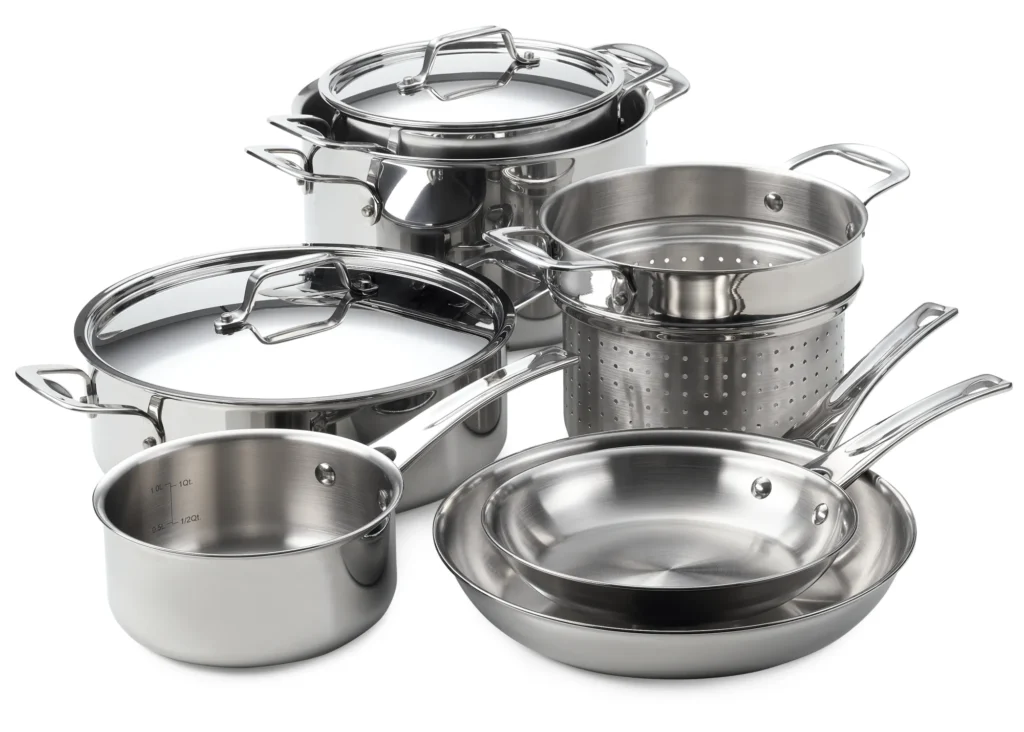

The cookware stainless steel products are manufactured by machinery that uses cookware aluminum or cookware stainless or generally speaking cookware steel to manufacture utensils
The kitchen utensils products can be classified as
- Stainless steel pots
- Stainless steel pans
- Stainless steel pressure cookers
- Stainless steel kettles, teapots, and coffeepot
Steel utensils are mostly preferred in the cookware or kitchenware industry because of their hygienic properties, easiness to clean, and manufacture with machinery.
Machinery for the Production of Cookware Stainless Steel
The production of stainless steel cookware involves a series of steps that transform raw materials into the finished products we use in our kitchens. Various machinery plays a crucial role in each stage of the manufacturing process, from shaping and forming the metal to polishing and finishing the cookware.
Here’s an overview of the key machinery used in the production of stainless steel cookware:
- Cutting Machines: Cutting machines, such as hydraulic shearing machines and laser cutting machines, are used to cut sheet metal into the desired shapes and sizes for the various components of cookware. These machines ensure precise cutting and minimize material waste.
- Stamping Presses: Stamping presses are used to form the basic shapes of cookware components, such as pots, pans, and lids. These presses apply high pressure to force the metal into the desired shape using dies or molds.
- Deep Drawing Machines: Deep drawing machines are used to create deeper shapes from sheet metal, such as the bodies of pots and pans. These machines pull the metal into the desired shape using a punch and die set.
- Hydraulic Presses: Hydraulic presses are used for various forming operations, such as beading, flanging, and trimming. These presses apply controlled pressure to shape and refine the edges of cookware components.
- Polishing Machines: Polishing machines are used to create a smooth and shiny finish on the surface of cookware. These machines employ abrasive belts, polishing wheels, or compounds to remove imperfections and achieve the desired luster.
- Welding Machines: Welding machines, including spot welders and TIG welders, are used to join various components of cookware, such as handles, lids, and reinforcing structures. These machines ensure strong and durable connections.
- Surface Treatment Machines: Surface treatment machines are used to apply protective or decorative coatings to cookware, such as non-stick coatings or color finishes. These machines ensure the cookware is resistant to wear, corrosion, and staining.
- Inspection and Testing Equipment: Inspection and testing equipment, such as ultrasonic testing machines and surface flaw detectors, are used to ensure the quality and integrity of the cookware. These tools detect defects and ensure the products meet safety and performance standards.
The specific machinery used in the production of stainless steel cookware may vary depending on the manufacturer, the complexity of the cookware design, and the desired finishes. However, the machinery listed above plays a vital role in transforming raw materials into high-quality, durable, and aesthetically pleasing cookware that meets the needs of modern kitchens.
The production of cookware stainless steel involves various machines and equipment to form, shape, polish, and finish the cookware. Some of the machinery used in the production of cookware stainless steel are:
- Hydraulic press: Hydraulic presses are used to form and shape the stainless steel sheets into the desired shape of the cookware. The sheets are placed on the press bed and the hydraulic ram applies pressure to the sheet to form it into the desired shape.
- Spinning machine: Spinning machines are used to shape the stainless steel sheets into round, flat, or concave shapes. The spinning machine rotates the sheet at high speed while a tool applies pressure to the sheet to shape it into the desired form.
- Polishing machine: Polishing machines are used to smooth and polish the stainless steel cookware to make it shiny and reflective. The cookware is placed on the machine bed and abrasive wheels or belts are used to polish the surface of the cookware.
- Welding machine: Welding machines are used to join two or more stainless steel parts together to form the cookware. The machine applies heat and pressure to the parts to fuse them together.
- Cutting machine: Cutting machines are used to cut the stainless steel sheets into the desired shape and size for the cookware. The machine uses a cutting tool, such as a laser or water jet, to cut the stainless steel sheet into the desired shape.
- Annealing furnace: Annealing furnaces are used to heat treat the stainless steel to remove stresses and improve its strength and durability. The stainless steel cookware is placed in the furnace and heated to a specific temperature and then slowly cooled.
- Grinding machine: Grinding machines are used to remove any burrs or rough edges on the stainless steel cookware after it has been formed, shaped, and welded. The machine uses abrasive wheels or belts to smooth and grind the edges of the cookware.
These machines are used in various industries that produce cookware stainless steel, including the home appliances, kitchenware, and catering equipment manufacturers.
Machinery for Cookware: Circle Sheet Cutter Machine for Cookware Stainless Steel

Circle sheet cutters are essential tools in the production of stainless steel cookware, enabling the efficient and precise cutting of circular components such as pot bottoms, pan lids, and decorative trims. These machines play a crucial role in ensuring the uniformity, dimension accuracy, and quality of cookware components.
Types of Circle Sheet Cutters:
- Hydraulic Shear Circle Cutters: These machines utilize hydraulic pressure to cut circular shapes from sheet metal. They are known for their power, precision, and ability to handle thick materials.
- Laser Circle Cutters: Laser circle cutters employ a focused beam of laser light to vaporize the material, creating clean, precise cuts with minimal heat-affected zones. They are particularly suitable for cutting thin sheet metal and intricate designs.
- CNC Circle Cutters: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) circle cutters incorporate computer programming to control the cutting process, ensuring precise dimensions, consistent shapes, and repeatability. They are widely used in high-volume production environments.
Operating Principles of Circle Sheet Cutters:
The operating principle of a circle sheet cutter varies depending on the type of machine, but the general process involves the following steps:
- Workpiece Positioning: The sheet metal workpiece is securely clamped onto the machine’s worktable, ensuring stability and precise positioning for cutting.
- Cutting Tool Positioning: The cutting tool, whether it’s a hydraulic shear blade, a laser beam, or a rotating punch, is positioned above the workpiece at the desired cutting location.
- Cutting Process: The cutting cycle is initiated, and the cutting tool moves along a circular path, cutting the sheet metal into a circular shape. The cutting speed, pressure, or laser power are controlled to achieve the desired cut quality and edge condition.
Safety Precautions for Using Circle Sheet Cutters:
When operating circle sheet cutters, it is crucial to prioritize safety to prevent injuries and ensure proper machine operation:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses, gloves, and hearing protection, to protect yourself from flying debris, sharp edges, and noise.
- Machine Guarding: Ensure all safety guards and interlocks are in place and functioning properly to prevent accidental contact with moving parts or hazardous areas of the machine.
- Secure Workpiece Clamping: Verify that the workpiece is securely clamped to the worktable to prevent movement during cutting, which could lead to inaccurate cuts or injuries.
- Proper Tool Selection and Maintenance: Choose the appropriate cutting tool and cutting parameters based on the material thickness, cutting speed requirements, and desired edge finish. Regularly maintain the cutting tool to ensure optimal performance and safety.
- Proper Tool Handling: Handle cutting tools with care, especially blades and laser emitters, to avoid accidental contact or injury.
- Clear Work Area: Maintain a clean and organized work area free from clutter and debris to prevent tripping hazards and ensure unobstructed movement around the machine.
- Emergency Stop Procedure: Familiarize yourself with the location and operation of the emergency stop button to immediately halt the machine in case of any unexpected situations.
- Authorization Restriction: Keep the machine out of reach of unauthorized individuals, especially children, to prevent accidental operation or injury.
By adhering to these safety guidelines and operating the circle sheet cutter responsibly, you can effectively produce precise, high-quality circular components for stainless steel cookware while maintaining a safe and controlled work environment.
The cook stainless steel cookware is manufactured by a series of machinery. The first of the line is a circle sheet cutter machine. The machine cuts roll steel sheets into such circles. Cooking on stainless is much more preferred by cooks and consumers than other materials. Utensils and kitchenware utensils are products that are covered in this chapter.
Customers usually want to find out if is it better to cook in stainless steel or in aluminum. Cooks’ kitchenware can be made of both stainless steel and aluminum. From our experience, the market has a bigger trend for stainless cooking utensils or generally speaking stainless steel cooking utensils. So below you will find some general information about the manufacturing of stainless steel cookware and kitchenware
The first step is cutting out sheet metal circles for the deep drawing press. This operation can either be carried out by a circle cutter or a mechanical press that cuts circles from sheet metal
Machinery for Cookware: Hydraulic Press
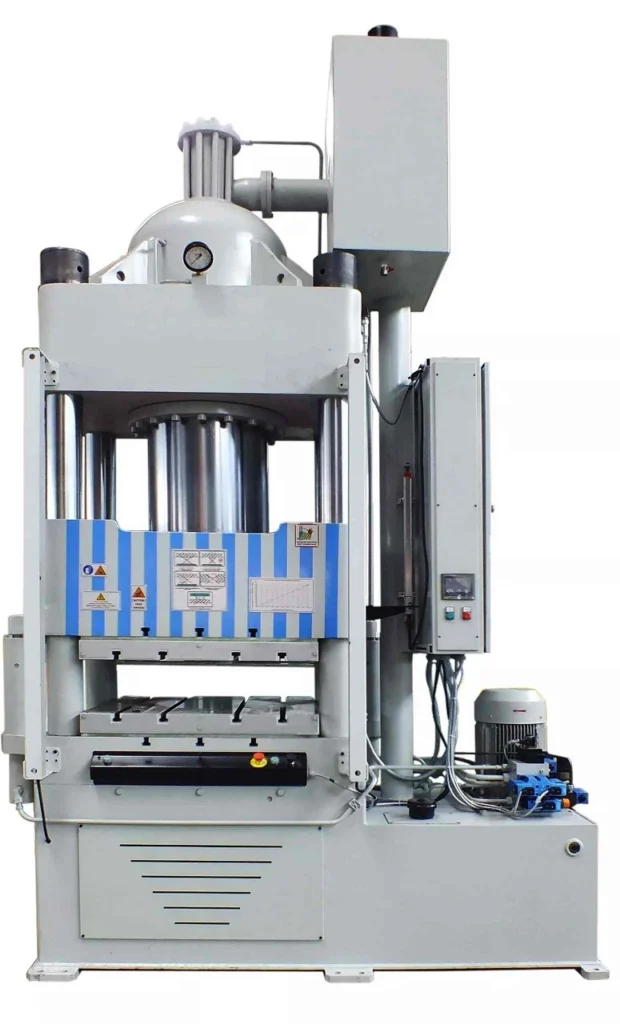

Hydraulic presses are versatile and powerful machines that play a crucial role in the manufacturing of cookware, particularly in the forming and shaping of stainless steel components. They utilize hydraulic pressure to apply force to workpieces, enabling the creation of various shapes, finishes, and features.
Key Applications of Hydraulic Presses in Cookware Manufacturing:
- Flanging: Hydraulic presses are commonly used for flanging, which involves creating a raised edge or rim on the edge of a cookware component. This process strengthens and reinforces the edge, enhances the aesthetics, and provides a mounting surface for other components.
- Beading: Beading involves forming a raised bead or ridge along the edge of a cookware component. This process enhances the strength and rigidity of the component, provides a smooth transition from the edge to the surface, and can serve as a decorative accent.
- Curling: Curling involves rolling the edge of a cookware component to create a smooth, rounded edge. This process protects the edge from damage, enhances the aesthetics, and provides a comfortable grip for handling.
- Stamping: Hydraulic presses can be used for stamping, which involves forcing sheet metal into a specific shape using a die or mold. This process is particularly useful for creating complex shapes and high-volume production.
- Trimming: Hydraulic presses can also be used for trimming, which involves removing excess material from the edges of a cookware component. This process ensures precise dimensions, removes burrs or imperfections, and prepares the edge for further processing.
Advantages of Hydraulic Presses in Cookware Manufacturing:
- High Precision and Control: Hydraulic presses offer precise control over pressure, force, and speed, enabling the creation of consistent, high-quality components.
- Versatility: Hydraulic presses can perform a wide range of forming operations, making them versatile tools for various cookware manufacturing processes.
- Power and Efficiency: Hydraulic presses generate high forces, allowing them to handle thick materials and complex shapes efficiently.
- Safety Features: Hydraulic presses incorporate safety features, such as interlocks, guards, and emergency stop buttons, to protect operators from hazards.
- Durability and Reliability: Hydraulic presses are built to withstand the rigors of industrial environments, ensuring long-term durability and consistent performance.
Hydraulic presses have become indispensable tools in cookware manufacturing, enabling the production of high-quality, aesthetically pleasing, and durable kitchenware components. Their versatility, precision, and power make them essential for shaping the future of cookware manufacturing.
Hydraulic presses are an important type of machinery used in the production of cookware made from stainless steel. These presses are used to form and shape the stainless steel into various shapes and sizes, including pots, pans, and other kitchenware items.
The hydraulic press consists of a large cylinder, a hydraulic pump, and a set of hydraulic valves. The cylinder is filled with hydraulic fluid, and a piston is used to create pressure in the system. When the hydraulic pump is activated, it forces the fluid through the valves and into the cylinder, creating pressure that is used to shape the stainless steel.
The cookware stainless steel is placed on a die, which is then lowered into the hydraulic press. The press then applies pressure to the die, shaping the stainless steel into the desired form. The hydraulic press is capable of exerting tremendous force, allowing it to shape even the toughest stainless steel materials.
The hydraulic press is an essential piece of machinery for the production of cookware stainless steel. It is used in a wide range of industries, including the food service and hospitality industries, as well as in commercial and industrial settings.
Spinning Machine
A spinning machine is a metalworking tool that uses the rotational force of a spinning mandrel to shape and form sheet metal components. It is a versatile machine that can produce a wide variety of shapes, including cylinders, cones, domes, and hemispheres.
Working Principle of a Spinning Machine:
The working principle of a spinning machine is relatively simple. The machine consists of a rotating mandrel that is typically made of a hard material, such as steel or tungsten carbide. The workpiece, which is typically a sheet metal blank, is clamped onto the mandrel. The mandrel is then rotated at a high speed, and a forming tool is applied to the workpiece. The forming tool applies pressure to the workpiece, gradually shaping it into the desired form.
Types of Spinning Machines:
There are several different types of spinning machines, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common types of spinning machines include:
- Hand spinning machines: These machines are typically used for small-scale production or for creating intricate shapes.
- Power spinning machines: These machines are more powerful than hand spinning machines and are typically used for larger-scale production.
- CNC spinning machines: These machines are computer-controlled and offer precise control over the spinning process.
Applications of Spinning Machines:
Spinning machines are used in a variety of industries, including:
- Appliance manufacturing: Spinning machines are used to create a variety of appliance components, such as pot bodies, pans, and drums.
- Automotive industry: Spinning machines are used to create a variety of automotive components, such as wheel covers, fuel tanks, and air intake ducts.
- Aerospace industry: Spinning machines are used to create a variety of aerospace components, such as rocket motor casings, fuel tanks, and radomes.
- Lighting industry: Spinning machines are used to create a variety of lighting components, such as lampshades, reflectors, and housings.
- Medical device industry: Spinning machines are used to create a variety of medical device components, such as surgical implants, prosthetics, and instrument housings.
Advantages of Spinning Machines:
Spinning machines offer several advantages over other metalworking methods, including:
- High productivity: Spinning machines can produce components at a high rate of speed.
- Low tooling costs: Spinning machines typically require less tooling than other metalworking methods.
- Versatility: Spinning machines can produce a wide variety of shapes and sizes.
- Good strength and surface finish: Spinning machines can produce components with good strength and a smooth surface finish.
Safety Precautions for Using a Spinning Machine:
When using a spinning machine, it is important to follow safety precautions to prevent injuries and ensure proper operation. These precautions include:
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety glasses, gloves, and hearing protection.
- Secure the workpiece to a stable work surface to prevent movement during spinning.
- Choose the appropriate spinning speed and force for the material and thickness of the workpiece.
- Avoid excessive force and pressure when spinning the workpiece.
- Regularly inspect the spinning tool for wear and damage.
- Keep the machine clean and free of debris to prevent malfunctions.
- Dispose of sharp spinning tools and blades properly.
By following these safety precautions and operating the spinning machine responsibly, you can effectively produce high-quality, precision-shaped metal components while maintaining a safe and controlled work environment. Spinning machines continue to be a valuable tool in metalworking operations, offering a versatile and efficient method for shaping a wide range of components.
Spinning machines are also commonly used in the production of cookware made from stainless steel. These machines are used to create a range of shapes and sizes, including bowls, plates, and other kitchenware items.
The spinning machine consists of a lathe that rotates the stainless steel blank and a spinning tool that shapes the metal as it rotates. The spinning tool is typically made of hardened steel or carbide and is shaped to create the desired form.
To use the spinning machine, the stainless steel blank is mounted on the lathe, and the spinning tool is positioned against the surface of the blank. The lathe is then turned on, causing the blank to rotate, while the spinning tool is pressed against the surface of the metal. As the spinning tool moves across the surface of the metal, it shapes it into the desired form.
Spinning machines are commonly used in the production of cookware stainless steel because they can create complex shapes quickly and efficiently. They are used in a wide range of industries, including the food service and hospitality industries, as well as in commercial and industrial settings.
Polishing Machines
Polishing machines are essential tools used in various industries to achieve a smooth, shiny finish on various surfaces, including metals, plastics, and composites. These machines employ different abrasives, polishing compounds, and techniques to remove imperfections, enhance gloss, and restore a polished appearance.
Types of Polishing Machines:
Polishing machines come in various types, each tailored to specific applications and materials. Some common types include:
- Buffing Machines: These machines use rotating buffing wheels covered with soft abrasives or polishing compounds to create a high-gloss finish. They are commonly used for polishing metals, plastics, and painted surfaces.
- Polishing Lathes: These machines rotate the workpiece against a stationary abrasive belt or polishing wheel, providing precise control over the polishing process. They are suitable for polishing cylindrical or flat surfaces.
- Tumbling Machines: These machines use tumbling action and abrasive media to polish workpieces. They are ideal for polishing small, irregularly shaped components or large quantities of parts.
- Vibratory Polishing Machines: These machines use a combination of vibration and abrasive media to polish workpieces. They are efficient for polishing large batches of small or irregularly shaped components.
Applications of Polishing Machines:
Polishing machines are widely used in various industries, including:
- Metalworking: Polishing machines are used to polish metal components for a variety of purposes, such as enhancing aesthetics, improving surface smoothness, and reducing friction.
- Automotive Industry: Polishing machines are used to polish car bodies, wheels, and other components to achieve a high-gloss finish.
- Jewelry Manufacturing: Polishing machines are used to polish gemstones, jewelry pieces, and other precious metals to enhance their brilliance and luster.
- Furniture Manufacturing: Polishing machines are used to polish wood surfaces, metal accents, and other components of furniture to create a smooth, finished appearance.
- Electronics Manufacturing: Polishing machines are used to polish electronic components, such as circuit boards and casings, to ensure a clean and aesthetically pleasing appearance.
Advantages of Polishing Machines:
Polishing machines offer several advantages over manual polishing methods, including:
- Increased Efficiency: Polishing machines can process components much faster than manual polishing, significantly increasing production output.
- Enhanced Consistency: Polishing machines ensure consistent polishing results, eliminating the variations that can occur with manual polishing.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Polishing machines reduce the need for manual labor, lowering labor costs and improving production efficiency.
- Improved Safety: Polishing machines minimize the risk of operator injuries associated with manual polishing methods.
- Achieving High-Quality Finishes: Polishing machines can achieve high-quality finishes that are difficult to replicate with manual polishing.
Safety Precautions for Using Polishing Machines:
When operating polishing machines, it is crucial to follow safety precautions to prevent injuries and ensure proper operation:
- Always wear appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), including safety glasses, gloves, and hearing protection.
- Ensure the workpiece is securely clamped to the machine to prevent movement during polishing.
- Select the appropriate polishing wheel, abrasive, and speed for the material and desired finish.
- Avoid excessive force and pressure when polishing the workpiece.
- Regularly inspect polishing wheels and abrasives for wear and damage.
- Keep the machine clean and free of debris to prevent malfunctions.
- Dispose of used abrasives and polishing compounds properly.
- Operate the machine in a well-ventilated area to prevent exposure to dust or fumes.
- Follow proper lifting techniques when handling heavy workpieces.
- Be aware of the machine’s emergency stop button and use it immediately in case of any unexpected situations.
By adhering to these safety guidelines and operating the polishing machine responsibly, you can effectively achieve high-quality polished surfaces while maintaining a safe and controlled work environment. Polishing machines remain indispensable tools in various industries, enabling the creation of aesthetically pleasing, functional, and durable products.
Polishing machines for the production of cookware stainless steel are used to give a smooth and shiny finish to the surface of the cookware. The polishing process involves removing any surface defects or imperfections that may be present on the cookware surface. Polishing machines typically use abrasive materials such as polishing compounds, sandpaper, or buffing wheels to remove any scratches, pits, or other surface marks.
The polishing machine consists of a rotating spindle that holds the polishing tool, which can be a polishing wheel or a buffing pad. The spindle rotates at a high speed, and the polishing tool is brought into contact with the surface of the cookware. The operator moves the polishing tool over the surface of the cookware in a circular motion, applying pressure as needed to remove any imperfections and achieve the desired finish.
Polishing machines for the production of cookware stainless steel are commonly used in the manufacturing industry to produce a high-quality finish on cookware products. These machines are also used in metalworking shops, automotive repair shops, and other industries that require metal surfaces to be polished to a high degree of smoothness and shine.
Sheet metal circle cutting machine
Companies use this machine to cut sheet metal into circles. It is an automatic cutter to form round sheet metal parts. Check the below video;
A sheet metal circle cutting machine, also known as a circle shear or circle cutter, is a specialized tool designed to precisely cut circular shapes from sheet metal. These machines are essential for producing a variety of circular components in various industries, including metalworking, manufacturing, and fabrication.
Types of Sheet Metal Circle Cutting Machines:
- Hydraulic Shearing Circle Cutters: These machines utilize hydraulic pressure to cut circular shapes from sheet metal. They are known for their power, precision, and ability to handle thick materials.
- Laser Circle Cutters: Laser circle cutters employ a focused beam of laser light to vaporize the material, creating clean, precise cuts with minimal heat-affected zones. They are particularly suitable for cutting thin sheet metal and intricate designs.
- CNC Circle Cutters: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) circle cutters incorporate computer programming to control the cutting process, ensuring precise dimensions, consistent shapes, and repeatability. They are widely used in high-volume production environments.
Working Principle of Circle Sheet Cutting Machines:
The operating principle of a circle sheet cutting machine varies depending on the type of machine, but the general process involves the following steps:
- Sheet Metal Positioning: The sheet metal workpiece is securely clamped onto the machine’s worktable, ensuring stability and precise positioning for cutting.
- Cutting Tool Adjustment: The cutting tool, whether it’s a hydraulic shear blade, a laser beam, or a rotating punch, is adjusted to the desired cutting diameter. The tool is positioned above the workpiece at the desired cutting location.
- Cutting Cycle Initiation: The cutting cycle is initiated, and the cutting tool moves along a circular path, cutting the sheet metal into a circular shape. The cutting speed, pressure, or laser power are controlled to achieve the desired cut quality and edge condition.
Safety Precautions for Using Sheet Metal Circle Cutting Machines:
When operating sheet metal circle cutting machines, it is crucial to prioritize safety to prevent injuries and ensure proper machine operation:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses, gloves, and hearing protection, to protect yourself from flying debris, sharp edges, and noise.
- Machine Guarding: Ensure all safety guards and interlocks are in place and functioning properly to prevent accidental contact with moving parts or hazardous areas of the machine.
- Secure Workpiece Clamping: Verify that the workpiece is securely clamped to the worktable to prevent movement during cutting, which could lead to inaccurate cuts or injuries.
- Proper Cutting Tool Selection and Maintenance: Choose the appropriate cutting tool and cutting parameters based on the material thickness, cutting speed requirements, and desired edge finish. Regularly maintain the cutting tool to ensure optimal performance and safety.
- Proper Tool Handling: Handle cutting tools with care, especially blades and laser emitters, to avoid accidental contact or injury.
- Clear Work Area: Maintain a clean and organized work area free from clutter and debris to prevent tripping hazards and ensure unobstructed movement around the machine.
- Emergency Stop Procedure: Familiarize yourself with the location and operation of the emergency stop button to immediately halt the machine in case of any unexpected situations.
- Authorization Restriction: Keep the machine out of reach of unauthorized individuals, especially children, to prevent accidental operation or injury.
By adhering to these safety guidelines and operating the sheet metal circle cutting machine responsibly, you can effectively produce precise, high-quality circular components while maintaining a safe and controlled work environment. Sheet metal circle cutting machines play a vital role in various industries, enabling the efficient and precise production of circular components for a wide range of applications.
There are several cutting machines that can be used in the production of cookware stainless steel. Some of them include:
- Laser cutting machine: This uses a high-powered laser beam to cut through the stainless steel material. It is precise, produces clean cuts, and can cut through thick materials.
- Waterjet cutting machine: This uses a high-pressure jet of water mixed with an abrasive substance to cut through the stainless steel material. It can cut through thick materials and produce clean edges.
- Plasma cutting machine: This uses a jet of plasma, which is a gas heated to a high temperature, to cut through the stainless steel material. It is suitable for cutting thick materials and can produce precise cuts.
- Shearing machine: This uses a cutting blade to shear through the stainless steel material. It is suitable for cutting thin sheets of material and can produce straight and clean cuts.
- Guillotine cutting machine: This also uses a cutting blade to shear through the stainless steel material, but it can handle thicker sheets of material than a shearing machine. It can also produce straight and clean cuts.
These cutting machines are used in the production of various cookware stainless steel products, such as pots, pans, and utensils, among others.
Annealing Furnace for the Production of Cookware Stainless Steel
An annealing furnace is a crucial piece of equipment in the production of stainless steel cookware, playing a vital role in stress relief and enhancing the formability and ductility of the material. These furnaces heat the cookware components to a specific temperature, allowing the internal stresses introduced during manufacturing processes to dissipate.
Purpose of Annealing in Cookware Manufacturing:
- Stress Relief: Annealing relieves internal stresses in the stainless steel, which can arise from processes such as forming, stamping, or welding. These stresses can make the material brittle and prone to cracking. Annealing helps to relax the internal structure, reducing the risk of cracks and improving the overall strength and toughness of the cookware.
- Enhancing Formability and Ductility: Annealing softens the stainless steel, making it more malleable and easier to form into various shapes. This improved formability is essential for creating the desired shapes and profiles of cookware components.
- Grain Refinement: Annealing can also refine the grain structure of the stainless steel, leading to a more uniform and consistent microstructure. This refined grain structure contributes to improved mechanical properties, including better strength, ductility, and impact resistance.
Types of Annealing Furnaces Used for Cookware:
- Batch Annealing Furnaces: These furnaces heat a batch of cookware components simultaneously, typically in a controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation or discoloration.
- Continuous Annealing Furnaces: These furnaces process cookware components in a continuous flow, offering higher throughput and automation in high-volume production environments.
- Vacuum Annealing Furnaces: These furnaces operate under a vacuum, preventing oxidation and ensuring a bright, clean finish on the cookware components.
Operating Principles of Annealing Furnaces:
- Loading and Charging: The cookware components are carefully loaded and positioned within the furnace chamber.
- Heating Cycle: The furnace is heated to the desired annealing temperature, typically between 800°C and 1100°C, depending on the specific stainless steel grade and desired properties.
- Soaking Period: The cookware components are held at the annealing temperature for a specified soaking period, allowing the internal stresses to dissipate and the microstructure to transform.
- Cooling Cycle: The furnace is gradually cooled to room temperature, typically at a controlled rate to prevent the reintroduction of stresses.
- Unloading and Inspection: Once cooled, the cookware components are carefully unloaded from the furnace and inspected for quality and consistency.
Safety Precautions for Operating Annealing Furnaces:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including heat-resistant gloves, safety glasses, and a protective apron, when operating or handling hot cookware components.
- Furnace Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain the annealing furnace to ensure proper operation and prevent malfunctions.
- Ventilation and Fume Extraction: Ensure adequate ventilation and fume extraction systems are in place to remove harmful gases or fumes generated during the annealing process.
- Emergency Shutdown Procedure: Familiarize yourself with the emergency shutdown procedures in case of any unexpected situations.
- Proper Component Handling: Use appropriate lifting techniques and tools to handle hot cookware components to prevent burns or injuries.
- Authorized Access: Restrict access to the annealing furnace area to authorized personnel only.
By adhering to these safety guidelines and operating the annealing furnace responsibly, you can effectively achieve the desired properties of stainless steel cookware while maintaining a safe and controlled work environment. Annealing furnaces remain essential tools in cookware manufacturing, ensuring the production of high-quality, durable, and stress-free stainless steel cookware.
An annealing furnace is an industrial machine used in the production of cookware stainless steel to heat treat the metal to improve its properties. During the manufacturing process of stainless steel cookware, the material is subjected to various mechanical and thermal treatments that can cause stress and alter the metal’s properties.
Annealing is the process of heating the stainless steel to a specific temperature, holding it at that temperature for a certain time, and then cooling it slowly. This process relieves internal stress and allows the stainless steel to soften, become more ductile, and improve its machinability.
The annealing furnace used in the production of cookware stainless steel can vary in size and type, depending on the volume of the production and the specific requirements of the material. The furnace is typically operated by a computer-controlled system that monitors the temperature and time during the annealing process, ensuring that the stainless steel is treated accurately and consistently.
Grinding machine for the Production of Cookware Stainless Steel
Grinding machines are commonly used in the production of cookware stainless steel to remove burrs, scratches, and other surface imperfections from the metal. These machines are typically equipped with abrasive grinding wheels that rotate at high speeds to remove material from the surface of the metal.
The grinding process involves feeding the cookware stainless steel pieces into the machine, where they are held against the rotating grinding wheel. The grinding wheel grinds away the surface material, leaving a smooth and polished finish.
Grinding machines are often used after other machining processes, such as cutting, shaping, or drilling, to prepare the metal for final finishing and polishing. They can be used to grind various shapes and sizes of cookware, including pots, pans, and lids, and can be programmed to grind specific shapes and sizes.
The use of grinding machines in the production of cookware stainless steel helps to ensure that the final product has a smooth and polished surface, which is not only aesthetically pleasing but also improves its durability and longevity.
Hydraulic Drawing Press as a Steel Cookware Stainless Steel Making Machine
The hydraulic drawing press forms deep-drawn parts by a method called deep drawing. The hydraulic press uses hydraulic power to move the molds. Here, the molds operate as the shaping element of the operation.
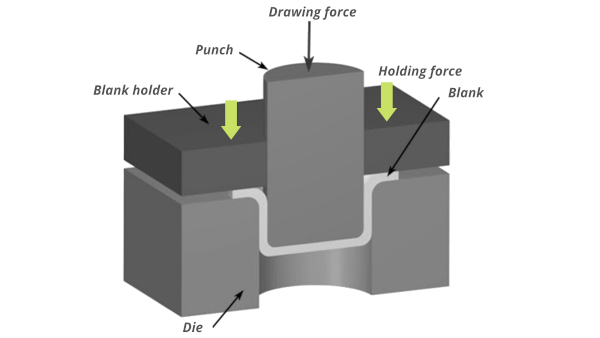
The operator activates the press by pressing 2 buttons simultaneously. The hydraulic pump pumps the oil into the press channels and the upper ram moves down and forms the necessary shape
Later, the operator removes the ready part and puts a new part between the molds. Deep drawing is the main operation in cookware production.
Hydraulic drawing presses play a crucial role in the manufacturing of stainless steel cookware, particularly in the forming of deep and complex shapes. These powerful machines utilize hydraulic pressure to force sheet metal into dies or molds, creating the desired shapes for pots, pans, and other cookware components.
Key Applications of Hydraulic Drawing Presses in Cookware Manufacturing:
- Deep Drawing: Hydraulic drawing presses are renowned for their ability to form deep shapes from sheet metal. They are commonly used to create the bodies of pots, pans, and other deep cookware components.
- Complex Shape Forming: Hydraulic drawing presses can handle intricate geometries and complex shapes, making them suitable for producing a wide range of cookware components with unique designs.
- High Production Efficiency: Hydraulic drawing presses offer high production rates, making them well-suited for mass production of stainless steel cookware.
- Dimensional Accuracy: Hydraulic drawing presses ensure precise dimensions and consistent shapes, contributing to the overall quality and uniformity of cookware components.
- Material Strength Enhancement: The drawing process can enhance the strength and ductility of the stainless steel material, improving the durability and performance of the cookware.
Advantages of Hydraulic Drawing Presses in Cookware Manufacturing:
- High Force and Pressure: Hydraulic drawing presses can exert high forces and pressures, enabling them to handle thick materials and form deep shapes effectively.
- Precise Control: Hydraulic systems provide precise control over the forming process, ensuring consistent and accurate results.
- Versatility: Hydraulic drawing presses can be adapted to produce a wide range of shapes and sizes, making them versatile tools for cookware manufacturing.
- Automation Capabilities: Hydraulic drawing presses can be integrated into automated production lines, enhancing efficiency and reducing labor costs.
- Safety Features: Hydraulic drawing presses incorporate safety features, such as interlocks and guards, to protect operators from hazards.
- Durability and Reliability: Hydraulic drawing presses are built to withstand the rigors of industrial environments, ensuring long-term durability and consistent performance.
By utilizing hydraulic drawing presses, cookware manufacturers can efficiently produce high-quality, durable, and aesthetically pleasing components for their products. These versatile and powerful machines have become indispensable tools in the production of stainless steel cookware, contributing to the overall quality and performance of these essential kitchenware items.
EMS Metalworking Machinery: Your Trusted Partner in Precision Metalworking

EMS Metalworking Machinery is a leading manufacturer of high-quality metalworking equipment, dedicated to providing innovative solutions that meet the evolving needs of industries worldwide. With a rich history of excellence and a commitment to technological advancement, we have earned a reputation for delivering cutting-edge machinery that ensures precision, efficiency, and durability.
Our Product Range:
- CNC Spinning Lathes: From precision bench lathes to heavy-duty industrial models, our lathes offer unmatched accuracy and performance for a wide range of applications, including machining shafts, gears, and other cylindrical components.
- Trimming Beading Machine: Our trimming beading machines are designed to provide exceptional cutting capabilities and versatility, enabling you to create complex shapes and intricate details with ease. Whether you need a horizontal or vertical trimming machine, we have the perfect solution for your needs.
- Hydraulic Deep Drawing Press Machines: Our hydraulic deep drawing press machines are built to deliver precise and powerful drawing operations, ensuring clean holes and exceptional surface finishes. We offer a comprehensive range to suit various applications.
- Grinding Machines: Our grinding machines are engineered for precision and efficiency, allowing you to achieve the highest levels of surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Whether you need a surface grinder, cylindrical grinder, or tool grinder, we have the equipment to meet your specific requirements.
- Sawing Machines: Our sawing machines are designed for fast and accurate cutting of metals, providing clean cuts and minimal burrs. From band saws to circular saws, we offer a variety of options to suit different materials and cutting needs.
- Custom Machinery: In addition to our standard product line, we also specialize in custom machinery fabrication. Our experienced engineers can work with you to design and build tailored solutions that meet your unique requirements and optimize your production processes.
Why Choose EMS Metalworking Machinery:
- Quality: Our machines are crafted with the highest quality materials and components, ensuring long-lasting performance and reliability.
- Precision: We are committed to delivering machinery that meets the most stringent tolerances and standards, ensuring exceptional accuracy in your metalworking operations.
- Innovation: We continuously invest in research and development to stay at the forefront of technological advancements, offering innovative solutions that enhance your productivity and efficiency.
- Customer Support: Our dedicated team of experts is always available to provide comprehensive support, from machine selection and installation to maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Customization: We understand that every business has unique needs, and we offer flexible customization options to tailor our machines to your specific requirements.
At EMS Metalworking Machinery, we are more than just a supplier of equipment; we are your trusted partner in metalworking success. By choosing EMS, you can be confident in the quality, reliability, and performance of your machinery, enabling you to achieve your business goals and stay ahead of the competition.
EMS Metalworking Machinery
We design, manufacture and assembly metalworking machinery such as:
- Hydraulic transfer press
- Glass mosaic press
- Hydraulic deep drawing press
- Casting press
- Hydraulic cold forming press
- Hydroforming press
- Composite press
- Silicone rubber moulding press
- Brake pad press
- Melamine press
- SMC & BMC Press
- Labrotaroy press
- Edge cutting trimming machine
- Edge curling machine
- Trimming beading machine
- Trimming joggling machine
- Cookware production line
- Pipe bending machine
- Profile bending machine
- Bandsaw for metal
- Cylindrical welding machine
- Horizontal pres and cookware
- Kitchenware, hotelware
- Bakeware and cuttlery production machinery
as a complete line as well as an individual machine such as:
- Edge cutting trimming beading machines
- Polishing and grinding machines for pot and pans
- Hydraulic drawing presses
- Circle blanking machines
- Riveting machine
- Hole punching machines
- Press feeding machine
You can check our machinery at work at: EMS Metalworking Machinery – YouTube
Applications:
- Beading and ribbing
- Flanging
- Trimming
- Curling
- Lock-seaming
- Ribbing
- Flange-punching