
Pipe welding machine is specialized welding equipment designed to join cylindrical and curved components, commonly pipes. They utilize various welding processes, such as gas metal arc welding (GMAW), gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), and submerged arc welding (SAW), to create strong and durable welds.
Types of Pipe Welding Machines:
- Rotary Welding Machines: These machines rotate the workpiece during welding, ensuring consistent weld quality and access to all weld seams.
- Orbital Welding Machines: These machines utilize an orbital motion to weld the joint, providing precise control over weld depth and penetration.
- Head-to-End Welding Machines: These machines are designed for welding pipes end-to-end, forming a continuous seam.
- Automatic Welding Machines: These machines are automated using robotic arms or other controlled systems, enabling high-speed and consistent welding operations.
Key Features of Pipe Welding Machines:
- Load Capacity: The maximum weight of the workpiece that the machine can handle.
- Pipe Diameter Range: The range of pipe diameters that the machine can weld.
- Rotation Speed: The speed at which the machine rotates the workpiece or travels along the weld seam.
- Welding Process Compatibility: The ability to weld using various welding processes, such as GMAW, GTAW, or SAW.
- Automation Capabilities: The ability to integrate with automation systems for automated welding operations.
- Safety Features: Interlocks, guards, and emergency stop buttons to prevent accidents and hazards.
Applications of Pipe Welding Machines:
- Oil and Gas Industry: Welding pipelines for oil and gas transportation.
- Power Generation Industry: Welding pressure vessels, pipes, and other components for power plants.
- Chemical Industry: Welding reactor vessels, piping systems, and storage tanks.
- Construction Industry: Welding pipe structures, scaffolding, and other steel components.
- Manufacturing Industry: Welding pipes for various applications, such as water supply, irrigation, and manufacturing equipment.
Pipe welding machines are essential tools for joining cylindrical and curved components in various industries. They provide efficient, high-quality welds and contribute to the infrastructure, manufacturing, and energy sectors.
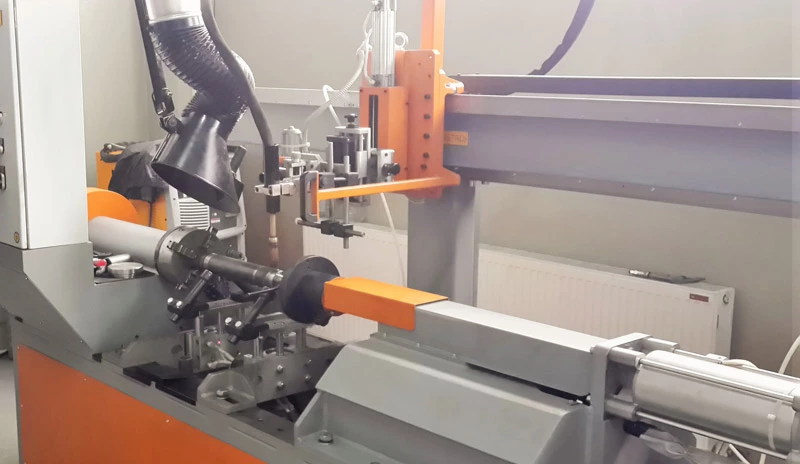
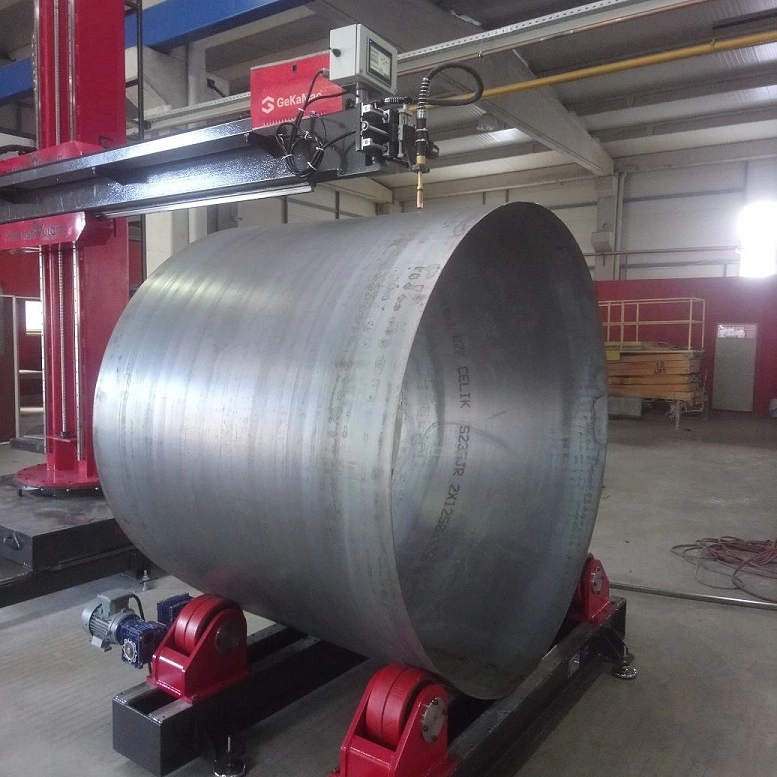
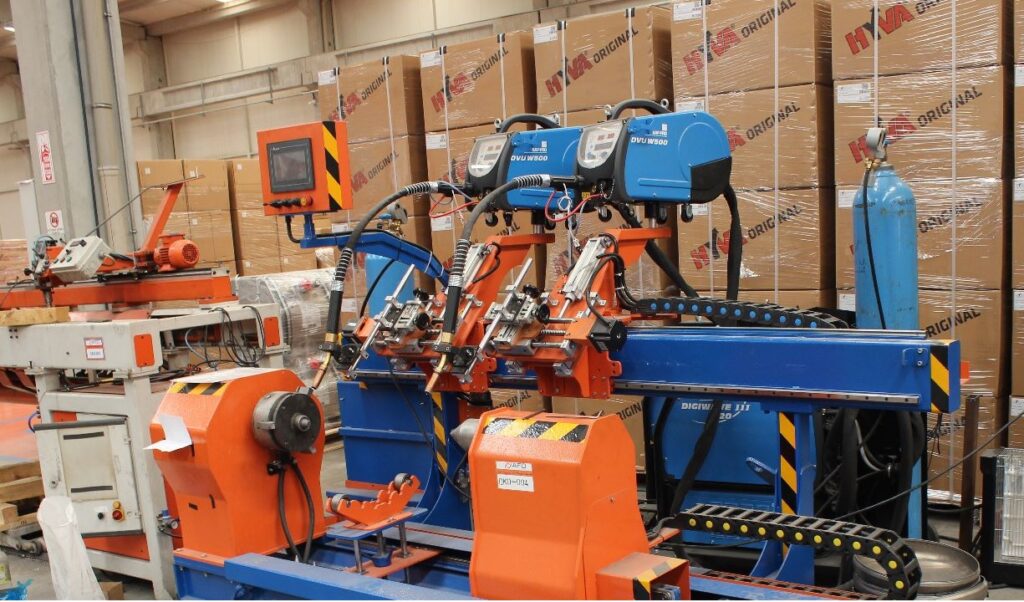
The proposed design of the pipe welding machine aims to give a solution to automate the tedious and repetitive Circular welding process of the exhaust system. The bent pipe, bellow, and straight pipe are the three parts of the exhaust system as shown in figure 1 below to join together with the help of the MIG circular welding process
The following are the major components of the assembly
- Base Plate
- Head Stock
- Tail Stock
- Headstock and flywheel part holding fixture
- Tailstock and flywheel part holding fixture
- Welding Torch assembly
- Bellow clamping and locking unit
Pipe Welding Machine
Pipe welding machines, also known as rotating welding machines or turning rolls, are specialized equipment used to join cylindrical and curved components, commonly pipes. These machines rotate the workpiece during the welding process, ensuring consistent access to all weld seams and enabling efficient, high-quality welds.
Types of Pipe Welding Machines:
1. Rotary Welding Machine:
This type of machine rotates the workpiece along its longitudinal axis, providing access to the entire weld seam. It is suitable for welding pipes of various diameters, from small-diameter tubing to large-diameter pipelines.
2. Orbital Welding Machine:
This machine moves the welding torch in an orbital motion around the weld joint, ensuring precise control over weld depth and penetration. It is particularly useful for joining pipes with complex geometries or where limited access is a concern.
3. Head-to-End Welding Machine:
This machine is designed specifically for welding pipes end-to-end, forming a continuous weld seam without any gaps or discontinuities. It is commonly used in oil and gas pipelines and similar applications.
4. Automatic Welding Machine:
This type of machine is integrated with robotic arms or other controlled systems to automate the welding process. This enables high-speed, consistent welding operations with minimal operator intervention, reducing labor costs and improving productivity.
Technical Specifications of Pipe Welding Machines:
Pipe welding machines are equipped with various technical specifications to ensure efficient and reliable welding operations. These include:
Load Capacity:
The maximum weight of the workpiece that the machine can handle. This is important to ensure the machine can support heavy pipes without compromising stability or precision.
Pipe Diameter Range:
The range of pipe diameters that the machine can weld. Pipe welding machines are typically designed to handle a variety of pipe sizes, from small-diameter tubing to large-diameter pipelines.
Rotation Speed:
The speed at which the machine rotates the workpiece or travels along the weld seam. This is crucial for ensuring consistent weld quality and controlling the deposition rate of the weld material.
Welding Process Compatibility:
The ability to weld using various welding processes, such as gas metal arc welding (GMAW), gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), or submerged arc welding (SAW). This flexibility allows the machine to handle different pipe materials and applications.
Automation Capabilities:
The ability to integrate with automation systems for automated welding operations. This feature is essential for high-volume production and reduces labor costs.
Safety Features:
Interlocks, guards, and emergency stop buttons to prevent accidents and hazards. These safety features protect operators from exposure to sparks, flying debris, and electrical hazards.
Applications of Pipe Welding Machines:
Pipe welding machines are used extensively in various industries to weld a wide range of pipes and components:
Oil and Gas Industry:
Welding pipelines for oil and gas transportation is a critical application where pipe welding machines are essential for ensuring the integrity of pipelines under high pressure and harsh conditions.
Power Generation Industry:
Welding pressure vessels, pipes, and other components for power plants is another major application where pipe welding machines are used to create strong and durable welds that withstand the rigors of power generation environments.
Chemical Industry:
Welding reactor vessels, piping systems, and storage tanks in the chemical industry is crucial for ensuring the safety and integrity of chemical processing equipment.
Construction Industry:
Welding pipe structures, scaffolding, and other steel components in construction projects is essential for building strong and stable structures that can withstand various loads and conditions.
Manufacturing Industry:
Welding pipes for various applications, such as water supply, irrigation, and manufacturing equipment, is essential in various manufacturing processes.
Shipbuilding:
Pipe welding machines are crucial in shipbuilding for welding pipes and tubes used in the construction and maintenance of ships. These welds must withstand the harsh marine environment and the stresses of ship operation.
Food and Beverage Industry:
Pipe welding machines are used in the food and beverage industry to manufacture containers and equipment, such as cans, bottles, and tanks. These welds must meet food safety standards and prevent contamination.
Medical Device Industry:
Pipe welding machines are employed in the medical device industry for producing implantable devices, such as surgical stents, catheters, and prosthetic components. These welds must be precise, durable, and biocompatible to ensure the safety and effectiveness of medical devices.
Appliance Manufacturing:
Pipe welding machines are used in appliance manufacturing for welding cookware, water heaters, and other cylindrical components. These welds must withstand the heat and pressure of appliance operation.
An Automatic Circular Welding Machine is a sophisticated piece of equipment designed to automate the welding process for circular components. These machines are widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and manufacturing, where precision and efficiency are critical. The primary function of an automatic circular welding machine is to ensure consistent, high-quality welds for components like pipes, flanges, cylinders, tanks, and other round structures. By automating the welding process, these machines significantly reduce human error, increase production rates, and enhance the overall quality of the finished product.
At the core of the machine is a rotating fixture or turntable that holds the workpiece in place. The fixture is designed to rotate the component at a controlled speed, allowing the welding head to move along a predetermined path. This ensures uniform weld deposition and eliminates inconsistencies that can occur with manual welding. The welding process can involve various techniques, including TIG (tungsten inert gas), MIG (metal inert gas), or plasma welding, depending on the material and application requirements. Advanced models of circular welding machines may also support laser or friction welding for specialized applications.
One of the key advantages of an automatic circular welding machine is its ability to handle complex welding tasks with minimal operator intervention. These machines are often equipped with programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or CNC (computer numerical control) systems that allow operators to input specific welding parameters, such as speed, voltage, current, and torch movement. Once programmed, the machine can execute the welding process consistently across multiple workpieces, ensuring repeatability and high throughput. This capability is particularly beneficial for mass production environments where identical welds must be produced on a large scale.
In addition to their precision and efficiency, automatic circular welding machines offer enhanced safety for operators. By automating the welding process, workers are less exposed to hazardous fumes, intense light, and high temperatures, which are inherent in manual welding operations. Many machines also include features such as fume extraction systems, shielding gas flow monitoring, and real-time diagnostics to ensure safe and reliable operation.
The versatility of automatic circular welding machines is another significant advantage. These machines can be adapted to weld a wide range of materials, including steel, aluminum, stainless steel, and exotic alloys. They are also capable of welding components of various sizes and thicknesses, making them suitable for diverse industrial applications. Some machines are designed with modular configurations, allowing for easy customization and integration with other automated systems, such as robotic arms or material handling equipment.
Despite their many advantages, the implementation of automatic circular welding machines does come with challenges. Initial investment costs can be high, particularly for advanced models with extensive features. Additionally, operators and maintenance personnel require specialized training to ensure proper operation and upkeep of the equipment. Downtime due to mechanical or software issues can also impact productivity, making regular maintenance and support crucial for long-term performance.
Recent advancements in automatic circular welding machine technology have further expanded their capabilities. Innovations such as real-time monitoring, adaptive control systems, and advanced sensors enable these machines to adjust welding parameters dynamically based on real-time feedback. This not only improves weld quality but also reduces material waste and energy consumption. The integration of Industry 4.0 principles, such as IoT connectivity and data analytics, allows for predictive maintenance and performance optimization, further enhancing the machine’s efficiency and reliability.
In conclusion, automatic circular welding machines represent a significant advancement in welding technology, offering unparalleled precision, efficiency, and safety. Their ability to perform complex welding tasks with minimal human intervention makes them an invaluable asset in modern manufacturing environments. While the initial investment and training requirements may pose challenges, the long-term benefits of increased productivity, consistent quality, and enhanced safety far outweigh the costs. As technology continues to evolve, these machines are likely to become even more versatile and capable, solidifying their role as a cornerstone of automated manufacturing processes.
Automatic Circular Welding Machine
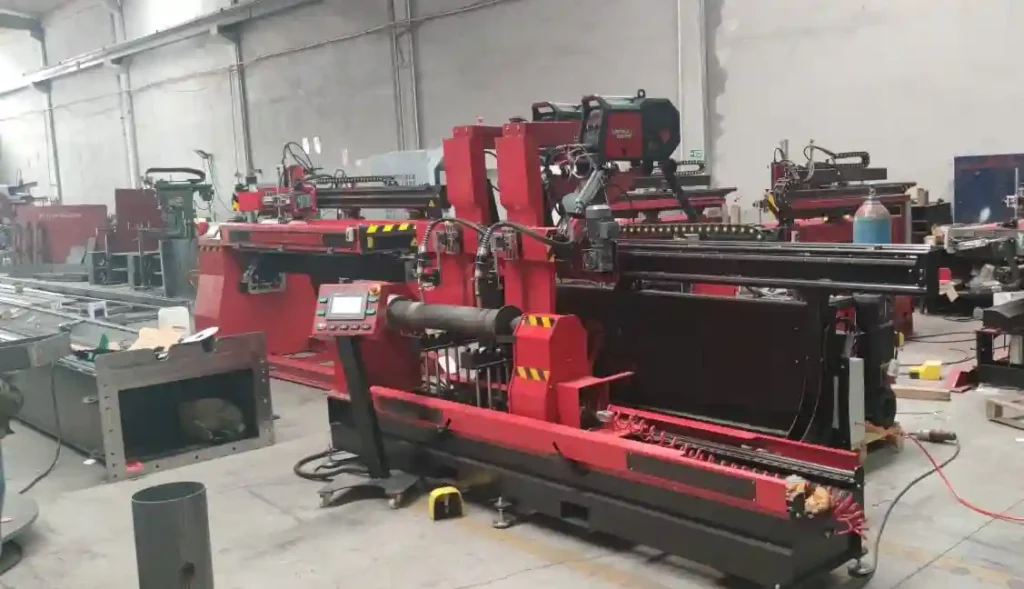

Automatic circular welding machines have continued to gain prominence due to their ability to streamline operations in a wide array of industries. These machines are particularly valuable in applications requiring the joining of circular or curved components, such as pressure vessels, pipelines, wheel rims, and large structural cylinders. Their integration into production lines not only reduces production times but also ensures that weld integrity meets stringent industry standards. High-quality welding is essential for structural and functional reliability, especially in sectors like oil and gas, automotive manufacturing, and aerospace, where the failure of a weld joint could have catastrophic consequences.
One of the key features driving the adoption of automatic circular welding machines is their adaptability to diverse welding processes. TIG welding, for instance, is often employed for precision applications requiring clean and aesthetically pleasing welds, such as in stainless steel or thin aluminum components. On the other hand, MIG welding is preferred for applications requiring high-speed operations and the ability to handle thicker materials. Plasma welding is another popular option for circular welding, offering high penetration and precision, especially for materials with varying thicknesses or challenging geometries. These options allow manufacturers to select a welding process that best suits their specific requirements, enhancing flexibility in production.
Advanced circular welding machines often incorporate high-precision components, such as servo-driven motors, to control the rotation of the workpiece and the movement of the welding torch. The use of servo motors ensures precise and repeatable control over the welding process, even at high speeds. Furthermore, many machines feature multi-axis capabilities, allowing the welding torch to move in complex patterns to accommodate non-standard or asymmetric shapes. This functionality is essential for welding components with intricate designs, such as turbine blades or custom-engineered parts in aerospace applications.
Modern circular welding machines are also equipped with sophisticated monitoring and quality assurance systems. Real-time feedback mechanisms enable the machine to detect deviations from programmed parameters and make adjustments on the fly. For example, sensors may monitor the arc length, shielding gas flow, or temperature of the weld pool, ensuring optimal conditions throughout the welding cycle. These systems not only improve weld quality but also minimize the likelihood of defects, such as porosity, undercutting, or excessive spatter, which can compromise the strength and appearance of the weld joint.
Another noteworthy development in this field is the incorporation of robotic technology into automatic circular welding machines. Robotic arms can be paired with the welding machine to automate the loading, positioning, and unloading of components, further reducing labor requirements and increasing production speed. This integration is especially beneficial in industries where large or heavy components need to be welded, as robots can handle these tasks with ease and precision. Additionally, robotic systems enable the welding machine to operate continuously with minimal downtime, significantly enhancing overall efficiency.
Environmental considerations are also playing a more significant role in the design and operation of automatic circular welding machines. With increasing emphasis on sustainability, many machines now incorporate energy-efficient components and processes that reduce power consumption. For example, advanced power supplies with high-efficiency ratings minimize energy losses during welding. Similarly, improved shielding gas systems ensure optimal gas usage, reducing waste and operational costs. Some machines are also equipped with systems for capturing and filtering welding fumes, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and improving workplace safety.
The market for automatic circular welding machines has expanded rapidly, driven by advancements in technology and growing demand for automation in manufacturing. Innovations in artificial intelligence and machine learning are beginning to influence this field, enabling machines to learn from past welding operations and optimize their performance over time. Predictive maintenance features, powered by AI, can analyze data from sensors and identify potential issues before they lead to machine downtime. These advancements not only improve the reliability and lifespan of the equipment but also provide manufacturers with valuable insights into their production processes.
Looking ahead, the future of automatic circular welding machines seems poised for further innovation. The integration of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies could revolutionize operator training and machine programming, making it easier for personnel to learn and interact with the equipment. Meanwhile, developments in material science may lead to new welding techniques and processes, expanding the range of materials and applications these machines can handle. As industries continue to demand higher efficiency and quality standards, automatic circular welding machines will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of welding technology, driving progress in automated manufacturing and ensuring a sustainable, efficient future for the welding industry.
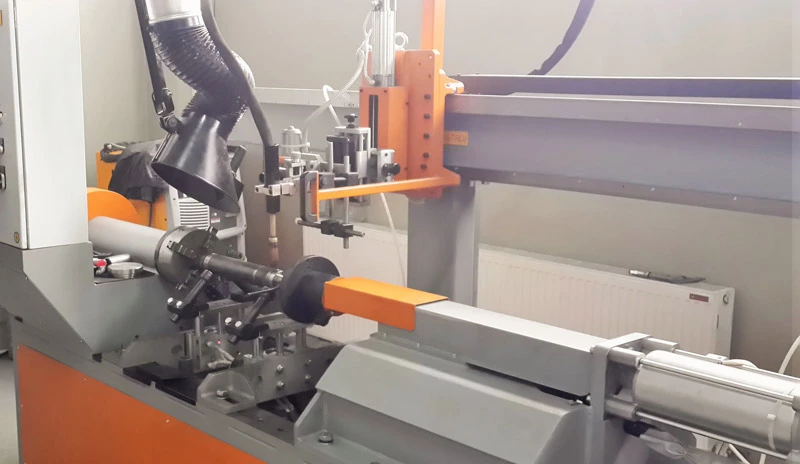

The continued evolution of automatic circular welding machines is closely tied to the broader trends in industrial automation and digitalization. Industry 4.0 technologies are playing a pivotal role in transforming these machines into smart, interconnected systems capable of seamless integration into advanced manufacturing ecosystems. By leveraging the Internet of Things (IoT), automatic circular welding machines can transmit data in real time to centralized monitoring systems, allowing for comprehensive oversight of the welding process. This connectivity not only facilitates predictive maintenance and performance analytics but also enables remote diagnostics and troubleshooting, minimizing downtime and ensuring uninterrupted production.
Another emerging trend is the development of hybrid welding processes, which combine multiple welding techniques to achieve superior results. For example, a hybrid TIG-MIG welding machine can leverage the precision of TIG welding for intricate welds while using the speed and material deposition efficiency of MIG welding for bulk sections. These hybrid machines are particularly beneficial in applications that demand both high productivity and exceptional quality, such as in the fabrication of critical infrastructure or high-performance aerospace components.
Material compatibility continues to be an area of focus for manufacturers of circular welding machines. The rise of advanced materials, such as high-strength alloys, composites, and superalloys, has necessitated the development of welding techniques that can accommodate these materials without compromising their structural properties. Automatic circular welding machines are increasingly equipped with advanced power sources capable of fine-tuning parameters like heat input, pulse frequency, and arc stability. This capability ensures that even challenging materials can be welded effectively, opening up new possibilities for innovation in product design and engineering.
Customization is another critical factor driving advancements in circular welding technology. Manufacturers are now offering highly customizable machines tailored to the specific needs of various industries. For instance, machines designed for the oil and gas industry may include features like submerged arc welding (SAW) capabilities for long, deep welds on large-diameter pipelines. In contrast, machines intended for medical device manufacturing might prioritize precision micro-welding for small, delicate components. This adaptability ensures that circular welding machines can meet the unique demands of any application, regardless of size, scale, or complexity.
Safety enhancements are also a major focus area, as automated welding processes need to comply with strict occupational health and safety standards. Modern machines come equipped with advanced safety features, such as automatic shutdown mechanisms in case of system malfunctions, real-time monitoring of harmful emissions, and protective enclosures to shield operators from intense light and heat. These measures not only protect workers but also ensure compliance with industry regulations, making the workplace safer and more efficient.
The economic benefits of automatic circular welding machines are also significant. While the initial investment in these machines can be substantial, their ability to reduce waste, improve cycle times, and minimize labor costs leads to a high return on investment over time. Automation also reduces dependency on skilled welders, whose availability can be limited in many regions. By standardizing the welding process, these machines deliver consistent results, reducing the need for rework and improving overall production efficiency.
As we look to the future, the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in circular welding machines is expected to expand. AI-driven systems will likely enable machines to analyze complex data sets, predict welding outcomes, and autonomously adjust parameters to optimize performance. For example, AI algorithms could detect subtle changes in material composition or environmental conditions and make real-time adjustments to ensure flawless weld quality. This level of intelligence will further reduce the need for human oversight, allowing operators to focus on strategic tasks rather than day-to-day machine management.
Furthermore, advancements in additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, are expected to influence circular welding technology. Hybrid machines that combine welding and additive manufacturing functions could enable the repair and refurbishment of large circular components, such as turbine casings or pressure vessels. These machines could deposit material layer by layer and weld it in place, offering a cost-effective solution for extending the life of critical assets.
In summary, automatic circular welding machines are at the forefront of welding innovation, combining precision, efficiency, and adaptability to meet the demands of modern manufacturing. Their ability to integrate seamlessly with emerging technologies, handle diverse materials, and deliver consistent, high-quality results positions them as an essential tool for industries worldwide. As advancements in automation, AI, and material science continue, these machines will only become more capable and indispensable, driving progress in manufacturing and shaping the future of industrial production.
Introduction to Automatic Circular Welding Machines
Automatic circular welding machines are essential in industries requiring high precision and efficiency for welding circular or cylindrical components. These machines automate the welding process for round structures such as pipes, tanks, pressure vessels, and wheel rims. By reducing human intervention, they ensure consistent, high-quality welds, making them indispensable in sectors like aerospace, automotive, and energy.
Core Components and Working Principles
Automatic circular welding machines consist of several critical components working together to deliver precise results.
- Rotating Fixture or Turntable: Holds and rotates the workpiece at a controlled speed, ensuring uniform weld deposition.
- Welding Head: Carries the torch or electrode, which moves along a programmed path to weld the component accurately.
- Control System: Typically uses CNC or PLC systems, allowing operators to input parameters like speed, voltage, and torch movement for automated operation.
- Power Source: Provides the energy required for welding, adaptable to different welding techniques such as TIG, MIG, or plasma welding.
The integration of these components ensures the machine can handle complex welding tasks with repeatable accuracy.
Types of Welding Processes Supported
Automatic circular welding machines can accommodate various welding processes, each suited to specific applications and materials:
- TIG Welding: Ideal for thin materials and applications requiring clean, precise welds, such as stainless steel and aluminum components.
- MIG Welding: Suitable for thicker materials and high-speed operations, commonly used in automotive and construction industries.
- Plasma Welding: Offers high penetration and precision, useful for specialized applications involving exotic alloys or varying thicknesses.
- Submerged Arc Welding (SAW): Often used for deep, long welds in large-diameter pipelines or pressure vessels.
These machines can be customized to support one or multiple processes, increasing their versatility.
Advantages of Automatic Circular Welding Machines
The benefits of these machines are extensive, driving their adoption across industries:
- Precision and Consistency: Ensures uniform weld quality, reducing defects and rework.
- Increased Productivity: Automates repetitive tasks, significantly enhancing production speed.
- Safety: Minimizes operator exposure to hazards such as fumes, heat, and light.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces material waste, labor costs, and downtime, providing a high return on investment.
- Versatility: Can handle a wide range of materials, sizes, and applications, from small medical devices to large industrial tanks.
Technological Innovations
Recent advancements have expanded the capabilities of automatic circular welding machines:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Sensors track parameters like arc length, temperature, and gas flow, enabling dynamic adjustments to maintain weld quality.
- AI Integration: Algorithms optimize welding parameters based on real-time data, improving efficiency and reducing waste.
- Hybrid Processes: Combining TIG and MIG or welding with additive manufacturing for innovative applications like component repair.
- IoT Connectivity: Enables remote diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and performance monitoring, aligning with Industry 4.0 principles.
These innovations enhance reliability, precision, and adaptability, keeping the machines at the cutting edge of manufacturing technology.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their advantages, implementing automatic circular welding machines comes with challenges:
- High Initial Costs: Advanced models with extensive features require significant investment.
- Specialized Training: Operators and technicians need expertise in programming and maintaining the machines.
- Maintenance Needs: Regular upkeep is critical to prevent downtime and maintain performance.
Addressing these challenges involves investing in skilled personnel and ensuring robust support systems for maintenance and training.
Applications Across Industries
The versatility of automatic circular welding machines makes them suitable for diverse applications:
- Automotive: Welding components like exhaust pipes, rims, and drive shafts.
- Aerospace: Fabricating high-precision components such as turbine blades and fuselage parts.
- Oil and Gas: Welding pipelines, pressure vessels, and storage tanks.
- Medical: Micro-welding for delicate instruments and devices.
- Construction: Fabricating structural elements like beams and columns.
Each industry benefits from the machine’s ability to deliver high-quality results while meeting specific operational requirements.
Future Trends
The future of automatic circular welding machines is shaped by ongoing advancements in technology:
- AI and Machine Learning: Enhancing adaptive capabilities for better weld quality and process optimization.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Assisting operators in programming and troubleshooting machines more intuitively.
- Sustainability: Developing energy-efficient systems and features like optimized gas usage to reduce environmental impact.
- Modular Designs: Allowing for easier customization and integration with other automated systems, such as robotic arms.
These trends indicate that automatic circular welding machines will continue to evolve, becoming even more efficient, versatile, and essential for modern manufacturing.
Conclusion
Automatic circular welding machines are a cornerstone of modern industrial automation, offering unparalleled precision, efficiency, and adaptability. By addressing challenges and embracing technological innovations, these machines are poised to meet the ever-growing demands of industries worldwide. As they integrate further with advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and AR, their capabilities will expand, ensuring their continued relevance in the future of manufacturing.
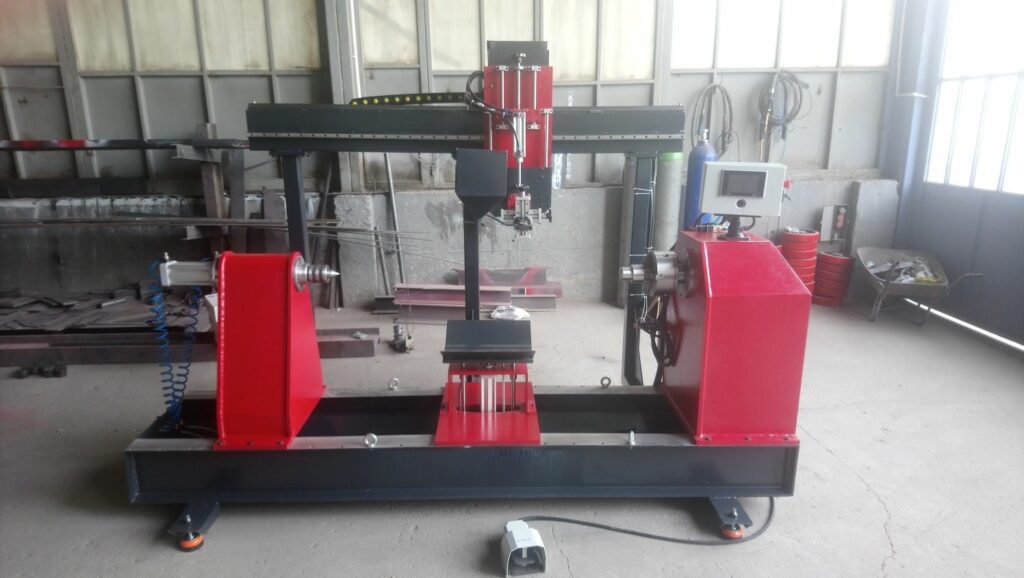
Rotating Fixture or Turntable
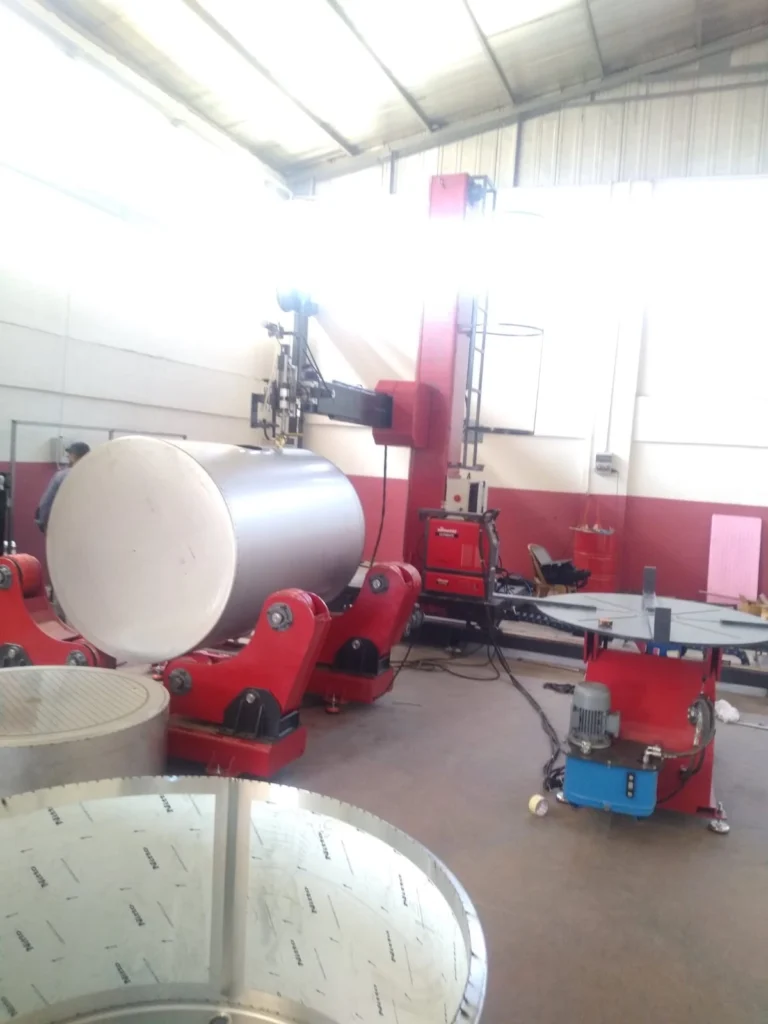

A rotating fixture or turntable is a vital component in many automated welding machines, particularly those designed for circular or cylindrical welding. It serves the primary function of holding and rotating the workpiece while the welding head or torch follows a predefined path to create consistent, high-quality welds. The rotation provided by the turntable ensures that the welding process is uniform around the entire circumference of the component, whether it’s a pipe, tank, wheel rim, or other circular object. This ensures that the weld bead is consistently applied and that the resulting joint is strong and precise.
The design of the rotating fixture is typically tailored to accommodate various sizes and shapes of components. These fixtures are often built with adjustable or flexible clamping systems to secure the workpiece firmly, preventing movement during the welding process. This clamping system ensures that the component stays in place as the fixture rotates, allowing for precise weld deposition without risk of distortion. Depending on the type of automatic welding machine, the rotating fixture may be designed to rotate the workpiece at a constant speed or vary the speed depending on the welding requirements. Some fixtures allow for both horizontal and vertical movement, offering versatility for welding different geometries or orientations.
The turntable’s role extends beyond simply rotating the workpiece. It is often integrated with the machine’s control system, which regulates factors such as the rotation speed, position, and alignment. This integration allows operators to program specific welding parameters and movements, ensuring optimal conditions for the welding process. For example, the rotation speed may need to be adjusted for different materials, thicknesses, or welding techniques, such as TIG, MIG, or plasma welding, to achieve the best weld quality. The turntable, therefore, works in tandem with the welding machine’s other components to deliver a highly efficient and automated process.
One of the key advantages of a rotating fixture or turntable is the consistent quality it provides in welding operations. When a workpiece is rotated smoothly and steadily, the welding head can focus on a continuous path without interruption. This constant motion is particularly important for circular welds, such as those found in pipe welding, where maintaining a consistent arc and heat input is crucial for achieving a strong, uniform weld. Moreover, the rotation of the workpiece helps prevent thermal distortion, which can be a common issue in welding. By rotating the piece evenly, the turntable helps distribute the heat more uniformly, reducing the risk of warping or other defects.
Rotating fixtures also contribute to increased productivity in automated welding environments. The ability to rotate large workpieces at a controlled speed enables faster welding cycles, as the machine can weld the entire circumference of the component in one pass. This is especially beneficial in high-volume production environments, where efficiency and speed are critical. The turntable’s role in automating the welding process reduces the need for manual labor, freeing operators from having to reposition components or adjust the workpiece during the welding cycle. As a result, welding operations become more streamlined and less dependent on human intervention.
Another benefit of a rotating fixture is its ability to handle various materials and component sizes. The versatility of modern rotating fixtures allows them to be used for a wide range of welding applications, from small, delicate components to large industrial parts. Some turntables are designed with adjustable diameter features, enabling them to accommodate different sizes of workpieces. These adjustable turntables can be especially useful in industries like aerospace, automotive, and energy, where components can vary significantly in size and complexity.
The use of a rotating fixture or turntable also enhances the safety of the welding process. Since the workpiece is securely held in place and rotated automatically, operators are less exposed to the risks associated with manual handling, such as burns, exposure to intense light, and inhalation of harmful fumes. The automated rotation ensures that the welding process is completed efficiently and accurately without requiring constant adjustments by the operator. Additionally, many modern turntables are equipped with safety features such as protective enclosures, emergency stop mechanisms, and sensors to detect issues like misalignment or mechanical failure. These safety features help ensure that the rotating fixture operates smoothly and reduces the risk of accidents during the welding process.
The development of more advanced rotating fixtures and turntables has led to further improvements in welding technology. For instance, some turntables are now equipped with advanced servo motors that allow for precise control over the rotation speed and position of the workpiece. These motors provide the ability to make fine adjustments during the welding process, ensuring that even complex welds can be performed with high accuracy. In addition, some turntables now feature integrated sensors and feedback mechanisms that provide real-time monitoring of the welding process. These sensors can track factors such as rotation speed, alignment, and temperature, providing valuable data to operators and enabling automated adjustments to optimize the weld quality.
In conclusion, the rotating fixture or turntable is a critical component in the functioning of automatic circular welding machines. It ensures that the workpiece is held securely and rotated smoothly during the welding process, allowing for consistent, high-quality welds. By automating the rotation of the workpiece, the turntable increases productivity, reduces the need for manual labor, and improves the overall quality of the weld. Whether used for small components or large industrial applications, rotating fixtures are integral to modern welding systems and continue to evolve with advancements in technology to meet the demands of various industries.
Welding Head

The welding head is a crucial component of automatic welding machines, serving as the interface between the welding system and the workpiece. It is responsible for directing the welding process, ensuring that the correct amount of heat, pressure, and filler material is applied to create strong, precise welds. In automated circular welding systems, the welding head is typically mounted on a mechanical arm or robotic system, allowing it to move along the predetermined path while the workpiece rotates. The welding head is integral to the quality and consistency of the weld, as it controls several key parameters, such as the welding arc, the speed of travel, and the delivery of shielding gases.
A primary function of the welding head is to hold the welding torch or electrode in the correct position relative to the workpiece. The torch is the tool that generates the heat required for welding, and it needs to be precisely controlled to maintain a consistent arc. For example, in TIG (tungsten inert gas) welding, the welding head holds a tungsten electrode that generates the arc, while in MIG (metal inert gas) welding, the welding head feeds a consumable wire into the arc to join the materials together. The position of the torch must be controlled accurately to ensure that the weld pool is of the right size and that the weld bead is applied in a uniform manner. A slight deviation in torch positioning can lead to weld defects such as undercuts, lack of fusion, or excessive spatter.
The welding head also controls the speed at which the torch moves along the workpiece. This speed must be adjusted based on various factors, such as the material type, thickness, and welding technique. For example, in MIG welding, the speed of travel is generally faster than in TIG welding due to the difference in the heat and deposition rates. The welding head is typically integrated with the machine’s control system, which allows operators to set the appropriate speed for different welding parameters. In automated systems, the movement of the welding head is often synchronized with the rotation of the workpiece, ensuring that the welding process is consistent around the entire circumference of the component.
Another important function of the welding head is the delivery of shielding gas. Shielding gases protect the weld from contamination by preventing the surrounding air from reacting with the molten metal. The welding head is equipped with nozzles or gas diffusers that control the flow of these gases. In TIG and MIG welding, shielding gases like argon, helium, or a mixture of gases are used to create an inert atmosphere around the weld pool. The welding head ensures that the gas flow is steady and consistent, preventing issues like oxidation or porosity in the weld. The correct gas flow is essential for achieving high-quality welds, especially in materials that are sensitive to contamination, such as aluminum and stainless steel.
The welding head also plays a critical role in maintaining the correct arc length, which refers to the distance between the welding torch and the workpiece. The arc length must be carefully controlled to ensure a stable and focused weld pool. If the arc is too short, it can lead to excessive spatter or an unstable weld, while a long arc can result in poor penetration or inconsistent heat distribution. Automatic systems adjust the position of the welding head dynamically to maintain the optimal arc length throughout the welding process. This control is especially important in automated systems where consistency across multiple workpieces is crucial.
In addition to these core functions, the welding head is often equipped with advanced features that enhance the quality and precision of the welding process. For example, some welding heads are equipped with oscillating mechanisms that allow the torch to move in a controlled pattern across the workpiece. This oscillation helps to distribute the heat more evenly, creating a wider, more uniform weld bead. Oscillation can be particularly beneficial when welding materials with irregular surfaces or in applications that require large, wide welds, such as tank fabrication or pipe welding.
In more advanced models, the welding head may also incorporate real-time monitoring systems that provide feedback to the control system. Sensors embedded in the welding head can track parameters such as arc stability, temperature, and gas flow, providing continuous data to optimize the welding process. For instance, if a sensor detects that the arc is becoming unstable, the control system can make automatic adjustments to the welding head’s position or the welding parameters, ensuring that the weld quality remains consistent. These systems are often integrated with machine learning algorithms that learn from past welding operations, further improving the accuracy and efficiency of the welding process over time.
The design of the welding head is highly dependent on the specific welding process being used and the requirements of the application. For instance, in high-precision welding applications, such as aerospace or medical device manufacturing, the welding head may be specially designed to deliver very fine, controlled welds. These heads may be equipped with micro-torches or advanced cooling systems to prevent overheating, which is critical when working with delicate components. In contrast, for high-volume production applications, such as automotive manufacturing, the welding head may be designed for rapid movement and robust performance under continuous operation.
In some automated systems, the welding head can be mounted on a robotic arm or gantry, which allows it to move not only along the workpiece but also in multiple axes. This ability to move in three dimensions provides flexibility in welding complex or non-circular parts, expanding the welding head’s range of applications. Robotic systems can further enhance the precision and repeatability of the welding process, as the welding head can be programmed to follow highly specific paths with minimal deviation. This level of control is particularly useful in industries where high standards of quality and consistency are required, such as in the fabrication of critical infrastructure or high-performance machinery.
In conclusion, the welding head is an integral part of any automatic welding system, responsible for directing the welding process and ensuring the quality of the weld. Its key functions include controlling the arc, maintaining the correct speed, and managing the delivery of shielding gases, all of which contribute to producing strong, uniform welds. The welding head’s design and functionality are critical in determining the performance of the welding machine and the success of the overall welding process. As welding technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities of the welding head, with innovations in sensors, control systems, and robotic integration enhancing the precision, efficiency, and versatility of the welding process.
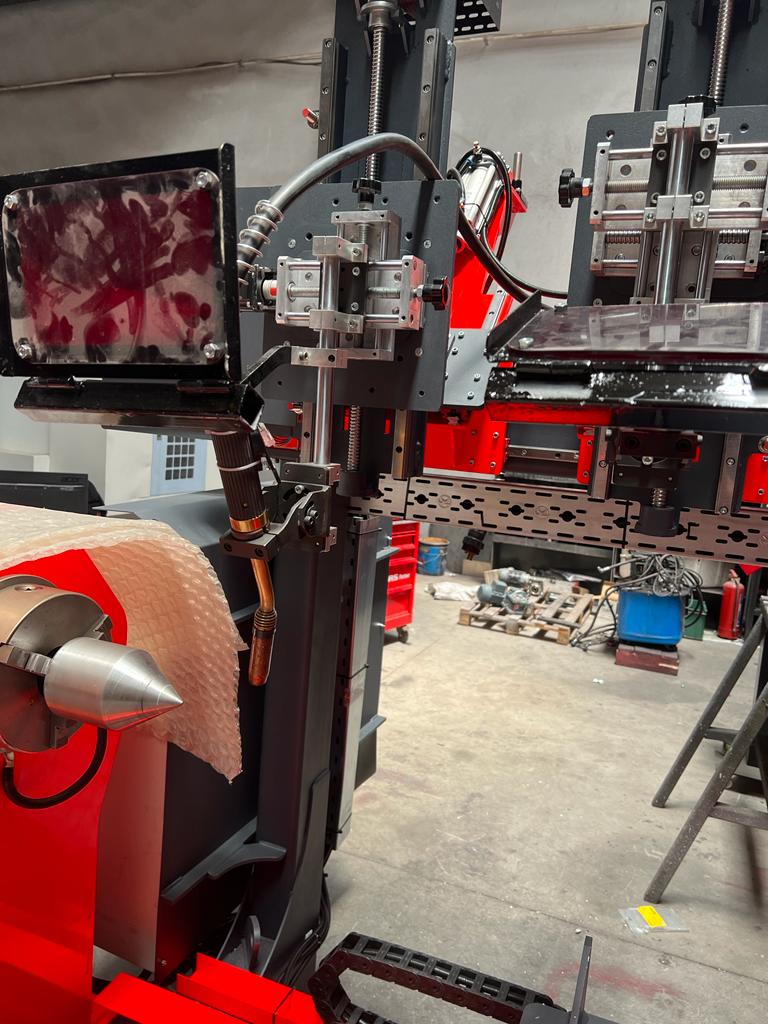
Control System
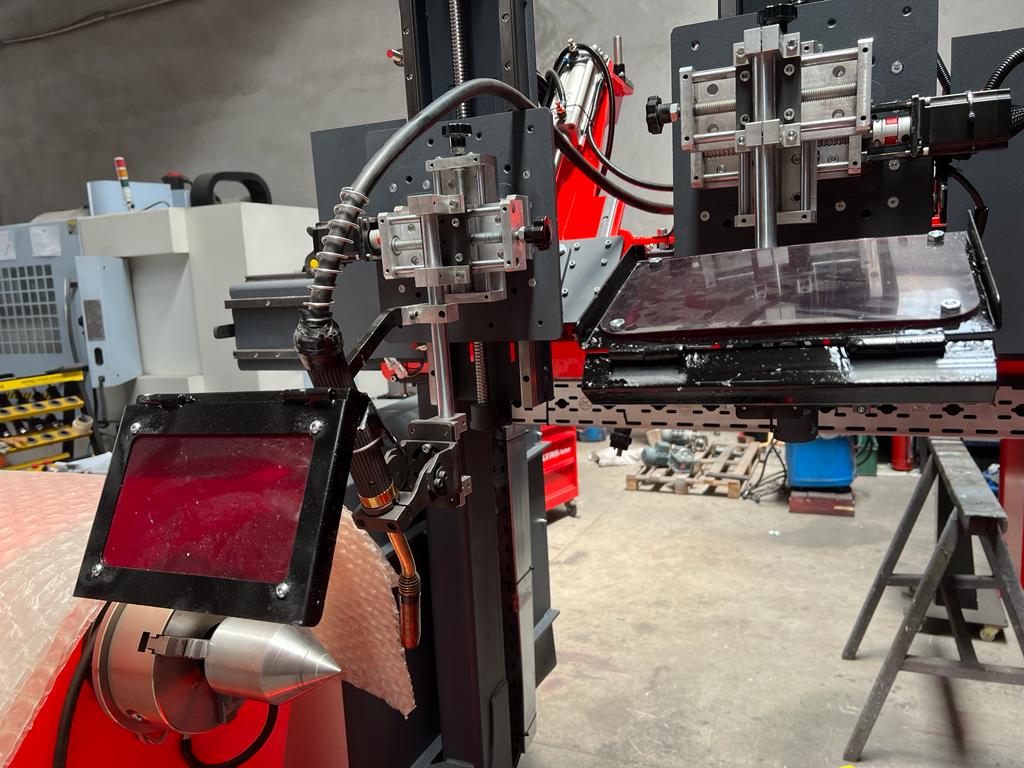
The control system in an automatic welding machine is one of the most important components, responsible for regulating and managing the various parameters of the welding process to ensure optimal performance and consistent weld quality. The control system coordinates the actions of the welding head, rotating fixture, power supply, and other machine components, making it the brain of the entire operation. By precisely controlling factors such as welding speed, arc length, power settings, gas flow, and electrode movement, the control system ensures that the welding process remains stable and efficient throughout.
A key feature of modern control systems is their ability to handle a wide range of welding parameters, which vary depending on the materials being welded, the type of welding process, and the specific requirements of the application. The control system uses a combination of hardware and software to monitor these variables and adjust them in real-time to achieve the best results. The system typically consists of a central processing unit (CPU), input and output modules, and an interface for operators to input settings and monitor the process.
At the heart of the control system is the software, which allows operators to input welding parameters and adjust settings to suit specific tasks. In many automated welding systems, the control software is highly customizable, allowing users to save predefined programs for various tasks. This means that the operator can set the system to automatically apply the optimal parameters for a particular material, thickness, or joint configuration. For instance, the system can automatically adjust welding speed, voltage, current, and wire feed rate for MIG welding or adjust arc voltage and gas flow for TIG welding. This customization allows for precise and efficient welding without the need for constant manual adjustments.
In addition to controlling welding parameters, the control system also manages the motion of the welding head and the workpiece. In an automated circular welding machine, the control system coordinates the movement of the rotating fixture, ensuring that the workpiece rotates at a constant speed to allow for a uniform weld around the circumference. The system also ensures that the welding head moves along the programmed path with the correct speed, maintaining the optimal arc length throughout the process. In some systems, the motion of the welding head may be adjusted dynamically based on real-time feedback from sensors, further enhancing the precision and quality of the weld.
The control system also plays a critical role in monitoring and adjusting the power supply to the welding machine. The power source must deliver the right amount of current and voltage to the welding arc to achieve the desired weld quality. The control system monitors the welding process and makes real-time adjustments to the power supply to maintain the ideal conditions. For example, if the system detects that the arc is becoming unstable or that the welding speed is too fast, it can automatically reduce the current or adjust the voltage to stabilize the process. This continuous feedback loop ensures that the weld quality is maintained, even in changing conditions or as the workpiece is completed.
Another important function of the control system is managing the delivery of shielding gas. Proper shielding is essential to prevent contamination of the weld pool, and the control system ensures that the right amount of gas is delivered at the right time. In addition to controlling the flow rate of the gas, the control system also monitors gas pressure and purity to ensure that the welding environment remains optimal. Many advanced control systems can even adjust the gas flow dynamically based on the welding parameters or environmental conditions, such as changes in temperature or humidity, to ensure a stable and high-quality weld.
Modern control systems in automatic welding machines often include advanced features such as real-time monitoring, diagnostics, and data logging. These systems collect and analyze data from various sensors and components throughout the machine, including temperature sensors, pressure sensors, and arc stability monitors. The data is then used to identify any issues or inconsistencies in the welding process, such as poor arc stability or incorrect gas flow. In some systems, this information is displayed on a user-friendly interface that allows the operator to make quick adjustments or initiate troubleshooting. This level of monitoring helps prevent potential problems before they affect the weld quality, reducing the need for rework and improving overall efficiency.
Furthermore, advanced control systems can integrate with other systems in the manufacturing environment. For example, in industries where multiple welding machines are used in a production line, the control systems of each machine can be interconnected to synchronize operations and improve overall workflow. In such cases, the central control system can coordinate the movement of multiple machines, ensuring that each one performs its task in sequence and minimizing downtime. This level of integration is particularly beneficial in high-volume manufacturing environments, where productivity and efficiency are key.
Some modern control systems are also equipped with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning capabilities. These systems can analyze large volumes of data from previous welding jobs to optimize welding parameters and improve future performance. For example, the AI algorithm might learn from past welding cycles to predict optimal settings for new materials or complex joint configurations. As these systems continue to evolve, they will further reduce the need for human intervention, providing a more autonomous and self-optimizing welding process.
Additionally, many control systems are designed to be user-friendly, with intuitive interfaces that simplify the programming and operation of welding machines. Touchscreens, graphical user interfaces (GUIs), and even remote access options make it easy for operators to adjust settings, monitor performance, and troubleshoot issues. With these advanced interfaces, even those with minimal welding experience can quickly become proficient in operating the system, reducing the learning curve and improving operational efficiency.
Safety is another critical aspect of the control system in automatic welding machines. The control system continuously monitors the operation of the machine to ensure that safety standards are met. If any dangerous conditions are detected, such as overheating, electrical malfunctions, or misalignment, the system can trigger alarms or automatically shut down the machine to prevent accidents. Additionally, some systems are equipped with safety interlocks that prevent operators from accessing hazardous areas during operation, further enhancing workplace safety.
In conclusion, the control system in an automatic welding machine is the cornerstone of the entire welding process, regulating key parameters like welding speed, arc length, gas flow, and power supply. By coordinating the movement of the welding head and workpiece, adjusting real-time settings, and providing continuous monitoring, the control system ensures that the welding process remains stable and produces high-quality results. With advancements in technology, control systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, integrating AI, machine learning, and real-time diagnostics to optimize the welding process and improve efficiency. As automation continues to shape the future of welding, the control system will remain central to the performance and success of welding operations across industries.
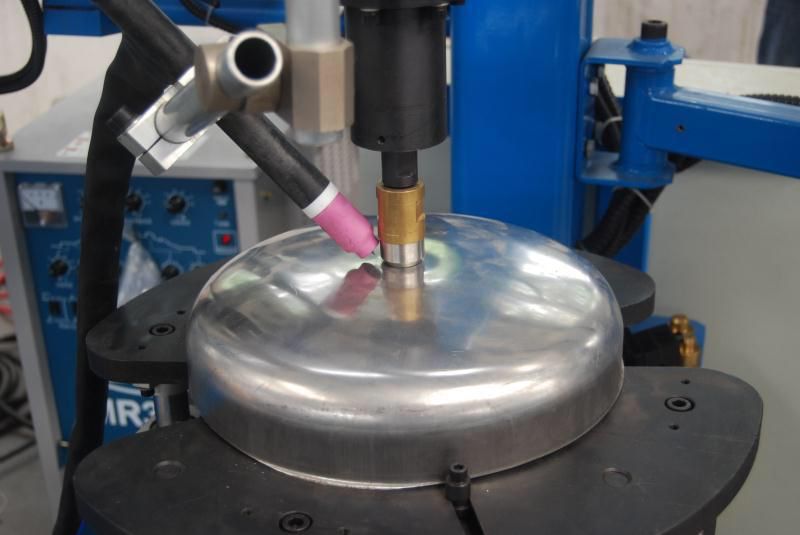
Power Source

The power source is a critical component in an automatic welding machine, as it provides the electrical energy needed to generate the welding arc and maintain its stability throughout the welding process. It is responsible for converting the incoming electrical power into a form that is suitable for welding, typically by adjusting the voltage and current to meet the specific requirements of the welding technique, material, and thickness. The power source must work in harmony with other components of the welding machine, such as the welding head, control system, and power supply cables, to ensure that the welding process is efficient, precise, and produces high-quality results.
The most common types of welding power sources are constant voltage (CV) and constant current (CC) systems. A constant current power source is typically used for processes like TIG (tungsten inert gas) welding or stick welding, where the arc length is manually controlled and the current must remain relatively constant to maintain a stable arc. On the other hand, a constant voltage power source is typically used for MIG (metal inert gas) welding, where the welding machine automatically adjusts the current to maintain a consistent arc length as the torch moves along the workpiece. The power source must provide the correct balance of voltage and current depending on the welding technique and the material being worked on.
The power source works by controlling the electrical characteristics of the welding arc, including the voltage and current. Voltage refers to the electrical potential difference between the electrode and the workpiece, while current refers to the flow of electricity through the arc. In a typical welding operation, the power source needs to provide enough current to melt the base material and create the desired weld pool while maintaining the correct voltage to ensure a stable and controllable arc. If the current is too high, it can cause excessive heat input, leading to weld defects such as burn-through or excessive spatter. Conversely, if the current is too low, the arc may become unstable or fail to penetrate the base material properly.
In addition to regulating voltage and current, the power source is also responsible for controlling other key parameters that affect the welding process, such as arc stability, electrode efficiency, and heat input. For example, many modern power sources include features like arc force control, which adjusts the arc characteristics to provide a more stable and smooth weld. Arc force control is particularly important in applications where the welding process involves a lot of movement or where the arc may be prone to fluctuations. This feature helps maintain a stable arc by automatically adjusting the power settings to counteract disturbances, such as changes in the distance between the electrode and the workpiece.
Power sources also often include features that enhance the efficiency and versatility of the welding process. One such feature is the ability to adjust the power output for different materials and joint configurations. For example, when welding thicker materials, the power source may increase the current to ensure sufficient heat penetration. In contrast, for thin materials, the power source may reduce the current to avoid overheating and warping. The ability to adjust power settings automatically or manually depending on the material and application allows for greater flexibility in welding operations, especially in automated systems where different materials and thicknesses are being worked on continuously.
A modern welding power source also typically incorporates advanced safety features. Welding can generate significant electrical hazards, and the power source is designed to mitigate these risks by including features such as overcurrent protection, thermal overload protection, and short-circuit protection. Overcurrent protection ensures that the welding machine does not draw too much current, which could damage the components or create dangerous conditions. Thermal overload protection prevents the power source from overheating, which could lead to equipment failure or fires. Short-circuit protection ensures that the system is protected from faults or improper connections, preventing damage to the power source or other components.
Another important aspect of the power source is its energy efficiency. Modern welding power sources are designed to be more energy-efficient, minimizing energy consumption while providing the necessary power for welding operations. Many newer systems utilize inverter technology, which allows for higher efficiency and more precise control over the power output. Inverter-based power sources can convert electrical power more efficiently than traditional transformer-based systems, leading to less energy waste and better overall performance. These power sources are often lighter and more compact, making them ideal for both portable and stationary applications.
In addition to these basic functions, the power source is often integrated with the welding machine’s control system, allowing for real-time monitoring and adjustments. In advanced automated welding systems, the power source can be controlled remotely or adjusted dynamically based on feedback from sensors or other components. For instance, if the control system detects a variation in arc length or a shift in material thickness, it can send a signal to the power source to adjust the voltage or current accordingly. This integration of the power source with the control system allows for highly precise and adaptive welding, particularly in automated environments where the machine needs to operate with minimal human intervention.
The power source must also be compatible with a range of welding processes. Different processes require different types of power sources to achieve optimal results. For example, TIG welding often requires a high level of precision and control, so the power source for this process may need to offer fine adjustments in voltage and current. MIG welding, on the other hand, requires a power source that can maintain a steady, high voltage to support the continuous wire feed and ensure proper weld formation. The power source must, therefore, be versatile enough to handle the demands of various welding techniques and applications, whether it’s used for thin sheet metal fabrication, heavy structural welding, or high-precision tasks.
Moreover, some advanced power sources come with specialized modes or features designed for specific welding applications. Pulse welding, for instance, is a technique commonly used in MIG and TIG welding to control heat input and reduce spatter. A power source with pulse welding capabilities can adjust the current in a controlled manner, delivering high current for a brief period and then reducing it, creating a pulsed arc. This helps control the heat input, preventing distortion and burn-through while improving weld quality.
In conclusion, the power source is a vital component in any automatic welding machine, responsible for delivering the electrical energy required to generate a stable and consistent welding arc. It controls key parameters such as voltage, current, and arc stability, ensuring that the welding process remains precise and effective across a variety of materials and applications. Modern power sources offer a wide range of features, including advanced control over arc characteristics, energy efficiency, and safety, making them essential for high-quality automated welding. By integrating seamlessly with other machine components and control systems, the power source ensures that the welding process is optimized for performance, productivity, and safety.
Types of Welding Processes Supported

Automatic welding machines are designed to support a variety of welding processes, each suited to specific materials, joint configurations, and production requirements. The versatility of these machines allows them to accommodate different welding techniques, making them valuable in industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to construction and manufacturing. The types of welding processes supported by an automatic welding machine determine the nature of the welding arc, the type of electrode or filler material used, and the manner in which the heat is applied to the workpiece. Some of the most commonly supported welding processes include MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, Stick welding, Submerged Arc Welding (SAW), and Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW).
MIG Welding (Metal Inert Gas Welding)
MIG welding, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), is one of the most widely used welding processes supported by automatic welding machines. This process involves feeding a continuous wire electrode into the weld pool while an inert or semi-inert gas, such as argon or a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide, is used to shield the molten weld pool from contamination. MIG welding is particularly favored for its speed and ease of automation, making it ideal for high-volume production applications such as automotive manufacturing and sheet metal fabrication. Automatic machines can precisely control parameters such as wire feed speed, voltage, and travel speed to ensure consistent and high-quality welds.
TIG Welding (Tungsten Inert Gas Welding)
TIG welding, or Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is another popular process supported by automatic welding systems. In TIG welding, a non-consumable tungsten electrode is used to generate the arc, and a filler rod is added manually or automatically, depending on the system. This process is known for producing clean, high-quality welds with excellent precision and minimal spatter, making it ideal for welding thin materials, stainless steel, and exotic metals like titanium. TIG welding requires a high degree of skill and control, which is why it is often integrated into automatic welding systems for applications that require fine weld beads, such as aerospace or precision manufacturing.
Stick Welding (Shielded Metal Arc Welding)
Stick welding, or Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), is one of the most traditional and commonly used welding processes, particularly in construction, repair, and maintenance work. This process uses a consumable electrode coated with a flux that creates a protective gas shield around the weld pool. While it is generally a more manual process, automatic welding systems can be adapted for stick welding in specialized applications, particularly where portability and high penetration are required. Stick welding is often used in heavy fabrication and outdoor applications because it can handle dirty or rusty surfaces and is less sensitive to wind compared to other welding techniques.
Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) is a highly efficient welding process that uses a continuous filler wire and an arc that is submerged under a blanket of granular flux. This process is primarily used for welding thick sections of steel and other heavy materials, particularly in industries such as shipbuilding, structural fabrication, and pipeline construction. The submerged arc provides a stable, consistent arc, which leads to deep penetration and high deposition rates. Automatic welding systems can manage the flux delivery, wire feed, and arc parameters to ensure optimal results, making SAW ideal for large-scale industrial applications that demand high-quality, high-volume welds.
Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) is a variant of MIG welding that uses a flux-cored wire instead of a solid wire electrode. The flux inside the wire generates a shielding gas when the arc is struck, eliminating the need for an external gas supply. FCAW is particularly useful for welding thicker materials, such as in the construction of heavy machinery or steel structures. There are two primary types of FCAW: self-shielded and gas-shielded. Self-shielded FCAW is used in outdoor or wind-prone environments, while gas-shielded FCAW is similar to MIG welding and requires an external shielding gas. Automatic welding systems for FCAW control wire feed rates, voltage, and arc length, ensuring a stable and efficient process suitable for industrial production.
Plasma Arc Welding (PAW)
Plasma Arc Welding (PAW) is a variation of TIG welding that uses a focused, high-temperature plasma arc to melt and join metals. This process is highly effective for precision welding and is often used for welding thin materials, fine-tuned control of the arc, and applications requiring high-quality welds. PAW can be more complex than traditional TIG welding but is increasingly supported by automatic welding machines due to its ability to achieve a narrow, concentrated heat source and fine control over the welding process. It is commonly used in industries such as aerospace and electronics, where precise and clean welds are critical.
Laser Beam Welding (LBW)
Laser Beam Welding (LBW) uses a high-powered laser to melt and join materials, producing extremely precise, narrow welds with minimal heat input. This welding process is ideal for applications where precision and speed are paramount, such as in the automotive, aerospace, and medical device industries. Automatic welding systems equipped with laser welding heads are capable of controlling the laser’s intensity, focus, and positioning to ensure precise and repeatable welds. The use of lasers also minimizes heat distortion and allows for high-quality welding of thin or delicate materials.
Electron Beam Welding (EBW)
Electron Beam Welding (EBW) is a high-precision welding process that uses a focused beam of high-energy electrons to heat and melt materials. EBW is typically used for applications that require extremely tight tolerances and minimal thermal distortion, such as in the aerospace and nuclear industries. Automatic welding machines that support EBW are equipped with specialized electron guns and vacuum chambers to ensure that the process is conducted under controlled conditions. While more complex than other welding methods, EBW offers unparalleled precision, depth of penetration, and speed in certain applications.
Resistance Welding
Resistance welding processes, such as Spot Welding and Seam Welding, are widely used in high-volume production settings, especially in the automotive and appliance industries. In these processes, heat is generated by passing a high current through the materials to be welded, creating a molten pool at the contact points. Resistance welding is typically used for joining sheet metal and is highly effective for mass production because of its speed, efficiency, and automation capabilities. Automatic welding machines support resistance welding by controlling parameters such as current, pressure, and welding time to ensure consistent and high-quality results.
Gas Welding (Oxy-Acetylene Welding)
Gas welding, specifically Oxy-Acetylene Welding (OAW), uses a flame produced by the combustion of acetylene and oxygen to melt the base material and form a weld. While this process is becoming less common in automated systems due to the rise of more efficient welding techniques, it is still used for certain specialized applications. Automatic machines supporting OAW are typically used for brazing, cutting, and welding thin materials or for applications that require localized heat. The process is controlled by adjusting the gas mixture and flame temperature to suit the specific welding task.
Hybrid Welding Processes
In recent years, hybrid welding processes have emerged, combining the advantages of different welding methods to optimize results. For example, Hybrid Laser-Arc Welding (HLAW) combines laser beam welding and arc welding to provide deep penetration and high-speed welding, particularly for thick materials. Automatic welding machines capable of supporting hybrid welding processes can adjust parameters from both welding processes simultaneously to achieve high-quality results in a variety of industries.
In conclusion, automatic welding machines are designed to support a wide array of welding processes, each tailored to specific material types, thicknesses, and applications. These processes range from traditional methods like MIG and TIG welding to more advanced techniques such as laser beam welding and hybrid welding. The ability of automatic welding machines to support multiple welding processes enhances their versatility and makes them indispensable in industries that require precision, efficiency, and high-quality welds. By selecting the appropriate welding process for a given application, manufacturers can achieve optimal results and streamline production operations.
Advantages of Automatic Circular Welding Machines

Automatic circular welding machines offer several significant advantages that make them highly beneficial in various industrial applications, particularly for high-volume, precision, and consistent welding needs. These machines are designed to handle circular or cylindrical workpieces, such as pipes, tubes, or tank sections, making them ideal for industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, shipbuilding, and oil and gas. The following are key advantages of using automatic circular welding machines:
1. Increased Productivity and Efficiency
One of the primary advantages of automatic circular welding machines is their ability to significantly increase productivity and efficiency in the welding process. Since the machine operates automatically, it can maintain a consistent welding speed and quality without the need for constant manual adjustments or supervision. This leads to faster cycle times and higher output, especially in mass production environments. The automation of the welding process also reduces downtime caused by human error, machine adjustments, or setup changes, allowing the welding system to operate continuously for longer periods. Additionally, automatic circular welding machines can perform high-speed, repetitive tasks with minimal human intervention, reducing labor costs and optimizing production rates.
2. Consistent Weld Quality
Automatic circular welding machines are capable of producing welds with a high degree of consistency and precision. The machine’s control system manages critical parameters such as welding speed, voltage, current, and arc length, ensuring that each weld is uniform and free from defects. This is particularly important when working with complex geometries or when the quality of the weld directly impacts the structural integrity of the finished product. Automatic machines also reduce the likelihood of human error, such as inconsistent torch movement or improper settings, resulting in higher-quality welds with fewer defects, such as porosity, spatter, or uneven bead formation. The consistency of the welds improves product reliability and ensures compliance with strict quality standards.
3. Improved Safety
Using automatic circular welding machines enhances safety in the workplace by minimizing the exposure of operators to hazardous conditions. Welding involves high heat, intense ultraviolet light, and the risk of electric shock, all of which pose safety hazards. Automatic welding machines reduce the need for manual handling and operator interaction during the welding process, which decreases the risk of accidents, burns, and injuries. Additionally, automatic machines are equipped with safety features such as emergency stop buttons, thermal overload protection, and automatic shutoff systems, ensuring that the system can be safely halted in the event of a malfunction or abnormal condition. Furthermore, automatic circular welding machines often come with built-in shielding and ventilation systems to protect operators from harmful fumes and gases.
4. Enhanced Precision and Control
The advanced control systems of automatic circular welding machines enable precise adjustments to welding parameters, allowing for fine control over the entire welding process. These machines can automatically adjust the arc length, heat input, welding speed, and other factors to achieve optimal weld quality. The ability to fine-tune these parameters in real-time ensures that the welding process is more precise than manual welding methods, especially in critical applications such as aerospace or medical device manufacturing. Automatic systems also allow for highly accurate positioning of the welding head, which is essential when working on circular or cylindrical parts that require precise alignment for proper weld formation.
5. Reduced Labor Costs
Automatic circular welding machines reduce the need for manual labor, which in turn helps lower overall labor costs. While operators are still required to monitor the process and ensure that the machine is functioning correctly, the need for skilled welders to perform the actual welding is reduced or eliminated. This is particularly advantageous in industries that require high-volume production or repetitive welding tasks, where automation can replace multiple manual laborers. The reduction in labor requirements not only cuts down on labor costs but also frees up operators to focus on higher-level tasks, such as machine maintenance, quality control, or process optimization.
6. Flexibility and Adaptability
Automatic circular welding machines are highly adaptable and can be programmed to perform a wide range of welding tasks with minimal setup. The ability to easily switch between different welding parameters, materials, and workpiece sizes makes these machines versatile for various applications. For example, an automatic welding system can be reprogrammed to weld different types of pipes, tubes, or cylindrical structures, adjusting settings such as voltage, current, and wire feed speed accordingly. This flexibility is especially beneficial in industries where production runs involve multiple product types or where different welding processes, such as MIG, TIG, or flux-cored welding, are needed.
7. Cost Savings in the Long Run
Although the initial investment in an automatic circular welding machine can be significant, it often leads to substantial cost savings over time. The high efficiency, reduced labor costs, and increased productivity translate into a lower cost per unit of production. Moreover, the consistent weld quality reduces the need for rework and scrap material, further lowering costs. The ability to perform high-volume, automated welding tasks also improves throughput, allowing businesses to meet tight production schedules and deliver products to market faster, which can improve their competitive edge. Additionally, the long lifespan and durability of these machines ensure that the investment is recouped over several years of operation.
8. Reduced Material Waste
Automatic circular welding machines are designed to optimize the use of materials by precisely controlling the heat input, weld speed, and other parameters. This helps minimize material waste by ensuring that the welds are consistent and properly formed, reducing the need for rework and the risk of defects that could lead to scrap. In some cases, automated systems can even detect issues with the welding process and make real-time adjustments, preventing excessive waste of both consumables (such as welding wire or electrodes) and base materials. By reducing material waste, automatic circular welding machines help lower production costs and contribute to more sustainable manufacturing practices.
9. Ability to Weld in Challenging Environments
Automatic circular welding machines are highly beneficial in applications where welding must be performed in difficult or hazardous environments. For instance, in the oil and gas industry, automatic welding systems can be used to weld pipelines in challenging conditions, such as in remote locations or under high-pressure situations. The machine’s ability to operate in a controlled, automated manner ensures that welds can be made safely and effectively, even in these demanding environments. Additionally, because the welding process is automated, it can be performed in controlled environments, such as within enclosed chambers or under water, where manual welding would be impractical or dangerous.
10. Capability for Continuous Operation
Many automatic circular welding machines are designed for continuous operation, making them ideal for applications where welding must be performed around the clock or for extended periods. Automated systems can be programmed to run for long durations without the need for breaks, reducing downtime and maximizing production efficiency. This capability is particularly valuable in industries where time is critical, and where high-volume or large-scale welding projects need to be completed within tight deadlines.
11. Improved Traceability and Data Collection
Modern automatic circular welding machines often come equipped with data logging and monitoring capabilities that provide detailed information about the welding process. These systems track parameters such as welding speed, voltage, current, and travel speed, allowing manufacturers to analyze the data and ensure that welding standards are met. In some cases, the data can be integrated with other production management systems, providing real-time insights into the performance of the welding process. This traceability enhances quality control, improves troubleshooting, and ensures compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Conclusion
In summary, automatic circular welding machines offer a range of advantages, including increased productivity, improved weld quality, enhanced safety, and reduced labor costs. Their ability to perform precise, consistent welds in high-volume production environments makes them indispensable in industries that require efficiency and reliability. The flexibility, cost savings, and ability to adapt to challenging conditions further contribute to the widespread adoption of these machines in modern manufacturing processes. As technology continues to evolve, automatic circular welding machines will continue to play a central role in improving the speed, accuracy, and sustainability of welding operations across various industries.
Orbital Welding Machine

Orbital welding machines are specialized automatic welding systems designed for performing high-precision, continuous circumferential welds on tubular components, typically in industries where cleanliness, quality, and repeatability are crucial. The orbital welding process uses a rotating electrode that moves around the circumference of a pipe or tube, creating a continuous, high-quality weld. These machines are widely used in industries such as aerospace, semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food and beverage processing, and the construction of high-purity pipelines.
Key Features of Orbital Welding Machines
Orbital welding machines are known for their precision, repeatability, and ability to produce consistent, high-quality welds with minimal human intervention. Key features of orbital welding systems include:
- Rotating Electrode
The core principle of orbital welding is the use of a rotating electrode (typically tungsten) that moves around the workpiece. The electrode maintains a constant arc, ensuring that the weld is uniform around the entire circumference of the tube or pipe. This allows for a high degree of control over the heat input and weld pool, which is essential for producing clean, strong, and precise welds. - Automated Process Control
Orbital welding machines are equipped with sophisticated control systems that automate various parameters during the welding process. These machines can control variables such as current, voltage, welding speed, and gas flow rate to maintain optimal conditions throughout the weld. The automatic adjustment of these parameters ensures that each weld meets specific quality standards, even in high-precision applications. - Real-Time Feedback and Monitoring
Many orbital welding machines are equipped with real-time monitoring systems that track key variables, such as arc stability, temperature, and weld bead formation. These systems can provide instant feedback to operators or be integrated with data logging software for later analysis. Real-time monitoring ensures that any potential issues, such as overheating or insufficient penetration, are detected early, allowing for quick adjustments to maintain weld quality. - Purging and Gas Control
Orbital welding often requires the use of an inert gas, typically argon, to shield the weld from contamination. In high-purity applications, the weld area is purged with gas to prevent oxidation or other contaminants from affecting the quality of the weld. Orbital welding machines typically include gas flow controls and purging systems to ensure that the entire weld zone remains protected throughout the process. The use of these controlled gas environments is essential in industries like semiconductor manufacturing, where even small amounts of contamination can compromise the integrity of the weld. - Tight Tolerances and Repeatability
One of the main advantages of orbital welding machines is their ability to achieve tight tolerances and repeatability. Once the machine is set up, it can perform identical welds with minimal variation, making it ideal for applications that require consistency, such as in the construction of pharmaceutical piping or aerospace components. Orbital welding machines are designed to ensure that each weld meets exact specifications, with minimal deviation from the desired weld size and shape.
Types of Orbital Welding
Orbital welding can be categorized into two primary types based on the process used: Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) orbital welding and Plasma Arc Welding (PAW) orbital welding.
- TIG Orbital Welding
TIG orbital welding is the most common type of orbital welding and uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create the arc. The machine automatically feeds a filler material (if required) into the weld pool, ensuring that the molten pool is stable and that the welding bead is uniform. TIG orbital welding is known for its high-quality, clean welds and is often used in industries that require excellent weld aesthetics and minimal contamination. It is ideal for welding materials such as stainless steel, titanium, and other alloys used in high-purity applications. - Plasma Arc Orbital Welding
Plasma arc orbital welding is a variation of TIG welding, where the welding arc is intensified using a plasma nozzle. This process allows for higher welding speeds, deeper penetration, and greater control over the arc. Plasma arc welding is used in more demanding applications, such as welding thicker materials or when greater heat input is required. While less common than TIG orbital welding, it is advantageous for certain industrial applications that require deep welds and faster processing times.
Applications of Orbital Welding Machines
Orbital welding is employed in industries that demand high precision, cleanliness, and repeatability in their welds. Common applications include:
- Pharmaceutical and Biotech Industries
In the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, orbital welding is used to create high-purity piping systems for the transport of liquids and gases in sterile environments. The welded joints must be free from contaminants to prevent contamination of sensitive substances. Orbital welding ensures that these piping systems are leak-tight and meet stringent cleanliness standards. - Aerospace Industry
In aerospace manufacturing, orbital welding is employed to join critical components, such as fuel lines, hydraulic tubing, and structural elements, where strength, reliability, and minimal defects are essential. The precision offered by orbital welding ensures that these high-performance components can withstand the demanding conditions of flight. - Food and Beverage Processing
Orbital welding is used in the food and beverage industry to fabricate sanitary piping systems that meet hygienic standards. The ability to produce consistent, high-quality welds that are free from contamination is crucial for ensuring that these systems do not introduce foreign substances into the products being processed. The use of orbital welding ensures compliance with sanitary regulations and reduces the risk of contamination. - Semiconductor Manufacturing
Orbital welding plays a critical role in semiconductor manufacturing, particularly in the construction of cleanroom piping systems used for the transportation of gases and chemicals. The welds need to be free from contamination and must provide a hermetic seal to avoid leaks. Orbital welding ensures the highest standards of cleanliness and precision in these systems. - Power Generation and Oil & Gas Industries
In industries like power generation and oil & gas, orbital welding is used for the construction of pipelines, pressure vessels, and other critical infrastructure. The ability to weld in difficult-to-reach or hazardous environments, coupled with the precision and repeatability of the welding process, makes orbital welding an essential tool in these industries.
Advantages of Orbital Welding Machines
Orbital welding machines offer several advantages over traditional manual welding methods, making them ideal for precision welding in critical applications:
- High Precision and Consistency
Orbital welding machines are capable of achieving extremely precise and repeatable welds, ensuring that the welds meet strict quality control standards. This consistency is crucial in industries like aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and semiconductor manufacturing, where even minor variations in the weld can lead to product failure or contamination. - Reduced Human Error
By automating the welding process, orbital welding machines reduce the risk of human error, such as inconsistent arc placement, incorrect heat settings, or misalignment. This leads to higher-quality welds and reduces the need for rework or scrap material. - Improved Weld Strength and Integrity
The precision and consistency of orbital welding result in welds that are stronger and more reliable. Since the process ensures that heat input is controlled, the welds exhibit fewer defects such as porosity, undercutting, or lack of fusion. This is especially important in industries where the strength and integrity of the weld are critical to the performance of the final product. - Reduced Material Waste
Orbital welding machines optimize the welding parameters to ensure that material usage is minimized while still achieving the desired weld strength. This leads to less waste of filler materials and base metals, reducing overall production costs and contributing to more sustainable manufacturing practices. - Enhanced Safety
Orbital welding machines can operate with minimal human interaction, reducing the risk of exposure to the hazards associated with manual welding, such as burns, fumes, and UV radiation. In industries where worker safety is a concern, orbital welding provides a safer alternative to traditional welding methods. - Ability to Weld in Challenging Environments
Orbital welding is well-suited for welding in confined spaces, high-purity environments, or hazardous locations. The machine’s ability to precisely control the welding parameters makes it ideal for welding in situations where manual welding would be difficult or unsafe.
Conclusion
Orbital welding machines are indispensable tools for industries that require high-precision, consistent, and clean welds. The ability to automatically control the welding parameters, coupled with the rotating electrode, allows for the production of high-quality welds on tubular components with minimal human intervention. Whether used in the aerospace, semiconductor, pharmaceutical, or power generation industries, orbital welding machines offer unmatched precision, repeatability, and reliability, ensuring that critical components meet stringent standards for performance and safety.
Key Features of Orbital Welding Machines
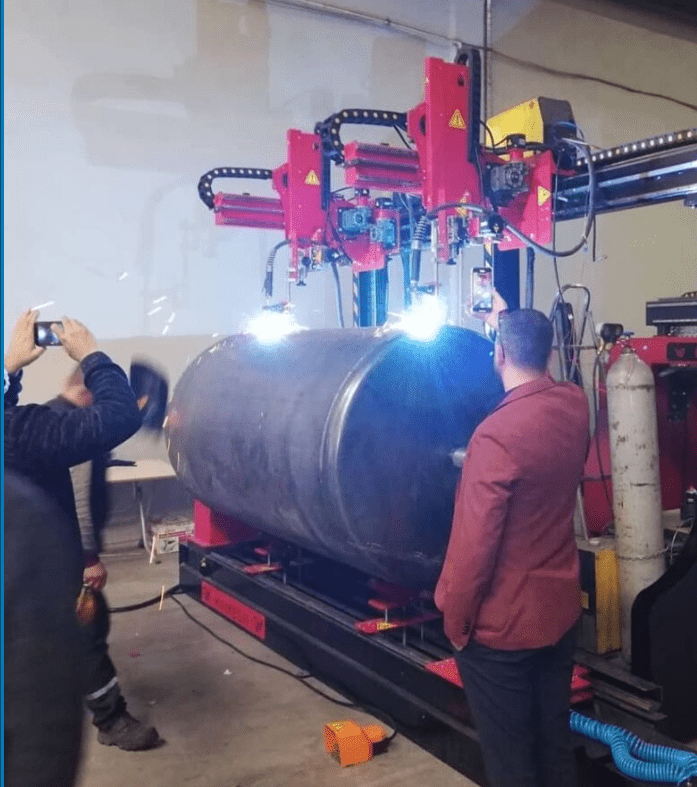

Orbital welding machines are highly specialized systems designed to produce precise, consistent, and high-quality welds, particularly on circular or tubular components such as pipes, tubes, and fittings. The key features of orbital welding machines enable them to perform complex welding tasks with minimal human intervention, ensuring optimal results in industries such as aerospace, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage processing, semiconductor manufacturing, and power generation. These features make orbital welding machines invaluable for applications where cleanliness, precision, and repeatability are paramount.
One of the most distinguishing features of orbital welding machines is the rotating electrode or tungsten electrode used to create the weld. The electrode rotates around the workpiece, typically a tube or pipe, to form a continuous, circumferential weld. The rotation ensures that the welding arc remains stable and consistent around the entire circumference, resulting in an even, uniform weld bead. The continuous arc created by the rotating electrode helps control the heat input, which is crucial for avoiding defects like overheating or insufficient penetration. This allows orbital welding to produce welds that are not only strong and durable but also free from contamination, which is particularly important in high-purity applications.
Another important feature of orbital welding machines is their sophisticated control systems. These systems are designed to automatically adjust various welding parameters, including current, voltage, travel speed, and gas flow, to maintain the optimal welding conditions throughout the process. The automated control of these variables ensures that the weld quality remains consistent, even when the machine is performing complex or repetitive tasks. The advanced controls also allow the machine to adapt to different materials, thicknesses, and joint configurations, making orbital welding machines versatile enough to handle a wide range of welding applications. This level of automation reduces the likelihood of human error, which can lead to defects and inconsistencies in the weld.
Orbital welding machines also typically feature real-time monitoring and feedback systems. These systems continuously track critical welding parameters, such as arc stability, temperature, and weld bead formation, providing instant feedback to operators or integrated data logging software. This allows for the detection of any issues, such as arc instability, overheating, or insufficient penetration, and enables immediate adjustments to maintain optimal weld quality. This real-time monitoring not only improves the precision of the welding process but also enhances overall quality control, ensuring that the final weld meets the required standards for strength, integrity, and appearance.
Gas control systems are another essential feature of orbital welding machines. In many applications, orbital welding requires the use of inert shielding gases, such as argon, to protect the weld area from contamination and oxidation during the welding process. The gas control system regulates the flow of gas to ensure the correct shielding environment is maintained, preventing impurities from compromising the quality of the weld. For high-purity applications, such as in the pharmaceutical or semiconductor industries, the gas flow must be carefully controlled, and orbital welding machines are designed to ensure a clean and contaminant-free weld environment. Additionally, some orbital welding machines are equipped with gas purging systems that remove air from the inside of the pipe or tube before welding, which further reduces the risk of oxidation and contamination.
The precision and repeatability offered by orbital welding machines are among their most important features. These machines are capable of producing high-quality welds with minimal variation, making them ideal for industries that demand consistent, reliable results. Once set up, orbital welding machines can perform the same weld repeatedly with very little deviation in size, shape, or quality. This precision is essential for applications such as aerospace, where the structural integrity of components depends on perfectly uniform welds. The repeatability of orbital welding also reduces the risk of defects and ensures that the final product meets strict industry standards.
Orbital welding machines are also known for their versatility. They are capable of welding a variety of materials, including stainless steel, titanium, carbon steel, and alloys, and can be used with different types of filler materials depending on the specific application. The ability to easily adjust the welding parameters allows orbital welding machines to handle different material thicknesses and joint configurations, making them adaptable to a wide range of welding tasks. This versatility is a key feature in industries where different types of welds are required for different products or components, such as in the pharmaceutical or food processing industries, where sanitary welding is often necessary.
Ease of use and automation are other important features of orbital welding machines. While orbital welding systems require an initial setup to configure the machine for a specific welding task, once set up, the machines are highly automated and require minimal operator intervention. The welding process is controlled by the machine’s advanced control system, which manages all parameters, such as arc voltage, travel speed, and gas flow. This reduces the need for skilled labor, as the machine can perform the welding process with little direct involvement from the operator. Many orbital welding machines also feature user-friendly interfaces that allow operators to easily set up, monitor, and control the welding process, making them more accessible to users with varying levels of experience.
One more notable feature of orbital welding machines is their ability to weld in challenging environments. These machines are often designed to operate in confined spaces or under difficult conditions, such as in high-purity cleanrooms, under extreme temperatures, or in hazardous environments. The compact design of many orbital welding systems makes them ideal for use in tight or hard-to-reach areas, where manual welding would be challenging or unsafe. In addition, some orbital welding machines are equipped with protective enclosures or shielding to prevent contamination or damage to sensitive components during the welding process. This makes orbital welding machines highly suited for industries where both the work environment and the quality of the weld need to meet strict standards.
Orbital welding machines are also known for their ability to produce high-strength, leak-tight welds. The consistent heat input and controlled arc movement ensure that the welds are strong and reliable, making them suitable for critical applications where the integrity of the weld is essential. For example, in the aerospace or nuclear industries, orbital welding is used to ensure that critical components, such as fuel lines, hydraulic tubing, or reactor pipes, are welded to the highest standards of strength and reliability. These machines can also produce hermetically sealed welds, which are essential for applications such as vacuum systems or pressure vessels, where leaks would be detrimental to performance.
Overall, the key features of orbital welding machines make them an indispensable tool for industries requiring high-quality, precise, and repeatable welding results. Their ability to automate the welding process, maintain consistent parameters, and produce clean, strong welds in various challenging environments has made them the preferred choice for industries such as aerospace, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage processing, and semiconductor manufacturing. These features not only improve the efficiency and productivity of the welding process but also ensure that the final product meets stringent quality standards, making orbital welding machines a critical part of modern manufacturing and fabrication processes.
Rotating Electrode
A rotating electrode is a key component in various welding processes, particularly in automated and precision applications like orbital welding. This technique involves the use of an electrode, typically made of tungsten, that continuously rotates around the circumference of a workpiece, such as a pipe or tube. The rotating electrode is an integral feature in orbital welding systems, where it is employed to create consistent, high-quality welds on tubular components. The electrode maintains an arc between itself and the workpiece, providing the necessary heat for welding, while its rotation ensures that the arc is stable and evenly distributed around the entire circumference. This allows the welding machine to produce continuous and uniform welds with high precision.
The rotating electrode serves several critical functions during the welding process. First and foremost, it ensures the uniform distribution of heat across the weld area. By continuously rotating, the electrode helps maintain a consistent arc, which is essential for preventing common welding defects, such as overheating or inadequate fusion. The rotation also provides better control over the molten weld pool, allowing the operator to manage the heat input more effectively, which is especially important in materials that are sensitive to thermal fluctuations. In many automated systems, the rotating electrode can be precisely controlled to adjust the welding parameters in real time, which leads to superior results, particularly in industries requiring high purity and cleanliness, such as pharmaceuticals or semiconductor manufacturing.
Another significant advantage of a rotating electrode is its ability to create high-quality, full-penetration welds on materials with varying thicknesses. The rotating motion allows the electrode to maintain a consistent arc length, which is crucial for ensuring that the weld penetrates the material adequately without creating weak spots or excessive heat that could damage the workpiece. The continuous movement of the electrode can also help minimize the occurrence of defects like porosity, cracks, or undercutting, as it ensures the arc remains stable and the weld pool is evenly distributed throughout the weld zone. This level of precision and consistency makes rotating electrodes particularly valuable in industries that require flawless, reliable welds, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing.
The rotating electrode also plays a vital role in reducing the overall complexity of the welding process. In traditional manual welding, the operator must constantly adjust the position of the electrode and maintain the proper arc length, which can be difficult and lead to inconsistencies. With a rotating electrode, these adjustments are handled automatically, allowing the machine to maintain optimal conditions throughout the weld. This is particularly important for applications involving long, continuous welds, as the rotating electrode can cover the entire circumference of the workpiece without the need for frequent repositioning. As a result, the overall speed and efficiency of the welding process are significantly improved, leading to faster production times and reduced labor costs.
In addition to enhancing the quality and consistency of the weld, the rotating electrode also contributes to the safety of the welding process. Since the machine automates much of the welding work, it minimizes human exposure to the hazards associated with manual welding, such as intense heat, ultraviolet radiation, and toxic fumes. The automation provided by the rotating electrode reduces the need for workers to be in close proximity to the welding arc, improving overall safety in the workplace. This is particularly beneficial in industries where workers must adhere to strict safety protocols, such as in aerospace, nuclear, or food processing environments.
Furthermore, the rotating electrode contributes to the versatility of the welding process. Orbital welding systems, which utilize rotating electrodes, can be adapted to handle a wide range of materials, joint configurations, and pipe sizes. The ability to precisely control the rotation of the electrode allows the machine to be adjusted for different types of welding applications, including pipe welding, tube-to-tube welding, and welding of other circular components. This flexibility is essential for industries that require a diverse range of welded components, such as in the construction of high-purity piping systems for pharmaceuticals or biotechnology.
The use of a rotating electrode also improves the cleanliness of the welding process. In many orbital welding applications, the process is performed in an inert gas environment, typically using argon, to shield the weld from contaminants in the air. The rotation of the electrode ensures that the entire weld zone is exposed to the inert gas, minimizing the risk of oxidation, contamination, or other defects. This is especially critical in applications that require welds with a high degree of purity, such as in the semiconductor, medical device, and food and beverage industries, where even minor contamination can affect the integrity of the final product.
Additionally, the rotating electrode provides the added benefit of ensuring the weld is free from spatter. In manual welding, spatter can be a common issue, requiring additional clean-up and inspection. The precision of the rotating electrode and the automated control of the welding process minimizes the formation of spatter, leading to cleaner, more aesthetic welds. This is important not only for the visual appearance of the weld but also for ensuring that the weld zone remains free from defects that could compromise the strength and integrity of the joint.
The rotating electrode also facilitates the creation of seamless welds, which are crucial in certain industries. In applications where leak-tight, continuous welds are required, such as in the aerospace, nuclear, and pharmaceutical industries, the ability to produce a flawless, uninterrupted weld around the circumference of a tube or pipe is essential. The continuous rotation of the electrode ensures that the weld is completed without any gaps or discontinuities, which could lead to potential failure points. This makes the rotating electrode ideal for critical applications where the integrity of the weld is paramount.
In conclusion, the rotating electrode is a vital feature of modern automated welding systems, particularly in orbital welding. Its ability to provide consistent heat distribution, maintain a stable arc, improve weld penetration, and reduce defects makes it invaluable in applications where precision and quality are essential. Whether used in industries like aerospace, pharmaceuticals, food processing, or semiconductor manufacturing, the rotating electrode enhances the overall efficiency, safety, and cleanliness of the welding process. Its precision and versatility enable it to handle a wide range of materials and joint configurations, ensuring that high-quality, reliable welds are produced with minimal human intervention.
Automated Process Control

Automated process control is a critical feature in modern manufacturing systems, particularly in precision welding applications. It refers to the use of advanced systems and technologies to automatically manage and regulate various process parameters during production, with minimal human intervention. In welding, automated process control ensures that key variables such as temperature, voltage, current, travel speed, and gas flow are precisely controlled throughout the welding cycle, leading to consistent, high-quality results. This level of automation improves the efficiency, accuracy, and repeatability of the welding process, making it ideal for industries that require high standards, such as aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and semiconductor manufacturing.
At the core of automated process control is the integration of sophisticated sensors and feedback systems that constantly monitor the welding conditions in real time. These sensors track various parameters, such as arc stability, weld pool temperature, and material composition, providing continuous data to the control system. The control system processes this data and makes immediate adjustments to the welding parameters to maintain optimal conditions. This ensures that the welding process remains stable, even when faced with variations in material properties, environmental conditions, or other variables that may impact the quality of the weld. For instance, if the temperature of the weld pool exceeds or falls below a certain threshold, the system can adjust the current or voltage to maintain the desired heat input, preventing issues such as overheating, undercutting, or insufficient fusion.
Automated process control allows for precise control over welding speed, which is critical for achieving the desired weld quality. By adjusting the travel speed of the welding torch or electrode in real time, the system ensures that the weld bead is consistent in size, shape, and appearance. The control system can also regulate the rate at which the filler material is fed into the weld pool, ensuring that the correct amount of material is deposited to form a strong, secure bond. This level of control is particularly important when welding thin-walled materials, where excessive heat input or an incorrect travel speed can easily lead to burn-through or distortion.
Another key aspect of automated process control in welding is the management of shielding gas flow. Shielding gases, such as argon, are used to protect the weld pool from contaminants in the atmosphere, preventing oxidation and other forms of contamination. The control system monitors the flow of gas to ensure that the weld area remains shielded throughout the process, maintaining the purity and integrity of the weld. Automated gas flow regulation also reduces the risk of human error, ensuring that the correct gas mixture and flow rate are maintained, even in complex welding environments.
One of the significant advantages of automated process control is its ability to enhance the repeatability and consistency of the welding process. In manual welding, variations in technique, experience, and environmental factors can lead to inconsistent results, with differences in the size, shape, and quality of welds. Automated process control eliminates these variables by ensuring that the same welding parameters are applied consistently, producing welds that meet exact specifications every time. This is particularly beneficial in industries that require high precision and reliability, such as the aerospace and medical device sectors, where even minor variations in the weld can compromise the integrity of the component.
The automation of process control also significantly reduces the risk of human error. In traditional manual welding, operators must constantly adjust parameters based on their observations and experience, which can lead to mistakes or inconsistencies, particularly in complex or high-stakes applications. Automated systems, however, take over much of the decision-making process, allowing operators to focus on higher-level tasks such as monitoring the overall system or making adjustments to the setup. By automating the control of welding parameters, automated systems reduce the likelihood of defects, rework, and scrap, leading to improved productivity and cost efficiency.
In addition to improving consistency and quality, automated process control can enhance the overall safety of the welding process. Welding involves high temperatures, intense electrical currents, and potentially hazardous fumes or gases. By automating the control of critical parameters, the system can ensure that the welding process stays within safe operating limits, minimizing the risk of accidents or injuries. For example, if the system detects an anomaly, such as an arc instability or an unsafe temperature level, it can automatically shut down the process or adjust the settings to prevent potential damage or hazards. This level of control reduces the need for operators to directly intervene in dangerous situations, promoting a safer work environment.
Automated process control systems can also facilitate data collection and analysis, providing valuable insights into the welding process. Many modern welding systems are equipped with data logging capabilities, allowing operators and engineers to track key metrics such as weld strength, heat input, and gas usage. This data can be used for process optimization, quality control, and troubleshooting. In industries that require strict documentation and traceability, such as aerospace or medical device manufacturing, the ability to collect and analyze data is crucial for ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and maintaining a high level of quality assurance.
The integration of automated process control with other advanced technologies, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, is also becoming increasingly common in welding. These technologies enable systems to learn from previous welds and make real-time adjustments based on historical data, improving the efficiency and quality of the welding process over time. For instance, machine learning algorithms can analyze data from past welds to identify patterns and predict the best settings for specific materials or joint configurations. This predictive capability can help optimize the welding process, reducing the time required for setup and adjustment while ensuring that the welds meet the desired standards.
Automated process control is also crucial in enabling the efficient integration of welding machines into larger production lines. In industries that require high-volume production, such as automotive manufacturing, the ability to seamlessly integrate welding machines with other automated systems, such as robotic arms, conveyors, and quality inspection stations, is essential for maintaining high throughput and reducing cycle times. Automated process control systems ensure that the welding process is synchronized with other stages of production, such as part handling, assembly, and testing, creating a streamlined, efficient workflow. This integration allows for faster production without sacrificing quality, leading to increased overall productivity.
In conclusion, automated process control plays a vital role in modern welding applications, providing numerous benefits such as increased precision, consistency, safety, and efficiency. By automatically regulating key welding parameters in real time, automated systems ensure that each weld meets the desired specifications, even in complex or high-precision applications. These systems not only reduce the risk of defects and human error but also enhance the overall quality and repeatability of the welding process. The ability to collect and analyze data further improves process optimization, quality assurance, and compliance with industry standards. As welding technology continues to evolve, the integration of automated process control with advanced technologies like machine learning and artificial intelligence will further enhance the capabilities of welding systems, leading to even greater efficiencies and higher-quality results in industries worldwide.
Real-Time Feedback and Monitoring
Real-time feedback and monitoring are essential components in modern automated welding processes, playing a crucial role in ensuring the quality, consistency, and efficiency of welds. These systems provide continuous, immediate data about the welding process, allowing operators and control systems to make adjustments in real-time to maintain optimal welding conditions. In a variety of industries, particularly those that require high precision, such as aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and semiconductor manufacturing, the ability to monitor and adjust parameters during the welding cycle is invaluable. Real-time feedback ensures that potential issues are identified and addressed before they lead to defects or failures in the final product.
At the heart of real-time feedback and monitoring is the use of various sensors and measurement devices that continuously track key welding parameters, such as arc stability, temperature, voltage, current, travel speed, and gas flow. These sensors are integrated into the welding system, providing a constant stream of data to the control system, which analyzes the information and adjusts the welding process as necessary. This feedback loop allows for continuous optimization of the welding parameters, ensuring that the process stays within predefined limits and meets the desired specifications. For example, if a sensor detects that the welding arc is becoming unstable or the temperature of the weld pool is too high or too low, the system can immediately adjust the current, voltage, or travel speed to maintain a stable and consistent welding process.
The ability to monitor the welding process in real-time is particularly beneficial in preventing defects such as porosity, undercutting, excessive spatter, or poor fusion. These types of defects are often the result of subtle variations in the welding process, such as slight changes in heat input, arc stability, or gas flow. Real-time feedback systems allow the welding machine to detect these variations as they occur and make corrective adjustments to prevent defects from forming. This proactive approach reduces the likelihood of costly rework and ensures that each weld meets the required quality standards without the need for extensive inspection or correction after the fact.
Real-time feedback and monitoring also play a crucial role in maintaining the safety of the welding process. Welding involves high temperatures, electrical currents, and the potential release of hazardous gases, making it important to keep the process within safe operating limits. Real-time monitoring allows the system to track critical parameters, such as the temperature of the weld zone or the stability of the arc, and ensure they remain within safe thresholds. If the system detects an unsafe condition, such as an arc that is too hot or a gas flow that is insufficient to protect the weld, it can take immediate corrective actions, such as reducing the current, adjusting the gas flow, or halting the process entirely. This built-in safety feature not only protects the workpiece but also helps prevent accidents and injuries, reducing risks to operators and the work environment.
Another key benefit of real-time feedback and monitoring is the ability to achieve consistent weld quality, even in high-volume or automated production environments. Manual welding often leads to variability in weld quality, as the operator’s technique, experience, and attention to detail can influence the outcome. With automated welding systems equipped with real-time monitoring, the process is much more controlled, and the welding parameters can be maintained consistently across multiple welds. This is particularly important in industries that require high levels of precision and repeatability, such as in the aerospace or medical device industries, where each weld must meet strict regulatory standards. The consistent feedback and adjustments provided by real-time monitoring ensure that every weld is produced to the same high standard, regardless of the number of parts being welded or the complexity of the task.
Real-time feedback systems can also enhance the efficiency of the welding process by allowing operators to detect and address issues as they arise, minimizing downtime and reducing the need for corrective actions. For example, if a minor issue is detected early in the welding cycle, such as a slight fluctuation in gas flow or a minor deviation in temperature, it can be corrected immediately without interrupting the entire process. This immediate feedback enables faster adjustments and helps maintain a steady workflow, which is particularly beneficial in industries that rely on high throughput and tight production schedules. By continuously optimizing the welding process, real-time monitoring helps reduce scrap rates, minimize material waste, and improve overall productivity.
Moreover, the data collected from real-time monitoring systems can be used for post-process analysis and documentation. Many modern welding systems are equipped with data logging capabilities that allow for the storage of feedback from each welding cycle. This data can be accessed later for quality control, troubleshooting, or process optimization. For example, engineers can analyze the feedback from multiple welds to identify trends, detect recurring issues, or assess the effectiveness of different welding parameters. This historical data provides valuable insights into the performance of the welding process and can be used to fine-tune the system for improved results in future cycles. In regulated industries, such as aerospace or medical device manufacturing, this data is also used to maintain compliance with industry standards, as it provides an accurate record of the welding process and ensures that all parameters were within specification.
Real-time feedback and monitoring also facilitate remote monitoring and control, which is especially useful in large-scale or hazardous environments. Operators can monitor the welding process from a distance, receiving real-time updates and alerts on system performance. In complex or hard-to-reach welding operations, such as in confined spaces or hazardous areas, the ability to remotely monitor the system allows for greater flexibility and safety. Additionally, remote monitoring allows for centralized oversight of multiple welding machines, making it easier to manage production processes across different shifts or locations. This capability is becoming increasingly important in industries where production lines are geographically dispersed or where welding operations must be continuously monitored to ensure compliance with strict quality standards.
The use of real-time feedback and monitoring systems also plays a critical role in process optimization. By continuously collecting and analyzing data, operators and engineers can gain a deeper understanding of the factors that influence the quality and efficiency of the welding process. Over time, this information can be used to make data-driven decisions that optimize the settings, reduce waste, and improve overall performance. For example, adjustments to welding parameters can be made based on feedback from the system, allowing for more efficient use of energy, materials, and labor. This ongoing optimization process helps companies stay competitive by improving both product quality and operational efficiency.
In conclusion, real-time feedback and monitoring systems are vital for maintaining the quality, consistency, and efficiency of modern welding processes. By providing continuous data on key parameters, these systems allow for immediate adjustments to be made to ensure that the welding process remains within optimal conditions. The benefits of real-time feedback include enhanced weld quality, increased safety, improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and the ability to maintain consistent results across high-volume production environments. Additionally, the data collected can be used for process optimization, quality control, and compliance, making real-time feedback and monitoring an indispensable tool in industries that require high-precision welding. As welding technology continues to advance, the role of real-time monitoring and feedback will only become more crucial in ensuring the reliability and success of the welding process.
Purging and Gas Control
Purging and gas control are vital elements in ensuring the quality and integrity of welded joints, especially in precision welding processes. These practices involve the use of gases, typically inert gases like argon, to shield the weld area from contamination during the welding process. Proper purging and gas control prevent oxidation, discoloration, and other defects that can occur due to exposure to atmospheric elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, and moisture. These controlled environments are especially crucial in industries that require high standards of cleanliness and quality, such as aerospace, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Purging refers to the process of filling the inside of a pipe or vessel with an inert gas to create a protective atmosphere around the weld zone. This is particularly important in processes like TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) and orbital welding, where the heat generated during welding can cause contamination if the weld area is exposed to atmospheric air. The primary goal of purging is to displace any oxygen, moisture, or other reactive gases that could negatively affect the quality of the weld. When welding materials like stainless steel or titanium, which are highly sensitive to oxidation, purging ensures that the weld bead remains clean and free from contaminants that could weaken the joint or cause discoloration.
The purging process involves introducing a specific gas into the workpiece, usually through one or more purge ports, while the welding operation is underway. The gas displaces any air or moisture inside the component, creating an inert atmosphere that shields the weld pool. Once the inert gas has filled the interior of the pipe or vessel, it effectively prevents any reaction between the molten metal and the atmosphere, which could otherwise lead to defects such as porosity, cracking, or loss of material strength. After welding, the gas is allowed to vent, ensuring that the component is free from any residual gases before it moves to the next stage of production or is sent for inspection.
Gas control, on the other hand, involves managing the flow, pressure, and composition of gases used in the welding process. It ensures that the right amount and type of gas are supplied to the welding environment, providing an optimal shield to protect the weld from atmospheric contamination. Gas flow must be carefully controlled to ensure that the weld pool is adequately protected without introducing excessive gas pressure that could cause turbulence or distortions in the weld. The pressure of the gas must be consistent throughout the welding process to maintain a stable shield and prevent any contaminants from entering the weld zone. The use of regulators, flow meters, and other control devices ensures precise control over the gas supply, providing the necessary conditions for achieving high-quality welds.
The composition of the shielding gas also plays an important role in purging and gas control. In most cases, argon is the gas of choice due to its inert properties, which prevent any reactions with the weld pool. However, in some welding applications, additional gases such as helium or a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide may be used to achieve specific weld characteristics. For instance, helium is often added to the argon to increase the heat input in the welding process, which can be beneficial when working with thicker materials or when higher welding speeds are required. The precise mixture of gases can be tailored to suit the material being welded, the type of welding process being used, and the desired weld properties.
The effectiveness of purging and gas control is closely linked to the type of weld being performed. For example, when welding titanium or other reactive metals, an inert gas atmosphere is essential not only to protect the weld pool but also to preserve the integrity of the base material. Titanium, in particular, is highly reactive with oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen, and exposure to these gases during the welding process can result in brittle welds and discoloration. In such cases, the use of purging and gas control is critical for achieving clean, strong, and aesthetically pleasing welds.
The need for proper purging and gas control also extends to welded joints that are subject to stringent inspection and testing, such as X-ray or ultrasonic inspection. Any defects, no matter how small, could compromise the integrity of the joint and lead to failure in critical applications. A proper purging and gas control system minimizes the likelihood of such defects by ensuring that the weld area remains free from contamination throughout the process. By maintaining a stable and controlled atmosphere during the welding operation, the likelihood of defects like porosity, lack of fusion, or inclusions is greatly reduced.
Additionally, purging and gas control contribute to the overall efficiency of the welding process. When proper shielding is in place, the welding operator can focus on other aspects of the work, knowing that the gas flow is protecting the weld from potential contamination. This reduces the need for rework and inspections, saving both time and resources. Moreover, with the right gas mixture and pressure, the welding process becomes more predictable and easier to control, improving the overall consistency of the welds produced.
Technological advancements have led to the development of automated purging and gas control systems that offer even greater precision and ease of use. These systems use advanced sensors, regulators, and software to monitor and adjust gas flow in real time, ensuring that the welding environment remains stable throughout the entire process. Automated systems can detect fluctuations in gas pressure, changes in flow rates, or leaks in the system, and they can automatically make adjustments or alert the operator to any issues. This level of control not only improves the quality of the weld but also reduces the chances of operator error and enhances the overall efficiency of the welding process.
In conclusion, purging and gas control are essential practices for ensuring the quality, strength, and integrity of welded joints, particularly in sensitive applications that demand high levels of cleanliness and precision. Through the use of inert gases, purging protects the weld area from contamination, preventing defects such as oxidation, porosity, and cracking. Gas control ensures that the right type and amount of shielding gas are supplied to the weld zone, providing optimal protection for the weld pool and maintaining the desired weld characteristics. Together, purging and gas control contribute to the overall efficiency, consistency, and safety of the welding process, making them indispensable in industries that require high-quality welded components.
Tight Tolerances and Repeatability
Tight tolerances and repeatability are fundamental aspects of modern manufacturing processes, especially in precision welding. The ability to consistently produce parts that meet exact specifications with minimal variation is critical in industries that demand high-quality, reliable components, such as aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and semiconductor manufacturing. Achieving tight tolerances means that the dimensions and characteristics of each welded part must fall within very narrow limits, while repeatability ensures that these results can be replicated with consistency across multiple production cycles. Both are essential for maintaining the integrity and functionality of the final product, ensuring it meets rigorous standards and performs reliably over its lifespan.
Tight tolerances in welding are especially challenging because of the variables involved in the welding process. Factors such as heat input, electrode positioning, travel speed, and gas flow all have an impact on the final weld, influencing its geometry, strength, and appearance. Even minor fluctuations in these parameters can result in welds that deviate from the desired dimensions, leading to defects such as misalignment, excess spatter, or poor fusion. To achieve tight tolerances, these variables must be precisely controlled and consistently maintained throughout the welding process. The use of advanced technologies like automated welding systems, sensors, and real-time monitoring helps achieve the accuracy needed for tight tolerances by continuously tracking and adjusting the welding parameters to ensure they remain within the desired specifications.
Precision welding techniques, such as laser welding, TIG welding, and orbital welding, are particularly effective for achieving tight tolerances. These methods allow for highly controlled heat input and precise movement of the welding electrode, reducing the likelihood of deviations. Laser welding, for instance, uses a focused laser beam to create a highly localized heat zone, allowing for extremely fine control over the weld size and depth. TIG welding provides similarly precise control, using a tungsten electrode to create a stable arc that can be fine-tuned to produce clean, narrow welds with minimal distortion. Orbital welding, which is often used for welding tubes and pipes in industries like aerospace and pharmaceuticals, utilizes a rotating electrode to produce consistent, high-quality welds with tight dimensional control.
To maintain tight tolerances, it is also essential to ensure proper joint preparation and alignment. Misalignment of the workpieces can lead to irregular welds that fall outside the desired specifications. Advanced fixturing and clamping systems are often employed to hold the workpieces in precise positions during the welding process, minimizing the risk of distortion or displacement. These systems ensure that the joint geometry remains consistent and that the weld is deposited accurately along the intended path, further improving the overall precision of the weld.
Repeatability, on the other hand, refers to the ability to reproduce identical results over multiple production cycles. In industries where high volumes of parts are being produced, such as automotive or electronics manufacturing, repeatability is essential to maintain product consistency and ensure that each part meets the same quality standards. Achieving repeatability in welding requires a high degree of control over the entire process, from setup and programming to the actual execution of the weld. Automated welding systems, with their ability to store and execute welding parameters with high precision, are key to achieving repeatability. Once a welding process is calibrated to produce a high-quality weld, automated systems can replicate the process consistently, ensuring that each part is welded to the same exact specifications.
Robotic welding systems are commonly used to achieve repeatability in high-volume manufacturing environments. These systems are programmed with specific welding parameters and can execute welds with a high degree of precision and consistency. Robots can perform the same welding motions and adjustments repeatedly, ensuring that each weld is performed identically. The integration of sensors and real-time feedback mechanisms further enhances repeatability by providing continuous data on the weld quality and allowing for minor adjustments to be made during the process to correct any deviations before they affect the final part.
In addition to automation, advanced process control systems also play a crucial role in ensuring repeatability. These systems use real-time data from sensors and monitoring devices to continuously adjust key welding parameters, such as current, voltage, travel speed, and heat input, to maintain optimal conditions throughout the entire welding cycle. By providing constant feedback and making adjustments as needed, automated control systems help ensure that the welding process remains stable and within the specified tolerances, even when variables such as material composition, joint fit-up, or environmental conditions change.
The ability to achieve both tight tolerances and repeatability in welding not only improves product quality but also reduces costs. By consistently producing parts that meet specifications, manufacturers can minimize the need for rework, scrap, and inspection. This improves overall efficiency and throughput, particularly in industries where time and cost pressures are significant. Additionally, by ensuring that each part meets the required tolerances, manufacturers can reduce the risk of product failures or recalls, which can be costly and damage a company’s reputation.
In industries like aerospace, where components must meet stringent safety and performance standards, tight tolerances and repeatability are especially critical. A slight deviation in a welded joint could compromise the strength, durability, or functionality of the final product, potentially leading to catastrophic failure. In such cases, achieving precise and repeatable welds is not only a matter of quality control but also a matter of safety. Ensuring that welds are produced to the exact specifications and can be reproduced consistently across multiple parts or production runs is essential for meeting the high standards required in these industries.
In conclusion, tight tolerances and repeatability are essential for ensuring the quality, functionality, and safety of welded components, particularly in industries that require high precision and reliability. Achieving tight tolerances involves controlling various welding parameters to ensure that the weld dimensions fall within narrow limits, while repeatability ensures that these results can be consistently reproduced across multiple cycles. Through the use of automated systems, robotics, and advanced process control, manufacturers can achieve both precision and consistency in their welding operations, leading to improved product quality, reduced costs, and enhanced safety.
Types of Orbital Welding

Orbital welding is a highly specialized and automated form of welding that is used primarily for the welding of tubular components, often in industries such as aerospace, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and semiconductor manufacturing. The key distinguishing feature of orbital welding is its ability to produce high-quality, precise welds in a continuous, circular motion around the workpiece. There are several types of orbital welding processes, each tailored to specific applications and materials. These types vary based on the method used to create the weld, the configuration of the equipment, and the materials being joined.
One of the most commonly used methods in orbital welding is Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW). In this process, a non-consumable tungsten electrode is used to create the welding arc, while an inert gas, typically argon, is used to shield the weld area from atmospheric contamination. TIG orbital welding is highly effective for welding stainless steel, titanium, and other non-ferrous metals, offering excellent control over heat input and weld quality. The process is particularly valuable when high precision and a clean, aesthetically pleasing weld are required, as it minimizes the risk of defects such as porosity or spatter. TIG orbital welding can be used for both manual and automated applications, with automated systems allowing for the precise movement of the electrode around the workpiece to produce consistent, high-quality welds.
Another popular orbital welding method is the use of the Plasma Arc Welding (PAW) process. Plasma arc welding is similar to TIG welding but uses a more concentrated and focused plasma arc, which is created by ionizing a gas. This arc provides a higher energy density and allows for faster welding speeds, making plasma arc welding an excellent choice for welding thicker materials or achieving higher penetration in welds. Plasma arc welding is used in many industries, particularly in applications that require welding of materials like copper, aluminum, and other metals that are difficult to weld with traditional methods. The high concentration of heat and precision of the arc makes this method effective in producing high-quality welds in a shorter amount of time, which is beneficial in high-volume production environments.
While TIG and plasma arc welding are the most commonly used methods in orbital welding, there are other specialized processes tailored to specific applications. One such process is the Electron Beam Welding (EBW) method, which uses a focused beam of electrons to generate heat and create a weld. This method is typically used in vacuum chambers to prevent contamination and oxidation of the material being welded. Electron beam welding is suitable for very precise, high-penetration welds, often in aerospace or other high-tech applications where high precision is critical. This process is capable of producing clean and strong welds without the need for filler materials, which is particularly useful in situations where the material being welded is expensive or where minimal distortion is required.
In some cases, automated orbital welding systems are equipped with additional capabilities, such as the use of filler metals during the welding process. This is often the case in applications where a strong weld with a larger bead is required. For instance, when welding larger pipes or tubes, the addition of filler material may be necessary to ensure proper weld penetration and strength. The use of filler metals can be automated and controlled through the orbital welding system, ensuring that the right amount of material is added during the welding process. This can be achieved using a variety of filler wire feed mechanisms, which can be integrated into the system to automatically supply the necessary filler material as the welding process progresses.
Another variant of orbital welding is the use of a hybrid system that combines laser welding with orbital motion. Laser orbital welding combines the precision of laser welding with the ability to move the laser in a circular pattern around the workpiece, allowing for very precise and controlled welds. This hybrid system is particularly useful in applications where a very small heat-affected zone (HAZ) is required, or where the weld needs to be made at high speeds with minimal distortion. Laser orbital welding systems are capable of producing high-quality welds in materials such as thin-walled tubes or components with complex geometries, which may be challenging for other types of orbital welding.
For some applications, the key to achieving optimal welds lies in controlling the welding environment. Some orbital welding systems incorporate advanced purging techniques to ensure that the weld area remains free from contaminants such as oxygen, nitrogen, or hydrogen, which could cause defects in the weld. Gas shielding, typically with inert gases such as argon, is used to create a protective atmosphere around the weld pool. This is especially important in materials like titanium and stainless steel, which are highly sensitive to contamination. In orbital welding applications, the purging process is often automated, with gas flow being precisely controlled to ensure that the right environment is maintained throughout the welding cycle.
The choice of orbital welding method depends largely on the specific application, the material being welded, and the desired characteristics of the weld. For example, TIG orbital welding is ideal for applications that require high precision and minimal heat distortion, such as in aerospace or medical device manufacturing, where cleanliness and strength are paramount. Plasma arc welding, on the other hand, is suited for thicker materials and higher speed applications, while laser orbital welding is typically used for ultra-precise, high-speed welds in advanced materials or thin-walled components. The hybrid laser and orbital welding system offers the advantages of both methods, combining the high-speed precision of lasers with the ability to move around the workpiece.
In high-volume production environments, automation plays a critical role in ensuring the repeatability and consistency of orbital welds. Automated orbital welding systems are programmed to perform precise, repeatable welds with little to no intervention from the operator. These systems can store parameters for multiple welding jobs and use sensors and real-time feedback to adjust the welding parameters on the fly, ensuring that each weld meets the required specifications. Automated systems are also capable of adjusting to variations in material composition, joint fit-up, or other factors that could affect the welding process. The ability to achieve consistent, high-quality welds with minimal operator involvement makes automated orbital welding particularly advantageous for industries that require large quantities of parts to be welded quickly and efficiently.
In conclusion, orbital welding encompasses a variety of welding techniques, each designed to meet specific needs in industries requiring precision and reliability. Whether using TIG, plasma arc welding, electron beam welding, or laser orbital welding, these methods offer distinct advantages depending on the materials, application, and desired outcome. Automated systems further enhance the efficiency, repeatability, and consistency of the orbital welding process, making it indispensable in industries where high-quality, clean welds are critical. The ongoing development and refinement of orbital welding technology ensure that it remains at the forefront of precision welding, offering solutions for increasingly complex and demanding manufacturing challenges.
Applications of Orbital Welding Machines
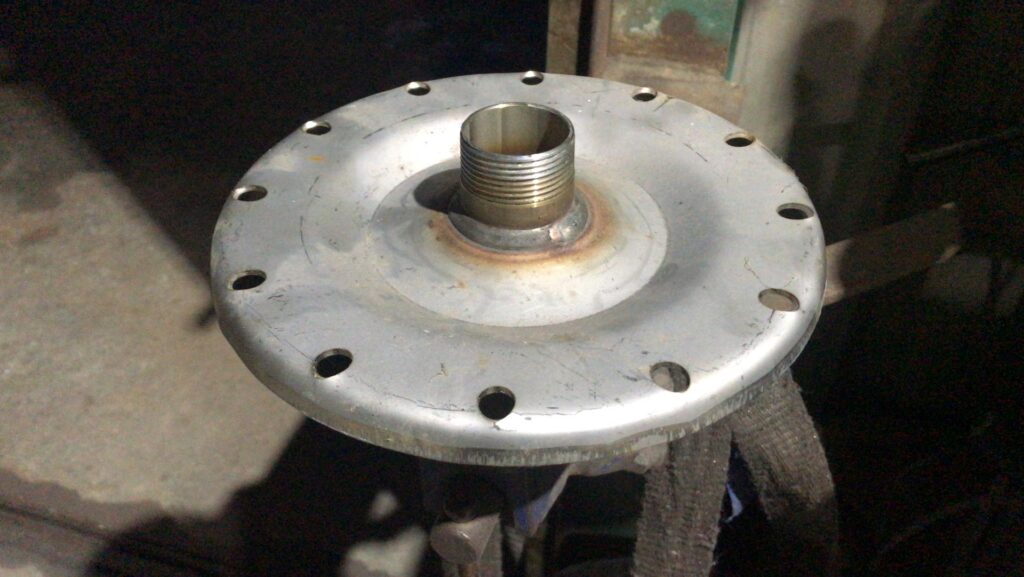

Orbital welding machines have become essential tools in industries that require high precision, quality, and consistency in their welding processes. These machines are particularly valuable for applications where the welding of tubular components or intricate parts is necessary. The main characteristic of orbital welding is the ability to create continuous, high-quality welds around a circular or tubular workpiece, which makes it ideal for a wide range of industries, including aerospace, pharmaceuticals, food processing, semiconductor manufacturing, and power generation. The unique capabilities of orbital welding machines ensure that the welds produced meet strict standards for strength, cleanliness, and precision, making them indispensable in these industries.
In the aerospace industry, orbital welding is commonly used to manufacture critical components such as fuel lines, hydraulic systems, and other tubular parts. The high level of precision required in aerospace applications demands that welds be flawless and free of defects, as even minor imperfections could compromise the safety and performance of an aircraft. Orbital welding machines are capable of producing clean, consistent, and strong welds in materials such as stainless steel, titanium, and other alloys commonly used in the aerospace sector. The ability to maintain tight tolerances and repeatability is essential for ensuring that components fit together as designed and function correctly under extreme conditions, such as high pressure and temperature variations. Orbital welding also helps reduce the risk of contamination, which is particularly important when welding sensitive components that will be used in the high-stakes environment of aerospace engineering.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries also rely heavily on orbital welding for the fabrication of sanitary, high-purity piping systems. These industries often require welds that are not only strong and durable but also meet stringent cleanliness standards to prevent contamination. In pharmaceutical manufacturing, orbital welding is used to weld stainless steel pipes and tubes that transport fluids, gases, or chemicals in a sterile environment. The precision and cleanliness achieved by orbital welding help prevent the introduction of contaminants that could affect the purity of the products being manufactured. Additionally, orbital welding ensures that the joints are smooth and free of crevices, which can harbor bacteria and other microorganisms. These characteristics are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the production environment and ensuring that pharmaceutical products are safe for consumers.
Similarly, the food and beverage industry employs orbital welding to ensure that pipes and other equipment used in the production process remain clean and free from contamination. Stainless steel, a material commonly used in food processing, is well-suited to orbital welding because it can be welded with minimal distortion and without the risk of contamination that could occur with traditional welding methods. Orbital welding machines can produce high-quality, hygienic welds in food processing systems, which helps ensure that these systems remain sterile and prevent the growth of harmful bacteria. The ability to perform precise welds on components such as pipes, tanks, and other processing equipment is crucial for maintaining safety standards and meeting regulatory requirements.
The semiconductor industry is another key area where orbital welding plays an important role. Semiconductor manufacturing requires a high level of precision, as even the slightest flaw in a weld could impact the performance of the final product. Orbital welding is used in the production of high-purity gas lines, vacuum chambers, and other critical components that must maintain the integrity of their internal environment. The cleanliness and repeatability of orbital welding make it well-suited to meet the strict requirements of semiconductor fabrication, where the risk of contamination is a major concern. The ability to produce strong, leak-proof welds in complex systems where precision is paramount is a significant advantage in the semiconductor sector.
In the power generation industry, orbital welding machines are used for welding pipes and tubes in nuclear, fossil fuel, and renewable energy plants. The strength and durability of the welds produced by orbital welding are essential for ensuring the reliability and safety of power generation equipment, which often operates under extreme pressures and temperatures. Orbital welding is used in critical applications such as steam piping, heat exchangers, and reactor vessels, where weld quality is crucial to the overall performance and safety of the plant. The ability to achieve tight tolerances and high-quality welds in these applications reduces the risk of weld failure, which could result in costly downtime or catastrophic accidents.
In addition to these major industries, orbital welding machines are also used in a variety of other fields, including automotive manufacturing, marine engineering, and medical device production. In automotive manufacturing, orbital welding is used to weld exhaust systems, fuel lines, and other tubular components where precision and strength are crucial. Orbital welding’s ability to create repeatable, high-quality welds ensures that automotive components meet strict safety and performance standards. In marine engineering, orbital welding is employed to fabricate pipes and other parts for ships and submarines, where the need for reliable and durable welds is essential for the safety and functionality of the vessel. Medical device manufacturers also use orbital welding to weld stainless steel tubing and components for devices such as catheters, IV lines, and surgical instruments, where high purity and cleanliness are paramount.
Another application of orbital welding machines is in the manufacturing of high-pressure gas and fluid systems. Orbital welding is ideal for producing leak-proof welds in systems where maintaining a secure seal is critical to the system’s integrity. In industries such as chemical processing, oil and gas, and aerospace, where high-pressure systems are common, orbital welding provides the precision and consistency necessary to create reliable, strong welds that can withstand the demands of high-pressure environments. This is particularly important in applications where even a small leak could lead to hazardous conditions or product failure.
Additionally, orbital welding machines are increasingly being used in research and development, where precision welding is required for experimental setups or prototype fabrication. The ability to make accurate, repeatable welds quickly and efficiently makes orbital welding an ideal choice for R&D environments, where new materials, designs, or products are being tested. Orbital welding machines can help ensure that the prototypes are welded to the required specifications, reducing the need for rework and ensuring that the results of experiments are not compromised by poor-quality welds.
In conclusion, orbital welding machines have a broad range of applications across various industries where precision, cleanliness, and repeatability are essential. From aerospace to pharmaceuticals, food processing, and power generation, the ability to create strong, durable, and high-quality welds in complex and often sensitive environments makes orbital welding an indispensable tool in modern manufacturing. The continued advancements in orbital welding technology ensure that it remains a critical process for meeting the increasing demands of industries requiring the highest standards of weld quality and precision.
Longitudinal Welding Machine
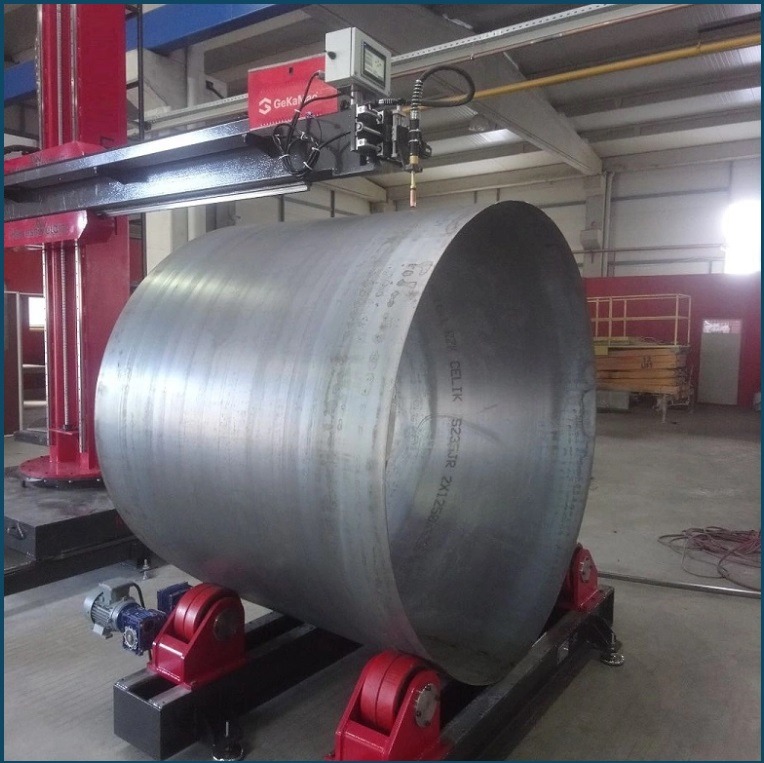

Longitudinal welding machines are specialized welding equipment designed to create welds along the length of a workpiece, typically in applications involving large, long, or cylindrical components such as pipes, tanks, and various structural elements. These machines are primarily used in industries that require high-quality, consistent welds on long joints, including the automotive, aerospace, shipbuilding, oil and gas, and energy sectors. The key feature of a longitudinal welding machine is its ability to apply a continuous, high-precision weld along a straight or curved path, ensuring uniformity and strength in the welded joint.
One of the most common applications for longitudinal welding machines is in the fabrication of pipes and tubes. These machines are used to weld the longitudinal seam of pipe sections, creating long, continuous tubes that are used in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemical, and water treatment. The process is ideal for joining pipes that require a strong and durable weld to ensure the integrity of the final product, particularly in applications where high pressure or harsh environmental conditions are present. Longitudinal welding machines are equipped with adjustable settings that allow operators to control welding parameters such as speed, heat input, and electrode positioning to achieve the optimal weld quality. This ensures that the pipe or tube meets the necessary strength, pressure resistance, and overall performance standards.
In addition to pipes, longitudinal welding machines are widely used in the production of tanks and pressure vessels. These components are typically fabricated by welding large, circular or cylindrical sheets of metal together along their edges. The ability to produce a continuous, uniform weld along the entire length of the component is essential for ensuring the structural integrity of the tank or vessel, especially when it is used to store or transport hazardous materials. Longitudinal welding machines are capable of welding both the internal and external seams of tanks and vessels, providing a high level of control over the quality of the weld. This is particularly important in industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food production, where contamination or failure of welded seams could have serious consequences.
The automotive industry also benefits from the use of longitudinal welding machines. These machines are commonly used in the production of car chassis, exhaust systems, and other automotive components that require long, continuous welds. For example, the welding of exhaust pipes, which require tight tolerances and consistent weld quality, is often performed using longitudinal welding machines. The ability to produce high-quality welds in a fast and efficient manner makes longitudinal welding machines particularly valuable in mass production settings, where large volumes of components need to be welded quickly and with minimal variation.
Shipbuilding is another industry that utilizes longitudinal welding machines to fabricate large steel sections for ships, submarines, and other marine vessels. The welding of these sections, which are often large and complex, requires a high degree of precision to ensure that the joints are strong, durable, and free from defects. Longitudinal welding machines are used to weld the seams along the length of the hull or other large structural components, ensuring that the joints can withstand the stresses and forces encountered during the ship’s operation in the marine environment. The ability to control the welding process and produce consistent, high-quality welds is critical in ensuring the safety and longevity of the vessel.
In the oil and gas industry, longitudinal welding machines are employed to weld pipelines used to transport oil, gas, and other fluids over long distances. These pipelines need to be constructed with the utmost precision to ensure that they can withstand high pressure, extreme temperatures, and corrosive environments. Longitudinal welding machines enable the production of long, continuous welds along the length of the pipe, minimizing the risk of leaks or failures. The machines can also be equipped with specialized features such as automatic alignment systems and weld tracking mechanisms to ensure that the weld is applied precisely along the intended path. This ensures the integrity and safety of the pipeline, which is vital in industries where the transportation of hazardous materials is involved.
Longitudinal welding machines are also increasingly used in the renewable energy sector, particularly in the manufacturing of wind turbine components. The production of large steel structures for wind turbines requires the ability to weld long seams with high precision. Longitudinal welding machines are used to weld the sections of the tower, as well as the components of the rotor blades and other structural parts. The durability and strength of these components are critical to the performance and safety of wind turbines, which must withstand extreme environmental conditions such as high winds and varying temperatures. The high-precision welding capabilities of longitudinal welding machines ensure that the seams are strong and free from defects, allowing the turbine to operate efficiently and safely.
One of the key advantages of longitudinal welding machines is their ability to produce high-quality welds with minimal distortion. This is particularly important when working with materials that are prone to warping or shrinking during the welding process. By using advanced control systems, longitudinal welding machines can regulate heat input, welding speed, and other parameters to minimize distortion and ensure that the final weld meets the required specifications. This is especially important in applications where dimensional accuracy is critical, such as in the production of pressure vessels or other components that must meet strict safety standards.
Another significant benefit of longitudinal welding machines is their ability to automate the welding process, improving efficiency and consistency. In industrial settings, automation helps reduce labor costs and improves throughput, allowing companies to produce large quantities of welded components quickly and with a high degree of consistency. Automated systems are capable of performing repetitive tasks with high precision, ensuring that each weld is consistent and meets the required standards. Furthermore, automated longitudinal welding machines can be programmed to handle different materials, joint configurations, and welding parameters, providing flexibility for manufacturers working with a range of materials and production requirements.
In addition to their use in industrial settings, longitudinal welding machines are also employed in research and development applications, where they are used to fabricate prototype components or conduct material testing. The precision and control offered by these machines make them ideal for producing experimental parts where the welding quality must be closely monitored and controlled. Researchers can use longitudinal welding machines to test new materials, welding techniques, or designs, ensuring that the resulting components meet the necessary performance and safety standards.
In conclusion, longitudinal welding machines play a critical role in a variety of industries where long, continuous welds are required. Their ability to produce high-quality, precise welds makes them indispensable in the fabrication of pipes, tanks, pressure vessels, automotive components, and large structural elements. These machines provide manufacturers with the ability to automate the welding process, improving efficiency, consistency, and weld quality. With their versatility and high precision, longitudinal welding machines are essential tools in industries ranging from energy and aerospace to shipbuilding and automotive manufacturing.
Longitudinal welding machines offer additional advantages in terms of the flexibility they provide in handling various types of welding processes. These machines can be adapted to support different welding techniques, such as MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, and even laser welding, depending on the requirements of the specific application. The ability to switch between welding methods ensures that manufacturers can optimize the welding process for different materials and joint configurations. For example, MIG welding may be used for higher-speed welding of thicker materials, while TIG welding may be preferred for applications requiring more precise control over heat input and weld quality. The versatility of longitudinal welding machines allows operators to select the optimal welding process for each job, providing the flexibility needed for modern, high-demand manufacturing environments.
Longitudinal welding machines are also equipped with advanced technology that improves their efficiency and the quality of the welds they produce. Features such as real-time monitoring, automated quality control, and advanced welding parameters make it possible to detect and correct issues during the welding process. This ensures that each weld meets the required specifications for strength, integrity, and appearance. Real-time feedback systems can alert operators to potential problems, such as deviations from the ideal welding parameters, allowing for immediate adjustments to be made before defects occur. This proactive approach to quality control minimizes the risk of defective welds and reduces the need for rework, improving overall production efficiency.
Another key advantage of longitudinal welding machines is their ability to integrate with other automated systems in the manufacturing process. For instance, these machines can be combined with robotic arms or conveyor systems to create fully automated production lines. This integration enhances throughput and ensures that components are welded consistently and efficiently, without the need for manual intervention. In high-volume manufacturing environments, automation is critical for reducing labor costs and increasing production speed. By combining longitudinal welding machines with other automation technologies, manufacturers can achieve a high level of productivity while maintaining the quality and precision of their welds.
In industries that require high-strength, high-performance components, such as aerospace, longitudinal welding machines are also equipped with specialized features that help produce welds capable of withstanding extreme conditions. For example, aerospace components often need to meet stringent requirements for fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance, and overall strength. Longitudinal welding machines can be equipped with advanced heat control systems to minimize distortion and ensure that the welds are uniform and strong. Additionally, specialized weld monitoring systems can be used to track the entire welding process, ensuring that parameters such as heat input, travel speed, and filler material deposition are optimized for maximum performance.
In the oil and gas industry, where pipelines often need to endure harsh environmental conditions, the strength and durability of the welds produced by longitudinal welding machines are of utmost importance. Longitudinal welding machines can be equipped with automated welding techniques that ensure the integrity of the weld joint in challenging environments. The machines can be used to weld pipelines that are laid underground or underwater, and they are capable of handling large diameters and long lengths of pipe. This is particularly valuable in the construction and maintenance of pipelines that transport oil, gas, and other fluids, where the reliability of the welds is crucial to prevent leaks, corrosion, or other failures that could result in catastrophic consequences.
Moreover, longitudinal welding machines are essential in the manufacturing of large steel components used in the construction of infrastructure projects. These machines are frequently used to weld beams, girders, and other structural elements that are then used in bridges, buildings, and other large-scale constructions. The precision and strength of the welds produced by these machines ensure that the structural integrity of the components is maintained, even under heavy loads and extreme weather conditions. In this context, the ability to produce uniform, defect-free welds is essential for ensuring the safety and longevity of the infrastructure being built.
The adaptability of longitudinal welding machines extends to their ability to work with a wide variety of materials. These machines can be used to weld not only traditional metals such as steel and aluminum but also advanced alloys and composite materials. This makes them suitable for industries like defense, where the use of high-performance materials is common. For example, titanium, which is often used in military and aerospace applications due to its strength-to-weight ratio, can be welded with the precision required by longitudinal welding machines. Similarly, composite materials that are becoming more prevalent in automotive and aerospace industries can be joined effectively using advanced welding technologies, ensuring strong, lightweight components that meet industry standards.
The precision and repeatability of longitudinal welding machines also make them invaluable in the production of medical devices. In the medical field, certain components, such as surgical instruments, catheters, and diagnostic equipment, must be welded with an extremely high level of precision and cleanliness. The ability to produce seamless, uniform welds ensures that these components function properly and do not present any risk to patients. Longitudinal welding machines, with their automated features and high-quality weld monitoring systems, are particularly useful in ensuring the production of high-quality, sterile components that meet the stringent regulatory requirements of the medical industry.
In research and development (R&D), longitudinal welding machines are also used to test new materials, processes, and welding techniques. R&D teams rely on the ability to produce precise, reproducible welds on experimental parts to evaluate the performance of new materials or designs under various conditions. The flexibility of longitudinal welding machines allows them to adapt to different welding methods, materials, and configurations, making them an invaluable tool in the development of new technologies and products.
In conclusion, longitudinal welding machines offer significant advantages in a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, shipbuilding, energy, and infrastructure construction. Their ability to produce high-quality, continuous welds along long joints is essential in applications where strength, durability, and precision are paramount. The integration of automation, real-time feedback, and advanced control systems further enhances their performance, ensuring that welds meet the highest standards of quality and consistency. As industries continue to evolve and demand more advanced materials and manufacturing processes, longitudinal welding machines will remain a critical tool in ensuring the production of reliable, high-performance welded components across various sectors.
Longitudinal welding machines continue to evolve with the advancements in technology, allowing industries to meet the increasing demand for high-performance, cost-effective manufacturing solutions. As industries push the boundaries of material science and manufacturing efficiency, these machines are adapting to accommodate new welding techniques and material types. For example, advancements in welding automation and integration with artificial intelligence (AI) are improving the accuracy and efficiency of longitudinal welding machines. AI can now be used to optimize welding parameters in real-time, improving weld quality and reducing the chances of defects or inconsistencies. This integration not only enhances the precision of the welding process but also significantly reduces the need for manual intervention, resulting in fewer errors and improved consistency.
As manufacturers focus on sustainability, the environmental impact of their operations becomes an important consideration. Longitudinal welding machines are being designed with energy efficiency and minimal material waste in mind. By optimizing energy usage during the welding process and reducing the amount of filler material required, these machines are helping companies reduce their carbon footprint and operating costs. For instance, some longitudinal welding machines use advanced control systems to minimize heat distortion and ensure that welding material is used only where needed, preventing excess consumption. Moreover, the ability to automate the process not only reduces human error but also leads to higher throughput, further contributing to the overall efficiency of the production process.
The continuous improvement in robotics is also playing a pivotal role in advancing longitudinal welding. Robotic arms are increasingly used to supplement longitudinal welding machines, providing greater flexibility and precision, particularly in complex or challenging welding applications. With robotic integration, manufacturers can automate the positioning of the workpiece, adjust the welding path dynamically, and even perform automated inspections. The combination of robotic precision and longitudinal welding’s inherent ability to create strong, continuous welds enables manufacturers to achieve higher-quality results in a fraction of the time compared to traditional manual welding processes.
Another key development in longitudinal welding machines is their ability to work with increasingly diverse and challenging materials. In addition to traditional metals like steel and aluminum, industries are increasingly working with advanced alloys, composites, and other high-performance materials. As these materials often require specialized welding techniques, longitudinal welding machines are being equipped with more advanced capabilities to handle these unique materials. For example, some longitudinal welding machines are capable of utilizing hybrid welding techniques, such as laser-arc welding, which allows for welding with high precision on materials that are difficult to weld using conventional methods. These hybrid techniques can improve the quality of the weld while also increasing the speed of production.
Furthermore, the development of advanced welding monitoring systems allows for the continuous inspection and analysis of the weld during production. Non-destructive testing (NDT) technologies, such as ultrasonic and x-ray inspections, can be integrated into the longitudinal welding process to detect internal defects in real-time. This ensures that any potential issues can be addressed immediately, reducing the need for post-weld inspections or rework. Continuous monitoring also provides detailed data on the welding process, which can be analyzed to improve future operations, identify trends, and ensure that the production process consistently meets quality standards.
The versatility of longitudinal welding machines also extends to their application in industries that require a combination of different welding methods within a single manufacturing process. Some longitudinal welding machines are designed to handle multiple welding processes simultaneously, such as TIG, MIG, and even friction stir welding. This flexibility allows manufacturers to select the most suitable welding process for the material being used, the joint configuration, and the specific requirements of the application. By having the capability to switch between welding processes on the same machine, manufacturers can achieve more efficient production times and reduce the complexity of their operations.
In addition to their technological advancements, longitudinal welding machines are becoming more user-friendly, with more intuitive interfaces that simplify operation and maintenance. Many modern machines come equipped with touchscreen controls, which allow operators to easily set up the machine, adjust parameters, and monitor the welding process in real time. Advanced diagnostics tools are also available, which can alert operators to potential issues before they become significant problems, minimizing downtime and improving the reliability of the equipment.
The global push for manufacturing excellence and Industry 4.0 is also influencing the development of longitudinal welding machines. With the advent of smart manufacturing, these machines are becoming an integral part of connected, data-driven production lines. Sensors, IoT connectivity, and cloud-based systems are enabling longitudinal welding machines to provide real-time data that can be analyzed and shared across an entire production facility. This connectivity allows for greater collaboration between different stages of the production process, real-time adjustments to workflows, and improved traceability of the welding process for quality assurance purposes.
As industries increasingly demand faster production cycles, longitudinal welding machines are being optimized for high-speed operations without compromising the quality of the weld. These machines are designed to maintain precision while also being capable of operating at higher speeds, helping companies meet tight deadlines and improve their overall competitiveness. High-speed longitudinal welding machines can perform continuous welds on long components at speeds much faster than traditional welding methods, which is especially beneficial in mass-production industries such as automotive manufacturing.
Longitudinal welding machines also contribute to the safety of the manufacturing process. Automated systems eliminate the need for manual intervention, reducing the risk of human error and the potential for workplace accidents. In addition, the integration of real-time monitoring and AI-based control systems can further enhance the safety of the welding process by detecting and responding to any abnormalities that may arise, such as overheating, misalignment, or material defects. This not only ensures a safer work environment but also improves the overall reliability and longevity of the machinery.
In conclusion, longitudinal welding machines are evolving to meet the demands of modern manufacturing, driven by technological advancements, automation, and the increasing need for high-quality, efficient, and sustainable production. The integration of robotics, AI, advanced monitoring systems, and the ability to work with a wider range of materials ensures that these machines remain a vital tool in industries that require continuous, high-performance welds. As industries continue to evolve, longitudinal welding machines will remain an essential part of the manufacturing process, providing the precision, speed, and flexibility needed to meet the ever-increasing challenges of modern production. Their continued development will ensure that they remain an integral part of a wide variety of sectors, from energy and infrastructure to automotive, aerospace, and beyond.
Circular Welding System

A circular welding system is a specialized welding solution designed to efficiently and accurately weld components that are circular or cylindrical in shape. This system is particularly valuable in industries where circular parts need to be welded along their circumference or in applications that require continuous circular welding for components such as pipes, tanks, pressure vessels, and cylindrical containers. The design of a circular welding system is focused on ensuring precise, strong, and uniform welds on circular joints, which are often challenging to achieve manually or using conventional welding equipment. Circular welding systems are used across various industries, including oil and gas, aerospace, automotive, food processing, pharmaceuticals, and heavy manufacturing.
The key feature of a circular welding system is its ability to work around the entire circumference of a circular component, creating consistent, high-quality welds along the seam. These systems typically consist of a rotating fixture or turntable that holds the component securely in place while the welding head or electrode moves along the circular path. The rotation of the component allows the welding process to be applied evenly around the joint, ensuring that the weld is continuous and free from defects. This is especially important for applications where strength and integrity are critical, such as pressure vessels, which must withstand high internal pressures without failure.
One of the main advantages of using a circular welding system is the precision it offers. Circular welding systems are equipped with advanced controls and automated features that allow operators to adjust welding parameters such as speed, heat input, filler material, and electrode position to achieve the desired results. This ensures that the weld quality is consistent, with minimal variation in bead size, penetration, and appearance. Additionally, the automated nature of the system reduces the potential for human error, leading to more reliable and repeatable welds. This level of control is especially important in industries where weld quality is closely monitored and subject to strict standards, such as aerospace and pharmaceuticals.
In industries such as the oil and gas sector, circular welding systems are essential for the fabrication of pipelines, storage tanks, and pressure vessels. These components are typically large, heavy, and require welds that are both strong and leak-proof. A circular welding system is capable of producing the continuous, uniform welds necessary to ensure that these components can withstand the extreme pressures and conditions they are exposed to. Whether it is welding the seam of a cylindrical storage tank or joining segments of a large pipeline, circular welding systems provide a fast, efficient, and precise solution to these challenges.
Circular welding systems are also used extensively in the automotive industry for manufacturing components such as exhaust systems, fuel tanks, and other cylindrical parts. The ability to produce high-quality, consistent welds around circular joints is essential in these applications, where welds must meet stringent safety and durability requirements. A circular welding system can handle the mass production of these components with minimal manual intervention, significantly improving production efficiency and reducing labor costs. Automated features, such as automatic torch alignment and travel speed adjustments, further enhance the speed and precision of the welding process.
In the aerospace industry, circular welding systems are often employed to fabricate critical components for aircraft and spacecraft. For example, parts such as fuel tanks, engine components, and pressure vessels require precise welding to ensure the structural integrity and safety of the final product. Circular welding systems allow manufacturers to achieve the necessary weld quality and consistency in these demanding applications, where failure is not an option. The high precision of circular welding systems ensures that welds meet the required strength, corrosion resistance, and fatigue resistance specifications necessary for aerospace components.
The food and pharmaceutical industries also benefit from circular welding systems in the production of equipment such as tanks, reactors, and processing vessels. These industries require welding processes that produce smooth, contamination-free seams to ensure the safety and quality of their products. Circular welding systems are equipped with features that allow for clean, hygienic welds that meet industry regulations, ensuring that no contamination is introduced during the manufacturing process. Additionally, automated systems can help ensure that welding parameters are consistently maintained, minimizing the risk of defects that could compromise product safety.
One of the key advantages of circular welding systems is their ability to handle large, heavy components. The rotating fixture or turntable used in these systems is designed to support the weight of the workpiece while maintaining precise rotational speed. This is especially important in the fabrication of large tanks or pressure vessels, which can be difficult to weld using traditional methods. Circular welding systems can handle these heavy components without compromising on the quality of the weld, ensuring that the final product meets the required specifications for strength and durability.
The automation of circular welding systems also plays a crucial role in improving manufacturing efficiency. By automating the welding process, manufacturers can reduce the need for manual labor, which not only lowers costs but also speeds up production times. Automated systems can also monitor the entire welding process in real time, making adjustments to the welding parameters as needed to ensure that the weld is being applied correctly. This real-time feedback and monitoring help to reduce the risk of defects and ensure that each weld meets the required quality standards.
Circular welding systems are also equipped with various advanced features that further enhance their performance and reliability. For example, some systems include integrated vision systems that allow for precise tracking of the welding torch along the joint. These systems can automatically adjust the position of the torch to ensure that the weld is applied evenly around the circumference of the component. Additionally, circular welding systems can be integrated with other manufacturing equipment, such as robotic arms or conveyor systems, to create fully automated production lines that handle the entire welding process with minimal human intervention.
The flexibility of circular welding systems also allows them to be used in a wide range of applications, beyond just cylindrical components. For example, some circular welding systems can be adapted to weld elliptical or other non-circular shapes. This flexibility allows manufacturers to use a single system for a variety of different parts, reducing the need for multiple specialized machines. This makes circular welding systems a versatile solution for industries that require a high level of precision and flexibility in their manufacturing processes.
In terms of innovation, circular welding systems are increasingly incorporating advanced welding technologies, such as laser welding and electron beam welding, to further improve the quality and speed of the welding process. Laser welding, in particular, offers several advantages, such as deep penetration, low heat input, and minimal distortion, which make it ideal for welding thin-walled or delicate components. Circular welding systems equipped with laser welding capabilities allow manufacturers to achieve high-quality, precise welds on components that may be challenging to weld using traditional methods.
Another important development is the integration of real-time monitoring and feedback systems, which are becoming more common in modern circular welding systems. These systems allow for constant surveillance of the welding process, ensuring that parameters such as heat input, travel speed, and weld depth are within the optimal range. If any deviations from the desired parameters occur, the system can automatically adjust the welding process to correct the issue. This ensures that each weld meets the necessary quality standards and helps reduce the need for manual inspection and rework.
In conclusion, circular welding systems offer a highly effective solution for welding cylindrical and circular components in a wide range of industries. Their ability to produce consistent, high-quality welds around the circumference of a component makes them essential in applications that require strong, durable, and defect-free joints. With their advanced automation, precision controls, and ability to handle large and heavy components, circular welding systems provide manufacturers with an efficient, reliable, and versatile tool for modern manufacturing. As technology continues to evolve, these systems are likely to incorporate even more advanced features, further improving the quality, speed, and flexibility of the welding process.
As the demand for higher production speeds, more complex components, and stricter industry standards continues to grow, circular welding systems are evolving to meet these challenges. One of the major trends in the development of these systems is their integration with Industry 4.0 technologies. The use of IoT (Internet of Things) connectivity, data analytics, and cloud computing is enhancing the functionality of circular welding systems by allowing real-time data sharing across production lines. With IoT sensors embedded in the system, manufacturers can track key welding parameters, such as temperature, voltage, current, and travel speed, and send this data to a central monitoring platform. This integration enables manufacturers to monitor and optimize the entire welding process remotely, providing operators with better insights into the performance of their equipment and allowing for proactive maintenance to prevent downtime.
Additionally, cloud-based systems allow for the analysis of large sets of data collected from various machines across a production facility. This data can be used to identify trends, troubleshoot issues, and continuously improve welding operations. Over time, the system can learn from historical data and make predictive adjustments to optimize welding parameters based on material types, joint configurations, and environmental conditions. The result is a more efficient and responsive welding process that minimizes the risk of defects, increases production efficiency, and reduces overall costs.
The rise of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is also influencing the development of circular welding systems. In some industries, components are now being produced using 3D printing technologies, which require precise and clean welding for post-processing or to join 3D-printed parts. Circular welding systems are being adapted to work with these new manufacturing techniques, allowing for the integration of 3D-printed parts into more traditional welded assemblies. This ability to work with advanced manufacturing methods further extends the versatility and applicability of circular welding systems across industries.
Moreover, circular welding systems are increasingly incorporating advanced cooling techniques to manage the heat generated during the welding process. Overheating can lead to warping, distortion, and other issues that affect the quality of the weld. To address this, modern systems are often equipped with water-cooling units, heat sinks, or advanced thermal management systems that help maintain consistent temperatures throughout the welding process. These cooling solutions are especially beneficial when welding materials that are prone to heat-related issues, such as high-strength alloys, thin metals, or heat-sensitive components. By maintaining a controlled temperature, circular welding systems ensure that weld quality remains consistent and that the final product meets stringent performance standards.
Another area of focus in the development of circular welding systems is their ability to handle materials with varying thicknesses or irregularities in shape. While traditional welding systems may struggle with components that have uneven thicknesses or varying diameters, circular welding systems are designed to accommodate these variations. The adjustable features of these systems, such as variable travel speed, adaptable torch positioning, and customizable welding parameters, allow for high-quality welds on parts that might otherwise require multiple passes or special equipment. This adaptability makes circular welding systems highly effective in industries where material characteristics can vary greatly, such as in the manufacturing of large pressure vessels or custom-designed industrial equipment.
The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is another consideration that is driving innovation in circular welding systems. Many industries are under increasing pressure to reduce their carbon footprint, minimize material waste, and improve energy efficiency. Circular welding systems are incorporating more environmentally friendly features, such as low-energy welding technologies and the ability to work with sustainable materials. For instance, some systems now feature advanced welding processes that use less heat and produce less spatter, resulting in cleaner welds and reduced consumption of filler materials. Additionally, the integration of automated controls and sensors allows for more efficient use of energy during the welding process, helping manufacturers reduce their overall energy consumption.
Circular welding systems are also being optimized for ease of use and maintenance. In modern manufacturing environments, downtime is costly, and having machines that are easy to operate, set up, and maintain is crucial. Many circular welding systems now come with intuitive touch-screen interfaces, which allow operators to easily adjust parameters, monitor the welding process, and troubleshoot any issues that may arise. These systems may also be equipped with automated self-diagnostics, which can detect faults or performance issues and alert operators before they lead to larger problems. This reduces the need for manual inspections and makes it easier for operators to maintain consistent weld quality.
Furthermore, the integration of robotic technology into circular welding systems is increasing the level of precision and repeatability. Robotic arms are now commonly used to assist in positioning, aligning, and moving components through the welding area. These robotic systems can be programmed to handle complex geometries and move components with a high degree of accuracy, ensuring that the weld is applied precisely to the joint. The combination of robotic technology and circular welding ensures that even intricate, high-precision parts can be welded with minimal human intervention.
Circular welding systems are also adapting to the increasing need for customization and short production runs. While traditional welding systems may be optimized for large-scale production, modern circular welding machines are becoming more flexible and capable of handling smaller batches or custom orders. Manufacturers can quickly change welding parameters, switch between different materials, or adjust the size of the components being welded. This flexibility is especially important in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing, where product designs can vary significantly and the ability to adapt quickly is crucial.
In conclusion, circular welding systems are at the forefront of modern manufacturing processes, providing industries with efficient, high-quality, and versatile solutions for welding cylindrical and circular components. The continued development of these systems, driven by automation, robotics, data analytics, and sustainability, ensures that manufacturers can meet the ever-increasing demands for precision, efficiency, and quality. By incorporating advanced technologies, real-time monitoring, and adaptive features, circular welding systems are transforming the way welded components are produced across a wide range of industries. As technology continues to advance, these systems will play an even more critical role in meeting the challenges of modern manufacturing, enabling companies to stay competitive while producing high-performance products that meet stringent quality standards.
Rotary Pipe Flange Welding Machine

A Rotary Pipe Flange Welding Machine is a specialized welding solution used for the fabrication and joining of pipe flanges to pipes or other cylindrical components. This machine is commonly utilized in industries where pipes and flanges must be securely welded together, such as in the oil and gas, chemical, power generation, and construction sectors. The primary advantage of using a rotary pipe flange welding machine is its ability to perform high-quality, consistent welds around the circumference of the flange, ensuring leak-proof and durable joints that can withstand high pressures and demanding environmental conditions.
The key feature of a rotary pipe flange welding machine is its rotational mechanism. The pipe and flange are securely mounted on a rotating turntable or fixture, allowing the welding head to travel around the joint as the pipe and flange rotate. This rotation ensures that the weld is applied evenly around the entire circumference of the flange, minimizing the risk of defects or inconsistencies in the weld. The ability to rotate the pipe and flange while the welding process is automated helps achieve precise, continuous, and uniform welds without the need for manual intervention.
One of the major benefits of using a rotary pipe flange welding machine is its high level of precision. These machines are equipped with advanced control systems that allow operators to fine-tune welding parameters such as heat input, travel speed, and filler material to achieve the desired weld quality. By controlling these parameters, the system ensures that the weld has the right penetration, bead consistency, and appearance. This level of precision is particularly critical in industries where pipe flanges are used in high-pressure applications, such as in the oil and gas industry, where even small defects in the weld can lead to dangerous leaks or failures.
Additionally, rotary pipe flange welding machines offer increased efficiency compared to traditional manual welding methods. The automation provided by these machines reduces the need for skilled manual labor, enabling faster production times and consistent results. Operators can set up the machine to perform multiple welds in succession with minimal intervention, which is particularly beneficial in high-volume production environments. This efficiency can significantly reduce manufacturing costs, especially in industries like pipeline construction or power plant fabrication, where large numbers of flanged joints must be welded in a short amount of time.
Another significant advantage of rotary pipe flange welding machines is their ability to weld pipe flanges of varying sizes, materials, and configurations. The versatility of these machines allows them to accommodate different pipe diameters and flange thicknesses, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Whether welding small diameter pipes for the food processing industry or large diameter pipes for offshore oil rigs, rotary pipe flange welding machines can handle the specific requirements of each project. These machines can also be configured to weld different materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy metals, allowing manufacturers to use a single machine for multiple welding tasks.
The design of rotary pipe flange welding machines often includes features that improve the overall welding process. For example, some machines are equipped with automated torch alignment systems, ensuring that the welding torch remains in the optimal position throughout the entire weld. This feature is particularly important when welding large-diameter pipes, where maintaining the correct alignment of the torch is crucial for achieving uniform welds. Some rotary pipe flange welding machines also include integrated purge gas systems, which provide a clean welding environment by purging the inside of the pipe with an inert gas such as argon. This helps to prevent oxidation and contamination of the weld, ensuring a cleaner, higher-quality result.
The welding process in rotary pipe flange welding machines can be further optimized with the use of advanced welding techniques. For example, TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding is often used in applications where high-quality, low-distortion welds are required. TIG welding provides a precise, controlled heat input, making it ideal for welding materials that are sensitive to heat, such as stainless steel and titanium. In some cases, rotary pipe flange welding machines can also accommodate MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding or SAW (Submerged Arc Welding) for applications where faster welding speeds or higher deposition rates are needed.
In industries like oil and gas, rotary pipe flange welding machines are essential for ensuring the integrity and reliability of pipeline systems. The welding of pipe flanges is critical in creating secure connections between pipe segments, valves, and other components in pipelines that transport oil, gas, and chemicals. The strength and reliability of the welded joints directly impact the safety and performance of the entire pipeline. A properly welded flange ensures that the pipeline can handle the high pressures and temperatures associated with fluid transport, while preventing leaks and failures that could have catastrophic consequences.
The quality of the weld is also crucial in industries such as power generation, where pipe flanges are used in steam, gas, and water pipelines. The rotary pipe flange welding machine ensures that the weld is free from defects, such as cracks, porosity, or undercut, which could compromise the strength and efficiency of the pipeline. Furthermore, the ability to create precise, leak-proof welds around the flange joint helps to minimize maintenance and repair costs over the lifespan of the pipeline or pressure vessel.
In the construction industry, rotary pipe flange welding machines are used for a variety of applications, such as the fabrication of HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, fire protection systems, and water treatment plants. The accuracy and speed of these machines make them ideal for projects that require large numbers of pipe flanges to be welded together quickly and efficiently. The use of a rotary pipe flange welding machine in these applications can significantly improve productivity and reduce the overall cost of construction.
As rotary pipe flange welding machines continue to evolve, their integration with modern technologies, such as robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and real-time monitoring, is increasing. Robotic systems can be used to assist in the positioning and alignment of pipe flanges, further improving the precision and repeatability of the welding process. AI-based systems can analyze the welding data in real time and make adjustments to the parameters, ensuring that the weld quality remains consistent across multiple welds. Additionally, real-time monitoring allows operators to track the progress of the weld and make adjustments as necessary, improving overall process control.
The safety of the welding process is another key consideration for rotary pipe flange welding machines. These machines are often used in high-pressure, high-temperature applications, where the risk of accidents or equipment failure is significant. Modern rotary pipe flange welding machines are designed with built-in safety features, such as automatic shutoffs, pressure sensors, and protective enclosures, to minimize the risks associated with welding. These safety features help ensure that the operator can focus on the task at hand without worrying about potential hazards.
The environmental impact of welding operations is also a consideration, and rotary pipe flange welding machines are being designed to be more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. Features such as advanced gas management systems, reduced energy consumption, and waste reduction technologies are helping to minimize the environmental footprint of welding operations. Additionally, the use of high-precision welding techniques ensures that there is minimal waste of material, which can contribute to both cost savings and sustainability efforts.
In conclusion, rotary pipe flange welding machines are an indispensable tool for industries that require reliable, high-quality, and efficient welding of pipe flanges to pipes or other components. With their ability to produce consistent, uniform welds, handle a wide range of materials and sizes, and improve production efficiency, these machines are crucial for industries such as oil and gas, power generation, construction, and manufacturing. As technology continues to advance, the integration of automation, robotics, AI, and real-time monitoring will further enhance the capabilities and performance of rotary pipe flange welding machines, allowing manufacturers to meet the increasing demands for precision, speed, and quality in modern manufacturing processes.
As the demand for greater efficiency and precision in industrial manufacturing grows, rotary pipe flange welding machines continue to evolve to meet these challenges. One of the key areas of innovation is the further automation of the welding process. Advanced automated systems can now perform precise adjustments to the welding parameters, such as travel speed, arc length, and heat input, based on real-time data analysis. This automation significantly reduces the need for manual intervention, allowing operators to focus on monitoring the overall welding process, rather than adjusting settings continuously. This increases not only productivity but also the overall consistency of weld quality.
The integration of robotics with rotary pipe flange welding machines has enhanced the flexibility and versatility of these systems. Robotic arms, equipped with welding torches, can be programmed to move along the circumference of the pipe flange, offering increased accuracy and repeatability in the welding process. Additionally, robotic systems can handle a variety of pipe sizes, shapes, and configurations, which is particularly useful when working with non-standard or custom-designed components. The ability to adjust and reprogram the robotic systems for different tasks enables manufacturers to improve both the efficiency and versatility of their welding operations, allowing them to handle multiple projects or part designs with ease.
Another significant advancement in rotary pipe flange welding machines is the use of advanced welding techniques such as Laser Beam Welding (LBW) and Electron Beam Welding (EBW). These welding methods offer higher precision and lower heat input compared to traditional arc welding techniques, making them ideal for applications that require minimal distortion or that involve sensitive materials. Laser welding, for example, can create deep, narrow welds with minimal heat affected zones (HAZ), which is particularly advantageous when working with thin-walled pipes or high-strength alloys. The incorporation of such cutting-edge welding techniques into rotary pipe flange welding machines ensures that manufacturers can meet the most stringent quality standards while reducing material wastage and distortion.
The application of real-time feedback and monitoring systems further enhances the capabilities of rotary pipe flange welding machines. These systems continuously track important welding parameters, such as temperature, voltage, current, and gas flow, and make automatic adjustments to optimize the welding process. Through continuous monitoring, operators can receive immediate alerts if any deviation from the desired parameters is detected. This proactive approach allows for early detection of potential issues, reducing the likelihood of defects and ensuring that the weld quality remains consistent throughout the entire process.
Additionally, the use of advanced sensor technologies has enabled the development of predictive maintenance systems. These sensors can monitor the performance of key components in the welding machine, such as the welding torch, motor, and turntable, and alert operators to potential issues before they lead to equipment failure. By predicting and addressing maintenance needs in advance, predictive maintenance helps reduce downtime and prolong the lifespan of the machine, ensuring that operations run smoothly and efficiently.
In terms of material handling, rotary pipe flange welding machines are also incorporating more sophisticated technologies to improve safety and reduce the risk of operator error. Many machines now feature automatic clamping systems that securely hold the pipe and flange in place during welding, preventing slippage or misalignment. This feature is especially important when working with large, heavy pipes, where manual handling could introduce risks of injury or equipment damage. Automatic alignment systems ensure that the flange and pipe are properly positioned before welding begins, further enhancing the precision and consistency of the weld.
The versatility of rotary pipe flange welding machines is also being expanded with the ability to handle a wider range of pipe materials. While traditional welding systems were limited to certain metals, modern rotary pipe flange welding machines can now accommodate an array of materials, including high-strength steels, corrosion-resistant alloys, and non-ferrous metals. This flexibility makes these machines invaluable in industries such as aerospace, petrochemicals, and power generation, where the need to weld various materials with different properties is common.
Sustainability is another important factor driving the development of rotary pipe flange welding machines. As industries become more focused on reducing their environmental impact, manufacturers are integrating energy-efficient features into welding machines. These include power-saving modes, advanced gas management systems that reduce waste, and optimized heat control that minimizes energy consumption during the welding process. By reducing energy use and material waste, rotary pipe flange welding machines help manufacturers achieve greener operations, while simultaneously cutting costs and increasing operational efficiency.
The increasing use of simulation software is another breakthrough in rotary pipe flange welding machines. Before initiating the welding process, operators can now simulate the entire welding procedure using computer-aided design (CAD) tools, which helps identify potential problems such as heat distortion, undercuts, or joint misalignment. This allows for adjustments to be made before the welding process begins, ensuring that the final weld will meet the required specifications. Simulation software also enables manufacturers to optimize welding parameters for specific materials and conditions, improving both the quality of the weld and the overall efficiency of the production process.
In some industries, such as the food and beverage or pharmaceutical industries, the cleanliness and hygiene of the welding process are critical. Rotary pipe flange welding machines are designed with features to address these concerns. For example, some machines come with clean, sealed welding enclosures that minimize the risk of contamination from environmental factors such as dust or moisture. In food and pharmaceutical applications, it is especially important that welding processes do not compromise the integrity of the materials or introduce contaminants. The ability to achieve high-quality welds while maintaining a contamination-free environment is one of the key advantages of rotary pipe flange welding machines in these sectors.
Moreover, modern rotary pipe flange welding machines offer enhanced user interfaces that make them easier to operate. Touchscreen controls, user-friendly programming software, and intuitive settings allow operators to quickly set up and adjust the machine according to their welding requirements. These improvements in user interfaces not only reduce the learning curve for new operators but also increase the overall efficiency of the system, as less time is spent on setup and adjustments. Additionally, some machines include remote access capabilities, allowing operators to control and monitor the welding process from a distance, further enhancing the flexibility and convenience of the system.
Looking to the future, the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in rotary pipe flange welding machines is expected to expand. AI technologies are capable of analyzing vast amounts of data collected from the welding process and identifying patterns that humans may not detect. This could lead to even more precise control of welding parameters and automated adjustments to optimize weld quality. For example, AI could detect subtle changes in material properties or joint configurations and automatically adjust the welding technique or settings to compensate for these variations. This level of automation and intelligence could further improve weld consistency, quality, and speed, making rotary pipe flange welding machines even more indispensable in modern manufacturing.
In conclusion, rotary pipe flange welding machines represent a vital component of modern manufacturing and construction processes that require high-quality, reliable, and efficient welding of pipe flanges. Their ability to produce precise, uniform, and strong welds around the circumference of a flange ensures that these components meet the rigorous demands of industries such as oil and gas, aerospace, power generation, and construction. With continued advancements in automation, robotics, AI, and energy efficiency, rotary pipe flange welding machines are poised to play an even more significant role in meeting the evolving needs of manufacturers. By offering flexibility, precision, and reduced production costs, these machines are integral to the success of industries that rely on welded pipe connections and flanged joints.
Boom Welding Machine

A Boom Welding Machine is an advanced piece of equipment primarily used in industrial welding operations for large or complex workpieces, especially in situations where the welding area is large, the parts are heavy, or access to certain weld points is difficult. This machine is designed to accommodate a wide range of welding tasks, from heavy-duty structural welding to precision applications, offering a versatile solution for industries like construction, shipbuilding, pipeline fabrication, and heavy machinery manufacturing. It integrates a boom—a large, articulated arm that holds and positions the welding torch—enabling welding over an extended area with high precision.
The defining feature of a Boom Welding Machine is its large-scale movement and flexibility. The boom can be adjusted vertically and horizontally, allowing it to reach difficult welding locations, even when working with oversized or immovable components. This capability is essential for projects that involve large pipes, tanks, or structural assemblies, where manual access would be limited or impractical. The ability to move the welding head across a large area without repositioning the workpiece ensures greater efficiency and precision, especially in welding tasks that require consistent, continuous bead application across various parts of the workpiece.
One of the primary advantages of Boom Welding Machines is their ability to automate the welding process. This automation allows for higher precision and repeatability in welding operations. Once the parameters are set, the machine can perform the entire welding task autonomously, reducing the need for manual labor and minimizing the potential for human error. Automated processes in Boom Welding Machines also help to increase production speed, reduce labor costs, and improve the overall quality of the weld, especially when dealing with large projects that require multiple, identical welds.
Boom Welding Machines are particularly beneficial in industries that require welding in confined or hard-to-reach areas. For instance, in shipbuilding, where large steel sections must be welded in tight spaces, the boom arm allows the welding torch to be maneuvered into position without the need for cumbersome equipment or the movement of the workpiece. This capability is invaluable in environments where space constraints could otherwise hinder the welding process, such as in the construction of industrial tanks, reactors, or in offshore pipeline construction.
The use of a boom allows for precise control over the welding process, which is essential when working with materials that are sensitive to heat or require a high level of precision. The ability to adjust the height and angle of the welding torch ensures that the right amount of heat is applied to the workpiece, preventing overheating and material distortion. This control is especially important when welding materials like stainless steel, aluminum, or high-strength alloys, which can be prone to warping or cracking if not properly managed during the welding process.
Boom Welding Machines offer versatility in terms of the welding techniques they support. These machines can be configured to accommodate different types of welding processes, including TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas), MIG (Metal Inert Gas), Submerged Arc Welding (SAW), and Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW), among others. The flexibility to switch between these processes allows manufacturers to select the most appropriate welding technique for the material, thickness, and application at hand. For example, TIG welding is often chosen for its precision and clean welds, while MIG welding may be preferred for its faster speed and higher deposition rates. The versatility of these machines makes them suitable for a wide variety of projects, from intricate, high-precision work to heavy-duty applications.
The ability to work with large components is another important benefit of Boom Welding Machines. In industries such as pipeline construction, where long lengths of pipe must be welded, the boom arm can position the welding torch along the entire length of the joint, ensuring that the weld is continuous and uniform. This is particularly valuable when welding large-diameter pipes or sections of pipe that are too heavy or unwieldy to be easily moved into position. The ability to handle large components with ease reduces the time and labor required for repositioning the parts and ensures that the weld is applied correctly.
Boom Welding Machines also offer significant improvements in speed and efficiency, which can have a direct impact on the bottom line for manufacturers. These machines are capable of performing continuous welds without the need for frequent stops, re-positioning, or manual adjustments. This increased efficiency can significantly reduce overall production time, allowing for faster turnaround on large-scale projects. Additionally, since the machine can operate autonomously once programmed, it frees up human resources to focus on other tasks, increasing overall productivity and reducing the reliance on skilled labor.
Another feature of modern Boom Welding Machines is their integration with advanced control systems and automation software. These systems allow operators to program the welding parameters, monitor the welding process in real time, and adjust settings remotely, ensuring that the weld is completed to the desired specifications. With features like data logging, operators can track performance, measure weld quality, and generate reports for quality assurance purposes. These advanced control systems make it easier to achieve consistent results across multiple welds, especially in large-scale production runs.
Safety is another important aspect of Boom Welding Machines. Welding is inherently a hazardous activity, with risks such as exposure to intense heat, fumes, and potential electrical hazards. Boom Welding Machines reduce some of these risks by keeping the operator at a safe distance from the weld area. The ability to remotely control the machine also reduces the operator’s exposure to dangerous environments, such as high-heat zones, and minimizes the risk of accidents. Furthermore, these machines often include safety features such as automatic shutdown systems, pressure sensors, and emergency stop functions, which enhance overall operational safety.
The integration of real-time monitoring systems further improves the performance and safety of Boom Welding Machines. These systems can detect potential issues such as irregularities in the welding process, temperature fluctuations, or deviations from the preset welding parameters. When such issues arise, the system can alert the operator, allowing them to take corrective action before the problem escalates. Real-time monitoring also ensures that the weld quality remains consistent throughout the entire process, leading to fewer defects and a higher-quality final product.
Another important aspect of Boom Welding Machines is their ability to adapt to different work environments. These machines are often designed to be portable and can be moved to various locations within a manufacturing plant or construction site, allowing for flexibility in operations. In addition, many models feature modular designs, enabling the welding machine to be customized for specific applications. This modularity is particularly beneficial in industries where projects vary in scale, material, and complexity.
In terms of material handling, Boom Welding Machines can be equipped with advanced clamping and positioning systems, which secure the workpiece in place and prevent misalignment during the welding process. These features help to ensure that the weld is applied accurately and that the workpiece remains stationary throughout the operation, improving weld consistency and reducing the likelihood of errors. Some machines also include automatic feed systems for the filler material, ensuring that the weld pool remains consistent and reducing the chances of defects caused by insufficient material.
The environmental impact of welding is an increasing concern, and Boom Welding Machines are becoming more energy-efficient as a result. These machines are often designed to optimize power consumption, reduce heat loss, and minimize gas consumption during the welding process. By using more efficient technologies, manufacturers can reduce their carbon footprint while maintaining the quality and consistency of their welds.
The future of Boom Welding Machines lies in continued advancements in automation, connectivity, and AI-driven optimization. With the development of smarter systems that can analyze data in real time, these machines will become even more efficient, precise, and capable of adapting to different materials, applications, and environmental conditions. The incorporation of AI and machine learning will allow Boom Welding Machines to optimize welding parameters on the fly, further enhancing weld quality and minimizing the need for manual adjustments.
In conclusion, Boom Welding Machines are crucial for industries that require high precision, flexibility, and the ability to handle large, complex components. Their ability to automate the welding process, improve weld quality, and increase production speed makes them invaluable in applications such as shipbuilding, pipeline construction, and heavy machinery manufacturing. With continuous improvements in automation, real-time monitoring, and energy efficiency, Boom Welding Machines will continue to play a pivotal role in modern manufacturing and fabrication, offering manufacturers a powerful tool for meeting the demands of today’s fast-paced, high-precision industries.
The ongoing development of Boom Welding Machines is focused on enhancing their usability, adaptability, and precision. Manufacturers are increasingly incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning into these machines, enabling them to autonomously adjust welding parameters in real-time based on the workpiece and material characteristics. AI systems can analyze the welding environment, make predictions about potential issues, and optimize the welding process for improved consistency and efficiency. For instance, AI-driven software can detect when the welding torch is beginning to wear out or when there’s a risk of misalignment, adjusting the settings or notifying the operator to take corrective action. This reduces the likelihood of human error, increases the overall quality of the weld, and allows the system to work more efficiently.
Additionally, advancements in robotic integration are pushing the boundaries of what Boom Welding Machines can achieve. By incorporating robotic arms with the welding boom, manufacturers can increase the flexibility of these machines even further. Robotic systems are capable of performing intricate movements with exceptional precision, which is particularly beneficial when welding components that require high levels of accuracy, such as parts used in aerospace or medical equipment manufacturing. These robotic systems can be programmed to handle a wide range of tasks, including welding in hard-to-reach or restricted areas, performing multi-pass welds, and switching between different welding processes based on the material or part requirements.
The continued integration of Industry 4.0 technologies is also playing a crucial role in shaping the future of Boom Welding Machines. With the growing trend of connected manufacturing, these machines are becoming an integral part of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). By being connected to centralized systems that collect and analyze data, Boom Welding Machines can contribute to a more efficient and streamlined production process. Operators can access real-time data, remote diagnostics, and maintenance alerts from anywhere in the world, improving operational efficiency and reducing downtime. Predictive analytics can also be applied to monitor the health of the machine and anticipate potential issues before they lead to costly repairs or production delays.
Another important factor in the development of Boom Welding Machines is their environmental footprint. As industries increasingly prioritize sustainability, manufacturers are incorporating energy-efficient technologies into their welding machines. For example, the machines now feature power-saving modes and optimized gas flow systems, which reduce the amount of energy consumed during operation and minimize material waste. Additionally, some Boom Welding Machines are designed to use environmentally friendly gases and consumables, which reduce their impact on the environment and contribute to greener production practices.
The ongoing focus on enhancing user experience is also driving improvements in the design and operation of Boom Welding Machines. Modern systems feature more intuitive interfaces, with touchscreens and advanced software that allow operators to easily control the welding parameters, set up new jobs, and troubleshoot issues. Additionally, advanced safety systems are becoming more common, including features like automatic emergency stops, thermal sensors, and safety barriers that protect operators from potential hazards. These safety features are designed to provide peace of mind while enhancing productivity, ensuring that operators can focus on the task at hand without worrying about safety risks.
The growing demand for flexible and customizable welding systems is another factor influencing the evolution of Boom Welding Machines. Many of these machines now come with modular designs, allowing manufacturers to configure the system to suit specific applications. For example, additional tools such as automatic wire feeders, pre-heating equipment, and weld inspection cameras can be added to the system, enhancing its capabilities and making it suitable for a broader range of welding applications. This modularity not only makes the machines more adaptable but also helps manufacturers get the most out of their investment by allowing them to scale or modify their equipment as their production needs evolve.
Boom Welding Machines also have an increasing role in welding automation for smaller to medium-scale manufacturers. In industries where the demand for custom, low-volume runs is growing, these machines can be programmed to handle shorter runs of diverse parts without sacrificing the consistency and quality that are necessary for high-end applications. This flexibility has allowed smaller manufacturers to take advantage of the efficiency and precision of automated welding, reducing the cost per unit and improving overall productivity.
Looking toward the future, the trend of increased connectivity and integration with cloud platforms is expected to further transform the way Boom Welding Machines are operated and maintained. Cloud-based platforms could enable centralized control and monitoring of multiple machines across different locations, allowing companies with multiple manufacturing facilities to synchronize their operations, share data, and implement best practices across their entire network. This would improve not only operational efficiency but also lead to better decision-making and resource allocation.
The development of Boom Welding Machines is also tied to the wider trends of digitalization and data-driven manufacturing. With sensors, real-time data analytics, and cloud connectivity, the welding process becomes more transparent, allowing manufacturers to track and measure key performance indicators such as weld quality, speed, and energy consumption. This data can be used to improve future welding projects, identify trends, and refine processes for greater efficiency and precision. The feedback loop created by this system also helps optimize machine performance, improve consistency in weld quality, and reduce waste—all contributing to more sustainable manufacturing practices.
In terms of specific industries, Boom Welding Machines continue to be indispensable in sectors such as construction, oil and gas, automotive, and shipbuilding. In the construction industry, where large metal structures need to be joined with high-strength welds, the machine’s ability to handle complex, oversized components is invaluable. For pipeline construction, where long lengths of pipe must be welded in challenging environments, the boom’s mobility and precision ensure that welds are strong, reliable, and consistent. In shipbuilding, the ability to weld large steel sections while maintaining accuracy is crucial for ensuring the safety and integrity of the final product. Furthermore, the versatility of these machines makes them suitable for various types of joints, such as butt, fillet, and corner joints, allowing them to adapt to the specific needs of each project.
The boom’s ability to reach difficult or confined spaces also proves essential for the maintenance and repair of complex equipment or structures. When it is not feasible to disassemble equipment to access welding points, the Boom Welding Machine can be maneuvered into place to perform necessary repairs without disrupting ongoing operations. This is especially critical in industries like aerospace or power generation, where downtime is costly and repairs must be performed quickly and accurately.
As the industrial landscape continues to evolve, Boom Welding Machines are likely to remain at the forefront of welding technology. The integration of more advanced technologies, including robotics, AI, and IoT, promises to make these machines more intelligent, adaptive, and efficient than ever before. As automation continues to shape manufacturing practices worldwide, the role of Boom Welding Machines will only expand, enabling manufacturers to meet the growing demands for speed, precision, and quality while reducing operational costs and improving safety. The combination of automation, versatility, and real-time data analysis makes the Boom Welding Machine an indispensable tool for industries seeking to remain competitive in an increasingly fast-paced and globalized marketplace.
Pipe Welding Machine
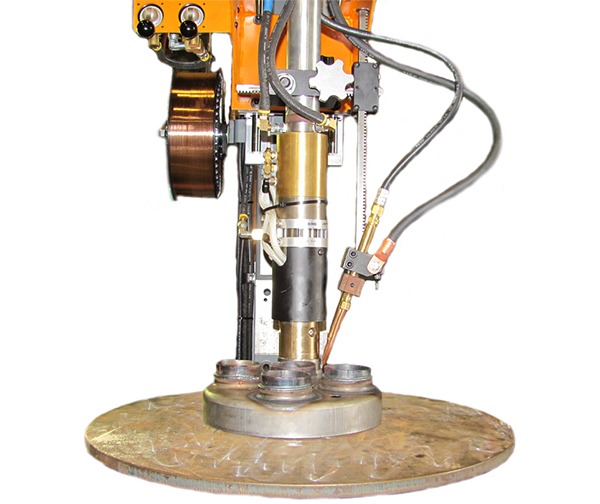

A Pipe Welding Machine is a specialized piece of equipment designed to automate and optimize the welding of pipes, whether for construction, manufacturing, or repair purposes. These machines are essential in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemicals, shipbuilding, and pipeline construction, where the joining of pipes is a critical part of the production process. The primary purpose of a Pipe Welding Machine is to deliver high-quality welds that ensure the structural integrity and safety of the pipes, which are often subject to high pressure and temperature fluctuations. These machines can be used to weld various pipe materials, including steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and more, offering a versatile solution for diverse applications.
The key feature of Pipe Welding Machines is their ability to perform high-precision welding tasks in challenging conditions, especially in large-scale pipe fabrication and repair work. The machine can be set up to automatically feed the welding consumables, control the heat input, and maintain consistent welding speed, all of which contribute to the quality of the weld. One of the most important advantages of these machines is their ability to produce repeatable results with minimal variation, which is crucial for ensuring the integrity of welded pipes used in high-stress environments such as in the oil and gas industry.
Pipe Welding Machines come in different configurations to suit specific applications. The most common types include orbital welding machines, which are particularly effective for welding pipes in a circular motion, and linear or longitudinal welding machines, which can be used for more straightforward welding tasks. Some machines are designed for manual operation, where the operator adjusts the welding parameters and positions the machine, while others are fully automated, allowing the entire welding process to be controlled through pre-programmed software. The automated machines significantly reduce the chances of human error and ensure high repeatability and efficiency, even in high-volume production settings.
A significant feature of Pipe Welding Machines is their ability to handle pipes of various sizes and thicknesses. The machines can be equipped with adjustable clamping systems that secure the pipes in place, preventing movement during the welding process, which is essential for maintaining weld quality. Many of these machines are also portable, which makes them ideal for on-site welding operations in industries like pipeline construction, where welding must be done in the field, often in remote or challenging environments. The portability of Pipe Welding Machines allows operators to bring the welding equipment directly to the job site, reducing the need for transporting large pipe sections and ensuring that the welding process is completed quickly and efficiently.
In terms of technology, modern Pipe Welding Machines often feature advanced control systems that enable precise regulation of welding parameters such as voltage, current, and speed. These systems can also incorporate feedback loops that monitor the quality of the weld in real-time and make adjustments as needed to ensure optimal results. For example, advanced sensors can detect variations in the welding arc, gas flow, or temperature, allowing the machine to make automatic adjustments to maintain a stable welding environment. This level of control is especially beneficial when working with materials that are sensitive to heat, such as stainless steel or exotic alloys, which require precise thermal management during the welding process.
The integration of automation into Pipe Welding Machines brings a significant reduction in labor costs and time, allowing for faster completion of welding tasks. The machines can be programmed to perform the same weld repeatedly, ensuring uniformity and eliminating variations that might otherwise occur with manual welding. This automation also reduces the reliance on skilled labor, allowing less experienced workers to operate the machines, provided they have the necessary training to set up and monitor the equipment. Furthermore, automation helps in achieving more consistent welds, reducing the number of reworks and rejections, which improves overall production efficiency.
Another advantage of Pipe Welding Machines is their ability to operate in harsh or hazardous environments, where human workers may face safety risks. For example, in the construction of offshore pipelines, welding is often performed in extreme weather conditions or confined spaces where safety is a concern. The ability to remotely control a Pipe Welding Machine allows operators to avoid direct exposure to dangerous conditions while still achieving high-quality welds. Some machines are also equipped with additional safety features, such as emergency shutdown systems and protective covers, which further reduce the risks associated with welding.
The flexibility of Pipe Welding Machines extends to their capability to perform various types of welds, depending on the application and the pipe material. They can carry out butt welds, fillet welds, and circumferential welds with the required precision, and the choice of welding process—whether TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas), MIG (Metal Inert Gas), or Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)—can be adapted to suit the specific requirements of the project. For example, TIG welding is often used for stainless steel and thin-walled pipes, offering precision and clean welds, while MIG welding is used for thicker pipes, providing faster deposition rates and higher productivity.
One of the key aspects of Pipe Welding Machines is their ability to support pipe alignment and fit-up. These machines are equipped with clamping systems that hold the pipes in place while the welding is performed. Proper alignment is crucial for ensuring that the weld is applied consistently and accurately along the joint, and advanced Pipe Welding Machines incorporate alignment mechanisms that automatically adjust the pipes to achieve the correct position. This feature reduces the need for manual intervention and helps maintain weld consistency, even in cases where pipes are slightly misaligned during assembly.
As with other advanced welding machines, Pipe Welding Machines are increasingly incorporating smart technologies that allow for real-time monitoring and remote diagnostics. These systems collect data on various aspects of the welding process, such as voltage, current, temperature, and welding speed. This data can be used to assess the quality of the weld and predict potential issues, such as undercutting, porosity, or lack of fusion. The data can also be stored for quality control and traceability purposes, ensuring that the welding process complies with industry standards and specifications. By continuously monitoring the welding process, these machines can adjust parameters on the fly to correct any deviations and ensure that each weld meets the required specifications.
Pipe Welding Machines can also be equipped with advanced purging and gas control systems, particularly when working with stainless steel or other high-quality materials. These systems are used to control the environment inside the pipe during the welding process, preventing contamination and oxidation that could compromise the strength and quality of the weld. The use of inert gases such as argon or helium ensures that the weld pool remains clean and free from impurities, while purging systems help to remove oxygen and moisture from the inside of the pipe before welding begins.
In addition to their core capabilities, modern Pipe Welding Machines are also designed to optimize their energy usage. As energy consumption becomes a more significant concern for manufacturers, these machines are increasingly built with features that minimize energy waste, such as more efficient power supply systems and energy-saving modes. These energy-efficient features not only reduce operational costs but also make the welding process more environmentally friendly.
Overall, Pipe Welding Machines are an indispensable tool in many industries where pipe welding is a critical part of the production or repair process. The ability to automate the welding process, ensure high-quality welds, and operate in challenging environments makes them essential for industries such as oil and gas, petrochemicals, construction, and shipbuilding. With the integration of advanced automation, real-time monitoring, and smart technologies, these machines will continue to evolve, offering greater precision, efficiency, and flexibility for pipe welding applications across the globe.
As the demand for more efficient, precise, and sustainable manufacturing processes continues to grow, the evolution of Pipe Welding Machines is accelerating. The ongoing advancements in technology are making these machines even more capable and adaptable, with features that further enhance their performance and overall value. These innovations not only streamline production workflows but also help address industry-specific challenges, making Pipe Welding Machines increasingly vital for a wide range of applications.
One significant area of development is the integration of robotics and automation. Robotics technology is being employed to improve the speed, accuracy, and flexibility of pipe welding. Robotic arms can be paired with pipe welding systems to handle complex tasks such as positioning, manipulation, and weld execution, all with a high degree of precision. This allows for automated pipe welding in a variety of settings, including production lines and remote locations, where traditional manual welding methods might be slow or difficult. By automating tasks like pipe positioning, the robot ensures that the welding process is performed consistently, minimizing errors and improving the overall quality of the finished welds.
The use of AI (Artificial Intelligence) in Pipe Welding Machines is another emerging trend. AI-powered systems can analyze data collected during the welding process and make real-time adjustments to optimize the welding parameters. This might include adjusting the heat input, welding speed, or gas flow to ensure optimal results. AI can also be used for predictive maintenance, where machine learning algorithms monitor the performance of the machine and identify potential issues before they lead to failures or downtime. This predictive capability reduces the need for manual inspections and allows for proactive measures to be taken, ensuring continuous and efficient operation.
Additionally, some Pipe Welding Machines are becoming more intuitive and user-friendly, with the integration of advanced control interfaces. Touchscreen panels, graphical user interfaces (GUIs), and easy-to-understand software make it easier for operators to set up and monitor the welding process. These intuitive systems can guide operators through the welding process, offer troubleshooting advice, and display real-time data, making it easier to identify potential issues and adjust parameters accordingly. Some systems can even provide real-time welding quality feedback, allowing operators to address issues immediately before they become critical.
Another noteworthy trend in Pipe Welding Machines is the focus on improving the portability and flexibility of these machines. In industries like pipeline construction, where welding often takes place in remote or challenging locations, the ability to quickly and easily transport welding equipment is crucial. Many of the latest Pipe Welding Machines are designed to be lightweight, compact, and easy to set up, making them suitable for use in the field. These machines are often mounted on trailers or specially designed carts, allowing them to be transported and set up quickly in a variety of environments. This mobility ensures that welding work can be performed efficiently, even in areas where space is limited or access is restricted.
The continued push for environmental sustainability is also influencing the development of Pipe Welding Machines. As industries strive to reduce their environmental footprint, manufacturers are designing welding machines that consume less energy and produce less waste. For example, some Pipe Welding Machines now come with features like energy-saving modes, which reduce power consumption during idle times. Others incorporate more efficient power supplies, reducing energy waste during the welding process itself. These machines are also being designed to use eco-friendly materials and consumables, further reducing their environmental impact.
Safety remains a critical consideration in the design of modern Pipe Welding Machines. Welding is inherently a high-risk process, with potential hazards such as exposure to intense heat, radiation, and fumes. To mitigate these risks, many machines now include enhanced safety features such as automatic shutoffs, protective enclosures, and fire suppression systems. Additionally, the use of remote operation capabilities allows operators to control the welding process from a safe distance, reducing their exposure to potential hazards. For example, in hazardous environments such as offshore oil rigs or chemical plants, the ability to operate a welding machine remotely can significantly reduce safety risks.
The integration of real-time data analytics and cloud-based systems is becoming increasingly common in Pipe Welding Machines, enabling manufacturers to collect and analyze performance data from the welding process. These systems allow operators and managers to access valuable insights that can be used to optimize welding operations. Data such as welding speed, temperature, current, and voltage can be monitored and analyzed to identify trends, measure efficiency, and improve overall performance. By incorporating data analytics into the welding process, companies can make more informed decisions, improve the quality of their welds, and reduce operational costs.
As the capabilities of Pipe Welding Machines continue to expand, their role in various industries is becoming even more critical. In the oil and gas industry, for example, Pipe Welding Machines are essential for the construction and maintenance of pipelines that transport oil and gas over long distances. These pipelines must withstand extreme conditions and be highly resistant to corrosion, which makes the quality of the welds critical. Pipe Welding Machines ensure that these welds are consistent, strong, and durable, helping to prevent leaks, failures, and other costly issues.
In the power generation sector, Pipe Welding Machines are used for welding pipes that transport steam, gas, and other fluids in power plants. The ability to perform high-quality welds on pipes subjected to high temperatures and pressure is vital for ensuring the safety and efficiency of the power plant. The machines’ precision and ability to control welding parameters make them an ideal tool for producing welds that meet stringent quality standards.
In addition to these industrial applications, Pipe Welding Machines are also essential for maintenance and repair work. For example, when a pipe becomes damaged or corroded, welding can be used to restore its structural integrity. Pipe Welding Machines are particularly useful in these situations because they allow for precise and efficient repairs, reducing downtime and extending the life of the equipment. In industries where equipment failure can have serious consequences, such as nuclear power plants or chemical refineries, the ability to quickly and safely perform pipe repairs is essential.
As these machines continue to evolve, their impact on the welding industry will only grow. The integration of advanced automation, AI, robotics, and data analytics will make Pipe Welding Machines even more efficient, adaptable, and reliable. With their ability to perform high-precision welds in a variety of settings and applications, these machines will remain an essential tool for industries around the world that rely on pipe welding for their operations. The ongoing advancements in technology ensure that Pipe Welding Machines will continue to play a key role in meeting the increasing demands for quality, efficiency, and sustainability in the manufacturing and construction sectors.
Welding Rotator
A Welding Rotator is an essential piece of equipment used in welding applications that require rotating cylindrical workpieces, such as pipes, tanks, and other large metal structures. The purpose of a Welding Rotator is to provide smooth and controlled rotation during the welding process, enabling operators to position the workpiece correctly for optimal welds. These machines help ensure high-quality welds by improving accessibility, reducing operator fatigue, and enhancing the overall efficiency of the welding process. Welding rotators are particularly valuable in industries like shipbuilding, pressure vessel manufacturing, pipe fabrication, and tank construction, where the welding of large, cylindrical components is commonplace.
The fundamental function of a Welding Rotator is to rotate the workpiece around its axis, allowing the welder to work on different sections of the weld seam without having to reposition the workpiece manually. This is crucial when welding long pipes, large tanks, or other cylindrical structures, as it ensures that the weld is applied consistently along the entire length of the joint. By rotating the workpiece, the Welding Rotator also minimizes the need for the welder to work in awkward positions, improving ergonomics and reducing the chances of operator fatigue.
There are several types of Welding Rotators, each designed for different applications. The most common types are self-aligning rotators, adjustable rotators, and motorized rotators. Self-aligning rotators are designed to automatically adjust to the diameter of the workpiece, ensuring that it is held securely in place while rotating. Adjustable rotators, on the other hand, allow for manual adjustments to accommodate workpieces of varying sizes, while motorized rotators provide controlled speed and rotation for precise welding. Many Welding Rotators come with variable speed control, allowing operators to adjust the rotation speed according to the requirements of the specific welding process.
Welding Rotators are often used in conjunction with other welding equipment, such as welding torches, robots, and manipulators, to provide a complete welding solution. For instance, when welding a large tank or pipe, a Welding Rotator can hold the workpiece in position while a robotic arm or welder applies the welding bead. The combination of these tools enables high-quality, uniform welds to be produced in less time, as the rotation of the workpiece eliminates the need for manual manipulation. The ability to rotate the workpiece also ensures that the weld seam is evenly distributed and reduces the risk of defects such as undercuts or voids.
In addition to improving the welding process, Welding Rotators contribute to better safety and efficiency on the shop floor. By securely holding the workpiece and rotating it at a controlled speed, these machines reduce the risk of accidents caused by improper handling or awkward welding positions. Furthermore, by eliminating the need for multiple operators to manually reposition large workpieces, Welding Rotators help streamline operations, increase throughput, and reduce labor costs.
The versatility of Welding Rotators makes them suitable for a wide range of welding processes, including TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, and submerged arc welding. The type of welding process used will depend on the material being welded, the thickness of the material, and the specific requirements of the project. For instance, when working with thicker materials or heavy-duty welds, submerged arc welding may be preferred, while TIG welding is ideal for high-precision, clean welds on thinner materials. Welding Rotators can be configured to work with various welding processes, ensuring that the equipment can be adapted to suit the needs of different projects.
A key advantage of Welding Rotators is their ability to improve the overall quality and consistency of welds. By providing precise and controlled rotation, these machines help maintain the correct welding position, which is essential for achieving uniform welds with consistent penetration. The rotation also allows for better control over the heat input, reducing the chances of overheating or distortion. This is particularly important when working with materials that are sensitive to heat, such as stainless steel or aluminum, where precise control over the welding process is crucial.
The design and construction of Welding Rotators are also evolving to meet the growing demands of modern welding applications. Many machines now come with advanced features such as digital controls, automated programming, and integrated monitoring systems. These features help operators maintain tight control over the welding process and provide real-time feedback on the quality of the weld. Some machines are equipped with sensors that monitor the alignment and position of the workpiece, ensuring that the rotation is smooth and accurate throughout the welding process. This level of precision helps minimize defects and ensures that the welds meet the required quality standards.
Welding Rotators are often equipped with adjustable supports and rollers to accommodate different sizes and weights of workpieces. These supports can be easily adjusted to fit the workpiece, allowing for greater flexibility in welding operations. Some advanced models also come with hydraulic or pneumatic features that enable automatic adjustments to the position and rotation speed of the workpiece. This added flexibility ensures that Welding Rotators can be used in a wide variety of applications, from small-scale repairs to large-scale manufacturing.
Maintenance and durability are also key considerations when it comes to Welding Rotators. Since these machines are often used in demanding environments, they must be built to withstand heavy use and harsh conditions. High-quality materials, such as steel and alloy components, are typically used in the construction of Welding Rotators to ensure their longevity and performance. Regular maintenance, including cleaning, lubrication, and inspections, is essential to keep the machines operating at peak efficiency and prevent downtime due to mechanical failures.
One of the challenges in using Welding Rotators is ensuring that the workpiece is properly aligned and balanced before the welding process begins. An unbalanced or misaligned workpiece can result in poor welds, excessive wear on the machine, and increased operator fatigue. To address this issue, many Welding Rotators come with advanced alignment systems that automatically adjust the workpiece’s position, ensuring it is securely held in place during rotation. Some models also include load sensing technology that monitors the weight and balance of the workpiece, making real-time adjustments to the rotation speed and position as needed.
Welding Rotators are increasingly being integrated into automated and robotic welding systems, which enhances their effectiveness and efficiency. By integrating Welding Rotators with robots and automated welding equipment, manufacturers can create fully automated welding cells capable of producing high-quality welds with minimal human intervention. These systems can be programmed to handle a wide range of tasks, including loading and unloading workpieces, positioning the workpiece for welding, and monitoring the quality of the weld in real time. Automation reduces the need for manual labor and improves the consistency of the welds, making it ideal for high-volume production settings.
In addition to their industrial applications, Welding Rotators are also used in maintenance and repair tasks, especially in industries like oil and gas, power generation, and chemical processing. For example, when a pipeline or pressure vessel requires maintenance or repairs, Welding Rotators can be used to rotate the damaged section for more efficient and precise welding. In these situations, the ability to manipulate the workpiece easily while ensuring the correct alignment is critical for achieving durable, long-lasting welds that will withstand the demanding operating conditions of the equipment.
The demand for Welding Rotators is expected to grow as industries continue to adopt automation and robotics, and as manufacturers seek to improve the quality, efficiency, and safety of their welding processes. The ongoing development of smart technologies, such as sensors, real-time data analytics, and cloud-based monitoring, is likely to further enhance the capabilities of these machines. With the addition of advanced features like predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, and integration with other automated equipment, Welding Rotators will continue to play a vital role in the evolution of welding technology.
Overall, Welding Rotators are a crucial tool for industries that require high-quality welds on cylindrical workpieces. With their ability to provide precise, controlled rotation and improve the overall welding process, these machines enhance productivity, quality, and safety in various welding applications. As technology continues to advance, Welding Rotators will remain an integral part of welding operations, ensuring that manufacturers can meet the increasing demands for speed, precision, and cost-effectiveness in their welding processes.
The continued development of Welding Rotators is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in welding technology, particularly in terms of automation, precision, and scalability. As industries across the globe demand higher quality, faster production times, and more adaptable equipment, Welding Rotators are evolving to meet these needs, offering more advanced features and capabilities.
One of the most notable trends in Welding Rotators is the integration of intelligent systems and data analytics. Many modern Welding Rotators are now equipped with advanced sensors and software that collect real-time data during the welding process. This data is crucial for monitoring the health and performance of the machine, tracking welding parameters, and ensuring that the weld meets required specifications. By incorporating cloud-based monitoring and data analysis, operators can access key performance metrics remotely, which is especially useful for large-scale operations or when managing multiple machines across different locations. The ability to access and analyze welding data in real-time also enables quick corrective actions, ensuring consistent quality and reducing the likelihood of defects.
Another significant innovation in Welding Rotators is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies can analyze welding data to optimize settings such as rotation speed, load positioning, and alignment adjustments automatically. This AI-driven optimization not only reduces the likelihood of human error but also increases the overall efficiency of the welding process. For example, AI can detect when a workpiece becomes misaligned and automatically adjust the position of the rotator to correct it. This results in fewer manual interventions, less downtime, and better consistency across welding jobs. In applications that require a high degree of precision, like aerospace or nuclear power, this level of automation helps to meet the strictest tolerances and quality standards.
The versatility of Welding Rotators is expanding as manufacturers design them to handle a broader range of materials and welding techniques. For example, some advanced Welding Rotators now feature customizable settings that allow for the use of different welding processes, such as TIG, MIG, or even laser welding. This adaptability makes these machines highly versatile, allowing them to be used in industries ranging from construction and shipbuilding to specialized applications like additive manufacturing and high-precision welding in the semiconductor industry. The ability to quickly switch between different processes and parameters allows for greater flexibility and the ability to meet a variety of production needs with one piece of equipment.
In addition to their versatility in material handling, Welding Rotators are becoming increasingly compact and portable. With the advent of modular systems and lightweight materials, some Welding Rotators are now designed for use in more confined spaces or on job sites that require mobility. This is particularly useful for applications in the field, where large, heavy machines are impractical. For instance, in pipeline construction or offshore oil drilling, having a portable Welding Rotator allows workers to perform high-quality welding on-site without having to transport the workpiece to a central welding facility. This can significantly reduce costs and production timelines.
The scalability of Welding Rotators is also being enhanced through the development of modular systems that can be adapted to specific needs. In high-volume production environments, such as the automotive or heavy equipment industries, companies may need multiple Welding Rotators that can work in tandem to weld several parts simultaneously. These systems can be designed with interchangeable components that allow for quick adjustments to accommodate different sizes and configurations of workpieces. The scalability aspect means that businesses can expand their welding operations without needing to invest in entirely new equipment, making Welding Rotators an economical solution for companies looking to scale up production.
As welding technology continues to evolve, the demand for Welding Rotators in additive manufacturing and 3D printing applications is increasing. In these cutting-edge industries, where precision and accuracy are paramount, Welding Rotators are being integrated into additive processes to rotate and position parts during multi-axis printing or welding operations. These machines help ensure that the part remains in the correct orientation during the build process, improving the accuracy and consistency of the printed or welded structure. Additive manufacturing applications often involve complex geometries and materials that require careful handling, making Welding Rotators a critical tool in ensuring the quality of these advanced parts.
The environmental considerations surrounding Welding Rotators are also becoming more prominent. With increasing pressure on industries to reduce energy consumption and minimize their environmental impact, modern Welding Rotators are designed to be more energy-efficient. Some machines are now equipped with energy-saving modes that reduce power consumption when the machine is not in active use. Others use regenerative braking systems to capture and reuse energy during the rotation process. Additionally, some Welding Rotators are built with environmentally friendly materials and coatings that reduce their carbon footprint and enhance their durability.
Safety features in Welding Rotators are also advancing, ensuring a safer working environment for operators. Many modern machines come with safety interlocks, emergency stop functions, and automatic shut-off mechanisms in case of malfunction. Additionally, some systems now incorporate laser scanning or other safety sensors that detect the presence of objects or personnel near the machine, automatically stopping rotation to prevent accidents. The ability to remotely monitor and control Welding Rotators also allows operators to maintain a safe distance from the welding process, reducing the risk of exposure to harmful fumes, radiation, or heat.
Welding Rotators are now also increasingly used for robotic welding applications, where they are paired with robotic arms to perform automated welding tasks. In these systems, the Welding Rotator holds the workpiece in place while the robot applies the weld. This combination of technologies allows for high-speed, high-precision welding, making it ideal for industries such as automotive manufacturing, where speed and consistency are crucial. By pairing Welding Rotators with robots, companies can further enhance productivity and reduce the risk of defects that may arise from manual handling.
As the demand for advanced welding techniques and precision grows, the importance of Welding Rotators in the manufacturing and construction sectors will continue to increase. These machines offer the flexibility, precision, and efficiency needed to meet the challenges of modern welding applications. Whether in the production of large-scale industrial equipment, the construction of pipelines and tanks, or in emerging fields like additive manufacturing, Welding Rotators play a pivotal role in ensuring the quality and reliability of welded joints.
In the coming years, we can expect to see even more innovations in Welding Rotators, driven by advances in automation, robotics, AI, and data analytics. These innovations will help industries further streamline their production processes, improve the quality of their welds, and reduce the overall cost of manufacturing. As technology continues to improve, Welding Rotators will remain a cornerstone of modern welding operations, supporting a wide range of industries and applications while delivering greater precision, speed, and efficiency in welding tasks.
Rotary Welding Machine

A Rotary Welding Machine is an advanced piece of equipment used in welding applications that require the rotation of workpieces during the welding process. These machines are designed to rotate cylindrical, tubular, or other round workpieces to enable seamless, high-quality welds along the circumference of the piece. Rotary Welding Machines are often used in industries where large pipes, tanks, or similar cylindrical components need to be welded, such as in the construction of pressure vessels, pipelines, boilers, and in shipbuilding. They offer significant advantages in terms of precision, efficiency, and automation, making them an essential tool in modern welding operations.
The primary function of a Rotary Welding Machine is to rotate the workpiece at a controlled speed while a welding torch or electrode applies the weld. This rotation allows the welder or welding robot to work continuously along the seam of the piece, ensuring that the weld is even and uniform throughout the process. By rotating the workpiece, the machine reduces the need for manual repositioning and helps maintain the correct angle for the welding process, which is crucial for producing high-quality, defect-free welds. Additionally, rotating the workpiece minimizes the chances of operator fatigue, as it eliminates the need for the operator to work in awkward or uncomfortable positions for extended periods.
A significant advantage of using a Rotary Welding Machine is its ability to perform precise, repeatable welds. The consistent rotation of the workpiece allows for uniform heat distribution and consistent arc control, which results in welds with excellent penetration, strength, and appearance. This level of precision is essential in industries where weld integrity is critical, such as in the aerospace, automotive, and pressure vessel industries. By ensuring that the welding process is performed consistently, the machine helps to minimize the risk of defects, such as porosity, cracking, or undercuts, which can compromise the strength and durability of the weld.
Rotary Welding Machines are available in various configurations to meet the specific needs of different welding applications. These machines can be motorized or manual, with motorized versions providing controlled rotation speed, which is essential for fine-tuning the welding process. Many Rotary Welding Machines are also equipped with adjustable supports or rollers that can accommodate workpieces of various sizes and weights. The ability to adjust the supports ensures that the machine can handle a wide range of workpieces, from small components to large, heavy-duty items. Some advanced models also feature automated systems that adjust the speed, position, and alignment of the workpiece during the welding process, further improving the efficiency and precision of the operation.
In addition to improving the quality and consistency of welds, Rotary Welding Machines also enhance safety and productivity in welding operations. By rotating the workpiece automatically, these machines reduce the physical strain on operators, allowing them to focus on controlling the welding parameters and ensuring the quality of the weld. This automation also minimizes the need for multiple operators to manually handle the workpiece, reducing the potential for accidents or errors. Furthermore, by providing a stable and controlled environment for welding, Rotary Welding Machines help to reduce the likelihood of distortions, warping, or misalignments that can occur when the workpiece is manually manipulated.
The integration of robotic systems with Rotary Welding Machines is becoming increasingly common, especially in high-volume manufacturing environments. Robotic arms or automated welding systems can be used in conjunction with the Rotary Welding Machine to perform complex welding tasks with minimal human intervention. In these systems, the Rotary Welding Machine rotates the workpiece while the robot or automated welding system applies the weld. This integration not only increases the speed and efficiency of the welding process but also improves the overall precision and quality of the welds. The combination of robotics and rotary motion enables manufacturers to produce consistent, high-quality welds with less labor and reduced operational costs.
Rotary Welding Machines are used in a wide range of welding processes, including MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, and flux-cored welding, among others. The choice of welding process depends on the specific material being welded, the thickness of the material, and the desired characteristics of the weld. For example, TIG welding is often used for high-precision applications, where a clean and strong weld is required, while MIG welding is commonly used for faster, higher-volume production welding. Rotary Welding Machines can be configured to accommodate these different processes, providing flexibility and adaptability in welding operations.
Another important feature of Rotary Welding Machines is their ability to perform both longitudinal and circumferential welding. Longitudinal welding involves welding along the length of the workpiece, while circumferential welding refers to welding around the circumference of a cylindrical object. The machine’s ability to handle both types of welding makes it an ideal tool for a wide range of applications, from the production of large tanks and pressure vessels to pipe fabrication and repair.
As technology advances, the capabilities of Rotary Welding Machines are expanding to include more sophisticated features. Many machines now come with digital controls and programmable settings, allowing operators to fine-tune the welding parameters for optimal results. These controls can adjust variables such as speed, heat input, and wire feed rate, ensuring that the weld is applied precisely according to the specifications of the job. Additionally, some machines are equipped with sensors and monitoring systems that provide real-time feedback on the quality of the weld, allowing operators to make adjustments as needed. This level of automation and control increases the consistency and quality of the welding process and helps reduce the chances of defects or rework.
The versatility of Rotary Welding Machines also extends to their ability to be used in both indoor and outdoor environments. Some models are designed to be portable, allowing them to be used in field applications where workpieces are too large or cumbersome to transport. In industries such as pipeline construction, offshore oil drilling, and heavy equipment manufacturing, portability is crucial, as it allows welding to be performed directly at the job site, saving time and reducing the need for additional equipment or labor.
The increasing demand for environmentally friendly manufacturing practices has also influenced the design of Rotary Welding Machines. Many modern machines are designed to be more energy-efficient, using less power during the welding process and incorporating features that reduce waste. For example, some machines are equipped with energy-saving modes that automatically reduce power consumption when the machine is idle. Additionally, some models are designed to be more compact and lightweight, reducing the environmental impact of transportation and setup.
In terms of safety, Rotary Welding Machines are equipped with a variety of features designed to protect operators and ensure the safe operation of the equipment. These features may include emergency stop buttons, safety interlocks, and protective enclosures that prevent exposure to welding fumes, heat, or radiation. Some machines are also equipped with automated shutoff functions that stop the machine if a fault is detected, preventing further damage to the workpiece or equipment.
As industries continue to seek greater efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness in their manufacturing processes, Rotary Welding Machines will continue to play a key role in modern welding operations. The integration of automation, robotics, and data analytics will further enhance the capabilities of these machines, allowing them to handle increasingly complex tasks with greater speed and accuracy. The continued development of smart technologies, such as predictive maintenance systems, real-time monitoring, and remote control features, will further improve the efficiency, safety, and reliability of Rotary Welding Machines.
In conclusion, Rotary Welding Machines are a vital tool for industries that require high-quality welds on cylindrical workpieces. Their ability to rotate workpieces smoothly and precisely during the welding process helps improve the quality, consistency, and speed of welds. With advancements in automation, robotics, and AI, these machines are becoming more efficient and adaptable, making them an essential part of modern welding operations. Whether in large-scale manufacturing, repair work, or specialized applications, Rotary Welding Machines will continue to play an integral role in ensuring the strength, durability, and precision of welded components across a variety of industries.
As Rotary Welding Machines continue to evolve, several trends and advancements are shaping their future capabilities. One of the major developments is the increased integration of smart technologies and IoT (Internet of Things) functionality. Modern Rotary Welding Machines are becoming connected to central control systems and cloud-based platforms, allowing for remote monitoring and diagnostics. Operators can track real-time data on machine performance, welding parameters, and output quality, helping to improve operational efficiency and reduce downtime. Predictive maintenance tools, powered by AI and machine learning algorithms, can analyze data trends to predict potential failures before they occur, allowing companies to schedule maintenance proactively and avoid costly repairs or unexpected breakdowns.
The flexibility of Rotary Welding Machines is also improving, especially in relation to multi-process capabilities. In the past, machines were often dedicated to a single welding process, but now, machines are being designed to seamlessly switch between different welding techniques, such as MIG, TIG, and Stick welding. This adaptability allows businesses to perform a wide range of welding tasks with one machine, reducing the need for multiple pieces of equipment. Some advanced Rotary Welding Machines now come equipped with interchangeable torches and automated tool changers, further enhancing the flexibility of the system. This is particularly beneficial in industries where different welding processes are required for different parts or materials, ensuring that the right process can be applied to each job.
The drive toward greater precision and quality control is also reflected in the development of advanced welding technologies that complement Rotary Welding Machines. For instance, the use of laser-based welding systems is becoming more common, and some Rotary Welding Machines are now designed to integrate laser welding heads for applications requiring fine, high-precision welds. Laser welding offers significant benefits, such as reduced heat input, minimal distortion, and the ability to weld thin materials with exceptional accuracy. Rotary machines equipped with these systems can handle intricate parts that require the precision of laser welding while maintaining the stability and rotation capabilities of traditional rotary welding.
Further improvements in power sources and welding consumables are also enhancing the performance of Rotary Welding Machines. Newer power supplies are more energy-efficient and provide better control over the welding process, allowing operators to adjust voltage and current with greater precision. Additionally, advances in welding wires, electrodes, and filler materials are improving the overall quality of welds, with more options available to suit different materials and applications. This is particularly important in industries that deal with high-performance alloys, such as the aerospace and automotive sectors, where the integrity of welds is critical to the overall performance of the end product.
In terms of safety and operator comfort, Rotary Welding Machines are also being designed with advanced safety features and ergonomics in mind. These machines often come with built-in safeguards, such as automated safety shutdowns, protective enclosures to shield operators from welding fumes and heat, and emergency stop buttons for rapid intervention. For operators working in heavy-duty applications, ergonomic designs are reducing strain by allowing for better access to controls and reducing the physical effort required to manipulate the machine. These design improvements are not only enhancing operator safety but also ensuring compliance with stricter safety regulations in many industries.
The demand for increased automation in welding operations is fueling the development of robotic Rotary Welding Machines. These machines incorporate robotic arms that can manipulate the workpiece, adjust the welding torch, and apply the weld without the need for manual intervention. Robotic integration significantly increases the speed and precision of welding tasks, making it possible to complete complex jobs quickly and efficiently. Robotics also help to eliminate human error, improve repeatability, and increase throughput, which is particularly beneficial in industries that require high-volume production, such as automotive manufacturing.
The environmental impact of Rotary Welding Machines is also a growing consideration, with manufacturers working to create more eco-friendly designs. Energy-efficient machines that consume less power during operation are becoming the norm, and many machines feature energy-saving modes that help reduce consumption during idle times. Additionally, welding fume extraction systems are being integrated into machines to ensure that operators are not exposed to hazardous fumes, improving overall workplace safety and reducing environmental impact. Some advanced models also incorporate recyclable materials in their construction, contributing to the overall sustainability of the equipment.
In industries where precision is paramount, such as semiconductor manufacturing or microelectronics, the role of Rotary Welding Machines is increasingly important. These industries require high-precision welding techniques to join delicate components without damaging them, and Rotary Welding Machines are particularly well-suited to this task. They offer the control and repeatability needed to produce precise, high-quality welds on small, intricate parts, which is essential for maintaining the performance and reliability of end products.
The versatility of Rotary Welding Machines also extends to their ability to handle various workpiece sizes and configurations. Adjustable chuck systems, turntables, and customizable supports make it possible for these machines to accommodate a wide range of workpieces, from small components to large industrial items. This flexibility allows companies to use the same machine for multiple projects, reducing the need for additional specialized equipment and streamlining the production process. Furthermore, the modular design of many Rotary Welding Machines enables easy integration with other manufacturing systems, such as conveyor belts or automated material handling systems, allowing for fully automated production lines.
As the demand for higher-quality products and faster production timelines continues to rise, Rotary Welding Machines will play an increasingly pivotal role in the global manufacturing landscape. These machines offer unparalleled precision, consistency, and flexibility, which are crucial for industries that require high-quality welded joints, such as aerospace, automotive, energy, and heavy manufacturing. By incorporating advanced features such as automation, smart technology, robotic integration, and energy efficiency, Rotary Welding Machines are becoming more adaptable to a wide range of applications, ensuring that they remain at the forefront of welding technology.
With the increasing complexity of manufacturing processes and the desire to meet stricter industry standards, the future of Rotary Welding Machines looks bright. Continuous improvements in automation, data analytics, and machine learning will continue to push the capabilities of these machines, making them more intelligent, efficient, and capable of handling the demands of modern manufacturing. Whether used for high-volume production, precision welding, or specialized applications, Rotary Welding Machines will remain a cornerstone of welding operations across a variety of industries, helping to ensure the strength, durability, and quality of welded components for years to come.
Types of Pipe Welding Machines
Pipe welding machines are specialized pieces of equipment designed to join cylindrical and curved components, commonly pipes. They play a crucial role in various industries, ensuring the integrity and functionality of critical pipelines, pressure vessels, and other structures. Here’s an overview of the main types of pipe welding machines:
- Rotary Welding Machines: Also known as turning rolls or welding positioners, rotary welding machines rotate the workpiece during the welding process, providing consistent access to all weld seams. This ensures uniform weld quality and efficient welding operations. Rotary welding machines are suitable for welding pipes of various diameters, from small-diameter tubing to large-diameter pipelines.
- Orbital Welding Machines: These machines utilize an orbital motion to weld the joint, precisely controlling weld depth and penetration. Orbital welding machines are particularly useful for joining pipes with complex geometries or where limited access is a concern. They are often employed in applications requiring high precision and cleanliness, such as aerospace, medical device manufacturing, and pharmaceutical industries.
- Head-to-End Welding Machines: Specifically designed for welding pipes end-to-end, head-to-end welding machines form a continuous weld seam without any gaps or discontinuities. They are commonly used in oil and gas pipelines and similar applications where a continuous, leak-proof weld is essential. These machines typically utilize specialized welding processes, such as submerged arc welding (SAW) or high-frequency induction welding (HFIW), to achieve the required weld quality and strength.
- Automatic Welding Machines: Integrated with robotic arms or other controlled systems, automatic welding machines automate the welding process, enabling high-speed, consistent welding operations with minimal operator intervention. This automation reduces labor costs, improves productivity, and ensures consistent weld quality, especially for high-volume production applications. Automatic welding machines can be programmed to follow specific weld paths and adjust welding parameters precisely, ensuring optimal weld penetration and fusion.
- Portable Welding Machines: Designed for portability and maneuverability, portable welding machines are suitable for use in confined spaces or where a fixed welding station is impractical. These machines are often lightweight and compact, making them easy to transport and utilize in various work environments. Portable welding machines typically handle smaller pipe diameters and may utilize various welding processes, such as gas metal arc welding (GMAW) or flux-cored arc welding (FCAW).
The choice of pipe welding machine depends on several factors, including the pipe diameter, material, welding process requirements, desired weld quality, and production volume. In addition to the main types mentioned above, there are specialized pipe welding machines designed for specific applications, such as:
- Internal Pipe Welding Machines: These machines are used to weld pipes from the inside, particularly for large-diameter pipes where access to the outer surface is limited.
- Column and Boom Welding Machines: Designed for welding pipes in elevated positions, column and boom welding machines provide a stable platform for the welder and welding equipment.
- Custom-Built Welding Machines: For specialized applications or unique pipe configurations, custom-built welding machines can be designed to meet specific requirements and achieve optimal welding results.
Pipe welding machines are indispensable tools in various industries, enabling the construction and maintenance of critical infrastructure, manufacturing of durable products, and production of precision components. With advancements in technology, pipe welding machines are becoming increasingly sophisticated, offering improved automation, precision, and safety features, further expanding their applications and impact across various sectors.
Rotary Welding Machine
Rotary welding machines, also known as turning rolls or welding positioners, are specialized pieces of equipment designed to rotate the workpiece during the welding process. This rotation provides consistent access to all weld seams, ensuring uniform weld quality and efficient welding operations.
Key Features of Rotary Welding Machines:
- Rotary Platform: A rotating platform that holds the workpiece and facilitates its continuous rotation during welding.
- Workpiece Clamping Mechanism: A secure clamping mechanism to firmly hold the workpiece in place during rotation, preventing movement and ensuring consistent weld placement.
- Welding Torch Positioning: Ability to position the welding torch precisely along the weld seam for optimal weld penetration and fusion.
- Welding Process Compatibility: Compatible with various welding processes, such as gas metal arc welding (GMAW), gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), and submerged arc welding (SAW), allowing for flexibility in material handling.
- Automation Integration: Can be integrated with robotic arms or other controlled systems for automated welding operations, enhancing productivity and reducing labor costs.
- Safety Features: Interlocks, guards, and emergency stop buttons to prevent accidents and hazards, ensuring operator safety during welding operations.
- Data Logging: Advanced rotary welding machines may have data logging capabilities to record welding parameters and weld quality information for process control, quality assurance, and traceability purposes.
- Portability: Some rotary welding machines are designed to be portable, allowing them to be moved easily from one work area to another, particularly useful for welding large or irregularly shaped workpieces that cannot be easily moved.
- Durability: Rotary welding machines are built to withstand the rigors of industrial environments, making them a reliable and long-lasting investment for welding operations.
Applications of Rotary Welding Machines:
Rotary welding machines are used extensively in various industries to weld a wide range of pipes and components:
- Oil and Gas Industry: Welding pipelines for oil and gas transportation is a critical application where rotary welding machines are essential for ensuring the integrity of pipelines under high pressure and harsh conditions.
- Power Generation Industry: Welding pressure vessels, pipes, and other components for power plants is another major application where rotary welding machines are used to create strong and durable welds that withstand the rigors of power generation environments.
- Chemical Industry: Welding reactor vessels, piping systems, and storage tanks in the chemical industry is crucial for ensuring the safety and integrity of chemical processing equipment.
- Construction Industry: Welding pipe structures, scaffolding, and other steel components in construction projects is essential for building strong and stable structures that can withstand various loads and conditions.
- Manufacturing Industry: Welding pipes for various applications, such as water supply, irrigation, and manufacturing equipment, is essential in various manufacturing processes.
- Shipbuilding: Welding pipes and tubes used in the construction and maintenance of ships is crucial in shipbuilding. These welds must withstand the harsh marine environment and the stresses of ship operation.
- Food and Beverage Industry: Welding containers and equipment, such as cans, bottles, and tanks, in the food and beverage industry is essential for maintaining product safety.
- Medical Device Industry: Welding implantable devices, such as surgical stents, catheters, and prosthetic components, in the medical device industry is crucial for manufacturing these critical medical devices.
- Appliance Manufacturing: Welding cookware, water heaters, and other cylindrical components in appliance manufacturing contributes to the production of durable and reliable appliances.
- General Manufacturing: Welding cylindrical and curved components in a range of products, such as bicycles, sports equipment, and industrial machinery, is a common application for rotary welding machines in various general manufacturing industries.
Conclusion:
Rotary welding machines are versatile and indispensable tools in various industries, providing efficient, precise, and reliable methods for joining cylindrical and curved components. Their adaptability, safety features, and wide range of applications make them indispensable tools for manufacturing pipes, tubes, pressure vessels, and other critical components. As technology advances, rotary welding machines are expected to become even more sophisticated, enhancing their efficiency, precision, and safety, further expanding their applications in various industries.
Rotary welding machines, also known as turning rolls or welding positioners, are specialized pieces of equipment used to rotate and position workpieces during the welding process. They provide a stable and controlled platform for welders to access all sides of the workpiece, ensuring consistent weld quality and efficient welding operations.
Key Features of Rotary Welding Machines:
- Load Capacity: Rotary welding machines are designed to handle workpieces of varying sizes and weights. The load capacity of a rotator is determined by its size, construction, and motor power.
- Rotation Speed: The rotation speed of a rotary welding machine can be adjusted to suit the specific welding process and workpiece material. Welding parameters, such as current and voltage, can also be adjusted to ensure optimal weld quality.
- Clamping Mechanism: Rotary welding machines incorporate secure clamping mechanisms to hold the workpiece firmly in place during rotation. This prevents movement and ensures consistent weld placement.
- Workpiece Alignment: Rotary welding machines are designed with leveling and alignment features to ensure the workpiece is properly positioned relative to the welding torch. This is particularly important for achieving uniform weld penetration and preventing undercut or overlap defects.
- Versatility: Rotary welding machines can be used to weld a wide range of workpiece shapes, including cylindrical, conical, and irregularly shaped components. They can also be adapted to various welding processes, such as gas metal arc welding (GMAW), gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), and submerged arc welding (SAW).
- Automation Integration: Rotary welding machines can be integrated into automated welding systems, enabling high-volume production and reducing labor costs. Automated rotators can follow pre-programmed weld paths and adjust welding parameters precisely.
- Safety Features: Rotary welding machines incorporate safety features to protect operators from hazards, such as sparks, flying debris, and accidental torch movement. These features may include interlocks, guarding, and emergency stop buttons.
- Data Logging: Some advanced rotary welding machines can record welding parameters and weld quality data. This information can be used for process control, quality assurance, and traceability purposes.
- Portability: Some rotary welding machines are designed to be portable, allowing them to be moved easily from one work area to another. This is particularly useful for welding large or irregularly shaped workpieces that cannot be easily moved.
- Durability: Rotary welding machines are built to withstand the rigors of industrial environments, making them a reliable and long-lasting investment for welding operations.
Applications of Rotary Welding Machines:
Rotary welding machines are widely used in various industries to weld cylindrical and curved components:
- Pipe and Tube Manufacturing: Rotary welding machines are commonly used to weld pipes, tubes, and pressure vessels. They ensure consistent weld quality and efficient production of these critical components.
- Automotive Manufacturing: Rotary welding machines are employed in automotive manufacturing for welding exhaust systems, fuel tanks, and air intake ducts. Their adaptability and precision are crucial for producing high-quality automotive components.
- Aerospace and Defense Industries: Rotary welding machines are used in aerospace and defense applications for welding aircraft fuselages, rocket motor casings, and other complex components. Their ability to handle large and irregularly shaped workpieces makes them essential for these industries.
- Food and Beverage Industry: Rotary welding machines are used in the food and beverage industry for manufacturing containers and equipment, such as cans, bottles, and tanks. Their ability to produce consistent and hygienic welds is essential for maintaining product safety.
- Medical Device Industry: Rotary welding machines are employed in the medical device industry for producing implantable devices, such as surgical stents, catheters, and prosthetic components. Their precision and reliability are crucial for manufacturing these critical medical devices.
- Construction Industry: Rotary welding machines are used in the construction industry for welding steel reinforcement bars, structural beams, and piping systems. Their ability to handle large and heavy workpieces makes them essential for construction projects.
- Appliance Manufacturing: Rotary welding machines are used in appliance manufacturing for welding cookware, water heaters, and other cylindrical components. Their efficiency and consistent weld quality contribute to the production of durable and reliable appliances.
- General Manufacturing: Rotary welding machines are used in various general manufacturing industries to weld cylindrical and curved components in a range of products, such as bicycles, sports equipment, and industrial machinery. Their versatility makes them valuable assets in various manufacturing sectors.
Conclusion:
Rotary welding machines play a pivotal role in various industries, providing efficient, precise, and reliable methods for joining cylindrical and curved components. Their adaptability, safety features, and wide range of applications make them indispensable tools for manufacturing pipes, tubes, pressure vessels, and other critical components. As technology advances, rotary welding machines are expected to become even more sophisticated, enhancing their efficiency, precision, and safety, further expanding their applications in various industries.
Overview of Pipe Welding Machines
Pipe welding machines are specialized welding equipment designed to join cylindrical and curved components, commonly pipes. They are indispensable in various industries, including oil and gas, power generation, chemical, construction, and manufacturing, for creating strong and durable welds that ensure the integrity of critical structures and systems.
Types of Pipe Welding Machines
There are four main types of pipe welding machines:
1. Rotary Welding Machines:
These machines rotate the workpiece during welding, providing consistent access to all weld seams and ensuring uniform weld quality. They are suitable for welding a wide range of pipe diameters, from small-diameter pipes to large-diameter pipelines.
2. Orbital Welding Machines:
Orbital welding machines utilize an orbital motion to weld the joint, precisely controlling weld depth and penetration. This type of machine is particularly advantageous for joining pipes with complex geometries or where limited access is a concern.
3. Head-to-End Welding Machines:
Head-to-end welding machines are specifically designed for welding pipes end-to-end, forming a continuous weld seam without any gaps or discontinuities. They are commonly used in oil and gas pipelines and similar applications.
4. Automatic Welding Machines:
Automatic welding machines are integrated with robotic arms or other controlled systems to automate the welding process. This enables high-speed, consistent welding operations with minimal operator intervention, reducing labor costs and improving productivity.
Key Features of Pipe Welding Machines
Pipe welding machines are equipped with several essential features to ensure efficient and reliable welding operations:
Load Capacity:
The maximum weight of the workpiece that the machine can handle. This is important to ensure the machine can support heavy pipes without compromising stability or precision.
Pipe Diameter Range:
The range of pipe diameters that the machine can weld. Pipe welding machines are typically designed to handle a variety of pipe sizes, from small-diameter tubing to large-diameter pipelines.
Rotation Speed:
The speed at which the machine rotates the workpiece or travels along the weld seam. This is crucial for ensuring consistent weld quality and controlling the deposition rate of the weld material.
Welding Process Compatibility:
The ability to weld using various welding processes, such as gas metal arc welding (GMAW), gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), or submerged arc welding (SAW). This flexibility allows the machine to handle different pipe materials and applications.
Automation Capabilities:
The ability to integrate with automation systems for automated welding operations. This feature is essential for high-volume production and reduces labor costs.
Safety Features:
Interlocks, guards, and emergency stop buttons to prevent accidents and hazards. These safety features protect operators from exposure to sparks, flying debris, and electrical hazards.
Applications of Pipe Welding Machines
Pipe welding machines are used extensively in various industries to weld a wide range of pipes and components:
1. Oil and Gas Industry:
Welding pipelines for oil and gas transportation is a critical application where pipe welding machines are essential for ensuring the integrity of pipelines under high pressure and harsh conditions.
2. Power Generation Industry:
Welding pressure vessels, pipes, and other components for power plants is another major application where pipe welding machines are used to create strong and durable welds that withstand the rigors of power generation environments.
3. Chemical Industry:
Welding reactor vessels, piping systems, and storage tanks in the chemical industry is crucial for ensuring the safety and integrity of chemical processing equipment.
4. Construction Industry:
Welding pipe structures, scaffolding, and other steel components in construction projects is essential for building strong and stable structures that can withstand various loads and conditions.
5. Manufacturing Industry:
Welding pipes for various applications, such as water supply, irrigation, and manufacturing equipment, is essential in various manufacturing processes.
Conclusion
Pipe welding machines are indispensable tools for joining cylindrical and curved components in various industries, providing efficient, high-quality welds that ensure the integrity of critical structures and systems. Their adaptability, automation capabilities, and wide range of applications make them valuable assets in various sectors, from infrastructure and manufacturing to oil and gas production. As technology advances, pipe welding machines are expected to become even more sophisticated, enhancing their efficiency, precision, and safety, further expanding their applications in various industries.
A pipe welding machine, also known as a pipe welder or pipe welding equipment, is a specialized machine used for joining sections of pipes by welding. These machines are employed in various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and oil and gas, to create secure and durable pipe connections. Here are key details about pipe welding machines:
1. Types of Pipe Welding Machines:
- Manual Welding Machines: These machines require the welder to control the welding process manually. They are often used for smaller-scale pipe welding projects and include equipment like shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) machines and gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) machines.
- Automatic/Orbital Welding Machines: Automatic welding machines are designed for high precision and are used in industries where consistent and high-quality welds are essential. They often utilize orbital welding technology, allowing for precise control over the welding process.
2. Welding Processes:
- Pipe welding machines can be configured for various welding processes, including:
- SMAW (Shielded Metal Arc Welding): Also known as stick welding, it uses a consumable electrode to create an arc that melts the base metal and the electrode, forming a weld bead.
- GTAW (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding): Also known as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, it uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode and a shielding gas to produce precise and high-quality welds.
- GMAW (Gas Metal Arc Welding): Also known as MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, it uses a consumable wire electrode and a shielding gas to create welds.
- FCAW (Flux-Cored Arc Welding): This process uses a flux-cored wire electrode and a shielding gas to produce welds, making it suitable for outdoor and windy conditions.
3. Pipe Diameter and Thickness:
- Pipe welding machines come in various sizes and are designed to accommodate different pipe diameters and thicknesses.
- The machine’s specifications should match the specific pipe welding requirements of the project.
4. Welding Position:
- Pipe welding machines can be used in various welding positions, including horizontal, vertical, and overhead welding.
- Some machines are designed for specific welding positions, while others offer versatility for different positions.
5. Welding Power Source:
- The power source for pipe welding machines can vary. Some machines run on electricity, while others are designed for gas-powered or diesel-powered operation.
- The choice of power source depends on the availability of electricity and the mobility required for the welding project.
6. Control and Automation:
- Automatic and orbital welding machines often feature advanced control systems, including programmable settings and remote control options.
- These control systems enable precise control over welding parameters such as voltage, amperage, travel speed, and torch angle.
7. Welding Productivity:
- Pipe welding machines are designed to increase welding productivity and efficiency, making them suitable for large-scale pipe fabrication projects.
8. Quality and Consistency:
- Pipe welding machines are favored for their ability to produce consistent and high-quality welds, meeting industry standards and specifications.
9. Welding Environment:
- Consideration should be given to the welding environment, including indoor or outdoor settings and whether the machine needs to withstand harsh conditions.
Pipe welding machines are essential tools in industries that rely on pipelines, including oil and gas, water distribution, and HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning). Proper training and certification are often required for operators to use these machines effectively and ensure the integrity of welded pipe joints.
Application Areas of the Pipe Welding Machine
Pipe welding machines are specialized tools used to join cylindrical and curved components, commonly pipes. They are crucial for creating strong and leak-free pipe connections, making them essential in various industries.
Here’s an overview of the primary application areas of pipe welding machines:
- Oil and Gas Industry: Pipe welding machines play a critical role in the construction and maintenance of pipelines for transporting oil and natural gas. These pipelines must withstand high pressures and harsh environments, requiring precise and durable welds. Pipe welding machines ensure the integrity of these pipelines, preventing leaks and ensuring the safe and efficient transportation of oil and gas.
- Construction Industry: Pipe welding machines are widely used in construction projects to weld various pipe structures, including scaffolding, water supply systems, and fire protection piping. These welds must be strong and reliable to support the weight of the structures and maintain the integrity of piping systems.
- Power Generation Industry: In the power generation industry, pipe welding machines are used to weld pressure vessels, pipes, and other components of power plants. These components operate under high pressures and temperatures, demanding high-quality welds to prevent accidents and ensure the safe and efficient operation of power plants.
- Chemical Industry: Pipe welding machines are essential in the chemical industry for welding reactor vessels, piping systems, and storage tanks. These welds must be resistant to corrosion and withstand the harsh chemicals used in chemical processes. Pipe welding machines ensure the integrity of chemical processing equipment and prevent hazardous leaks.
- Manufacturing Industry: Pipe welding machines are employed in various manufacturing processes to weld pipes for various applications, such as water supply, irrigation, and manufacturing equipment. These welds must be strong, durable, and meet specific standards to ensure the functionality and safety of the manufactured products.
- Shipbuilding: Pipe welding machines are crucial in shipbuilding for welding pipes and tubes used in the construction and maintenance of ships. These welds must withstand the harsh marine environment and the stresses of ship operation.
- Food and Beverage Industry: Pipe welding machines are used in the food and beverage industry to manufacture containers and equipment, such as cans, bottles, and tanks. These welds must meet food safety standards and prevent contamination.
- Medical Device Industry: Pipe welding machines are employed in the medical device industry to produce implantable devices, such as surgical stents, catheters, and prosthetic components. These welds must be precise, durable, and biocompatible to ensure the safety and effectiveness of medical devices.
- Appliance Manufacturing: Pipe welding machines are used in appliance manufacturing to weld cookware, water heaters, and other cylindrical components. These welds must withstand the heat and pressure of appliance operation.
- General Manufacturing: Pipe welding machines are used in various general manufacturing industries to weld cylindrical and curved components in a range of products, such as bicycles, sports equipment, and industrial machinery.
In summary, pipe welding machines are versatile and indispensable tools in various industries, providing efficient, precise, and reliable methods for joining cylindrical and curved components. Their adaptability, safety features, and wide range of applications make them valuable assets in manufacturing, construction, power generation, and other critical sectors.
Pipe welding machines find application in various industries and sectors where the joining of pipes is necessary. These machines are crucial for creating strong and leak-free pipe connections. Here are the primary application areas of pipe welding machines:
1. Oil and Gas Industry:
- Pipe welding machines are extensively used in the construction and maintenance of pipelines for transporting oil and natural gas.
- They are employed for both onshore and offshore pipeline projects to create reliable and durable welds that can withstand extreme conditions.
2. Construction Industry:
- Pipe welding machines are used in the construction of buildings, bridges, and infrastructure projects that involve the installation of plumbing, HVAC systems, and structural pipes.
3. Water and Wastewater:
- Water treatment plants and sewage systems require a network of pipes, and pipe welding machines play a crucial role in assembling and maintaining these systems.
4. Manufacturing and Fabrication:
- Manufacturing facilities use pipe welding machines to fabricate and assemble components for various industries, such as automotive, aerospace, and machinery manufacturing.
5. Shipbuilding:
- Shipyards use pipe welding machines for joining pipes used in ship construction, including plumbing, ventilation, and other onboard systems.
6. Chemical and Petrochemical Industry:
- Chemical and petrochemical plants rely on pipe welding machines to construct pipelines for the transport of chemicals, gases, and other fluids.
7. Power Generation:
- Power plants, including nuclear, coal, and gas-fired facilities, utilize pipe welding machines for assembling piping systems for cooling, steam, and other purposes.
8. Aerospace Industry:
- Pipe welding machines are used in the aerospace industry for fabricating and maintaining aircraft components, including hydraulic systems and fuel lines.
9. Food and Beverage Industry:
- Food processing plants require sanitary and hygienic pipe systems, and pipe welding machines are used to create clean and leak-free welds for these applications.
10. Pharmaceutical Industry: – The pharmaceutical industry relies on high-purity piping systems, and pipe welding machines are used to achieve contamination-free welds in the production of pharmaceutical products.
11. Mining and Minerals: – The mining industry uses pipe welding machines for assembling and repairing pipelines that transport ores, minerals, and water in mining operations.
12. Renewable Energy: – Pipe welding machines are employed in the renewable energy sector for assembling pipelines used in geothermal, solar, and wind energy projects.
13. Piping Systems: – Pipe welding machines are used in various piping systems, including compressed air, hydraulic, and pneumatic systems, as well as in the installation of sprinkler systems in fire protection.
14. Municipal Utilities: – Municipalities and utilities rely on pipe welding machines for repairing and maintaining water supply and wastewater systems.
15. Research and Development: – Laboratories and research facilities use pipe welding machines for creating specialized experimental setups and fluid-handling systems.
In each of these application areas, pipe welding machines are critical for ensuring the integrity, safety, and efficiency of pipe systems. They are essential tools that contribute to the construction, maintenance, and operation of vital infrastructure and industrial processes.
A circular welding machine is a type of automated welding equipment used primarily for welding circular or cylindrical objects. These machines are often used in industries such as pipe manufacturing, tank construction, or any process where round objects need to be welded efficiently and consistently.
Here are some key features and uses of circular welding machines:
- Application: Circular welding machines are designed for welding pipes, tanks, tubes, and similar cylindrical items. They ensure uniformity in weld quality by controlling the welding process around the entire circumference of the object.
- Types: There are different types of circular welding machines, such as:
- Orbital Welding Machines: These are used for high-precision welding, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals, food processing, and aerospace.
- Rotary Welding Machines: These machines use a rotating workpiece and a fixed welding torch to create the weld around the circumference.
- Mechanism: These machines often feature a rotating fixture or turntable that holds the part being welded. The welding head moves along the circumference of the part, ensuring a continuous weld. The rotation helps achieve uniformity.
- Automation: Many circular welding machines are fully automated, with the ability to adjust parameters like speed, voltage, and amperage based on the part size and material. This reduces human error and increases production efficiency.
- Materials: These machines can be used for a variety of metals such as stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloys, depending on the material properties required for the finished product.
- Advantages:
- Precision: Circular welding machines are known for their precise and uniform welds, which are crucial in high-quality industrial applications.
- Speed: Automation reduces welding time significantly, which improves production rates.
- Consistency: These machines are excellent for repetitive tasks, ensuring consistent weld quality for mass production.
A circular welding machine is an automated system designed to weld circular or cylindrical objects, commonly used in industries like pipe manufacturing, tank construction, and any other process involving round materials. The machine typically works by rotating the workpiece while the welding head stays fixed or moves along the circumference, ensuring a continuous weld all around the piece. These machines are essential in achieving uniform welds, especially in high-precision applications like pharmaceuticals, aerospace, and food processing.
Circular welding machines can be orbital, where the workpiece rotates and the welding head moves in a specific pattern, or rotary, where a rotating fixture holds the part and the welding torch remains fixed. The main advantage of using such machines is the high consistency and quality of the welds, along with the efficiency they bring to the production process. Automation in these systems reduces human error and allows for faster welding, making them ideal for mass production.
Circular welding machines can weld a variety of materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloys. The precision, speed, and consistency offered by these machines make them invaluable for industries that require high-quality, repeatable welds on cylindrical items.
Circular welding machines are specialized automated systems designed to handle the welding of cylindrical or circular workpieces, such as pipes, tubes, tanks, and other round objects. These machines are used in industries where precise, uniform welds are essential, including manufacturing, construction, aerospace, automotive, and energy sectors. The primary function of a circular welding machine is to deliver a consistent and high-quality weld around the entire circumference of a circular part, ensuring strength and durability.
One of the most common types of circular welding machines is the orbital welding machine. In this system, the workpiece itself rotates, while a stationary welding head moves in a specific path to create a uniform weld. Orbital welding is often used for high-precision applications, especially where cleanliness and structural integrity are crucial, such as in the pharmaceutical or food industries. This type of machine is highly valued for its ability to create consistent, repeatable welds with minimal operator intervention.
Another type is the rotary welding machine, where the workpiece is rotated, and the welding torch or head remains in a fixed position. The rotating workpiece moves through the welding zone, allowing the machine to make continuous welds along the circumference of the material. Rotary welding machines are commonly used for applications where the workpiece is large or needs to be rotated around a central axis, like in the manufacturing of large tanks, pipes, and pressure vessels.
Circular welding machines offer a range of advantages, especially when it comes to mass production or high-demand environments. Their ability to provide precise, consistent welds significantly reduces the risk of errors, which can be costly and time-consuming. With automation, these machines are not only faster but also more efficient than manual welding, cutting down on labor costs and improving throughput.
Moreover, these machines are capable of working with various materials, such as stainless steel, carbon steel, alloys, and other metals that require precise control over heat input, which is crucial to avoid warping or distortion. In industries where high-pressure or high-temperature components are needed, such as in the oil and gas industry or aerospace, the use of circular welding machines ensures the structural integrity and reliability of the final product.
Automation is a key feature in these systems. Circular welding machines are often programmed with sensors and controls that allow for real-time adjustments to welding parameters like speed, voltage, and amperage, depending on the material being welded, the thickness of the workpiece, and other factors. This level of control ensures that each weld is consistent and meets the required specifications without the need for manual intervention, making these machines ideal for environments where precision and repeatability are critical.
The integration of advanced technologies such as digital control systems and robotics into circular welding machines has also expanded their capabilities. These machines can now handle more complex geometries, different types of welds (e.g., butt welds, fillet welds), and a broader range of materials. Additionally, the use of automated inspection systems allows for real-time monitoring of the weld quality, enabling immediate adjustments to maintain high standards.
Circular welding machines are not just limited to large-scale industries; they are also highly beneficial in small-scale or specialized applications. For instance, industries that require small diameter pipes or intricate cylindrical parts can also rely on circular welding machines for high-quality welds without compromising on time or material efficiency.
In summary, circular welding machines are indispensable tools in modern manufacturing, offering significant advantages in terms of precision, speed, and consistency. Their automated nature allows for high-volume production while maintaining the highest quality of welds. Whether used for small-scale custom fabrication or large-scale industrial production, these machines are essential for producing reliable, durable welded parts, especially in industries that require high performance and structural integrity in their products.
Automatic Circular Welding Machine

An Automatic Circular Welding Machine is a highly specialized type of welding equipment designed to automatically perform welding operations on circular or cylindrical parts. These machines are essential in industries that require precision welding on pipes, tubes, tanks, and other round workpieces. The automation of these machines eliminates the need for manual intervention, which not only increases production speed but also ensures consistency and high-quality welds across all parts.
The working principle behind an automatic circular welding machine involves rotating the workpiece around its axis while a welding torch or head moves along its circumference. This allows for a continuous, uniform weld to be created around the entire circumference of the material. The process is typically automated with pre-programmed settings to control welding parameters such as speed, heat input, and welding path.
These machines come in several configurations, including orbital welding machines and rotary welding machines. Orbital machines are particularly known for their precision, where the workpiece rotates and the welding head follows a controlled orbital path. These are often used in industries requiring high-precision welding, such as aerospace, pharmaceutical, and food processing industries. On the other hand, rotary welding machines have a rotating fixture that holds the workpiece, while the welding torch remains stationary. The workpiece continuously rotates through the welding zone, making the process ideal for larger or cylindrical parts.
Key features of Automatic Circular Welding Machines include:
- Automation and Control: Automatic circular welding machines often come with advanced digital control systems that allow for precise adjustments to welding parameters. These can include weld speed, heat settings, voltage, and amperage. Automation ensures that the machine can run without continuous operator input, reducing human error and increasing production efficiency.
- High Precision: The automated nature of these machines ensures that each weld is precise and uniform, which is critical for industries where structural integrity and quality are non-negotiable. For example, in the aerospace and pharmaceutical sectors, the welds must be flawless to avoid defects that could compromise the safety or performance of the product.
- Speed and Efficiency: By automating the welding process, these machines reduce the time it takes to weld each part, which increases overall production rates. This is especially important in industries with high-volume manufacturing where time is a critical factor.
- Adaptability to Various Materials: Automatic circular welding machines are designed to weld a wide range of materials, such as stainless steel, carbon steel, alloys, and other metals. The machine can be set up to handle different material thicknesses and diameters, making it highly versatile for various applications.
- Consistent Quality: The automation and control features ensure that each weld is of the same high quality, with uniform heat input and minimal defects. This is especially important in industries like energy, where welded components must withstand extreme conditions, or in industries like food processing, where hygiene and safety are paramount.
- Inspection and Monitoring: Many modern automatic circular welding machines are equipped with real-time monitoring and inspection systems. These systems use sensors and cameras to detect weld quality, including potential defects such as porosity or cracks, during the welding process. This feedback allows for immediate adjustments, ensuring that any issues are addressed without affecting the final product.
- Customization: Automatic circular welding machines can be customized to suit specific manufacturing needs. Features such as adjustable welding heads, rotary tables, and various welding techniques (e.g., TIG, MIG, or laser welding) can be integrated into the machine depending on the application requirements.
Applications of Automatic Circular Welding Machines:
- Pipe and Tube Manufacturing: These machines are ideal for the continuous welding of pipes and tubes in industries such as oil and gas, water treatment, and construction.
- Tank Production: Automatic circular welding machines are often used to weld large, cylindrical tanks used in industries like chemical storage, water tanks, and pressure vessels.
- Automotive Industry: In automotive manufacturing, these machines are used for welding exhaust pipes, fuel tanks, and other cylindrical parts that require high-quality, durable welds.
- Aerospace and Defense: In aerospace applications, circular welding machines ensure the integrity of critical components that must withstand extreme conditions, such as fuel tanks and pressure vessels.
- Food and Beverage: For applications requiring strict hygiene standards, such as the production of tanks and pipelines for the food and beverage industry, automatic circular welding machines ensure clean, safe welds that meet industry standards.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: The high precision of these machines is particularly important in the pharmaceutical industry, where welded parts must meet stringent cleanliness and structural integrity standards.
In conclusion, automatic circular welding machines are essential tools for industries that require high-precision, consistent, and efficient welding of cylindrical parts. With their advanced automation, control systems, and versatility, these machines improve productivity, reduce operational costs, and maintain high weld quality, making them indispensable in modern manufacturing environments.
Automatic circular welding machines are an indispensable part of modern manufacturing, providing significant advantages over manual or semi-automated welding processes. These machines integrate advanced technologies to ensure that welding tasks are executed quickly, accurately, and with minimal human intervention, making them ideal for high-volume production environments where precision and efficiency are critical.
At the core of an automatic circular welding machine is its ability to rotate the workpiece around its axis, while the welding head, typically a stationary or orbiting torch, moves along the circular path to create a continuous and uniform weld. This rotation allows for the even distribution of heat around the entire circumference of the part, ensuring a strong, consistent weld without the risk of uneven heat distribution, which could lead to warping or structural weaknesses.
The automation aspect of these machines allows them to operate with minimal supervision, relying on pre-programmed settings and digital control systems to manage parameters such as welding speed, voltage, amperage, and even the type of welding process used (e.g., MIG, TIG, or laser welding). Once the parameters are set, the machine can run independently, making it possible to achieve the same high-quality welds across thousands of parts, reducing the need for manual adjustments and inspections during the welding process.
One of the standout benefits of automatic circular welding machines is their versatility. These machines can handle a wide range of materials, from lightweight metals like aluminum to more robust materials like stainless steel and titanium. They can also accommodate different material thicknesses, which makes them highly adaptable for various industries, including automotive, aerospace, food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and more.
In addition to their precision and adaptability, these machines also incorporate advanced safety features. Sensors and feedback loops continuously monitor the welding process, identifying issues like undercuts, porosity, or misalignment before they become problems. In some cases, these machines can even adjust the welding process in real-time, ensuring the final product meets the required specifications.
Another advantage of automatic circular welding machines is their ability to significantly improve productivity. With automated processes that can run continuously with minimal downtime, these machines increase the throughput of a factory or workshop, allowing manufacturers to meet higher production demands while reducing the need for additional labor. Furthermore, the consistent weld quality reduces the likelihood of rework, saving both time and materials.
As industries continue to push for greater automation and efficiency, the role of automatic circular welding machines will only expand. Their ability to provide precision, speed, and scalability makes them essential in the production of high-quality cylindrical and circular components. Whether in the creation of pipelines, tanks, automotive parts, or aerospace components, these machines ensure that manufacturers can meet the growing demands for high-performance, durable products.
As automatic circular welding machines continue to evolve, their integration with cutting-edge technologies opens up new possibilities for industries that rely on high-quality, consistent welding. One of the most significant advancements is the incorporation of robotics and AI (Artificial Intelligence) into these systems. With robotic arms or automated welding heads, these machines can now perform welding tasks with even more precision and flexibility, including the ability to weld complex geometries or intricate shapes. AI systems can analyze welding parameters in real time and optimize the process dynamically, further improving efficiency and reducing the chance of defects.
Another technological advancement is the use of advanced sensors and monitoring systems. These sensors can detect variations in material properties, temperature fluctuations, and even microscopic defects during the welding process. The data gathered is continuously analyzed by the machine’s control system, which can make real-time adjustments to ensure the highest possible quality for each weld. This level of continuous feedback is particularly beneficial for industries where weld integrity is critical, such as aerospace or nuclear energy, where even the smallest flaw can have catastrophic consequences.
Additionally, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities in automatic circular welding machines allows for real-time remote monitoring and maintenance. Operators can access machine data from anywhere, providing them with the ability to monitor performance, track welding quality, and perform diagnostic checks remotely. This capability reduces downtime and enhances the ability to perform predictive maintenance, minimizing the risk of machine failure and extending the lifespan of the equipment.
Customization options have also improved in modern automatic circular welding machines. With software that can be tailored to specific applications, manufacturers can create customized welding patterns and parameters for different types of materials, thicknesses, and geometries. This flexibility ensures that the machine can meet a broad range of welding needs, from simple cylindrical parts to more complex, multi-functional components that require intricate weld designs.
In terms of energy efficiency, newer models of automatic circular welding machines are designed to minimize power consumption without sacrificing performance. With features like variable speed drives and efficient cooling systems, these machines are becoming more sustainable and cost-effective, offering savings on energy costs while maintaining optimal performance.
Another trend is the use of wireless technology to simplify the connection between the welding equipment and other systems, such as control panels or inspection devices. Wireless systems reduce the need for physical connections and cables, which can be cumbersome in complex setups, and improve the machine’s mobility and flexibility within the workspace.
The growing trend of sustainability in manufacturing also plays a role in the design of modern circular welding machines. Manufacturers are increasingly focused on reducing material waste, optimizing energy use, and producing fewer harmful emissions during the welding process. Machines are now more efficient in terms of material handling, which results in less scrap and wasted energy, contributing to environmentally friendly practices in manufacturing.
As industries continue to push for higher production rates, lower costs, and better product quality, automatic circular welding machines are becoming more integrated into production lines. Their ability to handle large volumes of work, provide high-quality welds, and minimize human intervention has made them an essential tool in a variety of manufacturing sectors.
The future of automatic circular welding machines looks even more promising with continuous improvements in artificial intelligence, sensor technology, robotics, and data analytics. These innovations will help further refine welding quality, enhance productivity, and reduce costs, enabling manufacturers to meet the demands of increasingly complex, high-precision applications in a wide range of industries.
In conclusion, automatic circular welding machines are transforming modern manufacturing. With the combination of robotics, AI, advanced sensors, and connectivity, these machines are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in welding technology. As automation continues to evolve, these systems will not only improve efficiency and product quality but will also make manufacturing processes more flexible, adaptable, and sustainable, offering significant advantages in the highly competitive global market.
Longitudinal Welding Machine

A Longitudinal Welding Machine is a specialized piece of equipment used for welding along the length of a workpiece, particularly for long, straight materials such as pipes, tubes, and plates. The main function of a longitudinal welding machine is to create continuous, high-quality welds along the longitudinal axis (the length) of cylindrical or flat parts, ensuring uniformity and structural integrity across the entire welded seam. This type of welding is essential in various industries, including pipe manufacturing, tank production, automotive, and shipbuilding, where long, linear welds are required for joining metal parts.
These machines are typically designed to automate the welding process, reducing human error, increasing production speed, and ensuring consistent weld quality. They are used in a variety of applications, from manufacturing pipelines and tanks to welding automotive chassis and structural components. By using longitudinal welding machines, manufacturers can achieve high production rates while maintaining the integrity and durability of the welded parts.
How It Works:
The operation of a longitudinal welding machine typically involves the workpiece being moved along a fixed path while a welding head or torch follows the length of the material. The workpiece can be a flat plate, a pipe, or a tube, and the welding machine ensures that the entire seam along the length is welded, often in a continuous motion.
There are various welding methods that can be used on a longitudinal welding machine, including:
- Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding: Known for producing high-quality welds with precise control, TIG welding is often used for thin materials or when a clean, strong weld is required.
- Metal Inert Gas (MIG) Welding: This process uses a consumable wire electrode and is typically faster than TIG welding, making it more suitable for higher volume production.
- Submerged Arc Welding (SAW): In submerged arc welding, the arc is shielded by a blanket of flux, making it ideal for thicker materials and producing high-quality welds with minimal spatter.
- High-Frequency Induction (HFI) Welding: This method is commonly used in pipe manufacturing, where high-frequency electrical currents are used to heat and weld the edges of the material.
Key Components:
- Welding Head: The head contains the welding torch or electrode and moves along the length of the workpiece to create the weld. It is often adjustable to ensure precision in weld placement.
- Feed Mechanism: The workpiece is fed into the welding machine, and the speed at which it moves can be adjusted depending on the material, thickness, and welding process used.
- Cooling System: High heat generated during the welding process can affect both the machine and the workpiece. A cooling system is typically integrated to maintain optimal temperature conditions and prevent warping or damage.
- Control Systems: Modern longitudinal welding machines are equipped with advanced control systems that monitor and adjust parameters like welding speed, voltage, amperage, and gas flow to ensure consistent weld quality. These systems may also include sensors for real-time feedback, allowing adjustments during the process to address any issues immediately.
Advantages of Longitudinal Welding Machines:
- Efficiency: By automating the welding process, longitudinal welding machines can handle high-volume production, significantly improving the efficiency of the manufacturing process.
- Consistency: Automated systems ensure uniformity across all welded parts, reducing the likelihood of defects and ensuring high-quality welds.
- Reduced Labor: These machines require less manual intervention, which reduces labor costs and minimizes human error during the welding process.
- Versatility: Longitudinal welding machines can be adapted to different materials, thicknesses, and types of welds, making them highly versatile for a wide range of industrial applications.
- Speed: With continuous feeding and automated welding, these machines can operate at high speeds, making them ideal for mass production.
- Quality Control: Automated welding allows for precise control over welding parameters, which helps maintain high-quality standards across all parts being welded.
Applications of Longitudinal Welding Machines:
- Pipe Manufacturing: One of the most common applications for longitudinal welding machines is in the production of welded pipes and tubes, especially in industries like oil and gas, water treatment, and construction. These machines are used to weld the longitudinal seam of the pipe, which is critical for its strength and reliability.
- Tank Production: In industries that produce large tanks, such as for chemical or fuel storage, longitudinal welding machines are used to weld the seams along the length of the tank’s cylindrical walls.
- Automotive Industry: These machines are used to weld parts like chassis, exhaust systems, and other long metal components found in automotive manufacturing.
- Shipbuilding: Longitudinal welding is crucial for welding the hulls of ships, as these long seams are essential for maintaining the structural integrity of the vessel.
- Steel Fabrication: In structural steel fabrication, longitudinal welding machines are used to create strong, durable welds on beams, plates, and other large metal components used in construction projects.
Advanced Features:
In modern longitudinal welding machines, technological advancements such as robotics, vision systems, and automated inspection play an increasingly important role. Robots can handle the welding head with high precision, while vision systems are used to inspect the welds in real time, ensuring that any defects can be addressed immediately. Some machines are also equipped with adaptive control systems that automatically adjust the welding parameters based on changes in material thickness, composition, or alignment during the welding process.
Conclusion:
Longitudinal welding machines are vital for industries that require high-quality, high-efficiency, and high-volume welding of long, straight seams. By automating the welding process, these machines reduce labor costs, improve the quality of the weld, and ensure faster production times. Their versatility and ability to adapt to various materials and welding processes make them indispensable in applications ranging from pipeline manufacturing to automotive production and shipbuilding. As technologies continue to improve, longitudinal welding machines are likely to become even more precise, faster, and energy-efficient, further enhancing their role in modern manufacturing.
Longitudinal welding machines are integral to many industries due to their capacity to provide high-quality, efficient welding for long, straight seams. The automation provided by these machines ensures consistency, reducing the likelihood of defects and allowing manufacturers to produce large quantities of welded products quickly and reliably. By eliminating manual processes and human error, these machines can increase the overall production output, especially in industries that deal with high volumes of welded materials.
One of the primary benefits of using longitudinal welding machines is the improved weld quality. Automated systems can precisely control parameters such as welding speed, current, voltage, and heat input, leading to cleaner, stronger, and more consistent welds. This level of control is particularly important in industries that require high structural integrity, such as in the aerospace, energy, and automotive sectors. For example, in the manufacturing of fuel tanks, pressure vessels, and pipelines, the strength and durability of the weld are critical to the safety and reliability of the finished product.
Additionally, speed is another significant advantage. Since the process is automated and designed for continuous operation, longitudinal welding machines can achieve much faster welding rates compared to manual methods. For industries like pipe manufacturing, where large quantities of material need to be welded in a relatively short time, this speed is vital for meeting production targets. The high throughput and low downtime also contribute to a cost-effective manufacturing process, making it an ideal choice for mass production.
Another area where longitudinal welding machines excel is flexibility. While these machines are primarily designed for welding long, linear seams, they can often be adapted to different welding processes or configurations, depending on the needs of the manufacturer. For example, switching between different welding methods like MIG, TIG, or submerged arc welding is possible in some advanced machines, making them suitable for a wide range of materials, from thin sheets to thicker, high-strength alloys. This versatility allows manufacturers to use a single machine for various products, reducing the need for multiple machines and minimizing space requirements in the production facility.
In terms of maintenance and operational efficiency, modern longitudinal welding machines are designed with user-friendly control systems that allow operators to monitor performance and make adjustments as needed. Some machines include diagnostic tools that can predict when maintenance is required, helping to avoid unexpected downtimes. This predictive maintenance reduces the overall cost of repairs and ensures the machine operates at peak efficiency.
The integration of real-time monitoring and feedback systems further enhances the capabilities of longitudinal welding machines. Through the use of sensors and cameras, these systems can detect issues such as poor weld penetration, misalignment, or inadequate heat distribution during the welding process. When a potential issue is identified, the system can automatically adjust parameters or alert the operator to address the problem before it results in a defect. This constant monitoring ensures that the quality of the weld remains consistently high, even in long production runs.
Energy efficiency is another growing concern in modern manufacturing, and longitudinal welding machines have evolved to become more energy-efficient. With advanced features like variable-speed motors and optimized cooling systems, these machines reduce unnecessary energy consumption, lowering operational costs and environmental impact. The efficient use of energy in these systems not only contributes to lower operational costs but also supports sustainability efforts in the manufacturing industry.
Moreover, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies is transforming longitudinal welding machines into smarter systems. With data analytics and machine learning algorithms, manufacturers can gain deeper insights into their welding processes. This allows them to identify trends, predict issues, and optimize workflows for greater efficiency. For instance, by analyzing historical data, operators can adjust machine settings based on past performance to improve the quality and speed of future welds.
Longitudinal welding machines are also becoming more customizable. Manufacturers can adjust the machine’s settings to accommodate different sizes, materials, and welding processes, making it easier to handle a wide variety of parts and production requirements. Whether it’s adjusting the feed rate for a thicker workpiece or configuring the system for a specific type of weld, the machine can be tailored to meet specific needs.
Conclusion:
In summary, longitudinal welding machines are pivotal in modern manufacturing, offering unparalleled precision, speed, and versatility in welding long seams. Their ability to automate the process enhances consistency, reduces labor costs, and improves overall efficiency, making them indispensable in industries ranging from pipeline construction to automotive manufacturing. As technology continues to advance, these machines will only become more efficient, smarter, and capable of handling increasingly complex and diverse welding tasks, solidifying their role as a cornerstone of automated production systems.
As longitudinal welding machines continue to evolve, their role in improving manufacturing processes becomes increasingly significant. The integration of cutting-edge technologies like robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics has led to even higher levels of efficiency, quality, and adaptability. These advancements are transforming longitudinal welding machines into highly intelligent systems capable of continuous self-optimization, enabling manufacturers to meet the growing demand for high-quality, high-volume production.
One of the key developments is the integration of robotic arms in longitudinal welding machines. These robotic systems bring greater flexibility and precision to the welding process. By using multi-axis robotic arms, manufacturers can weld complex geometries or achieve extremely precise welds along irregular or curved surfaces, in addition to the traditional straight seams. This allows manufacturers to produce a wider range of products without the need to switch to different machines or systems, resulting in greater overall production efficiency.
The inclusion of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in modern longitudinal welding machines further enhances their capabilities. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data collected from sensors and cameras during the welding process, allowing the system to automatically adjust welding parameters like speed, voltage, and heat. This real-time feedback loop ensures that the welding process is continuously optimized, minimizing defects and improving the overall quality of the weld. Additionally, AI-based systems can detect anomalies, such as poor fusion or porosity, during the welding process and make immediate corrective adjustments, reducing the need for manual intervention.
Furthermore, these AI systems can analyze trends over time, learning from past welds to make predictive adjustments for future welding operations. This predictive maintenance capability is particularly valuable because it allows operators to address potential issues before they cause any downtime or defects. By predicting wear and tear on critical components, such as welding torches or motors, the system can schedule maintenance proactively, reducing the risk of unplanned stoppages.
Data analytics is another powerful tool being integrated into longitudinal welding machines. With the increasing volume of data being collected by sensors, cameras, and monitoring systems, manufacturers can now use advanced data analysis tools to gain actionable insights into the entire welding process. These insights can be used to optimize welding parameters, reduce material waste, and improve production rates. For example, analyzing the temperature profiles of a weld during the process can help adjust the cooling rates to prevent overheating or distortion of the material.
The integration of real-time monitoring and smart sensors is also enhancing the capabilities of longitudinal welding machines. These sensors can continuously track variables like arc stability, welding speed, and material flow, providing immediate feedback that allows for automatic adjustments in the welding process. This capability ensures the consistency and quality of every weld, even during long production runs. If any deviation from the desired welding parameters is detected, the system can alert the operator or automatically adjust the process to maintain the quality standards.
Another emerging trend is the use of advanced welding processes in longitudinal welding machines. For instance, the integration of laser welding technology into these systems enables high-precision welding with minimal heat input, reducing the likelihood of material distortion and improving the overall quality of the weld. Laser welding is particularly useful in applications requiring very fine, clean, and precise welds, such as in the electronics and medical device industries. Longitudinal welding machines equipped with laser welding technology can perform these delicate welds at a much faster rate than traditional welding methods.
Moreover, cobot integration—where collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside human operators—has further expanded the scope of longitudinal welding machines. Cobots can assist in loading and unloading workpieces, adjusting welding parameters, or performing secondary operations like grinding or polishing. The use of cobots not only reduces operator fatigue but also increases safety and efficiency on the production floor by reducing manual handling of heavy or dangerous parts.
Energy efficiency remains a major focus in the development of modern longitudinal welding machines. Newer machines are designed with optimized energy usage, reducing both operational costs and environmental impact. Features like variable frequency drives (VFDs) help control motor speeds more precisely, allowing for energy savings during the welding process. Additionally, improved cooling systems and heat recovery technologies contribute to maintaining the machine’s efficiency while minimizing energy consumption.
Sustainability is also becoming increasingly important in the context of longitudinal welding. Manufacturers are focusing on reducing the environmental impact of welding processes by minimizing material waste and improving resource efficiency. Some longitudinal welding machines are equipped with technologies that reduce fumes and harmful emissions, such as integrated fume extraction systems, which not only protect the environment but also improve the working conditions for operators. Moreover, the precise nature of modern welding machines leads to less material waste, as the welds are more consistent, requiring less rework or scrap.
Longitudinal welding machines are also evolving to become more user-friendly and easier to operate. With the integration of advanced human-machine interfaces (HMIs), operators can monitor the welding process more effectively, adjust settings intuitively, and gain access to real-time performance data. These intuitive interfaces reduce the learning curve for new operators and allow experienced workers to focus on overseeing the machine’s operations rather than troubleshooting issues. Moreover, remote diagnostics and cloud-based support enable manufacturers to troubleshoot and resolve issues without needing on-site visits, minimizing downtime and improving overall equipment efficiency.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the evolution of longitudinal welding machines is driven by advancements in automation, artificial intelligence, robotics, and data analytics, all of which contribute to higher efficiency, quality, and flexibility in the welding process. These machines are becoming increasingly intelligent, adaptable, and energy-efficient, making them indispensable in industries that rely on high-precision, high-volume welding. Whether it’s incorporating predictive maintenance, laser welding, or cobot collaboration, longitudinal welding machines are poised to continue shaping the future of manufacturing by enhancing productivity and ensuring consistently high-quality results.
Circular Welding System

A circular welding system is a specialized type of automated welding equipment designed to weld around the circumference of cylindrical or circular workpieces. This system is particularly important in industries that require precise and continuous welds on parts with a circular shape, such as pipes, tanks, reactors, and other cylindrical structures. The circular welding system ensures consistent, high-quality welds along the circumference of the workpiece, making it essential for a range of applications in the automotive, aerospace, chemical, energy, and construction industries.
How It Works:
The fundamental concept behind a circular welding system is to rotate the workpiece around its axis while the welding torch or head moves along the circular path, creating a continuous and uniform weld. There are two main configurations for circular welding systems:
- Rotary Welding Systems: In this configuration, the workpiece is held stationary, while a rotating welding head or torch moves along the circumference. This type of system is often used for large cylindrical parts, such as tanks or pressure vessels, where the part rotates during the welding process.
- Rotating Workpiece Systems: In this design, the workpiece itself rotates while the welding head or torch stays stationary. The workpiece’s rotation allows the welding system to create a continuous seam around the entire circumference. This configuration is commonly used for smaller cylindrical parts, such as pipes and tubes.
The system usually operates in a fully automated manner, allowing for a continuous, high-speed welding process that can be programmed for specific parameters such as welding speed, amperage, and voltage. These settings ensure a uniform, high-quality weld along the entire circumference of the piece.
Key Components:
- Rotational Mechanism: This component is responsible for rotating the workpiece. The rotational speed is carefully controlled to ensure that the welding head maintains the correct pace to produce a uniform and high-quality weld.
- Welding Head/Torch: The welding head is typically positioned either stationary or on a moving carriage, depending on the system design. The torch is the part that applies the heat to the material to create the weld bead. It can be equipped for different welding processes such as Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG), Metal Inert Gas (MIG), Submerged Arc Welding (SAW), or Laser Welding.
- Control System: Modern circular welding systems are equipped with programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or digital control systems that allow operators to input and adjust welding parameters. These controls manage important factors such as speed, heat input, and weld pattern, ensuring that the weld is performed consistently and within specified tolerances.
- Feed Mechanism: In some circular welding systems, especially those using wire-fed processes (like MIG or SAW), a wire feed mechanism is included to supply the welding material into the weld pool. The feed rate is typically controlled to match the welding speed.
- Cooling System: Welding generates significant heat, and a cooling system is necessary to prevent overheating of both the workpiece and the machine itself. Cooling is especially important in high-heat welding processes like TIG or MIG, where maintaining an optimal temperature is critical for high-quality welds.
- Safety and Inspection Features: Modern circular welding systems often include various safety features such as automatic shutoffs in case of malfunction, protective shielding to contain the welding arc, and fume extraction systems to maintain a safe work environment. Additionally, some systems include vision systems or in-process inspection technologies to detect defects like porosity or misalignment during the welding process.
Types of Welding Processes Used in Circular Welding Systems:
- Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding: Known for its high precision, TIG welding is often used in applications that require clean and strong welds, such as aerospace and medical devices. The use of a non-consumable tungsten electrode allows for a high degree of control over the welding process.
- Metal Inert Gas (MIG) Welding: This is a faster, more cost-effective process compared to TIG welding and is commonly used for welding thicker materials. MIG welding is more automated and is ideal for high-volume production.
- Submerged Arc Welding (SAW): This process is used for heavy-duty applications where thicker materials are involved. The weld is shielded by a layer of flux, allowing for deep penetration and a high-quality finish.
- Laser Welding: Laser welding is a highly precise and efficient process that uses a focused laser beam to melt and join the material. It is used for high-speed welding with minimal heat-affected zones, making it suitable for thin materials and high-precision applications.
- Electroslag Welding: This process is used for welding thick materials and is often seen in heavy industries like shipbuilding and pressure vessel manufacturing. It provides high penetration and strength for large, thick-walled components.
Advantages of Circular Welding Systems:
- Consistency and Quality: Automated circular welding systems ensure uniform heat distribution, which results in consistent welds with minimal defects. The precise control of welding parameters eliminates the risk of human error, making the system ideal for high-quality production.
- Increased Production Speed: Automated welding systems work much faster than manual processes, significantly increasing throughput and production rates. The ability to rotate the workpiece continuously allows for faster welding of long seams, which is essential for large-scale manufacturing.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Circular welding systems reduce the need for skilled labor since the process is highly automated. This results in cost savings, as fewer operators are needed to manage the system.
- Flexibility: Many circular welding systems can be configured for a variety of materials and welding processes. This flexibility is essential for manufacturers that produce a wide range of products with different material types, thicknesses, and weld requirements.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern circular welding machines are designed with energy efficiency in mind, using variable speed drives, advanced cooling systems, and optimized welding techniques that minimize energy consumption.
- Safety: The fully automated nature of the circular welding system reduces the exposure of operators to hazardous conditions like the high temperatures, ultraviolet radiation, and fumes produced during the welding process.
- Reduced Material Waste: With precise control over the weld bead and heat input, circular welding systems can minimize material waste, leading to a more efficient use of raw materials and reduced production costs.
Applications:
- Pipe and Tube Manufacturing: Circular welding systems are frequently used in the production of pipes and tubes, particularly in industries like oil and gas, petrochemical, and water treatment, where pipes are welded continuously along their circumferences.
- Tank and Pressure Vessel Production: Many industries, including chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing, require tanks and pressure vessels with welded seams along their circumference. Circular welding machines can efficiently handle these large, cylindrical components.
- Automotive and Aerospace: Circular welding systems are used in automotive and aerospace applications, where precise and strong welds are required for exhaust systems, fuel tanks, and structural components.
- Shipbuilding: The shipbuilding industry also relies on circular welding systems for welding cylindrical sections of ships, submarines, and other maritime vessels.
- Storage Tanks and Silos: Circular welding machines are commonly used to weld large storage tanks, silos, and other cylindrical containers, ensuring structural integrity and leak-tight welds.
Conclusion:
In summary, circular welding systems are critical for industries that require high-quality, efficient welding of cylindrical or circular parts. Their automated nature, combined with advanced welding techniques like TIG, MIG, and laser welding, ensures that manufacturers can produce strong, consistent welds at a high rate of speed and with minimal material waste. As technology continues to advance, these systems will only become more precise, versatile, and energy-efficient, further expanding their role in modern manufacturing.
As circular welding systems continue to evolve, several emerging trends and technologies are enhancing their capabilities and further expanding their range of applications. The integration of advanced automation, AI-driven process control, and industry-specific customization is driving the next generation of circular welding systems, enabling even greater precision, efficiency, and adaptability.
Emerging Technologies in Circular Welding Systems:
- Industry 4.0 Integration: The rise of Industry 4.0 technologies is transforming circular welding systems into smarter, connected machines. By integrating Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and devices, circular welding systems can continuously monitor and collect real-time data during the welding process. This data is transmitted to cloud-based systems or central control hubs, allowing manufacturers to remotely track performance, adjust settings, and perform diagnostics. Industry 4.0-enabled welding systems not only improve operational efficiency but also enhance predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and avoiding unexpected equipment failures.
- AI and Machine Learning for Process Optimization: With the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, modern circular welding systems can autonomously adjust welding parameters based on real-time data analysis. By continuously analyzing data from sensors (such as heat, voltage, and current) during the welding process, AI algorithms can identify patterns and predict potential issues like weld defects, misalignment, or material inconsistencies. The system can then make on-the-fly adjustments to correct these issues, ensuring optimal weld quality with minimal manual intervention. This level of process optimization can lead to faster production cycles, less material waste, and improved weld consistency over time.
- Advanced Weld Inspection Systems: As the demand for higher-quality and defect-free welds increases, so does the importance of in-process weld inspection. Circular welding systems are increasingly equipped with advanced visual and thermal inspection systems, such as ultrasonic testing, X-ray imaging, and infrared sensors. These systems continuously monitor the weld during the process, allowing for real-time detection of defects like cracks, porosity, or undercutting. By automatically detecting potential flaws, these inspection technologies provide early warnings, enabling operators to take corrective action before defective parts are produced. This reduces the need for costly post-production inspections and rework, improving overall productivity.
- Robot-Assisted Welding and Automation: The growing use of robot-assisted welding in circular welding systems allows for greater flexibility and precision. Robotic arms, equipped with advanced sensors and vision systems, can move around the workpiece or adjust the welding parameters during the process. This technology is particularly valuable for handling complex geometries or specialized welding tasks that require high accuracy. Robots can also be programmed to perform secondary operations, such as cleaning, grinding, or inspecting the welds, further reducing the need for manual labor.
- Multi-Process Welding: Many modern circular welding systems are designed to support multi-process welding, which allows operators to switch between different welding techniques depending on the material, thickness, and desired weld characteristics. For example, a system may be capable of switching from TIG welding to MIG welding or laser welding, all within the same setup. This flexibility helps manufacturers save time and costs by using one system to meet various welding needs, especially when working with a diverse range of materials, such as steel, stainless steel, or aluminum.
- Additive Manufacturing and Hybrid Welding: The fusion of traditional welding techniques with additive manufacturing (3D printing) technologies is also gaining traction in circular welding systems. In hybrid welding, traditional welding methods are combined with additive manufacturing techniques to build up material layers in areas that require additional reinforcement. This capability is especially useful in industries that require complex geometries or repairs to high-value components. Hybrid systems also enable the creation of multi-material welds, where different materials are combined to optimize the final part’s strength, weight, or other properties.
- Enhanced Energy Efficiency: As manufacturers look for ways to lower their environmental footprint and reduce operational costs, energy-efficient circular welding systems are becoming increasingly important. Innovations like energy recovery systems, high-efficiency welding power sources, and improved cooling systems contribute to the reduced energy consumption of circular welding processes. By optimizing the energy used during the welding process, manufacturers can lower costs, improve their sustainability, and increase the overall efficiency of their operations.
- Advanced Cooling Systems: Effective cooling is critical in circular welding, especially when dealing with high-heat welding processes like laser welding or submerged arc welding. To address this, manufacturers are developing more efficient cooling systems, such as closed-loop coolant systems, which are better at maintaining the welding head and workpiece at optimal temperatures. These cooling systems not only increase the lifespan of the machine components but also help maintain the quality of the weld by preventing overheating or material distortion.
Benefits of Advancements in Circular Welding Systems:
- Higher Precision and Consistency: With the integration of advanced sensors, AI, and robotic technologies, modern circular welding systems offer higher precision and consistency than ever before. This is especially important in industries such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing, where even minor defects in welds can lead to product failures.
- Reduced Operational Costs: The adoption of automation, predictive maintenance, and energy-efficient systems significantly reduces operational costs. These advancements minimize downtime, reduce scrap rates, and lower energy consumption, contributing to more cost-effective production.
- Greater Flexibility and Customization: The ability to switch between multiple welding processes, utilize robotic arms, and integrate advanced inspection technologies makes modern circular welding systems more flexible and customizable. Manufacturers can adapt to a wider range of materials, part sizes, and welding requirements, enhancing their ability to serve diverse industries and production demands.
- Improved Safety: Automation reduces the need for human involvement in hazardous aspects of the welding process, such as exposure to high heat, intense light, and fumes. Additionally, AI-based inspection systems can detect potential hazards before they escalate, further improving workplace safety.
- Faster Turnaround Times: By automating the welding process and incorporating real-time adjustments, modern circular welding systems can significantly reduce production time. The ability to weld large, complex parts continuously without the need for frequent manual intervention accelerates production, which is crucial for industries with high demand or tight deadlines.
- Sustainability: Energy-efficient technologies, coupled with waste-reducing welding practices, help reduce the environmental impact of circular welding processes. By optimizing energy use, reducing waste materials, and improving process accuracy, manufacturers contribute to sustainability while enhancing their bottom line.
Applications in Emerging Markets:
- Renewable Energy: Circular welding systems are increasingly used in the production of components for the renewable energy industry, such as wind turbines, solar panel frames, and storage tanks for biogas and other renewable energy sources. The ability to produce strong, leak-proof welds is crucial in these applications to ensure long-lasting, reliable performance.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): As the demand for electric vehicles continues to grow, circular welding systems are playing a pivotal role in the production of components like battery casings, electric motor housings, and charging stations. The precise, high-quality welds required in these applications are perfectly suited for automation using circular welding technologies.
- Medical Device Manufacturing: The medical device industry, especially in the production of surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment, and implants, requires highly precise and clean welding processes. Circular welding systems, particularly those that use TIG or laser welding, are ideal for ensuring the integrity and sterility of these critical components.
- Oil and Gas Industry: Circular welding systems are essential in the oil and gas sector for manufacturing high-strength pipelines, pressure vessels, and storage tanks. The ability to produce strong, durable welds that can withstand extreme conditions, such as high pressure and corrosive environments, makes circular welding systems indispensable for these applications.
Conclusion:
As circular welding systems continue to advance with the integration of automation, AI, robotics, and data analytics, their capabilities are expanding beyond traditional applications to meet the demands of emerging industries. These innovations provide manufacturers with the tools they need to increase precision, efficiency, and sustainability in their welding operations. With their versatility, speed, and quality, circular welding systems will remain a key component in the manufacturing processes of a wide variety of industries, from renewable energy to aerospace.
The continuous development and refinement of circular welding systems hold the potential for even greater advancements in efficiency, quality, and versatility, all of which will play an increasingly important role in industries ranging from construction and automotive to aerospace and energy. The evolution of these systems is closely tied to broader technological trends, including automation, smart manufacturing, and sustainability. These trends are not only optimizing the welding process but also contributing to new applications that were previously not possible or economically feasible.
Further Technological Innovations in Circular Welding:
- Hybrid and Advanced Welding Techniques:
- As the demand for higher-performance materials grows, hybrid welding techniques are gaining traction. In a hybrid welding system, multiple processes are combined in one machine to take advantage of their individual strengths. For example, laser welding combined with MIG welding or laser welding combined with TIG welding allows manufacturers to achieve deep penetration with high welding speeds while minimizing heat distortion and achieving cleaner, more precise welds.
- The combination of additive manufacturing with traditional welding methods, known as hybrid additive-subtractive manufacturing, is also making significant strides. This approach allows for the deposition of material while simultaneously using welding methods to create structures that were previously difficult or time-consuming to build, such as intricate geometries and custom components.
- Advanced Materials for Welding:
- The use of new, high-strength, lightweight materials in industries like automotive and aerospace is pushing the boundaries of what circular welding systems can achieve. Materials like titanium alloys, high-strength steels, and advanced composites often require specialized welding techniques. Circular welding systems are evolving to handle these materials, utilizing advanced power sources and precision controls that ensure the integrity of the welds without compromising the material properties.
- Stainless steel, aluminum, and copper alloys are becoming more common in many industrial applications. As a result, circular welding systems must be equipped with specialized torches and wire feeds to ensure optimal compatibility with these materials, which often require different parameters for welding.
- Real-Time Process Control and Adaptive Feedback Loops:
- Smart sensors and adaptive feedback systems in circular welding systems are enabling even greater precision. These sensors monitor factors such as temperature, arc behavior, and material deformation in real-time, sending data to the system’s control unit. Based on the sensor inputs, the system automatically adjusts parameters like welding speed, heat input, and voltage. This real-time process control not only ensures weld quality but also reduces the likelihood of defects and minimizes the need for post-welding inspections.
- For example, adaptive welding systems can detect slight variations in the material surface, such as thickness changes or surface contamination, and adjust the welding parameters to compensate for these inconsistencies. This results in a more robust and flexible welding process that can adapt to real-world variations in materials and environmental conditions.
- Integration with Digital Twins:
- The concept of digital twins, which involves creating a virtual replica of a physical system, is starting to be applied to welding systems. By integrating a digital twin into a circular welding machine, manufacturers can simulate the entire welding process before it takes place. This helps identify potential issues in the design, process parameters, or materials before they arise in the real world. Using simulations, manufacturers can optimize welding strategies, reduce trial-and-error, and predict the outcomes of complex welds, ensuring higher-quality results right from the start.
- A digital twin can also enable predictive analytics, forecasting when a machine will require maintenance or when components may wear out, allowing manufacturers to schedule downtime more effectively and minimize unexpected interruptions.
The Role of Automation and Robotics:
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots):
- Cobots are increasingly being integrated into circular welding systems, particularly for tasks like loading and unloading workpieces, changing consumables, or performing secondary operations such as grinding, polishing, or inspecting welds. Cobots work alongside human operators, assisting them in tasks that require precision and dexterity. By reducing the amount of manual labor, these cobots not only increase productivity but also reduce the risk of operator fatigue and injury.
- The integration of cobots with vision systems and AI algorithms allows the robots to perform tasks with high accuracy. For example, a cobot can automatically adjust the positioning of a workpiece during the welding process, ensuring the alignment remains perfect throughout the cycle. This reduces human error and increases the consistency of the welds.
- Automated Workpiece Handling:
- Advanced automated workpiece handling systems are designed to move large or heavy cylindrical components into position for welding. These systems utilize conveyors, automated clamps, and rotating tables to position the workpieces accurately and securely during the welding process. By automating this part of the operation, circular welding systems can improve throughput and reduce human labor requirements, while also enhancing safety by minimizing the risk of manual handling accidents.
- Automated Welding Heads:
- Modern circular welding systems often use automated welding heads that can move in all directions along the workpiece. These welding heads are capable of adjusting to changes in the workpiece’s geometry or material characteristics, ensuring that each weld is uniform and defect-free. Articulated robotic arms or linear slides enable the welding head to follow intricate or irregular contours along the cylinder or tube.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability:
- Energy-Efficient Systems:
- As industries become more focused on sustainability, there is a growing emphasis on reducing energy consumption in welding processes. New innovations in power source design, such as inverter-based power supplies, have led to more energy-efficient circular welding machines. These power sources use less electricity and produce lower heat, which reduces operational costs and the overall carbon footprint of manufacturing processes.
- Additionally, energy recovery systems are becoming more common in circular welding systems. These systems capture excess heat generated during welding and use it to preheat materials or support other parts of the production process, further enhancing energy efficiency.
- Fume Extraction and Pollution Control:
- The fume extraction systems in modern circular welding machines are also advancing to improve air quality in welding environments. These systems use high-efficiency filters to capture harmful fumes and particulate matter generated during the welding process, ensuring that the working environment remains safe for operators. Some advanced systems also incorporate carbon capture technologies to mitigate the release of pollutants into the atmosphere, aligning with the growing need for environmentally responsible manufacturing practices.
- Reduction in Material Waste:
- As circular welding systems continue to improve, they are contributing to a reduction in material waste. The precision of modern welding processes ensures that less filler material is required, and the risk of material defects is minimized, reducing the amount of scrap material. The exact control over the welding process also allows for better material use, which is particularly important when working with costly or specialized materials.
- Eco-Friendly Consumables:
- The development of eco-friendly consumables, such as welding wires and fluxes, has also played a role in reducing the environmental impact of welding operations. These consumables are designed to minimize harmful by-products and to work effectively in conjunction with the latest circular welding systems.
Conclusion:
As circular welding systems continue to evolve, they are becoming more advanced, adaptable, and environmentally conscious. The integration of technologies like AI, robotics, advanced sensors, and predictive maintenance is enhancing the quality, speed, and precision of welding processes, enabling manufacturers to meet the growing demands for complex, high-performance products. These systems are also becoming more sustainable, with innovations in energy efficiency, material waste reduction, and pollution control helping manufacturers reduce their environmental footprint.
Circular welding systems will continue to be at the forefront of manufacturing innovation, providing solutions for industries as diverse as aerospace, automotive, renewable energy, and medical devices. By embracing new technologies and trends, manufacturers can not only improve their production capabilities but also position themselves for long-term success in an increasingly competitive global market.
Rotary Pipe Flange Welding Machine

A Rotary Pipe Flange Welding Machine is a specialized piece of equipment designed for the welding of flanges onto pipes. This machine is widely used in industries where pipe flanges need to be welded to pipelines, such as in the oil and gas, chemical, power generation, and construction sectors. These systems provide efficient and precise welding of flanges, ensuring secure and leak-proof connections between pipes in various applications.
Here’s an overview of a Rotary Pipe Flange Welding Machine:
Key Components of the Machine:
- Rotary Table:
- The core feature of the machine is a rotary table or rotating fixture that holds the pipe while the welding process occurs. This table is motorized and can rotate the pipe flange at a consistent speed to ensure uniform welds. The rotation eliminates the need for manual movement and ensures consistent weld bead formation as the weld head moves around the flange.
- Welding Head/ Torch:
- The welding head or torch is an essential part of the rotary welding machine. It holds the welding electrode (in the case of TIG welding or MIG welding) or the wire feed for processes such as submerged arc welding. This head is mounted on an adjustable arm and is positioned in relation to the rotating pipe flange to ensure an even, high-quality weld.
- Welding Power Source:
- The power source supplies the necessary electrical energy to the welding process. In a rotary pipe flange welding machine, the power source can be adjusted to control the voltage, current, and other parameters needed for specific welding techniques like TIG, MIG, or Stick welding.
- Clamping Mechanism:
- A set of clamps or a chuck is used to hold the pipe securely in place. These mechanisms ensure that the pipe does not move during the welding process, preventing alignment errors or distortion. The clamping system may vary based on the diameter and material of the pipe being welded.
- Torch Oscillation Mechanism:
- In some systems, an additional mechanism for torch oscillation may be included to improve the uniformity of the weld. This feature is particularly useful when welding larger diameter flanges to pipes, where a wider area needs to be covered by the weld.
- Cooling and Fume Extraction:
- Cooling systems are used to prevent overheating of the welding torch and the workpiece. These systems ensure that the welding process is stable, and the machine components remain at optimal temperatures.
- Fume extraction systems are often incorporated into rotary pipe flange welding machines to eliminate harmful fumes and gases produced during welding, ensuring a safer working environment.
Types of Welding Techniques Used:
- TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) Welding:
- Often used for high-quality welds on pipes and flanges, especially when dealing with thin materials or when a clean, smooth finish is required. The TIG welding process provides excellent precision and control over the welding arc, making it ideal for critical applications.
- MIG (Metal Inert Gas) Welding:
- MIG welding is a faster process than TIG welding and is often used for welding thicker materials. It is less sensitive to contamination and is typically employed for larger, industrial applications.
- Stick Welding (SMAW):
- Stick welding is an older, simpler technique that uses an electrode to create the weld. While it is less common in modern pipe welding systems, it may still be used in certain environments or for repairs.
- Submerged Arc Welding (SAW):
- Submerged arc welding is ideal for heavy-duty pipe welding, particularly when welding thicker pipes and flanges. In this process, the arc is submerged under a layer of flux, providing deep penetration and excellent weld strength.
Features of a Rotary Pipe Flange Welding Machine:
- Precise Welding Control:
- Rotary machines offer excellent control over welding speed, angle, and heat input, which ensures high-quality welds, reducing the risk of defects like porosity, undercutting, or incomplete fusion.
- Automation and Consistency:
- These machines provide a high degree of automation, minimizing human intervention and reducing the potential for error. This leads to more consistent and reliable welds, which is critical for maintaining pressure integrity in pipelines.
- Versatility in Pipe Sizes:
- Many rotary pipe flange welding machines are designed to accommodate a range of pipe sizes, allowing for versatile use in various projects. Adjustable clamps, rotary tables, and positioning arms enable the machine to work with both small and large-diameter pipes and flanges.
- Increased Productivity:
- By automating the welding process and eliminating the need for manual movement of the pipe, rotary pipe flange welding machines reduce the overall time required to weld flanges, thus increasing the efficiency and throughput of production.
- Operator Safety:
- The machine can be designed to keep the operator at a safe distance from the heat and fumes produced during the welding process. Automated features such as remote controls and robotic arms further reduce operator exposure to potentially hazardous conditions.
- Improved Quality and Strength of Welds:
- Rotary pipe flange welding machines provide uniform heat distribution and consistent weld bead formation, which results in stronger, more durable welds. This is particularly important for industries such as oil and gas and nuclear power, where the integrity of the welds must meet stringent standards.
Applications of Rotary Pipe Flange Welding Machines:
- Oil and Gas Industry:
- In the oil and gas sector, rotary pipe flange welding machines are crucial for welding flanges onto pipelines and equipment, ensuring a leak-proof seal and structural integrity of the entire system. The ability to produce high-quality, reliable welds is essential in this sector, where failures can lead to costly downtime and environmental hazards.
- Chemical and Petrochemical Plants:
- Chemical and petrochemical facilities require precise and leak-proof pipe connections for the transport of hazardous fluids and gases. Rotary pipe flange welding machines are used to ensure the safe and efficient operation of piping systems in these industries.
- Power Generation:
- In power plants, rotary pipe flange welding machines are used to weld flanges onto steam, gas, and water pipes that carry critical fluids. These welds need to withstand high pressure and temperature conditions, and the automated process ensures high-quality welds with minimal risk of defects.
- Shipbuilding and Marine Industry:
- In shipbuilding, particularly for large vessels or submarines, rotary pipe flange welding machines are used to weld pipe flanges in systems such as fuel, hydraulic, and cooling pipes. The precision and automation offered by these machines are critical in maintaining the structural integrity of the vessel.
- Construction Industry:
- Construction of large industrial facilities often requires extensive piping systems that require reliable and efficient flange welding. The use of rotary machines helps streamline these processes, ensuring that flanges are welded correctly and securely to pipes during the construction phase.
Conclusion:
A Rotary Pipe Flange Welding Machine is an essential tool for industries that require precise and high-quality welds between pipes and flanges. By automating the welding process, these machines improve weld quality, increase productivity, and ensure the safety and integrity of welded joints. The use of advanced welding techniques, coupled with automation and customization, makes rotary welding machines indispensable in fields like oil and gas, power generation, and chemical processing. With the growing demand for reliable piping systems, rotary pipe flange welding machines will continue to play a crucial role in ensuring the success of large-scale industrial projects.
Continuing from the previous explanation, let’s explore further developments and considerations for Rotary Pipe Flange Welding Machines, focusing on their evolving capabilities, enhancements in technology, and their impact on the industries that use them.
Evolving Technology in Rotary Pipe Flange Welding Machines:
- Advanced Control Systems:
- Modern rotary pipe flange welding machines are equipped with advanced digital control systems that allow operators to fine-tune welding parameters with great precision. These systems often include touch-screen interfaces, programmable controls, and pre-set welding profiles tailored for different materials and welding techniques. Operators can quickly select the correct settings for different projects, ensuring minimal downtime and greater flexibility.
- Data logging and monitoring features are now available, allowing real-time tracking of welding parameters such as voltage, current, speed, and temperature. These logs can be stored for future reference and quality assurance purposes, making it easier to monitor and maintain welding standards over time.
- Integration with CAD/CAM Systems:
- The integration of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software with rotary pipe flange welding machines has led to more accurate and optimized weld paths. Through this integration, machine operators can import 3D models directly from design software, ensuring that the flange and pipe are correctly aligned, and the welding path is precise from the very start.
- CAD/CAM systems enable the automation of custom flanges by generating precise welding paths that can be used with robotic arms or welding heads. This means that even highly customized or complex flange configurations can be welded with greater speed and accuracy.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning:
- AI and machine learning algorithms are increasingly being incorporated into rotary welding machines. These algorithms can analyze welding performance data in real-time and adjust welding parameters for optimal results. Over time, the machine “learns” from past welds and can make predictive adjustments, such as anticipating heat distortion or material inconsistencies before they happen.
- AI-powered vision systems are being integrated to ensure that the alignment between the pipe and the flange is perfect. These systems use high-resolution cameras and machine vision software to scan the joint and provide instant feedback, correcting the position of the pipe if necessary. This reduces human error and ensures that the finished welds are flawless.
- Remote Monitoring and Control:
- The rise of Industry 4.0 technologies has led to the development of remote monitoring and control systems for rotary welding machines. These systems allow operators to monitor the machine’s performance from a distance via cloud-based software. In addition, operators can remotely adjust welding parameters or even troubleshoot minor issues without having to be physically present at the machine.
- Remote diagnostics tools are also becoming more common, where sensors on the machine can send data to a cloud platform or local network. These tools analyze the data and provide recommendations on adjustments, maintenance schedules, or potential system issues. This ensures continuous performance and allows for predictive maintenance to minimize downtime.
Operational Benefits and Economic Impact:
- Reduced Material Costs:
- The precision of rotary pipe flange welding machines helps reduce material waste by ensuring that the correct amount of welding material is used. The high control over the heat input and weld bead formation reduces the need for excessive filler material, leading to cost savings.
- In addition, the improved quality of welds leads to fewer defective or reworked pieces, reducing material losses and the need for repairs.
- Labor Efficiency:
- Automation in rotary welding machines has significantly reduced the need for manual labor, especially in heavy industries. The automated welding process minimizes the need for workers to handle heavy pipes or perform repetitive tasks, which reduces the risk of injury and fatigue.
- Automation also leads to higher production rates. The rotating system, combined with automated welding heads, enables faster welds with fewer errors, increasing throughput and reducing production time. This makes rotary pipe flange welding machines highly efficient in large-scale manufacturing environments.
- Improved Quality Control:
- With features like real-time monitoring, welding parameter logging, and automated alignment systems, rotary welding machines ensure that each flange weld meets strict quality standards. This is critical in industries like oil and gas, where the integrity of welded joints can directly impact the safety and performance of the entire pipeline system.
- High-quality welds produced by these machines ensure strong, leak-proof connections, minimizing the risk of failure in harsh environments. This quality assurance also reduces the need for extensive post-welding inspections and testing, which can be costly and time-consuming.
- Reduction in Downtime:
- Automated troubleshooting and predictive maintenance features ensure that potential issues are detected early, reducing unexpected downtimes. For instance, sensors may detect wear on key components such as welding electrodes, and the system can alert operators before a failure occurs. This proactive approach to maintenance keeps production lines running smoothly and minimizes unscheduled downtime.
- Customization and Flexibility:
- Rotary welding machines can be configured to handle different pipe diameters, flange sizes, and materials. By offering customizable features, these machines can be adapted to various production needs. For example, some models include adjustable clamping systems or interchangeable welding heads that make them suitable for different project specifications.
- Modular systems are increasingly popular, where individual components of the machine can be upgraded or replaced as needed. This modular approach ensures that the machine can grow with evolving industry demands, such as the need to work with more exotic materials or thicker pipes.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Initial Investment Costs:
- While rotary pipe flange welding machines offer significant long-term benefits, their initial cost can be high. The complexity of the technology, including advanced controls, automation, and robotics, means that these machines can require a substantial investment upfront. However, the reduction in labor costs, improved weld quality, and increased productivity can lead to a return on investment (ROI) within a few years.
- Skilled Operators and Maintenance:
- Despite the automation, skilled operators are still required to manage the machine and ensure that the settings are optimal. Operators need to be familiar with the machine’s control systems and welding processes to get the best results.
- Additionally, regular maintenance and calibration are necessary to keep the machine functioning properly. Even though the system is largely automated, routine inspections and care are essential for maintaining high performance.
- Training Requirements:
- Due to the complexity of rotary welding machines and their advanced control systems, operators and maintenance personnel often require specialized training. Proper training programs ensure that workers can troubleshoot problems, optimize settings, and maintain high-quality production.
- Furthermore, as technologies like AI and machine vision continue to be integrated into these systems, operators will need to stay updated with the latest trends and features, which may require ongoing training and support.
Conclusion:
The Rotary Pipe Flange Welding Machine is an indispensable tool in modern industrial manufacturing, offering significant benefits in terms of quality, productivity, and efficiency. Through the use of automation, advanced control systems, and integration with cutting-edge technologies like AI and machine vision, these machines are improving the consistency and precision of welded pipe and flange connections across various industries.
While the initial investment and operational complexity may pose challenges for some manufacturers, the long-term advantages—such as reduced labor costs, material waste, and downtime—make rotary welding machines an essential part of large-scale production operations. As technology continues to evolve, these systems will only become more capable, efficient, and integral to the manufacturing process, helping industries meet the growing demand for strong, reliable, and cost-effective piping systems.
Continuing further, we will look at how Rotary Pipe Flange Welding Machines are evolving in terms of technological integration, future trends, and their continued importance across industries.
Future Trends in Rotary Pipe Flange Welding Machines:
- Robotic Integration:
- Robots are increasingly being integrated into rotary pipe flange welding systems to further automate the process. In many cases, robotic arms can be used to handle, position, and weld pipe flanges, reducing human intervention and increasing efficiency. These robots are equipped with advanced vision systems and sensors to ensure precise positioning of the pipe and flange, resulting in accurate welds even in difficult-to-reach areas.
- Robotic arms also improve flexibility in handling irregularly shaped or heavy flanges, offering more versatility in welding different configurations. Furthermore, the robots can work continuously, providing greater uptime and more consistent results.
- Advanced Welding Processes:
- Laser welding and electron beam welding are gaining traction as alternative welding methods in high-precision industries. Laser welding is a non-contact process that offers minimal heat input, resulting in finer welds with reduced distortion, ideal for thin-walled pipes or materials prone to heat damage.
- In addition to laser welding, electron beam welding provides deep penetration with minimal heat-affected zones, making it suitable for highly demanding applications where maximum strength and integrity are required.
- These methods are being incorporated into rotary pipe flange welding machines to provide additional options for manufacturers, further enhancing welding capabilities for a wide range of materials and pipe sizes.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) for Pipe Flanges:
- The incorporation of 3D printing technology into the welding process could revolutionize the production of pipe flanges. Additive manufacturing allows for the creation of custom flanges with unique geometries, reducing the need for traditional machining processes and reducing material waste.
- In the future, 3D printing could be used to create both the flanges and the welds in a single step. Rotary pipe flange welding machines may be adapted to work in conjunction with 3D printers to offer a more streamlined production process.
- Advanced Materials:
- As industries evolve and new materials are introduced, rotary pipe flange welding machines will need to be able to handle a variety of specialized materials such as composite pipes, high-strength alloys, or corrosion-resistant coatings. These materials often require specialized welding techniques and settings.
- Future machines will be equipped with more advanced sensors and control systems that can automatically adjust the welding parameters based on the material being welded. This will further improve the efficiency and precision of the welding process.
- Increased Customization and Flexibility:
- As demand grows for more customizable pipe and flange systems, rotary welding machines will evolve to provide even greater flexibility. Modular systems that allow for quick adjustments to accommodate various pipe sizes, flange geometries, and welding techniques will become more common.
- Furthermore, machines may include multi-functional heads that can perform different welding processes (e.g., TIG, MIG, laser) within the same system. This will allow operators to tailor the welding approach based on the project’s specific requirements, reducing the need for multiple machines.
- Sustainability and Energy Efficiency:
- In response to growing environmental concerns, manufacturers are focusing on making rotary pipe flange welding machines more energy-efficient and sustainable. These machines are being designed to minimize energy consumption during the welding process, reducing both costs and the carbon footprint of manufacturing operations.
- Additionally, green welding technologies such as using low-emission gases, recycling welding materials, and reducing waste in the welding process are becoming more popular. Manufacturers are also focusing on reducing the amount of heat generated during welding to minimize energy consumption and reduce cooling requirements.
- Smart Features and IoT Integration:
- The Internet of Things (IoT) is making its way into welding machines, including rotary pipe flange welding systems. Through IoT, machines can be connected to a central database or cloud platform, allowing for real-time data collection and monitoring.
- Operators can track welding performance, machine diagnostics, and maintenance schedules remotely, improving the predictive maintenance capabilities. IoT-enabled systems can send alerts about potential issues before they become critical, allowing for faster troubleshooting and minimal downtime.
- The smart capabilities of these machines will also enable manufacturers to better manage production schedules, ensuring that the machines are running at peak efficiency.
- Artificial Intelligence in Quality Control:
- AI-powered vision systems and machine learning algorithms are being integrated into rotary pipe flange welding machines to improve quality control. These AI systems analyze the welds in real-time, detecting issues such as porosity, undercuts, and improper bead formations.
- AI can also predict the optimal welding conditions, automatically adjusting settings based on data gathered from previous welds. Over time, the system learns from a vast dataset of welding jobs, helping to ensure that each weld is as perfect as possible.
- Wearable Technology for Operators:
- Future advancements in wearable technology could provide operators with augmented reality (AR) or virtual reality (VR) devices that give real-time feedback and troubleshooting information. For example, AR glasses could overlay information about the welding process directly onto the operator’s field of view, helping them make adjustments without needing to leave the work area.
- Additionally, wearable exoskeletons could assist operators by supporting heavy lifting or maintaining posture, reducing physical strain during manual tasks. These innovations would help increase the comfort and safety of operators working with rotary pipe flange welding machines.
Impact on Industry Sectors:
- Oil and Gas Industry:
- The oil and gas industry heavily relies on the safe, efficient, and reliable transportation of oil and gas through pipelines. With increasing demands for higher quality and pressure-resistant pipelines, rotary pipe flange welding machines will play an even more critical role in maintaining the integrity of pipeline systems.
- Offshore drilling operations, in particular, will benefit from more automated welding solutions, where difficult working conditions can often hinder the welding process. Robotic arms and remotely operated welding systems will help perform precise welds even in extreme conditions.
- Chemical and Petrochemical Industries:
- In the chemical industry, pipes carry highly corrosive substances that require robust, leak-proof welds. Rotary welding machines, integrated with advanced materials handling and AI-driven monitoring systems, will ensure that the welded flanges can withstand harsh chemicals and extreme pressures.
- Petrochemical plants will use these advanced welding machines to maintain their extensive piping networks, which carry flammable and toxic materials. The ability to automate the welding process also reduces the risk of human error and enhances the safety of these critical infrastructure systems.
- Nuclear and Power Generation:
- In the nuclear industry, welding plays a crucial role in ensuring that pipes and flanges are sealed perfectly to avoid any leaks in systems that handle radioactive fluids or gases. Rotary pipe flange welding machines will continue to play a key role in maintaining the integrity and safety of these highly sensitive systems.
- Power generation plants also use these machines to weld flanges onto piping systems that carry steam, gas, and water. The ability to achieve precise welds ensures the plant’s efficient operation and reduces the chances of leaks or failures that could disrupt power generation.
- Shipbuilding and Aerospace:
- The shipbuilding industry, particularly for large vessels like tankers and cargo ships, will continue to rely on rotary pipe flange welding machines for the installation of piping systems that must operate under extreme conditions (e.g., high pressure, temperature, and corrosive environments).
- Similarly, aerospace companies are beginning to explore the use of advanced welding systems for the construction of pipelines and fuel systems within spacecraft. The precision and reliability of rotary welding machines are critical for these high-tech applications.
- Construction Industry:
- In the construction of large-scale industrial facilities, commercial buildings, and infrastructure, rotary pipe flange welding machines are essential for ensuring the quick and reliable installation of piping systems. The versatility of these machines allows them to be used in a variety of construction environments, improving project timelines and reducing the need for rework.
- As smart buildings and green construction projects become more popular, the demand for reliable piping systems that are safe, durable, and energy-efficient will increase, further highlighting the importance of efficient rotary pipe flange welding solutions.
Conclusion:
Rotary Pipe Flange Welding Machines are at the forefront of revolutionizing welding processes across multiple industries. As they continue to evolve with technological advancements, such as robotics, AI, and 3D printing, their ability to automate complex tasks, improve weld quality, and ensure safety will make them even more valuable to the manufacturing process.
These machines are an integral part of ensuring the strength and reliability of critical infrastructure, including pipelines, power plants, chemical facilities, and even space exploration technologies. The ongoing innovation in these systems will not only make welding more efficient but also provide more sustainable, customizable, and smarter solutions that can meet the growing demands of industries worldwide. With automation, better control systems, and the integration of AI, the future of rotary welding machines looks promising, promising even greater precision, efficiency, and productivity across industrial applications.
Boom Welding Machine

A Boom Welding Machine is a specialized type of welding equipment designed for large-scale, industrial applications. It is primarily used in environments where long or large components need to be welded with high precision and efficiency. The machine features a boom arm that holds the welding torch or head and can move along a designated path to provide automated welding for various types of joints, such as longitudinal or circumferential welds.
Key Features and Components of a Boom Welding Machine:
- Boom Arm:
- The boom arm is the central element of the machine. It is a long, extendable arm that allows the welding torch or head to reach and weld long sections of metal. The arm can often be adjusted or extended to accommodate various sizes of components or structures.
- The arm is usually mounted on a track or rail system to ensure smooth, accurate movement, and it can also pivot or rotate for flexible operation in different positions.
- Welding Head:
- The welding head is attached to the boom arm and holds the welding torch or electrode. The welding head is often equipped with advanced control systems that enable automatic adjustment of the welding parameters, including speed, heat input, and electrode feed rate.
- Some advanced welding heads are also equipped with vision systems or sensors to automatically monitor and adjust the welding process, ensuring consistent quality.
- Track or Rail System:
- A track or rail system supports the boom and guides its movement along the surface of the workpiece. This allows the machine to maintain a precise welding path, which is essential when working with long pipes, vessels, or other large structures.
- These systems can be configured in various ways, such as straight tracks for linear welding or curved tracks for welding around cylindrical components.
- Control System:
- Modern boom welding machines come equipped with advanced digital control systems. These systems allow operators to program and control the welding parameters, including the speed, position, and motion of the welding torch. Operators can store welding profiles for different materials or components, ensuring consistent results.
- Some machines include automated programs for specific tasks (e.g., pipe welding, tank welding) to simplify operation and reduce the need for manual adjustments.
- Drive Mechanism:
- The boom arm is typically moved using an electric or hydraulic drive system. These systems provide smooth, controlled movement to position the welding head accurately along the length of the workpiece.
- The drive system often includes a servo motor or gear system to enable fine adjustments and high precision during welding.
- Cooling and Protection Systems:
- Welding can generate significant heat, so boom welding machines are often equipped with cooling systems to prevent overheating of components like the torch or welding head. Water-cooled torches or fan cooling systems are commonly used.
- The machine may also include protective enclosures or fume extraction systems to ensure a safe working environment by removing harmful welding fumes and providing protection against splatter and heat.
Types of Welding Processes Used:
- MIG (Metal Inert Gas) Welding: Frequently used in boom welding machines for its ability to provide high-speed, high-quality welds, especially for non-ferrous metals like aluminum and steel.
- TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) Welding: Common for more precise, high-quality welds in industries like aerospace and automotive.
- Stick Welding (SMAW): In certain applications, stick welding may be used, particularly in more rugged environments where portability and ease of use are important.
- Submerged Arc Welding (SAW): This process is sometimes used in boom welding machines, particularly for welding large components like thick steel plates or pipes.
Applications of Boom Welding Machines:
- Pipe Welding:
- Boom welding machines are widely used in the oil and gas industry for welding pipelines. They can quickly weld long, continuous joints on large-diameter pipes, especially in fields like pipeline construction and offshore operations.
- The precise movement of the boom allows for high-quality circumferential and longitudinal welds, even in remote locations or harsh environments.
- Shipbuilding:
- In the shipbuilding industry, boom welding machines are used for welding large sections of ships and marine vessels. They help automate the welding process for critical components like hulls, tanks, and decks.
- The flexibility and reach of the boom allow for effective welding of hard-to-reach areas, contributing to faster and more accurate production.
- Tank Welding:
- For the storage tank manufacturing industry, boom welding machines are used to weld large cylindrical tanks. The machine’s ability to follow the circumference of the tank ensures uniform, high-quality welds, which are crucial for tank integrity, especially in industries such as chemical storage, oil refineries, and water treatment plants.
- Heavy Machinery and Structural Fabrication:
- In the heavy equipment manufacturing and structural steel fabrication industries, boom welding machines can be used to weld large beams, frames, and other components used in machinery, buildings, or bridges.
- The ability to weld long seams quickly and accurately contributes to enhanced productivity and ensures that welds meet strict engineering and safety standards.
- Pressure Vessel Manufacturing:
- Boom welding machines are commonly used to weld pressure vessels and reactor components in industries like nuclear, chemical, and petrochemical. These vessels require precise, high-strength welds to maintain their integrity under pressure, making boom welding an ideal solution.
Advantages of Boom Welding Machines:
- Increased Productivity:
- With automated movements and pre-programmed settings, boom welding machines can complete large welds much faster than manual welding processes, significantly increasing production throughput.
- The machine’s precision ensures consistent results, reducing the need for rework and reducing overall production time.
- Improved Weld Quality:
- The automated and controlled movement of the welding torch ensures high-quality, uniform welds with minimal defects. This is especially important in industries where structural integrity is critical, such as in the aerospace, automotive, and shipbuilding sectors.
- The machine’s ability to apply consistent heat and filler material leads to strong, durable welds, which are essential for safety and performance.
- Reduced Labor Costs:
- With the automation provided by boom welding machines, manufacturers can reduce the number of skilled workers required for welding tasks. This helps to lower labor costs and allows workers to focus on more complex tasks that require manual intervention.
- Automation also reduces the risk of human error, ensuring that the welds meet high-quality standards and minimizing the need for costly rework.
- Enhanced Safety:
- The automation of the welding process allows workers to be positioned at a safe distance from the welding area, reducing the risk of exposure to welding fumes, intense heat, and UV radiation.
- Many boom welding machines are equipped with built-in safety features, such as automatic shutdown in case of malfunction, protective shields to prevent accidents, and advanced cooling systems to prevent overheating.
- Flexibility and Customization:
- Boom welding machines can be adapted to various types of welding processes and workpieces, making them suitable for different industries and applications. With modular attachments and configurable settings, these machines can handle a wide range of welding tasks, from small components to large, complex structures.
- Machines can also be customized to fit specific operational needs, whether it’s for pipe welding, tank welding, or shipbuilding.
Conclusion:
Boom Welding Machines offer a powerful and efficient solution for industrial welding tasks, especially in sectors that require large-scale, high-quality welds. Their flexibility, speed, and precision make them indispensable in industries such as pipeline construction, shipbuilding, and pressure vessel manufacturing.
By automating the welding process, boom welding machines not only improve productivity and weld quality but also reduce labor costs and enhance safety for operators. As technology continues to advance, these machines will likely become even more automated, incorporating features such as robotic arms, AI-based control systems, and IoT integration, further enhancing their capabilities and the industries they serve.
Technological Advancements in Boom Welding Machines:
- Automation and Adaptive Welding Systems:
- Adaptive welding systems are a major development in boom welding machines. These systems automatically adjust welding parameters like speed, voltage, and wire feed rate in real time, depending on the material being welded. The ability to adapt to changes in the material or welding conditions increases the overall quality and efficiency of the welding process.
- Automatic path tracking systems are integrated into boom welding machines to follow pre-programmed paths on complex geometries. These systems are typically coupled with vision sensors or laser scanners that constantly monitor the welding area to ensure the welding head stays on track, regardless of any small shifts or misalignments.
- Advanced Welding Power Sources:
- Modern boom welding machines can be paired with advanced welding power sources that deliver more precise and stable arcs. These systems are equipped with inverter technology, which provides high-quality welds at reduced energy consumption.
- Some machines now integrate multi-process welding capabilities, allowing operators to switch seamlessly between welding methods like MIG, TIG, or Stick welding, depending on the specific application and material requirements.
- Real-Time Data Monitoring and Feedback Systems:
- Many newer boom welding machines are equipped with real-time monitoring systems that continuously track parameters like arc stability, heat input, and weld penetration. These systems alert operators if any parameters deviate from the desired range, allowing immediate corrective actions before defects occur.
- Integration with cloud-based platforms can allow for remote monitoring and diagnostics, enabling service teams to analyze machine performance and address potential issues without being physically on-site.
- Use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Quality Control:
- AI-powered algorithms are being employed to inspect and ensure the quality of the weld during the process. Using machine learning, these systems can compare the actual weld with an ideal weld profile, identifying defects like cracks, porosity, or lack of fusion in real-time.
- This integration helps ensure that the final weld quality meets industry standards and eliminates the need for time-consuming manual inspections.
- Energy-Efficient and Eco-Friendly Systems:
- As with many modern industrial machines, energy efficiency is becoming a significant focus in boom welding machines. Manufacturers are designing machines that require less energy while maintaining high welding performance. This includes using low-voltage, high-efficiency power sources, as well as integrating energy recovery systems that capture and reuse heat during the welding process.
- Additionally, some systems have been designed with environmental sustainability in mind. For example, advanced exhaust and fume extraction systems ensure that welding fumes and gases are captured and filtered, reducing the environmental impact of the operation.
Operational Benefits of Boom Welding Machines:
- High Precision and Consistency:
- One of the primary benefits of a boom welding machine is its ability to maintain high precision across long, continuous welds. The automation ensures that the welding head follows a consistent path, creating uniform bead patterns and high-quality welds throughout the entire joint.
- This is especially important in industries like aerospace, shipbuilding, and pressure vessel manufacturing, where even the smallest deviation in a weld can lead to structural failure.
- Improved Weld Penetration and Heat Control:
- The automated control systems in boom welding machines allow for better control over the heat input, helping to optimize weld penetration. This reduces the risk of undercutting, burn-through, or distortion of thin-walled materials, ensuring a stronger bond without damaging the workpiece.
- This level of heat control is particularly beneficial in welding high-strength materials or sensitive alloys, where precision is critical for both performance and safety.
- Reduced Downtime and Enhanced Productivity:
- Automation reduces the reliance on manual labor, which in turn minimizes downtime caused by human error or fatigue. Once programmed, the machine can operate continuously, producing welds at a faster rate compared to manual processes, increasing overall productivity.
- This constant, high-speed operation is ideal for industries with high-volume production needs, such as pipeline construction, tank manufacturing, and industrial equipment fabrication.
- Versatility for Large and Complex Projects:
- Boom welding machines are often used for projects that involve large, heavy components that are difficult to weld manually. Their ability to move along tracks or rails and reach difficult positions allows them to handle a variety of complex projects that would otherwise require multiple machines or manual labor.
- Whether it’s welding cylindrical tanks, pipes, or large plates, the boom welding machine provides a versatile solution for welding in confined spaces, high locations, or other challenging environments.
- Enhanced Safety:
- By automating the welding process, boom welding machines help reduce worker exposure to welding hazards such as UV radiation, molten metal, and harmful fumes. Workers are often positioned in more secure areas, reducing the risk of burns, eye injuries, or inhalation of toxic fumes.
- Additionally, many machines feature safety mechanisms like automatic shutoffs if a malfunction is detected, preventing damage to both the operator and the machine.
Challenges of Boom Welding Machines:
- Initial Investment Cost:
- One of the most significant challenges when acquiring a boom welding machine is the high initial cost. These machines require substantial capital investment, particularly when integrating advanced features like robotics, adaptive welding systems, and AI-powered monitoring. However, this cost is often offset by the long-term savings in labor, energy, and time.
- Maintenance and Technical Expertise:
- Like any industrial machine, boom welding machines require regular maintenance and servicing to ensure that they continue to operate efficiently. The complexity of the machinery, especially when incorporating automated and robotic elements, may require specialized technicians for maintenance and repairs, which can be costly and time-consuming.
- Regular calibration and troubleshooting are essential for ensuring that the machine is operating within the required parameters and producing high-quality welds.
- Limited Mobility:
- While the boom arm provides reach and flexibility for certain applications, mobility can sometimes be a limitation. In cases where the workpieces are irregularly shaped or need to be moved frequently, the machine’s fixed nature or reliance on tracks may present challenges. Some systems are portable, but they are often limited in size and capability compared to larger, fixed units.
- Material Compatibility:
- While modern boom welding machines are adaptable to various materials, there may still be challenges in welding certain materials or combinations of metals. For example, welding dissimilar materials (e.g., steel to aluminum) or highly reflective metals may require specialized equipment or settings that can add complexity to the welding process.
- Operator Training:
- The advanced technology in boom welding machines means that operators must undergo specialized training to effectively use the system. Operators need to understand complex control systems, interpret feedback from monitoring systems, and make adjustments as needed to ensure high-quality welds. Lack of proper training can lead to inefficiencies or mistakes, impacting weld quality and project timelines.
Conclusion:
Boom welding machines offer tremendous advantages for industries that require high-precision, high-efficiency welding of large components. With automation, advanced control systems, and improved safety features, these machines are capable of delivering high-quality welds with minimal human intervention, significantly improving productivity, reducing costs, and enhancing overall weld integrity.
However, the high initial cost, maintenance needs, and operator expertise requirements should be carefully considered when investing in boom welding machines. As technology continues to advance, innovations in automation, robotics, and AI integration are likely to make these machines even more effective, versatile, and accessible for a broader range of industries.
In summary, boom welding machines are essential for modern industries that require large-scale, high-quality welding solutions, and their continued development will further enhance their ability to meet the demands of an increasingly automated and precision-driven manufacturing world.
Future Trends in Boom Welding Machines:
- Integration with Robotic Welding Systems:
- Robotic arms integrated with boom welding machines will continue to enhance their functionality. By combining the precision of robotics with the flexibility of the boom arm, manufacturers can achieve multi-axis movement for even more complex welds and geometries. This would expand the range of applications from industrial manufacturing to research and development of highly specialized products.
- Robots can handle the welding torch while also incorporating additional functions such as part positioning or post-weld inspections. The integration of robots allows for improved speed, accuracy, and consistency in complex or repetitive tasks.
- Additive Manufacturing and Welding Fusion:
- The field of additive manufacturing (3D printing) is increasingly converging with traditional welding processes. In the future, boom welding machines might integrate additive manufacturing capabilities, allowing for the creation of complex structures directly from a CAD model by depositing material layer by layer during the welding process.
- This hybrid approach could enable manufacturers to build large parts or make repairs directly on-site without the need for expensive molds or casting. It’s a perfect synergy for industries like aerospace, automotive, or oil & gas, where lightweight, durable, and complex components are in demand.
- IoT and Data-Driven Welding:
- Internet of Things (IoT) technologies are likely to play a pivotal role in future boom welding machines. These machines will be able to collect data during welding processes and communicate it to cloud platforms for real-time analysis.
- Predictive maintenance can be achieved by analyzing this data to foresee potential failures, reducing unplanned downtime. Operators could receive notifications about equipment performance and suggested adjustments to improve weld quality or efficiency.
- Additionally, machine learning algorithms could help continuously optimize welding parameters based on historical data, improving weld quality over time.
- Increased Automation with AI:
- The role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in boom welding will continue to grow. AI-driven vision systems could be used to inspect the quality of each weld in real time, comparing the weld to pre-programmed standards. This would allow the machine to make corrections instantly, significantly reducing errors and improving productivity.
- AI will also facilitate self-learning systems where machines improve their welding capabilities by analyzing past operations. This self-optimization can further enhance consistency and speed, leading to fewer defects, better-quality welds, and more cost-effective operations.
- Increased Use of Augmented Reality (AR):
- Augmented Reality (AR) can be used to enhance operator interaction with the welding machine. By superimposing digital information onto the operator’s field of view, AR can assist operators in identifying key parameters such as welding temperature, speed, and material thickness in real-time. This ensures greater accuracy in the welding process.
- For training purposes, AR could be used to simulate different welding scenarios, allowing operators to familiarize themselves with machine settings and troubleshooting techniques without the need for physical machines.
- Robust Materials and Energy Efficiency:
- Future boom welding machines may use more energy-efficient components, such as advanced inverter-based power supplies. These systems provide higher efficiency by reducing energy consumption while maintaining consistent weld quality, which is crucial for reducing operational costs.
- The trend towards environmentally friendly materials could see a shift in the types of welding wires and consumables used in boom welding machines. Companies may look for low-emission or recyclable materials to meet environmental standards and improve sustainability.
Integration with Other Systems:
- MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems):
- Boom welding machines are increasingly being integrated with Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES). MES is responsible for tracking and controlling the entire production process, from raw materials to finished goods. By connecting boom welding machines to MES, manufacturers can achieve better production planning, resource allocation, and workflow management.
- This integration allows for real-time monitoring of each weld, ensuring it meets quality standards and enabling manufacturers to quickly identify any deviations in the process. This also allows for better tracking of inventory, machine usage, and work orders.
- CAD/CAM Systems:
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) systems can be seamlessly integrated with boom welding machines. These systems help design the weld path, material requirements, and process parameters before the welding begins.
- The integration allows for a direct link between design and manufacturing, ensuring that the machine can automatically adjust to the specific requirements of each part, even if the designs are modified or updated in real-time.
- ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) Systems:
- ERP systems will be crucial in integrating boom welding machines with broader business operations. These systems help streamline everything from inventory management to order fulfillment and workforce scheduling.
- By integrating ERP systems, manufacturers can ensure that the welding process is synchronized with other stages of production, reducing lead times and improving overall production efficiency.
- Automated Material Handling Systems:
- Many industries that utilize boom welding machines are implementing automated material handling systems like robotic arms or conveyor belts to transport workpieces to and from the welding stations. Integrating boom welding machines with these systems enhances the overall speed of the production line by minimizing manual labor and improving material flow.
- Automated systems can transport large components that would be difficult or dangerous for human workers to handle manually, providing an added layer of safety and efficiency.
Long-Term Impact on Industries:
- Manufacturing Efficiency:
- Boom welding machines will continue to improve manufacturing efficiency by reducing cycle times and minimizing waste. The automation of repetitive tasks allows human workers to focus on higher-level tasks such as quality control, system maintenance, and design innovation.
- As automation increases, manufacturers can scale up production without a corresponding increase in labor costs, which is critical in industries where demand fluctuates or where tight margins exist.
- Global Supply Chain Optimization:
- With advanced technologies like remote diagnostics, cloud-based monitoring, and real-time data sharing, boom welding machines can play a role in global supply chain optimization. Manufacturers can monitor operations across different geographies, troubleshoot remotely, and ensure that projects are completed on time, regardless of location.
- For industries like aerospace and oil and gas, where projects often require a global workforce and international collaboration, the ability to control welding processes from a distance can significantly improve operational efficiency and reduce logistical complexity.
- Quality Assurance and Compliance:
- With increasing demands for high-quality welds in industries like nuclear power, shipbuilding, and automotive manufacturing, the precision offered by boom welding machines will ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations.
- Automated inspection features like in-line ultrasonic testing or visual inspection using AI will be able to detect defects during the welding process, ensuring that the final product meets all necessary standards and reduces the likelihood of failures down the line.
- Labor Market Shift:
- While automation with boom welding machines reduces the need for manual labor, it also creates opportunities for skilled technicians and automation specialists. These workers will need advanced training in operating, programming, and maintaining these highly sophisticated machines.
- The shift toward automation will require a re-skilling of the labor force, with a focus on technical expertise and problem-solving. Additionally, it may lead to a reduction in demand for certain traditional welding roles while increasing demand for roles focused on machine operation and maintenance.
- Cost Reduction and Competitive Advantage:
- Manufacturers that adopt boom welding machines can gain a competitive advantage by reducing their production costs, improving weld quality, and speeding up their time to market. This can be especially valuable in industries that deal with large-scale projects or that operate in highly competitive markets.
- The ability to automate complex welding tasks will allow companies to offer products with improved durability and performance at competitive prices, making them more attractive to customers.
Conclusion:
The future of boom welding machines is closely tied to advancements in automation, robotics, AI, and IoT technologies. These machines are evolving from simple welding tools to integrated manufacturing solutions that enable industries to improve efficiency, quality, and safety while reducing costs.
Boom welding machines are already crucial in sectors like pipe welding, shipbuilding, and heavy machinery manufacturing, and their role will continue to expand. The integration of these machines with other systems, coupled with advances in machine learning and real-time data analytics, will provide manufacturers with powerful tools to streamline operations and stay competitive.
While there are challenges such as high initial investment and the need for specialized expertise, the long-term benefits—such as improved productivity, consistent weld quality, and operational flexibility—make boom welding machines an essential investment for industries looking to meet the growing demands of the global market. With continued advancements, these machines will play an even more critical role in shaping the future of modern manufacturing.
EMS Metalworking Machinery: Your Trusted Partner in Precision Metalworking

EMS Metalworking Machinery is a leading manufacturer of high-quality metalworking equipment, dedicated to providing innovative solutions that meet the evolving needs of industries worldwide. With a rich history of excellence and a commitment to technological advancement, we have earned a reputation for delivering cutting-edge machinery that ensures precision, efficiency, and durability.
Our Product Range:
- CNC Spinning Lathes: From precision bench lathes to heavy-duty industrial models, our lathes offer unmatched accuracy and performance for a wide range of applications, including machining shafts, gears, and other cylindrical components.
- Trimming Beading Machine: Our trimming beading machines are designed to provide exceptional cutting capabilities and versatility, enabling you to create complex shapes and intricate details with ease. Whether you need a horizontal or vertical trimming machine, we have the perfect solution for your needs.
- Hydraulic Deep Drawing Press Machines: Our hydraulic deep drawing press machines are built to deliver precise and powerful drawing operations, ensuring clean holes and exceptional surface finishes. We offer a comprehensive range to suit various applications.
- Grinding Machines: Our grinding machines are engineered for precision and efficiency, allowing you to achieve the highest levels of surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Whether you need a surface grinder, cylindrical grinder, or tool grinder, we have the equipment to meet your specific requirements.
- Sawing Machines: Our sawing machines are designed for fast and accurate cutting of metals, providing clean cuts and minimal burrs. From band saws to circular saws, we offer a variety of options to suit different materials and cutting needs.
- Custom Machinery: In addition to our standard product line, we also specialize in custom machinery fabrication. Our experienced engineers can work with you to design and build tailored solutions that meet your unique requirements and optimize your production processes.
Why Choose EMS Metalworking Machinery:
- Quality: Our machines are crafted with the highest quality materials and components, ensuring long-lasting performance and reliability.
- Precision: We are committed to delivering machinery that meets the most stringent tolerances and standards, ensuring exceptional accuracy in your metalworking operations.
- Innovation: We continuously invest in research and development to stay at the forefront of technological advancements, offering innovative solutions that enhance your productivity and efficiency.
- Customer Support: Our dedicated team of experts is always available to provide comprehensive support, from machine selection and installation to maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Customization: We understand that every business has unique needs, and we offer flexible customization options to tailor our machines to your specific requirements.
At EMS Metalworking Machinery, we are more than just a supplier of equipment; we are your trusted partner in metalworking success. By choosing EMS, you can be confident in the quality, reliability, and performance of your machinery, enabling you to achieve your business goals and stay ahead of the competition.
EMS Metalworking Machinery
We design, manufacture and assembly metalworking machinery such as:
- Hydraulic transfer press
- Glass mosaic press
- Hydraulic deep drawing press
- Casting press
- Hydraulic cold forming press
- Hydroforming press
- Composite press
- Silicone rubber moulding press
- Brake pad press
- Melamine press
- SMC & BMC Press
- Labrotaroy press
- Edge cutting trimming machine
- Edge curling machine
- Trimming beading machine
- Trimming joggling machine
- Cookware production line
- Pipe bending machine
- Profile bending machine
- Bandsaw for metal
- Cylindrical welding machine
- Horizontal pres and cookware
- Kitchenware, hotelware
- Bakeware and cuttlery production machinery
as a complete line as well as an individual machine such as:
- Edge cutting trimming beading machines
- Polishing and grinding machines for pot and pans
- Hydraulic drawing presses
- Circle blanking machines
- Riveting machine
- Hole punching machines
- Press feeding machine
You can check our machinery at work at: EMS Metalworking Machinery – YouTube
Applications:
- Beading and ribbing
- Flanging
- Trimming
- Curling
- Lock-seaming
- Ribbing
- Flange-punching