor that enhances their versatility. Most laboratory presses can be outfitted with custom platens, dies, or attachments to suit specific applications. This customization allows users to adapt the press to the unique requirements of their material or process. Some common customization options include:
- Interchangeable Platens: Different applications may require heated platens, vacuum platens, or cooling platens, depending on the material being worked on. For example, a press with heated platens might be used for compression molding of plastics, while a vacuum platen might be used for laminating thin films without introducing air bubbles.
- Specialized Dies: In pharmaceutical research, custom dies are used to create tablets of specific shapes and sizes, while in material science, dies may be used to form metal or ceramic parts. The ability to swap out dies makes laboratory presses highly adaptable for different tasks.
- Automation and Programmability: Many presses now come with programmable controls, which allow users to set specific pressure, temperature, and timing parameters for each cycle. This is particularly useful in production environments, where consistency and efficiency are critical.
This level of customization ensures that laboratory presses can meet the needs of specialized applications in industries ranging from biotechnology to automotive and electronics.
Time and Cost Efficiency
In both research and industrial settings, time and cost efficiency are critical considerations. Laboratory presses offer significant advantages in this area, providing fast, automated processes that reduce labor, increase productivity, and cut operational costs. By optimizing the pressing process, laboratory presses help businesses and research organizations get better results in less time, with lower overall costs.
4.1. Reduction in Labor and Human Error Through Automation
Automation is one of the key factors driving time and cost efficiency in laboratory presses. In the past, laboratory presses were largely manually operated, requiring skilled technicians to control the pressure, timing, and temperature of each press cycle. This not only increased labor costs but also introduced the potential for human error, leading to inconsistent results or even failed tests.
Modern laboratory presses are increasingly automated, with digital control systems that allow operators to set precise parameters for each press cycle. Once the settings have been configured, the press can run automatically, applying the same pressure, temperature, and cycle duration to each batch of material. This automation eliminates the need for constant monitoring and reduces the risk of human error, resulting in more consistent and reliable outcomes.
In an industrial setting, this reduction in labor can have a significant impact on overall productivity. For example, in a pharmaceutical manufacturing facility, laboratory presses are used to compress powders into tablets. By automating the process, the facility can produce more tablets per hour with fewer operators, reducing labor costs while increasing output.
4.2. Fast Testing and Production Cycles
Laboratory presses offer fast cycle times, which is especially important in industries where rapid prototyping or high-throughput testing is needed. In a research environment, fast testing cycles allow scientists to run multiple experiments in a shorter period, speeding up the pace of innovation and discovery. In a production environment, fast cycle times increase the rate at which products can be manufactured, helping companies meet production targets and demand.
For example, in the automotive industry, laboratory presses are used to create and test composite materials for use in lightweight vehicle components. The faster the press cycle, the more material samples can be produced and tested in a given time frame, enabling manufacturers to quickly evaluate different materials and select the most suitable one for production.
Fast cycle times also benefit industries like electronics, where laboratory presses are used to laminate multiple layers of materials in the production of flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs). The ability to complete press cycles quickly and accurately ensures that production can keep pace with demand while maintaining high-quality standards.
4.3. Cost Savings in Research and Quality Control
Laboratory presses contribute to cost savings in a variety of ways. In research settings, the precision and control offered by laboratory presses reduce the likelihood of failed experiments or wasted materials. By applying consistent pressure and temperature, laboratory presses help researchers get the desired results the first time, minimizing the need for costly re-tests or additional experiments.
In quality control environments, laboratory presses play a crucial role in ensuring that products meet the required specifications before they go to market. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, laboratory presses are used to test the hardness and dissolution rates of tablets. By ensuring that each batch of tablets meets the required quality standards, manufacturers can avoid costly recalls or product rejections. This not only saves money but also protects the company’s reputation.
Laboratory presses also help reduce the cost of prototyping in industries like automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics. Rather than committing to large-scale production runs of new products or materials, companies can use laboratory presses to create small batches for testing. This allows them to identify and resolve any issues before scaling up production, reducing the risk of costly design flaws or manufacturing errors.
4.4. Lower Maintenance and Operational Costs
Another key advantage of laboratory presses is their relatively low maintenance and operational costs. Modern laboratory presses are designed to be durable and reliable, with high-quality components that require minimal upkeep. This is particularly true of electric presses, which have fewer moving parts than hydraulic or pneumatic presses and therefore experience less wear and tear over time.
When maintenance is required, it is often simple and can be completed quickly, reducing downtime and keeping the press operational. Many laboratory presses are also designed with easy access to key components, making it easier for operators to perform routine maintenance or replace parts without the need for specialized technicians.
In addition to low maintenance costs, laboratory presses are often energy efficient, particularly in the case of electric models. These presses use less power than hydraulic or pneumatic models, resulting in lower energy bills and a smaller environmental footprint. This energy efficiency is particularly beneficial in industries where presses are used frequently or for extended periods, such as in manufacturing facilities or research laboratories.
The combination of low maintenance requirements and energy efficiency makes laboratory presses a cost-effective investment for businesses and research institutions. Over the long term, the savings generated by reduced maintenance, energy, and labor costs can more than offset the initial purchase price of the press.
Enhanced Safety Features
Safety is a top priority in any laboratory or industrial environment, particularly when working with machinery that generates high pressure or heat. Laboratory presses are designed with a range of enhanced safety features to protect operators and ensure that processes are carried out safely and efficiently.
5.1. Safety Protocols and Design Features
Laboratory presses are equipped with safety protocols that are designed to prevent accidents and protect both the operator and the machine. These protocols may include:
- Pressure Relief Valves: In hydraulic presses, pressure relief valves are used to release excess fluid pressure from the system if it exceeds the machine’s capacity. This prevents over-pressurization, which could damage the press or cause injury to the operator.
- Overload Protection: Many presses include overload protection systems that automatically shut down the press if the pressure applied exceeds safe limits. This not only protects the machine from damage but also ensures that the material being pressed is not over-compressed, which could compromise its integrity or lead to defects.
- Lockout Mechanisms: Some presses feature lockout mechanisms that prevent the press from being operated unless all safety systems are engaged. For example, a hydraulic press may be designed to prevent the application of pressure if the safety shields are not properly in place.
5.2. Operator Protection Systems (Shields, Emergency Stops)
Operator protection systems are a standard feature on most modern laboratory presses. These systems are designed to minimize the risk of injury to operators by preventing contact with the press’s moving parts or high-temperature surfaces.
One of the most common operator protection systems is the use of safety shields or guards, which enclose the press’s working area and prevent operators from coming into contact with the machine during operation. These shields are often made of transparent materials, such as tempered glass or polycarbonate, allowing the operator to monitor the pressing process without being exposed to potential hazards.
Most laboratory presses also feature emergency stop buttons, which allow operators to halt the pressing process immediately in the event of an emergency. These buttons are typically located near the control panel or on the side of the press, ensuring that they are easily accessible at all times. In some cases, the press may also include multiple emergency stop buttons placed at different locations around the machine, providing additional layers of safety.
5.3. Overload and Pressure Relief Systems
Overload protection and pressure relief systems are critical safety features in laboratory presses, particularly in hydraulic models where the pressure can reach extremely high levels. Overload protection systems monitor the pressure applied during the press cycle and automatically stop the machine if the pressure exceeds the pre-set limit. This prevents mechanical failure and ensures that the material being worked on is not damaged by excessive force.
In hydraulic presses, pressure relief valves are used to release excess pressure from the system. These valves are typically located within the hydraulic circuit and are designed to open automatically when the pressure exceeds a safe level. By releasing the excess fluid pressure, the valves prevent the press from overloading and ensure that the system remains within safe operating parameters.
In addition to overload and pressure relief systems, many laboratory presses are equipped with temperature sensors that monitor the heat applied to the material during the press cycle. If the temperature exceeds a safe limit, the press may automatically shut down to prevent overheating and protect the material being processed.
5.4. Adherence to International Safety Standards
Most laboratory presses are designed to meet international safety standards, providing peace of mind that the press is safe to use in a laboratory or industrial environment. Common safety certifications include:
- CE Marking: The CE marking indicates that a product meets the safety, health, and environmental protection standards set by the European Union. Laboratory presses with CE marking have undergone rigorous testing to ensure they meet the necessary safety requirements for use in European markets.
- ISO Certifications: The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) sets global standards for safety and quality across a wide range of industries. Laboratory presses that carry ISO certifications have been tested and verified to meet these standards, ensuring that they are safe and reliable.
Adherence to these safety standards is not only important for protecting operators but also for ensuring that the laboratory or industrial facility is compliant with local regulations. In many industries, failure to comply with safety standards can result in fines or penalties, making it essential for companies to invest in laboratory presses that meet these requirements.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
As industries around the world become more focused on reducing their environmental impact and improving sustainability, energy efficiency is becoming a top priority in the design and operation of laboratory presses. Modern laboratory presses are increasingly designed to minimize energy consumption, reduce waste, and contribute to long-term sustainability in both research and industrial settings.
6.1. Energy-Efficient Models (Electric Presses)
One of the most significant advancements in laboratory press technology is the development of energy-efficient models, particularly electric presses. Unlike hydraulic or pneumatic presses, which rely on constant pressure from fluids or air, electric presses generate force through the use of electric motors. These motors only consume energy when the press is in motion, making electric presses far more energy-efficient than their hydraulic or pneumatic counterparts.
In addition to their energy efficiency, electric presses tend to have fewer moving parts, which reduces wear and tear over time and minimizes the need for maintenance. This makes them a popular choice in research laboratories and industrial facilities where presses may be used intermittently. The reduced energy consumption not only lowers operating costs but also helps facilities reduce their carbon footprint, contributing to long-term sustainability goals.
For example, in a semiconductor manufacturing plant, electric presses are used to apply precise pressure during the wafer bonding process. The press only uses energy during the bonding cycle, reducing overall energy consumption compared to a hydraulic press that would require constant pressure to maintain the same process. This not only saves energy but also contributes to the plant’s broader sustainability objectives.
6.2. Reducing Waste in Production and Testing
Laboratory presses are often used in quality control and material testing, where their precision helps reduce waste. By applying consistent pressure and temperature, laboratory presses help ensure that products meet the necessary specifications the first time, reducing the need for rework or discarding defective batches.
In the pharmaceutical industry, for example, laboratory presses are used to test the hardness, weight, and dissolution rates of tablets. By ensuring that each tablet meets the required specifications, laboratory presses help prevent waste by reducing the likelihood of failed batches or product recalls. This not only saves materials but also reduces the environmental impact of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
In material testing, laboratory presses allow researchers to accurately test the mechanical properties of materials such as plastics, metals, or composites, ensuring that only the most suitable materials are selected for production. This helps manufacturers avoid the waste associated with using materials that do not meet the necessary performance standards, reducing both material costs and environmental impact.
6.3. Lower Environmental Impact Compared to Traditional Methods
Compared to traditional manufacturing and testing methods, laboratory presses offer a more environmentally friendly alternative. For example, many pressing processes can be completed without the need for additional chemicals or binders, which reduces the environmental impact of the process. Additionally, laboratory presses can often simulate real-world conditions in a controlled environment, allowing companies to conduct tests without the need for full-scale production runs.
This is particularly beneficial in industries like automotive and aerospace, where companies are increasingly focused on reducing the environmental impact of their production processes. By using laboratory presses to test materials and prototypes in small batches, companies can reduce the energy and resources required for large-scale production, contributing to more sustainable manufacturing practices.
In the food packaging industry, laboratory presses are used to test the barrier properties of packaging materials, such as plastic films or metal foils. These tests ensure that the packaging materials are strong enough to protect the product while minimizing material usage. By optimizing the material selection process, laboratory presses help reduce the amount of packaging waste generated, contributing to a more sustainable supply chain.
6.4. Long-Term Sustainability in Research and Industry
Laboratory presses are also playing a key role in the development of new sustainable materials. Researchers are using presses to create and test materials that are designed to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, minimize waste, and promote recyclability. For example, laboratory presses are being used to develop bio-based plastics, recycled composites, and lightweight materials for use in everything from automotive components to consumer products.
In the biotechnology sector, laboratory presses are helping to advance the development of biodegradable materials and green technologies. For instance, presses are used to compress bio-based polymers into films or mold biodegradable plastics into various shapes. These materials have the potential to reduce the environmental impact of industries like packaging and consumer goods, offering sustainable alternatives to traditional plastics.
Laboratory presses are also being used to develop lightweight materials for the transportation and construction industries, where reducing weight can have a significant impact on energy consumption and carbon emissions. For example, researchers are using laboratory presses to develop carbon fiber composites that are lighter and stronger than traditional materials. By reducing the weight of vehicles, airplanes, and other structures, these materials help improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
In addition to their role in developing new materials, laboratory presses are also helping industries reduce their environmental footprint by enabling more efficient use of resources. By providing precise control over pressure and temperature, laboratory presses help companies optimize their manufacturing processes, ensuring that materials are used efficiently and waste is minimized.
Compact Design and Space Utilization

In laboratory environments where space is often at a premium, the compact design of many laboratory presses is a significant advantage. These presses are designed to fit seamlessly into small workspaces without sacrificing performance, making them ideal for both research laboratories and industrial facilities. The space-saving features of modern laboratory presses allow businesses to maximize their use of available space while maintaining a high level of productivity.
7.1. Space-Saving Designs for Laboratory Use
Many laboratory presses are designed with a small footprint, allowing them to fit comfortably on benchtops or in limited workspaces. This is particularly important in research laboratories, where space may be shared by multiple pieces of equipment, and the efficient use of that space is critical to maintaining a productive environment.
Benchtop presses, in particular, are designed to provide the same level of precision and control as larger presses but in a more compact package. These presses are typically used for smaller-scale experiments or for preparing samples for testing, and their size makes them ideal for use in academic or industrial research labs. Despite their small size, benchtop presses offer the same advanced features as larger models, including programmable cycles, digital controls, and precise pressure and temperature control.
In addition to their compact size, many benchtop presses are designed to be lightweight and portable, making it easy for researchers to move them between different workstations or laboratories as needed. This flexibility is particularly valuable in dynamic research environments where equipment needs to be frequently reconfigured to accommodate new experiments or workflows.
7.2. Benchtop Presses vs. Full-Scale Industrial Presses
While benchtop presses are ideal for small-scale testing and research, full-scale industrial presses are designed to handle larger applications where higher pressure and larger materials need to be processed. However, even full-scale industrial presses are often designed to maximize space efficiency, with vertical designs or modular configurations that allow them to fit into existing production environments without taking up excessive floor space.
For example, in a semiconductor manufacturing facility, space is often at a premium, and equipment must be arranged efficiently to allow for smooth production workflows. Laboratory presses used for wafer bonding or component encapsulation are often designed with a vertical orientation, which reduces their footprint and allows them to be integrated into a cleanroom environment without disrupting other processes.
The ability to choose between benchtop and full-scale models allows businesses to select the size and type of press that best fits their needs, ensuring that they are making the most of their available space without compromising on functionality.
7.3. Mobility and Portability in Small Laboratories
In smaller laboratories, where space is limited and flexibility is essential, the portability of laboratory presses is another significant advantage. Many benchtop models are designed to be lightweight and easy to move, allowing them to be relocated as needed to different areas of the laboratory. This is particularly useful in laboratories that conduct a wide range of tests or experiments, as it allows researchers to set up and use the press wherever it is most convenient.
Portable laboratory presses are also useful for fieldwork or remote testing, where researchers may need to compress samples or conduct tests outside of a traditional laboratory setting. For example, a geologist studying rock formations in the field might use a portable laboratory press to compress and prepare samples for later analysis in the lab. The ability to bring the press directly to the testing site allows for more efficient sample preparation and reduces the risk of contamination or degradation during transportation.
In industrial settings, portable laboratory presses can be moved between different production lines or workstations as needed, providing flexibility in how the press is used. For example, a materials testing laboratory might use the same portable press to test the properties of different materials across multiple projects, reducing the need for multiple presses and optimizing space utilization.
7.4. Multi-Functionality in Limited Spaces
Another advantage of laboratory presses in small or crowded workspaces is their multi-functionality. Many presses are designed to handle a variety of tasks, from compression molding to material testing, allowing users to perform multiple functions on a single machine. This versatility reduces the need for additional equipment, further optimizing space utilization in laboratories or production facilities.
For example, in a university research lab, a single laboratory press might be used for a wide range of experiments, including testing the mechanical properties of polymers, compressing metal powders for sintering, and preparing composite materials for durability testing. By using one machine for multiple purposes, the lab can free up valuable workspace for other equipment or experiments.
In production environments, the multi-functionality of laboratory presses allows companies to streamline their processes and reduce the number of machines needed for testing and quality control. For example, a pharmaceutical manufacturer might use the same press to test the hardness, weight, and dissolution rates of tablets, ensuring that all quality control processes can be completed efficiently within a single workstation.
This multi-functionality not only optimizes space utilization but also improves productivity by reducing the time needed to switch between different machines or workstations. In industries where space is limited and efficiency is critical, the ability to perform multiple functions on a single laboratory press is a significant advantage.
Customization and Advanced Features
One of the most significant advantages of laboratory presses is their ability to be customized to meet the specific needs of different industries and applications. Whether it’s adding specialized dies, upgrading to programmable control systems, or integrating smart technologies, laboratory presses can be tailored to provide the exact functionality required for a given task. This flexibility in customization allows companies and research institutions to maximize the performance of their presses and adapt them to evolving demands.
8.1. Customizable Platens, Dies, and Attachments
A major advantage of laboratory presses is the ability to customize the platens, dies, and attachments used in the pressing process. This flexibility allows users to adapt the press for different materials, applications, or testing scenarios. For example:
- Interchangeable Platens: Presses can be equipped with different types of platens, such as heated platens, vacuum platens, or cooling platens, depending on the application. For example, a press with heated platens might be used for compression molding of plastics, while a vacuum platen might be used for laminating thin films without introducing air bubbles.
- Specialized Dies: In industries like pharmaceuticals, custom dies can be used to create tablets of specific shapes and sizes. In material science, different dies may be used to test how materials deform under pressure. Dies can be designed to mimic real-world conditions, such as the stress a material might face in an industrial application.
- Attachments: Additional attachments, such as vacuum systems, automatic ejection systems, or material feeders, can be added to laboratory presses to support specific processes or enhance productivity. For example, in the composite material industry, a vacuum attachment may be used to remove air bubbles during the lamination process, ensuring that the final product is free from voids or defects.
This level of customization ensures that laboratory presses can meet the needs of specialized applications in industries ranging from biotechnology to automotive and electronics. By tailoring the press to the unique requirements of the material or process, companies can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their testing and production workflows.
8.2. Programmable Cycles and Automated Processes
Many laboratory presses feature programmable cycles that allow users to automate the pressing process. This is particularly useful in production environments, where consistency and efficiency are key. By programming the press to follow a specific cycle, users can ensure that each batch of material is processed under identical conditions, reducing the risk of defects or errors.
Automated laboratory presses also allow for more complex processes to be carried out with minimal operator intervention. For example, in compression molding, the press can be programmed to apply pressure and heat for a specific duration, then automatically cool and release the material. This level of automation not only improves productivity but also ensures repeatable results, reducing the need for rework or additional testing.
In addition to improving consistency and efficiency, programmable cycles also allow users to optimize the pressing process for different materials or applications. For example, a pharmaceutical company might program the press to apply lower pressure for fragile tablet formulations and higher pressure for harder tablets. This customization ensures that each material is processed under the ideal conditions, improving product quality and reducing the risk of damage.
8.3. Integration with Industry 4.0 and Smart Technologies
With the rise of Industry 4.0, laboratory presses are becoming more integrated with smart technologies. Many modern presses are equipped with sensors, data logging capabilities, and remote monitoring systems that allow users to monitor the pressing process in real time. These systems provide valuable insights into how materials behave under pressure, helping researchers optimize their processes and improve product quality.
Smart laboratory presses can also be connected to cloud-based systems or Internet of Things (IoT) networks, enabling remote monitoring and control. This is particularly useful in large production facilities, where operators may need to monitor multiple presses from a central location. By integrating presses into an IoT network, companies can optimize their production processes, reduce downtime, and improve overall efficiency.
For example, in a pharmaceutical manufacturing facility, smart laboratory presses can be connected to the company’s enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, allowing managers to monitor the performance of the presses in real time. If a press experiences an issue, such as a drop in pressure or a malfunction in the heating system, the system can send an alert to the operator, allowing them to address the issue before it affects production.
The integration of smart technologies also allows companies to collect and analyze data from the pressing process, providing valuable insights into material performance, process optimization, and quality control. This data can be used to improve product designs, optimize manufacturing workflows, and ensure that products meet the highest quality standards.
8.4. Compatibility with Emerging Materials and Techniques
As industries continue to develop new materials and techniques, laboratory presses are evolving to keep pace. For example, researchers are using laboratory presses to test advanced materials like graphene, nanomaterials, and bio-based polymers. These materials often require specialized processes, such as ultra-high pressure or precise temperature control, which modern laboratory presses can provide.
In the field of biotechnology, laboratory presses are being used to develop new drug delivery systems, biodegradable materials, and other innovations that require highly controlled processing environments. The ability to customize laboratory presses for these emerging applications ensures that they remain relevant as new materials and technologies emerge.
For instance, in nanotechnology, laboratory presses are used to compress nanocomposites, which require extremely precise control of pressure and temperature to maintain their unique properties. As nanomaterials become more prevalent in industries like electronics, medicine, and energy storage, laboratory presses will continue to play a critical role in their development and testing.
In medical device manufacturing, laboratory presses are used to mold and shape biocompatible materials into implants and prosthetics. These materials must meet stringent regulatory standards for safety and durability, and laboratory presses provide the precise control needed to ensure that each device meets these requirements.
Long-Term Reliability and Durability
When it comes to laboratory equipment, reliability and durability are critical factors. Laboratory presses are built to last, with high-quality construction materials, minimal maintenance requirements, and consistent performance over time. For businesses and research institutions looking for equipment that will provide long-term value, laboratory presses are a smart investment.
9.1. High-Quality Construction Materials (Steel, Cast Iron, Aluminum)
Laboratory presses are typically constructed from high-quality materials such as steel, cast iron, or aluminum, which provide durability and resistance to wear and tear. These materials are chosen for their ability to withstand the high pressures and temperatures generated during the pressing process, ensuring that the press can continue to perform reliably over time.
For example, steel frames are commonly used in laboratory presses because of their strength and durability. Steel is capable of withstanding the high compressive forces generated by hydraulic or pneumatic presses without warping or degrading over time. Similarly, cast iron is often used in press construction because of its excellent compressive strength and resistance to deformation under pressure.
In addition to their strength, these materials are often coated with protective finishes, such as powder coatings or anti-corrosion treatments, to ensure that the press remains in good condition even when exposed to harsh operating environments. This further extends the lifespan of the press, making it a reliable long-term investment for businesses and research institutions.
9.2. Longevity and Consistent Performance Over Time
One of the key advantages of laboratory presses is their longevity. These machines are designed to provide consistent performance over many years, even in demanding industrial environments. This reliability is essential in industries where downtime or equipment failure can result in costly delays or production losses.
For example, in the electronics manufacturing industry, laboratory presses are used to laminate multiple layers of materials together to create flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs). These presses must be able to apply precise pressure and temperature over thousands of press cycles to ensure that each PCB meets the required specifications. The reliability of the press ensures that the production process can continue without interruptions, helping manufacturers meet production targets and avoid costly rework.
Similarly, in the pharmaceutical industry, laboratory presses are used to compress powders into tablets. The ability to maintain consistent pressure and temperature over time is critical for ensuring that each tablet is produced to the correct size, weight, and hardness. By providing consistent performance, laboratory presses help pharmaceutical companies maintain high quality standards and reduce the risk of product recalls.
9.3. Low Maintenance Requirements and Support Systems
Many laboratory presses are designed to require minimal maintenance, making them easy to operate and maintain over the long term. This is particularly true of electric presses, which have fewer moving parts than hydraulic or pneumatic models and therefore experience less wear and tear. As a result, electric presses often require less frequent servicing, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
When maintenance is required, many laboratory presses are designed for easy access to key components, making it simple for operators to perform routine maintenance tasks such as replacing worn parts or lubricating moving components. This helps to minimize downtime and keep the press operational, ensuring that production schedules are not disrupted.
In addition to their low maintenance requirements, many laboratory presses come with support systems such as warranties, maintenance plans, and customer service. These support systems ensure that any issues with the press can be addressed quickly and efficiently, further enhancing the reliability of the machine.
9.4. Warranty and Service Support from Manufacturers
Most laboratory press manufacturers offer comprehensive warranties and service support, providing peace of mind that the press will continue to operate reliably throughout its lifespan. These warranties typically cover repairs, replacement parts, and maintenance services for a specified period, ensuring that the press remains in optimal working condition.
Manufacturers often provide technical support and training to help operators get the most out of their laboratory presses. This ensures that users are familiar with the machine’s features and can perform routine maintenance tasks to extend the press’s lifespan.
For example, a manufacturer might offer a two-year warranty on a laboratory press, covering any repairs or part replacements needed during that period. In addition, the manufacturer may provide on-site training to teach operators how to use the press effectively and maintain it properly. This level of support ensures that the press remains reliable and productive over the long term, providing a strong return on investment.
Conclusion: The Growing Importance of Laboratory Presses
Laboratory presses offer a wide range of advantages across multiple industries and applications, from pharmaceuticals and electronics to material science and aerospace. Their precision, versatility, energy efficiency, safety features, and cost-effectiveness make them indispensable tools for research, development, and production processes.
The ability of laboratory presses to provide consistent, repeatable results is particularly valuable in industries where accuracy is paramount. Whether used for testing new materials, compressing powders into tablets, or laminating flexible electronics, laboratory presses deliver the precision and control needed to ensure high-quality outcomes.
As industries continue to evolve, laboratory presses are becoming more advanced, with new features such as programmable cycles, smart technologies, and IoT integration. These advancements are helping to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and contribute to more sustainable production processes.
For businesses and research institutions looking to invest in equipment that will provide long-term reliability, versatility, and performance, laboratory presses are a clear choice. Their ability to adapt to different applications, provide energy-efficient solutions, and deliver consistent results makes them an invaluable asset in today’s fast-paced, innovation-driven world.
As technology continues to evolve, laboratory presses will remain at the forefront of research and production, helping industries develop new materials, create innovative products, and optimize their processes. By providing the precision, control, and versatility needed to meet the demands of modern industry, laboratory presses are playing a critical role in advancing science and technology in the 21st century.
EMS Metalworking Machinery

We design, manufacture and assembly metalworking machinery such as hydraulic transfer press, glass mosaic press, hydraulic deep drawing press, casting press, hydraulic cold forming press, hydroforming press, composite press, silicone rubber moulding press, brake pad press, melamine press, SMC & BMC Press, Labrotaroy press, edge cutting trimming machine, edge curling machine, trimming beading machine, trimming joggling machine, cookware production line, pipe bending machine, profile bending machine, bandsaw for metal, cylindrical welding machine, horizontal pres and cookware, kitchenware, hotelware, bakeware and cuttlery production machinery as a complete line as well as an individual machine such as edge cutting trimming beading machines, polishing and grinding machines for pot and pans, hydraulic drawing presses, circle blanking machines, riveting machine, hole punching machines and press feeding machine,
You can check our machinery at work at: EMS Metalworking Machinery – YouTube
Applications:
- Beading and ribbing
- Flanging
- Trimming
- Curling
- Lock-seaming
- Ribbing
- Flange-punching