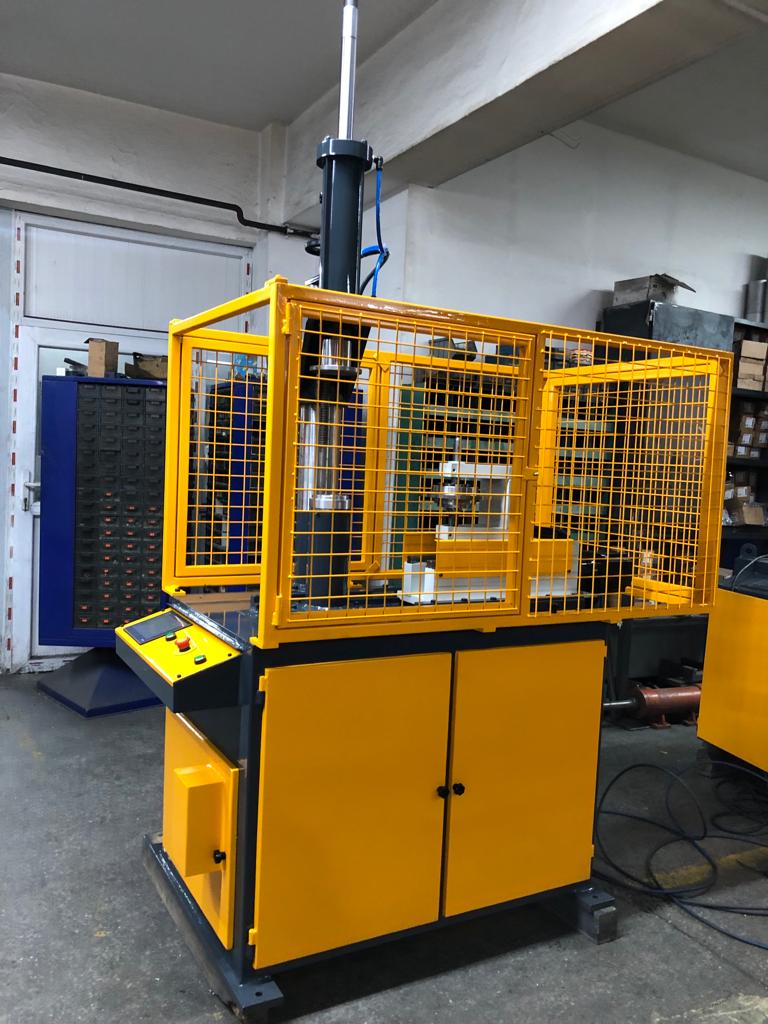

An edge cutting trimming beading curling machine is a device that has a set of blades that rotate at high speed in order to cut and trim sheet metal.
An edge cutting trimming beading curling machine is a versatile tool used in metalworking to simultaneously trim, form, and curl the edges of sheet metal components. It combines the functions of edge cutting, trimming, beading, and curling, saving time and effort compared to performing these operations separately.
Edge Cutting
Edge cutting involves removing excess material from the edges of a sheet metal workpiece. This is often done to ensure uniform dimensions, remove burrs or imperfections, or prepare the edge for further processing. The edge cutting operation of an edge cutting trimming beading curling machine typically involves a rotating cutting blade or disc that precisely cuts the edge of the workpiece. The blade or disc is typically made of a high-strength material, such as tungsten carbide, to maintain sharpness and edge retention.
Trimming
Trimming involves removing a small amount of material from the edge of a sheet metal workpiece to achieve a clean, uniform edge. This is often done to prepare the edge for further processing, such as beading or curling. The trimming operation of an edge cutting trimming beading curling machine typically involves a series of rollers or dies that press against the edge of the workpiece, removing a precise amount of material. The rollers or dies are typically made of a hard, wear-resistant material, such as steel or hardened plastic, to ensure long-term durability.
Beading
Beading involves creating a raised edge or bead along the periphery of a sheet metal component. Beading enhances the strength, rigidity, and aesthetics of the component, and it can also provide a mounting surface or a seal for joints. The beading operation of an edge cutting trimming beading curling machine typically involves a series of rollers or dies that form the bead or flange along the edge of the workpiece. The rollers or dies are typically made of a hard, wear-resistant material, such as steel or hardened plastic, to ensure long-term durability.
Curling
Curling involves rolling the edge of a sheet metal component into a cylindrical or conical shape. Curling enhances the strength, rigidity, and aesthetics of the component, and it can also provide a protective barrier against sharp edges. The curling operation of an edge cutting trimming beading curling machine typically involves a rotating curling tool or die that presses against the edge of the workpiece, causing it to roll into the desired shape. The curling tool or die is typically made of a hard, wear-resistant material, such as steel or hardened plastic, to ensure long-term durability.
Synchronized Operation
The edge cutting, trimming, beading, and curling operations are synchronized, ensuring that all four processes occur simultaneously along the edge of the workpiece. This synchronization saves time and effort compared to performing these operations separately.
Control Panel
The control panel allows the operator to adjust various parameters, such as the cutting speed, trimming pressure, beading profile, and curling radius. This control enables precise adjustments to achieve the desired edge finish, bead characteristics, and curled edge profile.
Safety Precautions
When operating an edge cutting trimming beading curling machine, it is crucial to follow safety precautions to prevent injuries and ensure proper operation:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear safety glasses, gloves, and a hearing protection device to protect yourself from flying debris, sparks, and noise.
- Workpiece Securement: Ensure the workpiece is firmly clamped to the machine’s worktable to prevent movement during cutting, trimming, beading, and curling.
- Tool Selection: Choose the appropriate cutting blade or disc, trimming rollers or dies, beading rollers or dies, and curling tool or die based on the material and thickness of the workpiece.
- Moderate Speed: Maintain a moderate operating speed to prevent overheating of the workpiece or damage to the cutting, trimming, beading, and curling tools.
- Avoid Overheating: Avoid applying excessive pressure or operating the machine for extended periods to prevent overheating the workpiece and potential damage.
- Regular Maintenance: Regularly inspect the edge cutting trimming beading curling machine for worn or damaged components and ensure proper maintenance to maintain its safety and effectiveness.
- Well-ventilated Area: Operate the machine in a well-ventilated area to minimize dust accumulation and protect yourself from harmful fumes.
- Safety Shut-off Switch: Be familiar with the location and operation of the safety shut-off switch to stop the machine immediately in case of any unexpected situations.
- Authorization Restriction: Keep the machine out of reach of unauthorized individuals, especially children, to prevent accidental operation or injury.
By adhering to these safety guidelines and operating the machine responsibly, you can effectively utilize edge cutting trimming beading curling machines to create precise, high-quality edges on various sheet metal components.
The machine is used in the production of round parts, rim cuts, beading, and edge cuts. It is also used for edging and trimming sheet metal. This machine can be operated manually or automatically. The blades are adjustable to the thickness of the sheet metal being cut, so they can be set up for different thicknesses automatically.
The edge cutting and trimming machine is used for cutting and trimming edges of metal sheets. The machine can be used for various operations such as edge cutting, trimming, curling, beading, rim cutting and bending.
The most common types of materials cut with this machine are sheet metal such as aluminum, copper, and brass. It can also be used on other materials such as stainless steel.
Edge Cutting Trimming Beading Curling Machine
Circle cutting tools for metal are specialized tools used to create precise circular openings or holes in sheet metal components. They are commonly used in various industries, such as metalworking, manufacturing, and construction.
Types of Circle Cutting Tools for Metal
There are several types of circle cutting tools for metal, each with its own advantages and limitations. Some of the most common types include:
1. Hole Saws: Hole saws are versatile tools that can cut holes in a variety of materials, including metal. They typically consist of a rotating cylindrical body with teeth on its circumference. The size of the hole is determined by the diameter of the hole saw.
2. Annular Cutters: Annular cutters, also known as donut cutters, are specifically designed for cutting clean, round holes in sheet metal. They consist of a hollow cylindrical body with teeth on its cutting edge. The annular cutter removes the entire material within the cutting circle, leaving a clean, burr-free hole.
3. Core Drills: Core drills are powerful tools used for cutting larger holes in thick metal plates. They typically consist of a rotating pilot drill and a hollow cylindrical body with teeth on its cutting edge. The pilot drill guides the core drill into the material, and the cutting teeth remove the material within the cutting circle.
4. Punch and Die Sets: Punch and die sets are used for high-volume production of holes in sheet metal. A punch is a hardened steel tool with a sharp cutting edge, while a die is a hardened steel plate with a corresponding hole. The punch is forced through the workpiece, forcing the material into the die, and creating a clean, round hole.
Safety Precautions
When using circle cutting tools for metal, it is important to follow safety precautions to prevent injuries and ensure proper operation:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses, gloves, and hearing protection, to protect yourself from flying debris, sparks, and noise.
2. Secure Workpiece: Ensure the workpiece is securely clamped to the machine’s worktable or chuck to prevent movement during cutting.
3. Tool Selection: Choose the appropriate tool based on the material, thickness, and desired hole size.
4. Proper Speed and Feed: Maintain a moderate cutting speed and feed rate to prevent excessive heat generation, tool wear, or damage to the workpiece.
5. Avoid Overheating: Avoid overheating the tool or workpiece by using a cutting lubricant or coolant and taking breaks to allow the tool to cool down.
6. Regular Maintenance: Regularly inspect the cutting tool for wear or damage and ensure proper maintenance to maintain its effectiveness and safety.
7. Well-ventilated Area: Operate the machine in a well-ventilated area to minimize dust accumulation and protect yourself from harmful fumes.
8. Safety Shut-off Switch: Be familiar with the location and operation of the safety shut-off switch to stop the machine immediately in case of any unexpected situations.
9. Authorized Personnel: Restrict access to the machine to authorized personnel only to prevent unauthorized operation or injury.
By following these safety guidelines and operating the machine responsibly, you can effectively utilize circle cutting tools for metal to create precise, clean, and burr-free holes in sheet metal components.
These machines are produced in series or customized according to the customer’s requirements in order to perform the following operations:
- Edge cutting
- Trimming Inward/outward
- Beading Inward/outward
- Ribbing Inward/outward
- Curling Inward/outward
- Flanging
- Threading
A circle cutting tool for metal is a specialized tool used to cut circular shapes out of sheet metal or other metalwork materials. These tools come in various forms, each with its own advantages and applications. Here are some common types of circle cutting tools for metal:
- Hole Saws: Hole saws consist of a cylindrical cutting blade with teeth around its circumference. They are typically attached to a drill or power drill and are used to cut large, clean holes in metal sheets. Hole saws come in various sizes to accommodate different hole diameters.
- Core Drills: Core drills are similar to hole saws but utilize a hollow cutting bit with teeth on the inner and outer edges. They are primarily used to cut larger holes or remove cores from metalwork pieces. Core drills provide a cleaner hole with a solid core.
- Circular Shears: Circular shears feature a pair of rotating blades that cut through metal sheets in a circular motion. They are handheld tools commonly used for cutting large circles or curves in metal sheets. Circular shears are versatile for various sheet metal cutting tasks.
- Plasma Cutters: Plasma cutters use a high-temperature plasma stream to melt and vaporize metal, creating a precise cut. They are ideal for cutting thick metal sheets and intricate circular shapes. Plasma cutters offer high cutting speeds and accuracy.
- Laser Cutters: Laser cutters utilize a focused laser beam to vaporize metal, creating a precise and clean cut. They are suitable for cutting complex circular shapes and thin metal sheets. Laser cutters offer high precision and minimal heat distortion.
- Punch Presses: Punch presses use a punch and die set to cut circular shapes out of metal sheets. They are typically used in industrial settings for high-volume production of circular metal components. Punch presses provide high production rates and consistent hole quality.
The choice of circle cutting tool for metal depends on the specific application, material thickness, desired hole size, and required accuracy. Hole saws and core drills are suitable for larger holes and thicker materials, while circular shears offer flexibility for cutting curves. Plasma cutters and laser cutters provide high-precision cutting for intricate shapes, while punch presses are ideal for high-volume production.
Circle cutting tools for metal are essential tools for metalworkers, enabling them to create precise and clean circular holes in various sheet metal components. These tools come in various forms, each with its own unique characteristics and applications.
Types of Circle Cutting Tools for Metal:
- Punch and Die Sets: Punch and die sets are traditional tools used for punching circular holes in sheet metal. They consist of a punch, a die, and a holder. The punch is a hardened steel cylinder with a sharp cutting edge, while the die has a corresponding hole to receive the punch. The holder securely holds the punch and die in alignment.
- Circle Saws: Circle saws, also known as hole saws, are versatile tools for cutting circular holes in various materials, including metal. They consist of a rotating blade with teeth arranged in a circular pattern. The blade is typically made of high-speed steel or carbide for enhanced durability and cutting performance.
- Core Drills: Core drills, also known as annular cutters, are specialized tools for drilling large-diameter holes in sheet metal and other materials. They consist of a cylindrical cutting head with teeth on the outer edge and a pilot drill in the center. The pilot drill guides the core drill, while the cutting head removes the material around the pilot hole, creating a large, clean hole.
- Plasma Cutters: Plasma cutters utilize a high-temperature plasma stream to cut through various materials, including metal. They are particularly effective for cutting thick or hard metals. For cutting circular holes, plasma cutters typically use a rotating nozzle that directs the plasma stream in a circular pattern.
- Laser Cutters: Laser cutters utilize a concentrated laser beam to vaporize material, enabling precise cutting of intricate shapes, including circular holes. They are particularly suitable for cutting thin sheet metal with high accuracy and minimal heat-affected zones.
Safety Precautions:
When using circle cutting tools for metal, it is crucial to follow safety precautions to prevent injuries and ensure proper operation:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses, gloves, and a hearing protection device, to protect yourself from flying debris, sparks, and noise.
- Secure Workpiece: Ensure the workpiece is securely clamped to a stable work surface to prevent movement during cutting.
- Proper Tool Selection: Choose the appropriate circle cutting tool based on the material thickness, hole diameter, and desired cutting speed.
- Moderate Speed: Maintain a moderate cutting speed to prevent overheating of the tool or workpiece and ensure a clean, precise cut.
- Avoid Overheating: Avoid excessive cutting duration or applying excessive force to the tool to prevent overheating and potential damage.
- Regular Maintenance: Regularly inspect the circle cutting tool for worn or damaged components and ensure proper maintenance to maintain its safety and effectiveness.
- Well-ventilated Area: Operate the tool in a well-ventilated area to minimize dust accumulation and protect yourself from harmful fumes.
- Safety Shut-off Switch: Be familiar with the location and operation of the safety shut-off switch to stop the tool immediately in case of any unexpected situations.
- Authorization Restriction: Keep the tool out of reach of unauthorized individuals, especially children, to prevent accidental operation or injury.
By adhering to these safety guidelines and operating the tool responsibly, you can effectively utilize circle cutting tools for metal to create precise, clean circular holes in various sheet metal components.
What is the Best Tool for Edge Cutting Trimming?
All EMS Metalworking Machinery trimming-beading machine models can be equipped with specific motorization according to the kind of machining to be performed and with working units driven by pneumatic-hydraulic, hydraulic, and/or brushless electric systems. The type of the motors chosen to drive the cutting knife depends on the operation complexity and it can change from an ordinary AC motor with an encoder or an AC Servo motor where greater precision is necessary
This automatic cutting, trimming & beading machine is used to effectively cut/trim or bead the edge of stainless steel/aluminum cookware & utensils, kitchenware, hotelware products, fire extinguishers, heat boilers and etc.
These machines can also be adjusted to work in multiple operations:
1) Cookware, kitchenware, hotelware, fire extinguishers, heat boilers, or utensils edges can be cut or trimmed.
2) Cookware, kitchenware, hotelware, fire extinguishers, heat boilers or utensils edges can be trimmed + beaded
3) Performing particular cookware, kitchenware, hotelware, fire extinguishers, heat boilers, or utensils edge operation.
Edge Cutting Trimming Beading Curling Machine Technology
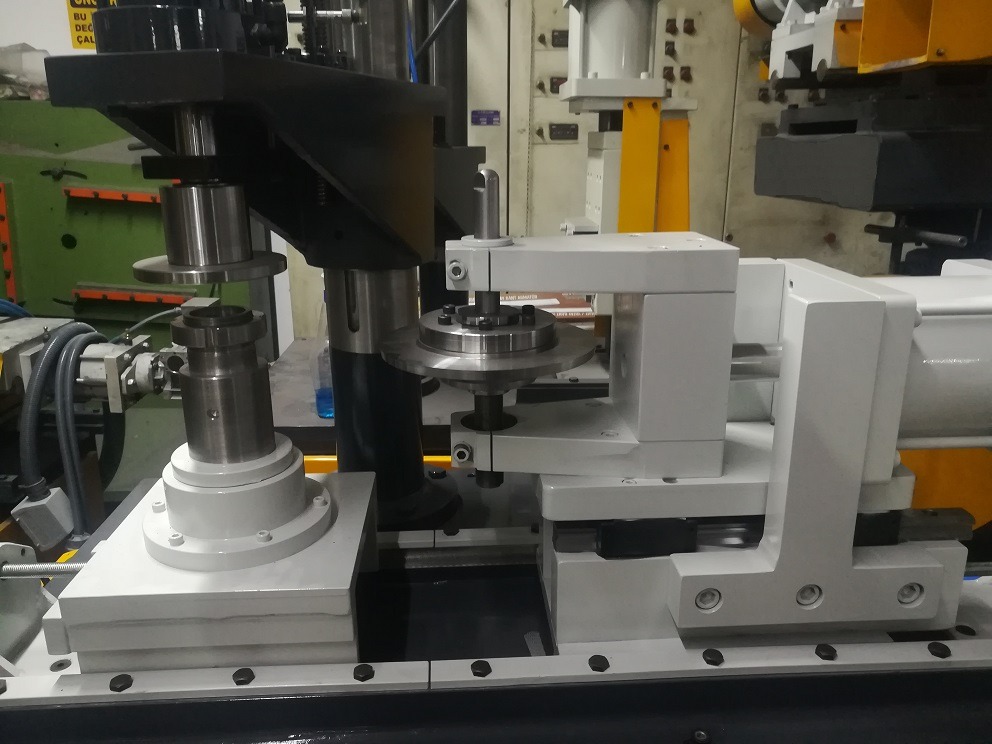

Edge cutting technology is a relatively new technology, developed in the industry in the 1980s when the production of tube-type sheet metal parts started to be made with deep drawing hydraulic presses. This new technology has been adopted by the related industries quickly and became the first machine in cookware kitchenware production companies.
Edge Cutting Trimming Beading Curling Machines, also known as edge forming machines, have undergone significant technological advancements in recent years, making them more precise, efficient, and versatile tools in the metalworking industry. These machines combine the functions of edge cutting, trimming, beading, and curling, enabling comprehensive edge processing for various sheet metal components.
Key Technological Advancements:
- Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Integration: CNC technology has revolutionized edge forming machines by providing precise control over the cutting, trimming, beading, and curling processes. This eliminates the need for manual adjustments and ensures consistent, high-quality results, even for complex edge profiles and intricate shapes.
- Servo Drive Technology: Servo drives have replaced traditional hydraulic or pneumatic systems, providing greater control over tool speed, force, and positioning. This enables smoother, more precise edge forming operations, reducing material waste and improving overall production efficiency.
- Sensor-based Monitoring and Feedback: Edge forming machines are increasingly incorporating sensors to monitor various parameters, such as tool wear, workpiece temperature, and edge profile accuracy. This real-time data allows for predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and ensuring consistent production quality.
- Laser Guided Edge Forming: Laser-guided edge forming systems utilize laser technology to project a precise edge profile onto the workpiece, providing a visual guide for the cutting and forming tools. This technology enhances accuracy and reduces the risk of errors, particularly for complex edge shapes.
- Advanced Tooling Materials and Designs: Tooling materials have evolved to withstand higher cutting forces, temperatures, and wear, extending tool life and reducing maintenance costs. Additionally, innovative tool designs have improved edge forming efficiency and reduced material distortion.
- Integration with Automated Manufacturing Systems: Edge forming machines are increasingly being integrated into automated manufacturing systems, enabling seamless communication and data exchange with other production processes. This integration optimizes production flow and reduces labor requirements.
Impact on Metalworking Industry:
These technological advancements have significantly impacted the metalworking industry by:
- Enhanced Precision and Quality: Edge forming machines can now produce edges with greater precision and consistency, meeting the stringent requirements of modern manufacturing.
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: Advanced technologies have streamlined edge forming processes, reducing cycle times and increasing production output.
- Versatility and Flexibility: Edge forming machines have become more versatile, capable of handling a wider range of materials, thicknesses, and edge profiles.
- Reduced Labor Requirements: Automation and improved machine control have reduced the need for manual intervention, minimizing labor costs and improving overall production efficiency.
- Enhanced Safety: Advanced safety features, such as sensor-based monitoring and emergency shut-off mechanisms, have made edge forming machines safer for operators.
Future Innovations:
The future of edge cutting trimming beading curling machine technology is expected to involve further advancements in automation, artificial intelligence, and materials science, leading to:
- Adaptive Process Control: AI-powered systems will analyze real-time data to optimize cutting parameters, tool wear compensation, and process adjustments, ensuring consistent edge quality.
- Self-learning Machines: Edge forming machines may incorporate machine learning algorithms to learn from production data and adapt to changing material properties or process conditions.
- Advanced Tooling Materials: Research is ongoing to develop even more durable and wear-resistant tooling materials that can withstand extreme cutting conditions and extend tool life.
- Integrated Inspection Systems: Edge forming machines may incorporate integrated inspection systems to detect defects and variations in edge quality, providing real-time feedback for process optimization.
- Human-Machine Collaboration: Edge forming machines may become more intuitive and user-friendly, enabling more seamless collaboration between operators and machines.
These advancements will further enhance the capabilities and efficiency of edge forming machines, making them even more valuable tools in the metalworking industry.
Edge Cutting Trimming Tools Examples
An edge cutting trimming beading curling machine is a versatile tool used in metalworking to perform various edge forming operations on sheet metal components. It combines the functions of edge cutting, trimming, beading, and curling, making it a valuable asset for a wide range of metalworking applications.
Edge Cutting:
Edge cutting involves precisely removing excess material from the edges of sheet metal components. This is often done to ensure uniform dimensions, eliminate burrs or imperfections, or prepare the edge for further processing. The edge cutting operation typically utilizes a rotating cutting blade or disk that precisely trims the edge of the workpiece.
Trimming:
Trimming is similar to edge cutting but typically refers to the process of removing a specific amount of material from the edge of a workpiece to achieve a desired dimension or profile. The trimming operation often utilizes a trimming tool or die that presses against the edge of the workpiece, removing excess material to achieve the desired edge profile.
Beading:
Beading involves creating a raised edge or bead along the periphery of a sheet metal component. Beading enhances the strength, rigidity, and aesthetics of the component, and it can also provide a mounting surface or a seal for joints. The beading operation typically utilizes a series of rollers or dies that form the bead or flange along the edge of the workpiece.
Curling:
Curling involves creating a rolled edge on a sheet metal component. Curling is often used to create a smooth, finished edge, reinforce the edge, or improve the aesthetics of the component. The curling operation typically utilizes a rotating curling tool or die that presses against the edge of the workpiece, gradually curling it into the desired shape.
Combined Operations:
The edge cutting trimming beading curling machine combines these four operations into a single unit, allowing for efficient and versatile edge forming on sheet metal components. This machine can handle various edge profiles and configurations, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Applications:
Edge cutting trimming beading curling machines are used in various industries, including:
- Sheet Metal Fabrication: These machines are used to prepare components for further processing or assembly in sheet metal fabrication shops.
- Appliance Manufacturing: They are employed to create clean, finished edges on appliance bodies, doors, panels, and other components.
- Automotive Industry: These machines are used to produce high-quality components for car bodies, bumpers, doors, and other sheet metal parts.
- Electronics Manufacturing: They are used to form beads on metal casings, enclosures, and brackets.
- HVAC and Ventilation Systems: Edge cutting trimming beading curling machines are used to create beads for ductwork, ventilation systems, and other components.
- Metal Furniture Manufacturing: They are used to form beads and edges on tabletops, cabinet frames, and other furniture components.
- Sign and Display Manufacturing: These machines are used to create precise edges and contours on signage, display panels, and other sheet metal components.
- Agricultural Equipment Manufacturing: They are used to form beads and edges on various components, such as hoppers, guards, and enclosures.
- Aerospace and Defense Industries: Edge cutting trimming beading curling machines are used for high-precision edge forming and trimming of aircraft components, missile parts, and other critical components.
- General Metalworking Shops: They are indispensable tools in general metalworking shops, where they are used to handle a wide range of edge forming tasks.
These machines have become essential tools across a wide spectrum of industries due to their versatility, precision, and ability to enhance the strength, rigidity, and aesthetics of sheet metal components.
The edge cutting tools used by edge cutting trimming and beading machinery are mainly divided into 2 main groups:
- Circular Slitting Blade ( Knife)
- Counter Cutting Tool
The circular edge cutting of round parts is carried out by a round cutting tool (also mentioned as the knife) and the counter cutting tool. the rim of the round part is fixed so that the counter-cutting tool stays inside the part diameter and the circular slitting blade is moved to the rim of the part from the outside with a pneumatic cylinder. The pneumatic cylinder is controlled with an electromagnetic valve and a PLC. The circular slitting blade moves to the edge of the part on the mold and slows down before the cutting tool gets into the cutting range.
Meanwhile, the upper mold is moved down with the help of another pneumatical cylinder to fix the sheet metal part vertically so that the part can be rotated around its own axis for the circular cutting tool to contact the edge of the part and start cutting it.
When the circular cutting tool touches the outer surface of the sheet metal part, the circular cutting tool also starts to rotate to lower the friction (here the friction is unwanted as it can cause heat and damage on the part surface) The cycle takes 4-5 seconds including the movement of the upper cylinder and the cutting tool movement. The cutting tools cut the edge and the cut part falls down. The EMS Edge cutting trimming machines have long years of experience and superiority in cutting the metal edges without any additional needs for burr removal from the edge surface.
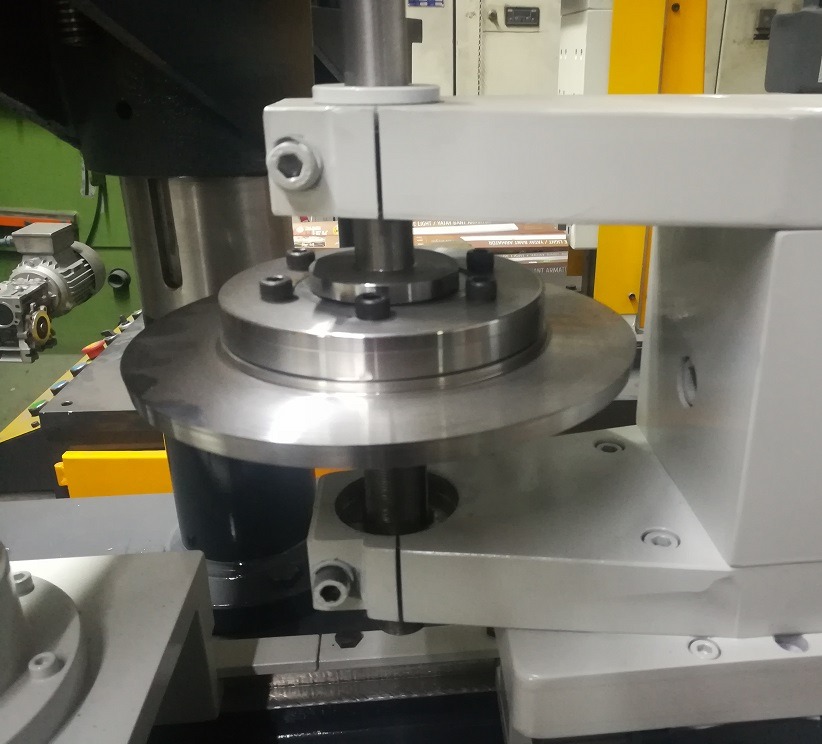

What machine to use to cut round sheet metal?
Edge cutting trimming beading curling machines, also known as edge forming machines or edge processing machines, have evolved significantly over time, incorporating advancements in technology to enhance their capabilities, precision, and efficiency. These machines play a crucial role in metalworking, enabling the creation of various edge profiles on sheet metal components.
Technological Advancements in Edge Forming Machines:
- Computer Numerical Control (CNC): CNC technology has revolutionized edge forming machines, providing precise control over the cutting, trimming, beading, and curling processes. CNC machines utilize computer software to program the machine’s movements, ensuring consistent and accurate edge profiles.
- Servo Motors and Drives: Servo motors and drives have become integral components of modern edge forming machines, offering greater control over speed, torque, and positioning. This enhanced control enables the machine to precisely follow programmed paths, resulting in consistent edge profiles and improved surface finishes.
- Sensor Technology: Sensors are increasingly being incorporated into edge forming machines to monitor various parameters, such as tool pressure, cutting force, and workpiece temperature. This real-time monitoring allows for adaptive control, ensuring optimal process parameters and preventing tool wear or workpiece damage.
- Automated Tool Change Systems: Automated tool change systems have streamlined edge forming operations by enabling the machine to automatically switch between different trimming, beading, and curling tools. This reduces downtime and increases production efficiency.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) Integration: VR and AR technologies are emerging in edge forming machines, providing operators with a visual representation of the edge forming process. This visualization can aid in programming, setup, and troubleshooting, improving operator efficiency and reducing errors.
Impact of Technological Advancements:
Technological advancements in edge forming machines have significantly impacted the metalworking industry:
- Improved Precision and Consistency: CNC control and servo drives have led to more precise and consistent edge profiles, reducing the need for manual adjustments and rework.
- Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: Automated tool change systems and improved process control have increased machine utilization and reduced downtime, boosting overall productivity.
- Reduced Operator Errors: Virtual reality and augmented reality guidance have minimized operator errors, leading to fewer defects and improved product quality.
- Expanded Application Range: Advancements have expanded the range of materials and edge profiles that can be processed, allowing for greater versatility in edge forming applications.
Future of Edge Forming Machine Technology:
The future of edge forming machine technology is likely to focus on further advancements in automation, process optimization, and integration with Industry 4.0 concepts:
- Adaptive Process Control: Real-time monitoring and adaptive process control will continue to evolve, enabling machines to adjust parameters based on material properties, workpiece conditions, and edge profile requirements.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI algorithms will be integrated to analyze process data, predict potential issues, and optimize machine settings for optimal performance and product quality.
- Smart Manufacturing Integration: Edge forming machines will become part of interconnected manufacturing networks, enabling real-time data exchange, predictive maintenance, and remote monitoring.
- Robotic Integration: Collaborative robots may be integrated to handle workpiece loading, unloading, and tool changing tasks, further automating the edge forming process.
- Digital Twin Technology: Digital twins of edge forming machines will be created to simulate and optimize machine performance, enabling proactive maintenance and process improvements.
These advancements will continue to enhance the capabilities, precision, and efficiency of edge forming machines, making them even more valuable tools in the metalworking industry.
An edge cutting trimming beading curling machine, also known as an edge forming machine or edge processing machine, is a versatile tool used in metalworking to perform a variety of operations on the edges of sheet metal components. It combines the functions of edge cutting, trimming, beading, and curling, providing a comprehensive solution for edge processing in various industries.
Edge Cutting Operation:
The edge cutting operation involves removing excess material from the edges of a sheet metal workpiece using a rotating cutting blade or cutter. The cutting blade is typically made of a high-strength material, such as tungsten carbide, to maintain sharpness and edge retention, ensuring a clean and precise cut.
Trimming Operation:
The trimming operation involves smoothing and refining the edges of a sheet metal workpiece after cutting or forming. It removes burrs, imperfections, and uneven edges, creating a smooth and uniform finish. The trimming operation can be performed using a dedicated trimming blade or by adjusting the edge cutting blade to a shallower cutting depth.
Beading Operation:
The beading operation involves forming a raised edge or bead along the periphery of a sheet metal component. The bead enhances the strength, rigidity, and aesthetics of the component, and it can also provide a mounting surface or a seal for joints. Beading is typically performed using a series of rollers or dies that apply pressure to the edge of the workpiece, gradually forming the bead.
Curling Operation:
The curling operation involves creating a rolled edge on a sheet metal component. The curled edge can be used for aesthetic purposes, to increase the strength and rigidity of the component, or to provide a protective barrier against sharp edges. Curling is typically performed using a curling tool or die that engages the edge of the workpiece and rotates it, gradually curling the material into the desired shape.
Applications:
Edge cutting trimming beading curling machines are widely used in various industries for a variety of applications, including:
- Sheet Metal Fabrication: These machines are used to prepare sheet metal components for further processing or assembly, ensuring consistent edge dimensions and finishes.
- Appliance Manufacturing: They are employed in appliance manufacturing to create clean, finished edges on appliance bodies, doors, panels, and other components.
- Automotive Industry: These machines are used in the automotive industry to produce high-quality components for car bodies, bumpers, doors, and other sheet metal parts.
- Electronics Manufacturing: They are used in electronics manufacturing to form beads and curled edges on metal casings, enclosures, and brackets.
- HVAC and Ventilation Systems: These machines are used to create beads and curled edges on ductwork, ventilation systems, and other components.
- Metal Furniture Manufacturing: They are employed in metal furniture manufacturing to form beads and edges on tabletops, cabinet frames, and other furniture components.
- Sign and Display Manufacturing: These machines are used to create precise edges and contours on signage, display panels, and other sheet metal components.
- Agricultural Equipment Manufacturing: They are employed in agricultural equipment manufacturing to form beads and edges on various components, such as hoppers, guards, and enclosures.
- Aerospace and Defense Industries: These machines are used for high-precision edge forming and trimming of aircraft components, missile parts, and other critical components.
- General Metalworking Shops: They are indispensable tools in general metalworking shops, where they are used to handle a wide range of edge cutting, trimming, beading, and curling tasks.
Edge cutting trimming beading curling machines offer versatility, precision, and efficient edge processing for sheet metal components. Their ability to perform multiple operations in a single machine makes them a valuable asset in metalworking operations worldwide.
Edge cutting trimming machines are also used for the round bending of sheet metals. The sheet metal part that needs to be edge trimmed and then bent inside goes through the same sort of operations where the sheet metal edges are cut first and then the circular cutting tool moves forward to bend the parts inside. This operation is usually made for cylindrical sheet metal parts that need to be welded later on or pots for cookware. The pots lids diameters need to be smaller than the pots themselves. This difference is carried by the edge bending operation of our machine.
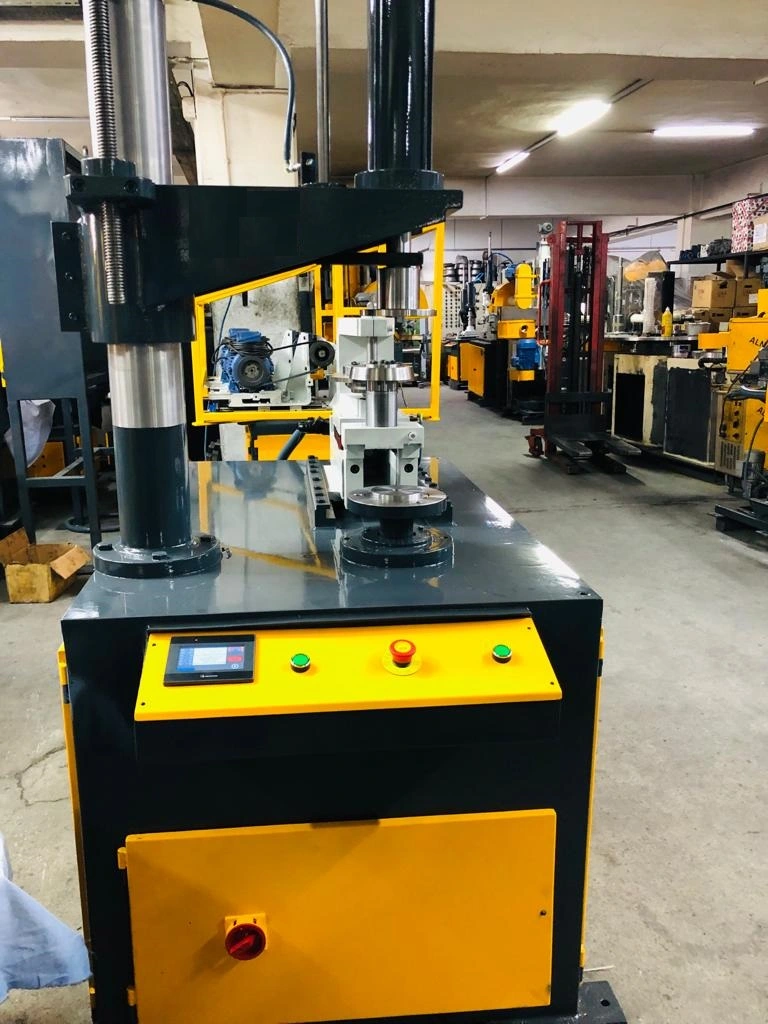

Edge cutting and trimming machine is used to cut and trim sheet metal, and round part, edge cutting and trimming machine. The Edge cutting and trimming machine is a kind of equipment that can cut the sheet metal into various shapes. It is widely used in the production of automobiles, electrical appliances, hardware tools, construction materials, etc.
The edge cutting and trimming machine has two types: one for the edge cutting of sheet metal; another for the edge bending of sheet metal. The former can cut square or rectangular edges on the sheet metal; while the latter can bend a certain radius on the edges of round parts.
Edge Curling Machine
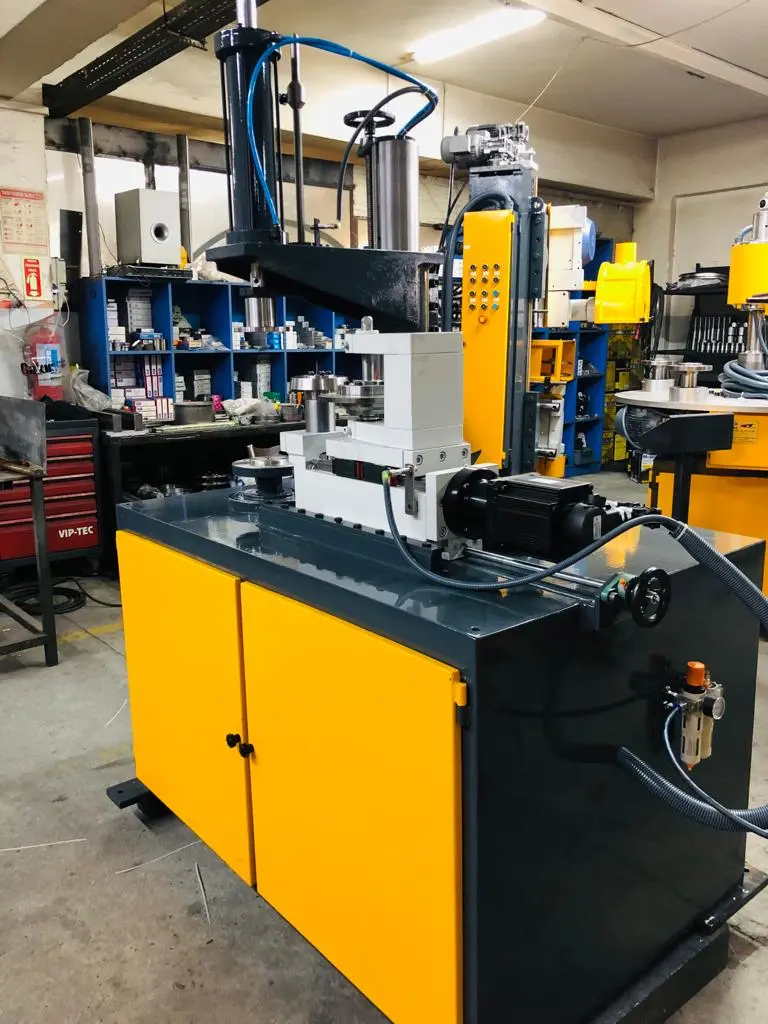

An edge curling machine, also known as a curl forming machine or edge forming machine, is a specialized tool used in metalworking to create a rolled edge on a sheet metal component. It is a versatile machine that can be used to create various curled edges, including tight curls, loose curls, and continuous curls. Edge curling machines are used in a variety of industries, including appliance manufacturing, furniture manufacturing, and HVAC and ventilation systems.
Working Principle of an Edge Curling Machine
The working principle of an edge curling machine is relatively simple. The machine consists of a rotating roller or die that engages the edge of the sheet metal component and curls it into the desired shape. The roller or die is typically made of a hard material, such as hardened steel or tungsten carbide, to withstand the pressure of curling the metal. The machine also has a control panel that allows the operator to adjust the speed, force, and curl profile of the machine.
Types of Edge Curling Machines
There are several different types of edge curling machines available, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common types of edge curling machines include:
- Benchtop edge curling machines: These machines are small and portable, making them ideal for use in small workshops or on the job site.
- Floor-mounted edge curling machines: These machines are larger and more powerful than benchtop machines, and they are typically used in larger production environments.
- CNC edge curling machines: These machines are computer-controlled, which allows for precise control of the curling process and the creation of complex curl profiles.
Applications of Edge Curling Machines
Edge curling machines are used in a variety of industries, including:
- Appliance manufacturing: Edge curling machines are used to create curled edges on appliance bodies, doors, and panels. These curled edges are used for aesthetic purposes and to reinforce the edges of the appliance.
- Furniture manufacturing: Edge curling machines are used to create curled edges on tabletops, cabinet frames, and other furniture components. These curled edges are used for aesthetic purposes and to protect the edges of the furniture from damage.
- HVAC and ventilation systems: Edge curling machines are used to create curled edges on ductwork, ventilation systems, and other HVAC components. These curled edges are used to improve the airflow through the system and to prevent debris from clogging the system.
Safety Precautions for Using an Edge Curling Machine
When using an edge curling machine, it is important to follow safety precautions to prevent injuries and ensure proper operation. These precautions include:
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety glasses, gloves, and hearing protection.
- Secure the workpiece to a stable work surface to prevent movement during curling.
- Choose the appropriate curling tool and settings for the material and thickness of the workpiece.
- Maintain a moderate curling speed to prevent overheating of the workpiece or the curling tool.
- Avoid excessive force and pressure when curling the workpiece.
- Regularly inspect the curling tool for wear and damage.
- Keep the machine clean and free of debris to prevent malfunctions.
- Dispose of sharp curling tools and blades properly.
By following these safety precautions, you can safely and effectively use an edge curling machine to create curled edges on sheet metal components.
How to curl the edge of sheet metal
Sheet metal edge curling machine is another metalworking machinery of our production. Curling of sheet metals is a mechanical process, where the curling press tool bends the edges of the sheet metal part out resulting in a hollow circle. These circles at the edges of round sheet metal parts are called “curls”.
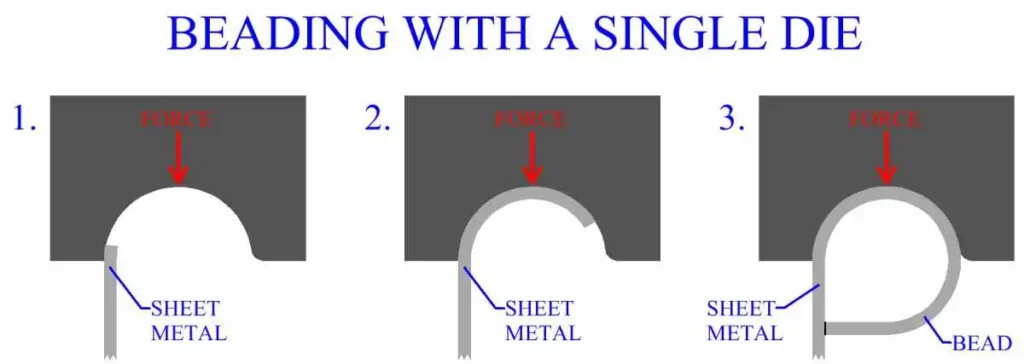
Curling the edge of sheet metal is a common metalworking operation that involves forming a rolled edge along the periphery of the workpiece. This process enhances the strength, rigidity, and aesthetics of the component, and it can also provide a mounting surface or a seal for joints.
Methods for Curling the Edge of Sheet Metal:
There are several methods for curling the edge of sheet metal, each with its own advantages and limitations. Common methods include:
- Edge Curling Machine: An edge curling machine is a specialized tool specifically designed for curling the edges of sheet metal components. It provides precise control over the curling process and can create various curl profiles, including tight curls, loose curls, and continuous curls.
- Hammer and Dolly: For smaller projects or field repairs, a hammer and dolly can be used to manually curl the edge of sheet metal. The process involves hammering the edge of the workpiece against a dolly, gradually forming the curled edge. This method requires skill and practice to achieve consistent results.
- Punch and Die Set: A punch and die set can be used to curl the edge of sheet metal by creating a series of small bends along the edge. The punch and die set is typically used for creating tight curls with a consistent profile.
- Roll Forming Machine: A roll forming machine is a specialized tool that can be used to continuously form sheet metal into various shapes and profiles, including curled edges. This method is particularly suitable for mass production scenarios.
Factors Affecting Curling Process:
Several factors can affect the curling process, including:
- Material Properties: The material of the sheet metal workpiece plays a significant role in the curling process. Ductile materials, such as aluminum and copper, are easier to curl than brittle materials, such as cast iron.
- Sheet Metal Thickness: Thinner sheet metal is generally easier to curl than thicker sheet metal. Thicker sheet metal may require more force or specialized tooling to achieve the desired curl.
- Curl Profile: The desired curl profile, such as tight curl, loose curl, or continuous curl, influences the curling process. Different curling methods and tooling may be better suited for specific curl profiles.
- Edge Preparation: The edge of the sheet metal workpiece should be clean and free from burrs or imperfections before curling. This ensures a smooth, uniform curl and prevents damage to the curling tool.
- Curling Speed and Force: The curling speed and force should be adjusted appropriately for the material, thickness, and desired curl profile. Excessive speed or force can lead to defects or damage to the workpiece.
- Tooling Selection and Maintenance: Using the appropriate curling tool and maintaining it properly are crucial for achieving consistent and high-quality curled edges. Worn or damaged tooling can produce defects and affect the curling process.
Safety Precautions:
When curling the edge of sheet metal, it is essential to follow safety precautions to prevent injuries and ensure proper operation:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses, gloves, and hearing protection, to protect yourself from flying debris, sparks, and noise.
- Secure Workpiece: Ensure the workpiece is firmly clamped to a stable work surface to prevent movement during curling.
- Proper Tool Selection: Choose the appropriate curling method and tooling based on the material, thickness, and desired curl profile.
- Moderate Speed and Force: Maintain a moderate curling speed and force to prevent overheating of the workpiece or curling tool and ensure a clean, precise curl.
- Avoid Overheating: Avoid excessive curling duration or applying excessive force to the tool to prevent overheating and potential damage.
- Regular Tool Inspection: Regularly inspect the curling tool for wear or damaged components and ensure proper maintenance to maintain its safety and effectiveness.
- Well-ventilated Area: Operate the curling machine in a well-ventilated area to minimize dust accumulation and protect yourself from harmful fumes.
- Safety Shut-off Switch: Be familiar with the location and operation of the safety shut-off switch to stop the machine immediately in case of any unexpected situations.
- Authorization Restriction: Keep the machine out of reach of unauthorized individuals, especially children, to prevent accidental operation or injury.
By adhering to these safety guidelines and operating the curling machine responsibly, you can effectively create precise, high-quality curled edges on sheet metal components, enhancing their strength, rigidity, and aesthetics.
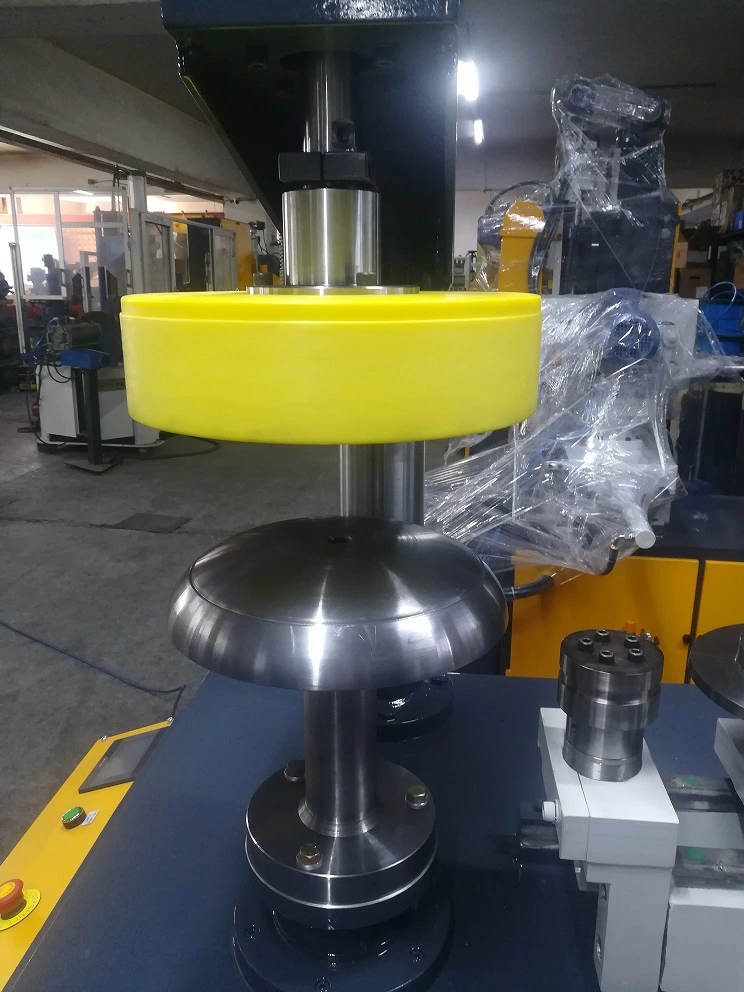
The curling press tool made of 2379 Hardened Steel, has a half-sphere surface which enables it to curl the sheet metal edge. The curling of the sheet metal leaves a hollow circle at the end of the operation. The diameter of this curl is called “sheet metal curling diameter”. This diameter can be arranged by changing the curling tool or curling die.
This curling process is mostly used for teapots, kettles, baking molds, cake molds, milk canisters, and in some other kitchenware products.
Trimming and Forming Machine
The edge cutting and trimming machine is also called the trimming and forming machine. The metal housing is trimmed and formed in a direction (inside or outside) This operation is called sheet metal forming. Here the formed part is a metal sheet. The sheet metal sheets that are trimmed by the beading trimming and forming machine can be removed from the molds manually or by automation

Trimming and forming machines play a crucial role in metalworking operations, serving as versatile tools for precisely shaping and finishing the edges of sheet metal components. These machines combine the functions of trimming and forming, enabling efficient and accurate edge processing for various applications.
Key Components of a Trimming and Forming Machine:
- Frame: A sturdy frame provides the structural support for the machine, ensuring stability and vibration dampening during operation.
- Worktable: The workpiece is securely clamped to the worktable, providing a stable platform for trimming and forming operations.
- Trimming Blade/Cutter: A rotating trimming blade or cutter precisely removes excess material from the edges of the workpiece, creating a clean and uniform edge.
- Forming Rollers or Dies: A series of rollers or dies apply pressure to the edge of the workpiece, gradually forming beads, flanges, or other desired edge profiles.
- Control Panel: The control panel allows the operator to adjust various parameters, such as trimming speed, beading pressure, and bead profile.
- Motor or Drive System: A motor or drive system provides the power to rotate the trimming blade or cutter and operate the forming rollers or dies.
Types of Trimming and Forming Operations:
- Trimming: Trimming involves removing excess material from the edges of a sheet metal workpiece to achieve uniform dimensions, remove burrs or imperfections, or prepare the edge for further processing.
- Beading: Beading involves forming a raised edge or bead along the periphery of a sheet metal component. This enhances the strength, rigidity, and aesthetics of the component, and it can also provide a mounting surface or a seal for joints.
- Flanging: Flanging involves creating a flange or edge bend along the periphery of a sheet metal component. Flanges provide reinforcement, increase surface area, and can serve as mounting points for other components.
- Curling: Curling involves forming a rolled edge on a sheet metal component. Curled edges can enhance the aesthetics, protect the edges from damage, or provide a smooth transition from the edge to the surface.
Applications of Trimming and Forming Machines:
Trimming and forming machines are widely used in various industries, including:
- Sheet Metal Fabrication: Trimming and forming machines are essential tools in sheet metal fabrication shops, where they are used to prepare components for welding, assembly, or further processing.
- Appliance Manufacturing: These machines are employed in appliance manufacturing to create clean, finished edges on appliance bodies, doors, panels, and other components.
- Automotive Industry: Trimming and forming machines are used in the automotive industry to produce high-quality components for car bodies, bumpers, doors, and other sheet metal parts.
- Electronics Manufacturing: They are used in electronics manufacturing to form beads and flanges on metal casings, enclosures, and brackets.
- HVAC and Ventilation Systems: These machines are used to create beads and flanges on ductwork, ventilation systems, and other components.
- Metal Furniture Manufacturing: They are employed in metal furniture manufacturing to form beads and edges on tabletops, cabinet frames, and other furniture components.
- Sign and Display Manufacturing: These machines are used to create precise edges and contours on signage, display panels, and other sheet metal components.
- Agricultural Equipment Manufacturing: They are employed in agricultural equipment manufacturing to form beads and edges on various components, such as hoppers, guards, and enclosures.
- Aerospace and Defense Industries: These machines are used for high-precision edge forming and trimming of aircraft components, missile parts, and other critical components.
- General Metalworking Shops: They are indispensable tools in general metalworking shops, where they are used to handle a wide range of trimming and forming tasks.
Trimming and forming machines have become essential tools across a wide spectrum of industries due to their ability to produce high-quality trimmed and formed edges efficiently and consistently. Their versatility, precision, and ability to enhance the strength, rigidity, and aesthetics of sheet metal components make them a valuable asset in metalworking operations worldwide.
The capabilities of this machine are trimming, flanging, turning, curling, beading, threading for deformation, and seaming of covers.
The trim tool is a special cutting knife used as one of the tools for trim and is manufactured by the DIN 2379 Cutting Steel.
EMS Metalworking Machinery
We design, manufacture and assembly metalworking machinery such as:
- Hydraulic transfer press
- Glass mosaic press
- Hydraulic deep drawing press
- Casting press
- Hydraulic cold forming press
- Hydroforming press
- Composite press
- Silicone rubber moulding press
- Brake pad press
- Melamine press
- SMC & BMC Press
- Labrotaroy press
- Edge cutting trimming machine
- Edge curling machine
- Trimming beading machine
- Trimming joggling machine
- Cookware production line
- Pipe bending machine
- Profile bending machine
- Bandsaw for metal
- Cylindrical welding machine
- Horizontal pres and cookware
- Kitchenware, hotelware
- Bakeware and cuttlery production machinery
as a complete line as well as an individual machine such as:
- Edge cutting trimming beading machines
- Polishing and grinding machines for pot and pans
- Hydraulic drawing presses
- Circle blanking machines
- Riveting machine
- Hole punching machines
- Press feeding machine
You can check our machinery at work at: EMS Metalworking Machinery – YouTube
Applications:
- Beading and ribbing
- Flanging
- Trimming
- Curling
- Lock-seaming
- Ribbing
- Flange-punching
