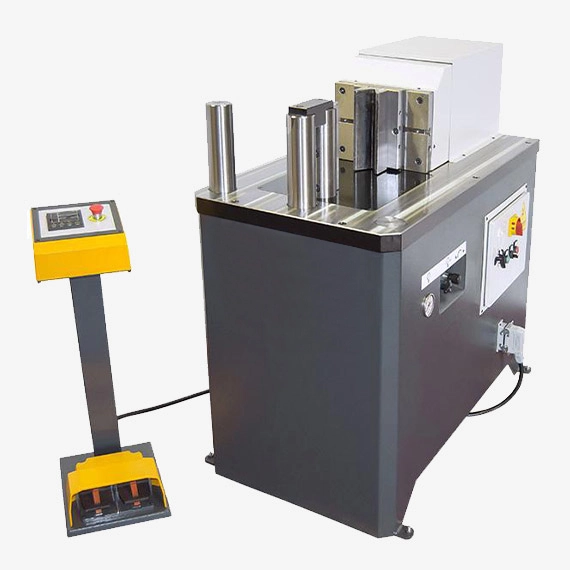

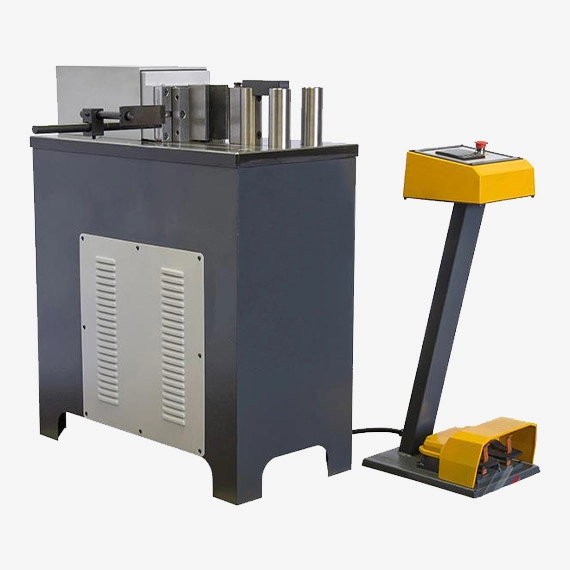
A hydraulic horizontal press brake is a machine that uses hydraulic pressure to bend metal sheets and plates into desired shapes. Unlike traditional press brakes, which bend plates vertically, horizontal press brakes bend plates horizontally, allowing for more complex bends and shapes.
The versatility of the Horizontal Press Brake allows us to bend, fold, bend, cut, form, enlarge and reduce flaring, swagging, assembling… all kinds of metal materials such as iron, steel, stainless, copper, brass, aluminium..
Pipe bending at fixed radius up to 150º could be considered one of the good features of these presses
Cutting, piercing and punching flat bars or metal sheets turn this horizontal bending press into a punching shears machine
Stretching and reducing pipes on the ends in order to make parts that fit or weld later.
It is also a solution to bend different profiles at different radius and keeping the ends straight, like when manufacturing handles and flanges.
Cold forge uses horizontal presses to make and form different shapes of balusters. Tube notching to assemble at 90 degrees.
Folding operations with wrought iron machines permit to completely bend the parts or pieces unlike conventional flat bar section bending machines
Its robustness, versatility, easy handling and 4.0 Technology are just four of the best features our hydraulic horizontal bending machine has. Folding operation with no risk of damaging the punches and dies with thick materials unlike conventional press brakes. Folding flat bars and sheets into completely close shapes. Conception of this horizontal bending press brake allows to make folding operations impossible to be carried out on a conventional press brake.
Fast tool change, punches and dies: This change does not take more than 30 seconds most of the times. A set of punch and folding die is supplied along with the machine. Performance by a safety double activation hold pedal. Low noise level, improving the quality of work of the operator. The machine is shipped completely assembled and ready to work. Palletized lower bench to easily transport the machine up to its working or storage site. Dies support shelf included. Lateral stop to place it right or left.
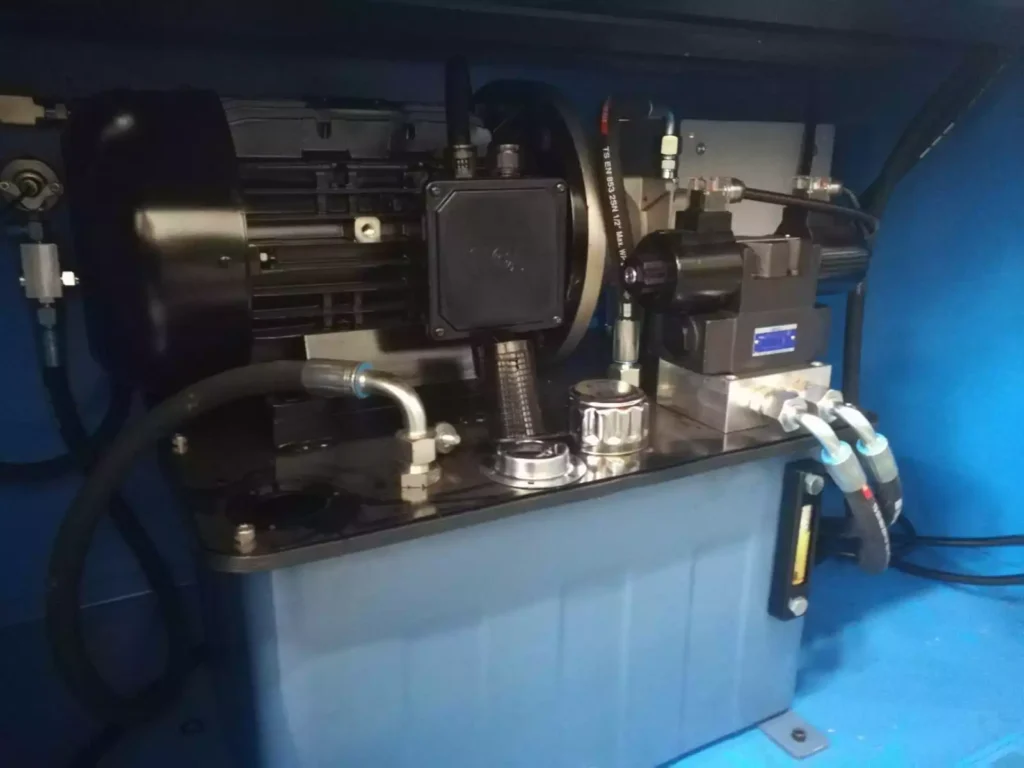
Hydraulic System
Monoblock hydraulic power unit with positioning and pressure regulation valves The hydraulic system can be regulated by means of pressure adjustment valves that affect the piston force. Pressure regulator with pressure gauge that allows to control the force carried out at any time.
Guided hydraulic cylinder: The hydraulic cylinder placed on the work bench allows us to transfer all the force directly on the tools. Fully guided hydraulic piston to prevent any bending during the folding operation.
Cylindrical fastening bolts: Cylindrical fastening bolts easy to install, to guarantee maximum firmness to the tools during machining operations. Plugs to prevent the residues of the folding from entering inside the machine.
Work table without frame: The work bench is frameless, this is great for the movement of the parts to be machined for there isn’t any element that obstructs its movement. The table is manufactured in a 60mm monoblock of welded steel, stabilized and machined. The operator’s working position must be at the side of the machine for accomplishing a better vision and control, as well as greater safety for the user since he will be outside the radius of action of the tools.
Key Features of Hydraulic Horizontal Press Brakes
- Horizontal Bending Capability: These machines bend plates horizontally, enabling the creation of complex bends and shapes not possible with vertical press brakes.
- Versatility: Horizontal press brakes can handle a wide range of plate thicknesses and materials, making them versatile tools for various applications.
- Precise Control: Hydraulic systems provide precise control over the bending force and speed, ensuring accurate and consistent bends.
- Ease of Operation: Horizontal press brakes typically feature user-friendly controls and intuitive programming interfaces.
- Safety Features: These machines incorporate safety features such as light guards, emergency stops, and interlocking mechanisms to protect operators.
Applications of Hydraulic Horizontal Press Brakes
- Sheet Metal Bending: Bending sheet metal for enclosures, ducts, housings, and other structural components.
- Plate Forming: Shaping plates for machinery frames, vehicle components, and industrial equipment.
- Bending Profiles: Creating bends and curves in metal profiles for architectural and structural applications.
- Complex Bends: Producing intricate bends and shapes that require precise control and flexibility.
- Specialty Applications: Custom bending for specific applications, such as automotive parts, aerospace components, and appliance manufacturing.
Selection and Operation of Hydraulic Horizontal Press Brakes
Choosing the appropriate hydraulic horizontal press brake depends on several factors, including:
- Plate Thickness: The machine should be capable of handling the plate thickness required for the application.
- Bending Force: The machine should provide sufficient bending force to achieve the desired bends in the material being used.
- Bending Length: The machine’s bending length should accommodate the maximum plate length to be bent.
- Accuracy Requirements: The machine should provide the desired level of accuracy and precision for the application.
- Production Volume: The machine should have sufficient capacity to meet the production demands.
When operating a hydraulic horizontal press brake, proper safety precautions should be followed to prevent accidents and injuries:
- Wear Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, safety glasses, and proper footwear, when operating a press brake.
- Securely Position the Plate: Ensure the plate is securely placed on the machine’s bed and properly aligned with the bending tools.
- Verify Bending Parameters: Double-check the bending parameters, including bend angle, bend radius, and bending speed, before initiating the bending process.
- Monitor the Bending Process: Closely monitor the bending process to detect any potential issues or irregularities.
- Follow Manufacturer Instructions: Strictly follow the manufacturer’s instructions and safety guidelines for the specific horizontal press brake in use.
Hydraulic horizontal press brakes are valuable tools for shaping and forming metal sheets and plates into desired shapes. Their ability to handle complex bends, provide precise control, and accommodate various materials makes them versatile and essential machines in various industries. By selecting the right machine, adhering to safety protocols, and following proper operating procedures, these machines contribute to efficient, safe, and productive manufacturing processes.
The versatility of the best Hydraulic Horizontal Press Brake Machine EMS HP20 makes it possible for us to make a great deal of forging parts and all kinds of operations in all kinds of materials: pipe, flat bar, several profiles, rods.
Hydraulic Press Machines

Hydraulic press machines are versatile and powerful tools that utilize hydraulic pressure to exert force and perform various tasks, including:
Metalworking: Hydraulic press machines are commonly used in metalworking applications such as:
- Bending: Pressing metal sheets and plates into desired shapes, such as angles, channels, and boxes.
- Punching: Pressing holes in metal sheets and plates using punches and dies.
- Blanking: Cutting out shapes from metal sheets using dies.
- Forming: Shaping metal parts into specific configurations using dies.
- Extruding: Forcing metal through a die to create various shapes, such as pipes or tubes.
Manufacturing: Hydraulic press machines are employed in various manufacturing processes, including:
- Assembly: Pressing components together to form assemblies.
- Embossing: Creating raised patterns or designs on metal surfaces.
- Coining: Pressing metal into dies to produce coins, medals, or other shaped parts.
- Laminating: Joining layers of different materials together using pressure.
- Testing: Compressing materials to assess their strength and properties.
Other Applications: Hydraulic press machines also find use in various industries beyond metalworking and manufacturing, such as:
- Agricultural: Pressing oilseeds to extract oil.
- Pharmaceutical: Compressing powders into tablets.
- Recycling: Compressing materials like cardboard or plastics for efficient waste disposal.
- Construction: Pressing concrete or other materials into desired shapes.
- Food Processing: Pressing juice from fruits or vegetables.
Key Components of Hydraulic Press Machines
The main components of a hydraulic press machine include:
- Frame: The frame provides the structural support for the machine and houses the other components.
- Hydraulic Cylinder: The hydraulic cylinder generates the force required for pressing operations. It contains a piston that is driven by hydraulic fluid.
- Hydraulic Pump: The hydraulic pump supplies hydraulic fluid to the hydraulic cylinder. It is typically powered by an electric motor.
- Press Ram: The press ram is the part that applies force to the workpiece. It is connected to the hydraulic cylinder and moves up and down to perform pressing operations.
- Bed: The bed is the surface where the workpiece is placed during pressing. It is typically adjustable to accommodate different workpiece sizes.
- Control Panel: The control panel allows the operator to control the machine’s functions, such as pressure, speed, and ram position.
- Tooling: Various tooling, such as dies, punches, and platens, are used to shape or form the workpiece during pressing.
Advantages of Hydraulic Press Machines
Hydraulic press machines offer several advantages over other types of presses:
- High Force Capability: They can generate high forces, making them suitable for pressing a wide range of materials.
- Precise Control: They provide precise control over the pressing force and speed, ensuring consistent and accurate results.
- Versatility: They can be adapted to a wide range of applications with different tooling options.
- Reliability: They are generally durable and reliable, requiring minimal maintenance.
- Safety: They incorporate safety features to protect operators from potential hazards.
Considerations When Choosing a Hydraulic Press Machine
Choosing the appropriate hydraulic press machine depends on several factors, including:
- Application Requirements: The machine should be capable of handling the specific task at hand, such as bending, punching, or forming.
- Workpiece Material: The machine should be compatible with the material being pressed.
- Workpiece Size: The machine should have sufficient capacity to accommodate the size of the workpiece.
- Force Requirements: The machine should provide sufficient force to achieve the desired pressing results.
- Production Volume: The machine should have sufficient capacity to meet the production demands.
- Budget and Cost-Effectiveness: The machine should fit within the project budget and offer cost-effective operation.
Hydraulic press machines are valuable tools in various industries, providing a combination of power, precision, and versatility. By selecting the right machine, adhering to safety protocols, and following proper operating procedures, these machines contribute to efficient, safe, and productive manufacturing processes.
Folding operations with a wrought iron press machine permit to completely bend the parts or pieces, unlike conventional flat bar section bending machines. Bending with a brake press at a fixed radius up to 150º could be considered one of the other good features of these presses. The stretching and reducing pipes on the ends in order to make parts that fit or weld later.
Cutting, piercing, and punching flat bars or metal sheets turn this horizontal bending press into a punching shears machine. Many workshops use these presses to stretch and form different kinds of profiles. It is also a solution to bend different profiles at the different radii and keep the ends straight, like when manufacturing handles and flanges.
Bending with Horizontal Press
Bending with a horizontal press is a versatile and efficient method for shaping and curving metal sheets and plates into desired angles or shapes. This technique involves applying pressure from a horizontally positioned ram or plunger to gradually deform the workpiece into the desired curvature. Horizontal presses offer several advantages over other bending methods, making them a preferred choice in various industries.
Folding die at 161 mm · V 16, 22, 35, 50 mm
Folding or bending die up to 161mm with 4 openings (16, 22, 35, 50mm) and a punch of 80º. This multi-V die allows 1mm up to 8mm sheet to be folded. The 70mm outer diameter punch allows to make completely closed shapes to a minimum of 75mm inner wing.
Folding die reference: 125-16-01-00006
Folding punch reference: 131-16-01-00041
V 16: Sheet from 1 to 3mm
V 22: Sheet from 2 to 4mm
V 35: Sheet from 3 to 6mm
V 50: Sheet from 4 to 8mm
Max. Folding length: 161mm
Max. Folding thickness: 8mm
- Baluster forming die
- Ring forming
- Bending tool for big radius
- Twisted bars forming die
- Flat bar cutting tooling 100x10mm
- Tool to shape pipe ends
- Diameter reduction tools
- Diameter expansion tools
- Die to straighten out profiles
- Punching die
- Promecam punch holder
- Clamp forming die
- Bar clamps forming die
- Special punches
- Round, square, oval and rectangular punches and dies
- Pipe notching tool
- Rounding corner tool
- Metal tabs forming tool
Key Characteristics of Horizontal Press Bending
- Large Bending Capacity: Horizontal presses can handle large-format metal sheets and plates, typically up to 12 feet (3.6 meters) in width and 0.5 inches (12.7 millimeters) in thickness.
- Long Bend Capability: Horizontal presses can produce long, continuous bends without abrupt transitions, ensuring smooth and aesthetically pleasing curves.
- Reduced Springback: Horizontal presses minimize springback, the tendency of the metal to partially straighten after bending, resulting in more accurate and consistent bend angles.
- Uniform Bending: Horizontal presses produce uniform bending along the entire length of the workpiece, ensuring a consistent bend shape and eliminating uneven or distorted bends.
- Versatility: Horizontal presses can handle a wide range of metal types, including steel, aluminum, stainless steel, and copper, making them adaptable to various applications.
Applications of Horizontal Press Bending
Horizontal press bending finds extensive use in various industries due to its efficiency and effectiveness. Here are some common applications:
- Sheet Metal Forming: Horizontal presses are employed to bend sheet metal for architectural components, enclosures, ducts, and housings.
- Plate Bending: Horizontal presses are used to shape plates for machinery frames, automotive components, and industrial equipment.
- Curved Shapes: Horizontal presses can produce curved shapes for structural supports, decorative elements, and specialized components.
- Complex Bends: Horizontal presses can handle complex bends and angles that are difficult to achieve with other methods.
- High-Volume Production: Horizontal presses are well-suited for high-volume production runs, ensuring consistent quality and efficiency.
Overall, horizontal press bending is a valuable technique that offers a combination of precision, versatility, and effectiveness in shaping metal sheets and plates into desired forms. Its ability to handle large dimensions, produce long bends, and minimize springback makes it a preferred choice in various manufacturing and fabrication processes.
Punching with Horizontal Press
Punching with a horizontal press is a versatile and efficient method for creating holes and perforations in metal sheets and plates. This technique involves applying force from a horizontally positioned ram or plunger to drive a punch tool through the workpiece, removing a defined section of material and leaving a clean, precise hole. Horizontal presses offer several advantages over other punching methods, making them a preferred choice in various industries.
Key Characteristics of Horizontal Press Punching
- High Punching Force: Horizontal presses can generate high punching forces, enabling them to penetrate a wide range of materials, including thick and hard metals.
- Precise Hole Production: Horizontal presses provide precise control over the punching force and speed, resulting in clean, accurate holes with consistent dimensions.
- Variety of Hole Shapes: Horizontal presses can accommodate a variety of punch shapes, including round, square, rectangular, and oval, catering to diverse application requirements.
- Automated Operation: Horizontal presses can be automated using programmable controllers, enabling efficient and consistent punching operations for high-volume production.
- Safety Features: Horizontal presses incorporate safety features such as light guards, emergency stops, and interlocking mechanisms to protect operators from potential hazards.
Applications of Horizontal Press Punching
Horizontal press punching finds extensive use in various industries due to its efficiency and precision. Here are some common applications:
- Sheet Metal Fabrication: Horizontal presses are employed to punch holes in sheet metal for various components, such as electrical panels, enclosures, and ducting systems.
- Plate Perforation: Horizontal presses are used to perforate plates for sieves, filters, and gratings, ensuring consistent hole patterns and precise dimensions.
- Component Manufacture: Horizontal presses can punch holes in various industrial components, such as automotive parts, appliance housings, and machinery frames.
- Prototyping and Design: Horizontal presses are used to create prototypes and make design modifications in sheet metal and plate components.
- Decorative Elements: Horizontal presses can punch decorative holes and patterns in metal panels for architectural applications and signage.
Overall, horizontal press punching is a valuable technique that offers a combination of precision, versatility, and effectiveness in creating holes and perforations in metal sheets and plates. Its ability to handle a wide range of materials, produce accurate holes, and accommodate various hole shapes makes it a preferred choice in various manufacturing and fabrication processes.
Safety Guidelines for Horizontal Press Punching
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses, gloves, and proper footwear, when operating a horizontal press.
- Secure Workpiece Positioning: Ensure the workpiece is securely clamped in place on the press bed to prevent movement during punching.
- Clearance from Punch and Die: Maintain adequate clearance between the punch and die to avoid hand injuries or damage to the tooling.
- Emergency Stop Awareness: Familiarize yourself with the emergency stop location and be prepared to activate it in case of any unsafe conditions.
- Proper Tooling Selection: Use the appropriate punch and die combination for the desired hole size, shape, and material.
- Regular Maintenance: Follow proper maintenance procedures to ensure the press is in good working condition and free from potential hazards.
Blanking with Horizontal Press
Blanking with a horizontal press is a versatile and efficient method for cutting out shapes from metal sheets and plates. This technique involves applying force from a horizontally positioned ram or plunger to drive a blanking tool through the workpiece, removing a defined section of material and leaving a clean, precise edge. Horizontal presses offer several advantages over other blanking methods, making them a preferred choice in various industries.
Key Characteristics of Horizontal Press Blanking
- High Blanking Force: Horizontal presses can generate high blanking forces, enabling them to cut through a wide range of materials, including thick and hard metals.
- Precise Cut Quality: Horizontal presses provide precise control over the blanking force and speed, resulting in clean, accurate cuts with consistent dimensions.
- Complex Shape Blanking: Horizontal presses can handle complex shapes, including intricate contours and sharp angles, making them suitable for a variety of cutting applications.
- Automated Operation: Horizontal presses can be automated using programmable controllers, enabling efficient and consistent blanking operations for high-volume production.
- Safety Features: Horizontal presses incorporate safety features such as light guards, emergency stops, and interlocking mechanisms to protect operators from potential hazards.
Applications of Horizontal Press Blanking
Horizontal press blanking finds extensive use in various industries due to its efficiency and precision. Here are some common applications:
- Sheet Metal Components: Horizontal presses are employed to blank out sheet metal components for various products, such as appliances, automotive parts, and electronic enclosures.
- Gasket and Washer Blanking: Horizontal presses are used to blank out gaskets and washers for various industrial applications, ensuring consistent dimensions and precise shapes.
- Profiling and Part Formation: Horizontal presses can blank out complex profiles and shapes for various components, such as machine parts, decorative elements, and architectural features.
- Prototype and Design: Horizontal presses are used to blank out prototypes and make design modifications in sheet metal components.
- Precision Blanking: Horizontal presses can perform precision blanking operations, producing clean, burr-free edges and minimizing material waste.
Overall, horizontal press blanking is a valuable technique that offers a combination of precision, versatility, and effectiveness in cutting out shapes from metal sheets and plates. Its ability to handle a wide range of materials, produce accurate cuts, and accommodate complex shapes makes it a preferred choice in various manufacturing and fabrication processes.
Safety Guidelines for Horizontal Press Blanking
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses, gloves, and proper footwear, when operating a horizontal press.
- Secure Workpiece Positioning: Ensure the workpiece is securely clamped in place on the press bed to prevent movement during blanking.
- Clearance from Blanking Tool: Maintain adequate clearance from the blanking tool to avoid hand injuries or damage to the tooling.
- Emergency Stop Awareness: Familiarize yourself with the emergency stop location and be prepared to activate it in case of any unsafe conditions.
- Proper Tooling Selection: Use the appropriate blanking tool for the desired shape, material, and thickness of the workpiece.
- Regular Maintenance: Follow proper maintenance procedures to ensure the press is in good working condition and free from potential hazards.
Forming with Horizontal Press
Forming with a horizontal press is a versatile and efficient method for shaping and deforming metal sheets and plates into desired three-dimensional shapes. This technique involves applying force from a horizontally positioned ram or plunger to gradually deform the workpiece using specialized dies, resulting in complex shapes and contours. Horizontal presses offer several advantages over other forming methods, making them a preferred choice in various industries.
Key Characteristics of Horizontal Press Forming
- Controlled Deformation: Horizontal presses provide precise control over the forming force and speed, enabling the creation of complex shapes with consistent dimensions and smooth transitions.
- Deep Draw Forming: Horizontal presses can perform deep draw forming, producing deep pockets, cups, and recesses in sheet metal components.
- Variety of Formed Shapes: Horizontal presses can form a wide range of shapes, including cones, cylinders, domes, and irregular shapes, catering to diverse application requirements.
- High Production Volume: Horizontal presses are well-suited for high-volume production runs, ensuring consistent quality and efficiency.
- Automated Operation: Horizontal presses can be automated using programmable controllers, enabling efficient and consistent forming operations for high-volume production.
Applications of Horizontal Press Forming
Horizontal press forming finds extensive use in various industries due to its versatility and effectiveness in shaping metal components. Here are some common applications:
- Automotive Parts: Horizontal presses are employed to form automotive parts, such as door panels, hoods, trunk lids, and structural components.
- Appliance Components: Horizontal presses are used to form appliance components, such as refrigerator panels, washing machine tubs, and oven housings.
- Electronic Enclosures: Horizontal presses can form electronic enclosures for various devices, ensuring precise dimensions and smooth contours.
- Aerospace Components: Horizontal presses are used to form aerospace components, such as aircraft skins, engine covers, and structural supports.
- Decorative Elements: Horizontal presses can form decorative elements for architectural applications, furniture components, and signage.
Overall, horizontal press forming is a valuable technique that offers a combination of precision, versatility, and effectiveness in shaping and deforming metal sheets and plates into complex three-dimensional shapes. Its ability to handle a wide range of materials, produce consistent shapes, and accommodate automated operation makes it a preferred choice in various manufacturing and fabrication processes.
Safety Guidelines for Horizontal Press Forming
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses, gloves, and proper footwear, when operating a horizontal press.
- Secure Workpiece Positioning: Ensure the workpiece is securely clamped in place on the press bed to prevent movement during forming.
- Clearance from Forming Tools: Maintain adequate clearance from the forming tools to avoid hand injuries or damage to the tooling.
- Emergency Stop Awareness: Familiarize yourself with the emergency stop location and be prepared to activate it in case of any unsafe conditions.
- Proper Lubrication: Ensure the forming dies and workpiece are properly lubricated to reduce friction and prevent wear.
- Regular Maintenance: Follow proper maintenance procedures to ensure the press is in good working condition and free from potential hazards.
Extruding with Horizontal Press
Extruding with a horizontal press, also known as horizontal extrusion, is a versatile and efficient method for producing continuous lengths of metal shapes, tubes, or rods. This technique involves forcing heated metal through a die opening using a horizontally positioned ram or plunger, resulting in a continuous profile with the desired cross-sectional shape. Horizontal presses offer several advantages over other extrusion methods, making them a preferred choice in various industries.
Key Characteristics of Horizontal Press Extrusion
- High Extrusion Force: Horizontal presses can generate high extrusion forces, enabling them to extrude a wide range of materials, including hard and viscous metals.
- Continuous Extrusion: Horizontal presses produce continuous lengths of extruded material, eliminating the need for welding or joining separate pieces.
- Variety of Extruded Shapes: Horizontal presses can extrude a wide range of shapes, including round, square, rectangular, and complex profiles, catering to diverse application requirements.
- Precise Dimensional Control: Horizontal presses provide precise control over the extrusion process, resulting in consistent dimensions and smooth surface finishes.
- Automated Operation: Horizontal presses can be automated using programmable controllers, enabling efficient and consistent extrusion operations for high-volume production.
Applications of Horizontal Press Extrusion
Horizontal press extrusion finds extensive use in various industries due to its versatility and ability to produce continuous lengths of shaped metal products. Here are some common applications:
- Tubing and Pipe Manufacturing: Horizontal presses are employed to extrude seamless tubes and pipes for various applications, such as structural components, fluid conveyance systems, and electrical conduits.
- Rod and Bar Production: Horizontal presses are used to extrude rods and bars for various industrial applications, such as machine parts, structural components, and fasteners.
- Wire and Cable Extrusion: Horizontal presses can extrude wire and cable sheathing, providing protection and insulation for electrical conductors.
- Aluminum Extrusions: Horizontal presses are widely used to extrude aluminum shapes for various applications, including architectural components, window frames, and automotive parts.
- Specialty Extrusions: Horizontal presses can extrude complex shapes and profiles for specialized applications, such as medical implants, aerospace components, and decorative elements.
Overall, horizontal press extrusion is a valuable technique that offers a combination of precision, versatility, and efficiency in producing continuous lengths of shaped metal products. Its ability to handle a wide range of materials, produce consistent dimensions, and accommodate automated operation makes it a preferred choice in various manufacturing and fabrication processes.
Safety Guidelines for Horizontal Press Extrusion
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses, gloves, and proper footwear, when operating a horizontal press.
- Secure Die Installation: Ensure the extrusion die is securely installed and aligned with the extrusion chamber to prevent material jams or accidents.
- Proper Heating and Lubrication: Maintain the appropriate temperature and lubrication for the extruded material to ensure smooth flow and prevent material defects.
- Safety Interlocks and Guards: Familiarize yourself with the safety interlocks and guards on the press and ensure they are functioning properly to prevent accidental operation or injuries.
- Emergency Stop Awareness: Familiarize yourself with the emergency stop location and be prepared to activate it in case of any unsafe conditions.
- Regular Maintenance: Follow proper maintenance procedures to ensure the press is in good working condition and free from potential hazards.
Pipe notching with Horizontal Press
Pipe notching with a horizontal press brake is a versatile and efficient method for creating notches or cutouts in metal pipes. This technique involves using a specialized notching tool or die mounted on the ram of the horizontal press brake to apply pressure and deform the pipe material, resulting in a precise notch or cutout of the desired shape and size.
Key Characteristics of Pipe Notching with Horizontal Press Brake
- Precision Notching: Horizontal press brakes provide precise control over the notching force and speed, ensuring clean, accurate notches with consistent dimensions.
- Variety of Notch Shapes: Horizontal press brakes can accommodate a variety of notch shapes, including rectangular, trapezoidal, and V-shaped notches, catering to diverse application requirements.
- Efficient Production: Horizontal press brakes enable efficient notching operations, especially for high-volume production runs.
- Versatility: Horizontal press brakes can handle a wide range of pipe diameters and materials, making them versatile for various applications.
- Safety Features: Horizontal press brakes incorporate safety features such as light guards, emergency stops, and interlocking mechanisms to protect operators from potential hazards.
Applications of Pipe Notching with Horizontal Press Brake
Pipe notching with a horizontal press brake finds extensive use in various industries, particularly in piping systems and structural applications. Here are some common applications:
- Pipe Fitting Connections: Pipe notching is employed to create notches in pipes for connecting various fittings, such as elbows, tees, and flanges.
- Structural Reinforcements: Pipe notching can create notches in pipes for structural reinforcements, such as attaching brackets or supports.
- Pipe End Preparations: Pipe notching is used to prepare pipe ends for welding or joining, ensuring proper alignment and fit.
- Custom Notches: Horizontal press brakes can create custom notches for specialized applications, such as clearance notches for pipe routing or notches for specific component integration.
- Prototyping and Design: Pipe notching with a horizontal press brake can be used for prototyping and design iterations in piping systems and structural components.
Overall, pipe notching with a horizontal press brake is a valuable technique that offers a combination of precision, versatility, and efficiency in creating notches or cutouts in metal pipes. Its ability to handle a wide range of pipe diameters, produce accurate notches, and accommodate various notch shapes makes it a preferred choice in various industries, particularly in piping systems and structural applications.
Safety Guidelines for Pipe Notching with Horizontal Press Brake
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses, gloves, and proper footwear, when operating a horizontal press brake.
- Secure Pipe Positioning: Ensure the pipe is securely clamped in place on the press bed to prevent movement during notching.
- Proper Tool Selection: Use the appropriate notching tool or die for the desired notch shape, pipe diameter, and material.
- Clearance from Notching Tool: Maintain adequate clearance from the notching tool to avoid hand injuries or damage to the tooling.
- Emergency Stop Awareness: Familiarize yourself with the emergency stop location and be prepared to activate it in case of any unsafe conditions.
- Regular Maintenance: Follow proper maintenance procedures to ensure the press is in good working condition and free from potential hazards.
Sheet Metal Bending Tool
Sheet metal bending tools are devices used to bend sheet metal into various shapes and forms. They are commonly used in metalworking industries to create components for various applications, such as automotive parts, appliances, and architectural elements.
Types of Sheet Metal Bending Tools
Several types of sheet metal bending tools are available, each with its own capabilities and applications. Some of the most common types include:
- Bending brakes: These machines use a ram or plunger to apply force to a workpiece, causing it to bend along a predefined line. They are suitable for bending large sheets of metal into simple shapes, such as angles and channels.
- Press brakes: These machines use a hydraulic or pneumatic press to apply force to a workpiece, allowing for more precise bending and the creation of complex shapes. They are often used in high-volume production environments.
- Roll benders: These machines use a series of rollers to gradually bend sheet metal into a curved shape. They are suitable for long, continuous bends and are often used for forming pipes and tubes.
- Hand benders: These are portable tools that are used for bending sheet metal by hand. They are commonly used for smaller jobs and for making quick adjustments.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Sheet Metal Bending Tool
When choosing a sheet metal bending tool, several factors should be considered:
- Type of bends: The type of bends required will determine the type of machine you need. For simple bends, a bending brake may be sufficient. For more complex bends, a press brake or roll bender may be necessary.
- Material thickness: The thickness of the material you will be working with will also influence your choice of machine. Thicker materials will require a machine with more power.
- Production volume: If you are producing high volumes of parts, an automated machine may be more efficient. However, for small-scale production or prototyping, a hand bender may be sufficient.
- Accuracy requirements: The accuracy required for your bends will also affect your choice of machine. Press brakes and roll benders can typically achieve higher levels of accuracy than bending brakes.
- Budget: The cost of sheet metal bending tools can vary significantly. It is important to consider your budget when making your decision.
Safety Precautions When Using Sheet Metal Bending Tools
When using sheet metal bending tools, it is important to follow safety precautions to prevent injuries:
- Wear personal protective equipment (PPE): This includes safety glasses, gloves, and a sturdy pair of shoes.
- Securely clamp the workpiece: The workpiece should be securely clamped in place before bending to prevent it from moving or slipping.
- Keep hands away from the bending area: Never place your hands near the bending area while the machine is in operation.
- Use the proper tools: Use the appropriate tools for the type of bend and material you are working with.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the specific machine you are using.
Horizontal press brake bending machine EMS HP20 includes the complete folding die. (See bottom of the page in standard accessories).
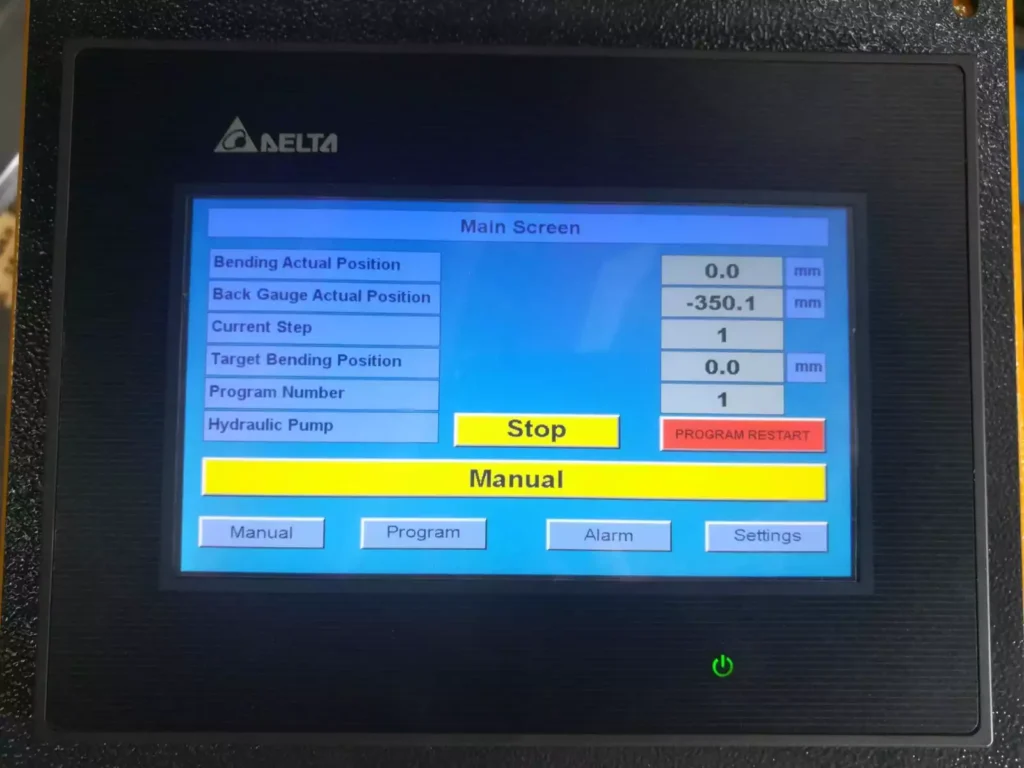
Technical Characteristics of the Horizontal Hydraulic Press Machine
- Working strength: 20.000 Kg (200 KN)
- Working speed: 10 mm/s.
- Return speed: 35 mm/s.
- Maximum displacement: 250 mm.
- Repetitivity: 0,05 mm.
- Bench size: 600×1170 mm.
- Working height: 950 mm.
- Programming mode: Manual or Automatic.
- Safety Double acting hold pedal.
- Mechanically Guided Piston.
- Piece counter.
- Pressure regulator.
- Engine power: 2.2 KW/3 HP a 1400 r.p.m.
- Electric Tension: 230/400 V three-phased.
- Intensity: 9/5 A.
- Hydraulic pressure: 50 a 215 Kg/cm2.
- Hydraulic pump: 7,5 litres/minute.
- Tank Capacity: 27 liters.
- Dies support shelf included.
- Palletized lower bench to easily transport the machine up to its working or storage site.
- The machine is sent wholly assembled.
- Packing included:
- Wooden pallet NIMF15 and three-layer cardboard apt for suitable for sea freight.
All our products are manufactured in our facilities in Turkey. Hydraulic and electrical components are all standard from the best leading European trademarks with technical support all over the world



Industrial Machinery for Bending

Industrial machinery for bending is used to shape and form metal sheets, plates, and tubes into various shapes and contours. These machines are essential tools in various industries, including metalworking, manufacturing, construction, and automotive production.
Types of Industrial Bending Machinery
Several types of industrial bending machinery are available, each with its own capabilities and applications. Some of the most common types include:
- Press Brakes: Press brakes are versatile machines that use a hydraulic or pneumatic press to apply force to a workpiece, causing it to bend along a predefined line. They can produce a wide range of bends, including angles, channels, and boxes.
- Roll Benders: Roll benders use a series of rollers to gradually bend metal into a curved shape. They are particularly well-suited for producing long, continuous bends and are often used for forming pipes and tubes.
- Horizontal Press Brakes: Horizontal press brakes are similar to press brakes but operate horizontally, allowing for the creation of complex bends and shapes that are difficult to achieve with vertical press brakes.
- Three-Roll Benders: Three-roll benders use three rollers to bend metal into a cylindrical or conical shape. They are commonly used for forming pipes, tanks, and other curved components.
- Rotary Benders: Rotary benders use a rotating mandrel to bend metal around a fixed axis. They are suitable for bending long, thin-walled tubes and pipes.
Applications of Industrial Bending Machinery
Industrial bending machinery is used in a wide variety of applications across various industries. Some common applications include:
- Sheet Metal Forming: Bending machines are used to form sheet metal into various shapes for components in appliances, automotive parts, architectural elements, and electrical enclosures.
- Pipe and Tube Bending: Bending machines are used to bend pipes and tubes for piping systems, structural supports, and fluid conveyance systems.
- Profile Bending: Bending machines can handle complex profiles, such as C-channels, I-beams, and angle irons, for structural components and industrial applications.
- Specialty Bending: Specialized bending machines can produce intricate bends, curves, and shapes for specialized applications, such as aerospace components, medical implants, and decorative elements.
Selection and Operation of Industrial Bending Machinery
Choosing the appropriate industrial bending machine depends on several factors, including:
- Workpiece Material: The machine should be compatible with the material being bent, such as steel, aluminum, or stainless steel.
- Workpiece Thickness: The machine should have sufficient capacity to handle the thickness of the workpiece being bent.
- Bending Requirements: The machine should be able to produce the desired bend angles, shapes, and precision.
- Production Volume: For high-volume production, an automated machine may be more efficient. For smaller-scale production or prototyping, a manual machine may suffice.
- Safety Features: Ensure the machine incorporates safety features such as light guards, emergency stops, and interlocking mechanisms.
When operating industrial bending machinery, proper safety precautions should be followed to prevent accidents and injuries:
- Wear PPE: Always wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses, gloves, and proper footwear, when operating bending machinery.
- Secure Workpiece Positioning: Ensure the workpiece is securely clamped in place on the machine bed to prevent movement during bending.
- Proper Tooling Selection: Use the appropriate bending tools for the desired bend shape, workpiece material, and thickness.
- Clearance from Bending Tools: Maintain adequate clearance from the bending tools to avoid hand injuries or damage to the tooling.
- Emergency Stop Awareness: Familiarize yourself with the emergency stop location and be prepared to activate it in case of any unsafe conditions.
- Follow Manufacturer Instructions: Strictly follow the manufacturer’s instructions and safety guidelines for the specific bending machine in use.
Industrial bending machinery plays a crucial role in shaping and forming metal components across various industries. By selecting the right machine, adhering to safety protocols, and following proper operating procedures, these machines contribute to efficient, safe, and productive manufacturing processes.
Parts bent by a sheet metal press brake
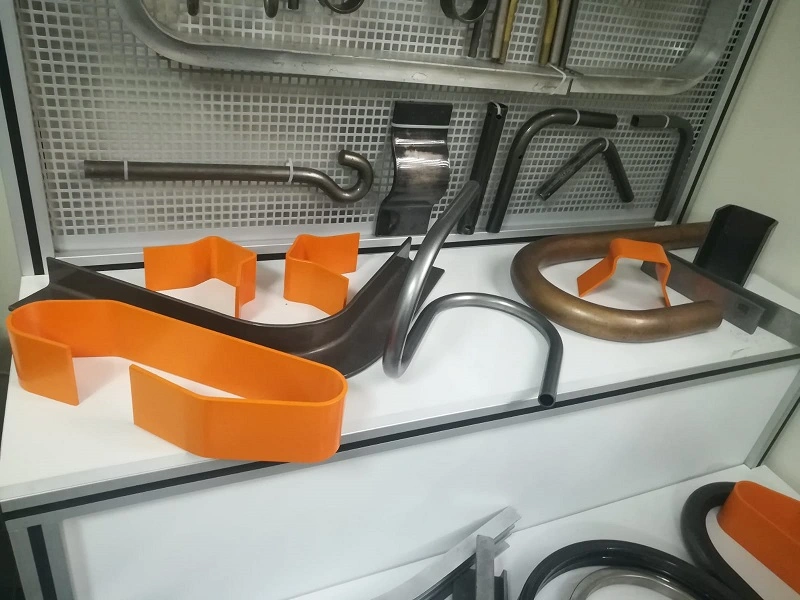

Sheet metal horizontal presses are versatile machines that can be used to bend a wide variety of parts, including:
Automotive Parts:
- Door panels
- Hoods and trunk lids
- Fender panels
- Structural bracing
- Brackets and mounts
Appliance Components:
- Refrigerator panels
- Washing machine tubs
- Oven housings
- Dishwasher racks
- Control panels
Electronic Enclosures:
- Computer cases
- Server cabinets
- Audio/video equipment casings
- Electrical control panels
- Instrument housings
Architectural Elements:
- Roofing panels
- Siding panels
- Ductwork
- Gutters and downspouts
- Decorative accents
Industrial Components:
- Machinery guards
- Safety covers
- Tooling and fixtures
- Storage containers
- Material handling equipment
The specific parts that can be bent by a sheet metal horizontal press will depend on the size and capacity of the machine, as well as the tooling that is available. However, in general, horizontal presses are well-suited for bending large, flat pieces of sheet metal into a variety of shapes.
Here are some additional examples of parts that can be bent by a sheet metal horizontal press:
- Angles and channels
- Boxes and enclosures
- U-shapes and Z-shapes
- Louvers and vents
- Curvilinear shapes (with the appropriate tooling)
With its versatility and precision, the sheet metal horizontal press is a valuable tool for a wide range of metalworking applications.
As a steel plate bender, our EMS HP series metal press brake is the best in performance/price ratio.
A manual steel bending machine is a lightweight metalworking machine with which you can also make punching. A Punching machine is used to punch sheet metals to drill them. This is one of the most used types of plant machinery. The iron punching machine is a power press cutting machine which is a hydraulic sheet cutting machine.
All the machines and machinery parts are manufactured in our own production facility in Turkey. A hydraulic punch press or sheet metal press brake is a vital production machine used to punch sheet metal as a manual punch press.
Warranty
EMS Metalworking machines have 3 years warranty. This one encloses any manufacturing default all along these 3 years for components. Any misuse is excluded from this condition. Labor, back and forth shipping and any eventual repair, are not included in this warranty
Hydraulic Press

A hydraulic press is a machine that uses a hydraulic cylinder to generate a compressive force. It operates based on Pascal’s Law, which states that when pressure is applied to a confined fluid, the pressure change occurs throughout the entire fluid. In a hydraulic press, this principle is used to multiply the input force applied by the user, producing a much larger output force that can be used for various industrial tasks.
Hydraulic presses are widely employed across different industries due to their ability to exert significant force with great precision and control. These machines are essential for tasks that involve compressing, shaping, or manipulating materials, especially metals. For example, they are often used to form car parts, assemble machinery, and create complex metal shapes that would otherwise require considerable manual labor.
The hydraulic press consists of a few essential components: a hydraulic cylinder, a piston, a hydraulic pump, and hydraulic fluid. The machine functions by pushing hydraulic fluid into the cylinder, which in turn pushes the piston down, applying pressure to the object being worked on. The amount of force the press can apply is determined by the size of the piston and the hydraulic system’s pressure level.
Hydraulic presses are versatile and come in various sizes, ranging from small tabletop units to massive industrial machines capable of generating thousands of tons of force. Their ability to produce immense pressure efficiently has made them invaluable in modern manufacturing and engineering processes. In addition to their use in industries like automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing, hydraulic presses are also found in smaller, more specialized applications such as plastic molding, metal forming, and even recycling industries for crushing waste materials.
The advantages of hydraulic presses are numerous. They are generally more compact than mechanical presses, requiring less space and offering smoother, more controlled operations. Additionally, they provide a higher degree of flexibility and can be used for a wider range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
In summary, hydraulic presses are crucial machines in the modern industrial landscape. Their efficiency, precision, and ability to generate enormous force make them an indispensable tool across a wide array of sectors. As technology continues to advance, hydraulic presses are also evolving, becoming more energy-efficient and integrating with smart manufacturing systems to meet the growing demands of modern industry.
History and Evolution of Hydraulic Presses
2.1. Origins of Hydraulic Technology
The history of hydraulic technology can be traced back to ancient times, long before the invention of the modern hydraulic press. Early civilizations such as the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans developed rudimentary hydraulic systems to manage water resources, including aqueducts, irrigation channels, and waterwheels. These innovations, while focused primarily on water flow, laid the groundwork for the more sophisticated hydraulic systems that would emerge in later centuries.
However, the application of hydraulics to generate mechanical force didn’t come until much later. It was during the Renaissance that scientists and inventors began to develop a deeper understanding of fluid mechanics. One of the key figures in the development of hydraulic principles was Blaise Pascal, a French mathematician and physicist, who formulated Pascal’s Law in the 17th century. Pascal’s Law states that pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions. This principle is foundational to the function of hydraulic presses, enabling them to multiply the force applied to the system.
2.2. The Invention of the Hydraulic Press
The development of the hydraulic press as we know it today is credited to Joseph Bramah, an English inventor, in the late 18th century. Bramah was primarily known for his work on the development of locks, but his interest in hydraulics led him to design the first hydraulic press in 1795. His invention, which was called the Bramah press, was a breakthrough in industrial machinery and provided a practical demonstration of Pascal’s Law.
Bramah’s hydraulic press was revolutionary because it allowed for the exertion of massive amounts of force using only a small input effort. By applying pressure to a small piston, the press could generate a significantly larger force on a larger piston, which was used to compress or shape materials. This principle of force multiplication made Bramah’s hydraulic press far more efficient than any mechanical press that had been developed up until that time.
The Bramah press found immediate use in industrial applications such as metal forming, stamping, and forging. It allowed manufacturers to shape metals and other materials with precision and ease, leading to the widespread adoption of hydraulic presses across a range of industries.
2.3. Evolution through Industrial Revolutions
The hydraulic press underwent significant evolution during the First Industrial Revolution (late 18th to early 19th century). As industries began to expand and new technologies emerged, there was a growing need for more efficient machinery capable of handling the increased demand for mass production. Hydraulic presses were instrumental in this process, as they enabled manufacturers to produce large quantities of goods with greater precision and control than was previously possible.
During the Second Industrial Revolution (late 19th to early 20th century), advances in materials science and engineering led to the development of more powerful and durable hydraulic presses. Steel became the material of choice for constructing hydraulic press frames, replacing the cast iron that had been used previously. Additionally, new hydraulic fluids were developed, improving the efficiency and reliability of the press’s hydraulic systems.
The introduction of electric motors and pumps during this period also revolutionized the hydraulic press. Previously, hydraulic systems had relied on manual pumps or steam engines to generate pressure. With the advent of electric power, hydraulic presses could operate more consistently and at higher pressures, allowing for greater force output and increased production capacity.
2.4. Major Milestones in Hydraulic Press Development
As the 20th century progressed, hydraulic presses continued to evolve and become more specialized. Several key developments marked the ongoing improvement of hydraulic press technology:
- Hydraulic Press in Metal Forming (Mid-20th Century) The use of hydraulic presses in metalworking industries expanded significantly during the early to mid-20th century. Presses were now capable of handling extremely high pressures, which made them ideal for tasks like deep drawing, extrusion, and forging. These processes allowed manufacturers to create complex metal parts for industries like automotive, aerospace, and defense.
- Advancement in Control Systems (1960s – 1980s) The integration of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and computerized numerical control (CNC) systems into hydraulic presses in the 1960s and 1970s greatly enhanced their precision and automation capabilities. These developments allowed operators to control the press with high levels of accuracy, ensuring repeatability and reducing errors in production.
- Servo-Hydraulic Systems (Late 20th Century) In the late 20th century, servo-hydraulic systems were introduced, which combined hydraulic power with electrical control systems. These systems offered significant advantages in terms of energy efficiency and precision. Servo-hydraulic presses allowed for precise control of speed, force, and position, making them ideal for applications requiring fine control, such as plastic molding or the production of delicate components.
- Emergence of Industry 4.0 Integration (21st Century) The 21st century brought with it the rise of Industry 4.0, the concept of smart manufacturing where machines are connected to the internet and can communicate data in real-time. Hydraulic presses have not been exempt from this transformation. Modern presses now feature smart sensors, remote monitoring capabilities, and predictive maintenance algorithms that help optimize performance and reduce downtime.
2.5. The Hydraulic Press Today
Today, hydraulic presses are more advanced than ever, with innovations that allow them to operate with precision, power, and efficiency. Modern presses can exert thousands of tons of force while maintaining tight tolerances, making them indispensable in industries ranging from automotive manufacturing to aerospace and beyond. Additionally, the continued development of energy-efficient systems and sustainable hydraulic fluids reflects the ongoing commitment to making hydraulic presses more environmentally friendly.
The hydraulic press remains a key player in modern industrial processes, and its evolution continues as new technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data are integrated into hydraulic systems to further enhance their capabilities. With this trajectory, hydraulic presses are poised to remain an essential tool in industrial manufacturing for years to come.
Components of a Hydraulic Press
Hydraulic presses are composed of various components that work together to generate and control the immense force required for tasks like metal forming, crushing, and stamping. Understanding the function and role of each part is crucial for grasping how these machines operate. Below, we’ll take an in-depth look at the main components of a hydraulic press.
3.1. Hydraulic System Overview
The hydraulic system is the heart of a hydraulic press. It uses hydraulic fluid to transmit power and amplify force. In essence, this system takes the mechanical input (manual or powered) and converts it into hydraulic pressure, which is used to perform tasks such as compressing, bending, or cutting materials.
A typical hydraulic system includes the following:
- Hydraulic fluid reservoir
- Hydraulic pump
- Cylinder
- Piston
- Control valves
- Pressure gauges
Let’s now examine each component in detail.
3.2. Key Components
3.2.1. Cylinder
The hydraulic cylinder is one of the most critical components of a hydraulic press. It is a mechanical actuator that converts hydraulic energy (pressure from the fluid) into linear motion. The cylinder houses the piston, which moves up and down within it.
- Construction: Typically, hydraulic cylinders are made from high-strength materials such as steel to withstand the immense pressures generated during operation.
- Single-acting vs. double-acting cylinders: In a single-acting cylinder, hydraulic fluid is applied to only one side of the piston, moving it in one direction, with a spring or other mechanism returning it to its original position. In contrast, a double-acting cylinder has fluid applied to both sides of the piston, allowing it to move in both directions, giving greater control and flexibility.
The force generated by the hydraulic press is directly proportional to the surface area of the cylinder and the pressure applied to the fluid.
3.2.2. Piston
The piston is another key part of the press. It is positioned inside the cylinder and moves up and down as hydraulic pressure is applied. The downward movement of the piston is what creates the compressive force used to shape or press materials.
- Force transmission: The piston transfers the hydraulic pressure into mechanical force. The larger the surface area of the piston, the greater the force it can apply. This is why hydraulic presses are capable of exerting much more force than what is applied by the operator or motor driving the system.
- Precision and control: Modern presses are equipped with highly responsive pistons, ensuring that they operate smoothly and with precision, even under significant loads.
3.2.3. Hydraulic Fluid
Hydraulic fluid is the medium that transmits force within the hydraulic system. It plays an essential role in the overall functioning of the hydraulic press, acting not only as a power transmitter but also as a lubricant and coolant.
- Types of hydraulic fluids: There are various types of hydraulic fluids used in presses, including:
- Mineral-based fluids: Most commonly used in general applications due to their affordability and effectiveness.
- Water-based fluids: Used in presses requiring fire resistance, as these fluids are less flammable.
- Synthetic fluids: Offer superior performance and longer lifespan in extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or where high corrosion resistance is needed.
The properties of hydraulic fluids, such as viscosity, thermal stability, and compressibility, affect the performance of the hydraulic press. Fluids must be regularly maintained and replaced to ensure consistent press operation.
3.2.4. Press Frame
The frame of the hydraulic press is its structural backbone, holding all the components together and providing the necessary rigidity to support the press’s operations. The frame design varies depending on the type of press, but the most common designs include:
- H-frame: Shaped like the letter “H”, this frame design provides strong support and is commonly used for heavy-duty applications.
- C-frame: Shaped like a “C”, this design is more compact and is typically used for lighter pressing tasks where space is limited.
- Four-column frame: This design uses four columns to support the press and is typically found in large presses used for manufacturing automotive or aerospace components.
The frame must be robust and durable to withstand the repeated high pressures that the press generates during operation.
3.2.5. Power Source (Hydraulic Pump)
The hydraulic pump is responsible for converting mechanical power into hydraulic energy by moving hydraulic fluid from the reservoir into the system. The pump creates a flow of fluid that allows the press to operate under pressure.
- Types of pumps: There are several different types of hydraulic pumps used in presses:
- Gear pumps: Simple and cost-effective, these pumps are suitable for applications with lower pressure requirements.
- Vane pumps: Known for being quiet and efficient, these pumps are often used in presses that require moderate pressures.
- Piston pumps: These pumps are the most powerful and are typically used in high-pressure hydraulic presses. They offer excellent precision and control.
The pump’s capacity directly affects how quickly the press can build pressure and how much force it can generate.
3.2.6. Valves and Controls
Hydraulic systems in presses use a variety of valves to control the flow and pressure of the fluid, ensuring that the press operates safely and efficiently. The key valves used in a hydraulic press include:
- Directional control valves: These valves control the direction of the fluid flow, determining whether the piston will move up or down.
- Pressure relief valves: To protect the system from over-pressurization, these valves release excess fluid back into the reservoir when pressure exceeds a safe level.
- Flow control valves: These valves regulate the speed of the press by controlling the flow rate of hydraulic fluid into the cylinder.
In modern presses, these valves are often operated electronically, providing precise control over the system’s pressure and motion.
3.2.7. Hydraulic Fluid Reservoir
The reservoir is where the hydraulic fluid is stored when not in use. It is typically a large tank that holds the fluid and allows it to be cooled, filtered, and cleaned before re-entering the hydraulic system.
- Cooling and filtering: Hydraulic fluid heats up during use, so the reservoir is equipped with cooling systems to dissipate heat. Additionally, filters remove impurities from the fluid, which could otherwise damage the system.
A well-maintained reservoir is crucial for preventing contamination and ensuring the longevity of the press.
3.2.8. Pressure Gauges and Sensors
Pressure gauges and sensors provide real-time data about the hydraulic system’s performance, allowing operators to monitor the pressure levels during press operation.
- Manual vs. digital gauges: Older hydraulic presses often use manual gauges, which require visual inspection. However, modern presses are equipped with digital sensors that feed information directly to the control systems, making monitoring more efficient.
- Safety and precision: These sensors are essential for maintaining safe operating conditions and ensuring that the press applies the correct force for each job.
3.3. The Interaction Between Components
All these components work together seamlessly to ensure the efficient operation of the hydraulic press. The pump sends hydraulic fluid from the reservoir into the cylinder, where pressure is applied to the piston. As the piston moves downward, it exerts force on the material placed beneath it. The valves and sensors regulate the flow and pressure of the fluid, while the frame provides structural support to withstand the forces generated by the press.
The effectiveness of a hydraulic press is dependent on the proper functioning and maintenance of each of these components. Any failure in one part of the system can lead to inefficiencies or even dangerous malfunctions. For example, leaks in the hydraulic fluid system can result in a loss of pressure, reducing the press’s ability to perform its tasks.
3.4. Modern Innovations in Hydraulic Components
Recent advancements in hydraulic technology have led to innovations in the components used in presses. Servo-hydraulic systems, for instance, have improved the efficiency and control of hydraulic presses, allowing for faster and more precise operations. Similarly, smart sensors are now being integrated into hydraulic systems, providing real-time feedback on performance and enabling predictive maintenance to avoid breakdowns.
The continuous evolution of these components ensures that hydraulic presses remain a critical tool in industrial processes, offering unmatched force and control for a wide range of applications.
Working Principle of a Hydraulic Press
The hydraulic press operates on the simple yet powerful principle of Pascal’s Law, which states that when pressure is applied to a confined fluid, the pressure is transmitted equally in all directions. This fundamental law of fluid mechanics enables hydraulic presses to amplify a small input force into a much larger output force. By manipulating hydraulic fluid in a sealed system, the hydraulic press can perform tasks such as compressing, bending, shaping, or cutting materials with remarkable efficiency.
In this section, we will explore the detailed working principle of hydraulic presses, focusing on how pressure is generated, how force is amplified, and how hydraulic systems manage energy efficiency and control.
4.1. Pascal’s Law and its Application in Hydraulic Presses
Pascal’s Law is the foundation of hydraulic technology. The law states that the pressure change in an incompressible and confined fluid is uniformly distributed throughout the fluid. The formula for Pascal’s Law is as follows:P=FAP = \frac{F}{A}P=AF
Where:
- P is pressure,
- F is force,
- A is the area over which the force is applied.
In a hydraulic press, this law is applied to multiply force through the use of two pistons—one smaller and one larger—connected by hydraulic fluid within a sealed system. When force is applied to the smaller piston, the pressure created is transmitted through the fluid to the larger piston, which results in a much larger force being exerted.
4.2. How Pressure is Generated
The basic operation of a hydraulic press begins with the generation of hydraulic pressure. This pressure is created by the hydraulic pump, which forces hydraulic fluid from the reservoir into the system. Once the fluid enters the cylinder, it pushes against the piston, causing it to move.
The pump provides the necessary energy to create this pressure. There are several types of hydraulic pumps, including:
- Gear pumps (common in smaller presses),
- Vane pumps (known for their efficiency),
- Piston pumps (used in high-pressure applications).
As the fluid is pushed into the cylinder, it creates a pressurized environment. This pressurized fluid exerts force on the piston, causing it to move in the direction of the applied pressure (usually downwards in most presses).
4.3. Force Amplification: From Small Piston to Large Piston
One of the most important aspects of a hydraulic press is its ability to amplify force. The hydraulic press uses two pistons of different sizes to achieve this amplification. Here’s how it works:
- Small piston: This piston has a smaller surface area and is the point at which the input force is applied, either manually (in smaller presses) or via a motor (in larger presses).
- Large piston: This piston has a much larger surface area and is responsible for generating the output force applied to the material being pressed.
Because Pascal’s Law states that pressure is constant throughout the system, the pressure generated at the small piston is transferred equally to the larger piston. However, since the larger piston has a greater surface area, the force it generates is proportionally larger.
Let’s break this down with an example:
- If you apply 100 Newtons of force to a small piston with a surface area of 1 cm², the pressure created is 100 N/cm².
- That same pressure is applied to the larger piston, which has a surface area of 10 cm². Therefore, the force on the larger piston will be 100 N/cm² × 10 cm² = 1000 Newtons.
This ability to amplify force makes hydraulic presses incredibly powerful. Even small input forces can generate thousands of Newtons of pressure, enabling the press to handle tasks like bending thick metal sheets or crushing large objects.
4.4. Hydraulic Fluid and Energy Transmission
The hydraulic fluid plays a crucial role in the transmission of force within the hydraulic press. As an incompressible medium, the fluid transmits pressure efficiently from the pump to the cylinder without significant losses.
- Types of hydraulic fluids: Commonly used fluids include mineral oils, water-based fluids, and synthetic fluids. The choice of fluid depends on the operating conditions of the press, including temperature, pressure, and the need for fire resistance.
Hydraulic fluid also acts as a lubricant for the moving parts within the system, reducing wear and tear on components like pistons, seals, and valves. Additionally, the fluid helps dissipate heat generated by the system, ensuring that the press operates efficiently even under high loads.
4.5. Control of Pressure and Force
Controlling the pressure within the hydraulic system is essential for ensuring that the press operates safely and efficiently. The pressure and force applied by the press can be controlled using several methods:
- Pressure relief valves: These valves release excess fluid back into the reservoir when the pressure exceeds safe operating limits. This prevents the system from becoming over-pressurized, which could cause damage or pose a safety hazard.
- Directional control valves: These valves direct the flow of hydraulic fluid within the system, determining whether the piston moves up or down. They allow the operator to control the direction of force application.
- Flow control valves: These valves regulate the flow rate of hydraulic fluid, which in turn controls the speed of the press. By adjusting the flow, operators can ensure that the press moves at the desired speed for each task.
In modern presses, these controls are often automated or managed via computer systems, allowing for precise and repeatable operations. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems enable operators to set specific pressure, force, and speed parameters, which the press then follows automatically.
4.6. Energy Efficiency and Conservation in Hydraulic Systems
One of the challenges associated with hydraulic presses is energy efficiency. Traditional hydraulic systems can be relatively inefficient because the pump runs continuously, even when the press is not in operation, consuming energy and generating heat. However, recent innovations have improved the energy efficiency of hydraulic presses:
- Variable displacement pumps: These pumps adjust the amount of hydraulic fluid being moved depending on the demand of the system. When the press is idle or requires less pressure, the pump reduces its output, conserving energy.
- Servo-hydraulic systems: These systems combine hydraulic power with electrical control. In servo-hydraulic presses, electric motors control the pump, adjusting its speed to match the force and speed requirements of the press. This results in lower energy consumption, reduced noise, and improved precision.
- Hydraulic accumulators: These devices store energy in the form of pressurized fluid, which can be released when needed. Accumulators help reduce the load on the pump during peak operation, improving overall system efficiency.
These advancements have made modern hydraulic presses far more energy-efficient than their predecessors, making them more environmentally friendly and cost-effective.
4.7. Advantages of Hydraulic Press Operation
The working principle of hydraulic presses offers several key advantages:
- Force multiplication: Hydraulic presses can amplify a relatively small input force into a much larger output force, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications like metal forming and compression.
- Precision: Hydraulic presses allow for precise control over pressure and speed, enabling manufacturers to produce complex, high-quality parts.
- Versatility: Hydraulic presses can be used for a wide range of materials and processes, from metal forming and plastic molding to recycling and waste management.
- Efficiency: Modern presses with servo-hydraulic systems and variable displacement pumps are energy-efficient and can reduce operational costs.
4.8. Limitations of Hydraulic Press Operation
While hydraulic presses offer numerous advantages, they also have some limitations:
- Energy consumption: Traditional hydraulic systems can consume significant amounts of energy, especially if the pump runs continuously.
- Maintenance: Hydraulic systems require regular maintenance, including checking fluid levels, replacing worn seals, and cleaning filters. Contamination in the hydraulic fluid can reduce system performance and lead to component wear.
- Noise: Hydraulic presses, particularly those with older pumps, can generate significant noise during operation, though modern systems are designed to be quieter.
Types of Hydraulic Presses
Hydraulic presses are available in various designs, each suited to specific industrial tasks. Depending on the force required, size, and operational method, different types of hydraulic presses are employed across industries, such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace, metalworking, plastic molding, and recycling. This section will explore the different types of hydraulic presses, comparing their designs and applications.
5.1. Manual Hydraulic Presses
Manual hydraulic presses are the simplest form of hydraulic presses, operated by hand. These presses are typically small, compact, and designed for tasks that require low to moderate pressure, such as small-scale metalworking, pressing bearings, or assembling components. They are often used in workshops, laboratories, and maintenance shops where precision work and control are needed, but high force is not necessary.
- Key features:
- Operated by a hand pump to generate hydraulic pressure.
- Usually consist of a single-acting cylinder that moves in one direction when pressure is applied and returns to its original position using a spring.
- Suitable for small, precise tasks like shaping or straightening metal parts, pressing in or removing bearings, and assembling components.
Advantages:
- Inexpensive and easy to operate.
- No need for external power sources, making them ideal for small workshops or remote locations.
- High precision for small-scale jobs.
Limitations:
- Limited force output compared to powered presses.
- Slower operation due to manual pumping.
- Suitable only for light-duty applications.
5.2. Powered Hydraulic Presses
Powered hydraulic presses are larger and more versatile than manual presses. These presses are driven by either electric or pneumatic systems and can generate much higher forces, making them suitable for industrial applications. There are several types of powered hydraulic presses, each designed for specific tasks.
5.2.1. Electric Hydraulic Presses
Electric hydraulic presses use an electric motor to drive the hydraulic pump, which generates pressure in the hydraulic system. These presses are common in manufacturing and metalworking industries, where consistent, high-force applications are required.
- Key features:
- Powered by an electric motor that drives the hydraulic pump.
- Offers precise control over force and speed through adjustable settings.
- Can be equipped with CNC or programmable control systems for automation.
Applications:
- Metal forming, stamping, and bending.
- Deep drawing processes in the automotive and aerospace industries.
- Precision tasks in plastic molding or die cutting.
Advantages:
- High force generation for heavy-duty applications.
- Precise control over force and speed, ideal for complex, high-volume tasks.
- Can be integrated into automated production lines for efficiency.
Limitations:
- Higher energy consumption compared to manual or pneumatic presses.
- Requires regular maintenance of the electrical and hydraulic systems.
- Can be expensive to purchase and operate.
5.2.2. Pneumatic Hydraulic Presses
Pneumatic hydraulic presses use compressed air to generate hydraulic pressure. While not as powerful as electric hydraulic presses, they are more energy-efficient and often used in applications that do not require extremely high forces.
- Key features:
- Powered by compressed air rather than electricity.
- Ideal for lighter tasks that still require hydraulic force but do not need the high power output of electric presses.
- Used in environments where electrical power may not be readily available or where lower force and speed are acceptable.
Applications:
- Assembly lines for light manufacturing tasks.
- Punching, bending, and forming lighter materials.
- Plastic molding and small-scale metalworking.
Advantages:
- More energy-efficient than electric presses for lighter tasks.
- Lower operating costs due to reduced energy consumption.
- Suitable for environments where electrical systems pose a safety risk (e.g., explosive or flammable environments).
Limitations:
- Limited force output compared to electric-powered presses.
- Slower operational speeds.
- Not suitable for heavy-duty applications.
5.3. Specialized Hydraulic Presses
In addition to manual and powered presses, there are also specialized hydraulic presses designed for specific industrial processes. These presses vary in their frame design, size, and operational capabilities.
5.3.1. H-Frame Presses
H-frame hydraulic presses are named for the shape of their frame, which resembles the letter “H.” They are among the most common hydraulic presses used in industries due to their versatility and ability to handle both light and heavy-duty applications.
- Key features:
- A strong, rigid frame shaped like an “H,” which provides excellent structural support and stability during operation.
- Can be equipped with single or double-acting cylinders.
- Available in both manual and powered configurations, making them suitable for a range of applications.
Applications:
- Metal forming, stamping, and punching.
- Straightening, bending, and assembling large parts.
- Automotive repair (e.g., pressing out bearings or bushings).
Advantages:
- Versatile and capable of handling both small and large tasks.
- High force output, suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Widely used across many industries due to their robust construction.
Limitations:
- The larger size of some models can take up significant floor space.
- Requires careful alignment during operation to ensure even force distribution.
5.3.2. C-Frame Presses
C-frame hydraulic presses are more compact than H-frame presses and are shaped like the letter “C.” This design provides easy access to the work area from three sides, making C-frame presses ideal for tasks that require loading and unloading materials quickly.
- Key features:
- Open-front design allows for easy access to the pressing area.
- Generally smaller and more compact than H-frame presses.
- Ideal for tasks that require frequent adjustments or quick material changes.
Applications:
- Light to medium-duty applications such as punching, bending, and forming smaller parts.
- Assembling components in the electronics or automotive industries.
- Precision pressing tasks where easy access to the workpiece is necessary.
Advantages:
- Compact and space-efficient.
- Easy access to the pressing area, reducing downtime between tasks.
- Precise control over force and speed for smaller applications.
Limitations:
- Limited to lighter tasks compared to H-frame presses.
- The open design can cause slight deformation under extreme loads, reducing its effectiveness for heavy-duty tasks.
5.3.3. Four-Column Hydraulic Presses
Four-column hydraulic presses have four vertical columns that provide structural support for the press. This design is ideal for applications that require evenly distributed force across a large workpiece.
- Key features:
- Four vertical columns provide excellent stability and even force distribution.
- Can handle large workpieces and high force applications.
- Commonly used in heavy-duty industries such as automotive and aerospace manufacturing.
Applications:
- Metal forming, die cutting, and large-scale forging.
- Deep drawing processes that require precise, even pressure.
- Pressing large or heavy workpieces where even force is critical.
Advantages:
- Excellent stability and even force distribution, reducing the risk of material deformation.
- Capable of handling large workpieces.
- High force output, suitable for heavy-duty industrial tasks.
Limitations:
- Large and heavy, requiring significant floor space.
- Higher energy consumption due to the size and force capabilities of the press.
5.3.4. Bench Presses
Bench hydraulic presses are smaller presses designed to be mounted on a workbench or table. These presses are used for light-duty applications in workshops, laboratories, and small-scale manufacturing environments.
- Key features:
- Small, compact design that fits on a workbench or tabletop.
- Usually operated manually or with a small hydraulic pump.
- Ideal for light-duty tasks where precision is more important than force.
Applications:
- Assembling small components, such as in electronics or jewelry making.
- Light metalworking tasks, such as bending or pressing small parts.
- Laboratory testing and material sample preparation.
Advantages:
- Compact and easy to use in small workspaces.
- Precise control over pressing force.
- Inexpensive and suitable for small-scale tasks.
Limitations:
- Limited force output, unsuitable for large or heavy-duty applications.
- Small size limits the range of tasks that can be performed.
5.4. Comparative Analysis of Hydraulic Press Types
Each type of hydraulic press has its strengths and is suited to particular applications. The following table summarizes the key characteristics of the different press types:
| Type | Force Output | Size | Applications | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Press | Low | Small | Light assembly, workshops | Low cost, portable | Limited force, slower operation |
| Electric Hydraulic Press | High | Medium-Large | Manufacturing, metal forming | High force, precision control, automation | Higher energy consumption, requires maintenance |
| Pneumatic Press | Moderate | Medium | Assembly lines, lighter manufacturing | Energy efficient, lower operating costs | Limited force output, slower than electric presses |
| H-Frame Press | High | Large | Metal forming, straightening, heavy-duty tasks | High force, versatile | Requires floor space, careful alignment needed |
| C-Frame Press | Moderate | Small-Medium | Precision tasks, light to medium duty | Compact, easy access to work area | Limited to lighter tasks, less stable under heavy loads |
| Four-Column Press | High | Large | Large-scale metal forming, deep drawing | Excellent force distribution, handles large workpieces | Requires significant space, high energy consumption |
| Bench Press | Low | Small | Small-scale assembly, testing | Compact, precise control, low cost | Limited force output, small work area |
Applications of Hydraulic Presses
Hydraulic presses are versatile machines used across a broad range of industries, from automotive manufacturing and aerospace to plastic molding and recycling. Their ability to generate immense force while maintaining precision makes them essential in various industrial processes, including forming, cutting, shaping, and assembling materials. In this section, we’ll explore the key industries and applications where hydraulic presses play a vital role.
6.1. Automotive Industry
The automotive industry heavily relies on hydraulic presses for a variety of tasks, particularly in manufacturing car components, bodywork, and assemblies. The versatility of hydraulic presses allows for the precise and repeatable production of complex metal and plastic parts used in vehicles.
6.1.1. Pressing Car Parts
Hydraulic presses are used to manufacture critical car components such as:
- Chassis parts: The frames that provide structural support for vehicles are often formed using hydraulic presses. The high force generated allows the press to mold thick sheets of metal into the desired shapes.
- Body panels: Hydraulic presses are essential for creating body panels and hoods, where precise shaping is required to ensure proper fit and finish. The metal stamping process uses high-force hydraulic presses to cut, bend, and shape large sheets of metal into the necessary parts.
6.1.2. Brake and Clutch Plates
In the production of brake and clutch plates, hydraulic presses are used to compress and shape friction materials. These materials need to be highly durable and accurately produced to ensure vehicle safety. The controlled force of a hydraulic press ensures that each component meets the required specifications, contributing to the vehicle’s overall performance and reliability.
6.1.3. Assembly and Fabrication
Hydraulic presses also assist in the assembly of vehicle parts, such as joining or securing metal pieces together through compression. This process is particularly important in tasks like fastening bushings, bearings, and seals into their respective housings.
6.2. Manufacturing Industry
In general manufacturing, hydraulic presses are indispensable for processes like metal forming, stamping, forging, and plastic molding. The precision and power of hydraulic presses make them ideal for handling both lightweight and heavy-duty applications.
6.2.1. Metal Forming, Stamping, and Forging
One of the most significant uses of hydraulic presses is in metal forming, where the press shapes and molds metal into complex parts. Stamping and forging are specific methods within this category:
- Stamping: Involves pressing sheet metal into a die to create precise shapes or patterns. Hydraulic presses are used to cut, bend, or punch holes in metal sheets, creating components used in everything from household appliances to industrial machinery.
- Forging: Hydraulic presses apply immense force to a piece of metal, shaping it while it is hot. This process is used to create stronger, more durable parts, such as gears, engine components, and tools. Forging under hydraulic pressure ensures consistent material strength and structural integrity.
6.2.2. Plastic Molding
Hydraulic presses are essential in plastic injection molding and compression molding. In these processes, hydraulic presses:
- Inject molten plastic into molds to create parts with precise dimensions, such as automotive interiors, medical devices, or packaging components.
- In compression molding, plastic material is placed in a mold, and the hydraulic press applies force to shape the plastic. This process is often used to make large plastic components, such as housings or casings.
6.3. Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry demands highly specialized components with precise dimensions and superior strength-to-weight ratios. Hydraulic presses are essential in forming parts for aircraft, spacecraft, and defense systems.
6.3.1. Shaping Aircraft Parts
In aerospace, hydraulic presses are used for metal forming, extrusion, and deep drawing to shape metal into complex, lightweight parts that meet stringent performance and safety requirements. Examples include:
- Fuselage panels: Large hydraulic presses shape the lightweight aluminum or composite materials used in aircraft fuselages.
- Wings and structural components: Precision is critical when forming aircraft wings and structural components to ensure they meet aerodynamics and load-bearing specifications.
The ability of hydraulic presses to handle materials like titanium and aluminum alloys, which are commonly used in aerospace due to their strength and low weight, makes them indispensable in aircraft manufacturing.
6.3.2. Assembly of Aerospace Systems
Hydraulic presses are also used in assembling and joining parts in aerospace systems. For example:
- Hydraulic riveting presses secure fasteners in aircraft body panels and components.
- Assembly presses are used to install precision bearings, bushings, and other critical components.
6.4. Construction and Engineering
In the construction and heavy engineering industries, hydraulic presses are used for various applications, including compressing construction materials, assembling heavy machinery, and shaping structural components.
6.4.1. Compression of Construction Materials
Hydraulic presses are often used to compress and shape materials such as concrete, brick, and tiles. For example:
- Pre-cast concrete components: Hydraulic presses shape and compress concrete into pre-cast blocks or panels used in building construction.
- Brick and tile production: In this process, the press compresses raw materials like clay or cement into bricks or tiles with consistent shapes and sizes.
6.4.2. Assembly of Heavy Machinery
Hydraulic presses play a crucial role in the assembly of heavy machinery and equipment used in construction. They are often used to press bearings, bushings, or other components into machinery parts like hydraulic cylinders, engines, and gear systems. The controlled application of force ensures that parts are assembled securely and without damaging sensitive components.
6.5. Agricultural Industry
Hydraulic presses also find applications in the agricultural industry, where they are used to process materials and create equipment parts.
6.5.1. Compressing Hay Bales
Hydraulic presses are used in agriculture to compress hay, straw, or other forage into compact bales for easy storage and transport. The press applies significant pressure to reduce the volume of the material while retaining its quality for feeding livestock.
6.5.2. Farm Equipment Assembly
Similar to the automotive and construction industries, hydraulic presses are used in the assembly of farm equipment, such as pressing bearings, bushings, and other components into tractors, plows, and harvesters. The precision of hydraulic presses ensures that the parts are securely and accurately installed, enhancing the reliability of agricultural machinery.
6.6. Recycling Industry
Hydraulic presses play a critical role in the recycling industry, particularly in the processing of scrap materials and waste management. They are used to crush, compact, or bale materials to prepare them for recycling or disposal.
6.6.1. Metal Recycling
In metal recycling, hydraulic presses are used to compress scrap metal into compact blocks or bales for easier transportation and processing. For example:
- Car body recycling: Hydraulic presses crush old car bodies into manageable sizes for melting down and recycling.
- Scrap metal baling: Loose metal scrap, such as aluminum cans, steel, and copper, is baled using a hydraulic press, reducing its volume and making it easier to transport and store before it is reprocessed.
6.6.2. Waste Management
Hydraulic presses are also used in waste management facilities to compact household and industrial waste into dense, manageable bales. This process reduces the space needed for waste storage and simplifies transportation to recycling or disposal facilities. The ability to compress materials like plastic, cardboard, and paper ensures more efficient waste handling and disposal.
6.7. Home Workshops and DIY
Hydraulic presses are not limited to large industrial applications. Smaller hydraulic presses are commonly used in home workshops and for do-it-yourself (DIY) projects. These compact presses offer hobbyists and small businesses a versatile tool for various applications.
6.7.1. Metalworking
In home workshops, hydraulic presses are frequently used for:
- Bending and shaping metal: Small hydraulic presses are used to bend metal bars, rods, or sheets into desired shapes for custom projects, such as making furniture, gates, or decorative items.
- Removing or installing bearings: Home mechanics and hobbyists use hydraulic presses to remove old bearings from machines or vehicle parts and press in new ones, ensuring proper fit and function.
6.7.2. Woodworking and Crafting
Hydraulic presses are sometimes used in woodworking and crafting, particularly in tasks that require compression or molding. For example:
- Veneer pressing: Hydraulic presses are used to compress thin sheets of wood veneer onto furniture surfaces, creating a smooth, uniform bond.
- Custom molds: In crafting, hydraulic presses can be used to create custom molds for making unique items like jewelry, art pieces, or decorative panels.
6.8. Hydraulic Press in Research and Testing
Hydraulic presses are widely used in research and testing environments for materials testing, particularly in laboratories where the mechanical properties of materials are evaluated.
6.8.1. Compression Testing
In materials science, hydraulic presses are used for compression testing to determine the strength and durability of materials. For example, concrete, metals, plastics, and composites are tested to see how much force they can withstand before deforming or breaking. The controlled pressure applied by the hydraulic press allows researchers to study how materials behave under stress.
6.8.2. Product Testing and Prototyping
Hydraulic presses are also used to test the durability and performance of finished products or prototypes. This includes tasks like:
- Durability testing: Products like car parts, electronics, or industrial components are subjected to high pressures to determine their durability and resistance to wear.
- Prototyping: In the development phase of new products, hydraulic presses can be used to shape or mold prototype parts to ensure that they meet design specifications before mass production begins.
6.9. Other Specialized Applications
Hydraulic presses can also be found in many other specialized applications, ranging from medical device manufacturing to the production of consumer goods.
6.9.1. Medical Device Manufacturing
In the medical field, hydraulic presses are used to manufacture precision components for devices like pacemakers, prosthetics, and surgical tools. The high precision offered by hydraulic presses ensures that each component meets strict medical standards for quality and safety.
6.9.2. Jewelry and Watchmaking
Hydraulic presses are also used in the jewelry and watchmaking industries to create intricate designs and shapes. For example:
- Metal stamping: Hydraulic presses are used to stamp designs onto metal sheets for jewelry making.
- Shaping watch components: Precision hydraulic presses form parts like watch cases, bezels, and straps, ensuring a perfect fit and high-quality finish.
Outline for Components of a Hydraulic Press
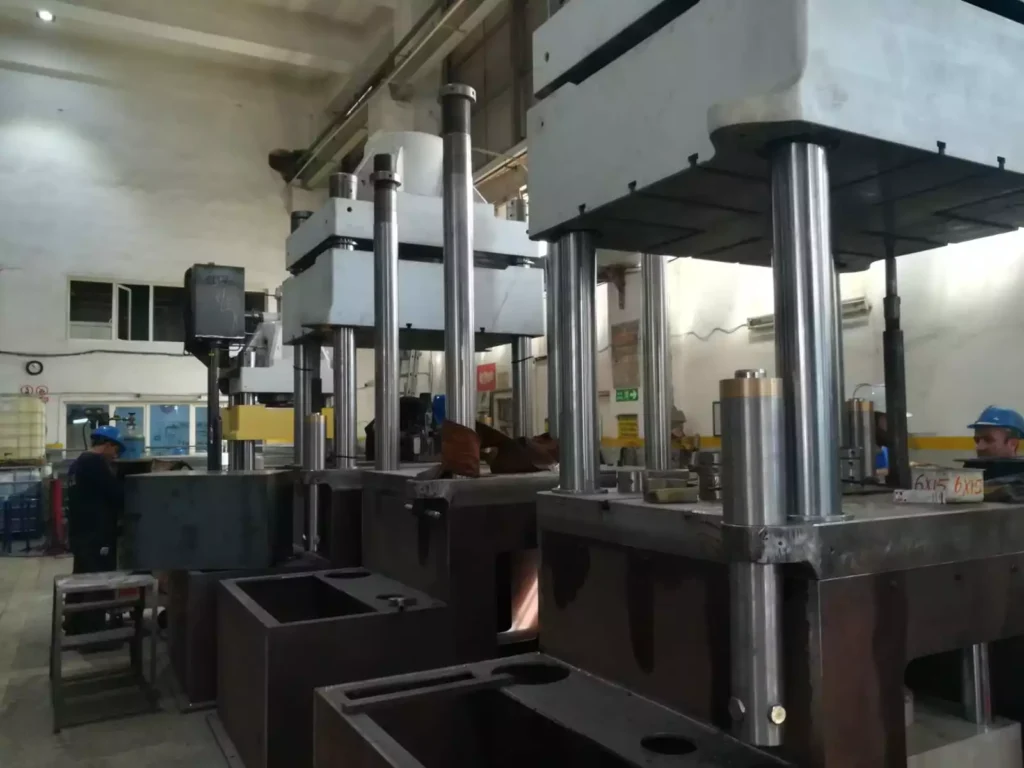

A hydraulic press is a mechanical machine that uses hydraulic pressure to compress, bend, shape, or cut materials. The core principle behind a hydraulic press is Pascal’s Law, which states that pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions. This principle allows hydraulic presses to amplify force, enabling the machine to perform heavy-duty tasks with minimal input force.
At the heart of a hydraulic press is its hydraulic system, which consists of several key components: the hydraulic cylinder, piston, hydraulic fluid, pump, valves, and reservoir. These components work together to generate pressure, transmit force, and control the operation of the press. The hydraulic system allows for smooth, consistent application of force, making the press highly efficient and reliable.
Hydraulic presses are used in a wide range of industries, from automotive manufacturing and metalworking to plastic molding and recycling. Understanding the components of a hydraulic press is essential for maintaining its performance, optimizing its efficiency, and preventing breakdowns. Each part of the hydraulic system plays a critical role in its overall operation, and even minor issues with one component can impact the entire machine.
The hydraulic press system is highly adaptable, with different types of presses and configurations designed for specific applications. From small bench presses used in workshops to massive four-column presses in automotive plants, hydraulic systems can be tailored to the task at hand, whether it involves forming metal parts, shaping plastic components, or compressing scrap materials for recycling.
The efficiency of hydraulic presses has also improved significantly over the years, thanks to innovations in hydraulic fluid, pump design, and control systems. Modern hydraulic presses now integrate smart sensors, programmable controls, and servo-hydraulic systems, allowing operators to control pressure, force, and speed with extreme precision.
Maintaining a hydraulic press involves regular monitoring of components like the hydraulic cylinder, pump, and fluid system. Regular maintenance ensures that the press operates safely and effectively, minimizing downtime and extending the life of the equipment.
In summary, the hydraulic press system is a finely tuned machine composed of various interdependent components. A well-maintained hydraulic system ensures that the press operates efficiently, delivering the force and precision required for industrial applications.
Hydraulic Cylinder
The hydraulic cylinder is one of the most crucial components of a hydraulic press, responsible for converting hydraulic pressure into linear motion. It is the part of the system that directly generates the force required to press, compress, or shape the material. The cylinder houses the piston and is filled with hydraulic fluid, which, when pressurized, pushes the piston forward to perform the desired task.
2.1. Function and Significance of the Hydraulic Cylinder
The primary role of the hydraulic cylinder is to create the force needed to perform the press’s work. When hydraulic fluid is pumped into the cylinder, the resulting pressure pushes against the piston, causing it to move in a linear motion. This movement is transferred to the material being worked on, whether it involves compressing metal, forming plastic, or bending steel.
Hydraulic cylinders are designed to handle immense pressures, often in the range of several hundred to several thousand PSI (pounds per square inch), depending on the size and capacity of the press. The strength of the cylinder, along with its design and material construction, determines the overall force output of the press.
2.2. Types of Hydraulic Cylinders
There are several types of hydraulic cylinders, each designed for specific applications and press designs.
2.2.1. Single-Acting Cylinders
A single-acting cylinder uses hydraulic pressure to move the piston in one direction only. The return stroke is typically powered by a spring or gravity. These cylinders are simpler in design and are often used in presses where the return stroke does not require significant force.
- Advantages:
- Simple and cost-effective design
- Requires less hydraulic fluid and a smaller pump
- Commonly used in manual presses or lighter-duty applications
2.2.1. Single-Acting Cylinders (Continued)
- Limitations (continued):
- The return stroke relies on external forces (such as springs or gravity), which may result in slower or less controlled movements.
- They are less suitable for applications requiring consistent force in both directions (pressing and releasing).
Single-acting cylinders are often found in smaller hydraulic presses, especially in tasks such as light pressing, assembling, or simple bending. They are typically used when the return stroke does not need to be fast or forceful, such as in certain assembly line tasks or in small workshops where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are prioritized.
2.2.2. Double-Acting Cylinders
In contrast to single-acting cylinders, double-acting cylinders are designed to exert force in both directions—both during the forward (pressing) and the return strokes. This is achieved by applying hydraulic pressure alternately to either side of the piston. Double-acting cylinders are more versatile and powerful, as they offer full control over the press’s movements.
- Advantages:
- Force can be applied in both directions, offering greater control over the entire operation.
- They are faster and more efficient than single-acting cylinders, as the return stroke can be powered hydraulically rather than relying on gravity or springs.
- Ideal for applications that require high precision and speed, such as metal forming, stamping, and forging.
- Limitations:
- More complex and expensive than single-acting cylinders.
- Requires a larger hydraulic pump and more hydraulic fluid to operate effectively.
Double-acting cylinders are commonly used in heavy-duty hydraulic presses, especially those found in large-scale industrial applications like automotive manufacturing and metalworking. Their ability to exert force in both directions makes them ideal for tasks requiring precision and speed, such as deep drawing, metal extrusion, and heavy-duty forging.
2.2.3. Telescopic Cylinders
A telescopic hydraulic cylinder, also known as a multi-stage cylinder, consists of several smaller cylinders nested within each other. These cylinders extend in stages, allowing for a longer stroke in a more compact design. Telescopic cylinders are often used in applications where space is limited, but a long stroke length is required, such as in lifting or pressing operations.
- Advantages:
- Capable of delivering a very long stroke in a compact form.
- Useful for applications where space is limited but the press needs to extend over a large distance.
- Commonly used in heavy machinery, dump trucks, and other lifting devices.
- Limitations:
- More complex design and construction lead to higher costs.
- Potential for more frequent maintenance due to the multiple stages of extension and retraction.
In hydraulic presses, telescopic cylinders are typically used when space is a concern, and a longer extension is needed to reach or compress materials. They are often found in construction equipment, large industrial presses, and certain custom-designed presses where long reach is essential.
2.3. Construction of Hydraulic Cylinders
The construction of a hydraulic cylinder is critical to its performance and longevity. The materials and manufacturing methods used must ensure that the cylinder can withstand high pressure, friction, and repeated use without failure.
2.3.1. Materials Used
Most hydraulic cylinders are made from high-strength steel or alloy materials. Steel is favored for its durability and ability to withstand the extreme pressures generated by hydraulic systems. Some components, such as the cylinder’s rod, are often plated with chrome or other anti-corrosive coatings to reduce friction and wear, and to protect the rod from corrosion.
- Steel: The primary material used in heavy-duty cylinders due to its high strength and resistance to deformation under pressure.
- Composite materials: In some specialized applications, lightweight composite materials may be used to reduce the weight of the cylinder while maintaining strength.
2.3.2. Seals and Rod Coatings
The seals used within hydraulic cylinders are critical to maintaining pressure and preventing fluid leaks. Common types of seals include O-rings, U-cups, and rod seals, all designed to prevent the escape of hydraulic fluid around the piston and rod.
- Seals: Typically made from materials like rubber, polyurethane, or PTFE (Teflon), seals are chosen based on their resistance to heat, wear, and hydraulic fluid. High-performance presses may use self-lubricating seals, which reduce the friction between moving parts and extend the lifespan of the cylinder.
- Rod coatings: To reduce wear and increase longevity, hydraulic cylinders often have chrome-plated rods. The chrome plating provides a hard, smooth surface that resists corrosion and minimizes friction between the rod and seals.
2.4. Cylinder Dynamics: Fluid Movement and Force Transmission
The movement of the hydraulic fluid within the cylinder is what enables the press to generate force. When the hydraulic pump pushes fluid into the cylinder, it creates pressure behind the piston, causing it to move forward. The size of the cylinder, the amount of hydraulic fluid pumped into it, and the surface area of the piston all affect how much force is generated.
- Force transmission: Pascal’s Law is central to the operation of a hydraulic press. The pressure applied to the fluid in the cylinder is transmitted equally in all directions, pushing the piston forward with amplified force. The size of the piston and cylinder determines the force multiplication.
- Cylinder size and pressure: Larger cylinders can exert more force because of the greater surface area over which the hydraulic pressure acts. However, the larger the cylinder, the more hydraulic fluid is required to move the piston, which means the press’s pump and reservoir must be appropriately sized.
2.5. Innovations in Cylinder Design for Longevity and Efficiency
Recent advancements in hydraulic cylinder design have focused on improving efficiency, durability, and energy savings. Some innovations include:
- Servo-hydraulic systems: These systems allow for more precise control over the movement of the piston, improving the accuracy of the press’s operation and reducing energy consumption. Servo-hydraulic systems adjust the pressure and flow of hydraulic fluid based on the task, resulting in less wasted energy.
- Lightweight materials: While most hydraulic cylinders are made from steel, some newer designs use composite materials to reduce the weight of the press without sacrificing strength. This is especially useful in mobile or lightweight presses where portability is a concern.
- Improved seal technology: Advances in sealing materials, such as the use of self-lubricating seals, have extended the lifespan of hydraulic cylinders by reducing wear and preventing leaks.
2.6. Common Hydraulic Cylinder Issues
Despite their robust design, hydraulic cylinders can experience problems, often related to wear and tear or improper maintenance.
2.6.1. Leaks
Leaks are one of the most common issues in hydraulic cylinders, often caused by worn or damaged seals. A leaking cylinder will lose pressure, reducing the press’s effectiveness and potentially causing the machine to malfunction. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of seals can prevent leaks.
2.6.2. Pressure Loss
Pressure loss can occur if there is damage to the cylinder or its seals, or if there is air trapped in the hydraulic system. Low pressure reduces the force generated by the press and can lead to uneven or incomplete pressing.
2.6.3. Wear and Tear
Over time, the piston rod, seals, and cylinder walls can become worn due to friction and repeated use. Wear and tear are particularly common in presses that operate under high pressures or in harsh environments. Regular inspection and maintenance are necessary to extend the life of the hydraulic cylinder.
3. Pistons
The piston in a hydraulic press is a critical component responsible for transferring the hydraulic pressure generated in the cylinder to the material being pressed. It is the moving part that directly interacts with the hydraulic fluid and converts this pressure into mechanical force.
3.1. Role of the Piston in a Hydraulic Press
The piston’s primary role is to convert the pressure from the hydraulic fluid into the linear motion required for pressing, forming, or compressing materials. When the hydraulic fluid enters the cylinder, it pushes against the piston, causing it to move. This motion is what allows the press to apply force to the material being worked on, whether it’s bending metal, compressing plastic, or cutting sheet metal.
3.2. Force Transmission: Amplification of Input Force
The piston in a hydraulic press works in tandem with the hydraulic cylinder to amplify the input force. Through Pascal’s Law, the small force applied to the hydraulic fluid at the pump is multiplied when transmitted to the larger piston surface area inside the cylinder. The larger the piston, the greater the force that can be applied to the material.
For example:
- In a hydraulic press with a small input piston and a large output piston, even a small amount of pressure at the input results in a much larger force being applied by the output piston. This is the key to the hydraulic press’s ability to generate high forces with minimal input effort.
3.3. Materials and Coatings: Ensuring Durability Under Pressure
The materials used in the construction of the piston are crucial to its durability, as it must withstand high pressures and repeated cycles of movement. Most pistons are made from high-strength steel, with certain coatings applied to reduce friction and prevent corrosion.
- Steel pistons: Steel is the most commonly used material for pistons due to its strength and durability. Steel pistons can handle the high pressures typically found in hydraulic presses without deforming or wearing down quickly.
- Coatings: To reduce friction and extend the life of the piston, it is often coated with materials such as chrome or nickel. These coatings provide a hard, smooth surface that resists wear and corrosion, allowing the piston to operate smoothly over time.
3.4. Interaction with Hydraulic Fluid: Sealing and Pressure Maintenance
The piston must maintain a perfect seal with the cylinder walls to ensure that hydraulic pressure is contained and transmitted effectively. To achieve this, piston seals are used. These seals prevent hydraulic fluid from leaking past the piston, which would reduce the press’s effectiveness and lead to pressure loss.
- Seals: Piston seals are typically made from rubber, PTFE (Teflon), or polyurethane, depending on the press’s operating conditions. These materials are chosen for their ability to withstand high pressures, temperatures, and exposure to hydraulic fluids.
A well-maintained seal ensures that the piston can move freely within the cylinder while maintaining constant pressure on the material being pressed.
3.5. Types of Pistons for Different Press Designs
Different types of pistons are used in hydraulic presses, depending on the press’s design and intended application. Some of the common piston designs include:
- Single-piece pistons: These are the most common type of piston used in hydraulic presses. They are made from a single piece of material, typically steel, and are designed for standard pressing tasks.
- Telescopic pistons: Used in presses where a longer stroke is needed, telescopic pistons consist of multiple segments that extend outward during operation, allowing the press to apply force over a longer distance.
- Custom pistons: In specialized presses, pistons may be custom-designed to meet the unique requirements of the application. These pistons may include additional features, such as integrated sensors or advanced coatings to handle extreme conditions.
3.6. Common Problems with Pistons and Solutions
Like hydraulic cylinders, pistons are subject to wear and tear, and issues can arise if they are not properly maintained. Common problems include:
3.6.1. Wear and Scoring
Over time, the piston can become worn or develop scoring (scratches or grooves) due to friction between the piston and the cylinder walls. This can reduce the piston’s effectiveness and lead to pressure loss. Regular inspection and replacement of worn pistons can prevent this issue.
3.6.2. Seal Failures
If the piston seals wear out or become damaged, hydraulic fluid can leak past the piston, reducing pressure and force. Replacing worn seals regularly and ensuring that the piston is properly lubricated can prevent seal failures.
3.6.3. Piston Deformation
In high-pressure applications, the piston can become deformed if it is not designed to handle the force generated by the press. Deformed pistons can lead to uneven pressure distribution and inefficient operation. Using pistons made from high-strength materials and ensuring that they are correctly sized for the application can prevent deformation.
Hydraulic Fluid
Hydraulic fluid is the lifeblood of any hydraulic press, responsible for transmitting the force generated by the pump to the cylinder and piston. It plays a critical role in ensuring the smooth operation of the press, lubricating moving parts, and dissipating heat generated during operation. The choice of hydraulic fluid has a significant impact on the performance, efficiency, and longevity of the hydraulic system.
4.1. Importance of Hydraulic Fluid in Force Transmission
The primary function of hydraulic fluid is to transmit force within the press. When the hydraulic pump pressurizes the fluid, the pressure is transmitted through the fluid to the cylinder and piston. Hydraulic fluid is incompressible, meaning that any pressure applied to it is transmitted equally throughout the system, ensuring efficient force transmission.
- Force transmission: Pascal’s Law is the guiding principle behind the use of hydraulic fluid. The pressure applied to the fluid at the pump is transmitted to the piston, where it is converted into mechanical force. This allows the hydraulic press to exert significant force with relatively low input effort.
- Fluid dynamics: The movement of hydraulic fluid within the system must be smooth and consistent to avoid pressure spikes or drops. Proper fluid management, including filtering and temperature control, is essential for maintaining consistent pressure throughout the hydraulic system.
4.2. Types of Hydraulic Fluids
The type of hydraulic fluid used in a press depends on the specific requirements of the application, including operating temperature, pressure, and environmental considerations. The most common types of hydraulic fluids are:
4.2.1. Mineral Oils
Mineral oils are the most commonly used hydraulic fluids in presses due to their affordability, availability, and overall effectiveness. Derived from petroleum, mineral oils offer good lubricating properties and are capable of withstanding the high pressures typically found in hydraulic systems.
- Advantages:
- Widely available and cost-effective.
- Good lubrication and anti-wear properties.
- Suitable for a wide range of hydraulic press applications.
- Disadvantages:
- Mineral oils can degrade at high temperatures.
- They are not environmentally friendly and can pose disposal challenges.
4.2.2. Water-Based Fluids
Water-based hydraulic fluids are typically used in applications where fire resistance is a concern. These fluids are less flammable than mineral oils and are often used in presses that operate in environments with high heat or where the risk of fire is present.
- Advantages:
- Non-flammable, making them ideal for high-heat environments.
- Provide good cooling properties due to their water content.
- Disadvantages:
- Water-based fluids offer less lubrication than mineral oils.
- They are prone to corrosion and must be carefully managed to prevent damage to the hydraulic system.
4.2.3. Synthetic Fluids
Synthetic hydraulic fluids are engineered to provide superior performance in extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or environments requiring high resistance to oxidation and wear. These fluids are often used in high-performance hydraulic presses that operate under demanding conditions.
- Advantages:
- Excellent thermal stability and resistance to oxidation.
- Long lifespan and reduced maintenance requirements.
- Suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
- Disadvantages:
- More expensive than mineral oils and water-based fluids.
- Disposal can be more complex due to their chemical composition.
4.2.4. Biodegradable Fluids
Biodegradable hydraulic fluids are gaining popularity due to their reduced environmental impact. These fluids are made from renewable sources, such as vegetable oils, and are designed to degrade naturally without harming the environment.
- Advantages:
- Environmentally friendly and biodegradable.
- Suitable for presses used in environmentally sensitive applications, such as agriculture or marine industries.
- Disadvantages:
- Biodegradable fluids may not perform as well at extreme temperatures or pressures.
- More expensive than traditional mineral oils.
4.3. Properties of Hydraulic Fluid
The properties of hydraulic fluid have a significant impact on the performance and efficiency of the hydraulic press. The most important properties include:
4.3.1. Viscosity
Viscosity refers to the fluid’s resistance to flow. Hydraulic fluids with the proper viscosity ensure smooth operation and efficient force transmission within the system.
- Low viscosity: Fluids with low viscosity flow more easily, but may not provide enough lubrication, leading to increased wear on moving parts.
- High viscosity: Fluids with high viscosity provide better lubrication but may flow too slowly, resulting in inefficient force transmission.
Selecting a hydraulic fluid with the appropriate viscosity for the operating conditions of the press is essential for maintaining performance and preventing wear.
4.3.2. Compressibility
Hydraulic fluids must be incompressible to effectively transmit force. Any compressibility in the fluid would result in energy loss and reduced efficiency. Fluids designed for hydraulic presses are formulated to minimize compressibility, ensuring that all applied pressure is transferred directly to the piston.
4.3.3. Thermal Stability
Hydraulic presses generate heat during operation, and the hydraulic fluid must be able to withstand high temperatures without breaking down. Thermal stability refers to the fluid’s ability to maintain its properties under heat. Fluids with high thermal stability resist oxidation and degradation, ensuring consistent performance even under heavy loads.
4.3.4. Lubricity
Hydraulic fluids must also act as a lubricant, reducing friction between moving parts within the hydraulic system. Proper lubrication reduces wear and extends the lifespan of components such as the cylinder, piston, and seals.
4.4. Fluid Contamination: Causes, Effects, and Prevention
Contamination of hydraulic fluid is one of the most common causes of hydraulic press failure. Contaminants such as dirt, metal particles, or water can enter the hydraulic system and reduce the effectiveness of the fluid, leading to damage and system failure.
4.4.1. Causes of Contamination
- External contamination: Dust, dirt, and debris can enter the hydraulic system through leaks, worn seals, or during fluid changes.
- Internal contamination: Wear and tear on the system’s components can generate metal particles or other debris, which then circulate within the fluid.
- Water ingress: Moisture can enter the system through condensation or leaks, leading to corrosion and reduced fluid performance.
4.4.2. Effects of Contamination
- Reduced fluid efficiency: Contaminants reduce the fluid’s ability to transmit pressure effectively, leading to inefficiencies in force transmission.
- Increased wear: Contaminated fluid can accelerate wear on the cylinder, piston, and seals, leading to premature failure of these components.
- Corrosion: Water contamination can cause corrosion within the hydraulic system, leading to leaks and system failure.
4.4.3. Preventing Fluid Contamination
- Filtration: Installing high-quality filters in the hydraulic system helps remove contaminants before they can cause damage. Regularly changing or cleaning filters is essential for preventing contamination.
- Seals and gaskets: Ensuring that seals and gaskets are in good condition prevents external contaminants from entering the system.
- Proper fluid handling: When adding or replacing hydraulic fluid, it’s important to ensure that the new fluid is clean and free of contaminants. Using proper containers and handling methods can prevent contamination during fluid changes.
4.5. Hydraulic Fluid Maintenance: Filtering, Cooling, and Fluid Replacement
Maintaining the hydraulic fluid is critical for the press’s long-term performance. This includes regular filtering, cooling, and fluid replacement.
4.5.1. Filtering
Regular filtering removes particles and contaminants from the fluid, preventing them from circulating through the system. Presses are typically equipped with inline filters that capture debris as the fluid moves through the system.
- Filter replacement: Filters should be inspected and replaced at regular intervals to ensure that they remain effective. A clogged or worn filter can reduce fluid flow and cause pressure loss.
4.5.2. Cooling
Hydraulic fluid can become hot during operation, leading to degradation and reduced performance. A cooling system, such as a heat exchanger or a reservoir with cooling fins, helps regulate the fluid’s temperature and prevents overheating.
- Fluid cooling systems: Some hydraulic presses are equipped with active cooling systems, such as liquid cooling or air-cooled heat exchangers, which help maintain optimal fluid temperatures during operation.
4.5.3. Fluid Replacement
Over time, hydraulic fluid degrades and loses its effectiveness. Regularly replacing the fluid ensures that the press continues to operate efficiently. Fluid replacement intervals depend on the type of fluid used, the operating conditions, and the press’s workload.
5. Press Frame
The press frame is the backbone of a hydraulic press, providing the structural support necessary to handle the immense forces generated during operation. The frame plays a crucial role in maintaining the alignment of the hydraulic cylinder, piston, and other components, ensuring that force is applied evenly to the material being worked on. In this section, we will explore the different types of press frames, their construction materials, and how frame design impacts the performance and durability of a hydraulic press.
5.1. Role of the Press Frame
The primary role of the press frame is to support the components of the hydraulic press and to withstand the forces generated during pressing operations. The frame must be rigid enough to prevent deformation or flexing under pressure, which could lead to misalignment of components and uneven force application. A strong, well-designed frame ensures that the press operates efficiently and safely, especially when handling high-force applications such as metal stamping, forging, or deep drawing.
Additionally, the frame must be designed to accommodate the specific tasks for which the press is used. For example, presses designed for metal forming may require larger, more robust frames to handle the increased stresses, while smaller presses for light assembly work can utilize more compact frames.
5.2. Types of Press Frames
There are several types of hydraulic press frames, each designed for specific applications. The choice of frame design depends on factors such as the size of the press, the force required, and the type of material being worked on.
5.2.1. H-Frame Hydraulic Press
The H-frame press is one of the most common types of hydraulic press frames, named for its resemblance to the letter “H.” This design features two vertical columns (the “legs” of the H) connected by horizontal beams (the “crossbar” of the H). The hydraulic cylinder and piston are mounted in the center of the crossbar, with the workpiece placed between the legs.
- Key features:
- Versatility: H-frame presses are used in a wide variety of applications, from metal forming and punching to straightening and bending.
- Strength: The frame provides excellent structural support, allowing the press to generate high forces without flexing or deforming.
- Open design: The open structure of the H-frame allows for easy access to the work area, making it easier to load and unload materials.
- Applications: H-frame presses are commonly used in heavy-duty applications such as automotive repair, metal fabrication, and industrial manufacturing.
5.2.2. C-Frame Hydraulic Press
The C-frame press, also known as a gap-frame press, is designed with an open front that resembles the letter “C.” This design provides easy access to the work area from three sides, allowing operators to load and unload materials quickly. C-frame presses are typically more compact than H-frame presses and are often used for smaller, lighter-duty tasks.
- Key features:
- Compact design: C-frame presses are ideal for applications where space is limited, as they take up less floor space than larger H-frame presses.
- Easy access: The open-front design allows operators to access the work area from multiple sides, making it easier to position materials and tools.
- Moderate force: While C-frame presses can handle moderate forces, they are generally not suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Applications: C-frame presses are commonly used for tasks such as punching, stamping, and light assembly work. They are often found in workshops, small manufacturing facilities, and maintenance shops.
5.2.3. Four-Column Hydraulic Press
The four-column press features four vertical columns that provide structural support for the press. This design is often used in large, high-force applications where even pressure distribution and structural rigidity are critical. Four-column presses are typically used in industries such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace, and heavy machinery production.
- Key features:
- Even force distribution: The four-column design ensures that force is applied evenly across the entire workpiece, reducing the risk of material deformation.
- Large work area: Four-column presses can accommodate large workpieces, making them ideal for tasks such as metal forming, die cutting, and deep drawing.
- High force capacity: These presses are capable of generating extremely high forces, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Applications: Four-column presses are commonly used in large-scale industrial operations, such as metal forming, forging, and deep drawing in the automotive and aerospace industries.
5.2.4. Custom-Designed Frames
In some cases, hydraulic presses are designed with custom frames to meet the specific needs of the application. Custom-designed frames may incorporate elements of H-frame, C-frame, or four-column designs, but are tailored to the unique requirements of the press, such as handling irregularly shaped materials or operating in confined spaces.
- Key features:
- Tailored design: Custom frames are engineered to meet the specific demands of the task, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
- Specialized materials: Custom frames may be made from specialized materials or alloys to withstand extreme forces, temperatures, or environmental conditions.
- Applications: Custom hydraulic press frames are often used in specialized industries such as medical device manufacturing, electronics production, and advanced materials processing.
5.3. Frame Materials: Steel, Composites, and Lightweight Designs
The materials used in the construction of a press frame have a significant impact on its strength, durability, and performance. Most hydraulic press frames are made from high-strength steel, which offers excellent resistance to deformation under pressure. However, advances in materials science have led to the development of composite materials and lightweight designs that offer similar strength with reduced weight.
5.3.1. Steel Frames
Steel is the most commonly used material in hydraulic press frames due to its high tensile strength, durability, and ability to withstand heavy loads. Steel frames can be manufactured to handle both light and heavy-duty applications, making them versatile and reliable.
- Advantages:
- High strength and durability.
- Suitable for a wide range of applications, from light assembly to heavy metal forming.
- Can be easily fabricated into various frame designs (H-frame, C-frame, four-column).
- Disadvantages:
- Steel frames are heavy, which can make installation and transportation more difficult.
- Susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated or maintained.
5.3.2. Composite Materials and Lightweight Frames
In some specialized applications, composite materials are used to reduce the weight of the press frame without sacrificing strength. Composites such as carbon fiber or fiberglass-reinforced plastics offer high strength-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for presses that need to be portable or operate in weight-sensitive environments.
- Advantages:
- Lightweight, making the press easier to move and install.
- Resistant to corrosion and environmental degradation.
- Suitable for specialized applications where weight is a concern.
- Disadvantages:
- More expensive to manufacture than steel frames.
- May not offer the same level of durability as steel in heavy-duty applications.
5.4. Stress Distribution and Frame Performance
The design of the press frame plays a crucial role in how well it distributes the forces generated during pressing operations. Stress distribution refers to how evenly the force is spread across the frame and the workpiece. A well-designed frame ensures that the force is applied uniformly, reducing the risk of material deformation and improving the quality of the final product.
5.4.1. Preventing Frame Deformation
Press frames must be designed to resist deformation, which can occur if the frame is not strong enough to handle the forces generated by the hydraulic system. Deformation can lead to misalignment of the hydraulic cylinder and piston, reducing the efficiency of the press and potentially causing damage to the workpiece.
- Reinforcement: Frames can be reinforced with additional supports or crossbeams to increase their rigidity and prevent bending or flexing under pressure.
- Material selection: Using high-strength materials such as steel or composites can reduce the risk of frame deformation.
5.4.2. Impact on Press Performance
The rigidity and design of the press frame directly impact the performance of the hydraulic press. A strong, well-designed frame ensures that the press operates efficiently and consistently, allowing for precise control over force application. This is particularly important in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where even small deviations in force distribution can affect the quality and safety of the final product.
Power Source: Hydraulic Pump
The hydraulic pump is the heart of the hydraulic press, responsible for generating the hydraulic pressure that powers the press’s operations. The pump converts mechanical energy into hydraulic energy by moving hydraulic fluid from the reservoir into the system, creating the pressure necessary to move the piston and apply force to the material. In this section, we will explore the different types of hydraulic pumps, their efficiency, and recent innovations in pump design.
6.1. Function of the Hydraulic Pump
The primary function of the hydraulic pump is to create a flow of hydraulic fluid that is pressurized and directed into the hydraulic cylinder. The pump determines the amount of force that the press can generate, as the pressure in the system is directly related to the flow rate and the size of the hydraulic cylinder.
When the hydraulic pump is activated, it draws fluid from the reservoir and forces it into the cylinder. As the fluid enters the cylinder, it pushes the piston forward, creating the force needed to press, compress, or shape the material. The amount of pressure generated by the pump is a key factor in determining the overall force output of the hydraulic press.
6.2. Types of Hydraulic Pumps
There are several types of hydraulic pumps used in presses, each with its own advantages and limitations. The choice of pump depends on the specific requirements of the press, such as the desired pressure, flow rate, and energy efficiency.
6.2.1. Gear Pumps
Gear pumps are one of the most common types of hydraulic pumps used in smaller hydraulic presses. They are simple, reliable, and cost-effective, making them ideal for applications where moderate pressure and flow rates are required.
- Advantages:
- Simple design with few moving parts, reducing the risk of mechanical failure.
- Inexpensive and easy to maintain.
- Suitable for low to moderate pressure applications.
- Disadvantages:
- Less efficient than other types of pumps, especially at higher pressures.
- Limited pressure output, making them unsuitable for heavy-duty applications.
6.2.2. Vane Pumps
Vane pumps are known for their quiet operation and efficient performance. These pumps use rotating vanes to move fluid through the system, providing smooth, consistent flow. Vane pumps are often used in presses that require moderate pressure and flow rates, such as those found in plastic molding or assembly operations.
- Advantages:
- Quiet operation and smooth fluid flow.
- Efficient and reliable in moderate pressure applications.
- Longer lifespan due to reduced wear on components.
- Disadvantages:
- More expensive than gear pumps.
- Not suitable for high-pressure applications.
6.2.3. Piston Pumps
Piston pumps are the most powerful type of hydraulic pump, capable of generating extremely high pressures. These pumps use a series of pistons to move fluid through the system, providing precise control over pressure and flow rate. Piston pumps are commonly used in heavy-duty hydraulic presses, such as those found in metal forging, deep drawing, and large-scale manufacturing.
- Advantages:
- Capable of generating very high pressures, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications.
- Precise control over pressure and flow rate, allowing for accurate operation.
- Durable and long-lasting, even under extreme conditions.
- Disadvantages:
- More complex and expensive than gear or vane pumps.
- Requires regular maintenance to prevent wear and mechanical failure.
6.2.4. Fixed vs. Variable Displacement Pumps
Hydraulic pumps can be categorized as either fixed displacement or variable displacement based on how they control the flow of fluid.
- Fixed displacement pumps deliver a constant flow of hydraulic fluid at a set rate, regardless of the pressure in the system. These pumps are simpler and less expensive but are less energy-efficient, as they cannot adjust the flow rate to match the demands of the press.
- Variable displacement pumps can adjust the flow rate of hydraulic fluid based on the system’s needs. These pumps are more energy-efficient, as they only deliver the amount of fluid necessary to perform the task. Variable displacement pumps are commonly used in modern hydraulic presses, where energy efficiency and precision are important.
6.3. Pump Efficiency: Power-to-Pressure Ratio
The efficiency of a hydraulic pump is determined by its power-to-pressure ratio, which refers to how much mechanical energy is required to generate a given amount of hydraulic pressure. Efficient pumps can generate high pressures with minimal energy input, reducing operating costs and energy consumption.
- Energy-efficient pumps: Pumps with variable displacement designs are generally more energy-efficient than fixed displacement pumps, as they can adjust their output based on the press’s needs. This reduces the amount of energy wasted when the press is operating at lower pressures or during idle periods.
- Servo-hydraulic pumps: Some modern hydraulic presses use servo-hydraulic pumps, which combine hydraulic power with electrical control. These pumps use a servo motor to control the speed and flow of the hydraulic fluid, allowing for precise pressure control and reduced energy consumption. Servo-hydraulic systems are becoming more common in high-performance presses due to their energy efficiency and improved control.
6.4. Innovations in Pump Design: Energy-Efficient Models
Recent advancements in pump design have focused on improving energy efficiency and reducing the environmental impact of hydraulic presses. Some of the key innovations include:
- Servo-hydraulic systems: As mentioned earlier, servo-hydraulic systems offer precise control over the pump’s operation, allowing the press to adjust its pressure and flow rate in real-time based on the task at hand. This leads to significant energy savings and improved performance.
- Variable speed pumps: Pumps that can adjust their speed based on the press’s needs are becoming increasingly popular in industrial presses. By reducing the pump’s speed during low-demand periods, these systems reduce energy consumption and heat generation, improving the overall efficiency of the press.
- Compact pump designs: Advances in materials and manufacturing techniques have led to the development of compact hydraulic pumps that offer high pressure in a smaller footprint. These pumps are ideal for presses where space is limited, such as portable or bench-mounted presses.
6.5. Pump Maintenance and Common Issues
Hydraulic pumps are subject to wear and tear over time, and regular maintenance is essential for ensuring that the press continues to operate efficiently. Some of the most common issues with hydraulic pumps include:
6.5.1. Wear and Mechanical Failure
Over time, the internal components of the pump, such as gears, vanes, or pistons, can become worn due to friction and heat. This can lead to reduced efficiency, noise, and eventual mechanical failure. Regular inspection and maintenance of the pump’s moving parts are essential for preventing breakdowns.
- Preventive maintenance: Replacing worn components and ensuring that the hydraulic fluid is clean and free of contaminants can extend the lifespan of the pump and reduce the risk of mechanical failure.
6.5.2. Fluid Flow Issues
Pumps can experience problems with fluid flow due to blockages, leaks, or air bubbles in the system. These issues can reduce the pump’s efficiency and lead to pressure loss, reducing the overall performance of the press.
- Troubleshooting: Regularly checking the hydraulic system for leaks, blockages, and proper fluid levels can help identify and resolve flow issues before they impact the press’s operation.
6.5.3. Noise and Vibration
Excessive noise and vibration are often signs of issues with the hydraulic pump, such as worn bearings or misaligned components. If left unchecked, these problems can lead to mechanical failure and reduced performance.
- Inspection: Regularly inspecting the pump for signs of wear, alignment issues, or abnormal noise can help prevent more serious problems from developing.
7. Valves and Controls
Valves and controls are crucial elements of a hydraulic press, managing the flow and pressure of hydraulic fluid to ensure smooth, efficient, and safe operation. These components determine the direction of fluid movement, regulate pressure, and control the flow rate, allowing the hydraulic press to perform precise operations such as pressing, stamping, molding, or forging. This section will cover the types of valves used in hydraulic presses, their function, modern control systems, and common issues related to valves and control mechanisms.
7.1. Control Systems in a Hydraulic Press
The control system in a hydraulic press consists of a series of valves, switches, and sensors that regulate the movement of hydraulic fluid through the system. The operator can adjust these controls to manage the speed, pressure, and direction of the press’s movement. The main components of the control system include:
- Valves: These control the flow and pressure of the hydraulic fluid within the system.
- Sensors: These monitor the system’s pressure, position, and temperature, providing real-time feedback to the control system.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): In modern presses, PLCs are used to automate and manage the operation of the press. They allow the operator to program specific tasks and control the press remotely.
Together, these components ensure that the press operates with precision, safety, and efficiency, allowing for repeatable and accurate results in industrial applications.
7.2. Types of Valves in Hydraulic Presses
Hydraulic systems use a variety of valves to control the direction, pressure, and flow rate of the fluid. The main types of valves include directional control valves, pressure relief valves, and flow control valves.
7.2.1. Directional Control Valves
Directional control valves are responsible for directing the flow of hydraulic fluid within the system. These valves determine whether the fluid is sent to the piston to extend or retract the press. Directional control valves can be manually operated or automated, depending on the press’s design.
- Types of directional control valves:
- Manual valves: Operated by hand, these are typically used in smaller, simpler presses.
- Solenoid valves: Electrically operated, solenoid valves are commonly used in modern hydraulic presses for more precise control of fluid direction.
- Pilot-operated valves: These valves use hydraulic or pneumatic signals to control the flow of fluid, allowing for faster and more efficient operation.
7.2.2. Pressure Relief Valves
Pressure relief valves play a critical safety role in hydraulic presses by preventing over-pressurization. These valves automatically release hydraulic fluid when the pressure in the system exceeds a predetermined level, protecting the press from damage and ensuring safe operation.
- Adjustable pressure relief valves: Operators can adjust the pressure threshold at which the valve opens, allowing for flexibility in different applications.
- Safety function: Pressure relief valves prevent damage to the hydraulic system by releasing excess pressure and returning fluid to the reservoir.
7.2.3. Flow Control Valves
Flow control valves regulate the speed at which hydraulic fluid flows through the system. By controlling the flow rate, these valves determine how fast the press moves, ensuring smooth operation and precise control over pressing tasks.
- Types of flow control valves:
- Throttle valves: These allow the operator to manually adjust the flow rate, providing precise control over the press’s speed.
- Pressure-compensated valves: These valves automatically adjust the flow rate based on the system’s pressure, ensuring consistent speed even under varying load conditions.
7.3. Modern Control Innovations
Advancements in hydraulic press technology have led to the development of more sophisticated control systems, including PLCs, CNC integration, and smart sensors. These innovations allow for greater automation, precision, and safety in hydraulic press operations.
7.3.1. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
PLCs are computerized control systems that allow operators to program and automate the operation of the hydraulic press. PLCs enable the press to perform complex tasks with minimal human intervention, improving efficiency and repeatability in industrial applications.
- Automation: PLCs allow operators to program specific pressing sequences, adjust pressure and speed settings, and monitor performance remotely.
- Improved accuracy: PLCs ensure that pressing tasks are performed consistently, reducing errors and improving product quality.
7.3.2. CNC Integration
Some hydraulic presses are equipped with CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems, which provide even greater precision and control over pressing operations. CNC systems allow for highly accurate positioning and force control, making them ideal for tasks such as metal forming, stamping, and precision assembly.
- Precision: CNC systems provide real-time feedback and adjustments, ensuring that the press operates within exact tolerances.
- Flexibility: CNC-controlled presses can be programmed to handle a wide range of tasks, from simple pressing to complex multi-step operations.
7.3.3. Smart Sensors and Remote Monitoring
Modern hydraulic presses are increasingly equipped with smart sensors that provide real-time data on the system’s pressure, temperature, and position. These sensors allow operators to monitor the press’s performance remotely, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Remote monitoring: Sensors send data to a centralized control system, allowing operators to monitor the press’s performance and detect potential issues before they cause breakdowns.
- Predictive maintenance: By analyzing data from smart sensors, operators can schedule maintenance based on the actual condition of the press, reducing the risk of unexpected failures and extending the lifespan of the machine.
7.4. Valve Issues and Maintenance
Valves are subject to wear and tear over time, and issues with valves can lead to poor press performance or system failure. Common problems with valves in hydraulic presses include leaks, blockages, and pressure loss.
7.4.1. Leaks
Leaks in directional control valves or pressure relief valves can cause a drop in hydraulic pressure, reducing the force generated by the press. Leaks are often caused by worn seals, damaged valve components, or contamination in the hydraulic fluid.
- Solution: Regular inspection and maintenance of valves can help identify and fix leaks before they lead to larger issues. Replacing worn seals and cleaning valve components are common preventive measures.
7.4.2. Blockages
Blockages in flow control valves can disrupt the smooth movement of hydraulic fluid through the system, causing the press to operate erratically. Blockages are typically caused by dirt, debris, or contamination in the hydraulic fluid.
- Solution: Installing high-quality filters in the hydraulic system can prevent contaminants from entering the valves. Regularly cleaning or replacing filters is essential to preventing blockages.
7.4.3. Pressure Loss
Pressure loss in the system can occur if pressure relief valves open prematurely or if directional control valves are not functioning properly. This can result in reduced pressing force and inconsistent operation.
- Solution: Calibrating the pressure relief valves and ensuring that all valves are functioning correctly can help maintain consistent pressure levels in the system.
Reservoir and Cooling System
The reservoir and cooling system of a hydraulic press play a crucial role in maintaining the performance and longevity of the machine. The reservoir stores the hydraulic fluid, while the cooling system regulates the fluid’s temperature, preventing overheating and ensuring efficient operation. This section will explore the design and function of the hydraulic reservoir and cooling system, as well as the importance of regular maintenance.
8.1. Role of the Reservoir
The hydraulic reservoir serves as the storage tank for the hydraulic fluid used in the press. Its primary functions include:
- Storing hydraulic fluid: The reservoir holds the hydraulic fluid when it is not being circulated through the system, ensuring that there is always a sufficient supply of fluid for the press to operate.
- Cooling: As hydraulic fluid passes through the system, it absorbs heat generated by the press’s components. The reservoir allows the fluid to cool before it is recirculated back into the system.
- Contamination management: The reservoir also serves as a settling tank where contaminants such as dirt, metal particles, and air bubbles can be removed from the fluid before it re-enters the hydraulic system.
The size and design of the reservoir depend on the size of the press and the amount of fluid required for its operation. Larger presses require larger reservoirs to ensure an adequate supply of fluid and efficient cooling.
8.2. Reservoir Design Considerations
The design of the hydraulic reservoir is critical to the performance of the press. Key design considerations include:
- Size and capacity: The reservoir must be large enough to store sufficient hydraulic fluid to keep the press operating smoothly. A well-sized reservoir also allows enough time for the fluid to cool before it is recirculated.
- Ventilation: Reservoirs are typically designed with vented lids or breathers to allow air to escape as the fluid level changes. Proper ventilation prevents pressure build-up and reduces the risk of contamination entering the system.
- Filtration: Many reservoirs are equipped with filters or strainers to remove contaminants from the fluid. Filtering the fluid before it is recirculated helps prevent damage to the hydraulic system and improves overall performance.
8.3. Cooling Systems
Hydraulic presses generate heat during operation, primarily due to the friction between moving parts and the compression of hydraulic fluid. If the fluid becomes too hot, it can degrade, reducing its effectiveness and causing damage to the hydraulic system. The cooling system is essential for maintaining optimal fluid temperature and ensuring the longevity of the press.
8.3.1. Types of Cooling Systems
There are several types of cooling systems used in hydraulic presses, each designed to manage the heat generated during operation.
- Air-Cooled Systems: In air-cooled systems, the hydraulic fluid is circulated through a radiator or cooling fins, where it is cooled by air flow. This type of cooling system is typically used in smaller presses or applications where heat generation is minimal.
- Advantages: Simple and cost-effective design. No need for additional coolant.
- Disadvantages: Less effective in high-temperature environments or for heavy-duty presses.
- Liquid-Cooled Systems: Liquid cooling systems use water or another coolant to absorb heat from the hydraulic fluid. The coolant circulates through a heat exchanger, where it transfers the heat away from the fluid. Liquid-cooled systems are more efficient than air-cooled systems and are typically used in larger or high-performance presses.
- Advantages: More effective at managing high heat loads. Suitable for heavy-duty and high-speed presses.
- Disadvantages: Requires more complex maintenance, including regular coolant checks and potential leaks.
8.3.2. Heat Exchangers
In many hydraulic presses, heat exchangers are used to transfer heat from the hydraulic fluid to the surrounding air or coolant. These devices are critical in maintaining the optimal operating temperature of the fluid, especially in large or high-speed presses where heat generation is significant.
- Plate heat exchangers: These devices use a series of metal plates to transfer heat between the hydraulic fluid and the coolant. Plate heat exchangers are compact and efficient, making them ideal for modern hydraulic systems.
- Shell-and-tube heat exchangers: These are larger, more industrial heat exchangers used in heavy-duty presses. They consist of a series of tubes through which the hydraulic fluid and coolant flow, transferring heat between them.
8.4. Reservoir and Cooling System Maintenance
Proper maintenance of the hydraulic reservoir and cooling system is essential for ensuring the longevity and performance of the press. Key maintenance tasks include:
8.4.1. Fluid Level Checks
The hydraulic fluid level in the reservoir should be checked regularly to ensure that there is always sufficient fluid to operate the press. Low fluid levels can lead to overheating, cavitation, and reduced system performance.
- Topping off fluid: If the fluid level is low, the reservoir should be topped off with the appropriate hydraulic fluid to prevent damage to the system.
8.4.2. Cleaning and Filtering
The reservoir and cooling system should be cleaned regularly to remove dirt, debris, and contaminants that can degrade the performance of the press. Filters and strainers should be checked and replaced as needed to ensure that the fluid remains clean and free of debris.
- Changing filters: Filters should be replaced at regular intervals, as recommended by the manufacturer. Dirty or clogged filters can reduce fluid flow and increase pressure, leading to system inefficiencies.
8.4.3. Coolant Checks
In liquid-cooled systems, the coolant should be checked regularly for proper levels and potential contamination. Leaks in the cooling system can lead to overheating, reducing the performance and lifespan of the press.
- Leak prevention: Inspecting hoses, connections, and heat exchangers for signs of leaks or damage is critical to maintaining the effectiveness of the cooling system.
8.5. Impact of Overheating and Fluid Degradation
Overheating can have a detrimental effect on the hydraulic fluid, causing it to degrade and lose its effectiveness. Thermal breakdown of the fluid can lead to reduced lubrication, increased wear on components, and eventual system failure. Regular maintenance of the reservoir and cooling system is essential to preventing overheating and ensuring that the press operates efficiently and reliably.
9. Seals and Gaskets (600 words)
Seals and gaskets play an essential role in maintaining the pressure and fluid integrity of a hydraulic press. These components ensure that the hydraulic fluid is contained within the system, preventing leaks and maintaining consistent pressure. Without effective seals and gaskets, the hydraulic system would suffer from pressure loss, contamination, and inefficient operation, which could lead to damage to the press and costly downtime.
9.1. Importance of Seals in Maintaining Fluid Pressure
The primary function of seals in a hydraulic press is to prevent hydraulic fluid from leaking out of the system. Hydraulic systems operate under extremely high pressure, and even a small leak can lead to significant pressure loss and reduced efficiency. Seals are used in various parts of the press, including the hydraulic cylinder, piston, and valves, to ensure that hydraulic fluid is contained and pressure is maintained.
Seals also play a secondary role in lubricating the moving parts of the press. Many seals are designed to retain a thin film of hydraulic fluid between the moving parts, reducing friction and wear. This ensures that components such as the piston and cylinder walls move smoothly and efficiently without excessive heat or damage.
9.2. Types of Seals Used in Hydraulic Presses
There are several types of seals used in hydraulic presses, each designed for specific functions and operating conditions. The most common types of seals include O-rings, U-cups, rod seals, and piston seals.
9.2.1. O-Rings
O-rings are the most common type of seal used in hydraulic systems. They are typically made from rubber or synthetic materials like Nitrile or Viton and are designed to sit in grooves between two surfaces, creating a tight seal to prevent fluid leakage.
- Applications: O-rings are commonly used in static applications, such as sealing the joints between two non-moving components.
- Advantages: They are inexpensive, easy to replace, and suitable for a wide range of operating pressures and temperatures.
9.2.2. U-Cups
U-cups are used in dynamic applications, such as sealing the piston or rod in a hydraulic cylinder. Their “U”-shaped design allows them to flex under pressure, providing a tight seal even when the piston or rod is in motion.
- Applications: U-cups are often found in the hydraulic cylinder and rod assemblies.
- Advantages: Their flexible design ensures a strong seal while allowing for the movement of components.
9.2.3. Rod Seals
Rod seals are used to seal the area where the piston rod exits the hydraulic cylinder. They prevent hydraulic fluid from leaking out of the cylinder and also keep contaminants, such as dirt or dust, from entering the system.
- Applications: Found in the rod assembly of hydraulic cylinders.
- Advantages: Rod seals ensure long-term performance by preventing leakage while protecting the cylinder from external contamination.
9.2.4. Piston Seals
Piston seals are used to seal the gap between the piston and the cylinder walls, ensuring that hydraulic fluid does not pass from one side of the piston to the other. Piston seals are critical in maintaining pressure within the cylinder and ensuring that the piston moves smoothly and efficiently.
- Applications: Installed on the piston head within hydraulic cylinders.
- Advantages: Provide a tight seal and reduce friction, improving the efficiency of the hydraulic press.
9.3. Seal Materials: Rubber, Polyurethane, and PTFE
Seals are typically made from materials that offer high durability, resistance to wear, and the ability to withstand the high pressures and temperatures found in hydraulic systems. The most common materials used in hydraulic seals include:
- Rubber: Rubber seals are widely used due to their flexibility, resilience, and affordability. However, rubber can degrade over time when exposed to extreme heat or certain types of hydraulic fluid.
- Polyurethane: Polyurethane seals are known for their excellent abrasion resistance and durability, making them ideal for applications where seals are subjected to significant wear.
- PTFE (Teflon): PTFE seals offer high resistance to heat and chemical degradation, making them ideal for use in hydraulic systems that operate at high temperatures or with aggressive fluids.
9.4. Common Seal Failures: Causes and Prevention
While seals are designed to last, they can wear out or fail over time, leading to leaks and reduced system performance. Common causes of seal failure include:
9.4.1. Wear and Tearing
Seals are subject to wear and tear due to friction between moving parts. Over time, this can cause seals to crack, degrade, or lose their flexibility, leading to leaks. Using high-quality materials and maintaining proper lubrication can help extend the life of seals.
9.4.2. Contamination
Contaminants such as dirt, dust, or metal particles can damage seals by causing them to wear out faster. Installing proper filters and regularly maintaining the hydraulic system can prevent contamination and reduce seal wear.
9.4.3. Improper Installation
Seals that are improperly installed can become pinched, twisted, or damaged during operation. Ensuring that seals are installed correctly and in the right position can prevent these issues.
9.5. Innovations in Seal Technology
Recent advances in seal technology have led to the development of self-lubricating seals and longer-lasting materials, which can help reduce maintenance costs and extend the lifespan of hydraulic presses.
- Self-lubricating seals: These seals are made from materials that naturally reduce friction between the moving parts, reducing wear and extending the life of the seal.
- Improved materials: Seals made from advanced materials such as PTFE or reinforced polyurethane offer better resistance to heat, wear, and chemical degradation, improving their durability in demanding applications.
Sensors, Gauges, and Monitoring Systems
The integration of sensors, gauges, and monitoring systems into hydraulic presses has revolutionized how these machines operate, providing real-time data on the press’s performance and condition. These components enhance the safety, accuracy, and efficiency of the press by monitoring key parameters such as pressure, temperature, and piston position. In this section, we will explore the role of sensors, gauges, and monitoring systems in hydraulic presses and how they improve the operation and maintenance of the machine.
10.1. Monitoring Systems in Hydraulic Presses
Monitoring systems in hydraulic presses track the system’s performance and provide real-time feedback to operators and control systems. These systems help detect potential issues before they lead to system failure, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. Monitoring systems also improve the precision of pressing operations by providing accurate data on force, pressure, and piston position.
10.2. Types of Sensors in Hydraulic Presses
Sensors are used throughout the hydraulic press to measure different parameters. The most common types of sensors include pressure sensors, temperature sensors, and position sensors.
10.2.1. Pressure Sensors
Pressure sensors measure the hydraulic pressure within the system, providing real-time data on the force being applied during pressing operations. Pressure sensors ensure that the press is operating within safe limits and help maintain consistent force application.
- Application: Pressure sensors are typically placed in the hydraulic cylinder or near the pump to monitor the fluid pressure.
10.2.2. Temperature Sensors
Temperature sensors monitor the temperature of the hydraulic fluid and other components to prevent overheating. If the fluid temperature rises too high, it can degrade the fluid and reduce the efficiency of the system.
- Application: Temperature sensors are often installed in the hydraulic reservoir or near heat-generating components such as the pump or cylinder.
10.2.3. Position Sensors
Position sensors track the movement and position of the piston within the hydraulic cylinder. These sensors help ensure that the press applies the correct amount of force over the desired distance, improving the accuracy and repeatability of pressing operations.
- Application: Position sensors are typically placed on the hydraulic cylinder to monitor the piston’s movement.
10.3. Pressure Gauges: Analog vs. Digital
Pressure gauges are used to visually monitor the hydraulic pressure within the system. Traditional analog gauges use mechanical components to display the pressure, while modern digital gauges provide more precise, real-time data.
- Analog gauges: Simple, reliable, and easy to read, analog gauges are commonly used in smaller or older presses.
- Digital gauges: Digital gauges provide more accurate readings and can be integrated with monitoring systems to provide real-time data for automated control.
10.4. Role of Monitoring Systems in Improving Performance and Safety
The integration of sensors and monitoring systems improves the safety, performance, and efficiency of hydraulic presses in several ways:
- Real-time feedback: Monitoring systems provide real-time data on key performance metrics, allowing operators to make adjustments on the fly and ensure consistent press operation.
- Predictive maintenance: By tracking parameters such as pressure, temperature, and component wear, monitoring systems can help operators schedule maintenance before issues lead to costly breakdowns.
- Improved accuracy: Position sensors and digital pressure gauges allow for more precise control over pressing operations, ensuring that the press applies the correct force and completes tasks with high accuracy.
10.5. Predictive Maintenance Using Real-Time Data
One of the most significant benefits of modern monitoring systems is their ability to facilitate predictive maintenance. By analyzing real-time data from sensors, operators can identify potential issues, such as fluid leaks, overheating, or pressure loss, before they lead to system failure.
- Predictive maintenance: This approach reduces the risk of unexpected downtime and extends the life of the press by addressing issues early. Monitoring data can also be used to schedule routine maintenance tasks based on the actual wear and condition of components, rather than following a fixed maintenance schedule.
Introduction to Hydraulic Presses
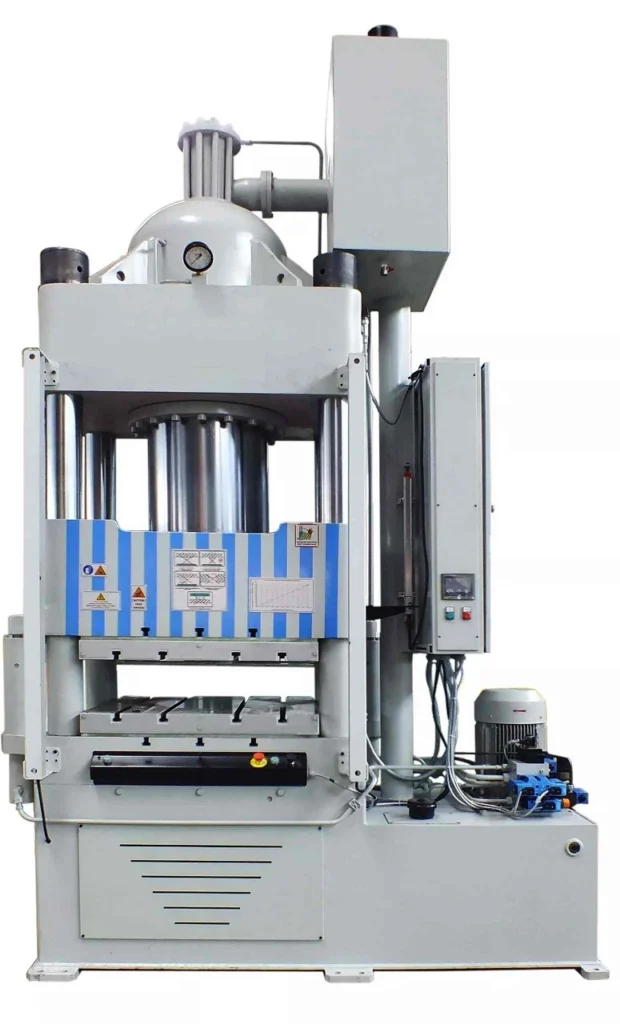

A hydraulic press is a mechanical device that uses hydraulic force to compress, shape, or mold materials into specific forms. It is widely regarded as one of the most important machines in industrial manufacturing due to its ability to apply immense force with precision and control. This force is generated by the hydraulic system, which operates based on Pascal’s Law, allowing a small input force to be multiplied into a much larger output force. Hydraulic presses are used in a variety of industries, including automotive manufacturing, aerospace, metalworking, and plastic molding, where they perform tasks such as metal forming, stamping, deep drawing, and forging.
The working principle of a hydraulic press revolves around the movement of hydraulic fluid under pressure, which is directed into a cylinder to push a piston. This piston, in turn, applies a compressive force on the material placed beneath it. By manipulating the size of the cylinder and piston, hydraulic presses can generate forces ranging from a few tons to thousands of tons, making them highly versatile machines.
Hydraulic presses are favored for their precision and control, enabling manufacturers to produce consistent, high-quality parts. They are also more compact compared to mechanical presses, and their force can be applied more evenly, which is particularly important in tasks requiring smooth, controlled deformation of materials.
This principle of multiplying force has applications far beyond presses. Hydraulic systems are used in a wide range of machinery and tools, including hydraulic lifts, jacks, and braking systems in vehicles. The versatility and efficiency of hydraulic systems make them a cornerstone of modern engineering and manufacturing.
Despite their widespread use and importance, the operation of hydraulic presses remains based on a simple concept—containing and controlling fluid pressure to achieve a desired mechanical outcome. The ability to harness the power of fluid dynamics enables hydraulic presses to perform complex and demanding tasks with minimal input force.
In the following sections, we will explore in detail the scientific principles that underpin hydraulic press operation, the components that make up these systems, and the various types of hydraulic presses used across industries. Additionally, we will delve into the energy efficiency, control mechanisms, and future innovations that continue to make hydraulic presses indispensable in the modern industrial landscape.
Fundamental Science Behind Hydraulic Presses
The working principle of a hydraulic press is based on the foundational concept of Pascal’s Law, which governs the behavior of fluids in confined spaces. Understanding the physics behind hydraulic systems is essential to grasp how hydraulic presses can generate such significant force with relatively little input.
2.1. Pascal’s Law and Its Application in Hydraulic Systems
Pascal’s Law, named after the French mathematician Blaise Pascal, states that when pressure is applied to a confined fluid, it is transmitted equally in all directions. This means that any change in pressure in one part of a confined fluid is reflected throughout the entire fluid. In a hydraulic press, this principle is used to multiply force and transfer it efficiently across a system.
The mathematical expression of Pascal’s Law is:P=FAP = \frac{F}{A}P=AF
Where:
- P is pressure,
- F is force, and
- A is the area over which the force is applied.
In a hydraulic press, this equation explains how a small input force can be transformed into a much larger output force. By increasing the area of the output piston while keeping the pressure constant, the force exerted by the press can be amplified. This is the fundamental principle behind force multiplication in hydraulic systems.
2.2. Force Multiplication in Hydraulic Systems
To understand how Pascal’s Law applies in a hydraulic press, consider a simple system with two connected cylinders of different sizes. A small input force is applied to the smaller piston (called the master cylinder), creating pressure in the hydraulic fluid. Because pressure is transmitted equally in all directions, this pressure is also applied to the larger piston (called the slave cylinder). Since the area of the larger piston is greater, the force it exerts is proportionally larger, even though the pressure in the system remains constant.
For example, if a 100 Newton force is applied to a small piston with an area of 1 square centimeter, the resulting pressure is 100 N/cm². If this pressure is applied to a larger piston with an area of 10 cm², the force exerted by the larger piston will be 100 N/cm² × 10 cm² = 1,000 Newtons. This ability to multiply force makes hydraulic systems incredibly powerful and efficient.
This concept is the core of how hydraulic presses operate: a small force applied at the input is transformed into a much larger force at the output, allowing for tasks such as metal forming, forging, stamping, and crushing to be carried out with great efficiency.
2.3. How Pressure is Distributed Through a Confined Fluid
In a hydraulic press, the hydraulic fluid plays a critical role in force transmission. Hydraulic fluids are generally incompressible, meaning they do not significantly change in volume when subjected to pressure. This property allows the fluid to transmit force consistently and efficiently.
When pressure is applied to the fluid, the fluid distributes that pressure equally in all directions within the confined space of the hydraulic cylinder. This even distribution is key to ensuring that the press applies uniform pressure across the material being worked on. Whether the press is used to form metal sheets, mold plastics, or perform deep drawing operations, the hydraulic fluid ensures that the force is applied consistently across the entire surface area of the workpiece.
In practical terms, this means that the hydraulic press can handle complex shapes and materials that require smooth, even deformation, such as in metal forming or precision assembly tasks.
2.4. Real-World Examples of Pascal’s Law Beyond Hydraulic Presses
While hydraulic presses are perhaps the most well-known application of Pascal’s Law, this principle is utilized in many other areas of engineering and machinery. Some real-world examples include:
- Hydraulic car jacks: Used to lift heavy vehicles with minimal input force. A small pump applies pressure to the hydraulic fluid, lifting the vehicle with the help of a larger piston.
- Hydraulic braking systems: Found in cars, trucks, and airplanes, hydraulic brakes use fluid pressure to multiply the force applied by the driver’s foot on the brake pedal, applying enough force to stop the vehicle.
- Hydraulic lifts: Commonly used in construction, warehouses, and factories, hydraulic lifts use Pascal’s Law to raise and lower heavy loads with great precision.
In each of these examples, the ability to multiply force using hydraulic systems allows for efficient operation of equipment, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing productivity.
2.5. Hydraulic Force vs. Mechanical Force
Hydraulic presses differ from mechanical presses in how they generate and apply force. While both types of presses are used to deform, shape, or compress materials, the mechanisms they use are quite different.
- Hydraulic presses use hydraulic fluid to apply pressure, allowing for smoother and more controlled force application. The force in a hydraulic press is applied uniformly, which is ideal for tasks that require precision, such as metal forming and plastic molding.
- Mechanical presses, on the other hand, rely on mechanical linkages and flywheels to generate force. While mechanical presses can be faster and are suitable for repetitive tasks like stamping, they are less versatile when it comes to handling complex shapes or materials.
The key advantage of hydraulic presses is their ability to apply constant pressure over a long stroke length. This makes them ideal for tasks like deep drawing, metal extrusion, and compression molding, where materials need to be shaped gradually and with high precision.
Components of a Hydraulic Press and Their Roles in the Working Principle

A hydraulic press consists of several key components, each of which plays an essential role in converting hydraulic energy into mechanical force. Understanding how these components function and interact with each other is crucial to comprehending the overall working principle of hydraulic presses. In this section, we will explore the most important components of a hydraulic press and their specific contributions to the system’s operation.
3.1. Hydraulic Cylinder
The hydraulic cylinder is the heart of the hydraulic press. It is responsible for converting hydraulic pressure into linear mechanical force, which is then used to deform or shape the material. The cylinder houses the piston, and the pressurized hydraulic fluid is pumped into the cylinder, creating pressure behind the piston. This pressure causes the piston to move, applying force to the material beneath the press.
Types of Hydraulic Cylinders
Hydraulic cylinders come in different designs depending on the application of the press:
- Single-acting cylinders: These cylinders have hydraulic fluid applied to only one side of the piston, causing the piston to move in one direction. The return stroke is powered by external forces, such as springs or gravity.
- Double-acting cylinders: In these cylinders, hydraulic fluid is applied to both sides of the piston, allowing it to move in both directions. This design offers more control over the movement of the piston and is commonly used in modern hydraulic presses that require precision and speed.
Function of the Cylinder in the Hydraulic Press
The force generated by the hydraulic press is proportional to the surface area of the cylinder and the pressure applied to the hydraulic fluid. This makes the cylinder’s design critical to determining how much force the press can exert. Larger cylinders can generate more force due to the increased area over which the hydraulic fluid applies pressure.
In a typical operation cycle, the press’s hydraulic pump forces fluid into the cylinder, pushing the piston downward. The material placed beneath the press is deformed or compressed as the piston moves. Once the task is completed, the hydraulic fluid is either released (in single-acting cylinders) or pumped back (in double-acting cylinders) to retract the piston.
3.2. Piston
The piston is another vital component of a hydraulic press, as it is responsible for transferring the hydraulic pressure into mechanical force. The piston moves within the hydraulic cylinder as pressurized fluid is pumped in, causing it to push down on the material being pressed. The force exerted by the piston depends on its size, the pressure of the hydraulic fluid, and the area over which the pressure is applied.
Piston’s Role in Force Transmission
In hydraulic systems, the piston acts as the intermediary between hydraulic pressure and mechanical action. The movement of the piston is what ultimately causes the deformation, compression, or shaping of the material. The larger the surface area of the piston, the greater the force it can exert. For example, a larger piston will apply a higher force to the material even with the same amount of hydraulic pressure.
Pistons are typically made from high-strength materials like steel or cast iron, ensuring they can withstand the immense pressures generated by the hydraulic system. To ensure smooth operation, pistons are often coated with chrome or other wear-resistant materials to reduce friction and prevent corrosion.
Precision and Control
Modern hydraulic presses rely on highly precise pistons that can handle extremely high loads while maintaining smooth, controlled movement. In presses used for precision tasks, such as in the automotive or aerospace industries, the piston’s movement must be carefully controlled to ensure that the material is shaped or pressed accurately. The responsiveness of the piston allows operators to achieve fine control over the force and speed of the press, ensuring high-quality results.
3.3. Hydraulic Fluid
Hydraulic fluid plays a critical role in the operation of a hydraulic press by serving as the medium through which force is transmitted. When hydraulic fluid is pressurized, it transmits this pressure to the piston, causing the piston to move. The properties of hydraulic fluid, such as viscosity, thermal stability, and compressibility, directly impact the performance and efficiency of the press.
Types of Hydraulic Fluids
Several types of hydraulic fluids are used in hydraulic presses, each with different properties suited to specific operating conditions:
- Mineral-based hydraulic fluids: These are the most common and cost-effective fluids used in general-purpose presses. They offer good lubrication and heat dissipation properties but may not perform well in extreme temperatures.
- Water-based hydraulic fluids: These fluids are used in applications where fire resistance is important. They are less flammable than mineral oils, making them suitable for presses used in environments with a higher risk of fire.
- Synthetic hydraulic fluids: These are high-performance fluids designed for extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or heavy loads. They offer superior stability and performance but are more expensive than other types of hydraulic fluids.
Role of Hydraulic Fluid in Energy Transmission
The hydraulic fluid is incompressible, which allows it to transmit force efficiently. When pressurized by the hydraulic pump, the fluid moves through the system and into the cylinder, where it applies pressure to the piston. This pressure causes the piston to move, exerting force on the material. The ability of hydraulic fluid to transmit force without significant loss is what makes hydraulic systems so efficient.
In addition to transmitting force, hydraulic fluid also acts as a lubricant, reducing friction between the moving parts of the press, such as the piston and cylinder walls. It also helps dissipate heat generated during operation, preventing the system from overheating and maintaining consistent performance.
3.4. Hydraulic Pump
The hydraulic pump is responsible for pressurizing the hydraulic fluid and driving the movement of the piston. It converts mechanical energy (from a motor or engine) into hydraulic energy by moving the fluid through the system. The pump is a critical component in determining the overall performance and speed of the hydraulic press, as it directly affects how quickly pressure builds up in the system.
Types of Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic presses use several types of pumps, depending on the press’s size, application, and desired performance:
- Gear pumps: These are simple, cost-effective pumps that are commonly used in smaller presses or low-pressure applications. They are less efficient than other types of pumps but are reliable and easy to maintain.
- Vane pumps: Known for their quiet operation and smooth fluid flow, vane pumps are used in presses that require moderate pressure and efficiency.
- Piston pumps: These are the most powerful and efficient hydraulic pumps, capable of generating extremely high pressures. Piston pumps are typically used in heavy-duty industrial presses that require precise control and high force.
Pump’s Role in Generating Pressure
The hydraulic pump draws fluid from the reservoir and forces it into the hydraulic system, creating pressure. This pressure is what drives the movement of the piston, allowing the press to apply force to the material. The pump’s efficiency and capacity determine how quickly pressure builds up in the system and how much force the press can generate.
Modern hydraulic pumps are often designed to adjust their output based on the press’s operating conditions. For example, variable displacement pumps can change the amount of fluid they move depending on the press’s needs, improving energy efficiency and reducing waste.
3.5. Valves and Controls
Valves and control systems in a hydraulic press manage the flow of hydraulic fluid and ensure that pressure is applied safely and efficiently. Valves are used to control the direction, speed, and pressure of the fluid as it moves through the system.
Types of Valves
- Directional control valves: These valves control the direction of the hydraulic fluid, determining whether the piston moves up or down. They are essential for controlling the operation of the press.
- Pressure relief valves: These valves protect the system from over-pressurization by releasing excess fluid back into the reservoir when the pressure exceeds a safe limit.
- Flow control valves: These valves regulate the speed of the press by controlling the flow rate of hydraulic fluid into the cylinder. This allows operators to adjust the press’s speed for different tasks.
Control Systems and Automation
In modern hydraulic presses, valves are often controlled electronically, using Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) or Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems. These control systems allow operators to automate the press’s operation, adjusting parameters such as pressure, speed, and stroke length with high precision.
Automation improves the efficiency and accuracy of hydraulic presses, making them suitable for tasks that require repetitive or precise operations. Smart control systems also enable real-time monitoring of the press’s performance, helping operators identify potential issues before they cause downtime or damage.
3.6. Reservoir and Cooling System
The reservoir stores the hydraulic fluid when it is not in use and provides a place for the fluid to cool before it is recirculated back into the system. The reservoir plays an important role in maintaining the efficiency and longevity of the hydraulic press by ensuring that the fluid remains clean and at an optimal temperature.
Reservoir’s Role in Fluid Management
The hydraulic fluid in the system heats up during operation due to friction and pressure. The reservoir allows the fluid to cool before it is pumped back into the system, preventing overheating and maintaining consistent pressure. In addition, the reservoir often contains filters that remove impurities from the fluid, preventing contamination that could damage the hydraulic components.
Cooling Systems
Some hydraulic presses are equipped with cooling systems, such as heat exchangers or radiators, to further control the temperature of the hydraulic fluid. Keeping the fluid at the correct temperature is essential for maintaining the press’s performance and preventing premature wear on components.
Pascal’s Law in Detail
Pascal’s Law is the fundamental scientific principle behind the operation of hydraulic presses. It explains how hydraulic systems can efficiently multiply force, making hydraulic presses capable of performing heavy-duty tasks such as forming, molding, and cutting with minimal input force. In this section, we will delve deeper into the mathematical foundation of Pascal’s Law, explore the concept of force multiplication in hydraulic systems, and discuss how pressure is transmitted through hydraulic fluid. Understanding Pascal’s Law is crucial to appreciating the inner workings and efficiency of hydraulic presses.
4.1. Mathematics of Pascal’s Law
Pascal’s Law, formulated by the French mathematician Blaise Pascal in the 17th century, states that when pressure is applied to a confined fluid, it is transmitted equally in all directions within the fluid. This simple yet powerful concept is the key to understanding how hydraulic systems work.
The equation for Pascal’s Law can be expressed as:P=FAP = \frac{F}{A}P=AF
Where:
- P is the pressure in the system (measured in Pascals, Pa),
- F is the force applied (measured in Newtons, N), and
- A is the area over which the force is applied (measured in square meters, m²).
This equation shows that pressure in a hydraulic system is a function of the force applied to the fluid and the area over which that force is distributed. By rearranging the formula to solve for force, we get:F=P×AF = P \times AF=P×A
This tells us that the force generated by the hydraulic system is directly proportional to the pressure applied and the surface area of the piston or cylinder. This relationship allows hydraulic presses to generate enormous forces with relatively small input pressures, making them highly efficient and powerful machines.
4.2. Pressure and Force Distribution
In a hydraulic press, Pascal’s Law ensures that the pressure applied to the hydraulic fluid is transmitted uniformly throughout the system. This means that the force generated by the press is distributed evenly across the entire surface area of the piston, resulting in uniform force application to the material being worked on.
For example, consider a hydraulic system with two pistons: a smaller input piston and a larger output piston. When pressure is applied to the input piston, the hydraulic fluid transmits that pressure to the larger output piston. Since pressure is constant throughout the fluid, the larger piston generates a much greater force because it has a larger surface area over which the pressure is applied.
If the input piston has an area of 1 square centimeter and the output piston has an area of 10 square centimeters, the force exerted by the output piston will be 10 times greater than the force applied to the input piston. This is known as force multiplication, and it is the reason why hydraulic presses can generate such large forces with minimal input effort.
The concept of force multiplication can be further illustrated using the example of a car jack. When you pump the handle of a hydraulic jack, you are applying a small force to a small piston. The hydraulic fluid then transmits this pressure to a larger piston, which exerts enough force to lift a car. The principle at work is the same as in a hydraulic press: pressure is distributed evenly, and the force is multiplied based on the difference in piston areas.
4.3. Formula for Force Multiplication
To better understand the concept of force multiplication, let’s break down the calculation:
Consider a hydraulic press with an input piston that has an area of 2 cm² and an output piston with an area of 50 cm². If you apply a force of 100 Newtons to the input piston, we can calculate the pressure applied to the hydraulic fluid using the following formula:P=FA=100 N2 cm2=50 N/cm2P = \frac{F}{A} = \frac{100 \, \text{N}}{2 \, \text{cm}^2} = 50 \, \text{N/cm}^2P=AF=2cm2100N=50N/cm2
This pressure is transmitted equally throughout the hydraulic fluid, so the same pressure (50 N/cm²) is applied to the output piston. To calculate the force exerted by the output piston, we multiply the pressure by the area of the output piston:Foutput=P×Aoutput=50 N/cm2×50 cm2=2500 NF_{\text{output}} = P \times A_{\text{output}} = 50 \, \text{N/cm}^2 \times 50 \, \text{cm}^2 = 2500 \, \text{N}Foutput=P×Aoutput=50N/cm2×50cm2=2500N
In this example, a small input force of 100 N is multiplied into a much larger output force of 2500 N. This illustrates how hydraulic presses can generate extremely high forces by applying relatively small forces at the input.
The ratio of the areas of the pistons is what allows the system to multiply force. In this case, the ratio of the areas is 50 cm² (output piston) to 2 cm² (input piston), or 25:1. This means that for every 1 unit of force applied to the input piston, 25 units of force are generated at the output piston.
4.4. Pressure Applied to Different Pistons
In hydraulic systems, pressure is the same throughout the fluid, regardless of the size of the pistons. However, the force generated at each piston varies depending on the surface area of the piston. This is what allows hydraulic presses to achieve force multiplication.
Let’s take another example where the hydraulic press has two pistons—an input piston with an area of 5 cm² and an output piston with an area of 25 cm². If a force of 200 N is applied to the input piston, the pressure in the system will be:P=FinputAinput=200 N5 cm2=40 N/cm2P = \frac{F_{\text{input}}}{A_{\text{input}}} = \frac{200 \, \text{N}}{5 \, \text{cm}^2} = 40 \, \text{N/cm}^2P=AinputFinput=5cm2200N=40N/cm2
This pressure is transmitted to the output piston, and the force generated by the output piston will be:Foutput=P×Aoutput=40 N/cm2×25 cm2=1000 NF_{\text{output}} = P \times A_{\text{output}} = 40 \, \text{N/cm}^2 \times 25 \, \text{cm}^2 = 1000 \, \text{N}Foutput=P×Aoutput=40N/cm2×25cm2=1000N
As seen here, the output force is five times greater than the input force because the area of the output piston is five times larger than the area of the input piston. This proportional relationship between piston area and output force is the foundation of the hydraulic press’s ability to generate large amounts of force.
4.5. Hydraulic Press Efficiency
One of the key benefits of hydraulic presses is their efficiency in converting input force into output force. Hydraulic systems are typically more efficient than mechanical systems because they transmit force directly through the incompressible fluid. This allows hydraulic presses to maintain consistent pressure and smooth force application over long distances, making them ideal for tasks that require precision and uniformity.
However, the overall efficiency of a hydraulic press depends on several factors, including:
- Hydraulic fluid properties: The viscosity and compressibility of the hydraulic fluid can affect how efficiently pressure is transmitted. High-quality hydraulic fluids with low compressibility are essential for maintaining efficient operation.
- System leaks: Leaks in the hydraulic system can result in pressure loss, reducing the efficiency of the press. Proper sealing and regular maintenance are necessary to prevent fluid leaks.
- Friction and heat: Friction between moving parts can generate heat, which reduces the overall efficiency of the system. Proper lubrication and cooling systems are needed to minimize friction and prevent overheating.
Hydraulic presses are particularly efficient when performing tasks such as deep drawing, forging, and stamping, where smooth and consistent force application is required over extended periods. The ability of hydraulic systems to maintain constant pressure ensures that the material is shaped uniformly, resulting in high-quality products with minimal defects.
4.6. Real-World Applications of Pascal’s Law in Hydraulic Presses
The principles of Pascal’s Law are applied in various industries where hydraulic presses are used to perform tasks that require large amounts of force. Some common applications of hydraulic presses include:
- Automotive manufacturing: Hydraulic presses are used to shape metal parts such as car body panels, engine components, and chassis frames.
- Aerospace: Hydraulic presses are essential for manufacturing high-strength metal parts used in aircraft, such as wing components, landing gear, and turbine blades.
- Metalworking: Hydraulic presses are used in metal forming, stamping, forging, and extrusion processes to shape and mold metals into complex shapes.
- Plastic molding: Hydraulic presses are used in the plastic molding industry to shape plastic materials into various products, such as automotive interiors, packaging, and consumer goods.
- Recycling: Hydraulic presses are used to compact scrap metal, plastics, and other materials into dense bales for easy transportation and recycling.
Working Process of a Hydraulic Press
The working process of a hydraulic press is a well-orchestrated mechanical and fluid dynamic cycle. It involves the application of pressure through a hydraulic system, causing a piston to move, which in turn applies force to the material being worked on. The entire process revolves around the efficient transmission of force through hydraulic fluid, ensuring that large forces can be applied to the material with precision and control. This section will provide a step-by-step explanation of how a hydraulic press operates, from the input of hydraulic pressure to the final force application on the material.
5.1. Basic Operation Cycle of a Hydraulic Press
The operation of a hydraulic press involves several key steps, each of which plays a vital role in shaping or compressing the material being processed. The entire cycle can be divided into three primary stages: fluid pressurization, piston movement, and material deformation.
Step 1: Pressurizing the Hydraulic Fluid
The first step in the operation of a hydraulic press is pressurizing the hydraulic fluid, which is stored in a reservoir. The hydraulic pump is responsible for drawing the fluid from the reservoir and pressurizing it. This pump can be powered by an electric motor or a pneumatic system, depending on the design of the press.
As the hydraulic pump operates, it forces the hydraulic fluid into the hydraulic cylinder. This fluid, being incompressible, transmits the pressure evenly throughout the cylinder. The pressure applied to the fluid is what creates the force needed to move the piston.
- Hydraulic fluid pressurization: The pump applies mechanical energy to the fluid, increasing its pressure. The pressure level depends on the type of press and the amount of force required for the task. For example, in high-force applications such as forging or deep drawing, the pressure might reach thousands of PSI (pounds per square inch).
Step 2: Piston Movement
Once the hydraulic fluid is pressurized, the next step is the movement of the piston within the hydraulic cylinder. The pressurized fluid pushes against the surface area of the piston, causing it to move downward (in the case of a vertical press) or in another direction, depending on the press design.
As the piston moves, it transfers the hydraulic force to the material placed on the press’s bed or anvil. The force is applied uniformly across the material, enabling tasks such as compression, bending, cutting, or molding.
- Control over piston movement: The movement of the piston is controlled by directional control valves, which determine whether the fluid enters one side of the piston or the other. For presses that require precision, the flow control valves can also regulate the speed at which the piston moves, ensuring smooth and controlled operation.
- Force generation: The force applied by the piston is proportional to the pressure in the hydraulic system and the surface area of the piston. Larger pistons with greater surface areas generate more force, making hydraulic presses highly efficient for heavy-duty applications like metal stamping or forging.
Step 3: Material Deformation
The final stage in the operation of a hydraulic press is the deformation of the material being processed. As the piston applies force to the material, the material is compressed, bent, or shaped according to the specific requirements of the task.
- Material behavior under pressure: Different materials respond to pressure in various ways. Metals, for example, deform plastically when subjected to enough force, allowing them to be shaped into desired forms without breaking. Plastics, on the other hand, may require less force but must be handled carefully to avoid cracking or warping.
- Even force distribution: One of the advantages of hydraulic presses is their ability to apply force evenly across the surface of the material. This even distribution of force ensures that the material is deformed consistently, reducing the risk of defects such as uneven thickness, cracks, or warping.
Once the task is complete, the hydraulic system reduces the pressure, and the piston retracts, either by releasing the hydraulic fluid or by using a return spring (in single-acting cylinders) or applying pressure to the opposite side of the piston (in double-acting cylinders). This completes the operational cycle.
5.2. Input Force to Output Force: A Detailed Breakdown
One of the key principles behind the working process of a hydraulic press is the multiplication of force. Hydraulic presses are designed to take a small input force and amplify it into a much larger output force, thanks to the mechanics of Pascal’s Law and the difference in surface areas between the input and output pistons.
Let’s break down this process in more detail:
- Small input force: In a hydraulic press, the operator or an automated system applies a relatively small input force to the hydraulic fluid, either by operating the hydraulic pump or using a manual lever (in the case of manual presses).
- Pressure generation: This input force creates pressure within the hydraulic fluid, which is then transmitted through the system. Since the fluid is incompressible, the pressure is distributed evenly throughout the hydraulic system.
- Force amplification: The force applied by the piston to the material is determined by the surface area of the piston and the pressure in the hydraulic system. Because the piston typically has a much larger surface area than the input mechanism, the force exerted by the piston is amplified many times over.
For example, if a hydraulic press has an input piston with an area of 2 square centimeters and an output piston with an area of 50 square centimeters, the output force will be 25 times greater than the input force. This ability to multiply force is what makes hydraulic presses so effective in tasks that require immense force, such as forging, stamping, or metal forming.
5.3. Stroke Length and Speed Control
The stroke length refers to the distance the piston travels during the operation of the hydraulic press. Stroke length is an important parameter in press operation because it determines how far the material is compressed, bent, or shaped. In many applications, precise control over stroke length is necessary to ensure that the material is processed correctly.
- Adjusting stroke length: Hydraulic presses are typically equipped with controls that allow operators to adjust the stroke length. For example, when pressing large or thick materials, the stroke length may need to be longer to ensure full compression. In contrast, for smaller, more delicate tasks, a shorter stroke length is often sufficient.
- Speed control: The speed at which the piston moves is another critical factor in the operation of a hydraulic press. The speed is controlled by regulating the flow rate of the hydraulic fluid through the system. Flow control valves are used to adjust the fluid flow, allowing operators to slow down or speed up the piston’s movement based on the requirements of the task.
In applications that require precision forming, such as in the automotive or aerospace industries, the ability to control the speed of the press is essential. Slower speeds allow for greater precision and help avoid defects, while faster speeds increase productivity when handling simpler tasks.
5.4. Reverse Stroke: The Return Process
In addition to the pressing stroke, hydraulic presses also have a reverse stroke, where the piston is retracted after the pressing operation is complete. The reverse stroke is essential for resetting the press so that the next operation can be performed.
Single-Acting Cylinders
In hydraulic presses with single-acting cylinders, the piston is powered by hydraulic pressure in only one direction—typically the downward stroke. After the pressing operation is completed, the piston is returned to its starting position using either a return spring or gravity. These systems are simpler but may not offer as much control over the reverse stroke.
- Return spring: A spring attached to the piston helps pull it back to the starting position once the hydraulic pressure is released.
- Gravity return: In vertical presses, the weight of the piston itself can help it return to the starting position.
Double-Acting Cylinders
In double-acting cylinders, hydraulic pressure is applied to both sides of the piston, allowing for controlled movement in both directions. This means the piston can be powered both during the pressing stroke and the reverse stroke. Double-acting cylinders are more versatile and allow for greater control over the reverse stroke, making them ideal for precision tasks.
- Hydraulic return: Pressure is applied to the opposite side of the piston to move it back to its starting position after the operation. This offers more control and ensures that the piston retracts at a consistent speed.
5.5. Hydraulic Press Cycle Time
The cycle time of a hydraulic press refers to the amount of time it takes to complete one full operation, including the pressing stroke, the reverse stroke, and the resetting of the press. Several factors affect the cycle time, including:
- Hydraulic pump capacity: The pump’s ability to generate pressure quickly can reduce the cycle time. High-capacity pumps allow for faster pressurization of the hydraulic fluid, resulting in quicker piston movement.
- Piston speed: The speed at which the piston moves during both the pressing and reverse strokes also affects the cycle time. Flow control valves help regulate this speed to achieve the desired balance between precision and productivity.
- Material properties: The material being pressed can impact cycle time. Harder materials, such as metals, may require more time for compression, while softer materials like plastics can be processed more quickly.
- Stroke length: Longer strokes require more time to complete, extending the overall cycle time. Shorter strokes are faster but may not be suitable for all applications.
In high-volume production environments, minimizing cycle time is crucial to maintaining efficiency and productivity. Modern hydraulic presses are designed with automated controls and efficient hydraulic systems to optimize cycle time while maintaining high levels of precision and quality.
Types of Hydraulic Presses and Their Variations in Working Principles
Hydraulic presses come in a wide variety of designs, each tailored to specific applications and industries. While the basic principle of operation—applying hydraulic pressure to a piston to generate force—remains the same, the differences in frame construction, force output, and functionality make each type of hydraulic press suited for particular tasks. In this section, we will explore several common types of hydraulic presses and the variations in their working principles.
6.1. Manual Hydraulic Presses
Manual hydraulic presses are operated by hand, typically using a lever or hand pump to generate hydraulic pressure. These presses are simple in design and do not require external power sources like electricity or pneumatic systems. Manual presses are most commonly used for small-scale tasks where precision and high force are needed but speed is not a priority.
Working Principle of Manual Hydraulic Presses
- Hand-powered pump: In a manual press, the operator applies force to a lever or hand pump, which drives the hydraulic fluid into the cylinder. This creates pressure in the hydraulic system and moves the piston to apply force to the material.
- Force application: Despite being manually powered, these presses can generate significant force, thanks to Pascal’s Law. The operator can apply a relatively small amount of force, which is multiplied through the hydraulic system, allowing for tasks like pressing bearings, small metal forming, or assembly work.
- Control: Manual presses allow for precise control over the amount of force applied, as the operator can stop or adjust the lever or pump as needed. However, the process can be slow compared to automated systems.
Applications
- Workshops and laboratories: Manual hydraulic presses are often found in small workshops and laboratories where precision and control are more important than speed. They are used for tasks such as press fitting, bearing insertion, jewelry making, and small metal forming.
- Low-volume production: These presses are ideal for low-volume or one-off production runs, as they are cost-effective and easy to operate.
Advantages
- Portability: Manual hydraulic presses are often compact and portable, making them easy to move and set up in different locations.
- Low cost: They are more affordable than powered hydraulic presses, making them ideal for smaller operations or hobbyists.
- Precision: The operator has full control over the amount of force applied, allowing for precise and careful operations.
Limitations
- Limited force: While manual presses can generate significant force, they are limited in comparison to powered hydraulic presses. They are not suitable for tasks requiring very high pressure or force.
- Slower operation: Manual presses are slower than powered presses, as the operator must manually pump the hydraulic fluid into the cylinder.
6.2. Powered Hydraulic Presses
Powered hydraulic presses use an external power source, such as an electric motor or pneumatic system, to drive the hydraulic pump. This allows for faster and more consistent operation compared to manual presses, making them ideal for industrial applications that require high force and rapid cycle times.
Electric Hydraulic Presses
Electric hydraulic presses are driven by electric motors that power the hydraulic pump, generating fluid pressure automatically. These presses are commonly used in large-scale manufacturing environments where high force and precision are required.
Working Principle of Electric Hydraulic Presses
- Electric motor: The electric motor drives the hydraulic pump, which pressurizes the hydraulic fluid. The pressurized fluid is then directed into the cylinder, moving the piston and applying force to the material.
- Automated control: Electric presses often feature programmable controls, allowing operators to set specific parameters such as pressure, stroke length, and speed. This automation improves consistency and reduces operator error.
- Continuous operation: Unlike manual presses, electric hydraulic presses can operate continuously, making them suitable for high-volume production environments.
Applications
- Metal forming and stamping: Electric hydraulic presses are widely used in the metalworking industry, where they perform tasks such as metal stamping, bending, and punching.
- Plastic molding: These presses are also used in the plastic molding industry, where they shape plastic materials into various components.
- Automotive manufacturing: Electric hydraulic presses are essential in automotive production, where they are used to press car body panels, engine components, and structural elements.
Advantages
- High force output: Electric presses can generate much higher force than manual presses, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Precision and automation: Programmable controls allow for precise force application, ensuring consistency and reducing the need for manual intervention.
- Faster cycle times: Electric presses operate more quickly than manual presses, allowing for higher productivity in industrial settings.
Limitations
- Higher cost: Electric hydraulic presses are more expensive than manual presses, both in terms of initial investment and ongoing energy costs.
- Maintenance: These presses require more maintenance due to their complex electrical and hydraulic systems.
Pneumatic Hydraulic Presses
Pneumatic hydraulic presses are driven by compressed air, which is used to power the hydraulic pump. These presses are often used in light industrial applications where lower force is required, but speed and efficiency are still important.
Working Principle of Pneumatic Hydraulic Presses
- Compressed air: The press is powered by an air compressor, which provides the energy needed to drive the hydraulic pump. The compressed air creates pressure in the hydraulic fluid, which moves the piston and applies force to the material.
- Faster operation: Pneumatic presses are known for their quick operation, making them suitable for tasks that require rapid cycle times.
Applications
- Light assembly work: Pneumatic hydraulic presses are often used for assembly line tasks such as pressing bearings, fasteners, and small components into place.
- Low to moderate force applications: These presses are ideal for tasks that require moderate force, such as plastic forming, light metal forming, and punching.
Advantages
- Energy efficiency: Pneumatic presses are more energy-efficient for light-duty tasks, as they consume less power than electric presses.
- Fast operation: These presses offer rapid cycle times, making them ideal for repetitive tasks in assembly lines.
- Environmentally friendly: Pneumatic systems are often considered environmentally friendly, as they use compressed air instead of electricity.
Limitations
- Lower force output: Pneumatic presses cannot generate the same level of force as electric hydraulic presses, limiting their use in heavy-duty applications.
- Air consumption: They require a constant supply of compressed air, which may not be practical in all environments.
6.3. H-Frame Hydraulic Presses
H-frame hydraulic presses are named for their distinctive frame shape, which resembles the letter “H.” This frame design provides excellent stability and force distribution, making H-frame presses one of the most versatile and widely used types of hydraulic presses in manufacturing and repair applications.
Working Principle of H-Frame Hydraulic Presses
- H-frame structure: The press consists of two vertical columns (the legs of the “H”) connected by horizontal crossbars. The hydraulic cylinder and piston are mounted in the center of the crossbar, allowing the piston to move vertically and apply force to the material placed between the columns.
- High force capacity: H-frame presses are capable of generating large amounts of force, making them suitable for tasks such as metal forming, stamping, bending, and forging. The frame design ensures that the force is evenly distributed across the material, preventing deformation or misalignment.
- Manual or powered operation: H-frame presses can be operated manually, with a hand pump, or powered by an electric or pneumatic system, depending on the size and force requirements.
Applications
- Metalworking and fabrication: H-frame hydraulic presses are commonly used in the metalworking industry for tasks such as bending, straightening, stamping, and forming metal components.
- Automotive repair: These presses are often found in automotive repair shops, where they are used for tasks such as pressing bearings, straightening chassis components, and forming metal parts.
- General manufacturing: H-frame presses are versatile machines used in a wide range of manufacturing industries, including construction, aerospace, and machinery production.
Advantages
- Versatility: H-frame presses can be used for a wide range of tasks, from small-scale repairs to large-scale industrial manufacturing.
- High stability: The H-frame design provides excellent structural stability, ensuring that the force is applied evenly and accurately.
- Customizability: H-frame presses can be customized with different hydraulic systems, bed sizes, and accessories to meet specific production needs.
Limitations
- Large footprint: H-frame presses require a significant amount of floor space, making them less suitable for small workshops or facilities with limited space.
- Heavier: These presses tend to be heavier and more difficult to move compared to other types of hydraulic presses.
6.4. C-Frame Hydraulic Presses
C-frame hydraulic presses are designed with an open-front structure that resembles the letter “C.” This design provides easy access to the work area, making C-frame presses ideal for tasks that require quick loading and unloading of materials. C-frame presses are commonly used for smaller-scale applications where precision and speed are important.
Working Principle of C-Frame Hydraulic Presses
- Open-front design: The C-frame design allows for easy access to the pressing area from three sides, making it easier to position and remove materials. The hydraulic cylinder is mounted at the top of the frame, with the piston moving downward to apply force to the material placed on the bed.
- Single-point force application: In C-frame presses, the force is applied at a single point directly beneath the piston. While this provides precise control, it can also result in uneven force distribution if the material is not properly aligned.
Applications
- Precision metalworking: C-frame presses are often used in precision metalworking tasks such as punching, stamping, and forming small metal components.
- Assembly line work: These presses are commonly found in assembly lines for tasks such as pressing fasteners or components into place, particularly in industries like electronics and automotive.
- Small part production: C-frame presses are ideal for producing small parts or components that require high precision and frequent handling.
Advantages
- Compact and space-efficient: C-frame presses have a smaller footprint than H-frame presses, making them ideal for smaller workshops or production lines with limited space.
- Easy access: The open-front design allows for quick and easy loading and unloading of materials, improving productivity in high-volume applications.
- Precision: These presses offer excellent precision, making them ideal for tasks that require careful control of force and alignment.
Limitations
- Lower force capacity: C-frame presses typically generate less force than H-frame presses, limiting their use in heavy-duty applications.
- Frame deformation risk: The open-front design can result in frame deformation under extreme loads, so these presses are best suited for lighter tasks.
Fluid Dynamics in Hydraulic Presses
Fluid dynamics is a critical aspect of hydraulic press operation, governing how hydraulic fluid behaves within the system and ensuring the efficient transmission of force from the hydraulic pump to the piston. The properties of hydraulic fluid—such as viscosity, compressibility, and temperature tolerance—play a significant role in the performance of the hydraulic press. Understanding the principles of fluid dynamics in hydraulic systems helps in optimizing press efficiency, minimizing losses, and maintaining consistent pressure during operation.
In this section, we will explore how hydraulic fluid behaves under pressure, the role of flow rate and pressure regulation, the importance of cooling systems, and the effects of fluid contamination on press performance.
7.1. Understanding Fluid Behavior in Hydraulic Systems
Hydraulic presses rely on hydraulic fluid to transmit force from the pump to the piston. The fluid must be incompressible and able to withstand high pressures without degrading or causing system failures. The key properties of hydraulic fluid, which directly impact the operation of the press, are viscosity, compressibility, and thermal stability.
Viscosity
Viscosity refers to the resistance of a fluid to flow. In hydraulic systems, the viscosity of the hydraulic fluid is crucial because it determines how easily the fluid can move through the system and how effectively it can transmit force.
- Low viscosity fluids: Fluids with low viscosity flow easily, which can reduce friction and allow for faster operation of the press. However, if the viscosity is too low, the fluid may not provide sufficient lubrication for the moving parts of the hydraulic system, leading to increased wear and tear.
- High viscosity fluids: Fluids with higher viscosity provide better lubrication, which helps protect the components of the hydraulic press from friction and wear. However, high-viscosity fluids flow more slowly, which can reduce the overall speed of the press and cause energy losses due to internal friction in the fluid.
Maintaining the optimal viscosity for the hydraulic fluid is essential for ensuring that the press operates efficiently. The viscosity of the fluid can change with temperature, so hydraulic systems often include temperature control features to keep the fluid within its optimal viscosity range.
Compressibility
Compressibility is the degree to which a fluid can be compressed when subjected to pressure. In hydraulic presses, the ideal hydraulic fluid is incompressible, meaning that it does not significantly change in volume when pressure is applied. Incompressibility allows the fluid to transmit pressure efficiently and consistently across the system.
- Incompressible fluids: When the hydraulic fluid is incompressible, the pressure generated by the pump is transmitted directly to the piston, allowing for smooth and precise operation. Most hydraulic fluids are designed to be nearly incompressible, which is why they are effective in generating and transmitting large forces.
- Compressible fluids: If the hydraulic fluid were compressible, it would absorb some of the pressure applied by the pump, leading to losses in force transmission. This would result in inefficiencies in the press’s operation and potential inconsistencies in the application of force to the material.
Thermal Stability
Hydraulic fluid absorbs heat generated by the operation of the press, particularly due to the friction between moving parts and the compression of fluid under pressure. Thermal stability refers to the fluid’s ability to maintain its properties, such as viscosity and pressure tolerance, even at elevated temperatures.
- Thermally stable fluids: Hydraulic fluids with high thermal stability can withstand high operating temperatures without degrading. This ensures that the fluid continues to transmit force effectively, even during prolonged use or under heavy loads.
- Degradation at high temperatures: If the hydraulic fluid is not thermally stable, it may break down at high temperatures, losing its viscosity and becoming less effective at transmitting pressure. This can lead to reduced performance, increased wear on components, and eventual system failure.
For presses that operate at high speeds or under heavy loads, it is important to use hydraulic fluids that can tolerate high temperatures without losing their essential properties.
7.2. Flow Rate and Pressure Regulation
The flow rate and pressure of hydraulic fluid within the system are two of the most important factors that determine the performance of a hydraulic press. The flow rate affects the speed at which the piston moves, while the pressure determines how much force is applied to the material. Proper regulation of both flow and pressure is critical to ensuring that the press operates efficiently and effectively.
Flow Control in Hydraulic Presses
The flow rate of hydraulic fluid refers to how quickly the fluid moves through the system. Flow rate is typically measured in liters per minute (LPM) or gallons per minute (GPM), and it directly influences the speed of the piston.
- High flow rate: A higher flow rate allows the hydraulic press to complete its stroke more quickly, increasing the speed of operation. This is particularly useful in high-volume production environments where short cycle times are essential.
- Low flow rate: Lower flow rates result in slower piston movement, which can be beneficial in applications that require precise control or gradual deformation of the material, such as deep drawing or precision molding.
Flow control is managed by flow control valves, which adjust the rate at which hydraulic fluid is supplied to the cylinder. These valves allow operators to regulate the speed of the press, ensuring that the flow rate is appropriate for the task at hand. For example, tasks that require high precision may benefit from slower piston movement, while tasks that prioritize speed over precision may require higher flow rates.
Pressure Regulation in Hydraulic Presses
The pressure in a hydraulic system is what generates the force that moves the piston and applies pressure to the material. Pressure is measured in pounds per square inch (PSI) or bars, and it determines the amount of force that the hydraulic press can exert.
- High pressure: Higher pressures result in greater force being applied by the piston, allowing the press to handle heavy-duty tasks such as forging, metal forming, and cutting.
- Low pressure: Lower pressures may be used for tasks that require less force, such as assembly work, light metal forming, or plastic molding.
Pressure regulation is achieved using pressure control valves, including pressure relief valves and pressure-reducing valves. These valves ensure that the hydraulic system maintains a safe and consistent pressure level, preventing over-pressurization that could damage the press or the material being worked on.
- Pressure relief valves: These valves open when the pressure in the system exceeds a certain limit, allowing excess fluid to return to the reservoir. This prevents the system from becoming over-pressurized, which could lead to component failure or safety hazards.
- Pressure-reducing valves: These valves reduce the pressure to a specific level required for certain tasks. For example, when working with delicate materials that cannot withstand high pressure, a pressure-reducing valve can lower the force applied by the press to avoid damaging the material.
7.3. Heat Generation and Fluid Cooling
Hydraulic systems generate heat as a result of fluid compression, friction between moving parts, and resistance within the hydraulic lines. If the hydraulic fluid becomes too hot, its viscosity may decrease, leading to reduced efficiency and potential damage to the hydraulic components. Cooling systems are therefore an essential part of most hydraulic presses, ensuring that the fluid remains at an optimal temperature during operation.
Heat Generation in Hydraulic Systems
Several factors contribute to heat generation in hydraulic presses:
- Fluid compression: When hydraulic fluid is pressurized, it generates heat. This is particularly true in high-force applications where the fluid is subjected to extreme pressures.
- Friction: As the hydraulic fluid moves through the system, it encounters friction between the various components, including valves, hoses, and cylinders. This friction generates heat, particularly in systems that operate at high speeds.
- Energy losses: Some of the energy applied to the hydraulic fluid is lost in the form of heat due to internal resistance within the fluid. This is why hydraulic systems are often equipped with cooling systems to dissipate the heat and maintain fluid performance.
Cooling Systems for Hydraulic Presses
To prevent the hydraulic fluid from overheating, most hydraulic presses are equipped with cooling systems. These systems help regulate the temperature of the hydraulic fluid, ensuring that it remains within the optimal range for efficient operation. Common types of cooling systems include:
- Air-cooled systems: In air-cooled systems, the hydraulic fluid is passed through a heat exchanger or cooling fins, where it is cooled by ambient air. These systems are simple and cost-effective but may not be sufficient for heavy-duty presses that generate a lot of heat.
- Liquid-cooled systems: Liquid cooling systems use water or another coolant to absorb heat from the hydraulic fluid. The coolant is circulated through a heat exchanger, where it transfers the heat away from the fluid. Liquid-cooled systems are more effective at managing high heat loads and are commonly used in large or high-performance presses.
- Reservoir cooling: The hydraulic reservoir itself can act as a cooling mechanism by allowing the hydraulic fluid to cool before being recirculated through the system. Larger reservoirs provide more surface area for heat dissipation, improving cooling efficiency.
Maintaining the proper temperature of the hydraulic fluid is critical to preventing performance degradation and prolonging the life of the press. Overheating can cause the fluid to break down, leading to reduced lubrication, increased wear, and potential system failure.
7.4. Fluid Contamination and Its Effect on Performance
One of the most common causes of hydraulic press failure is fluid contamination. Contaminants such as dirt, metal particles, and water can enter the hydraulic system and degrade the performance of the hydraulic fluid. This can lead to inefficiencies in force transmission, increased wear on components, and eventual system failure.
Causes of Fluid Contamination
Contamination of hydraulic fluid can occur for several reasons:
- External contamination: Dirt, dust, and other debris can enter the hydraulic system through leaks, damaged seals, or during fluid changes. External contamination is especially common in presses that operate in harsh or dirty environments, such as factories or construction sites.
- Internal contamination: Over time, the components of the hydraulic system—such as seals, hoses, and cylinders—can wear down, generating metal particles or other debris. These contaminants then circulate within the fluid, causing further damage to the system.
- Water ingress: Water can enter the hydraulic system through condensation, leaks, or improper fluid handling. Water contamination can lead to corrosion of hydraulic components and reduce the effectiveness of the hydraulic fluid.
Effects of Contamination on Hydraulic Press Performance
Fluid contamination can have several negative effects on the performance of a hydraulic press:
- Reduced efficiency: Contaminants can reduce the efficiency of the hydraulic fluid by obstructing fluid flow, leading to pressure losses and reduced force output.
- Increased wear: Contaminants such as metal particles or dirt can increase the wear on hydraulic components, leading to premature failure of seals, cylinders, and valves.
- Corrosion: Water contamination can cause corrosion of the press’s metal components, leading to leaks, reduced pressure, and potential system failure.
- Cavitation: If air bubbles enter the hydraulic system, they can cause cavitation, where the air pockets collapse under pressure, damaging the components and reducing system efficiency.
Preventing Fluid Contamination
Proper fluid management is essential to preventing contamination and maintaining the performance of the hydraulic press. Some common preventive measures include:
- Using high-quality filters: Installing filters in the hydraulic system helps remove contaminants from the fluid before they can cause damage. Regularly inspecting and replacing filters is crucial to preventing contamination.
- Proper fluid handling: When adding or replacing hydraulic fluid, it is important to ensure that the new fluid is clean and free of contaminants. Using clean containers and handling the fluid in a controlled environment can prevent contamination.
- Seal maintenance: Ensuring that seals and gaskets are in good condition can prevent external contaminants from entering the system. Regular inspection and replacement of seals are essential for maintaining system integrity.
EMS Metalworking Machinery: Your Trusted Partner in Precision Metalworking

EMS Metalworking Machinery is a leading manufacturer of high-quality metalworking equipment, dedicated to providing innovative solutions that meet the evolving needs of industries worldwide. With a rich history of excellence and a commitment to technological advancement, we have earned a reputation for delivering cutting-edge machinery that ensures precision, efficiency, and durability.
Our Product Range:
- CNC Spinning Lathes: From precision bench lathes to heavy-duty industrial models, our lathes offer unmatched accuracy and performance for a wide range of applications, including machining shafts, gears, and other cylindrical components.
- Trimming Beading Machine: Our trimming beading machines are designed to provide exceptional cutting capabilities and versatility, enabling you to create complex shapes and intricate details with ease. Whether you need a horizontal or vertical trimming machine, we have the perfect solution for your needs.
- Hydraulic Deep Drawing Press Machines: Our hydraulic deep drawing press machines are built to deliver precise and powerful drawing operations, ensuring clean holes and exceptional surface finishes. We offer a comprehensive range to suit various applications.
- Grinding Machines: Our grinding machines are engineered for precision and efficiency, allowing you to achieve the highest levels of surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Whether you need a surface grinder, cylindrical grinder, or tool grinder, we have the equipment to meet your specific requirements.
- Sawing Machines: Our sawing machines are designed for fast and accurate cutting of metals, providing clean cuts and minimal burrs. From band saws to circular saws, we offer a variety of options to suit different materials and cutting needs.
- Custom Machinery: In addition to our standard product line, we also specialize in custom machinery fabrication. Our experienced engineers can work with you to design and build tailored solutions that meet your unique requirements and optimize your production processes.
Why Choose EMS Metalworking Machinery:
- Quality: Our machines are crafted with the highest quality materials and components, ensuring long-lasting performance and reliability.
- Precision: We are committed to delivering machinery that meets the most stringent tolerances and standards, ensuring exceptional accuracy in your metalworking operations.
- Innovation: We continuously invest in research and development to stay at the forefront of technological advancements, offering innovative solutions that enhance your productivity and efficiency.
- Customer Support: Our dedicated team of experts is always available to provide comprehensive support, from machine selection and installation to maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Customization: We understand that every business has unique needs, and we offer flexible customization options to tailor our machines to your specific requirements.
At EMS Metalworking Machinery, we are more than just a supplier of equipment; we are your trusted partner in metalworking success. By choosing EMS, you can be confident in the quality, reliability, and performance of your machinery, enabling you to achieve your business goals and stay ahead of the competition.
EMS Metalworking Machinery
We design, manufacture and assembly metalworking machinery such as:
- Hydraulic transfer press
- Glass mosaic press
- Hydraulic deep drawing press
- Casting press
- Hydraulic cold forming press
- Hydroforming press
- Composite press
- Silicone rubber moulding press
- Brake pad press
- Melamine press
- SMC & BMC Press
- Labrotaroy press
- Edge cutting trimming machine
- Edge curling machine
- Trimming beading machine
- Trimming joggling machine
- Cookware production line
- Pipe bending machine
- Profile bending machine
- Bandsaw for metal
- Cylindrical welding machine
- Horizontal pres and cookware
- Kitchenware, hotelware
- Bakeware and cuttlery production machinery
as a complete line as well as an individual machine such as:
- Edge cutting trimming beading machines
- Polishing and grinding machines for pot and pans
- Hydraulic drawing presses
- Circle blanking machines
- Riveting machine
- Hole punching machines
- Press feeding machine
You can check our machinery at work at: EMS Metalworking Machinery – YouTube
Applications:
- Beading and ribbing
- Flanging
- Trimming
- Curling
- Lock-seaming
- Ribbing
- Flange-punching