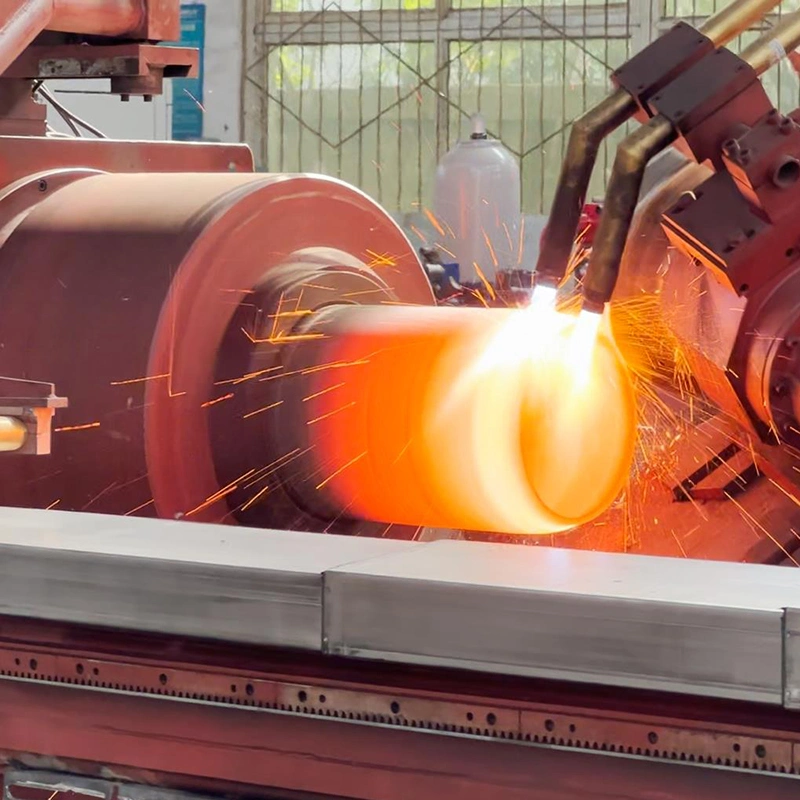
Tube (Cylinder) Necking machines are specialized equipment used in metalworking and manufacturing processes to shape and seal the ends of cylindrical tubes or containers. These machines perform a crucial role in various industries where the production of sealed and functional tubes is required for packaging, automotive components, aerospace applications, and more. The tube necking-in and closing process involves reducing the diameter of the tube end and forming it into a specific shape to accommodate closures or fittings.
Tube (Cylinder) Necking-In & Closing Machines
Tube necking-in and closing machines operate based on precise mechanical principles:
- Tube Feeding and Clamping: The process begins with feeding a cylindrical tube or container into the machine. The tube is securely clamped in place to ensure stability during the forming and closing operations.
- Necking-In: The machine gradually reduces the diameter of the tube’s open end using specialized forming dies or rollers. This necking-in process reshapes the tube end to a smaller diameter, preparing it for closure or sealing.
- Forming and Closing: After necking-in, the machine further shapes the tube end to create specific features such as flanges, lips, or threads. This step is crucial for accommodating closures, caps, or other components that seal the tube.
- Sealing or Joining: Depending on the application, the machine may incorporate additional processes such as crimping, welding, or soldering to seal or join the closure with the tube end securely.
Key Components of the Tube (Cylinder) Necking-In & Closing Machines
Tube necking-in and closing machines consist of essential components to facilitate precise and efficient tube processing:
- Feeding Mechanism: Enables the smooth and controlled feeding of tubes into the machine for processing.
- Clamping System: Holds the tube securely in place during the forming and closing operations to prevent slippage or misalignment.
- Forming Dies or Rollers: Specialized tooling that applies controlled pressure to the tube end to achieve the desired diameter reduction and shape.
- Closing Tools: Implements various closing techniques such as crimping, welding, or soldering to seal the tube end with closures or fittings.
- Control System: Modern machines utilize advanced control systems, including computer numerical control (CNC), to program and monitor the forming and closing processes for precise results.
How does the Tube (Cylinder) Necking-In & Closing Machine work?
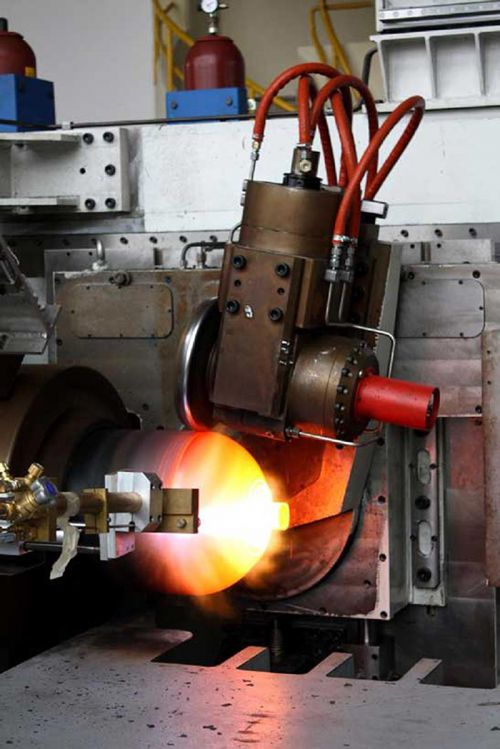
A Tube Necking-In and Closing Machine is used to reduce the diameter of tubes or cylinders at one end (necking-in) and sometimes to close or seal the end completely. This process is common in industries where tubes or cylinders need to be shaped into various forms, such as automotive exhaust pipes, aerosol cans, or even medical device components. Here’s a detailed explanation of how this machine typically works:
Components of the Machine
- Base and Frame
- Provides stability and support for all components of the machine.
- Spindle
- Holds and rotates the tube or cylinder during the necking-in and closing process.
- Clamping Mechanism
- Securely holds the tube in place during forming to prevent movement.
- Tooling
- Includes forming tools and dies that shape the tube.
- Necking-in Tool: Reduces the diameter of the tube gradually towards one end.
- Closing Tool: For machines that also close or seal the end of the tube, this tool shapes the end to achieve the desired closure.
- Hydraulic or Mechanical Actuators
- Provide the force needed to move the tooling and apply pressure to the tube.
- Control System
- Includes a CNC controller or manual controls to manage the operation of the machine.
- Allows operators to set parameters such as dimensions, speed, and pressure.
- Cooling and Lubrication System
- Keeps the tools and workpiece cool during the forming process to prevent overheating and reduce wear.
Operation of the Machine
- Loading the Tube
- A tube or cylinder is placed into the machine and secured in the clamping mechanism.
- Positioning
- The tube is positioned under the spindle and aligned with the necking-in and closing tools.
- Necking-In Process
- The spindle rotates the tube while the necking-in tool moves towards the end of the tube.
- The necking-in tool gradually reduces the diameter of the tube, forming a tapered or narrowed section at one end.
- This process is controlled by the CNC system to achieve precise dimensions and shape.
- Closing Process (if applicable)
- If the machine is equipped to close or seal the end of the tube, the closing tool is engaged after necking-in.
- The closing tool shapes the end of the tube to form a sealed or closed surface, which can be flat or domed depending on the design requirements.
- Cooling and Finishing
- Coolant may be applied during the process to manage heat generated by friction between the tooling and the tube.
- Once forming is complete, any excess material or burrs may be trimmed or removed.
- Unloading
- The finished tube is removed from the machine, ready for further processing or assembly.
Key Considerations
- Material Compatibility: The machine and tooling must be suitable for the type and thickness of the tube material (e.g., steel, aluminum, plastics).
- Precision and Tolerance: CNC control ensures high accuracy and repeatability in forming dimensions.
- Tooling Maintenance: Regular maintenance of tooling and replacement of worn parts are necessary to maintain quality and productivity.
Tube necking-in and closing machines are essential in industries requiring custom-shaped tubes or cylinders, offering efficient and precise forming capabilities for a variety of applications.
Applications
Tube necking-in and closing machines have diverse applications across industries:
- Packaging: Used in the production of metal tubes for packaging cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, food products, and chemicals. These machines enable the efficient sealing of tubes with caps or closures to preserve product integrity and freshness.
- Automotive: Applied in the manufacturing of exhaust systems, fuel pipes, and hydraulic components where sealed tubes are required to maintain performance and safety standards.
- Aerospace and Defense: Utilized for fabricating precision-engineered tubes and containers used in aircraft fuel systems, hydraulic systems, and missile casings.
- Industrial Equipment: Used in various industrial applications for producing tubes and pipes used in HVAC systems, plumbing, and fluid handling equipment.
- Medical Devices: Applied in the production of medical tubing and containers used for packaging and delivering pharmaceuticals, medical gases, and fluids.
Advantages
Tube necking-in and closing machines, also known as end forming machines, are specialized equipment used in metalworking and manufacturing processes. These machines play a crucial role in shaping and sealing the ends of cylindrical tubes or containers.
The core function of a tube necking-in and closing machine involves two key steps:
- Necking-In: The machine applies pressure to a specific region of the tube, progressively reducing its diameter. This creates a “neck” at the end of the tube, often to accommodate closures or fittings like valves, caps, or connectors. The final diameter of the neck can be precisely controlled by the machine’s settings.
- Closing: Once the desired neck is formed, the machine closes the open end of the tube. This can be achieved through various methods depending on the application:
- Folding: The machine folds the remaining material at the end of the neck over itself, creating a sealed closure.
- Forging: In some cases, the machine applies high pressure to compress and forge the remaining material, forming a solid, leak-proof closure.
- Welding: The machine might integrate a welding process to create a permanent, hermetic seal on the closed end.
These machines offer several advantages over traditional methods of shaping and sealing tube ends:
- Precision and Consistency: They ensure precise and consistent necking-in and closure across all tubes, minimizing variations and enhancing product quality.
- Efficiency: These machines are capable of high production rates, significantly speeding up the manufacturing process.
- Versatility: Modern machines can handle a wide range of tube diameters, wall thicknesses, and materials, making them adaptable to various applications.
- Reduced Waste: By forming and closing the tube ends in one operation, these machines minimize material waste compared to methods involving cutting and welding separate closures.
Tube necking-in and closing machines find application in a diverse range of industries:
- Automotive: They are used to create fuel lines, brake lines, and other components with formed and sealed ends.
- Aerospace: The machines play a role in shaping and sealing tubes for hydraulic systems, landing gear components, and even rocket engine parts.
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries: These machines contribute to the production of containers for chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and pressurized gases.
- Food and Beverage Industry: They are used to shape and seal tubes for beverage cans, food processing equipment, and storage containers.
- Construction: The machines can be used to form and seal tubes for plumbing applications, HVAC systems, and other structural uses.
In conclusion, tube necking-in and closing machines are essential tools for shaping and sealing the ends of metal tubes in various industries. Their ability to provide precise, efficient, and versatile end forming makes them a valuable asset in modern manufacturing processes.
Tube necking-in and closing machines offer several advantages in tube manufacturing processes:
- Precision and Consistency: Achieve precise tube dimensions and shapes with consistent quality, reducing material waste and production costs.
- Versatility: Can process a wide range of tube materials, including metals like aluminum, stainless steel, and alloys.
- Efficiency: Streamline tube production by integrating multiple forming and closing operations into a single machine, improving overall productivity.
- Customization: Enable the creation of custom tube designs and configurations to meet specific application requirements.
- Sealing Integrity: Ensure secure and leak-proof closures, enhancing product reliability and safety.
In summary, tube necking-in and closing machines play a critical role in the manufacturing of sealed tubes and containers for various industries. The technology continues to evolve with advancements in automation, materials science, and quality control, driving innovation and efficiency in tube processing applications globally.
EMS Metalworking Machines
We design, manufacture and assembly metalworking machinery such as:
- Hydraulic transfer press
- Glass mosaic press
- Hydraulic deep drawing press
- Casting press
- Hydraulic cold forming press
- Hydroforming press
- Composite press
- Silicone rubber moulding press
- Brake pad press
- Melamine press
- SMC & BMC Press
- Labrotaroy press
- Edge cutting trimming machine
- Edge curling machine
- Trimming beading machine
- Trimming joggling machine
- Cookware production line
- Pipe bending machine
- Profile bending machine
- Bandsaw for metal
- Cylindrical welding machine
- Horizontal pres and cookware
- Kitchenware, hotelware
- Bakeware and cuttlery production machinery
as a complete line as well as an individual machine such as:
- Edge cutting trimming beading machines
- Polishing and grinding machines for pot and pans
- Hydraulic drawing presses
- Circle blanking machines
- Riveting machine
- Hole punching machines
- Press feeding machine
You can check our machinery at work at: EMS Metalworking Machinery – YouTube
Applications:
- Beading and ribbing
- Flanging
- Trimming
- Curling
- Lock-seaming
- Ribbing
- Flange-punching
