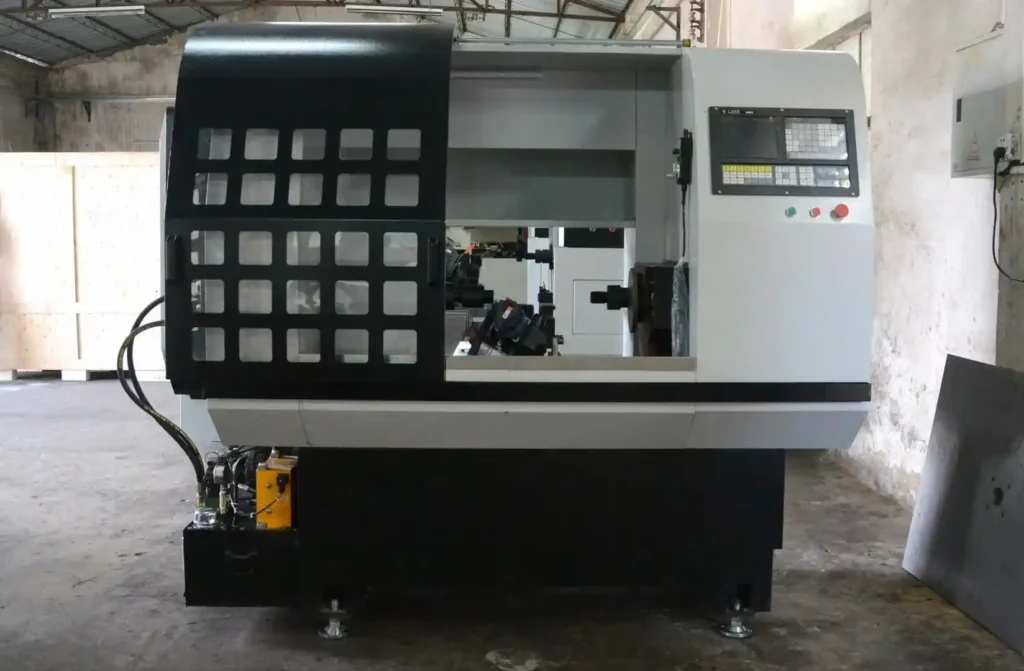

CNC (Computer Numerical Control) metal spinning machine is a sophisticated industrial tool used in metalworking processes to create cylindrical or conical shapes from flat metal discs or blanks. This manufacturing technique, also known as spin forming or metal turning, utilizes precision-controlled rotation and shaping tools to form metal parts. CNC technology has revolutionized metal spinning by enabling high levels of automation, accuracy, and repeatability in production.
Running one of these machines involves many steps, and the operator needs to be aware of the oncoming process to plan the intermediate steps. When the final work is finished, the workpiece is removed, and the dies are prepared for final component removal. Typical components include light fixture parts, aluminum cooking pots, base plates, satellite ground station components, and many other specially shaped items which sell to the customer at high prices. The process is relatively economical once the proper machine and tooling combination is chosen. Continuing sheet and coil developments have kept the Boys very busy continuing to adapt these materials to modern component materials. Always at the forefront is the need to provide these components on very short deliveries. The machine is designed to provide these components with production schedules from a few hours to a few days.
Today, a fully modern spinning machine consists of numerous controls capable of exerting force on the sheet metal with the greatest precision, and many other refinements. One of these is the electromagnetic clamp, which applies the spinning roller to the metal. It should be noted that the rotational speed of the rollers is variable, thus giving the operator control of the final form of the workpiece. The modern control system provides easy, repetitive operation and simple die changing. There are many controls in the spinning machine, but the primary purpose of these servo-driven units is to control the contact angle between the workpiece and the roller, and the curve progression of the workpiece as it is worked. Additionally, there are the many programmable stopping points, which include both a retract stroke (to allow component removal) and a total sheet-removal stroke advanced by the required preselected amount.
CNC Metal Spinning Machine: A High-Speed, Precise, and Efficient Manufacturing Solution
CNC metal spinning machines have revolutionized the manufacturing process by providing a fast, precise, and efficient method for producing complex metal parts with high accuracy. These machines utilize a combination of computer-controlled cutting and forming tools to shape and spin metal sheets into various forms, allowing for the creation of intricate designs and shapes with unmatched precision.
Principle of Operation
The CNC metal spinning machine operates on the principle of using a rotating tool to shape and form a metal sheet. The machine consists of a spindle, a worktable, and a control system. The spindle is mounted on the worktable and is equipped with a rotating tool that is designed to cut and form the metal sheet. The control system is responsible for controlling the movement of the spindle, the speed of the rotation, and the direction of the cutting and forming process.
Advantages
The CNC metal spinning machine offers several advantages over traditional manufacturing methods, including:
- High-speed production: CNC metal spinning machines can produce parts at a rate of up to 100 pieces per hour, making it an ideal solution for high-volume production.
- High precision: The machine’s precision cutting and forming tools ensure that the produced parts have high accuracy and surface finish.
- Complex design capabilities: CNC metal spinning machines can produce complex shapes and designs with ease, making it an ideal solution for creating intricate parts.
- Reduced labor costs: The automation of the manufacturing process reduces labor costs, making it an attractive solution for companies looking to reduce production costs.
- Increased flexibility: CNC metal spinning machines can be easily programmed to produce different parts, allowing for increased flexibility in production.
Applications
CNC metal spinning machines have a wide range of applications in various industries, including:
- Aerospace: CNC metal spinning machines are used in the aerospace industry to produce lightweight, high-strength parts such as aircraft components, satellite components, and rocket parts.
- Automotive: CNC metal spinning machines are used in the automotive industry to produce complex shapes and designs for automotive parts such as steering columns, airbags, and fuel tanks.
- Medical: CNC metal spinning machines are used in the medical industry to produce medical devices such as surgical instruments, implants, and other medical equipment.
- Industrial: CNC metal spinning machines are used in various industrial applications such as producing industrial machinery components, gears, and other industrial equipment.
Types of CNC Metal Spinning Machines
There are several types of CNC metal spinning machines available in the market, including:
- Vertical CNC metal spinning machines: These machines are designed for producing parts with complex shapes and designs.
- Horizontal CNC metal spinning machines: These machines are designed for producing large parts with high accuracy.
- Specialized CNC metal spinning machines: These machines are designed for specific applications such as aerospace or medical devices.
Design Considerations
When designing a CNC metal spinning machine, several factors must be considered including:
- Material selection: The selection of the right material is crucial for ensuring the quality and accuracy of the produced parts.
- Tooling design: The design of the cutting and forming tools must be carefully planned to ensure that they can accurately shape and form the metal sheet.
- Machine configuration: The configuration of the machine must be designed to ensure that it can accurately position and rotate the metal sheet during the manufacturing process.
- Control system: The control system must be designed to ensure accurate movement of the spindle, rotation speed, and direction of cutting and forming process.
Conclusion
CNC metal spinning machines have revolutionized the manufacturing process by providing a fast, precise, and efficient method for producing complex metal parts. With its ability to produce high-accuracy parts with complex shapes and designs, CNC metal spinning machines are an ideal solution for various industries. By understanding the principle of operation, advantages, applications, types, design considerations, and limitations of CNC metal spinning machines, manufacturers can make informed decisions about investing in this technology.
CNC Metal Spinning Machine
CNC metal spinning machines operate by securing a metal blank (typically aluminum, steel, or copper) on a spinning mandrel or chuck. The machine’s computerized controls then articulate specialized tools, such as rollers or forming tools, which gradually shape the spinning metal into the desired form. The entire process is meticulously programmed using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software to achieve precise dimensions and geometries.
Components of a CNC Metal Spinning Machine
- Spindle and Mandrel: The spindle holds and rotates the metal blank, while the mandrel supports the inner surface of the workpiece during forming.
- Tooling: CNC metal spinning machines use various tooling configurations depending on the desired shape and complexity of the part. This may include rollers, pressure pads, or specialized forming tools.
- Control System: Modern CNC systems integrate sophisticated software and controls to manage machine movements, tool paths, and part dimensions. Operators input design specifications and monitor the production process through user interfaces.
- Drive System: Precision motors drive the rotation of the spindle and tooling components, ensuring smooth and accurate movement during forming.
- Safety Features: CNC metal spinning machines are equipped with safety interlocks, emergency stops, and guarding to protect operators and prevent accidents.
Advantages of CNC Metal Spinning Machines
- Cost-Effective Production: Metal spinning offers cost advantages over traditional machining methods for producing cylindrical or conical shapes, especially for low to medium production volumes.
- Complex Geometries: CNC controls enable the creation of complex shapes and contours with high accuracy and consistency.
- Material Efficiency: Metal spinning minimizes material waste compared to subtractive manufacturing techniques like milling or turning.
- Quick Setup: CNC programming allows for rapid tooling changes and setup, reducing downtime between production runs.
- Versatility: CNC metal spinning machines can work with a wide range of metals, including aluminum, stainless steel, brass, and titanium.
Applications
CNC metal spinning machines find applications across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, lighting, and architectural sectors. Common products produced by metal spinning include:
- Lighting fixtures
- Reflectors and lampshades
- Pressure vessels and tanks
- Decorative and architectural components
- Aerospace components (e.g., engine housings)
- Cooking and kitchenware
Future Trends
The future of CNC metal spinning is likely to be shaped by advancements in automation, robotics, and materials science. Integration with AI (Artificial Intelligence) for predictive maintenance and quality control is anticipated to further enhance productivity and reduce production costs. Additionally, additive manufacturing techniques may complement metal spinning by enabling the fabrication of hybrid parts with intricate geometries.
In conclusion, CNC metal spinning machines represent a pivotal technology in modern manufacturing, offering efficiency, precision, and versatility in shaping metal components for diverse applications. The continued evolution of CNC systems promises to expand the capabilities and competitiveness of metal spinning as a manufacturing process.
CNC Operated Metal Spinning Machines
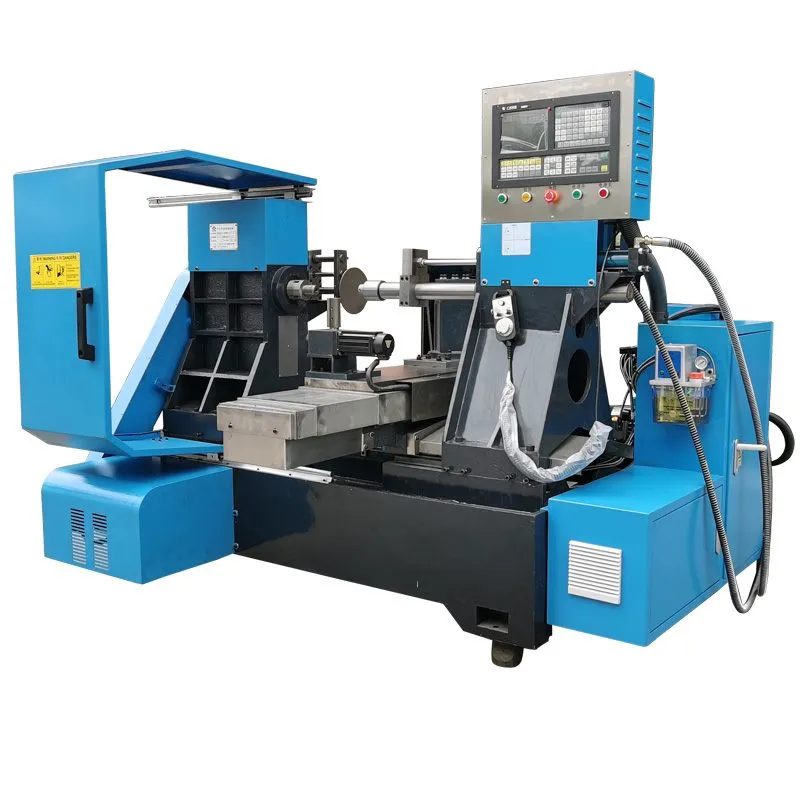

CNC-operated metal spinning machines are advanced tools used for forming metal sheets into symmetrical shapes such as cones, cylinders, and hemispheres. These machines use computer numerical control (CNC) to automate and precisely control the spinning process. Here are the key aspects and benefits of CNC-operated metal spinning machines:
Key Aspects
- Computer Numerical Control (CNC):
- CNC systems use pre-programmed software to control the movement of the spinning machine. This ensures high precision and repeatability.
- Spindle and Mandrel:
- The workpiece is mounted on a mandrel attached to the spindle, which rotates the workpiece at high speeds.
- Rollers/Tooling:
- Tools or rollers press against the rotating workpiece to shape it according to the desired profile. These tools can be adjusted and controlled by the CNC system.
- Control Panel:
- An interface where the operator can input the desired parameters and monitor the machine’s performance. It includes a computer that interprets the CNC code.
- Tailstock:
- Provides support for the workpiece, especially for longer or more complex shapes. It can be moved to accommodate different workpiece lengths.
- Bed:
- The base of the machine that provides stability and support for all other components.
- Coolant System:
- A system that delivers coolant to the working area to reduce heat and friction, thereby extending the life of the tooling and improving workpiece quality.
Benefits
- Precision and Accuracy:
- CNC control ensures precise and consistent shaping of metal parts, reducing errors and material waste.
- Repeatability:
- Once a program is set, the machine can produce identical parts repeatedly, ensuring uniformity in production.
- Efficiency:
- Automation speeds up the production process, allowing for higher throughput compared to manual metal spinning.
- Complex Shapes:
- Capable of producing complex and intricate shapes that would be difficult or impossible to achieve manually.
- Reduced Labor Costs:
- Automation reduces the need for skilled labor, lowering overall production costs.
- Versatility:
- Can work with various metals including aluminum, steel, copper, and more, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Safety:
- Enhanced safety features reduce the risk of accidents compared to manual spinning processes.
Applications
CNC-operated metal spinning machines are used in numerous industries, including:
- Aerospace: Manufacturing nose cones, rocket casings, and satellite dishes.
- Automotive: Producing parts like wheels, hubcaps, and exhaust components.
- Lighting: Creating light fixtures and reflectors.
- Cookware: Fabricating pots, pans, and other kitchenware.
- HVAC: Making components for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
- Medical: Producing surgical instruments and medical device housings.
- Industrial Machinery: Creating machine parts like pulleys and hoppers.
- Consumer Goods: Manufacturing musical instruments, decorative objects, and more.
CNC-operated metal spinning machines offer significant advantages in terms of precision, efficiency, and versatility, making them essential tools in modern manufacturing.
Delving into the World of CNC Metal Spinning Machines

The CNC metal spinning machine stands as a marvel of precision and metal manipulation. It takes a traditional metalworking technique and infuses it with computer-controlled automation, resulting in a powerful tool for modern manufacturing. This text will delve into the intricacies of these machines, exploring their workings, capabilities, and advantages.
Core Functionality: The Art of Spinning Metal
At its heart, a CNC metal spinning machine replicates the ancient art of metal spinning. A metal sheet, typically referred to as a blank, is secured on a mandrel. The mandrel replicates the desired final shape of the spun object. A spinning roller, guided by the CNC program, presses against the blank, forcing the metal to conform to the contours of the mandrel. Through a delicate interplay of pressure and rotation, the blank is progressively shaped into the final form.
The Power of CNC: Precision and Repeatability
While traditional metal spinning relied on the skill of the operator, CNC technology revolutionizes the process. The CNC (Computer Numerical Control) unit acts as the brain of the machine. It translates a digital design, created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, into a precise set of instructions for the machine’s motors. These instructions dictate the movement of the spinning roller along various axes, ensuring an accurate and consistent shaping of the metal.
Advantages of CNC Metal Spinning Machines
CNC metal spinning machines offer a plethora of advantages over traditional methods:
- Precision and Repeatability: CNC control guarantees consistent wall thickness and precise form, critical for applications demanding high accuracy.
- Complex Shapes: CNC allows for the creation of intricate and complex shapes, previously difficult or impossible to achieve with manual techniques.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Automation minimizes the need for highly skilled labor, leading to cost savings in production.
- Increased Production Rates: CNC machines operate faster and more consistently than manual processes, boosting production output.
- Material Versatility: These machines can handle a wide range of metals, including aluminum, copper, stainless steel, and even some exotic materials.
Applications of CNC Metal Spinning
CNC metal spinning finds application across various industries due to its ability to produce high-quality, complex metal parts. Here are some key examples:
- Automotive: Air intake systems, lighting components, and wheel covers.
- Aerospace: Lightweight, high-strength components for aircraft.
- Lighting: Reflector housings and lampshades.
- Electronics: Shielding enclosures and heat sinks.
- Medical Equipment: Instrument housings and surgical components.
Specifying a CNC Metal Spinning Machine
Selecting the right CNC metal spinning machine requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Maximum Workpiece Size: The machine’s capacity to handle the desired blank size.
- Material Capabilities: The types of metal the machine can work with.
- Mandrel Compatibility: The ability to accommodate the specific mandrels required for your application.
- CNC Control System: The user-friendliness and features offered by the CNC software.
Conclusion
CNC metal spinning machines represent a significant advancement in metalworking technology. By combining tradition with cutting-edge automation, they offer a powerful solution for the production of high-precision, complex metal parts. Understanding the core principles, advantages, and applications of these machines empowers manufacturers to leverage their capabilities and achieve success in their respective fields.
CNC Metal Spinning Machine
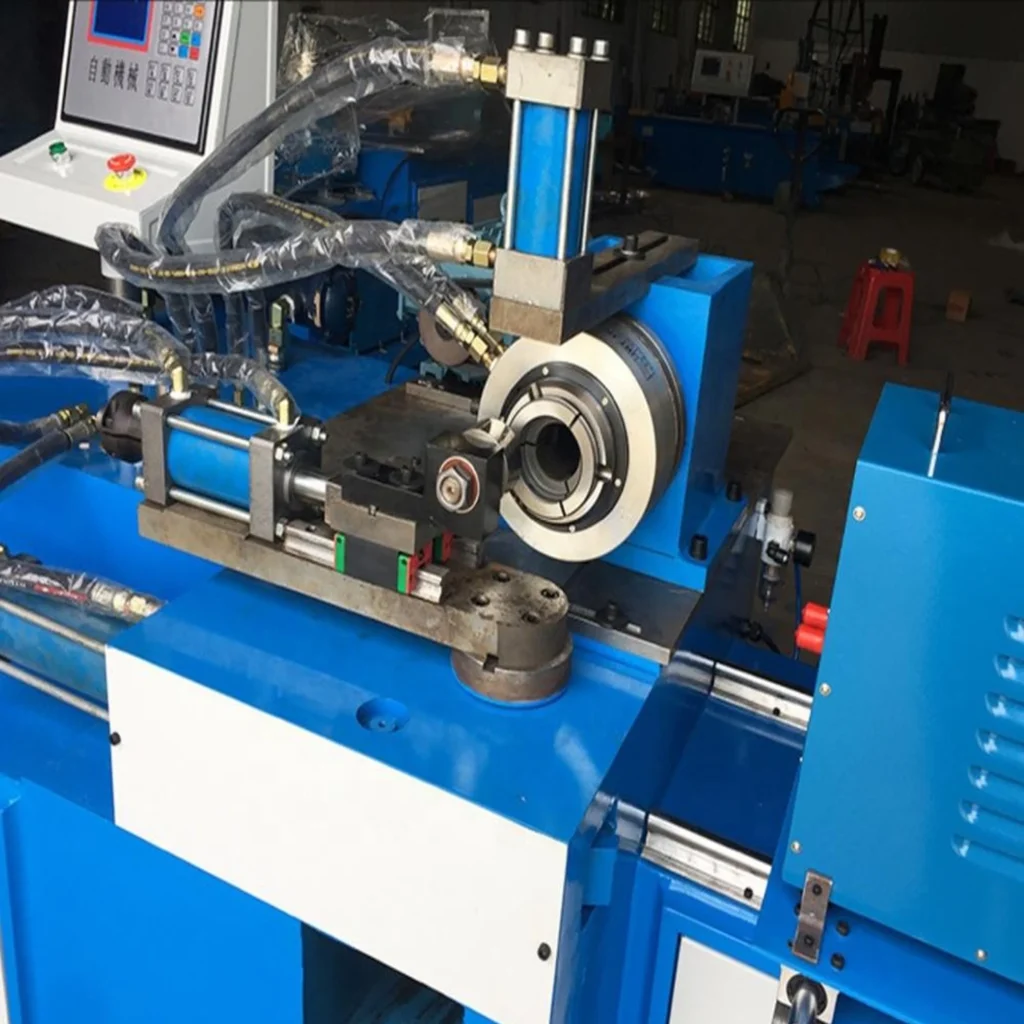

CNC metal spinning, also known as spin forming, metal turning, or metal spinning, is a metalworking process by which a disc or tube of metal is rotated at high speeds and formed into an axially symmetric part. This process is performed using computer numerical control (CNC) machines to precisely control the spinning and forming of the metal.
Working Principle
The CNC metal spinning machine starts with a metal disc or tube clamped and rotated by a motor. The CNC controls the movement of rollers or tools that shape the metal over a mandrel or form block. The spinning tools move in a programmed pattern, gradually forming the metal into the desired shape. This process allows for the production of seamless, high-strength parts with excellent structural integrity.
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems control metal spinning machines through a combination of software and hardware that automates and precisely manages the movements and operations of the machine. Here’s a detailed explanation of how CNC controls metal spinning machines:
1. Programming
- CAD/CAM Software: The process begins with Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software. The desired shape or part is designed using CAD software, and then CAM software generates the CNC code (G-code or M-code) that instructs the machine on how to create the part.
- G-code/M-code: G-code provides the specific instructions for machine movements, tool paths, and operational parameters. M-code controls miscellaneous functions such as coolant on/off and spindle start/stop.
2. Controller
- CNC Controller: The CNC controller is the brain of the machine. It reads the G-code and translates it into electrical signals that control the machine’s movements and operations.
- User Interface: The controller typically includes a user interface (control panel) where the operator can input commands, start and stop programs, and monitor machine status.
3. Machine Movements
- Servomotors/Stepper Motors: The CNC system uses servomotors or stepper motors to control the movements of the machine. These motors are responsible for the precise positioning of the spindle, tailstock, and tooling.
- Axis Control: CNC metal spinning machines typically operate on multiple axes (e.g., X-axis for cross-slide movement, Z-axis for carriage movement). The controller coordinates the movements along these axes to shape the workpiece accurately.
4. Spinning Process
- Spindle Rotation: The CNC system controls the spindle speed, ensuring that the workpiece rotates at the desired rate for optimal forming.
- Tooling Control: The CNC controller manages the position and pressure of the spinning tools or rollers. It ensures that the tools follow the programmed path to shape the metal as specified in the CAD design.
- Feed Rate: The controller adjusts the feed rate, which is the speed at which the tool advances along the workpiece, to ensure a smooth and precise forming process.
5. Feedback Systems
- Sensors and Encoders: CNC machines are equipped with sensors and encoders that provide real-time feedback to the controller. This feedback helps the system make adjustments to maintain accuracy and precision.
- Closed-Loop Control: The feedback from sensors and encoders enables closed-loop control, where the system continuously monitors and adjusts the machine’s operations to correct any deviations from the programmed path.
6. Additional Features
- Coolant Control: The CNC system can control the coolant flow to manage heat and reduce friction during the spinning process.
- Safety Systems: CNC machines often include safety features such as interlocks, emergency stop buttons, and protective enclosures, all controlled by the CNC system to ensure operator safety.
7. Execution
- Automated Operation: Once the program is loaded and started, the CNC system takes over the entire operation, executing the instructions to form the metal workpiece with high precision and repeatability.
- Monitoring and Adjustments: The CNC system continuously monitors the process and makes necessary adjustments to ensure the final product meets the desired specifications.
By automating and precisely controlling the metal spinning process, CNC systems significantly enhance productivity, accuracy, and consistency in manufacturing complex metal parts.
Components of CNC Metal Spinning Machine
The CNC metal spinning machine consists of several key components, including:
- Spindle and Chuck: The spindle holds and rotates the metal workpiece, while the chuck ensures secure clamping during the spinning process.
- Tooling: The tooling includes rollers, forming tools, and mandrels that shape the metal as it spins.
- CNC Control System: The CNC system precisely controls the movement of the spinning tools and the rotation of the workpiece, allowing for complex and accurate part production.
- Drive System: The drive system provides the necessary torque and speed to rotate the workpiece at high speeds.
- Safety Features: These include interlocks, guards, and emergency stop mechanisms to ensure safe operation.
Parts of the CNC Metal Spinning Lathe
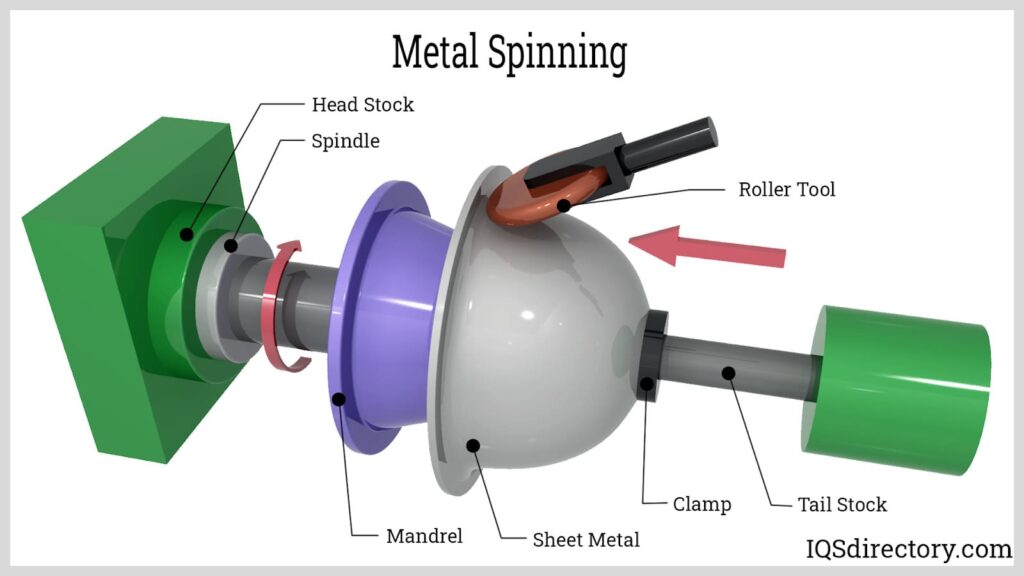
A CNC metal spinning lathe is a sophisticated machine designed for precision metalworking. It consists of several key components, each serving a specific function. Here are the main parts of a CNC metal spinning lathe:
- Bed:
- The base of the lathe, providing stability and support for the entire machine.
- Headstock:
- Located at one end of the bed, it houses the main spindle and motor. The spindle holds the workpiece and rotates it during the machining process.
- Tailstock:
- Positioned on the opposite end of the headstock, it supports the other end of the workpiece, especially for longer pieces. It can be moved along the bed to accommodate different workpiece lengths.
- Spindle:
- The rotating axis that holds and spins the workpiece. It is driven by the motor and is crucial for the spinning process.
- Tool Post/Tool Turret:
- A structure that holds the cutting tools. In CNC lathes, this can be an automated turret that changes tools as needed during the machining process.
- Carriage:
- Moves along the bed and supports the cutting tools. It includes the cross slide and compound slide for precise control of tool movement.
- Cross Slide:
- Mounted on the carriage, it moves the cutting tool in and out, perpendicular to the workpiece axis.
- Compound Slide:
- Mounted on the cross slide, it allows angular adjustment of the cutting tool for precise machining operations.
- Control Panel/Controller:
- The interface where the operator programs and controls the CNC machine. It includes a computer system that interprets the CNC code and controls the lathe’s movements.
- Chuck:
- A clamping device that holds the workpiece securely on the spindle. It can be adjusted to fit different sizes and shapes of workpieces.
- Tailstock Quill:
- A part of the tailstock that can be moved in and out to accommodate the workpiece and provide additional support.
- Lead Screw:
- A long threaded rod that moves the carriage and cross slide along the bed. It is driven by the motor and ensures precise positioning of the cutting tool.
- Coolant System:
- A system that delivers coolant to the cutting area to reduce heat and friction, enhancing tool life and workpiece quality.
- Chip Pan:
- A tray or pan located at the base of the lathe to collect metal shavings (chips) produced during the machining process.
- Guarding/Safety Features:
- Protective covers and safety features to ensure the operator’s safety during operation.
These components work together to perform precise metal spinning operations, allowing the CNC metal spinning lathe to create complex shapes and parts with high accuracy and repeatability.
Advantages of CNC Metal Spinning
CNC metal spinning offers several advantages, including:
- Cost-Effective: The process is cost-effective for producing prototypes, small batches, and large production runs.
- Design Flexibility: It allows for the production of complex and intricate shapes with ease.
- Material Savings: Minimal material waste due to the forming process.
- High Strength: The resulting parts exhibit high structural integrity due to the absence of seams or welds.
Applications of CNC Metal Spinning

CNC metal spinning is widely used in various industries, including:
- Aerospace: For producing components such as engine housings, missile nose cones, and satellite dishes.
- Automotive: In the production of exhaust components, decorative trim, and lighting fixtures.
- Housewares: For manufacturing cookware, lampshades, and decorative items.
- Custom Fabrication: In the creation of custom metal parts for architectural and artistic purposes.
Conclusion
CNC metal spinning machines offer a versatile and cost-effective method for producing a wide range of metal components with high precision and strength. The ability to create complex shapes and the suitability for various industries make CNC metal spinning an invaluable process in the manufacturing sector.
For further technical details and specifications, it is recommended to consult specific machine manufacturers and industry publications.
CNC Metal Spinning Applications

CNC metal spinning machines are the workhorses of various industries, shaping a wide array of components due to their ability to produce complex shapes with excellent precision. Here’s a deeper dive into some key applications:
Automotive Industry:
- Air Intake Systems: CNC spinning is ideal for crafting smooth, aerodynamic air intake systems that optimize engine performance.
- Lighting Components: Headlight reflectors, taillight housings, and other lighting components benefit from the precise shaping and lightweight properties achievable with metal spinning.
- Wheel Covers: The ability to create complex curves and domes makes CNC spinning perfect for manufacturing stylish and durable wheel covers.
Aerospace Industry:
- Lightweight, High-Strength Components: Aircraft prioritize minimal weight without compromising strength. CNC metal spinning allows for the creation of parts like fuselage components and engine nacelles from materials like aluminum and titanium, achieving this critical balance.
- Ducts and Fairings: The smooth, seamless shapes produced by spinning are ideal for air ducts and fairings in aircraft, reducing air resistance and improving fuel efficiency.
Lighting and Décor:
- Reflector Housings: CNC spinning excels at creating the precise shapes required for efficient light reflection in lamps and spotlights.
- Lampshades: From modern, geometric designs to traditional, curved forms, CNC spinning allows for the creation of unique and visually striking lampshades.
- Decorative Elements: Metal spun parts can be incorporated into furniture, architectural features, and even art installations, adding a touch of elegance and sophistication.
Electronics Industry:
- Shielding Enclosures: Electronic components often require protection from electromagnetic interference (EMI). CNC metal spinning can produce seamless enclosures that effectively shield delicate circuitry.
- Heat Sinks: Managing heat dissipation is crucial for electronic devices. CNC spinning allows for the creation of intricate heat sinks with high surface area, efficiently transferring heat away from critical components.
Medical Equipment Industry:
- Instrument Housings: The sterile and precise nature of CNC metal spinning makes it suitable for crafting housings for medical instruments that require a high degree of cleanliness and durability.
- Surgical Components: Certain surgical components, like implant housings or specific instruments, benefit from the complex geometries achievable with CNC spinning.
Beyond these core applications, CNC metal spinning can be found in various other industries, including:
- Food and Beverage (Cookware, Dispensing Equipment)
- Military (Components for Missiles and Defense Systems)
- Telecommunications (Antenna Housings)
This versatility underscores the true power of CNC metal spinning machines. Their ability to produce complex shapes, high-precision parts, and seamless finishes from various metals makes them a valuable asset for a vast array of manufacturing applications.
EMS Metalworking Machines
We design, manufacture and assembly metalworking machinery such as:
- Hydraulic transfer press
- Glass mosaic press
- Hydraulic deep drawing press
- Casting press
- Hydraulic cold forming press
- Hydroforming press
- Composite press
- Silicone rubber moulding press
- Brake pad press
- Melamine press
- SMC & BMC Press
- Labrotaroy press
- Edge cutting trimming machine
- Edge curling machine
- Trimming beading machine
- Trimming joggling machine
- Cookware production line
- Pipe bending machine
- Profile bending machine
- Bandsaw for metal
- Cylindrical welding machine
- Horizontal pres and cookware
- Kitchenware, hotelware
- Bakeware and cuttlery production machinery
as a complete line as well as an individual machine such as:
- Edge cutting trimming beading machines
- Polishing and grinding machines for pot and pans
- Hydraulic drawing presses
- Circle blanking machines
- Riveting machine
- Hole punching machines
- Press feeding machine
You can check our machinery at work at: EMS Metalworking Machinery – YouTube
Applications:
- Beading and ribbing
- Flanging
- Trimming
- Curling
- Lock-seaming
- Ribbing
- Flange-punching
