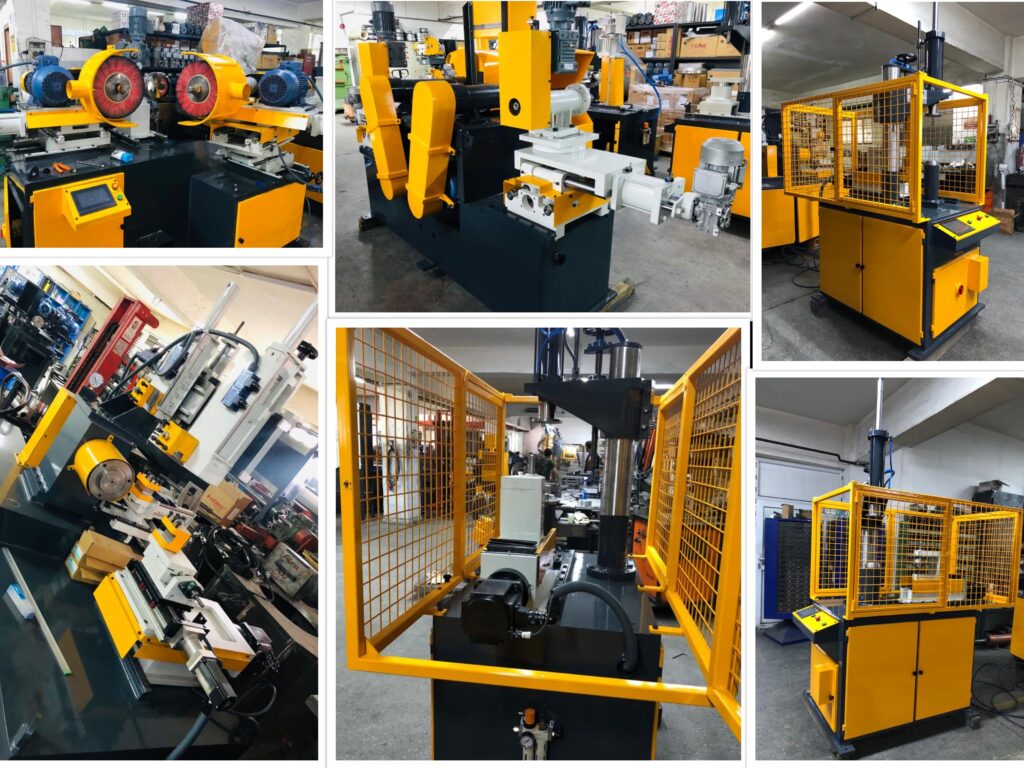

Utensil Surface Polisher and Grinder for Polishing Grinding Finishing Buffing: A Utensil Surface Polishing Machine is a specialized device used to polish and finish the surface of metal utensils—such as stainless steel plates, bowls, spoons, pots, and pans—to enhance their appearance and remove surface imperfections like scratches, oxidation, or weld marks. These machines are widely used in kitchenware manufacturing units and metal finishing industries.
Key Components
- Abrasive Polishing Wheels or Belts: Used to smooth and shine the surface of utensils.
- Motor and Drive System: Powers the rotation of the abrasive tools.
- Workpiece Holding Fixtures: Secure utensils in place during the polishing process.
- Dust Collection System: Captures metal dust and particles generated during polishing.
- Control Panel: Allows the operator to adjust speed, pressure, and cycle time.
Types of Utensil Polishing Machines
- Manual Polishing Machines: Operator handles the utensil and guides it against the rotating polishing wheel.
- Semi-Automatic Machines: Utensils are loaded manually, but polishing is controlled by a programmed cycle.
- Fully Automatic Machines: Robotic arms or rotating holders manage the entire process with minimal human intervention.
Polishing Techniques
- Dry Polishing: Uses dry abrasives and is suitable for basic finishing.
- Wet Polishing: Involves the use of water or polishing compound to reduce heat and enhance the finish.
- Buffing: A finer stage that gives a mirror-like finish using cloth wheels and polishing compounds.
Common Materials Polished
- Stainless steel
- Aluminum
- Copper
- Brass
Applications
- Commercial kitchenware manufacturing
- Hotel and catering equipment production
- Metalware finishing and refurbishing
A utensil surface polishing machine is designed to enhance the finish of metal utensils such as pots, pans, plates, and other kitchen items by removing surface imperfections, oxidation, welding marks, or scratches. The machine typically employs rotating abrasive wheels or belts to polish the surface of the utensil. These wheels can be made from materials like emery, non-woven nylon, sisal, or cotton and may be combined with various polishing compounds to achieve a smooth or mirror-like finish.
The polishing process starts with the utensil being mounted on a fixture or held manually, depending on whether the machine is manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic. In manual machines, an operator guides the utensil over the rotating abrasive. In semi-automatic versions, the machine controls the movement of the utensil but still requires manual loading and positioning. Fully automatic machines use robotic arms or rotating fixtures to handle utensils throughout the polishing cycle, often including multiple stages from coarse grit to fine buffing for a high-gloss finish.
The polishing action is driven by an electric motor that rotates the abrasives at high speeds. Operators can adjust variables such as rotation speed, pressure, and contact angle to match the utensil shape and desired finish quality. For better results and to control heat and dust generation, wet polishing may be used, involving water or a polishing slurry that also helps prevent scratching.
Dust extraction systems are commonly integrated to collect metal dust and fine particles, improving safety and cleanliness. These machines are usually made from robust materials to handle continuous operation in industrial environments. They’re widely used in kitchenware production lines, especially where a high aesthetic standard is expected, such as in cookware brands or commercial kitchen equipment manufacturing.
Overall, the utensil surface polishing machine plays a vital role in producing kitchenware that is both functional and visually appealing, combining speed, consistency, and surface quality in the final product.
These machines can be configured to handle various shapes and sizes of utensils, from flat plates to deep bowls and complex cookware forms. The adaptability often comes from interchangeable tooling, adjustable arms, and programmable motion controls, especially in CNC-based or robotic systems. Some advanced machines feature servo-controlled axes that allow precise positioning and orientation of the utensil during the polishing process, ensuring uniform surface treatment even on intricate geometries.
The efficiency and output quality of the polishing machine also depend on the type and sequence of abrasives used. Typically, a multi-stage process starts with a coarse abrasive to remove major imperfections, followed by medium-grit wheels for refining, and ends with a soft buffing wheel that applies polishing compounds like rouge or white buff to achieve a mirror finish. This sequence may be automated within a single machine or distributed across multiple stations in a production line.
Polishing machines can be integrated into broader manufacturing systems where utensils move through cleaning, forming, welding, and polishing in a continuous flow. In such setups, polishing is not just for aesthetics but also to improve corrosion resistance by smoothing the surface, reducing micro-crevices where contaminants might lodge.
Maintenance of the machine includes periodic replacement of abrasives, lubrication of moving parts, and cleaning of dust collectors and coolant systems in wet operations. Proper maintenance ensures consistent performance, minimizes downtime, and extends the life of the equipment.
In summary, utensil surface polishing machines are essential for mass-producing kitchenware with high-quality finishes. Their design and capabilities can vary from basic manual models to sophisticated, fully automated systems tailored to meet production demands and finish standards in the metal goods industry.
Rotary Shine Machine for Stainless Steel Utensils
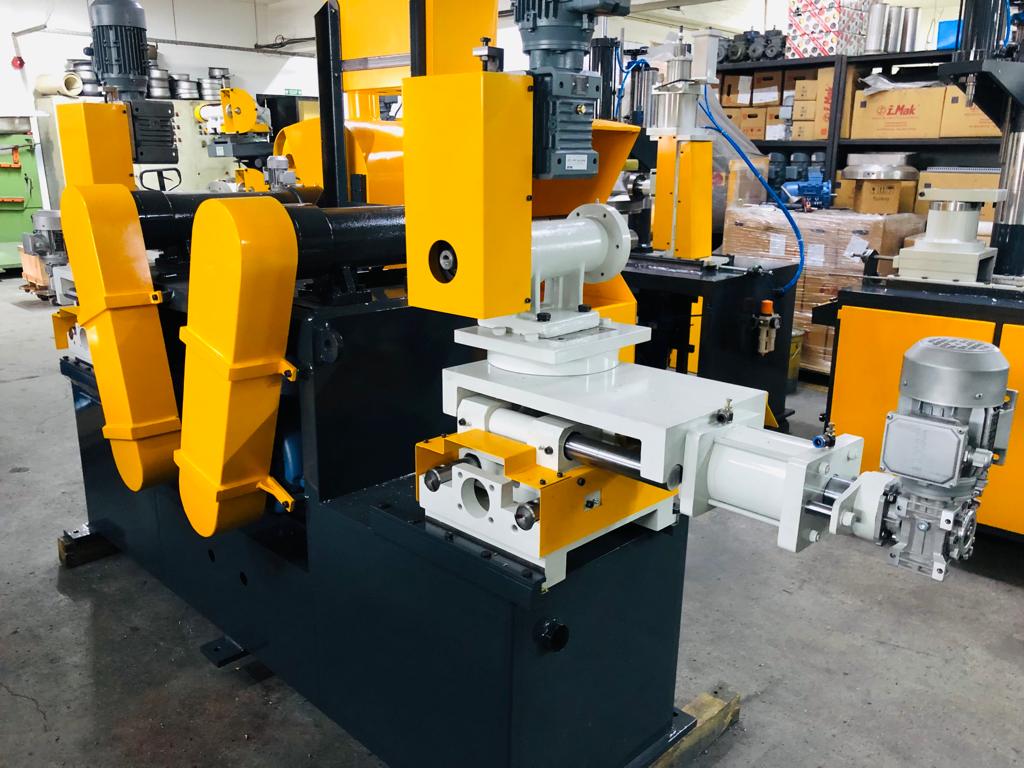

A Rotary Shine Machine for stainless steel utensils is a specialized polishing machine that uses a rotating mechanism to impart a high-gloss, mirror-like finish to various types of utensils, such as plates, bowls, cups, and cookware. These machines are widely used in the kitchenware manufacturing industry to automate and standardize the final finishing process.
The core mechanism of a rotary shine machine involves a rotary table or fixture that securely holds the utensil while rotating it against one or more polishing wheels. These wheels are typically mounted on motorized spindles and are fitted with abrasive or buffing materials depending on the stage of the polishing process. The rotation of the utensil allows even and consistent contact with the polishing wheel, ensuring a uniform finish across the entire surface, including curves and edges.
In many machines, the polishing process is divided into stages. The initial stage may involve a coarse buff to remove surface defects and oxide layers, followed by finer buffs and finally a soft cotton or felt wheel for the high-shine finish. Polishing compounds like white buff, green rouge, or tripoli may be applied to enhance the effect and protect the surface.
Rotary shine machines are available in different configurations. Some are designed for batch processing, where multiple utensils are mounted on a rotating disk, while others are set up for single-item precision polishing. Automatic versions may include pneumatic or hydraulic clamps, programmable speed controls, and adjustable polishing angles. These features help maintain consistent pressure and contact time, which are critical for achieving a quality mirror finish without overheating or deforming the utensil.
The key benefits of rotary shine machines include high throughput, consistency in finish, reduced reliance on manual labor, and the ability to handle complex utensil geometries. They also often include integrated dust collection systems and may use wet polishing methods to minimize heat buildup and control airborne particles.
In commercial manufacturing, rotary shine machines help companies meet aesthetic and hygiene standards for stainless steel products while significantly reducing production time compared to manual polishing.
The rotary shine machine operates by fixing the utensil onto a rotating head or platform that spins at a controlled speed, usually adjustable depending on the type and size of the utensil. As the utensil spins, it is brought into contact with rotating polishing wheels that may be positioned at different angles to ensure comprehensive surface coverage. The machine typically allows for the adjustment of both the utensil’s rotation speed and the polishing wheel speed, which is essential for optimizing the shine without damaging the surface due to frictional heat or excessive abrasion.
Polishing wheels used in these machines can range from abrasive-impregnated fiber wheels for the initial stages to soft cloth wheels for the final shine. Polishing compounds are often dispensed either manually or automatically during operation to enhance the smoothness and brightness of the finish. Compounds are selected based on the desired outcome—some are better for removing fine scratches, while others are designed to bring out a brilliant luster.
Rotary shine machines are especially efficient for symmetrical utensils such as plates, thalis, and bowls, where consistent rotation allows for even pressure and polish. For more complex items like pans with handles or multi-contoured items, specialized fixtures or multi-axis rotary arms may be used to maintain the correct contact with polishing tools throughout the cycle. This ensures that every part of the surface receives equal treatment, eliminating dull spots and reducing manual touch-ups after machine polishing.
In automated or semi-automated systems, programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or CNC interfaces can be used to store multiple polishing programs. This allows for quick switching between utensil types and polishing specifications, increasing productivity in high-volume production environments. Additionally, safety features like guarding, emergency stop systems, and enclosed polishing chambers help protect operators from moving parts, flying debris, or exposure to fine metal particles.
Regular maintenance is crucial for consistent performance. This includes cleaning or replacing polishing wheels, ensuring polishing compound nozzles are not clogged, checking the integrity of fixtures, and inspecting motors and belts for wear. With proper upkeep, these machines can run continuously with minimal downtime, making them ideal for manufacturers aiming for both efficiency and high product quality.
Overall, the rotary shine machine represents a balance of mechanical precision and surface finishing expertise. It allows manufacturers to deliver utensils that not only look appealing but also meet hygiene and quality standards, reflecting light evenly and resisting corrosion more effectively due to the smooth, polished surfaces.
Over time, the use of rotary shine machines has significantly transformed the stainless steel utensil manufacturing process by reducing reliance on manual polishing, which is labor-intensive, inconsistent, and prone to operator fatigue. Manual methods can also introduce variations in finish quality due to human error or inconsistent pressure, whereas rotary shine machines provide a controlled, repeatable process that ensures every item meets a uniform standard. This consistency is especially important for large production runs, where customer expectations for appearance and quality are high.
Another advantage of these machines is their adaptability. They can be customized or equipped with interchangeable heads, clamps, and polishing assemblies to accommodate a wide range of utensil shapes and sizes. Some machines can polish both the interior and exterior surfaces of hollow items, such as deep vessels or glasses, by using specialized tooling that accesses hard-to-reach areas without requiring manual repositioning. This versatility makes the machine a valuable asset for manufacturers who produce diverse product lines.
In terms of operational efficiency, rotary shine machines can be integrated into continuous production lines where utensils pass through forming, welding, cleaning, and polishing stages in a seamless sequence. Polishing time per unit can range from a few seconds to a couple of minutes, depending on the complexity of the utensil and the finish required. Faster cycle times can be achieved with dual-head or multi-station machines, which allow simultaneous polishing of multiple surfaces or multiple utensils, further increasing output.
The aesthetic value added by the mirror polish produced by rotary shine machines is not just for appearance. A highly polished stainless steel surface is easier to clean and more resistant to bacterial growth, which is critical in kitchen environments. The smoothness achieved at a microscopic level means fewer crevices for food particles or contaminants to cling to, enhancing the utensil’s hygienic properties.
Economically, while the initial investment in a rotary shine machine can be significant, the long-term gains in productivity, reduced labor costs, and lower rejection rates often make it a cost-effective solution. Additionally, machines that support automatic polishing compound feeding, dust collection, and self-cleaning features reduce the need for manual intervention and improve the working environment.
In conclusion, the rotary shine machine plays an essential role in modern utensil manufacturing, delivering not only speed and consistency but also enhancing the market appeal and functional performance of stainless steel products. Its ability to deliver flawless, mirror-like finishes with minimal human effort makes it a cornerstone technology in both large-scale manufacturing and premium kitchenware production.
Utensil Buffing & Polishing Turntable Machine

A Utensil Buffing & Polishing Turntable Machine is a specialized device designed to perform efficient, high-quality buffing and polishing of stainless steel and other metal utensils using a rotating turntable mechanism. This machine is widely used in utensil manufacturing units for mass finishing of items like plates, bowls, trays, and other cookware, providing a uniform surface finish with minimal manual effort.
The core of the machine is a motorized turntable that holds one or multiple utensils in fixed positions. As the turntable slowly rotates, polishing and buffing wheels—usually mounted on vertical or horizontal arms—make continuous contact with the utensil surface. These wheels can be loaded with various abrasive materials or polishing compounds depending on the required stage of finishing. The rotary motion of the turntable ensures even exposure of the utensil surface to the buffing tools, eliminating inconsistencies and missed areas.
This type of machine is often preferred in batch production processes due to its ability to handle several utensils simultaneously. The fixtures on the turntable are customizable and can be adapted to different utensil shapes and sizes, allowing flexibility in production. Polishing wheels are typically made from sisal, cotton, or felt and may be impregnated with polishing pastes such as green rouge, white buff, or emery bar for specific finish grades—ranging from a satin sheen to a mirror polish.
The machine may feature adjustable speeds for both the turntable and the buffing wheels. This control allows operators to fine-tune the process based on the material type, surface condition, and desired finish. For example, a slower rotation and finer buff may be used on delicate items requiring a flawless, high-gloss finish, while a faster, more aggressive setup might be chosen for initial buffing stages or to remove weld marks and deep scratches.
In more advanced versions, the buffing arms may be pneumatically or hydraulically actuated, pressing the wheels against the utensils with consistent pressure. Some systems also integrate compound dispensers that apply the polishing material automatically, improving efficiency and reducing waste. Dust collection units are often built into the machine to capture fine metal particles and compound residue, keeping the workplace clean and safe.
Turntable buffing and polishing machines significantly reduce the need for manual labor, increasing productivity and ensuring consistent output. They are particularly useful for achieving uniform finishes across high volumes of similar items, such as production runs of standard-size dinner plates or serving bowls. Moreover, their repetitive precision helps reduce rework and maintain high quality standards in the final product.
These machines can also be integrated into automated production lines where utensils are fed onto the turntable, polished, and then transferred to packaging or further processing stations without manual handling. Their versatility, speed, and quality make them a staple in the utensil manufacturing industry, especially for companies aiming to combine high throughput with superior surface finishes.
The utensil buffing and polishing turntable machine operates on a simple yet highly effective principle—by rotating the workpieces steadily beneath or against a set of motorized polishing heads, it ensures a consistent application of abrasive and buffing action across every part of the utensil surface. This continuous and even contact eliminates the variations often introduced by manual handling, resulting in a smooth and uniform finish that meets commercial standards. The turntable can typically hold several utensils at once, mounted in specially designed fixtures that grip the items firmly without damaging their surface. These fixtures are often adjustable or interchangeable to accommodate different shapes and sizes of utensils, such as flat plates, deep bowls, or irregularly contoured kitchenware.
The polishing heads themselves can be configured with various types of wheels depending on the stage of the process. For initial smoothing, coarser wheels made from sisal or abrasive-coated fabric may be used. As the process moves toward finer finishing, the wheels are replaced or followed by softer cloth buffs that are loaded with polishing compounds to bring out the mirror-like luster characteristic of high-quality stainless steel utensils. In some machines, the buffing wheels are mounted on adjustable arms that allow operators to control the angle and pressure of contact, ensuring optimal results even for utensils with complex geometries.
Speed control is another critical aspect of the machine. Both the rotational speed of the turntable and the RPM of the polishing heads can be precisely adjusted. This flexibility enables the operator to tailor the machine’s operation based on material properties, utensil thickness, and the type of finish required. For delicate, thin-walled utensils, slower speeds and lighter pressure help avoid deformation or overheating, while more robust items can withstand higher intensity polishing to remove tough blemishes or welding lines.
To maintain polishing efficiency and surface quality, the machine may include a polishing compound feeder system. This system automatically dispenses a controlled amount of compound onto the buffing wheels during operation, ensuring continuous lubrication and abrasive effectiveness without manual interruption. This also reduces wastage and keeps the process clean and efficient.
Many turntable machines are equipped with integrated dust collection systems to capture the fine particles, lint, and compound residue generated during polishing. These systems not only improve air quality and safety for operators but also reduce maintenance downtime by keeping the machine and surrounding work area cleaner.
Operators benefit from user-friendly control panels that allow easy adjustment of all machine parameters. In more advanced models, programmable logic controllers (PLCs) enable automation of entire polishing cycles, allowing for preset routines based on utensil type or finish grade. This level of automation significantly increases throughput while reducing skill dependency and training requirements.
Maintenance of the machine is relatively straightforward but essential for long-term performance. Regular tasks include checking the wear on buffing wheels, cleaning compound dispensers, inspecting rotating parts for alignment, and ensuring dust extraction systems are functioning properly. When maintained correctly, these machines offer high durability and continuous operation suitable for demanding industrial environments.
In manufacturing setups where high volume and consistent quality are priorities, the utensil buffing and polishing turntable machine becomes a critical part of the production line. Its ability to process multiple utensils at once, deliver uniform finishes, and operate with minimal manual intervention makes it not just a time-saver but also a tool for ensuring product excellence and manufacturing reliability.
As production demands increase, especially in mid- to large-scale utensil manufacturing units, the utensil buffing and polishing turntable machine proves indispensable not only for its output speed but also for the reduction of labor-intensive tasks. Workers who would otherwise be required to manually polish each item now only need to load, monitor, and unload the machine. This shift not only improves workplace safety and ergonomics by reducing repetitive motion and exposure to dust but also allows labor to be reallocated to higher-skill areas of the production process.
The machine’s capacity for repeatable accuracy means every utensil, from the first in the batch to the last, can exhibit the same surface texture and shine, which is essential for brand consistency and customer satisfaction. The mirror finish achieved by the machine not only appeals to the consumer visually but also makes utensils more resistant to stains and easier to clean—two key selling points for stainless steel cookware.
In terms of layout, the turntable machine is generally compact and designed for easy integration into a linear or U-shaped production line. Some systems may include conveyor belts or robotic arms to automate the loading and unloading process, especially where high volumes are required. With sensors and feedback mechanisms, the machine can also detect issues such as tool wear, overheating, or misalignment, alerting the operator or triggering automatic shutdowns to prevent damage or defective output.
The design of the machine can be further enhanced with soundproofing covers or enclosures to reduce operational noise levels, creating a more comfortable and compliant working environment. Lighting, visibility windows, and safety interlocks ensure that the machine remains user-friendly while still adhering to industrial safety standards. Some models also come equipped with data logging features to track production metrics, polish cycle times, and maintenance schedules, aiding in quality assurance and process optimization.
From a business standpoint, investing in a turntable buffing and polishing machine is often justified by the improved production rate, decreased scrap rates, and the high-end finish that adds value to the final product. The scalability of these machines allows manufacturers to start with a semi-automatic version and upgrade to a fully automated setup as their needs grow, making it a flexible solution for both small workshops and large factories.
In summary, the utensil buffing and polishing turntable machine represents a key advancement in the utensil manufacturing process. It blends mechanical efficiency with the fine touch needed to produce aesthetically superior and hygienically sound cookware. Its role in elevating production quality, consistency, and output capacity makes it a cornerstone of any modern kitchenware production facility.
Rotary Action Utensil Surface Smoothing Machine
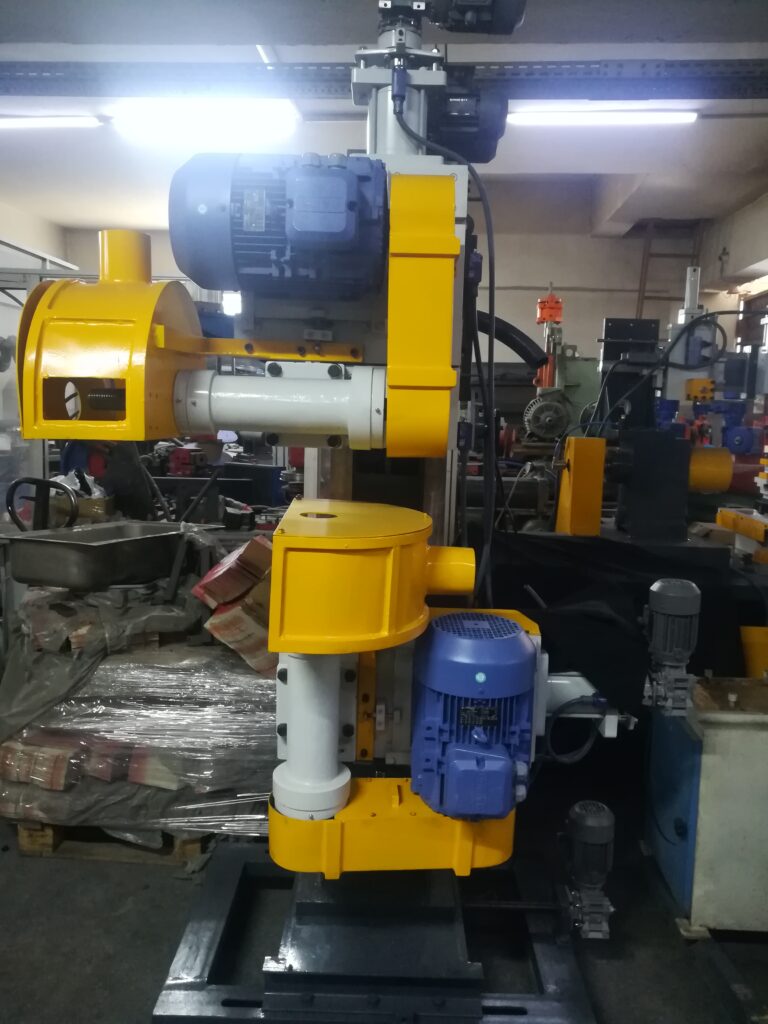

A Rotary Action Utensil Surface Smoothing Machine is an industrial device designed to smooth and finish the surfaces of metal utensils, particularly stainless steel cookware and tableware, by using a rotary motion mechanism. This machine focuses on removing surface imperfections such as scratches, weld marks, and rough spots, preparing the utensil surface for further polishing or finishing processes.
The fundamental principle of the rotary action smoothing machine involves rotating the utensil or the smoothing tool to create uniform abrasion across the surface. The machine typically features a rotary platform or chuck that holds the utensil securely while it spins. Simultaneously, one or more abrasive tools or pads—such as sanding discs, grinding wheels, or abrasive belts—are applied either directly to the utensil or positioned to engage the surface during rotation. This rotary movement ensures even coverage, reducing the risk of uneven smoothing or surface damage.
These machines are engineered to accommodate a variety of utensil shapes and sizes, from flat plates to deeper vessels and complex cookware forms. Adjustable fixtures or multi-axis rotary arms enable the machine to maintain optimal contact angles with the utensil surface, ensuring thorough smoothing even on curved or intricate parts. The speed of rotation and the pressure applied by the abrasive tools can usually be adjusted to match the material hardness and the extent of surface defects.
Rotary action smoothing machines often use abrasive media ranging from coarse grit for heavy material removal to finer grits for surface refinement. In some cases, the machine is integrated with a coolant or lubrication system to prevent overheating, reduce dust, and extend the life of abrasives. The process is highly repeatable and faster than manual surface finishing, making it ideal for medium to large-scale utensil manufacturing operations.
The primary goal of this smoothing stage is to prepare the utensil surface for subsequent polishing or buffing, creating a consistent and defect-free base. By removing roughness and minor imperfections early on, the machine helps improve the quality and durability of the final polished surface.
In addition to enhancing surface quality, the rotary action smoothing machine contributes to overall production efficiency by reducing manual labor, lowering defect rates, and shortening processing times. It is commonly integrated into production lines where utensils pass through forming, welding, smoothing, polishing, and finishing stages in sequence.
Maintenance typically involves replacing worn abrasive pads or belts, cleaning dust and debris, and checking rotational components for alignment and wear. Well-maintained rotary smoothing machines can deliver consistent performance over long production cycles, making them a valuable asset for utensil manufacturers focused on quality and productivity.
The rotary action utensil surface smoothing machine works by combining rotational movement of the utensil or the abrasive tool with controlled pressure and speed to systematically remove surface irregularities. The utensil is securely clamped onto a rotary platform or held by adjustable fixtures, which rotate it steadily to ensure the entire surface area is exposed to the smoothing media. Meanwhile, abrasive wheels, discs, or belts move into contact with the surface either from a fixed position or on moving arms, providing consistent abrasion that gradually evens out the metal’s texture.
The flexibility of the machine allows it to handle a wide range of utensil designs, from simple flat plates to complex-shaped cookware with curves, edges, and handles. This is achieved through multi-axis adjustment capabilities, enabling the abrasive heads or the workpiece to tilt, swivel, or move linearly so that every part of the utensil receives adequate smoothing. Operators can program or manually adjust the machine parameters to accommodate different materials, thicknesses, and surface conditions.
A key advantage of this machine is its ability to perform heavy material removal and surface refinement in one integrated process. Coarse abrasives remove welding seams, deep scratches, or other surface defects, while progressively finer abrasives refine the texture in preparation for polishing. Some machines include coolant systems that spray water or lubricant during operation, reducing heat buildup, minimizing dust, and extending the life of abrasive components.
The rotary action smoothing machine significantly increases production efficiency by automating what would otherwise be a labor-intensive and time-consuming manual process. Its consistent and repeatable action reduces the likelihood of surface defects, rework, and material wastage, contributing to better quality control in the manufacturing line. The smooth, uniform surface it produces serves as an ideal base for subsequent polishing or finishing steps, ensuring the final product meets both aesthetic and functional standards.
Dust and debris generated during smoothing are usually collected via integrated extraction systems, which improve workplace safety and machine longevity by preventing abrasive contamination and buildup. Operators benefit from intuitive controls, including variable speed drives and pressure settings, allowing fine-tuning of the smoothing process to meet specific production needs.
Maintenance routines typically involve inspecting and replacing abrasive pads or belts, checking alignment and wear of rotating components, and cleaning dust collection units. Proper maintenance ensures the machine operates at peak efficiency and maintains consistent output quality over extended production runs.
Overall, the rotary action utensil surface smoothing machine is a vital tool in modern utensil manufacturing, offering precision, speed, and consistency in surface preparation. Its ability to handle diverse utensil geometries and deliver uniform smoothing enhances downstream polishing and finishing processes, contributing to the production of high-quality, visually appealing, and durable kitchenware.
The integration of a rotary action utensil surface smoothing machine into a manufacturing workflow also enables manufacturers to meet increasingly stringent quality standards and customer expectations. By producing uniformly smooth surfaces free from defects, the machine helps improve not only the aesthetic appeal of utensils but also their functional performance. For example, smoother surfaces are less prone to corrosion and easier to clean, which is critical in maintaining hygiene for kitchenware.
Moreover, these machines support scalable production. They can be used in small workshops with semi-automatic controls or in fully automated, high-volume factories with robotic loading and unloading systems. The ability to customize smoothing cycles and adapt to different utensil types makes them versatile enough to serve diverse product lines without extensive downtime for changeover.
From a cost perspective, investing in rotary action smoothing machines can significantly reduce manual labor expenses and minimize material waste caused by inconsistent manual finishing. The consistency of the smoothing process also reduces the rate of rejects and rework, saving both time and resources. This, combined with faster cycle times compared to manual methods, enhances overall operational efficiency.
In terms of safety, the machine’s enclosed design and dust extraction capabilities reduce worker exposure to metal dust and particles, promoting a healthier work environment. Automation and ergonomics also reduce repetitive strain injuries associated with manual polishing and grinding.
As technology advances, newer models of rotary smoothing machines are incorporating smart features like sensors for real-time monitoring of surface quality, predictive maintenance alerts, and integration with factory management software. These innovations help maintain optimal machine performance, improve quality control, and reduce downtime.
In summary, the rotary action utensil surface smoothing machine is a cornerstone in the modern production of stainless steel and metal utensils. It delivers precise, repeatable smoothing that lays the foundation for superior polishing and finishing, enhancing both the look and longevity of kitchenware products while driving manufacturing efficiency and quality assurance.
Beyond its core functionality, the rotary action utensil surface smoothing machine often serves as a gateway technology that enables manufacturers to adopt more advanced surface finishing processes. By reliably preparing utensil surfaces with consistent smoothness, it allows subsequent steps like electro-polishing, passivation, or high-gloss buffing to be more effective and efficient. This layered approach to finishing can significantly enhance the durability, corrosion resistance, and overall appearance of the final product.
The machine’s adaptability to various abrasive materials also makes it suitable for different grades of stainless steel or even other metals such as aluminum or copper alloys used in specialty utensils. This versatility means manufacturers can diversify their product offerings without investing in multiple dedicated machines, optimizing capital expenditure and floor space.
Furthermore, the steady improvements in automation and control technology have made these machines increasingly user-friendly. Touchscreen interfaces, programmable recipes, and automated diagnostics reduce the skill level required to operate and maintain the equipment. This democratizes high-quality finishing, allowing smaller manufacturers to compete with larger players by producing products with a professional-grade surface finish.
Environmental considerations are also increasingly influencing machine design. Modern rotary action smoothing machines emphasize energy efficiency, use of recyclable consumables, and improved dust capture to minimize ecological impact. Some manufacturers incorporate water recycling systems or dry polishing technologies to reduce resource consumption and waste generation.
In the broader context of Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing, these machines are gradually being integrated into connected production lines where data from surface smoothing operations feeds into quality management systems. Real-time monitoring helps detect anomalies early, ensuring consistent output and enabling quick adjustments to maintain product standards.
Ultimately, the rotary action utensil surface smoothing machine embodies a blend of mechanical precision, process control, and operational efficiency that is essential for producing high-quality metal utensils in today’s competitive market. It not only improves product aesthetics and function but also drives productivity and sustainability goals for manufacturers worldwide.
Cookware Rotary Finishing and Buffing System
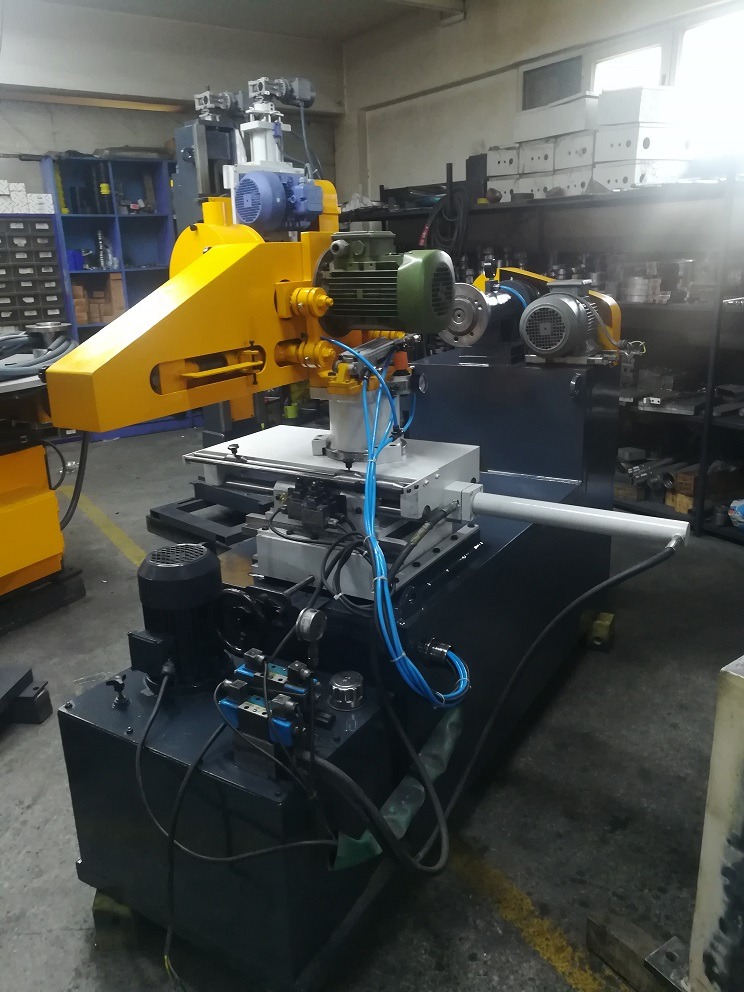

A Cookware Rotary Finishing and Buffing System is an advanced industrial machine designed to perform comprehensive surface finishing and polishing of cookware items such as pots, pans, lids, and other metal kitchenware. This system uses rotary motion combined with specialized finishing tools to deliver smooth, polished surfaces that enhance both the aesthetic appeal and functional performance of cookware.
The system typically features a rotary platform or turret that securely holds cookware pieces while they rotate. Polishing and buffing heads equipped with various abrasive wheels, brushes, or polishing pads engage the cookware surfaces during rotation. These heads may be mounted on adjustable arms that apply consistent pressure and maintain precise contact angles to ensure uniform treatment across curved, flat, and complex surfaces.
Multiple polishing stages can be incorporated within the system, starting with coarse abrasives to remove surface defects like weld marks or scratches, followed by finer polishing wheels and buffing compounds to achieve a high-gloss mirror finish. The rotary motion ensures even exposure of the cookware surface to the finishing media, preventing uneven polishing and minimizing manual labor.
Speed controls for both the rotary platform and polishing heads allow customization of the process according to cookware material, thickness, and desired finish quality. Automated compound dispensers and coolant systems may be integrated to maintain optimal polishing conditions, reduce heat buildup, and prolong consumable life.
Dust extraction and filtration units are often included to capture airborne particles and maintain a clean working environment, which is essential for operator safety and product quality.
The cookware rotary finishing and buffing system significantly boosts manufacturing efficiency by enabling continuous, consistent, and repeatable finishing operations. It is widely used in large-scale cookware production facilities where high throughput and quality standards are required.
Maintenance routines involve periodic inspection and replacement of polishing wheels, cleaning of compound dispensers and dust collection systems, and ensuring mechanical components remain aligned and properly lubricated to sustain peak performance.
Overall, this system enhances the durability, hygiene, and visual appeal of cookware by delivering smooth, corrosion-resistant surfaces that are easier to clean and more attractive to consumers, making it a vital component in modern cookware manufacturing.
The cookware rotary finishing and buffing system operates by continuously rotating cookware pieces on a sturdy platform, allowing polishing heads to maintain steady contact with the surfaces. This rotation combined with the movement of polishing wheels or brushes ensures every part of the cookware—whether it’s the curved body of a pot, the flat surface of a pan, or the intricate edges of a lid—receives uniform treatment. The precision of the system helps eliminate inconsistencies common in manual polishing, such as uneven shine or missed spots, delivering a consistent high-quality finish across all items.
The polishing heads are often mounted on adjustable arms or spindles that can be fine-tuned to apply the right amount of pressure and angle for different cookware geometries and materials. This adaptability is crucial because cookware varies widely in shape, size, and thickness, and each requires a slightly different polishing approach to avoid damage or deformation while achieving the desired finish. Some systems offer multi-axis movement to reach difficult areas or internal surfaces, increasing versatility.
To optimize the finishing process, the system typically integrates automated polishing compound dispensers that supply the right amount of abrasive or buffing paste continuously during operation. This not only improves polishing efficiency but also reduces waste and the need for manual reapplication. Coolant or lubrication systems may also be incorporated to prevent overheating, reduce friction, and extend the life of polishing consumables.
Dust and debris generated during polishing are captured by built-in extraction and filtration units, which improve operator safety by reducing airborne particles and help maintain a clean production environment. This feature is especially important given the fine metal particles and abrasive compounds involved in cookware finishing.
The entire process is controlled via user-friendly interfaces, often with programmable settings to handle different types of cookware or finish specifications. These settings enable operators to switch between rough polishing, intermediate smoothing, and final buffing cycles with minimal manual adjustment, streamlining production and reducing operator training requirements.
Maintenance of the system is straightforward and essential for consistent performance. Regular replacement of worn polishing wheels, cleaning of compound delivery systems, and inspection of moving parts ensure the machine runs smoothly and produces reliable results over long production runs.
The integration of the rotary finishing and buffing system into cookware manufacturing lines has revolutionized surface finishing by improving throughput, reducing labor costs, and ensuring consistent, high-quality finishes. Cookware finished with this system not only looks more attractive to consumers but also benefits from improved durability and ease of cleaning, which are key selling points in a competitive market.
By automating the polishing and buffing steps, manufacturers can maintain tighter quality control, reduce product returns due to surface defects, and meet higher industry standards for both aesthetics and hygiene. This system has become an indispensable tool for modern cookware manufacturers aiming to deliver superior products efficiently and reliably.
As cookware manufacturers face increasing demands for higher production volumes and superior product quality, the rotary finishing and buffing system plays a crucial role in meeting these challenges. Its automation capabilities allow for continuous operation with minimal human intervention, which not only speeds up the finishing process but also minimizes errors and inconsistencies associated with manual polishing.
The system’s modular design often allows it to be easily integrated into existing production lines or combined with other finishing equipment, such as washing stations or quality inspection units. This integration facilitates a smooth workflow from raw cookware parts to finished, market-ready products, reducing handling time and the risk of damage during transfers.
Advanced models of these systems also incorporate sensors and monitoring technology that track parameters such as polishing pressure, wheel wear, and surface finish quality in real time. This data-driven approach enables predictive maintenance, ensuring the machine operates at peak efficiency and reducing unplanned downtime. Additionally, feedback loops can automatically adjust process settings to maintain consistent finish quality even as consumables wear or product variations occur.
Energy efficiency is another focus area, with modern rotary finishing and buffing systems designed to consume less power and utilize sustainable polishing compounds. Some systems support water-based polishing solutions or employ dry polishing technologies, helping manufacturers reduce environmental impact and comply with increasingly strict regulations.
The safety features built into these machines—such as emergency stop buttons, protective guards, and noise reduction enclosures—help create a safer working environment for operators. Ergonomic designs reduce physical strain by automating repetitive and labor-intensive polishing tasks, improving worker comfort and productivity.
For manufacturers targeting premium cookware markets, the system’s ability to produce flawless mirror finishes and refined textures enhances product value and consumer appeal. This is especially important in competitive retail environments where surface quality can influence purchasing decisions.
Ultimately, the cookware rotary finishing and buffing system represents a synthesis of precision engineering, automation, and process control. It enables manufacturers to achieve high-quality surface finishes efficiently, reliably, and sustainably—helping them stay competitive in a demanding global marketplace.
Rotary Pad Polisher for Kitchen Utensils

A Rotary Pad Polisher for Kitchen Utensils is a specialized machine designed to polish and enhance the surface finish of various kitchen utensils such as spoons, forks, knives, and small cookware items. Utilizing rotary motion combined with soft polishing pads, this machine efficiently removes minor scratches, oxidation marks, and dullness, restoring a bright, smooth, and aesthetically appealing surface.
The core mechanism involves mounting the kitchen utensils securely while they are rotated either individually or in batches against rotating polishing pads made of soft materials such as felt, cotton, or microfiber. These pads are often impregnated with polishing compounds or buffing pastes that aid in gently refining the utensil surfaces without causing damage or altering their shape. The rotary action ensures consistent contact and uniform polishing over curved, flat, or intricately shaped surfaces, which are common in kitchen tools.
The machine’s speed and pressure are adjustable, allowing operators to tailor the polishing intensity according to the utensil material, thickness, and the level of surface wear. This adaptability is crucial for handling a wide range of utensils made from stainless steel, aluminum, or other metals.
Rotary pad polishers are valued for their gentle yet effective polishing action, which enhances shine while preserving fine details such as engravings or patterns on utensil handles. The compact design of these machines makes them suitable for use in both small workshops and larger manufacturing setups where space efficiency is important.
Many rotary pad polishers are equipped with dust extraction ports to capture metal particles and polishing residues, promoting a cleaner and safer working environment. User-friendly control panels simplify operation, and quick-change pad systems allow for efficient maintenance and adaptation to different polishing tasks.
In summary, the rotary pad polisher offers an efficient, consistent, and gentle solution for finishing kitchen utensils, improving their appearance and market value while streamlining the polishing process in manufacturing or refurbishment operations.
The rotary pad polisher for kitchen utensils functions by securely holding the utensils in place, either manually or with automated fixtures, while the polishing pads spin at controlled speeds. This rotary motion, combined with the abrasive action of the polishing compounds on the pads, gradually removes surface imperfections such as fine scratches, tarnish, or dullness that accumulate during manufacturing or use. Because the pads are made from softer materials, they are effective at enhancing shine without aggressive abrasion, making them ideal for delicate or intricately designed utensils where maintaining detail is important.
The machine’s adjustability in terms of rotational speed and applied pressure allows operators to fine-tune the polishing process to match the specific requirements of different utensil types and materials. For instance, thinner aluminum utensils may require gentler polishing compared to heavier stainless steel items. This flexibility ensures optimal results across a diverse range of kitchenware.
Dust and polishing residue generated during the process are typically managed through integrated extraction systems, which help maintain a clean work environment and protect operator health. The machine’s design often emphasizes ease of maintenance, with quick-change pads and accessible components that reduce downtime and improve overall productivity.
Because of its relatively compact size and focused polishing action, the rotary pad polisher fits well into production lines where final finishing or touch-ups are needed after initial surface smoothing or buffing steps. It can also be used in repair shops or refurbishment facilities to restore the appearance of used utensils, extending their useful life and reducing waste.
The consistent, high-quality finish produced by rotary pad polishers enhances not only the visual appeal of kitchen utensils but also their resistance to stains and corrosion. This makes the utensils more attractive to consumers and easier to maintain, which is a key selling point in competitive markets.
Overall, the rotary pad polisher is an essential tool for manufacturers and refurbishers looking to achieve a balance of efficiency, surface quality, and protection of delicate details on kitchen utensils, helping to elevate the finished product to commercial standards.
The use of a rotary pad polisher also contributes to improved workflow efficiency within manufacturing and refurbishment operations. By automating what would otherwise be a time-consuming manual polishing task, it allows workers to focus on other value-added processes, reducing bottlenecks and increasing overall throughput. The uniformity of the polishing action ensures that every utensil leaving the machine meets consistent quality standards, minimizing rejects and rework.
In addition, the gentle polishing provided by the rotary pads helps extend the lifespan of utensils by avoiding excessive material removal, which can weaken thin edges or delicate designs. This is especially important for premium or intricately crafted kitchenware where maintaining the integrity of the original shape and finish is critical.
Many modern rotary pad polishers come equipped with programmable controls or automated cycles, allowing for repeatable, hands-free operation. This reduces operator fatigue and the risk of human error, contributing to more predictable and reliable production outcomes. Some machines also feature interchangeable pad sizes and materials, enabling quick adaptation to different utensil shapes and polishing requirements without significant downtime.
Environmental considerations have led manufacturers to design rotary pad polishers that use water-based or eco-friendly polishing compounds, as well as improved dust collection systems to limit airborne contaminants. These features help facilities comply with health and safety regulations while reducing environmental impact.
The versatility of the rotary pad polisher makes it suitable not only for new utensil production but also for after-market services like refurbishing used or damaged kitchenware. By restoring the shine and surface smoothness of these items, refurbishers can offer cost-effective alternatives to replacement, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and reducing material waste.
In summary, the rotary pad polisher for kitchen utensils is a highly effective tool that balances efficiency, quality, and care in the polishing process. Its precision and adaptability support manufacturers and refurbishers in delivering attractive, durable, and market-ready kitchenware with minimal labor and operational cost.
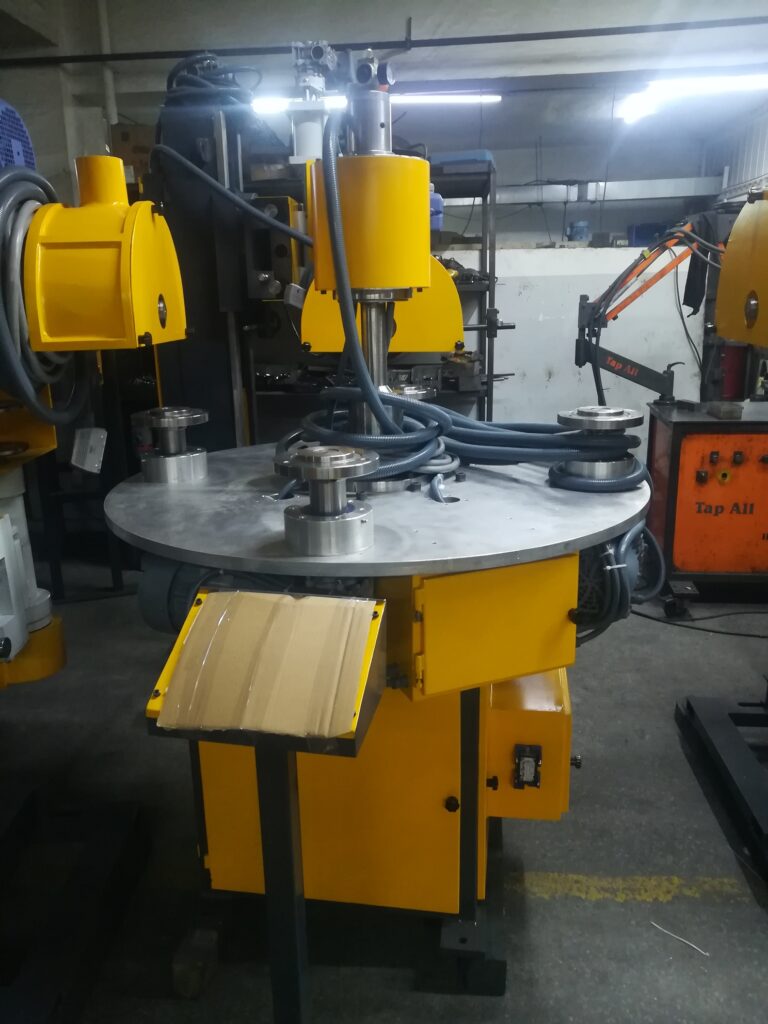
Multi-Head Rotary Utensil Polishing Machine
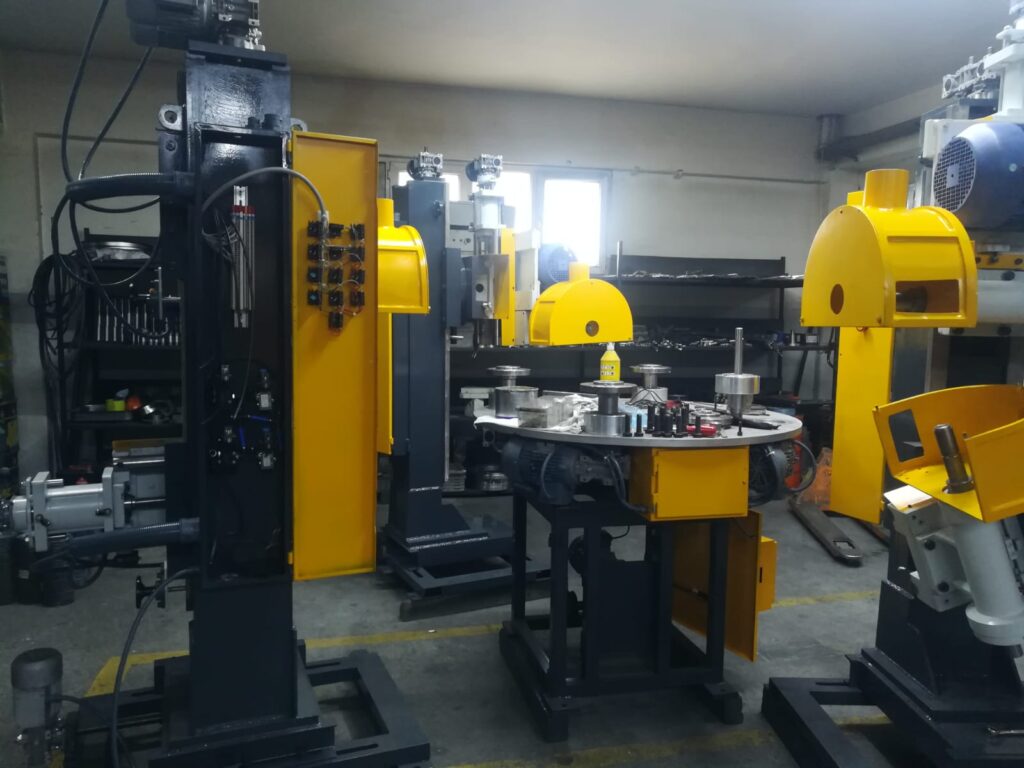

A Multi-Head Rotary Utensil Polishing Machine is an advanced industrial polishing system designed to efficiently polish multiple kitchen utensils simultaneously, significantly boosting productivity and ensuring uniform surface finishes. This machine is equipped with several polishing heads arranged around a central rotary platform or conveyor, enabling simultaneous processing of multiple items or multiple areas of a single utensil.
Each polishing head typically consists of abrasive wheels, polishing pads, or buffing brushes that rotate independently or in coordination with the main rotary mechanism. The multiple heads can be set at different angles and pressures to target various parts of utensils—such as flat surfaces, curved edges, and intricate details—allowing comprehensive polishing in a single cycle.
The machine’s rotary platform holds utensils securely, either by custom fixtures or adjustable clamps, rotating them steadily to expose all surfaces evenly to the polishing heads. This synchronized movement ensures consistent contact, eliminating polishing gaps or uneven finishes common with manual or single-head polishing methods.
Adjustable speed controls for both the rotary platform and individual polishing heads enable precise tuning to accommodate different utensil materials, shapes, and finishing requirements. Automated compound dispensers and integrated coolant systems may be incorporated to optimize polishing efficiency, reduce heat buildup, and extend consumable life.
Dust extraction and filtration units are generally built into the system to capture metal particles and polishing residues, maintaining a clean and safe working environment. User-friendly interfaces with programmable cycles allow operators to customize polishing routines for specific utensil types or batch sizes, improving process repeatability and reducing setup times.
Maintenance involves periodic inspection and replacement of polishing heads, cleaning dust collection components, and ensuring mechanical parts remain aligned and lubricated. Well-maintained multi-head rotary polishers deliver high throughput, superior finish quality, and operational reliability.
By enabling simultaneous multi-point polishing, this machine significantly accelerates production rates while delivering consistent, high-quality surface finishes. It is widely used in medium to large-scale utensil manufacturing facilities aiming to maximize efficiency, product quality, and cost-effectiveness.
The multi-head rotary utensil polishing machine operates by rotating utensils on a central platform while multiple polishing heads simultaneously work on different sections or multiple items at once. This configuration greatly reduces processing time compared to single-head or manual polishing, allowing manufacturers to increase output without compromising on quality. The synchronized movement between the rotary platform and polishing heads ensures that each utensil is uniformly polished on all exposed surfaces, reducing the risk of uneven finishes or missed spots.
Each polishing head can be independently adjusted in terms of speed, pressure, and angle, providing flexibility to handle various utensil shapes and materials. This adaptability allows the machine to polish a wide range of kitchenware, from flat spatulas and ladles to complex-shaped pots and pans, by targeting hard-to-reach areas without the need for multiple separate machines or manual intervention.
Automated systems within the machine often manage the application of polishing compounds and coolants, ensuring optimal abrasive action while minimizing waste and preventing overheating of both the utensils and the polishing components. These features contribute to extended consumable life and reduced operating costs.
The inclusion of dust extraction systems is vital in maintaining a clean workspace and protecting operators from inhaling fine metal dust and polishing residues. These systems collect debris efficiently, ensuring compliance with health and safety standards and prolonging the life of the machine by preventing buildup in critical areas.
The multi-head rotary polisher’s control interface typically allows for programming multiple polishing cycles, enabling operators to switch quickly between different utensil types or desired finish levels. This programmability supports batch production and small-lot flexibility, which is important in modern manufacturing environments that require rapid changeovers and high customization.
Maintenance of the machine is straightforward, with modular polishing heads that can be easily replaced or serviced. Regular upkeep of the dust collection units, lubrication of mechanical parts, and alignment checks help maintain consistent performance and minimize downtime.
Overall, the multi-head rotary utensil polishing machine offers a powerful combination of speed, precision, and versatility. It significantly enhances manufacturing efficiency while producing high-quality, visually appealing surfaces on kitchen utensils, making it an indispensable asset for manufacturers aiming to meet growing market demands and stringent quality standards.
The benefits of using a multi-head rotary utensil polishing machine extend beyond speed and efficiency. Its capability to deliver consistent and repeatable finishes ensures that every utensil leaving the production line meets uniform quality standards, which is critical for brand reputation and customer satisfaction. By automating multiple polishing points simultaneously, it reduces dependency on skilled manual labor, helping manufacturers maintain productivity even when experienced operators are in short supply.
The machine’s versatility also supports a wide range of production scales—from medium-sized workshops to large industrial plants—making it accessible for various business sizes. Its modular design often allows manufacturers to add or remove polishing heads as needed, adapting to changing production demands without significant capital investment.
In addition, the precise control over polishing parameters helps minimize material removal, preserving the integrity and lifespan of the utensils. This is particularly important for high-value or delicately constructed kitchenware where maintaining thickness and structural strength is essential.
Modern multi-head rotary polishers may also feature integration capabilities with factory automation and quality control systems. Real-time monitoring of process parameters and surface finish quality helps detect deviations early, reducing waste and enabling corrective actions without interrupting production.
Safety features built into the machine, such as emergency stops, protective enclosures, and noise reduction elements, contribute to a safer working environment. Ergonomic design considerations reduce operator fatigue by minimizing manual handling and repetitive motions associated with traditional polishing methods.
Environmentally, many machines incorporate energy-efficient motors, optimized abrasive usage, and advanced dust filtration to reduce ecological impact. Some systems also support the use of eco-friendly polishing compounds, aligning with growing sustainability goals in manufacturing.
In summary, the multi-head rotary utensil polishing machine represents a key technological advancement in kitchenware manufacturing. By combining automation, precision, flexibility, and safety, it enables manufacturers to produce high-quality polished utensils at scale, improving competitiveness and meeting the evolving expectations of consumers and regulators alike.
Rotary Abrasive Polishing Machine for Utensils

A Rotary Abrasive Polishing Machine for Utensils is an industrial device specifically designed to refine and enhance the surfaces of metal kitchen utensils through controlled abrasive polishing. Using rotary motion combined with abrasive materials such as polishing belts, wheels, or pads, this machine effectively removes surface imperfections like scratches, oxidation, weld marks, and roughness to produce a smooth, uniform finish.
The machine typically features a rotating platform or fixture that holds the utensils securely while exposing their surfaces to abrasive media mounted on spinning heads or drums. The abrasive components may vary in grit size depending on the polishing stage, ranging from coarse abrasives for initial surface leveling to fine abrasives for final finishing.
Adjustable parameters such as rotational speed, abrasive pressure, and feed rate allow operators to tailor the polishing process to different utensil materials (commonly stainless steel, aluminum, or copper alloys), shapes, and thicknesses. This flexibility ensures effective polishing without causing deformation or excessive material removal.
The rotary abrasive polishing machine can be equipped with multiple abrasive heads arranged to target various utensil surfaces simultaneously, accelerating processing times and improving consistency. Automated compound dispensers may apply polishing pastes or lubricants to enhance abrasive efficiency and reduce heat buildup.
Dust extraction and filtration systems are integrated to capture metal dust and abrasive debris generated during polishing, ensuring a safer and cleaner working environment while protecting machine components from contamination.
This machine is widely used in utensil manufacturing plants and refurbishment facilities to achieve high-quality surface finishes that improve the aesthetic appeal, corrosion resistance, and ease of cleaning of kitchenware. Its automated and repeatable polishing process reduces reliance on manual labor, lowers production costs, and enhances overall operational efficiency.
Routine maintenance includes replacing worn abrasive belts or wheels, cleaning dust collection units, and inspecting mechanical parts to ensure smooth operation and consistent polish quality. The rotary abrasive polishing machine represents a critical asset for manufacturers aiming to deliver durable, visually appealing utensils that meet market and regulatory standards.
The rotary abrasive polishing machine for utensils works by rotating the utensil or the abrasive heads in a controlled manner to ensure even and thorough contact between the abrasive surface and the utensil’s metal. This continuous rotary motion helps remove surface irregularities such as burrs, scratches, and discoloration, resulting in a smooth and visually appealing finish. The abrasives used can range from coarse to fine grades, allowing the machine to be used for multiple polishing stages—from initial surface preparation to final finishing—within a single setup or through sequential passes.
Operators can adjust parameters like speed, pressure, and polishing duration to match the specific characteristics of the utensils being processed. For instance, more delicate utensils require gentler polishing to avoid deformation, while sturdier items can withstand more aggressive abrasive action. This customization ensures that each type of utensil receives optimal surface treatment without compromising its structural integrity.
The machine often incorporates multiple abrasive heads positioned strategically to cover different areas of the utensil simultaneously. This multi-head arrangement boosts productivity by processing several surfaces at once and reduces the need for manual repositioning, minimizing labor and cycle time. Some models feature automated feeding and unloading mechanisms, further enhancing throughput and reducing operator intervention.
To maintain cleanliness and ensure operator safety, dust and particulate matter generated during polishing are captured by integrated extraction systems. These systems prevent metal dust from contaminating the workspace and protect machinery components from premature wear due to abrasive residue buildup.
The rotary abrasive polishing machine is commonly integrated into production lines, complementing other finishing processes such as grinding, buffing, or electro-polishing. By delivering consistent and repeatable surface finishes, it helps manufacturers meet strict quality control standards and improve product aesthetics and performance.
Regular maintenance, including timely replacement of worn abrasive materials and routine cleaning of dust extraction filters, is essential to preserve the machine’s efficiency and polish quality. Proper upkeep minimizes downtime and prolongs the lifespan of both mechanical components and consumables.
In summary, the rotary abrasive polishing machine for utensils combines precision rotary motion with adjustable abrasive application to efficiently produce high-quality polished surfaces. It plays a vital role in modern utensil manufacturing by improving finish consistency, increasing productivity, and ensuring durable, attractive kitchenware products.
The versatility of the rotary abrasive polishing machine allows it to handle a wide range of utensil types and materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. This flexibility makes it suitable not only for mass production of standard kitchen utensils but also for specialty items that require specific surface finishes or custom polishing profiles. By adjusting abrasive types and operational settings, manufacturers can achieve finishes ranging from matte to mirror-like gloss, catering to different consumer preferences and market segments.
The machine’s design often prioritizes operator ergonomics and ease of use. Intuitive control panels, safety interlocks, and protective guarding ensure that the polishing process is both safe and efficient. Quick-change abrasive systems enable rapid swapping of belts or wheels to accommodate different polishing stages without significant downtime, enhancing production flexibility.
Moreover, modern rotary abrasive polishing machines may incorporate sensors and automation technologies that monitor polishing parameters such as pressure, speed, and temperature in real time. This feedback allows for automatic adjustments during operation, ensuring consistent polish quality and reducing the likelihood of defects caused by operator error or material inconsistencies.
Environmental considerations have also influenced machine design, with many models adopting energy-efficient motors and low-waste abrasive consumables. Water-based or eco-friendly polishing compounds are increasingly used to reduce environmental impact while maintaining effective polishing performance.
In the context of the competitive kitchenware industry, the ability to produce consistently polished utensils quickly and cost-effectively offers manufacturers a significant advantage. Finished utensils with smooth, blemish-free surfaces not only appeal to consumers aesthetically but also provide functional benefits such as improved corrosion resistance and easier cleaning, which enhance product longevity and customer satisfaction.
By integrating rotary abrasive polishing machines into their production workflows, manufacturers can streamline operations, reduce labor costs, and meet stringent quality standards more reliably. This contributes to stronger brand reputation and greater market competitiveness, especially as consumer demand for high-quality, durable kitchen utensils continues to grow globally.
Circular Buffing Station for Metal Utensils

A Circular Buffing Station for Metal Utensils is a specialized finishing machine designed to polish and enhance the surface of metal kitchen utensils using a circular buffing wheel or series of wheels. This station is engineered to provide a high-gloss, smooth finish by gently removing surface imperfections, oxidation, and fine scratches, restoring the metal to a bright, mirror-like shine.
The core component is one or more circular buffing wheels made from soft materials such as cotton, felt, or muslin, which spin at high speeds. Polishing compounds or buffing pastes are applied to the wheels to facilitate the abrasion and polishing process. Metal utensils are held manually or by fixtures and pressed against the rotating buffing wheels, allowing the wheels to evenly polish the surfaces.
The circular motion of the buffing wheels ensures consistent contact over the curved and flat areas of utensils, including handles, bowls, edges, and intricate details. This method is effective for stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and other common utensil materials.
Adjustable speed controls allow operators to tailor the buffing intensity depending on the utensil material and desired finish. Safety features such as guards, emergency stops, and dust extraction systems are typically integrated to protect operators and maintain a clean working environment by capturing polishing debris and metal dust.
The circular buffing station is widely used in both small workshops and large-scale manufacturing facilities as a final finishing step to enhance product aesthetics and improve corrosion resistance. It can be standalone or part of a larger polishing line.
By automating and standardizing the buffing process, this station improves productivity, reduces manual labor, and ensures a consistent high-quality finish that increases the market value and consumer appeal of metal kitchen utensils.
The circular buffing station operates by spinning the buffing wheels at controlled speeds, allowing operators to apply consistent pressure as they guide the metal utensils against the rotating surfaces. This ensures an even polish across all parts of the utensil, including hard-to-reach curves and edges. The use of specialized buffing compounds enhances the abrasive action, helping to remove minor imperfections while producing a smooth and reflective surface finish.
Many circular buffing stations are designed with multiple wheels positioned to work on different areas of the utensil simultaneously, which increases efficiency by reducing the time required for a complete polish. These wheels may vary in texture and hardness, allowing operators to progress through different stages of polishing—from rough buffing to fine finishing—without changing equipment.
Safety and operator comfort are key considerations in the design of these stations. Protective guards prevent accidental contact with the high-speed wheels, and dust extraction systems capture metal particles and polishing residue to keep the workspace clean and minimize health hazards. Ergonomic features such as adjustable height and angled work surfaces help reduce operator fatigue during prolonged use.
The circular buffing station can be integrated into automated production lines or used as a manual finishing station, depending on the scale and requirements of the manufacturing process. Its relatively simple operation combined with effective results makes it suitable for both small workshops and high-volume factories.
In addition to improving the visual appeal of metal utensils, the buffing process also enhances functional qualities such as corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning. This adds value to the finished products and supports manufacturers in meeting stringent quality standards and consumer expectations.
Routine maintenance of the station includes replacing worn buffing wheels, cleaning dust collection filters, and checking motor and mechanical components for proper function. Well-maintained buffing stations deliver reliable performance and consistent finishing quality over long production cycles.
Overall, the circular buffing station for metal utensils is a vital piece of equipment that balances efficiency, safety, and polish quality, helping manufacturers produce attractive, durable kitchenware that stands out in competitive markets.
The circular buffing station also offers versatility in handling a variety of utensil shapes and sizes, from flat spatulas and ladles to rounded bowls and handles with intricate patterns. This adaptability is achieved through adjustable wheel positioning and interchangeable buffing pads or wheels, allowing operators to customize the polishing action to suit different metal types and surface geometries.
Because the buffing process is relatively gentle compared to abrasive grinding, it preserves the structural integrity of the utensils while enhancing their surface appearance. This is particularly important for thin or delicately designed kitchenware where excessive material removal could compromise strength or detail.
Integration with automated feeding and handling systems is common in larger manufacturing setups, further increasing throughput and reducing manual labor. Such automation can include robotic arms or conveyor systems that position utensils precisely against the buffing wheels, enabling continuous operation and minimizing downtime between batches.
Environmental considerations have influenced modern buffing stations to include energy-efficient motors and advanced dust extraction filters, which reduce power consumption and minimize airborne particulate emissions. Many facilities also use biodegradable or water-based polishing compounds to lessen environmental impact while maintaining effective surface finishing.
The consistent high-quality finish produced by circular buffing stations helps manufacturers meet demanding consumer expectations and industry standards, contributing to enhanced brand reputation and customer loyalty. Polished utensils not only look more appealing but also resist staining and corrosion better, which extends product life and satisfaction.
Training operators to use the buffing station properly is essential to maximize results and maintain safety. Proper techniques in applying pressure, selecting buffing materials, and monitoring wear on wheels and compounds ensure optimal polishing and reduce the risk of damage to the utensils or equipment.
In conclusion, the circular buffing station is an essential component in the metal utensil manufacturing process. It combines efficient polishing, adaptability, safety features, and environmental responsibility to deliver superior surface finishes that enhance both the aesthetic and functional qualities of kitchenware products.
Rotary Brushing & Buffing Equipment for Utensils

Rotary Brushing & Buffing Equipment for Utensils is specialized machinery designed to combine the cleaning, surface preparation, and polishing of metal kitchen utensils in a single, efficient operation. This equipment utilizes rotary brushes and buffing wheels to remove surface contaminants, smooth rough areas, and produce a bright, polished finish suitable for final presentation or further processing.
The brushing component typically employs abrasive or nylon brushes that rotate at controlled speeds to scrub away dirt, oxidation, scale, or light surface imperfections. These brushes are effective in cleaning complex shapes and textured areas where traditional polishing might struggle, preparing the surface for the subsequent buffing stage.
Following brushing, the buffing section uses soft, rotating wheels made from materials like cotton or felt, often combined with polishing compounds. This stage smooths the utensil’s surface and imparts a glossy finish, enhancing both aesthetics and corrosion resistance.
The equipment can be configured with multiple rotary heads positioned to work on different parts of the utensil simultaneously, improving throughput and ensuring uniform treatment. Adjustable speeds, brush types, and buffing materials provide versatility to handle various metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, or brass, and to accommodate different utensil designs and finishing requirements.
Dust extraction and filtration systems are integrated to capture debris from brushing and buffing, maintaining a clean work environment and protecting both operators and machinery from contamination. Safety features like protective guards and emergency stops are standard, ensuring safe operation.
This combination of brushing and buffing in one machine reduces handling and process time, improving production efficiency. It’s widely used in utensil manufacturing and refurbishment facilities to achieve consistent surface quality, enhance product durability, and meet consumer expectations for polished, hygienic kitchenware.
Routine maintenance involves replacing worn brushes and buffing wheels, cleaning extraction filters, and inspecting mechanical parts to sustain optimal performance and finish quality. The rotary brushing and buffing equipment represents a versatile and effective solution for achieving superior finishes on metal utensils with minimal labor and time investment.
The rotary brushing and buffing equipment streamlines the finishing process by combining two essential surface treatments into one continuous operation. The rotary brushes remove residues such as oils, oxidation, and light burrs left from previous manufacturing steps, preparing the utensil surface for a smoother and more effective buffing stage. This preparation helps the buffing wheels achieve a higher-quality shine and more uniform finish.
By using multiple rotary heads simultaneously, the machine can polish complex utensil shapes more thoroughly and efficiently than single-action machines or manual processes. Operators can adjust the speed and pressure of both brushing and buffing elements to suit different materials and desired finishes, whether aiming for a matte, satin, or mirror-like appearance. This flexibility supports a wide range of utensil types, from thick heavy-duty cookware to delicate, thin kitchen tools.
The integrated dust extraction system is crucial for maintaining air quality by capturing fine metal particles and polishing residues generated during operation. This not only protects worker health but also prevents accumulation of abrasive dust that can degrade machinery performance over time. Regular cleaning and filter replacement ensure that the system remains effective and reduces maintenance-related downtime.
Safety features like emergency stop buttons, wheel guards, and ergonomic designs help minimize operator risks and improve comfort during extended use. The ability to quickly switch out brushes and buffing wheels also reduces setup times, enabling manufacturers to adapt swiftly to changing production demands or utensil models.
In production environments, this combined brushing and buffing equipment often interfaces with automated handling systems, further accelerating throughput and reducing manual labor requirements. Automated loading and unloading mechanisms allow for continuous operation with minimal human intervention, increasing consistency and productivity.
Overall, rotary brushing and buffing equipment enhances surface quality, operational efficiency, and safety in metal utensil manufacturing. Its dual-action design reduces processing steps, lowers labor costs, and delivers polished, durable kitchenware that meets high consumer expectations for appearance and hygiene.
The versatility of rotary brushing and buffing equipment also allows manufacturers to implement customized finishing protocols tailored to specific utensil materials and end-use requirements. For example, tougher abrasives and higher brush pressures can be applied to raw or heavily oxidized surfaces to rapidly restore metal cleanliness, while gentler settings and finer buffing compounds are used for final finishing to achieve a flawless shine without damaging delicate surfaces.
This adaptability is especially valuable in mixed production lines where different utensil types—such as stainless steel spoons, aluminum pots, or brass serving trays—need distinct polishing approaches. Operators can program or manually adjust machine parameters to switch seamlessly between these different cycles, reducing changeover times and improving overall workflow efficiency.
Integration with quality control systems is another advanced feature found in some rotary brushing and buffing setups. Sensors and vision systems can monitor surface finish in real-time, detecting inconsistencies or defects and prompting automatic adjustments or alerts for manual intervention. This helps maintain consistently high-quality output while minimizing scrap and rework.
From a maintenance perspective, the equipment’s modular design often allows for quick replacement of brushes, buffing wheels, and polishing compounds. This modularity simplifies upkeep and keeps downtime to a minimum, helping manufacturers maintain continuous operation and meet production targets.
Energy efficiency and sustainability are increasingly prioritized in modern polishing equipment. Many rotary brushing and buffing machines use energy-saving motors and environmentally friendly consumables, such as water-based polishing pastes, to reduce the environmental footprint of finishing operations. Additionally, effective dust collection minimizes particulate emissions, contributing to cleaner manufacturing environments and compliance with environmental regulations.
By combining cleaning, surface preparation, and polishing into a streamlined process, rotary brushing and buffing equipment plays a crucial role in elevating the quality and durability of metal kitchen utensils. The improved finish not only enhances visual appeal but also contributes to corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning, factors that are highly valued by consumers.
Ultimately, manufacturers who invest in this technology benefit from faster production cycles, reduced labor costs, and higher-quality products, giving them a competitive edge in the kitchenware market. The machine’s balance of efficiency, precision, and safety makes it a cornerstone of modern utensil manufacturing and finishing workflows.
Rotating Head Polishing Machine for Utensils
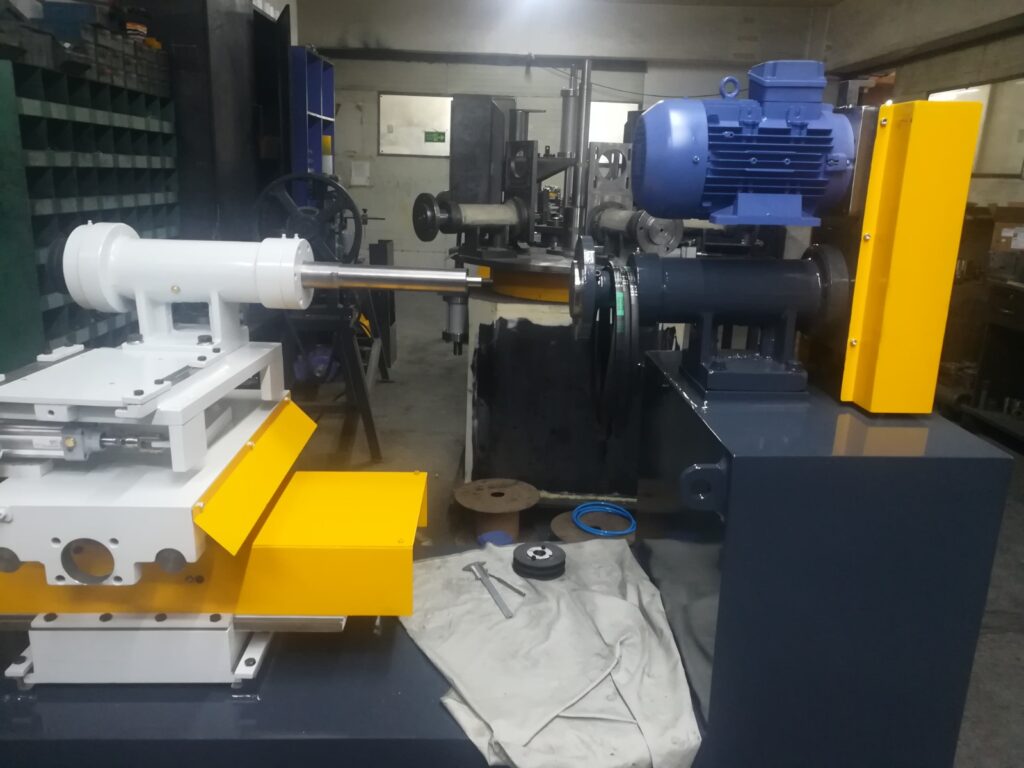

A Rotating Head Polishing Machine for Utensils is a specialized piece of equipment designed to efficiently polish metal kitchen utensils by utilizing one or more rotating polishing heads. These heads are equipped with abrasive pads, polishing wheels, or buffing materials that spin at controlled speeds to remove surface imperfections, enhance smoothness, and impart a high-quality finish.
The rotating heads are mounted on adjustable arms or spindles, allowing them to move and conform to the contours of various utensil shapes, including curved surfaces, edges, and intricate details. This flexibility ensures thorough polishing coverage across all areas of the utensil, from flat surfaces to complex curves, which is especially important for items like ladles, spatulas, and serving spoons.
Operators can control parameters such as rotational speed, pressure applied by the polishing heads, and polishing duration to customize the finish according to the utensil’s material and desired surface quality. Common polishing materials used include felt, cotton, or foam wheels paired with specific polishing compounds tailored to stainless steel, aluminum, or brass.
The machine often features a robust frame and ergonomic design, providing stable and safe operation while minimizing operator fatigue. Safety mechanisms like protective guards, emergency stop buttons, and dust extraction systems are integrated to ensure workplace safety and maintain cleanliness by capturing metal dust and polishing residue.
Rotating head polishing machines can be configured with single or multiple polishing heads, enabling simultaneous polishing of several utensil surfaces or multiple utensils at once. This multi-head setup enhances productivity by reducing cycle times and improving throughput without compromising finish quality.
Used extensively in utensil manufacturing and finishing shops, these machines offer a balance of precision, speed, and flexibility. They are capable of producing finishes ranging from matte to mirror-like gloss, meeting various market demands and quality standards. Maintenance is straightforward, focusing on replacing worn polishing heads and ensuring the smooth operation of mechanical parts.
In summary, the rotating head polishing machine is an essential tool for manufacturers seeking consistent, high-quality surface finishes on metal kitchen utensils. It combines advanced polishing technology with operator-friendly features to improve efficiency, product appeal, and production scalability.
The rotating head polishing machine operates by spinning the polishing heads at high speeds while the utensil is held steadily against them or moved through the machine using fixtures or conveyors. This continuous rotary motion ensures even abrasion and polishing across the utensil’s surface, effectively removing scratches, weld marks, discoloration, and other imperfections. The adaptability of the polishing heads allows them to reach tight corners and curved areas that might be difficult to polish manually, resulting in a more uniform and professional finish.
Adjustability is a key feature, enabling operators to fine-tune speed, pressure, and polishing time according to the specific material and design of each utensil. Softer metals or thinner utensils require gentler handling, while sturdier items can withstand more aggressive polishing to achieve a brighter shine. The ability to switch polishing wheels and compounds easily also allows the machine to accommodate various stages of finishing, from initial surface smoothing to final high-gloss buffing.
Safety is prioritized through the inclusion of protective shields around rotating components, emergency stop controls, and efficient dust extraction systems that capture fine metal particles and polishing debris. These features help maintain a clean and safe working environment, reducing health risks and protecting machinery from contamination.
The machine’s design often incorporates ergonomic considerations, reducing operator strain by minimizing manual handling and repetitive motions. Automation options such as programmable cycles, automatic feeding, and unloading further enhance productivity and reduce labor costs. In large-scale production environments, multiple rotating heads can work simultaneously on different utensil areas or multiple utensils, significantly increasing output without sacrificing finish quality.
Routine maintenance includes inspecting and replacing worn polishing pads or wheels, cleaning dust collection filters, and ensuring that mechanical components operate smoothly. Proper upkeep extends the lifespan of the machine and maintains consistent polishing performance.
In conclusion, the rotating head polishing machine is a versatile and efficient solution for producing high-quality polished finishes on metal kitchen utensils. Its combination of precise control, safety features, and automation capabilities makes it an indispensable asset in modern utensil manufacturing, helping businesses meet customer demands for attractive, durable, and hygienic kitchenware.
The rotating head polishing machine’s versatility extends to handling a wide range of utensil sizes and shapes, from small teaspoons to large serving ladles and cookware lids. Its adjustable heads and adaptable polishing materials enable manufacturers to tailor the process for different metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper alloys, ensuring optimal results across diverse product lines.
Manufacturers benefit from the machine’s repeatability and consistency, which minimize variations in surface finish that can occur with manual polishing. This consistency is crucial for maintaining high-quality standards, meeting industry certifications, and satisfying consumer expectations for aesthetically pleasing and durable utensils.
In addition to surface enhancement, the polishing process can improve the functional properties of utensils by reducing surface roughness, which helps inhibit corrosion and makes cleaning easier. This contributes to the longevity and hygiene of kitchenware, important factors in both commercial and home cooking environments.
Integration with upstream and downstream processes, such as washing, drying, or packaging, is often possible, creating streamlined production lines that reduce handling time and labor costs. Some advanced models include programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs) that enable operators to customize polishing cycles, monitor machine status, and diagnose issues remotely.
The machine’s design also facilitates scalability, allowing manufacturers to add more polishing heads or integrate multiple units as production demands grow. This modularity supports business expansion without requiring complete overhauls of finishing infrastructure.
Training operators on the correct use of rotating head polishing machines is important to maximize efficiency and prevent damage to both utensils and equipment. Proper techniques in adjusting pressure, selecting polishing materials, and maintaining the machine help ensure consistent high-quality finishes and extend the machine’s operational lifespan.
Overall, the rotating head polishing machine plays a vital role in modern utensil manufacturing by combining precision, efficiency, and flexibility. It helps manufacturers produce visually appealing, durable, and hygienic kitchenware that stands out in a competitive market while optimizing production workflows and reducing costs.
Rotary Wheel Buffing Machine for Cookware
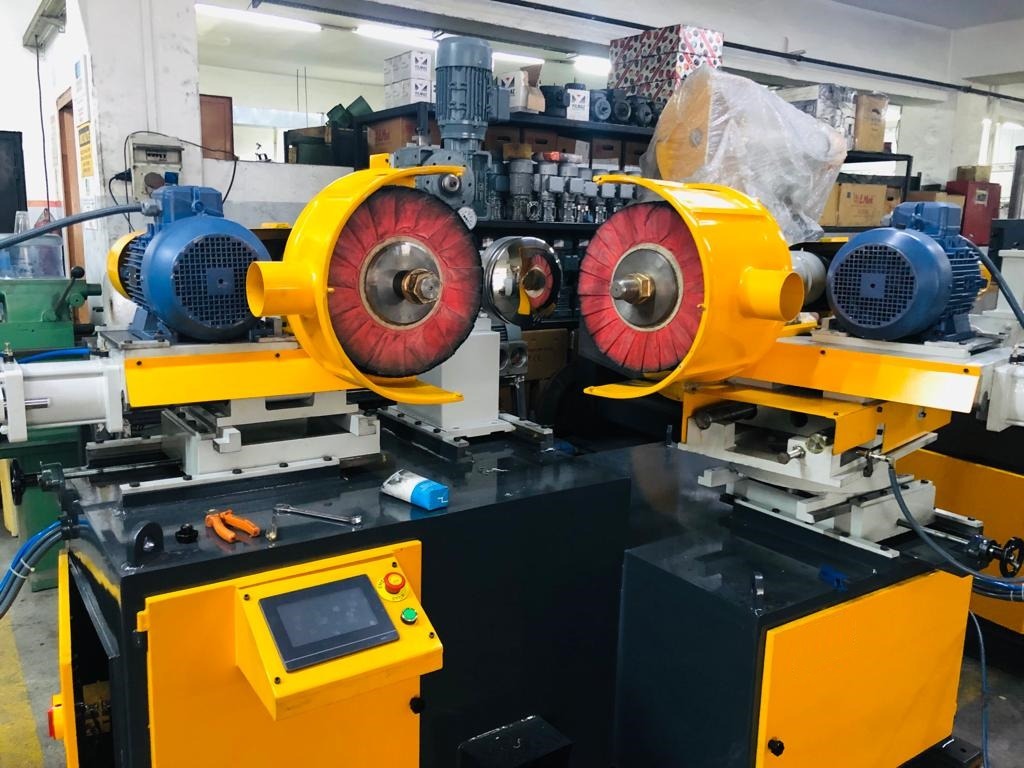

A Rotary Wheel Buffing Machine for Cookware is a specialized polishing device designed to enhance the surface finish of metal cookware such as pots, pans, lids, and other kitchen vessels. This machine employs one or more high-speed rotating buffing wheels, typically made of soft materials like cotton, felt, or muslin, combined with polishing compounds to produce a smooth, shiny, and aesthetically appealing finish on cookware surfaces.
The buffing wheels rotate continuously, and cookware items are either manually or mechanically pressed against them, allowing the wheels to remove surface imperfections, oxidation, minor scratches, and residues left from manufacturing or usage. This process restores the cookware’s natural luster and can also improve corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning.
The machine is often equipped with adjustable speed controls, enabling operators to fine-tune the rotation speed of the buffing wheels according to the type of cookware material—such as stainless steel, aluminum, or copper—and the desired finish quality. Some models feature multiple buffing wheels arranged side-by-side or in stacked configurations, allowing simultaneous polishing of different cookware parts or different polishing stages in one pass.
Safety features like protective guards, dust extraction systems, and emergency stop buttons are integrated to ensure operator safety and maintain a clean working environment by capturing polishing dust and metal particles generated during operation.
Rotary wheel buffing machines are used extensively in cookware manufacturing and refurbishment facilities. They contribute significantly to improving the visual appeal and surface quality of cookware, meeting consumer expectations for shiny, smooth, and durable kitchen products.
The machine’s design may include ergonomic considerations to reduce operator fatigue, and some models incorporate automation elements such as conveyor feeding systems or robotic arms to increase throughput and reduce manual labor.
Maintenance of the machine involves regular replacement of worn buffing wheels, cleaning of dust collection filters, and lubrication of mechanical parts to ensure smooth and efficient operation over time.
In summary, the rotary wheel buffing machine for cookware is an essential finishing tool that combines precision, safety, and efficiency to deliver high-quality polished cookware with enhanced durability and aesthetic appeal.
The rotary wheel buffing machine functions by spinning its buffing wheels at controlled speeds, allowing operators to press cookware surfaces gently and evenly against the rotating wheels. This consistent contact removes surface defects such as scratches, weld marks, discoloration, and light corrosion, resulting in a smooth and reflective finish. The continuous rotation ensures that even curved or irregular surfaces of cookware—like rounded pan bottoms or contoured handles—are polished uniformly.
Multiple buffing wheels can be arranged to perform different stages of polishing in a single operation. For instance, one wheel may carry a coarse polishing compound to remove rough imperfections, while another applies a finer compound for a mirror-like finish. This staged approach reduces handling time and enhances production efficiency.
Adjustable speed and pressure settings allow operators to customize the process based on cookware material and thickness. Heavier gauge stainless steel cookware can withstand more aggressive buffing, while delicate aluminum or copper pieces require gentler treatment to avoid surface damage.
Integrated dust extraction systems play a crucial role in maintaining a clean workspace by capturing fine metal particles and polishing residues produced during buffing. This protects operator health, minimizes contamination risks, and extends the lifespan of the machine by preventing buildup on moving parts.
Safety features such as shields around rotating wheels, emergency stop controls, and ergonomic workstations help prevent accidents and reduce operator fatigue during prolonged use. Some modern machines include automated loading and unloading mechanisms, allowing continuous operation and further increasing productivity.
Regular maintenance, including replacing worn buffing wheels, cleaning dust filters, and lubricating mechanical components, is essential to ensure consistent performance and prolong machine life. Proper upkeep also helps maintain the quality of the polished finish on cookware.
By enhancing both the appearance and functional properties of cookware, rotary wheel buffing machines help manufacturers deliver products that appeal to consumers’ aesthetic preferences and practical needs. The polished surfaces resist staining and corrosion better, making cookware easier to clean and more durable over time.
Overall, the rotary wheel buffing machine is a vital asset in cookware production and finishing processes, offering a reliable, efficient, and safe means of achieving high-quality polished surfaces that meet industry standards and market demands.
The versatility of the rotary wheel buffing machine also makes it suitable for a wide range of cookware sizes and shapes, from small saucepans and frying pans to large stockpots and roasting pans. Adjustable fixtures and work-holding devices can secure different cookware pieces in place during buffing, ensuring consistent pressure and contact with the buffing wheels. This adaptability reduces setup times and allows manufacturers to switch easily between product types without extensive reconfiguration.
In larger manufacturing facilities, rotary wheel buffing machines are often integrated into automated finishing lines. Conveyor systems transport cookware items through sequential buffing stations, where each wheel applies a specific polishing stage. This automation streamlines production, reduces manual labor, and ensures uniform quality across high volumes of output.
The choice of polishing compounds used with the buffing wheels is critical for achieving the desired finish and protecting the cookware material. Manufacturers select compounds based on the metal type and surface condition, ranging from mild cleaners to more abrasive polishes that can remove stubborn discoloration or surface roughness.
Energy efficiency is another focus area for modern rotary buffing machines. Advanced motors and control systems optimize power usage, reducing operational costs and environmental impact. Additionally, environmentally friendly polishing compounds and improved dust collection technologies support sustainability goals in production facilities.
Operator training is essential to maximize the benefits of rotary wheel buffing machines. Skilled operators understand how to adjust machine settings, select appropriate buffing wheels and compounds, and recognize when maintenance is needed. This expertise helps maintain consistent finish quality, minimize waste, and extend equipment longevity.
By producing cookware with a smooth, reflective surface, rotary wheel buffing machines add significant value to the final product. A polished finish not only enhances visual appeal but also improves resistance to corrosion, prevents food sticking, and facilitates easier cleaning—features highly valued by both home cooks and professional chefs.
In summary, rotary wheel buffing machines for cookware represent a critical investment for manufacturers aiming to deliver superior products efficiently and consistently. Their combination of precision, adaptability, and automation capabilities makes them indispensable tools in modern cookware production and finishing operations.
Utensil Outer Surface Rotary Polisher

A Utensil Outer Surface Rotary Polisher is a specialized machine designed to enhance the external finish of metal kitchen utensils by using rotary polishing mechanisms. This equipment focuses on polishing the outer surfaces of items such as spoons, forks, ladles, and various cooking tools, improving their appearance and surface smoothness.
The machine typically features one or more rotary polishing heads or wheels that spin at adjustable speeds, allowing operators to press the utensil’s outer surface against them. Polishing compounds may be applied to the wheels to aid in removing surface imperfections, oxidation, stains, and fine scratches, resulting in a shiny, smooth, and visually appealing finish.
The rotary action ensures consistent and even polishing around curved or flat surfaces, including handles and bowl sections of utensils. Adjustable arms or fixtures may be used to hold the utensils securely while allowing the polishing heads to reach difficult contours and edges without causing damage.
Safety features such as protective shields, emergency stop buttons, and dust extraction systems are often incorporated to protect operators from debris and airborne particles generated during polishing, while maintaining a clean working environment.
This type of rotary polisher can be configured with multiple heads or wheels to increase productivity and enable multi-stage polishing, where initial coarse polishing is followed by finer buffing for a mirror-like finish.
Ideal for both small-scale workshops and large manufacturing facilities, the utensil outer surface rotary polisher enhances production efficiency by reducing manual labor and ensuring uniform, high-quality surface finishes that meet consumer expectations for kitchenware aesthetics and hygiene.
Maintenance is straightforward and involves regular inspection and replacement of polishing wheels, cleaning of dust filters, and lubrication of moving parts to ensure reliable, long-term operation.
Overall, the utensil outer surface rotary polisher is a vital tool in utensil manufacturing and finishing processes, combining precision, safety, and efficiency to deliver superior polished products with improved durability and appeal.
The utensil outer surface rotary polisher operates by rotating polishing heads at controlled speeds, enabling consistent contact with the utensil’s exterior surfaces. This rotary motion effectively smooths out irregularities such as scratches, oxidation marks, and minor dents, restoring the utensil’s original shine and improving its overall aesthetic appeal. The polishing heads are designed to adapt to various utensil shapes, allowing for thorough finishing even on curved or contoured parts like spoon bowls or fork tines.
Adjustable settings for speed and pressure allow operators to tailor the polishing process to different materials and finish requirements. Softer metals or delicate utensils receive gentler polishing to avoid surface damage, while sturdier stainless steel or aluminum items can be treated more aggressively to achieve a brighter shine in less time. Polishing compounds applied to the rotary wheels aid in efficiently removing surface blemishes and enhancing the reflective quality of the metal.
The machine’s design often includes fixtures or clamps to securely hold utensils in place during polishing, ensuring consistent pressure and preventing accidental slippage that could cause uneven finishes or damage. For higher throughput, some models feature multiple polishing heads that work simultaneously on different parts of a utensil or several utensils at once, significantly improving production efficiency.
Dust extraction systems integrated into the machine capture fine metal particles and polishing debris generated during operation, maintaining air quality and keeping the work environment clean. Safety shields and emergency stop mechanisms protect operators from exposure to moving parts and potential hazards, promoting a safer workplace.
Maintenance involves periodic replacement of polishing wheels as they wear down, cleaning or replacing dust filters, and routine lubrication of mechanical components to maintain smooth operation. Proper maintenance ensures consistent polishing quality and extends the machine’s service life.
This rotary polisher is commonly used in utensil manufacturing, refurbishment, and finishing shops where a high-quality, uniform outer surface finish is critical. By automating the polishing process, it reduces manual labor, speeds up production cycles, and delivers polished utensils that meet stringent quality standards for appearance, hygiene, and durability.
The utensil outer surface rotary polisher also supports versatility in production by accommodating a wide range of utensil sizes and types. Adjustable holders and interchangeable polishing heads enable manufacturers to process everything from small teaspoons to large serving spoons and cooking utensils without extensive downtime for setup changes. This flexibility is valuable for mixed production lines or custom orders where different utensil designs require varied polishing approaches.
Automation features, such as programmable speed controls and timed polishing cycles, allow operators to standardize finishing processes, ensuring consistent results across batches. Some advanced models integrate sensors to monitor polishing pressure and surface condition in real-time, automatically adjusting parameters to prevent over-polishing or surface damage.
In larger manufacturing environments, multiple rotary polishers can be arranged in sequence or operated in parallel, forming an efficient polishing line that minimizes manual handling and speeds up throughput. This setup helps meet high-volume production demands while maintaining a high level of surface quality.
Energy efficiency considerations are increasingly integrated into machine design, with modern motors and control systems reducing power consumption and operational costs. Environmentally friendly polishing compounds and improved dust extraction technologies also contribute to sustainable manufacturing practices.
Operator training is essential to maximize the benefits of the utensil outer surface rotary polisher. Skilled operators can optimize machine settings for different materials and utensil geometries, troubleshoot minor issues, and perform routine maintenance to keep the equipment running smoothly.
The polished finish achieved through this rotary polishing process not only enhances the visual appeal of utensils but also improves functional qualities like corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning. Smooth, reflective surfaces resist staining and buildup, which is especially important in kitchen environments where hygiene and durability are paramount.
Ultimately, the utensil outer surface rotary polisher is a key asset in modern utensil production, combining precision, flexibility, and efficiency to produce high-quality finished products that satisfy both manufacturers’ productivity goals and consumers’ expectations for durable, attractive kitchenware.
Rotary Dish and Pot Surface Finisher
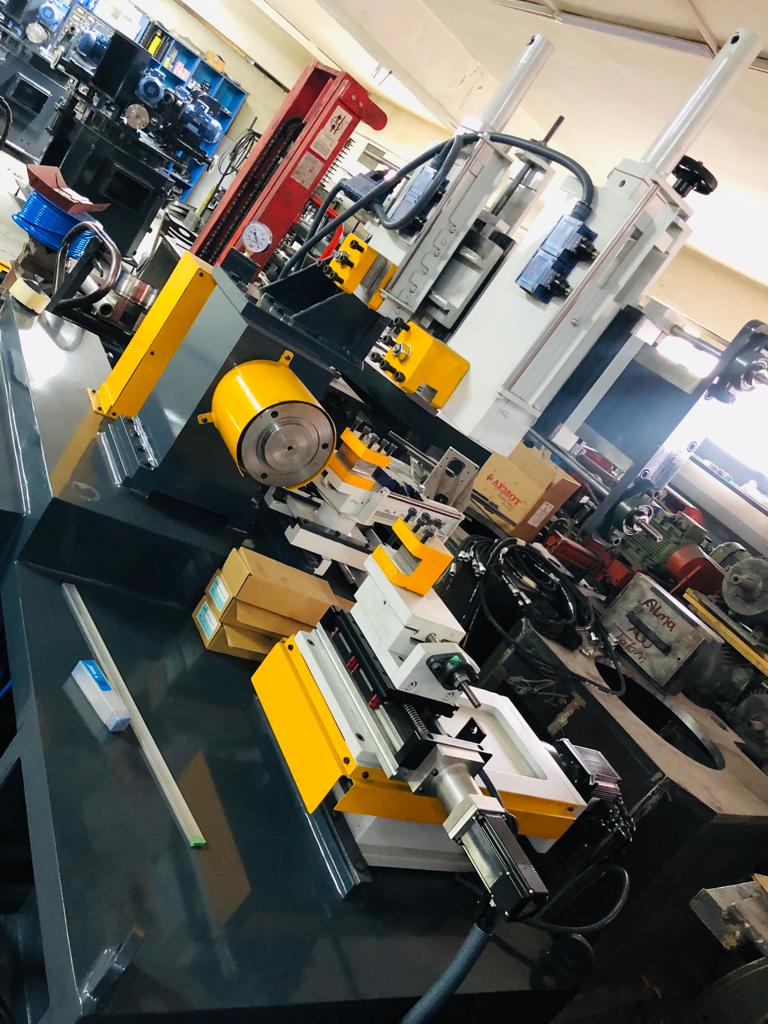

A Rotary Dish and Pot Surface Finisher is an industrial polishing machine designed specifically to enhance the exterior surfaces of dishes, pots, and similar cookware. Using one or more rotating polishing wheels or heads, this machine smooths, buffs, and polishes metal cookware surfaces to achieve a clean, uniform, and attractive finish.
The rotating polishing elements—often made from materials like cotton, felt, or foam—are spun at adjustable speeds to apply consistent friction and polishing action across the curved and flat surfaces of dishes and pots. Polishing compounds can be applied to the wheels to assist in removing surface imperfections such as scratches, weld marks, oxidation, and discoloration that occur during manufacturing or use.
This finisher is engineered to accommodate a variety of cookware sizes and shapes, from small plates and shallow dishes to large pots and deep pans. Adjustable fixtures or clamps hold items securely, while the rotary polishing heads conform to the contours of the cookware, ensuring even surface treatment without causing damage.
Safety features such as protective guards, dust extraction systems, and emergency stop buttons are integrated to safeguard operators and maintain a clean workspace by collecting polishing debris and metal dust generated during the finishing process.
The machine’s settings, including wheel speed, pressure, and polishing time, can be fine-tuned to match the cookware material—stainless steel, aluminum, or copper alloys—and the desired level of finish, ranging from matte to mirror-like gloss. Some models feature multiple polishing heads arranged to perform different finishing stages sequentially, improving efficiency and reducing handling time.
Maintenance involves regular inspection and replacement of polishing wheels, cleaning dust collection filters, and lubricating mechanical components to ensure consistent performance and prolong machine life.
By automating the polishing process, the rotary dish and pot surface finisher significantly improves production speed, reduces manual labor, and ensures consistent high-quality finishes. The resulting polished cookware is not only visually appealing but also more resistant to corrosion and easier to clean, enhancing both product durability and consumer satisfaction.
In summary, the rotary dish and pot surface finisher is an essential tool in cookware manufacturing and finishing, combining precision, efficiency, and safety to deliver superior polished kitchenware that meets industry standards and market demands.
The rotary dish and pot surface finisher operates by spinning polishing wheels at high speeds, allowing operators to press the cookware firmly yet carefully against the rotating surfaces. This consistent rotary motion removes surface flaws such as scratches, discoloration, and manufacturing residues while smoothing the metal to enhance its appearance. The design of the polishing heads allows them to adapt to various shapes and curves, ensuring that even the rounded edges and inner rims of pots and dishes receive thorough and even polishing.
Adjustable speed and pressure controls enable customization of the finishing process to suit different materials and product requirements. For example, stainless steel cookware can be polished more aggressively to achieve a bright, mirror-like shine, while softer metals like aluminum require gentler handling to avoid damage. The use of specific polishing compounds tailored to each metal type further optimizes the finish quality and protects the surface.
The machine often includes fixtures or clamps to securely hold cookware items during polishing, preventing movement that could lead to uneven finishes or damage. In higher-capacity production settings, multiple polishing heads can work simultaneously, either on different areas of a single item or on multiple items in parallel, increasing throughput without sacrificing quality.
Dust extraction systems integrated into the machine play a vital role in maintaining a safe and clean working environment by capturing fine particles and debris generated during polishing. Safety features such as guards around rotating components and emergency stop buttons protect operators from injury.
Routine maintenance, including replacing worn polishing wheels, cleaning dust filters, and lubricating moving parts, is essential to keep the machine running smoothly and ensure consistent polishing results over time. Proper maintenance also extends the equipment’s lifespan, reducing downtime and repair costs.
By automating and standardizing the finishing process, the rotary dish and pot surface finisher improves production efficiency and reduces labor intensity compared to manual polishing methods. This leads to faster turnaround times and consistent, high-quality surface finishes that enhance the cookware’s visual appeal and functional durability.
The polished surfaces produced by this machine not only look attractive but also contribute to cookware performance by improving corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning—important factors for both commercial kitchens and consumer use. The ability to deliver uniform finishes helps manufacturers meet stringent quality standards and customer expectations.
Overall, the rotary dish and pot surface finisher is a critical asset in modern cookware production lines, combining precision, flexibility, and safety to produce superior finished products efficiently and reliably. Its integration into manufacturing workflows supports high-volume output while maintaining the premium surface quality that distinguishes market-leading kitchenware.
The rotary dish and pot surface finisher’s versatility allows it to handle a broad range of cookware designs and sizes, accommodating everything from small plates and shallow dishes to large stockpots and casserole pans. Adjustable fixtures and polishing heads can be tailored to fit the contours and dimensions of each item, ensuring thorough and uniform polishing without damaging delicate edges or handles.
In large-scale production environments, these machines are often integrated into automated finishing lines. Conveyors or robotic arms feed cookware items into the polishing stations, where multiple finishing heads perform different stages of polishing sequentially. This automation reduces manual labor, minimizes handling time, and boosts overall production capacity while maintaining consistent finish quality.
The choice of polishing compounds and wheel materials is critical for achieving optimal results. Manufacturers select compounds based on the cookware material and the desired finish—ranging from satin or matte textures to high-gloss mirror surfaces. Using the correct compound and wheel combination prevents surface damage and extends the lifespan of both the cookware and the polishing equipment.
Energy-efficient motors and advanced control systems contribute to lower operational costs by optimizing power consumption during polishing cycles. Improved dust extraction technologies and environmentally friendly polishing agents also support sustainable manufacturing practices, reducing environmental impact.
Training operators on the proper use and maintenance of the rotary dish and pot surface finisher is essential to maximize productivity and product quality. Skilled operators can adjust machine settings, recognize signs of wear or malfunction, and perform routine upkeep to prevent downtime.
The polished finish achieved through this machine enhances cookware not only aesthetically but also functionally. Smooth, shiny surfaces are less prone to corrosion and easier to clean, which is highly valued in both commercial kitchens and home use. Uniform polishing also helps cookware meet regulatory and industry standards for hygiene and durability.
In conclusion, the rotary dish and pot surface finisher plays a vital role in modern cookware manufacturing by delivering efficient, consistent, and high-quality surface finishes. Its combination of precision engineering, adaptability, and automation makes it indispensable for producers aiming to compete in demanding markets with superior kitchenware products.
Rotating Table Buffing and Polishing Machine

A Rotating Table Buffing and Polishing Machine is a specialized industrial machine designed to polish and buff metal surfaces, commonly used in manufacturing and finishing processes for kitchen utensils, cookware, and other metal products. The core feature of this machine is a rotating circular table or platform on which workpieces are placed, allowing operators to move items steadily against stationary or rotating buffing wheels or polishing heads.
The rotating table enables continuous, smooth motion, which helps achieve uniform surface finishing by evenly exposing the workpiece to the polishing materials. This design is particularly effective for handling items with varying shapes and sizes, as the rotating platform can accommodate multiple products simultaneously or allow a single item to be polished evenly around all its surfaces.
Typically, the machine is equipped with multiple buffing wheels arranged around the rotating table, each carrying different polishing compounds for a multi-stage finishing process. Coarse buffing wheels might be used first to remove surface defects and oxidation, followed by finer wheels to achieve a mirror-like shine. Operators can adjust the rotation speed of the table and the pressure applied to the buffing wheels, tailoring the process to the material and finish requirements.
Safety features include protective guards around buffing wheels, emergency stop buttons, and dust extraction systems to capture polishing debris and maintain a clean work environment. Ergonomic design elements help reduce operator fatigue, making the machine suitable for extended use in high-volume production settings.
Maintenance involves regular replacement of buffing wheels, cleaning dust filters, and lubrication of mechanical parts to ensure consistent performance and prolong machine life.
The rotating table buffing and polishing machine is widely used in industries where surface finish quality is crucial, such as cookware manufacturing, metal utensil production, and decorative metalworking. It enhances the durability, corrosion resistance, and visual appeal of finished products, helping manufacturers meet quality standards and consumer expectations efficiently and reliably.
The rotating table buffing and polishing machine operates by spinning its circular platform at a controlled speed, allowing workpieces placed on it to move continuously beneath or alongside stationary polishing wheels. This steady motion ensures that every part of the surface receives consistent contact with the buffing material, reducing unevenness and producing a smooth, uniform finish. Because the table rotates, operators can easily manage the polishing process by placing items on the platform and guiding them gently toward the buffing wheels without needing to reposition the workpieces manually.
The machine often features multiple buffing stations arranged around the perimeter of the rotating table, enabling a sequential polishing process in one setup. Each station can apply different polishing compounds or abrasives to progressively refine the surface finish—from removing rough imperfections to delivering a high-gloss shine. This setup not only speeds up production but also ensures that products receive comprehensive, multi-stage finishing without additional handling.
Adjustable speed controls allow operators to fine-tune both the rotation of the table and the buffing wheels, adapting the process to different materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, or brass. The pressure applied during polishing can also be regulated, which is essential for preventing damage to delicate items while still achieving effective surface refinement on tougher materials.
Ergonomic design features, including comfortable working height and easy access to the rotating table, help reduce operator fatigue, improving efficiency and safety during long production runs. Integrated dust extraction systems capture the fine particles generated during buffing, maintaining a clean work environment and reducing health risks associated with metal dust inhalation.
Maintenance routines include regular inspection and replacement of buffing wheels as they wear down, cleaning or replacing dust collection filters, and lubricating the table’s rotational bearings and mechanical components to ensure smooth and reliable operation. Proper maintenance is critical for consistent finish quality and machine longevity.
The rotating table buffing and polishing machine is widely used in industries that require high-quality surface finishing, such as kitchenware manufacturing, metal furniture production, automotive parts finishing, and decorative metal fabrication. By automating and standardizing the polishing process, the machine enhances productivity, reduces manual labor, and delivers polished products with improved corrosion resistance, aesthetic appeal, and surface durability.
Overall, this machine provides an efficient, versatile, and safe solution for polishing a wide variety of metal products, helping manufacturers meet demanding quality standards while optimizing workflow and minimizing production costs.
The rotating table buffing and polishing machine’s adaptability allows it to handle a diverse range of product sizes and shapes, from small utensils and cookware to larger metal components. Adjustable fixtures and customizable buffing stations make it easy to switch between different items without lengthy changeovers, supporting flexible production schedules and mixed product runs.
In high-volume manufacturing settings, multiple machines can be integrated into automated finishing lines where items move through successive polishing stages with minimal human intervention. Conveyor systems or robotic arms place and remove parts from the rotating tables, further increasing throughput and reducing operator workload.
The selection of polishing compounds and buffing wheel materials is critical to achieving desired finishes and protecting the workpiece surfaces. Manufacturers tailor these choices based on metal type, surface condition, and finish specifications—whether aiming for a matte, satin, or mirror-like gloss. Using the correct combinations not only improves finish quality but also extends the lifespan of both the tooling and the polished products.
Energy-efficient motor systems and advanced electronic controls contribute to lower operating costs and reduced environmental impact. Many modern machines incorporate features such as variable frequency drives and programmable logic controllers, enabling precise control over polishing parameters and optimizing power consumption.
Operator training plays a crucial role in maximizing the benefits of the rotating table buffing and polishing machine. Skilled operators understand how to set machine parameters appropriately, identify signs of equipment wear, perform routine maintenance, and troubleshoot minor issues, all of which contribute to consistent product quality and minimal downtime.
The polished surfaces produced by this machine enhance both the functional and aesthetic qualities of metal products. Smooth finishes improve corrosion resistance, reduce dirt and grime buildup, and facilitate easier cleaning—important factors for kitchenware, automotive parts, and decorative items alike. Additionally, a high-quality polish boosts product appeal, helping manufacturers differentiate their offerings in competitive markets.
In conclusion, the rotating table buffing and polishing machine is a vital asset in modern metal finishing operations. Its combination of precision, efficiency, flexibility, and safety makes it an indispensable tool for producing superior polished surfaces, meeting stringent quality requirements, and supporting streamlined, cost-effective manufacturing processes.
Utensil Rotary Shine & Polish Machine
A Utensil Rotary Shine & Polish Machine is a specialized industrial device designed to polish and enhance the outer surfaces of kitchen utensils such as spoons, forks, ladles, and other metal tools. The machine uses rotary motion combined with polishing wheels or pads to deliver a consistent, high-quality shine and smooth finish on various utensil materials, most commonly stainless steel.
This machine typically features one or more rotating polishing heads or buffing wheels that spin at adjustable speeds. Operators hold or secure the utensils against these rotating surfaces, which are often treated with polishing compounds to remove surface imperfections like scratches, discoloration, and oxidation. The rotary action ensures even polishing coverage over curved and complex utensil shapes, reaching handles, bowls, and edges uniformly.
Adjustability is a key feature, allowing operators to control speed, pressure, and polishing time to match the specific utensil type and desired finish. This flexibility enables the machine to work effectively on different metals and utensil sizes without damaging delicate parts or over-polishing.
Ergonomic design elements help reduce operator fatigue, and safety features such as protective shields and dust extraction systems enhance workplace safety by minimizing exposure to airborne particles and debris. The dust extraction system also helps maintain a clean working environment, essential in food-related manufacturing areas.
Maintenance is straightforward and involves periodic replacement of polishing wheels, cleaning or replacing dust filters, and lubrication of mechanical parts. This routine upkeep ensures consistent polishing quality and extends the machine’s operational lifespan.
The utensil rotary shine & polish machine improves production efficiency by automating what would otherwise be labor-intensive manual polishing. It produces utensils with smooth, reflective surfaces that not only enhance aesthetic appeal but also improve corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning, important qualities for kitchenware used daily.
Ideal for both small workshops and large-scale manufacturing plants, this machine supports high-volume finishing with consistent results, helping manufacturers meet stringent quality standards and customer expectations in competitive markets.
In summary, the utensil rotary shine & polish machine combines precision, versatility, and safety to deliver superior polished finishes on metal utensils, boosting product value and manufacturing productivity.
The utensil rotary shine & polish machine works by rotating polishing heads or buffing wheels at controlled speeds, allowing operators to press the utensils against the moving surfaces for thorough polishing. The continuous rotary motion ensures even abrasion and polishing action, effectively removing surface defects such as fine scratches, oxidation, and stains, resulting in a uniform and glossy finish. The design of the polishing wheels enables them to adapt to different utensil shapes and sizes, covering flat surfaces as well as curves and edges.
Adjustable speed and pressure settings allow operators to tailor the polishing process to various metals and finishes, ensuring delicate utensils are treated gently while more robust items receive more intensive polishing. Polishing compounds are typically applied to the wheels to enhance the removal of surface imperfections and to achieve the desired level of shine.
To facilitate efficient production, the machine may include multiple polishing heads, enabling simultaneous polishing of different parts of a utensil or multiple utensils at once. Fixtures or holders can be used to secure utensils during the process, preventing slippage and ensuring consistent contact with the polishing surfaces.
Integrated dust extraction systems help capture fine metal particles and polishing debris, improving operator safety and keeping the work environment clean. Safety shields and emergency stop functions protect users from exposure to moving parts and potential hazards during operation.
Routine maintenance is essential to keep the machine operating smoothly and to maintain consistent polishing quality. This includes replacing worn polishing wheels, cleaning dust filters, and lubricating moving components. Proper maintenance minimizes downtime and extends the machine’s service life.
By automating the polishing process, the utensil rotary shine & polish machine significantly reduces manual labor, increases throughput, and produces consistently high-quality finishes. The polished surfaces not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of utensils but also improve their durability and resistance to corrosion, important factors for kitchenware longevity and hygiene.
This machine is suitable for a wide range of production environments, from small artisan workshops to large-scale manufacturing facilities. Its versatility, precision, and safety features make it a valuable asset for manufacturers aiming to deliver premium quality utensils efficiently and reliably.
The utensil rotary shine & polish machine also offers versatility in handling various utensil types and sizes, from small teaspoons and dessert forks to larger serving spoons and cooking utensils. Its adaptable design allows for quick adjustments or swapping of polishing heads and fixtures, minimizing downtime between different production batches and enabling efficient processing of mixed product lines.
In more advanced models, programmable controls and automation features help standardize polishing parameters such as speed, pressure, and duration, ensuring consistent quality across large production runs. Some machines include sensors to monitor polishing progress and surface conditions, allowing real-time adjustments that prevent over-polishing or surface damage.
For manufacturers with high output demands, multiple machines can be integrated into assembly lines where utensils are fed automatically, polished, and transferred to subsequent finishing or packaging stages. This integration streamlines workflow and maximizes productivity while maintaining high finish standards.
Energy-efficient motors and improved dust extraction technologies contribute to lower operational costs and a safer working environment, aligning with modern manufacturing sustainability goals. The use of environmentally friendly polishing compounds further supports green production practices.
Operator training is important to fully leverage the machine’s capabilities. Skilled operators understand how to optimize settings for different materials, perform routine maintenance, and quickly troubleshoot minor issues, reducing downtime and maintaining production efficiency.
The final polished finish enhances not only the visual appeal but also the practical qualities of utensils. Smooth, shiny surfaces resist tarnishing and corrosion, are easier to clean, and contribute to better hygiene — all critical for kitchen tools regularly exposed to food and moisture.
Ultimately, the utensil rotary shine & polish machine is an indispensable tool in contemporary utensil manufacturing and finishing, combining efficiency, precision, and safety to meet the demands of quality-conscious markets and ensure that products stand out in competitive retail environments.
Rotary Metalware Buffing Unit

A Rotary Metalware Buffing Unit is an industrial machine designed to polish and buff various metal products, commonly used for finishing metalware such as utensils, cookware, decorative items, hardware components, and other metal parts. The unit employs rotary motion combined with buffing wheels or pads to remove surface imperfections, enhance shine, and improve the overall surface quality of metal objects.
This machine typically features one or more rotating buffing wheels mounted on a stationary frame or a movable arm. The metal items are brought into contact with these wheels, which rotate at adjustable speeds. The rotary action, combined with abrasive compounds applied to the wheels, smooths out scratches, oxidation, discoloration, and other surface defects, resulting in a uniform, polished finish.
The buffing unit is designed to accommodate various metal types, including stainless steel, aluminum, brass, copper, and alloys. Operators can adjust parameters such as wheel speed, pressure, and polishing time to suit different materials and achieve the desired finish—from a matte surface to a high-gloss mirror polish.
Ergonomics and safety are important aspects of the rotary metalware buffing unit. The machine is often equipped with protective guards around the buffing wheels, emergency stop buttons, and dust extraction systems to capture metal particles and polishing debris, thereby maintaining a safe and clean working environment.
Maintenance involves periodic replacement of buffing wheels, cleaning dust filters, and lubricating mechanical components to ensure smooth operation and consistent finishing quality.
Widely used in metal manufacturing and finishing industries, the rotary metalware buffing unit enhances product durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal, helping manufacturers meet quality standards and consumer expectations efficiently. Its automation capabilities and precision polishing make it a valuable asset in both small workshops and large-scale production facilities.
The rotary metalware buffing unit operates by spinning one or multiple buffing wheels at controlled speeds, allowing operators to press metal items firmly yet carefully against these rotating surfaces. This continuous rotary motion ensures even and thorough polishing across the entire surface of the metalware, effectively removing imperfections such as fine scratches, oxidation, discoloration, and surface roughness. The buffing wheels, often made from materials like cotton, felt, or sisal, are typically charged with polishing compounds that enhance abrasive action and help achieve the desired finish.
The machine’s design allows it to handle a wide variety of metal shapes and sizes, from flat sheets and plates to complex curved or irregular objects like utensils, hardware fittings, and decorative metal pieces. Adjustable settings for wheel speed, pressure, and polishing duration give operators precise control over the process, enabling them to tailor the finish quality to different metal types and customer requirements.
Safety features play a crucial role, with protective guards surrounding the buffing wheels to prevent accidental contact, as well as emergency stop buttons for quick shutdown in case of hazards. Integrated dust extraction systems capture the fine metallic particles and polishing residues generated during buffing, maintaining a cleaner and healthier workspace while minimizing environmental impact.
Routine maintenance is necessary to keep the unit performing reliably, involving tasks such as replacing worn buffing wheels, cleaning or replacing dust filters, and lubricating moving parts to reduce wear and friction. Proper upkeep helps avoid production delays and maintains consistent polishing results over time.
The rotary metalware buffing unit is widely used in industries focused on metal finishing, including cookware and utensil manufacturing, automotive parts production, metal furniture fabrication, and decorative metalworking. By automating the polishing process, it reduces manual labor intensity, increases production speed, and delivers uniform, high-quality surface finishes that enhance both the visual appeal and functional durability of metal products.
Ultimately, this machine supports manufacturers in meeting stringent quality standards and customer expectations by providing efficient, precise, and safe metal polishing solutions. Its flexibility and robustness make it a valuable component of modern metal finishing operations, contributing significantly to improved product value and competitive advantage.
The rotary metalware buffing unit’s versatility allows it to adapt to various production scales, from small workshops to large manufacturing plants. Its modular design often enables the addition of multiple buffing wheels or polishing stations, facilitating multi-step polishing processes within a single unit. This configuration can include coarse buffing wheels to remove heavy surface defects, followed by finer wheels for smoothing and shining, enabling manufacturers to complete complex finishing jobs efficiently.
In high-volume settings, these units may be integrated into automated production lines, where metal components are fed continuously onto the buffing station via conveyors or robotic handling systems. This automation not only boosts throughput but also ensures consistent polishing quality by minimizing human error and maintaining precise control over process parameters.
The selection of polishing compounds and buffing wheel materials is critical to achieving optimal results. Different metals require specific abrasives and polishing agents to avoid surface damage while maximizing shine and smoothness. Manufacturers often experiment with various compound formulations to balance finishing speed, surface quality, and tool longevity.
Energy efficiency is an increasingly important consideration, with modern rotary buffing units incorporating variable speed drives and energy-saving motors to reduce power consumption. Additionally, advances in dust extraction technology improve particle capture rates and reduce noise levels, contributing to healthier workplaces and lower environmental impact.
Operator training remains essential to maximize the unit’s benefits. Skilled personnel can adjust machine settings accurately, perform preventative maintenance, and quickly troubleshoot issues, all of which help maintain production flow and consistent quality.
The polished finishes produced by the rotary metalware buffing unit improve not only aesthetics but also the functional performance of metal items. Smoother surfaces resist corrosion better, facilitate cleaning, and reduce friction in moving parts. These enhancements increase product lifespan and customer satisfaction, especially in industries such as cookware, automotive, and hardware manufacturing.
In summary, the rotary metalware buffing unit is a vital tool in metal finishing, combining precision, efficiency, and safety to deliver superior polished surfaces. Its ability to handle diverse metal products and integrate into automated workflows makes it indispensable for modern manufacturers striving for high-quality, cost-effective production.
Circular Motion Polishing Machine for Utensils

A Circular Motion Polishing Machine for Utensils is a specialized industrial machine designed to polish and finish metal kitchen utensils by applying a consistent circular or orbital motion to polishing pads or wheels. This machine is engineered to deliver smooth, even surface finishes on various utensils such as spoons, forks, ladles, and other cookware components made from metals like stainless steel, aluminum, or brass.
The core principle behind this machine is the circular or orbital movement of the polishing heads, which helps reduce uneven polishing marks and swirl patterns often caused by linear polishing methods. This motion ensures that polishing compounds are distributed evenly over the surface, producing a uniform, high-quality shine and smoothness.
Typically, the machine consists of one or more polishing pads or wheels mounted on rotating arms or spindles that move in a circular path. The utensils are held stationary or guided gently against these moving pads, allowing the circular motion to work across all surfaces, including curved and intricate areas, without causing damage or distortion.
Speed controls enable operators to adjust the rotation speed and the intensity of the polishing action, making the machine suitable for different metal types and desired finishes. The circular motion is particularly effective in reducing polishing time while enhancing surface quality, making it a popular choice in both small workshops and large-scale manufacturing environments.
Safety features such as protective guards, emergency stop switches, and dust extraction systems are integral to the machine’s design, protecting operators from flying debris and airborne polishing particles while maintaining a clean work environment.
Maintenance involves routine cleaning, replacement of polishing pads or wheels, and lubrication of moving components to ensure smooth, consistent operation and prolong machine life.
The circular motion polishing machine improves production efficiency by automating what would otherwise be time-consuming manual polishing, delivering consistent, professional-grade finishes that enhance the aesthetic appeal and functional durability of metal utensils.
Overall, this machine is an essential tool in utensil manufacturing and finishing, combining precision, efficiency, and safety to produce high-quality polished products that meet rigorous industry and consumer standards.
The circular motion polishing machine for utensils operates by moving polishing pads or wheels in a continuous orbital pattern, which evenly distributes polishing pressure across the utensil surface. This movement minimizes the risk of visible polishing lines or uneven finishes, common with straight-line or fixed rotational polishing methods. The gentle but effective circular action adapts well to the complex curves and shapes typical of kitchen utensils, reaching areas that might be difficult to polish thoroughly with traditional equipment.
Operators can control various parameters such as the speed of the orbital motion, the pressure applied, and the duration of polishing. This flexibility allows the machine to handle a wide range of metals and finishes, from light buffing to deep polishing, accommodating different product specifications and quality standards. The adjustable nature of the machine ensures delicate utensils are polished without damage, while heavier or more tarnished items can receive more intensive treatment.
The machine often features multiple polishing heads that work simultaneously or sequentially, enabling multi-stage polishing in a single operation. Polishing compounds are applied to the pads to enhance surface abrasion and shine, facilitating faster and more uniform finishing. Fixtures or holders may be used to secure utensils during the process, ensuring stability and consistent contact with the polishing surfaces.
Dust extraction systems integrated into the machine remove fine polishing residues and metal particles from the workspace, reducing health risks and maintaining cleanliness. Protective guards and emergency stop mechanisms enhance operator safety, preventing accidents around the moving parts.
Routine maintenance is necessary to keep the machine running efficiently, including regular replacement of polishing pads, cleaning of dust filters, and lubrication of mechanical components. Proper upkeep helps maintain consistent polishing results and extends the operational life of the equipment.
The circular motion polishing machine significantly increases throughput by automating the polishing process, reducing manual labor, and delivering consistent, high-quality finishes. The polished surfaces not only improve the aesthetic appeal of utensils but also enhance their corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning, important factors for kitchenware exposed to frequent use and moisture.
This machine is ideal for various manufacturing scales, from small workshops producing artisanal utensils to large factories with high-volume output. Its ability to deliver precise, efficient, and safe polishing makes it a valuable asset in modern utensil production, helping manufacturers meet stringent quality demands and customer expectations with greater speed and reliability.
The circular motion polishing machine for utensils also supports versatility in handling different utensil sizes and shapes, from small teaspoons to larger serving spoons and ladles. Its adaptable design allows quick adjustments or the interchange of polishing pads to suit specific products, minimizing downtime and enabling seamless transitions between production batches.
In advanced models, programmable controls allow operators to set and save specific polishing cycles tailored to particular utensil types or finish requirements. This automation ensures consistent quality across production runs and reduces the chance of operator error. Some machines include sensors or feedback systems that monitor polishing performance in real-time, adjusting speed or pressure as needed to maintain optimal results.
For high-volume manufacturing environments, these polishing units can be integrated into automated production lines. Conveyors or robotic systems load and unload utensils from the polishing stations, enabling continuous operation and maximizing productivity. This integration reduces manual handling, cuts labor costs, and supports more streamlined workflow management.
Energy-efficient motors and components contribute to lower power consumption and quieter operation, which benefits both operational costs and workplace comfort. Moreover, many modern machines employ eco-friendly polishing compounds and improved dust management systems that reduce environmental impact and comply with health and safety regulations.
Operator training remains crucial to fully utilize the machine’s capabilities. Skilled personnel understand how to fine-tune machine parameters, conduct preventive maintenance, and address minor technical issues promptly, ensuring consistent output quality and minimizing downtime.
The polished finishes achieved with the circular motion polishing machine enhance not only the visual appeal of utensils but also their practical performance. Smooth, reflective surfaces resist corrosion and staining better, simplify cleaning, and provide a premium look and feel that appeals to consumers.
Overall, the circular motion polishing machine is a vital piece of equipment in modern utensil manufacturing, combining precision, flexibility, and safety to produce superior polished surfaces efficiently. Its integration into manufacturing processes supports higher product quality, increased throughput, and competitive advantage in the market.
Utensil Surface Rotary Finishing System

A Utensil Surface Rotary Finishing System is an advanced industrial machine designed specifically for the surface finishing of metal utensils such as spoons, forks, ladles, and other kitchenware. This system uses rotary motion to apply polishing, buffing, or smoothing actions that improve the utensil’s surface quality, enhancing both appearance and durability.
The core of the system consists of one or more rotating finishing heads equipped with polishing wheels, brushes, or abrasive pads. These heads spin at controlled speeds and work in conjunction with polishing compounds or abrasives to remove surface defects like scratches, stains, oxidation, and uneven textures. The rotary action ensures consistent contact with the utensil surface, producing an even finish across complex shapes and curved profiles.
The finishing system typically includes adjustable settings for speed, pressure, and polishing time, allowing operators to tailor the process to different metal types and desired finish levels—from matte to mirror-like gloss. Fixtures or holders secure utensils during finishing, ensuring stability and repeatability while protecting delicate parts from damage.
Safety features such as protective shields, emergency stop buttons, and dust extraction systems are integral to the design, safeguarding operators from debris and airborne particles while maintaining a clean working environment.
Maintenance involves routine replacement of polishing media, cleaning filters, and lubricating moving parts to ensure consistent performance and extend equipment lifespan.
The utensil surface rotary finishing system improves production efficiency by automating labor-intensive manual finishing tasks, delivering uniform high-quality finishes that enhance product aesthetics and corrosion resistance. This system is widely used in both small workshops and large manufacturing facilities, enabling manufacturers to meet stringent quality standards and increase throughput while reducing operational costs.
Overall, the utensil surface rotary finishing system is a vital tool in modern utensil production, combining precision, versatility, and safety to deliver superior surface finishes that meet customer expectations and industry requirements.
The utensil surface rotary finishing system functions by rotating polishing or buffing heads at controlled speeds, allowing the abrasive media to work uniformly across the utensil’s surface. This rotary motion ensures thorough coverage of all areas, including curved or hard-to-reach sections, resulting in a smooth and consistent finish. Operators can adjust the speed and pressure applied to accommodate various metal types and surface conditions, ensuring delicate utensils receive gentle polishing while more robust items can undergo more intensive finishing.
The system often supports multiple finishing heads or stations, enabling multi-stage processing within a single unit. For example, a utensil might first pass through a coarse polishing stage to remove significant surface defects, followed by finer buffing stages to achieve the desired gloss and smoothness. This integrated approach reduces handling time and improves workflow efficiency.
To maintain product quality and operator safety, the system is usually equipped with dust extraction units that capture metal particles and polishing debris generated during finishing. Protective shields prevent accidental contact with moving parts, and emergency stop mechanisms allow for immediate shutdown in case of emergencies.
Regular maintenance is essential to sustain optimal operation. This includes replacing worn polishing wheels or pads, cleaning dust filters, and lubricating mechanical components. Timely upkeep reduces downtime and ensures consistent finishing results.
The utensil surface rotary finishing system greatly enhances manufacturing productivity by automating what would otherwise be manual, time-consuming polishing tasks. It produces utensils with uniform, high-quality surface finishes that improve corrosion resistance, ease of cleaning, and aesthetic appeal. These factors are crucial for kitchenware products, which require both functional durability and attractive presentation.
This finishing system is adaptable for various production scales, from artisanal workshops focusing on custom or small-batch items to large factories managing high-volume output. Its versatility, combined with precise control and safety features, makes it an essential asset in modern utensil manufacturing, helping companies meet demanding quality standards while optimizing operational efficiency.
The utensil surface rotary finishing system’s flexibility extends to handling a wide range of utensil shapes and sizes, from slender forks and delicate teaspoons to larger serving spoons and ladles. This adaptability is achieved through adjustable fixtures and customizable polishing heads, allowing quick changeovers between different product types and minimizing production downtime. The system can be configured to accommodate both flat and contoured surfaces, ensuring comprehensive finishing regardless of utensil design complexity.
Advanced models may include programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and digital interfaces, enabling operators to set, save, and recall specific finishing programs tailored to particular utensil materials and desired surface finishes. This level of automation not only enhances consistency across production batches but also simplifies training requirements for operators by standardizing finishing procedures.
In high-volume production environments, the rotary finishing system can be integrated into automated assembly lines. Utensils are loaded automatically via conveyors or robotic arms, processed through the finishing stages, and then transferred to subsequent production or packaging stations. This integration maximizes throughput, reduces manual handling, and supports lean manufacturing principles by minimizing waste and inefficiencies.
Energy-efficient motor designs and improved dust extraction technology contribute to lower operational costs and a safer work environment. The extraction systems efficiently capture fine polishing residues, preventing them from contaminating the workspace or posing health hazards to operators. Noise reduction features are also incorporated in some models to improve operator comfort.
Operator training remains a key factor in achieving optimal results with the system. Well-trained operators can fine-tune machine settings for different metals and finishes, perform preventive maintenance, and quickly address any technical issues, thus reducing downtime and maintaining product quality.
The polished finishes produced by the rotary finishing system not only enhance the visual appeal of utensils but also improve their functional characteristics. Smooth, reflective surfaces resist corrosion better, are easier to clean, and contribute to overall product longevity—critical attributes for utensils used in demanding kitchen environments.
In conclusion, the utensil surface rotary finishing system is an essential tool in modern utensil manufacturing, combining precision, efficiency, and safety. Its ability to deliver high-quality, consistent finishes while supporting scalable production makes it indispensable for manufacturers aiming to meet rigorous industry standards and consumer expectations in a competitive market.
Rotary-Type Buffing Machine for Kitchenware
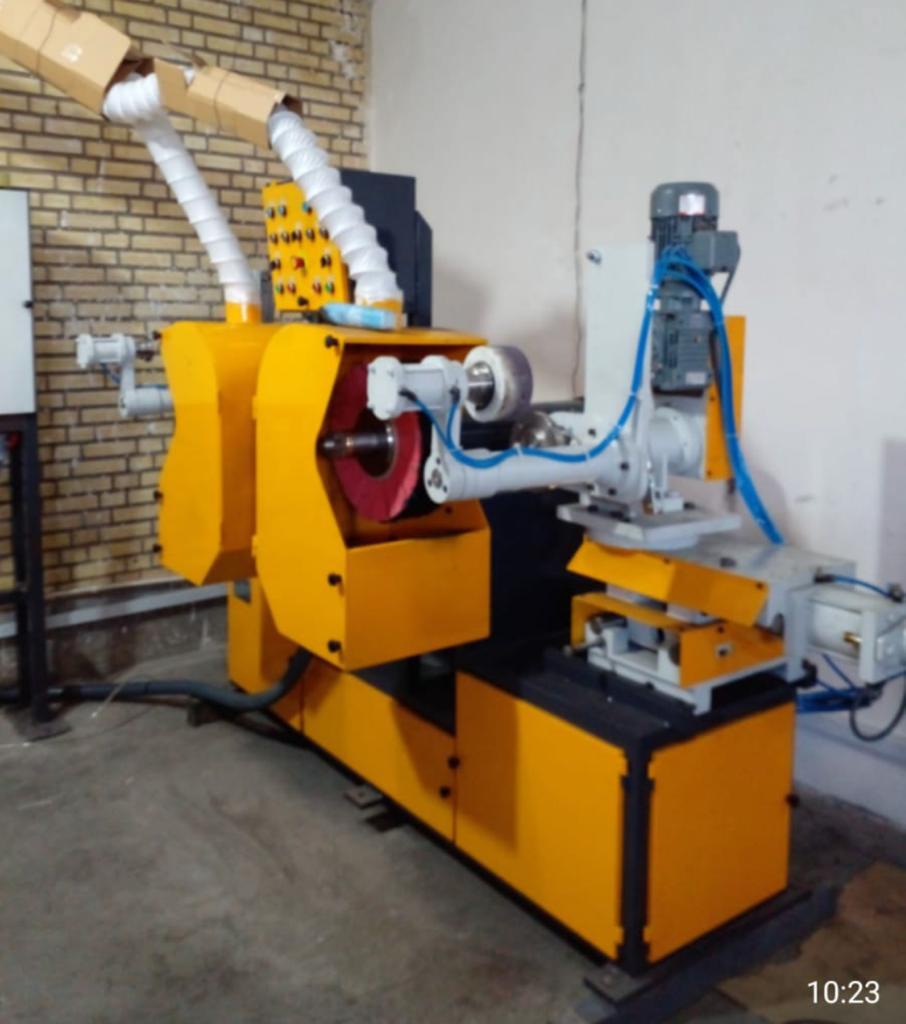

A Rotary-Type Buffing Machine for Kitchenware is a specialized industrial machine designed to polish and buff various kitchenware items, such as pots, pans, utensils, and other metal cookware. This machine uses rotary motion—where buffing wheels or polishing pads spin around an axis—to remove surface imperfections and impart a smooth, shiny finish to metal surfaces.
The machine typically consists of one or multiple rotating buffing wheels mounted on a sturdy frame. These wheels are often made from materials like cotton, sisal, or felt and are coated with polishing compounds tailored to the specific metal type, such as stainless steel, aluminum, or brass. The rotary action combined with the abrasives helps to efficiently smooth out scratches, stains, oxidation, and other surface blemishes.
Operators press kitchenware items against the rotating buffing wheels, applying controlled pressure to achieve uniform polishing. Adjustable speed controls allow for fine-tuning of wheel rotation speed, ensuring the right balance between aggressive material removal and delicate finishing, which is crucial for different kitchenware materials and thicknesses.
The rotary-type buffing machine enhances production efficiency by automating a traditionally manual process, reducing labor intensity, and delivering consistent, high-quality finishes. It is equipped with safety features such as protective guards, emergency stop buttons, and integrated dust extraction systems to capture polishing debris and metal particles, creating a safer and cleaner work environment.
Maintenance of the machine involves regular replacement of buffing wheels, cleaning of dust extraction filters, and lubrication of moving parts to ensure smooth operation and prolong equipment life. The versatility of the rotary buffing machine allows it to handle a wide range of kitchenware shapes and sizes, from flat pans to intricately shaped utensils.
Overall, the rotary-type buffing machine is an essential tool in kitchenware manufacturing and finishing, offering precise, efficient, and safe polishing that improves both the aesthetic appeal and functional durability of metal cookware and utensils.
The rotary-type buffing machine for kitchenware operates by spinning buffing wheels at controlled speeds, allowing operators to apply kitchenware items directly against the rotating surfaces. This rotary motion ensures even and consistent polishing over the entire surface, including curved or intricate areas, resulting in a uniform finish that enhances both appearance and durability. The combination of wheel material and polishing compounds is carefully selected to match the specific metal type, optimizing the removal of surface imperfections such as scratches, oxidation, and dullness without causing damage.
Adjustability is a key feature of this machine, with controls for wheel speed and pressure enabling operators to customize the buffing process according to the material thickness, hardness, and desired finish. This flexibility allows for polishing a wide variety of kitchenware, from lightweight aluminum pots to heavier stainless steel pans, ensuring each item receives the appropriate treatment.
Safety mechanisms like protective guards shield the operator from accidental contact with the spinning wheels, while emergency stop buttons allow for quick shutdown if needed. Integrated dust extraction systems efficiently capture fine metal particles and polishing debris, reducing airborne contaminants and maintaining a clean work environment that protects operator health.
Routine maintenance is crucial to keep the machine functioning smoothly. This involves replacing worn buffing wheels, cleaning or changing dust filters regularly, and lubricating bearings and other moving parts to minimize friction and wear. Proper upkeep ensures consistent polishing quality and extends the machine’s service life, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
By automating the buffing process, the rotary-type buffing machine significantly boosts production speed and consistency compared to manual polishing methods. It reduces labor intensity and operator fatigue while producing high-quality finishes that improve the kitchenware’s corrosion resistance, ease of cleaning, and overall market appeal.
The machine’s adaptability makes it suitable for use in various production environments, from small artisan workshops producing limited batches to large-scale manufacturing plants requiring high throughput and uniform quality. Its capability to handle different kitchenware sizes and shapes adds to its versatility and value in modern metal finishing operations.
In summary, the rotary-type buffing machine is a vital asset in kitchenware manufacturing, combining precision, efficiency, and safety to deliver superior polished surfaces. Its use enhances product quality and durability while optimizing production workflows, helping manufacturers meet competitive industry standards and customer expectations.
The rotary-type buffing machine’s ability to deliver consistent, high-quality finishes also contributes to reducing the need for rework or scrap, thereby saving material costs and improving overall manufacturing efficiency. By maintaining tight control over polishing parameters such as wheel speed, pressure, and polishing compound application, the machine ensures repeatable results that align with product specifications and quality standards.
In addition, many modern rotary buffing machines feature ergonomic designs to improve operator comfort and reduce strain during extended use. Adjustable work rests, optimized wheel placement, and vibration-dampening components all contribute to a safer and more user-friendly working environment. This focus on ergonomics helps enhance productivity by minimizing fatigue and the risk of repetitive strain injuries among operators.
The integration of automation and digital controls in some rotary buffing machines further elevates their capabilities. Programmable settings allow operators to easily switch between different polishing cycles tailored for various kitchenware types and finishes, improving workflow efficiency and reducing setup times. Advanced models may also include monitoring systems that track machine performance and alert maintenance personnel when service is needed, preventing unexpected downtime.
Environmental considerations are increasingly influencing machine design, with manufacturers incorporating energy-efficient motors and improved dust collection technologies to reduce power consumption and emissions. The adoption of eco-friendly polishing compounds and waste management practices aligns with broader sustainability goals and regulatory compliance.
Ultimately, the rotary-type buffing machine plays a crucial role in ensuring that kitchenware products meet both aesthetic and functional demands. The polished surfaces not only enhance visual appeal but also contribute to corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning, factors that are especially important in cookware subjected to frequent use and exposure to moisture and heat.
By combining precision engineering, adaptable operation, and safety features, the rotary buffing machine remains a cornerstone of modern kitchenware finishing processes. Its ability to increase productivity, improve product quality, and support sustainable manufacturing makes it indispensable for businesses aiming to compete in a demanding global market.
Metal Surface Finishing Machine

A Metal Surface Finishing Machine is an industrial device designed to improve the surface quality of metal components by processes such as polishing, buffing, grinding, or smoothing. These machines enhance the appearance, durability, and performance of metal parts by removing surface imperfections like scratches, oxidation, burrs, and roughness, and by providing a uniform, aesthetically pleasing finish.
The core functionality of a metal surface finishing machine involves the use of abrasive materials, polishing compounds, or brushes applied through various mechanical actions—such as rotary, vibratory, or orbital motions—to treat the metal surface. The specific process and equipment design depend on the desired finish quality, the type of metal being processed, and the shape and size of the workpiece.
Metal surface finishing machines come in various configurations, including single-spindle polishers, multi-head rotary machines, vibratory tumblers, and automated finishing lines integrated with robotic handling. These machines often feature adjustable speed controls, pressure settings, and tooling options, allowing operators to tailor the finishing process to different metals like stainless steel, aluminum, brass, or copper.
Safety features such as protective guards, emergency stops, and dust or particle extraction systems are commonly incorporated to ensure operator safety and maintain a clean working environment. Routine maintenance involves replacing abrasive media, cleaning dust collectors, and lubricating mechanical parts to maintain optimal performance and prolong machine lifespan.
By automating and standardizing the finishing process, metal surface finishing machines improve production efficiency, reduce manual labor, and ensure consistent high-quality surface finishes. They are widely used in industries such as kitchenware manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, electronics, and metal fabrication, where surface quality directly impacts product performance and marketability.
Overall, metal surface finishing machines play a crucial role in modern manufacturing, enhancing product aesthetics, functionality, and longevity while supporting efficient, safe, and cost-effective production workflows.
A metal surface finishing machine works by applying mechanical action through rotating wheels, belts, pads, or abrasive media that come into contact with the metal workpiece. This contact removes surface defects such as scratches, corrosion, oxidation, or scale, and creates a smooth, polished, or matte finish depending on the process settings and materials used. The machine’s versatility allows it to handle a wide range of metal types and thicknesses, from thin sheets to thick castings or machined components.
The design often includes multiple finishing stations or heads that perform sequential steps, such as grinding to remove major imperfections followed by polishing for shine and smoothness. Some machines incorporate vibration or centrifugal action to enhance the finishing effect, especially useful for small or complex parts. Adjustable parameters like speed, pressure, and abrasive type enable fine control over the surface quality, ensuring consistent results tailored to specific production requirements.
Safety and environmental controls are integral to the machine’s operation. Enclosed polishing areas, dust extraction, and filtration systems reduce exposure to airborne particles and fumes, protecting both operators and the surrounding workspace. Emergency stop mechanisms and interlocked guards provide additional safety by preventing accidental contact with moving parts.
Regular maintenance is essential to maintain performance and prolong machine life. This includes periodic replacement of abrasive belts, wheels, or pads, cleaning of dust and debris, lubrication of moving components, and calibration of control systems. Proper maintenance reduces downtime and ensures the machine consistently produces high-quality finishes.
By automating the surface finishing process, these machines increase throughput and reduce the variability often associated with manual finishing methods. The improved consistency and efficiency directly translate to higher product quality and lower production costs. The finished metal surfaces not only look more attractive but also gain improved resistance to corrosion, wear, and contamination, which enhances the durability and functionality of the final product.
Metal surface finishing machines are widely used across many industries including automotive, aerospace, electronics, consumer goods, and construction. Their ability to produce precise, repeatable finishes makes them indispensable for manufacturers aiming to meet strict quality standards and customer expectations. Whether used for decorative purposes or functional improvements, these machines play a vital role in the modern metalworking landscape.
Metal surface finishing machines also offer scalability, making them suitable for a broad spectrum of production volumes—from small batch or custom jobs to large-scale manufacturing. Their modular designs often allow manufacturers to add or remove finishing stations or upgrade components as production needs evolve, providing flexibility and future-proofing investments.
In addition to traditional polishing and grinding, some advanced metal surface finishing machines incorporate hybrid technologies such as electro-polishing, laser finishing, or ultrasonic-assisted processes. These enhancements enable manufacturers to achieve extremely fine surface textures, reduce processing times, and handle delicate or high-precision components with minimal risk of damage.
Integration with modern automation systems further enhances the capabilities of these machines. Robotic loading and unloading, inline quality inspection, and digital process control allow for seamless operation within smart factories. Real-time monitoring and data analytics help identify process deviations early, optimize finishing parameters, and schedule preventive maintenance, thereby minimizing downtime and maintaining consistent product quality.
The choice of abrasives and polishing compounds is critical for achieving desired finishes and varies depending on the metal type and application. Environmentally friendly and biodegradable compounds are increasingly favored to reduce the environmental impact of finishing operations. Additionally, efficient waste collection and recycling systems are often incorporated to manage spent abrasives and residues responsibly.
Operator training remains a cornerstone of successful metal surface finishing. Skilled technicians understand how to adjust machine settings, select appropriate finishing media, and perform routine maintenance, all of which contribute to maximizing machine uptime and ensuring high-quality output.
Ultimately, metal surface finishing machines are key enablers of product excellence, enhancing both functional performance and aesthetic appeal. Their adoption supports manufacturers in delivering competitively finished metal products that meet regulatory standards and customer expectations in a cost-effective and sustainable manner.
Stainless Utensil Shine Enhancement Machine

A Stainless Utensil Shine Enhancement Machine is a specialized industrial device designed to improve the surface brightness and luster of stainless steel kitchen utensils such as spoons, forks, ladles, and serving tools. Its primary function is to restore and enhance the natural shine of stainless steel surfaces by removing dullness, minor scratches, stains, and oxidation, resulting in a polished, mirror-like finish.
The machine typically uses rotary polishing wheels, abrasive pads, or buffing brushes that rotate at controlled speeds to gently but effectively treat the utensil surfaces. Polishing compounds or fine abrasives formulated specifically for stainless steel are applied during the process to maximize the reflective quality and protect against future tarnishing.
Adjustable settings allow operators to control variables such as rotation speed, pressure, and polishing duration, tailoring the process to different utensil shapes and sizes and ensuring consistent results without damaging the metal. Fixtures or holders may be included to securely position utensils during polishing, preventing movement and ensuring even contact.
Safety features like protective shields, dust extraction systems, and emergency stops help maintain a safe and clean working environment by controlling airborne particles and minimizing operator exposure to moving parts. Regular maintenance, including replacement of polishing media and cleaning of filters, ensures the machine operates efficiently and maintains high polishing quality.
The stainless utensil shine enhancement machine boosts production efficiency by automating what is traditionally a labor-intensive manual polishing task. It produces uniform, high-quality finishes that enhance both the aesthetic appeal and functional durability of stainless steel utensils. The polished surface is easier to clean, more resistant to corrosion, and visually appealing—qualities highly valued by consumers and manufacturers alike.
Suitable for both small workshops and large-scale manufacturing, this machine plays a critical role in delivering premium-quality stainless steel utensils that meet market demands for durability and attractive finishes. Its use not only improves product quality but also reduces labor costs and speeds up finishing processes, making it an essential asset in modern utensil production.
The stainless utensil shine enhancement machine operates by applying a controlled rotary action where polishing wheels or buffing pads spin at adjustable speeds to evenly work over the utensil surfaces. This consistent rotary motion ensures that every curve and contour is reached, delivering a uniform shine without leaving uneven spots or swirl marks. The polishing compounds used are specially formulated for stainless steel to bring out its natural brightness while protecting the metal from oxidation and corrosion.
Operators can fine-tune the machine’s parameters such as speed, pressure, and duration to accommodate different utensil sizes and thicknesses, ensuring delicate items receive gentle treatment while heavier or more worn utensils undergo more intensive polishing. The machine may include adjustable fixtures or holders to secure the utensils firmly in place during the process, preventing slippage and enhancing safety.
Safety measures like dust extraction systems capture the fine polishing residues and metal particles generated during buffing, maintaining a clean work environment and protecting operator health. Protective guards prevent accidental contact with moving parts, and emergency stop functions allow quick shutdown in case of any issues.
Maintenance of the machine is straightforward and includes routine replacement of polishing wheels and pads, cleaning dust collection filters, and lubricating mechanical components. Regular upkeep ensures the machine runs efficiently and consistently produces high-quality finishes, minimizing downtime and repair costs.
By automating the polishing process, the machine significantly reduces the time and labor traditionally required for manual finishing, increasing production throughput and lowering operational costs. The resulting polished utensils not only have improved visual appeal but also benefit from enhanced surface properties like smoother texture and better corrosion resistance, which contribute to longer product life and customer satisfaction.
This shine enhancement machine is versatile enough to be used in various manufacturing setups, from small artisan workshops focusing on custom pieces to large industrial plants producing high volumes of stainless steel utensils. Its ability to deliver consistent, high-quality finishes makes it indispensable in competitive markets where appearance and durability are critical selling points.
Overall, the stainless utensil shine enhancement machine combines precision engineering, user-friendly controls, and safety features to deliver efficient polishing solutions that elevate the quality and value of stainless steel kitchenware products.
The stainless utensil shine enhancement machine also supports scalability, allowing manufacturers to adjust production rates according to demand. Whether producing small batches of premium handcrafted utensils or large volumes for commercial distribution, the machine’s flexibility accommodates varying workloads without compromising finish quality.
Advanced versions of this machine may incorporate programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or touchscreen interfaces that enable operators to store and recall specific polishing programs. This automation reduces setup time and ensures repeatability across different production runs, which is particularly valuable for manufacturers handling diverse product lines with varying surface finish requirements.
Integration with automated handling systems such as robotic arms or conveyor belts further streamlines the polishing process, enabling continuous operation with minimal manual intervention. This reduces operator fatigue and increases overall production efficiency, especially in high-volume manufacturing environments.
Environmental considerations are increasingly important in modern manufacturing, and the machine’s design often reflects this by incorporating energy-efficient motors and environmentally friendly polishing compounds. Effective dust and residue management systems reduce waste and prevent contamination of the work area, aligning with workplace safety standards and environmental regulations.
Training and skill development for operators remain essential to fully leverage the machine’s capabilities. Well-trained personnel can optimize machine settings for different utensil materials and designs, perform preventative maintenance, and quickly troubleshoot issues, thereby minimizing downtime and maintaining consistent quality.
The enhanced shine achieved through this machine not only improves the visual appeal of stainless steel utensils but also enhances their resistance to tarnishing, staining, and corrosion. This ensures that the utensils retain their attractive appearance and functional integrity over extended periods of use, meeting the high expectations of consumers and commercial users alike.
In summary, the stainless utensil shine enhancement machine is a vital asset in utensil manufacturing, combining advanced technology, operational flexibility, and safety features. Its ability to produce high-quality polished finishes efficiently supports manufacturers in delivering durable, visually appealing stainless steel products that satisfy both industry standards and customer demands.
Polishing Line for Kitchen Utensils

A Polishing Line for Kitchen Utensils is a streamlined, automated production setup designed to efficiently polish and finish large quantities of kitchenware items such as spoons, forks, ladles, knives, and other stainless steel or metal utensils. This integrated system combines multiple polishing stations arranged sequentially to perform step-by-step surface finishing processes, ranging from rough grinding to fine buffing and shining.
The line typically includes conveyor systems or robotic handling mechanisms that transport utensils through various polishing units, each equipped with specialized abrasive wheels, brushes, or polishing pads tailored to progressively refine the surface. Starting with coarse abrasive stages to remove major surface defects and scale, the line moves toward finer polishing stages to achieve a smooth, mirror-like finish, ensuring uniform quality across every item.
Speed and pressure controls are adjustable at different points along the line, allowing operators to customize the finishing process based on utensil material, shape, and desired finish quality. Fixtures and clamps securely hold the utensils in place during polishing, minimizing movement and maximizing contact with polishing media.
Integrated dust collection and extraction systems manage metal particles and polishing residues generated at each station, maintaining a clean working environment and protecting worker health. Safety features, including emergency stop buttons and protective guards, ensure safe operation despite the high-speed mechanical processes.
Automation within the polishing line reduces manual labor, increases throughput, and enhances consistency, significantly cutting production time compared to standalone polishing machines. The system is scalable, with the ability to add or remove polishing stations to suit production volume and complexity requirements.
Routine maintenance involves checking and replacing polishing wheels and abrasive materials, cleaning dust extraction filters, lubricating moving parts, and inspecting conveyor mechanisms to maintain optimal performance and prevent downtime.
This polishing line is widely used in medium to large-scale utensil manufacturing plants aiming for high productivity and uniform finish quality. By delivering polished, corrosion-resistant, and visually appealing kitchen utensils efficiently, it helps manufacturers meet market demand while maintaining competitive production costs.
Overall, the polishing line for kitchen utensils represents an essential investment for manufacturers focused on quality, efficiency, and scalability in surface finishing operations.
The polishing line for kitchen utensils operates as a continuous workflow where raw or semi-finished utensils enter one end and progressively pass through multiple polishing stages until they exit with a finished, high-quality surface. Each stage is designed to perform a specific finishing task, starting from heavier material removal and progressing to fine polishing and buffing to enhance shine and smoothness. This systematic approach ensures that the final products have consistent appearance and meet rigorous quality standards.
The conveyor or automated handling system plays a crucial role in maintaining a steady and controlled flow of utensils throughout the line. It minimizes manual handling, reducing the risk of damage or contamination while also speeding up the entire polishing process. Sensors and control units monitor the position and progress of utensils, coordinating the timing between stations to optimize efficiency and throughput.
Adjustable parameters across the line allow for tailoring the process to different types of kitchen utensils. For example, flatware like spoons and forks may require different polishing speeds or abrasive materials compared to larger items like ladles or cooking spoons. The ability to fine-tune each station ensures that all utensil types receive appropriate treatment, resulting in uniform surface finishes across diverse product lines.
Safety remains a priority in the design and operation of polishing lines. Enclosed polishing stations and interlocked guards prevent accidental access to moving parts, while integrated dust extraction systems capture metal dust and polishing compounds, keeping the air clean and reducing hazards. Emergency stop mechanisms positioned along the line allow operators to quickly halt operations if necessary.
Maintenance procedures are streamlined through easy access to polishing components and modular station design, enabling quick replacement of worn wheels, belts, or pads with minimal disruption. Regular upkeep of conveyor systems, motors, and dust collection units ensures smooth operation and longevity of the equipment, ultimately supporting consistent production quality.
By automating the polishing workflow, the line significantly boosts manufacturing capacity, allowing companies to meet growing demand without compromising on surface finish quality. The reduction in manual labor not only lowers operational costs but also decreases worker fatigue and the potential for repetitive strain injuries associated with manual polishing.
Additionally, the polished kitchen utensils emerging from the line exhibit improved resistance to corrosion, easier cleaning, and enhanced aesthetic appeal—all key attributes sought by consumers. This combination of performance and appearance helps manufacturers maintain strong market competitiveness and customer satisfaction.
In summary, a polishing line for kitchen utensils is a comprehensive, efficient solution that integrates multiple polishing processes into a seamless, automated production flow. It balances productivity, quality, safety, and flexibility, making it indispensable for modern kitchenware manufacturing operations aiming to deliver superior finished products at scale.
The polishing line can also be designed for integration into broader utensil manufacturing systems, allowing direct transition from upstream processes like forming or welding into polishing without interruption. This integration helps streamline production flow and reduces intermediate handling, saving time and minimizing the risk of surface damage before finishing. In advanced setups, automated inspection systems can be embedded within the line, using cameras and sensors to detect surface defects, uniformity of shine, or dimensional accuracy, enabling immediate rejection or reprocessing of substandard pieces.
Another key feature of modern polishing lines is recipe-based programming. Operators can load pre-configured settings based on utensil type, size, or customer specifications, allowing the line to automatically adjust polishing speeds, abrasive types, pressure levels, and cycle times. This not only reduces setup time between batches but also ensures high repeatability and finish consistency across all production runs.
Polishing compounds used in these lines are carefully selected to balance performance and safety. Liquid and solid compounds are often applied through nozzles or contact wheels in controlled amounts to avoid excess buildup and reduce waste. Many manufacturers are moving toward environmentally friendly and water-soluble compounds that are easier to clean and safer to handle, aligning with stricter environmental and occupational health standards.
Noise reduction and vibration isolation are also considered in the layout and engineering of polishing lines, especially in large-scale operations where dozens or hundreds of units may be processed simultaneously. Soundproof enclosures, vibration-dampening frames, and balanced rotating elements help maintain a safer and more comfortable environment for workers, contributing to overall workplace efficiency.
Flexibility in fixture design is crucial when dealing with varied utensil geometries. Fixtures and holders must accommodate round, flat, concave, and embossed shapes without slippage or misalignment. Quick-change systems for these fixtures further support high-mix production environments, where different utensil models are processed in short intervals.
Training and operator interface design are also refined in modern polishing lines. User-friendly touchscreens, clear diagnostic messages, and guided setup procedures reduce the learning curve for new workers while minimizing human error. Training programs often focus not just on operation, but also on process optimization, maintenance best practices, and troubleshooting.
Overall, the polishing line represents a fusion of mechanical engineering, automation, surface science, and ergonomic design. It ensures kitchen utensils emerge from production with a flawless finish that not only meets but exceeds consumer expectations. The line plays a vital role in enabling manufacturers to produce high volumes of attractive, hygienic, and durable kitchenware efficiently and consistently, giving them a crucial competitive edge in both domestic and international markets.
Outer Tank Shell Grinding and Polishing System
An Outer Tank Shell Grinding and Polishing System is a specialized industrial solution designed to process the external surfaces of cylindrical tanks—commonly used in industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, brewing, chemical storage, and kitchen equipment manufacturing. These systems are engineered to deliver a smooth, uniform, and often mirror-like finish to the outer shell of stainless steel or metal tanks, enhancing both aesthetic appeal and functional performance such as corrosion resistance and cleanliness.
The system typically consists of automated or semi-automated grinding heads and polishing units mounted on movable arms or tracks that can travel longitudinally and circumferentially around the tank. These heads apply controlled pressure using abrasive belts, wheels, or pads to remove weld marks, surface irregularities, oxidation layers, or previous coatings. This is followed by finer polishing stages that gradually refine the surface, eliminating scratches and leaving a consistent finish across the tank’s exterior.
The machine’s framework is designed to accommodate various tank diameters and lengths. Clamping or rotation systems may be employed to either hold the tank stationary while the polishing heads move, or rotate the tank itself while the heads remain in a fixed or oscillating position. Adjustable speed controls and programmable settings allow operators to fine-tune the surface treatment process based on the tank’s material and desired finish grade, ranging from brushed to satin to mirror polish.
Dust and residue extraction systems are integrated to capture metal particles, spent abrasives, and polishing compound residue, maintaining a clean work zone and reducing environmental hazards. Coolant or lubricants are sometimes used in the grinding stages to reduce heat buildup and extend the life of the abrasives.
The system supports high repeatability and consistent finish quality, especially important for industries with strict surface hygiene or visual standards. It significantly reduces labor intensity compared to manual grinding and polishing, increases productivity, and ensures operator safety with features like enclosed polishing heads, automatic emergency stops, and programmable limit zones.
An outer tank shell grinding and polishing system is essential for manufacturers aiming to deliver tanks that are not only structurally sound but also visually and hygienically compliant. It integrates precision mechanics, surface finishing technology, and automation to meet the high standards expected in today’s industrial and commercial equipment markets.
The outer tank shell grinding and polishing system operates as a coordinated mechanism where abrasive and polishing heads move along the tank surface in a controlled, uniform pattern. These heads may be mounted on articulated arms, gantries, or rotating rigs depending on the system configuration, and they apply even pressure across the curved tank surface to achieve consistent results. The grinding phase typically begins with coarse abrasives to remove surface welds, oxidation, and other imperfections. Once a uniform base is established, the system transitions to finer abrasives and polishing pads that gradually build up the surface finish to the desired level of smoothness and shine.
Tanks are usually mounted horizontally or vertically on motorized rollers or rotating supports that allow the entire shell to turn at controlled speeds. This rotation enables full circumferential access for the polishing heads, which can either remain stationary or move axially during operation. In some designs, the heads oscillate slightly to avoid streaking and improve finish uniformity. Speed, pressure, and feed rate are all programmable to ensure that each pass produces a consistent effect, and these variables can be customized depending on the diameter, wall thickness, and material composition of the tank.
A central control system, often operated via a touch panel interface, allows technicians to set process parameters, monitor operational status, and store multiple programs for different tank types or finish requirements. This greatly enhances repeatability and efficiency in high-volume production environments. Safety features are also built into the system to automatically shut down operations in the event of overload, misalignment, or foreign object detection. Operators can intervene through manual controls if fine adjustments are needed, but the overall system is designed to minimize human involvement once the process is initiated.
Dust extraction and filtration systems are integrated to manage airborne particles generated during grinding, especially important when working with stainless steel. Some systems also include wet grinding options where water or coolant is applied to reduce heat buildup, suppress dust, and prolong abrasive life. The coolant is typically collected and filtered for reuse, reducing waste and improving environmental compliance.
One of the system’s most valuable features is its ability to deliver a high-end finish consistently across large and complex cylindrical surfaces. Whether the goal is a matte industrial-grade surface, a sanitary brushed finish for food or pharmaceutical applications, or a decorative mirror polish for visible installations, the system ensures each tank meets exacting standards. Its automation reduces operator fatigue, eliminates variation, and significantly cuts down polishing time compared to manual methods.
This polishing solution is essential for manufacturers who demand high throughput and uniform results without sacrificing quality or worker safety. Its scalable design allows adaptation to a range of tank sizes and production requirements, making it suitable for both batch production and continuous operations. The outer tank shell grinding and polishing system represents a modern approach to surface finishing, merging mechanical precision with automation to enhance product quality, operational efficiency, and long-term durability of the tanks it processes.
The system’s adaptability extends beyond standard cylindrical tanks. With appropriate fixture adjustments and programmable head movements, it can handle elliptical, conical, or even irregularly shaped shell segments. This flexibility is especially valuable for custom or high-end equipment manufacturers where design specifications vary widely. By incorporating servo motors and CNC-based control for arm positioning, the machine can follow complex surface contours accurately, ensuring that every part of the shell receives equal treatment regardless of geometry.
A critical performance factor is the selection and maintenance of abrasives. Operators monitor wear levels of belts, wheels, and polishing pads closely, as degraded abrasives can lead to uneven finishes or increased processing time. Some systems come equipped with tool wear detection and automatic compensation features, adjusting the feed pressure or issuing alerts when replacements are needed. This not only ensures consistency in output but also extends the life of consumables and reduces operational downtime.
For industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing, the system is often calibrated to meet stringent sanitary standards such as those outlined by the FDA or EU regulations. In such cases, the polishing process must eliminate all micro-grooves and irregularities where bacteria could harbor, achieving a surface finish in the range of Ra 0.4 µm or finer. The polishing heads are engineered to maintain this level of precision, often with multiple passes and compound applications to gradually refine the surface to a hygienic and easy-to-clean state.
To further improve productivity and data transparency, some systems integrate with plant-level MES or ERP systems. This allows operators and managers to track production output, machine utilization, maintenance cycles, and quality control metrics in real time. Such integration supports predictive maintenance, ensuring the machine operates at peak efficiency while minimizing the risk of unplanned downtime.
Worker training is also streamlined by the intuitive user interface and clear fault diagnostics. Operators can be trained quickly to load tanks, initiate preset polishing programs, and monitor machine status, reducing the need for highly skilled manual polishers. This democratization of finishing expertise helps manufacturers scale up production without being limited by specialized labor.
As market expectations for both aesthetic and functional surface finishes continue to rise, the outer tank shell grinding and polishing system becomes not just a convenience but a necessity for manufacturers aiming to maintain brand value and regulatory compliance. It helps elevate the perceived quality of the finished product while ensuring operational efficiency, cost control, and environmental responsibility. In sectors where surface condition directly affects product performance and customer perception, this system offers a repeatable, scalable, and industry-ready solution.
Tank Luster Enhancement Machine

A Tank Luster Enhancement Machine is a specialized surface finishing system designed to impart a high-gloss, reflective, or mirror-like appearance to the outer surface of metal tanks—typically made from stainless steel. These machines are commonly used in industries where the visual appeal of storage or processing tanks is important, such as in high-end commercial kitchens, breweries, pharmaceutical plants, cosmetic manufacturing, and architectural installations.
The machine uses a combination of fine abrasive polishing pads, buffing wheels, and high-performance polishing compounds to progressively refine the tank’s surface. Starting from a relatively smooth, pre-treated exterior—often already ground or brushed in earlier processes—the machine polishes the surface in multiple passes to remove micro-scratches, oxidation, and dullness. The goal is to enhance reflectivity, uniformity, and shine, creating a luster that not only looks premium but also helps with easier cleaning and corrosion resistance.
Luster enhancement machines often employ rotary or orbital polishing heads mounted on movable gantries or robotic arms. These heads may operate in synchronized paths over the tank’s curved or cylindrical surfaces, ensuring complete and even coverage. For vertically or horizontally mounted tanks, rotating fixtures or rollers may be used to keep the tank turning slowly while polishing heads work across its length or circumference.
The pressure, speed, and motion of the polishing tools are precisely controlled to avoid overheating or surface distortion while maximizing the gloss level. High-end models include compound dispensing systems that apply polishing agents in controlled amounts, improving efficiency and finish quality while reducing material waste.
Safety and cleanliness are also key considerations. Integrated dust and fume extraction systems collect residues from the buffing compounds, while enclosures or shields prevent operator exposure to moving parts or fine particulates. Many machines are designed for easy cleanup and fast tool changeovers, supporting high-volume or multi-product environments.
A luster enhancement machine contributes significantly to product value and brand image, especially in sectors where equipment visibility matters. The bright, polished surface signals quality and hygiene, supporting both functional and aesthetic goals. In this way, the machine is not just a surface finisher but a strategic investment in manufacturing excellence and product presentation.
The Tank Luster Enhancement Machine operates as an integrated polishing and buffing unit that elevates the visual quality of cylindrical or shaped tank surfaces by producing a brilliant, uniform shine. The machine typically begins with a pre-polished or ground tank surface and refines it through a series of finely controlled polishing stages. These stages use soft buffing wheels, felt pads, or microfiber-based applicators, combined with high-grade polishing compounds, to gradually eliminate micro-scratches, haze, and any dull patches that reduce surface reflectivity. The result is a clean, mirror-like finish that reflects light evenly across the tank’s entire exterior, significantly enhancing its perceived quality.
The polishing heads in the machine are mounted on programmable arms or movable gantries that follow the tank’s contours precisely. Depending on the setup, the tank itself may rotate slowly on powered rollers, or the heads may travel along the tank’s length while applying consistent pressure and compound. The motion is smooth and repetitive, ensuring that no area is over-polished or left under-treated. This consistency is essential in high-end manufacturing applications, where the appearance of tanks plays a role in both functionality and brand image.
To achieve and maintain a high luster, the machine often includes an automated compound delivery system. This system dispenses precise amounts of polishing paste or liquid directly onto the wheel or tank surface at specific intervals. The automation helps maintain a consistent gloss level throughout the cycle and avoids excessive compound usage or uneven coverage, which can lead to streaking or rework. Temperature control may also be integrated, as heat buildup during prolonged polishing can alter the surface quality or warp thin-walled tanks. Cooling systems or intermittent cycles may be used to manage surface conditions and tool wear.
Operator interaction is minimal once the machine is programmed. An intuitive control panel allows for quick recipe selection based on tank size, material, or required luster grade. Custom parameters can be adjusted and saved for repeated use, ensuring high repeatability in serial production. Advanced systems also provide real-time feedback on polishing quality through sensors that monitor surface reflectivity or gloss levels, allowing for immediate corrections or adjustments.
Dust and residue control are crucial, especially when using polishing compounds that can produce airborne particles. Integrated vacuum or extraction systems keep the workspace clean and prevent contamination of adjacent equipment or polished surfaces. This contributes to a safer, more efficient work environment and protects the integrity of the finished product.
The machine’s value lies not only in aesthetics but also in performance. A polished tank surface resists bacterial buildup, is easier to clean, and improves durability by minimizing surface defects where corrosion might begin. In industries where hygiene and presentation are equally critical—like dairy, beverage, pharma, or food equipment manufacturing—a luster-enhanced surface is often a key selling point.
In modern production lines, this machine is used either as a standalone finishing stage or integrated into a complete polishing and inspection loop. It supports high throughput, reduces labor intensity, and produces a result that is consistently beyond the capabilities of manual polishing. For companies seeking to add value through visual quality and surface performance, the Tank Luster Enhancement Machine is an essential part of the production process.
To maintain high operational efficiency, many Tank Luster Enhancement Machines are equipped with auto-diagnostics and predictive maintenance alerts. These systems monitor parameters like motor load, vibration levels, polishing head wear, and compound consumption to detect issues before they lead to downtime. By predicting when consumables or mechanical components need attention, the system ensures continuous operation with minimal interruptions, which is particularly valuable in facilities that run 24/7 or produce large volumes of equipment on tight delivery schedules.
Customization is another strength of these machines. The system can be configured to suit a wide range of tank sizes and geometries, from small vessels and drums to large vertical silos. Modular head designs allow quick swapping of polishing tools or the addition of extra buffing stages for more demanding finishes. Some machines also support multi-head configurations, where multiple polishing arms work simultaneously on different sections of the tank, drastically reducing cycle time while maintaining precision.
In premium manufacturing environments, the machine’s output directly impacts product classification and pricing. Tanks with flawless, high-gloss finishes are often positioned as high-end, sanitary-grade or architecturally visible products. The enhanced reflectivity not only contributes to aesthetics but also serves practical purposes such as improved visibility of surface contaminants, quicker visual inspections, and better thermal reflectivity in outdoor or high-temperature settings.
Digital integration capabilities are increasingly common. Machines can be networked to factory management systems, allowing real-time monitoring, remote diagnostics, and production analytics. Parameters such as number of units polished, finish grades achieved, compound usage rates, and polishing cycle durations can all be logged and analyzed. This data helps in optimizing production planning and quality control, ensuring the polishing process remains consistent across shifts, operators, and product types.
The operator interface is designed for simplicity and reliability. Visual prompts guide the user through setup, parameter selection, and cycle initiation. Emergency stops, tool interlocks, and safety barriers ensure that even during manual loading or maintenance, risks are minimized. Training requirements are low, as most of the process is automated and menu-driven, allowing manufacturers to scale labor quickly without specialized polishing expertise.
Polishing quality is often verified post-process using gloss meters or surface roughness testers. The Tank Luster Enhancement Machine makes it easier to meet or exceed these benchmarks by removing process variation. Whether the goal is a soft, brushed satin or a deep, mirror finish, the machine ensures repeatability and finish quality across all units.
This makes the system indispensable for manufacturers who need to meet both technical specifications and visual expectations, ensuring that each tank not only performs flawlessly in service but also represents the highest standards of craftsmanship and design. As demand grows for precision, hygiene, and brand differentiation, the Tank Luster Enhancement Machine plays a central role in delivering excellence in modern tank manufacturing.
Cylindrical Vessel Surface Grinding Machine
A Cylindrical Vessel Surface Grinding Machine is a precision-engineered system designed to grind and smooth the external surface of cylindrical tanks and vessels, particularly those made from stainless steel, mild steel, or other industrial metals. Its main purpose is to remove weld seams, surface irregularities, oxidation, and scale while preparing the vessel for polishing or coating. This machine is widely used in industries such as food processing, chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and beverage production, where both structural integrity and surface quality are essential.
The core of the machine features abrasive grinding heads or belts mounted on adjustable arms or gantries. These grinding elements are positioned to contact the vessel’s curved surface uniformly, often while the vessel is rotated slowly on motorized rollers. The combination of vessel rotation and controlled grinding head movement ensures that the entire circumference is treated evenly without leaving flat spots or inconsistent finish lines. The grinding heads may oscillate laterally during rotation to ensure full surface coverage and uniform abrasion.
A typical process starts with a coarse abrasive grit to aggressively remove weld beads, surface defects, or manufacturing residues. Successive passes use finer grits to refine the surface, improving flatness and texture in preparation for downstream finishing processes like buffing or electropolishing. Grinding speed, pressure, and feed rate are precisely regulated by a digital control system, allowing operators to tailor the process to each vessel’s diameter, wall thickness, and material properties.
Advanced machines may offer multiple grinding heads working in tandem to speed up the process, or feature CNC-guided axes for programmable path control. These features are critical for ensuring high repeatability, especially in batch production environments where consistency across vessels is required. The machine may also include automatic tool wear compensation, vibration damping, and coolant systems to prevent thermal distortion or surface damage during extended grinding cycles.
Dust extraction units and spark arrestors are integrated to handle airborne particles and grinding debris, keeping the workspace clean and safe. For applications involving stainless steel or hygiene-sensitive sectors, wet grinding options may be used to further suppress dust and heat, improve abrasive life, and deliver a smoother surface.
Control interfaces are usually touchscreen-based with intuitive menus that allow the operator to load vessel dimensions, select abrasive grit sequences, adjust grinding parameters, and monitor system performance in real time. Stored programs make repeat jobs easy to recall, reducing setup time and improving throughput.
By providing a uniform, defect-free surface, the Cylindrical Vessel Surface Grinding Machine lays the foundation for superior finish quality, better corrosion resistance, and improved aesthetic value. It significantly reduces the labor, time, and variability associated with manual grinding, making it a key asset in modern tank and vessel fabrication.
The Cylindrical Vessel Surface Grinding Machine operates as a continuous finishing solution for metal vessels, particularly those with round or tubular geometry. The machine is designed to remove surface imperfections, weld scars, heat discoloration, and other fabrication marks, providing a smooth, clean, and uniform finish across the entire cylindrical shell. It typically works by rotating the vessel slowly while abrasive grinding heads or belts apply consistent pressure as they traverse longitudinally or oscillate laterally across the surface. This ensures that the vessel receives even treatment across its full circumference and length, eliminating uneven patches or grinding lines.
The grinding elements used may include belt-driven abrasive bands, flap wheels, or composite abrasive pads, depending on the required finish quality and the type of material being processed. These tools are mounted on adjustable arms or gantry systems that can be programmed or manually set to adapt to different vessel diameters and wall profiles. The machine ensures stable contact pressure and consistent material removal, reducing the risk of overgrinding or thermal warping, which is particularly important when working with thin-walled stainless steel tanks. Grinding speed, pressure, and abrasive grit selection are critical variables, all of which are controllable through a centralized digital interface, allowing the operator to fine-tune the process for different vessel sizes or end-use applications.
A key advantage of the system is the integration of rotating rollers or chucks that hold the vessel securely while allowing it to spin at a low but constant speed. This motion, synchronized with the movement of the grinding head, ensures that every part of the external shell is exposed to the same grinding conditions, producing a consistent surface texture free of low spots or grind lines. In more advanced configurations, CNC-controlled axes can map the vessel’s geometry and execute multi-pass operations with varying grit levels automatically, reducing human error and improving repeatability across production batches.
Dust and particle control is handled by extraction hoods or wet grinding attachments that keep airborne contaminants at bay while extending abrasive life and maintaining a safer, cleaner work environment. Coolant systems are often integrated to suppress heat buildup and improve the surface finish, particularly when preparing vessels for subsequent polishing, coating, or hygienic treatment. These systems also minimize the risk of heat-induced distortion, which can compromise the vessel’s roundness or structural properties.
The user interface is designed to minimize complexity while maximizing control. Operators can quickly enter vessel dimensions, select grinding recipes, and monitor system performance in real time through touchscreens or programmable logic controllers. Recipe storage enables fast changeovers, making the machine suitable for both one-off and serial production. Real-time monitoring systems can detect excessive tool wear, motor load fluctuations, or process interruptions and alert the operator before defects occur.
By automating a task that would otherwise require skilled manual effort, the Cylindrical Vessel Surface Grinding Machine boosts production efficiency, consistency, and overall product quality. It enables manufacturers to meet tight tolerance requirements, aesthetic standards, and hygienic specifications without sacrificing speed or increasing labor intensity. Whether used as a pre-polishing stage or a standalone process for matte or brushed finishes, this machine represents a vital investment for any facility involved in stainless steel vessel fabrication, especially where appearance, hygiene, and long-term durability are critical to the end application.
The grinding machine’s flexibility in handling vessels of various diameters and lengths is one of its core advantages, allowing it to accommodate a wide range of production needs without extensive retooling. The vessel is typically mounted horizontally on motorized rollers that rotate it slowly, enabling the grinding heads to make full circumferential contact as they traverse the surface. This approach ensures that even large tanks receive an even, uninterrupted finish without requiring repositioning, which improves productivity and surface uniformity. For applications requiring specific textures such as a satin, matte, or directional grain finish, the machine parameters can be adjusted accordingly by changing belt types, grit sequences, and feed rates.
The machine may use dry or wet grinding methods. In dry grinding, powerful extraction systems are crucial to handle the metallic dust and abrasive residue generated during operation. In wet grinding, a controlled flow of coolant or water with additives helps reduce heat, flush away debris, and achieve finer finishes. Wet systems are preferred in applications where a high-quality pre-polish surface is needed or where heat-sensitive materials are involved. These systems also help preserve the cutting efficiency of the abrasives and reduce the frequency of tool replacement.
Abrasive wear tracking and compensation systems are often integrated into higher-end models, allowing the machine to automatically adjust pressure or tool path to account for changing abrasive profiles. This ensures a stable finish throughout long runs and helps prevent under-processing or rework. In machines equipped with load sensors and servo control, feedback from the grinding head can trigger real-time corrections in pressure or speed to accommodate slight variations in vessel surface hardness or wall thickness.
Some configurations also allow the grinding heads to pivot or articulate, which is useful for grinding near flanges, welded attachments, or vessel ends. This flexibility is essential in custom fabrication shops where not all vessels are perfectly cylindrical or free of obstructions. The system may also support multi-head setups, where coarse and fine grinding heads are positioned in sequence to perform progressive grinding in a single machine pass, drastically improving throughput and consistency.
The integration of this machine into a production line allows seamless transition from welding and fabrication to final finishing, reducing the need for material handling and work-in-progress storage. When combined with automated polishing or inspection stations, the grinding process becomes a key element in a closed-loop surface preparation line, supporting lean manufacturing principles and minimizing cycle times.
Ultimately, the Cylindrical Vessel Surface Grinding Machine helps deliver vessels that meet both functional and regulatory demands, such as low surface roughness for sanitary compliance, consistent cosmetic appearance for exposed installations, and dimensional precision for downstream assembly or coating. It replaces slow, inconsistent manual processes with a reliable, automated system that boosts productivity and finish quality, making it an essential component for manufacturers seeking efficiency, consistency, and high-performance surface treatment.
Belt-Type Cookware Polisher

A Belt-Type Cookware Polisher is a specialized industrial machine designed to polish and finish the surfaces of cookware items such as pots, pans, kettles, and other kitchen utensils. The machine uses continuous abrasive belts to smooth, refine, and enhance the exterior or interior surfaces of metal cookware, typically made from stainless steel, aluminum, or other alloys. This process improves both the aesthetic appeal and functional qualities of the cookware, such as corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning.
The core mechanism involves one or more abrasive belts driven by electric motors that move at controlled speeds across the surface of the cookware. The cookware pieces are either manually fed or automatically conveyed into position, where they come into contact with the moving belts. The abrasive belts are selected based on the desired finish—coarser grits for initial grinding or weld seam removal, and finer grits for polishing and shine enhancement.
The machine often features adjustable belt tension and tracking systems to maintain consistent abrasive contact and belt alignment during operation. Multiple belts may be arranged in series or parallel, allowing progressive finishing stages without removing the cookware from the machine. This setup increases efficiency and ensures a uniform finish throughout.
In addition to surface polishing, belt-type polishers can also help remove minor surface defects, scratches, or discolorations caused by prior manufacturing steps, providing a smooth and consistent surface ready for packaging or further processing. The machine’s adjustable pressure and speed controls allow operators to tailor the polishing intensity to different cookware sizes and materials, preventing surface damage while achieving the desired gloss level.
Safety features such as guards, emergency stops, and dust extraction systems are integral, ensuring operator protection and a clean work environment by minimizing airborne metal dust and polishing debris. Some machines also incorporate coolant or lubrication systems to reduce heat buildup and extend abrasive life.
Overall, the Belt-Type Cookware Polisher enhances production throughput, quality consistency, and the visual and functional appeal of cookware products, making it an essential tool in modern kitchenware manufacturing.
The Belt-Type Cookware Polisher functions by continuously running abrasive belts that contact the cookware surfaces, removing imperfections like weld marks, scratches, or discoloration while simultaneously smoothing and brightening the metal. Cookware items are fed either manually or via automated conveyors, positioning them precisely against the moving belts. The belts, often made of materials like coated abrasives or non-woven fibers, are selected based on the desired finish—starting from coarse grits for heavy material removal and gradually moving to finer grits for polishing and enhancing the shine.
The machine typically features adjustable mechanisms that control belt speed, tension, and tracking to ensure consistent contact and prevent misalignment, which could cause uneven polishing or belt damage. Pressure rollers or adjustable arms apply controlled force to the cookware, allowing the abrasive surface to work effectively without causing dents or deformation. This balance is crucial since cookware pieces vary in thickness and shape, requiring flexible operation settings to accommodate different models without sacrificing surface quality.
In many configurations, multiple abrasive belts are arranged sequentially, enabling a stepwise polishing process that progresses from grinding to fine finishing without manual intervention. This arrangement greatly increases efficiency by reducing handling time and minimizing errors between stages. The conveyor or feeding system moves cookware steadily through the polishing zones, ensuring uniform treatment across all surfaces.
Dust and particulate matter generated during polishing are managed by integrated extraction systems that maintain a clean and safe environment. These systems not only protect workers from inhaling metal dust but also prevent debris from settling on the freshly polished cookware, which could cause blemishes or reduce product quality. Additionally, some machines incorporate coolant sprays or lubrication mechanisms to reduce friction heat, extend belt life, and improve finish quality, especially when working with heat-sensitive materials like aluminum.
Operators interact with the polisher via user-friendly control panels that allow quick adjustments of belt speeds, pressures, and process timing. This flexibility enables rapid changeover between different cookware types or finish requirements, making the machine suitable for both small batch and high-volume production runs. Automated sensors may monitor belt wear or motor load, prompting maintenance alerts to prevent unexpected downtime and maintain consistent output quality.
The result is cookware with a smooth, even surface free from visible defects, exhibiting enhanced corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. This improved finish contributes not only to the product’s market value but also to its functional longevity, as polished surfaces are easier to clean and less prone to food sticking or staining. By automating the polishing process, the Belt-Type Cookware Polisher reduces labor costs, increases throughput, and delivers consistent quality that manual polishing cannot reliably achieve. It stands as a vital asset for manufacturers aiming to meet modern consumer expectations for durable, attractive kitchenware.
The Belt-Type Cookware Polisher is also valued for its versatility in handling different cookware shapes and sizes. Whether it’s flat-bottomed pans, curved pots, or tapered kettles, the machine can be adjusted to maintain consistent belt contact across various contours. This is often achieved through adjustable conveyor guides, flexible belt arms, or specialized fixtures that securely hold the cookware during polishing without causing deformation. Such adaptability allows manufacturers to polish a wide range of product lines using the same equipment, maximizing return on investment.
Maintenance and operational uptime are key considerations in the design of these machines. Quick-change belt systems reduce downtime by allowing operators to replace worn belts rapidly without extensive disassembly. Additionally, belt tracking systems minimize off-center belt wear, ensuring the abrasive surface is used efficiently and lasts longer. Routine cleaning and lubrication points are accessible to facilitate regular upkeep, further improving machine reliability.
Integration with upstream and downstream processes is another advantage. The polisher can be installed as part of an automated production line, linking directly to forming, welding, or inspection stations. This streamlines production flow and reduces manual handling, lowering the risk of surface damage between stages. When paired with robotic loading and unloading systems, the Belt-Type Cookware Polisher contributes to a highly automated, efficient manufacturing environment.
In terms of finish quality, the machine can produce a variety of surface effects depending on abrasive selection and process parameters. For example, a matte or brushed finish can be achieved by using non-woven abrasive belts and controlled pressure, while high-gloss mirror finishes require finer grit belts and slower polishing speeds. This flexibility allows manufacturers to tailor their products to specific market preferences or branding requirements.
Safety considerations are paramount. Enclosures, emergency stop buttons, and interlocked access panels ensure that operators can quickly halt the machine in case of an emergency. Dust extraction not only protects health but also prevents buildup that could cause mechanical issues or fire hazards. Many machines include sensors and alarms to detect abnormal operating conditions, such as belt slippage or motor overload, allowing preventive action before costly failures occur.
Ultimately, the Belt-Type Cookware Polisher combines precision, speed, and adaptability, enabling manufacturers to deliver cookware that meets stringent quality standards while maintaining efficient production. It is a critical piece of equipment for those looking to enhance both the functional performance and visual appeal of their kitchenware products.
Utensil Body Belt Grinding System

An Utensil Body Belt Grinding System is a specialized machine designed to grind and smooth the main bodies of kitchen utensils such as pots, pans, bowls, and other metal containers. The system employs continuous abrasive belts to remove surface defects like weld seams, rough edges, scratches, and oxidation marks from the utensil bodies, preparing them for further finishing processes such as polishing or coating.
The machine works by feeding the utensil bodies onto a conveyor or positioning them against abrasive belts that run at controlled speeds. The belts, which vary in grit size depending on the stage of grinding, apply uniform pressure to the utensil surface, effectively leveling uneven areas and refining the texture. The abrasive belts may be mounted on adjustable arms or plates that can be set to match different utensil sizes and shapes, ensuring consistent contact and optimal material removal.
Typically, the system includes multiple grinding stations arranged in sequence to allow progressive surface refinement—from coarse grinding for heavy material removal to finer grinding for smoothing. This setup increases productivity by reducing manual handling and ensuring each utensil body receives a consistent finish.
Precision controls regulate belt speed, tension, and pressure to avoid overgrinding, which could deform thin-walled utensils. The system may also incorporate sensors to monitor belt wear and adjust operational parameters automatically, maintaining uniform grinding quality throughout production runs.
Dust and debris generated during grinding are managed with integrated extraction systems that capture particles at the source, protecting operators and maintaining a clean environment. Some machines also include coolant spray systems to reduce heat buildup, prolong abrasive life, and enhance surface finish quality.
The operator interface is user-friendly, often featuring touchscreens for quick adjustments, recipe storage for different utensil models, and real-time monitoring of system status. Safety features such as emergency stops, protective guards, and interlocks are standard to ensure safe operation.
Overall, the Utensil Body Belt Grinding System improves manufacturing efficiency and product quality by automating the surface preparation of utensil bodies. It reduces manual labor, ensures consistent surface texture, and creates an ideal base for subsequent polishing or coating, making it an essential machine in modern utensil production lines.
The Utensil Body Belt Grinding System operates by continuously running abrasive belts against the surfaces of utensil bodies to remove imperfections such as weld beads, rough spots, or uneven textures. Utensils are positioned either manually or automatically on conveyors or holding fixtures that ensure steady, uniform contact with the moving belts. These abrasive belts vary in grit size, starting with coarser materials for initial material removal and transitioning to finer abrasives for smoothing and surface refinement.
The machine is designed to accommodate a wide range of utensil shapes and sizes through adjustable belt angles, tension controls, and positioning mechanisms. This adaptability helps maintain consistent grinding pressure and contact area, which is essential to avoid deforming thin or delicate utensil walls while achieving an even finish. Typically, multiple grinding stations are arranged in sequence to allow a stepwise approach that enhances productivity and finish quality by progressing through stages from rough grinding to fine smoothing without the need to move the parts between machines.
Key operational parameters such as belt speed, pressure, and feed rate are precisely controlled via digital interfaces, enabling operators to tailor the grinding process to different utensil materials and thicknesses. Advanced models include sensors that monitor belt wear and tension, automatically adjusting settings to maintain optimal grinding performance and prolong belt life. These systems minimize downtime and reduce the risk of surface inconsistencies caused by abrasive degradation.
The grinding process generates metallic dust and particles that are efficiently captured by integrated dust extraction units, helping maintain a clean and safe work environment. Some systems also incorporate coolant sprays to manage heat buildup, enhance abrasive efficiency, and prevent thermal damage to the utensil surfaces. These cooling systems contribute to achieving a smoother surface and longer tool life.
Operator interfaces are designed for ease of use, often featuring touchscreen controls with programmable settings to store grinding profiles for different utensil designs. This capability streamlines changeovers and supports consistent results across production batches. Safety features such as guards, emergency stop buttons, and interlocked access panels ensure operator protection during operation and maintenance.
By automating the grinding of utensil bodies, the system significantly reduces manual labor and variability, delivering consistent, high-quality surface finishes essential for downstream polishing, coating, or inspection. It enhances throughput, minimizes rework, and helps manufacturers meet stringent quality and aesthetic standards, making it a critical component in modern utensil production facilities.
The Utensil Body Belt Grinding System also offers flexibility in handling varying production volumes, from small batches to high-volume manufacturing runs. Its modular design allows manufacturers to customize the number of grinding stations or integrate additional finishing processes, such as buffing or polishing, directly into the line. This modularity supports scalability and adaptability as production demands change or new product lines are introduced.
To further improve efficiency, many systems incorporate automated loading and unloading mechanisms, reducing manual handling and operator fatigue while speeding up the overall process. Integration with robotic arms or conveyors allows seamless transfer of utensils between grinding, polishing, and inspection stations, creating a fully automated production workflow that minimizes human error and enhances repeatability.
The choice of abrasive belts is critical in determining the final surface quality. Manufacturers often select belts with specific abrasive materials such as aluminum oxide, zirconia alumina, or ceramic grains depending on the hardness of the utensil material and desired finish. Non-woven abrasive belts are also commonly used for finishing and blending to achieve a uniform matte or satin texture. Belt changeovers are designed to be quick and straightforward, reducing downtime and increasing operational uptime.
Maintenance routines are simplified with easy access to key components like belt tensioners, motors, and dust collection units. Regular inspection and replacement of worn belts and filters help maintain optimal grinding performance and consistent finish quality. Some advanced machines feature predictive maintenance alerts based on sensor data, allowing preventative servicing before breakdowns occur.
The system’s ergonomic design reduces operator strain by positioning controls within easy reach and minimizing the need for manual adjustments during production. Clear visual indicators and alarms keep operators informed of machine status, ensuring rapid response to any issues. Training requirements are minimized thanks to intuitive interfaces and standardized operating procedures.
By delivering consistent surface finishes that meet strict dimensional and cosmetic specifications, the Utensil Body Belt Grinding System plays a vital role in producing high-quality kitchenware. The smooth, defect-free surfaces it creates facilitate subsequent polishing, coating, or printing processes, enhancing product durability and consumer appeal. Ultimately, the system supports manufacturers in achieving higher productivity, reduced labor costs, and improved product quality, making it indispensable in modern utensil manufacturing.
Additionally, the Utensil Body Belt Grinding System often includes customizable programming capabilities, allowing manufacturers to save and recall specific grinding profiles for different utensil types and materials. This ensures consistent repeatability across production runs, minimizing variability and waste. By automating these parameters—such as belt speed, pressure, and feed rate—the system reduces the need for skilled manual adjustments, enabling less experienced operators to achieve professional-grade finishes.
The integration of real-time monitoring technologies is becoming more common, with sensors tracking belt condition, motor load, and surface quality. These data-driven insights allow operators and maintenance teams to make informed decisions on belt replacement or process adjustments, optimizing machine uptime and extending abrasive tool life. This proactive approach also helps in maintaining product quality standards by identifying potential issues before they affect the finished goods.
Energy efficiency is another consideration in modern systems, with variable frequency drives (VFDs) regulating motor speeds to minimize power consumption without sacrificing performance. This not only reduces operational costs but also aligns with sustainability goals increasingly prioritized in manufacturing environments.
The versatility of the Utensil Body Belt Grinding System extends to its compatibility with various metal alloys and composite materials used in kitchen utensils. Whether processing stainless steel, aluminum, copper, or multi-layered materials, the machine’s adaptable controls and abrasive selections ensure effective surface preparation tailored to each material’s characteristics.
Safety remains a top priority, with machines designed to meet or exceed industry standards and regulations. Features such as enclosed grinding zones, emergency stop systems, interlocked access doors, and dust extraction safeguards protect operators from hazards like flying debris, dust inhalation, and accidental contact with moving parts. Some systems also incorporate noise reduction elements to create a more comfortable work environment.
In summary, the Utensil Body Belt Grinding System is a highly efficient, adaptable, and safe solution for preparing utensil surfaces at scale. Its automation, precision control, and integration capabilities make it a cornerstone in modern kitchenware manufacturing, delivering consistent quality, improved throughput, and cost savings across production lines.
Heavy-Duty Belt Grinder for Pots

A Heavy-Duty Belt Grinder for Pots is an industrial-grade machine designed specifically to handle the robust grinding and surface finishing needs of large, thick-walled cooking pots and similar heavy cookware. Built to withstand continuous, high-intensity use, this machine efficiently removes weld seams, surface irregularities, and rough edges from pots made of stainless steel, aluminum, or other durable metals.
The machine features wide, durable abrasive belts with coarse to medium grit sizes suitable for aggressive material removal without damaging the pot’s structural integrity. The belts are powered by high-torque motors capable of maintaining consistent speed and pressure even under heavy loads, ensuring uniform grinding across the entire pot surface.
Adjustable fixtures or conveyors securely hold the pots in place, accommodating varying diameters and shapes while enabling precise contact between the abrasive belt and the pot body. The machine often includes heavy-duty belt tracking and tensioning systems designed to handle the strain from large, heavy workpieces and maintain optimal abrasive belt alignment.
Multiple grinding stations can be configured in series to progressively refine the pot’s surface, starting with coarse belts for rough grinding and advancing to finer abrasives for smoothing. This setup reduces manual handling and speeds up the finishing process, increasing overall productivity.
To manage the significant dust and metal particles generated, the system integrates powerful dust extraction units that keep the workspace clean and safe, protecting operators from harmful airborne contaminants. Some machines also incorporate cooling or lubrication sprays to reduce heat buildup, prolong belt life, and improve surface finish quality, especially when working with heat-sensitive metals.
The Heavy-Duty Belt Grinder includes operator-friendly control panels that allow for easy adjustment of belt speed, pressure, and grinding duration, providing flexibility for different pot sizes and metal types. Safety features such as emergency stop buttons, protective guards, and interlocked access panels ensure safe operation during intense grinding tasks.
Overall, the Heavy-Duty Belt Grinder for Pots is essential for manufacturers seeking to efficiently produce high-quality cookware with smooth, defect-free surfaces, capable of withstanding rigorous cooking conditions while maintaining an attractive finish.
The Heavy-Duty Belt Grinder for Pots operates by continuously running wide abrasive belts powered by high-torque motors, allowing for effective material removal even on thick, heavy pot surfaces. Pots are securely held in adjustable fixtures or on conveyors that accommodate a range of diameters and shapes, ensuring stable positioning and consistent contact with the moving belts. The abrasive belts, typically made of durable materials suited for coarse to medium grit grinding, are tensioned and tracked by robust systems designed to withstand the stresses of grinding large, heavy cookware.
Multiple grinding stations are often arranged in sequence within the machine, enabling a progressive finishing process that moves from aggressive rough grinding to smoother surface refinement without the need to manually transfer pots between operations. This arrangement boosts throughput and ensures uniform surface quality across each pot. Belt speed, pressure, and grinding duration are all adjustable via operator-friendly controls, allowing customization based on pot size, material type, and the desired finish.
The grinding process produces substantial amounts of metal dust and debris, which are captured by integrated dust extraction systems to maintain a clean, safe working environment and prevent contamination of the finished products. Cooling or lubrication sprays may also be applied during grinding to reduce heat buildup, protect the metal from thermal damage, and extend abrasive belt life. These features contribute to achieving consistent surface finishes while maximizing operational efficiency.
Safety measures are built into the machine, including protective guards around moving parts, emergency stop mechanisms, and interlocked access panels to prevent accidental contact or entry during operation. These safeguards protect operators despite the machine’s high power and intense grinding action.
Designed for durability and continuous use, the Heavy-Duty Belt Grinder withstands the demanding requirements of pot manufacturing, offering reliable performance that enhances product quality and production speed. By automating heavy surface grinding tasks, it reduces manual labor and ensures that pots leave the production line with smooth, defect-free surfaces ready for further finishing or direct use. This makes it a critical piece of equipment for cookware manufacturers focused on efficiency and high-quality output.
The Heavy-Duty Belt Grinder for Pots also offers versatility in handling various pot designs, including different diameters, heights, and wall thicknesses. Its adjustable fixtures and programmable controls allow quick changeovers between different product types, minimizing downtime and increasing overall production flexibility. This adaptability is crucial for manufacturers producing diverse cookware lines or custom orders.
The machine’s construction uses heavy-gauge steel frames and reinforced components to withstand constant vibration and mechanical stresses, ensuring long-term durability and stable operation. Bearings, motors, and belt drive assemblies are selected for high reliability and low maintenance requirements, reducing operational interruptions and costs.
In addition to grinding the pot body, some models include specialized attachments or secondary stations for refining pot rims, handles, or bases, providing a more comprehensive finishing solution within a single integrated system. This consolidation reduces the need for multiple machines and manual handling steps, further streamlining the manufacturing process.
Operators benefit from intuitive interfaces that often include touchscreen controls, preset programs, and real-time monitoring of machine parameters such as motor load and belt condition. This user-friendly design shortens training times and supports consistent quality by minimizing operator error. Diagnostic features and maintenance alerts help predict service needs before breakdowns occur, maximizing machine uptime.
Environmental and workplace safety standards are met through efficient dust collection, noise reduction features, and ergonomic machine layouts. These elements contribute to a healthier, safer, and more comfortable working environment, which is increasingly important in modern manufacturing facilities.
Overall, the Heavy-Duty Belt Grinder for Pots combines rugged design, operational flexibility, and advanced control features to deliver efficient, high-quality surface grinding. It enables cookware manufacturers to maintain competitive production speeds while ensuring their products meet strict quality and durability standards demanded by consumers.
Tank Surface Polishing Machine

A Tank Surface Polishing Machine is a specialized industrial device designed to polish and finish the exterior and sometimes interior surfaces of large tanks made from metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, or carbon steel. These tanks are commonly used in industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and water treatment, where smooth, polished surfaces are essential for hygiene, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal.
The machine typically features one or more rotating polishing heads equipped with abrasive pads, polishing wheels, or buffing belts that apply controlled pressure and motion to the tank surface. Depending on the tank size and shape, the machine may be stationary with a movable polishing arm or configured as a portable unit that operators can maneuver around the tank.
Adjustable speed controls allow operators to select the optimal rotational and polishing speeds based on the tank material, surface condition, and desired finish. The polishing heads can be fitted with various abrasives or polishing compounds to achieve finishes ranging from matte to mirror-like gloss.
For larger tanks, the machine may incorporate extendable arms or telescopic mechanisms to reach high or difficult-to-access areas without requiring scaffolding or manual labor-intensive methods. In some cases, the machine is integrated with automated positioning systems or robotic arms to provide consistent and repeatable polishing results across the entire tank surface.
Dust and debris generated during polishing are managed through built-in extraction systems, maintaining a clean work environment and preventing contamination. Water or polishing fluids may also be applied to cool the surface, reduce friction, and improve polishing efficiency.
Safety features include emergency stop buttons, protective guards around moving parts, and ergonomic handles or controls to reduce operator fatigue. The machine’s design prioritizes ease of use, rapid setup, and adaptability to various tank sizes and surface conditions.
Overall, the Tank Surface Polishing Machine enhances productivity and finish quality, providing a reliable solution for manufacturers and maintenance teams to maintain or restore the smooth, corrosion-resistant surfaces critical for tank longevity and compliance with industry standards.
The Tank Surface Polishing Machine operates by applying abrasive and polishing materials through rotating heads or belts that make contact with the tank’s metal surface. Depending on the machine design, polishing heads may move along adjustable arms or be manually guided over the surface, ensuring even pressure and consistent motion to remove surface imperfections such as scratches, weld marks, oxidation, or corrosion. Variable speed controls allow operators to tailor the polishing action to different metals and surface conditions, enabling a wide range of finishes from brushed textures to high-gloss mirror effects.
For large tanks, the machine’s extendable or telescopic mechanisms enable access to difficult areas without extensive manual effort or scaffolding, improving safety and reducing labor time. Some advanced models incorporate automated positioning or robotic control systems that systematically cover the entire tank surface, delivering uniform polishing quality while minimizing operator fatigue.
The polishing process often involves the use of water or polishing fluids to cool the surface, reduce dust, and enhance abrasive effectiveness. Integrated dust extraction systems capture airborne particles generated during polishing, helping maintain a clean environment and protect operator health. The machine’s ergonomic design includes features such as easy-to-grip handles, adjustable control panels, and safety guards to facilitate comfortable and safe operation.
Durability and adaptability are key characteristics of Tank Surface Polishing Machines, with construction materials and components chosen to withstand industrial use and resist corrosion from polishing compounds and cleaning agents. The machines can accommodate a wide range of tank sizes and shapes, making them versatile tools for industries requiring regular tank maintenance or finishing during manufacturing.
By automating and standardizing the polishing process, these machines help manufacturers achieve higher surface quality, reduce manual labor, and shorten maintenance downtime. The resulting polished surfaces improve tank hygiene, corrosion resistance, and visual appeal, which are critical for meeting industry regulations and extending tank service life.
The Tank Surface Polishing Machine often includes customizable settings that allow operators to save specific polishing programs tailored to different tank materials and surface conditions. This repeatability ensures consistent results across multiple tanks, reducing variability caused by manual polishing. The ability to quickly switch between presets also shortens setup times when processing tanks with varying requirements.
Maintenance is streamlined with easy access to key components such as polishing pads, belts, motors, and extraction filters. Regular replacement of consumables like abrasive pads and polishing compounds keeps the machine operating at peak efficiency, while sensors and diagnostic features may provide alerts when service is needed, minimizing unplanned downtime.
The machine’s modular design allows integration with other surface treatment systems, such as cleaning, passivation, or inspection units, creating a comprehensive tank finishing line. This integration can further optimize workflow and reduce handling between different processes.
In addition to industrial manufacturing, the Tank Surface Polishing Machine is valuable for on-site maintenance and refurbishment, where it can restore the finish of existing tanks to like-new condition. Portable versions with adjustable arms or handheld polishing units provide flexibility for working in confined spaces or on large, stationary tanks.
Safety protocols incorporated in the design include emergency stop functions, interlocked covers, and noise reduction features to create a safer and more comfortable working environment. Training programs supported by intuitive controls and clear user manuals enable operators to quickly master the equipment, ensuring safe and effective operation.
Overall, the Tank Surface Polishing Machine significantly enhances operational efficiency and surface finish quality in tank fabrication and maintenance. Its combination of precision, adaptability, and user-friendly features makes it an essential tool for industries demanding clean, corrosion-resistant, and visually appealing tank surfaces.
Industrial Tank Polisher
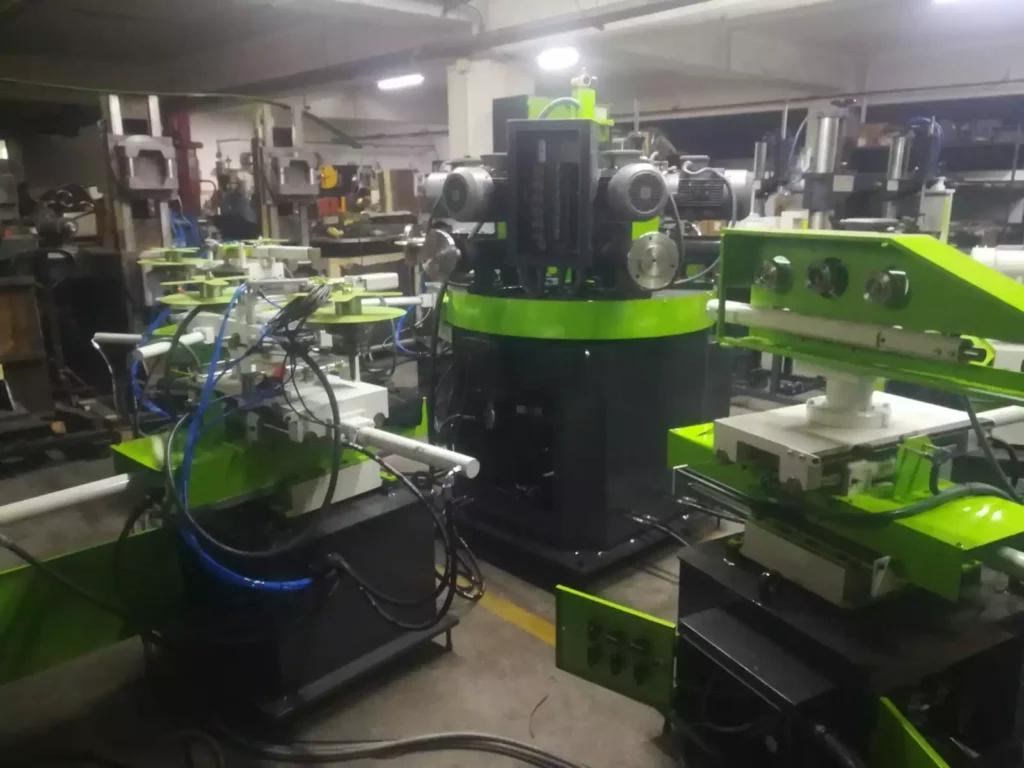

An Industrial Tank Polisher is a robust, heavy-duty machine designed specifically for polishing large industrial tanks used in sectors such as chemical processing, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and water treatment. These tanks often require smooth, defect-free surfaces to meet hygiene standards, prevent corrosion, and ensure durability.
The Industrial Tank Polisher typically features powerful rotating polishing heads or wheels mounted on adjustable arms or booms that can extend and maneuver around the tank’s cylindrical or irregular surfaces. The machine applies consistent pressure and controlled motion to evenly polish the tank’s exterior, removing weld seams, oxidation, scale, and other surface imperfections.
Equipped with variable speed controls, the polisher allows operators to fine-tune polishing intensity according to tank material, surface condition, and desired finish, ranging from matte to mirror-like gloss. For very large tanks, some models incorporate automated or robotic positioning systems that ensure comprehensive coverage with minimal manual intervention.
To handle the substantial debris and dust generated during polishing, these machines include integrated dust extraction units, promoting a clean work environment and protecting worker health. Cooling sprays or lubricants may also be used to reduce friction and heat buildup, improving abrasive performance and extending tool life.
Safety features are critical and typically include emergency stop buttons, protective guards around moving parts, ergonomic controls, and interlocked access points to prevent accidents during operation. The sturdy construction of Industrial Tank Polishers ensures durability and reliable performance in demanding industrial environments.
This machine enhances production efficiency by significantly reducing manual labor, improving finish consistency, and speeding up the polishing process. The polished tank surfaces contribute to improved corrosion resistance, easier cleaning, and compliance with strict industrial standards, making the Industrial Tank Polisher indispensable in modern tank fabrication and maintenance.
The Industrial Tank Polisher operates by using rotating polishing heads or wheels that apply abrasive materials to the tank’s surface, smoothing out imperfections such as weld seams, oxidation, and surface roughness. These polishing heads are mounted on adjustable arms or booms, which can be extended or positioned to reach all areas of the tank, including hard-to-access spots. The machine’s variable speed controls allow operators to adjust polishing intensity and speed to suit different tank materials and desired finishes, ensuring consistent and high-quality results.
For very large tanks, some machines incorporate automated or robotic positioning systems that move the polishing heads systematically over the surface, minimizing the need for manual labor and reducing operator fatigue. This automation helps achieve uniform surface finishes and improves overall efficiency by reducing polishing time.
During operation, dust and metal particles generated from the polishing process are captured by built-in dust extraction systems, maintaining a cleaner and safer workspace and protecting operators from inhaling harmful particles. Cooling sprays or lubricants can be applied to the surface to reduce heat generated by friction, which helps prolong the life of abrasive tools and prevents damage to the tank material.
The machine’s design prioritizes operator safety and comfort, featuring protective guards around moving parts, emergency stop buttons, ergonomic control panels, and interlocked access points to prevent accidental exposure to hazards. Robust construction ensures the polisher can withstand the demanding conditions of industrial environments, maintaining reliable performance over extended periods of use.
Overall, the Industrial Tank Polisher improves productivity by automating and standardizing the polishing process, delivering superior surface finishes that enhance corrosion resistance and facilitate cleaning. These improvements help manufacturers meet strict industry regulations while extending the service life of their tanks. The machine’s combination of precision, safety, and adaptability makes it a vital asset in industrial tank fabrication and maintenance operations.
The Industrial Tank Polisher often includes features that allow customization and repeatability, such as programmable polishing cycles and memory settings for different tank sizes and materials. This functionality helps operators quickly switch between jobs without extensive setup, ensuring consistent results across multiple tanks and reducing downtime.
Maintenance is designed to be straightforward, with easy access to polishing heads, abrasive pads, motors, and filtration systems. Regular replacement of consumables like polishing pads and filters keeps the machine operating efficiently, while diagnostic indicators can alert operators to wear or maintenance needs before breakdowns occur, maximizing uptime.
Some models offer modular designs, enabling integration with other finishing processes such as cleaning, passivation, or inspection stations, creating streamlined production lines that minimize handling and transport between steps. This integration supports faster turnaround times and higher throughput.
In addition to fixed installations, portable or semi-portable versions of the Industrial Tank Polisher exist for on-site polishing and refurbishment. These units often come with adjustable arms or handheld polishing heads, allowing operators to work on tanks that are already installed or too large to move. This flexibility is especially valuable for maintenance teams in industries where tanks are used continuously and downtime must be minimized.
Environmental and operator comfort considerations are also addressed through noise reduction technologies, efficient dust extraction, and ergonomic machine layouts. Training programs and user-friendly interfaces help operators quickly become proficient with the equipment, ensuring safe and effective use.
Ultimately, the Industrial Tank Polisher provides a reliable, efficient, and adaptable solution for achieving high-quality polished finishes on industrial tanks. Its combination of automation, safety features, and ease of maintenance makes it an indispensable tool for manufacturers and maintenance teams committed to quality and operational excellence.
Tank Shell Finishing Machine

A Tank Shell Finishing Machine is an industrial machine designed specifically to perform surface finishing operations on the cylindrical shells of tanks used in various industries such as chemical processing, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and storage. The machine’s primary function is to smooth, polish, and prepare the tank shell surface by removing weld marks, surface imperfections, oxidation, and scale, resulting in a uniform, clean, and corrosion-resistant finish.
The machine usually consists of rotating abrasive heads, polishing wheels, or grinding belts mounted on adjustable arms or frames that can be moved around the tank shell surface. It can be a fixed or portable unit, depending on the size of the tank shell and production requirements. The adjustable arms allow the machine to accommodate different tank diameters and heights, ensuring comprehensive surface coverage.
Equipped with variable speed drives, the machine allows precise control over the polishing or grinding speed to match different metal types and surface conditions. This flexibility enables operators to achieve finishes ranging from rough grinding for weld removal to fine polishing for a mirror-like appearance.
Integrated dust extraction systems capture the metal particles and dust generated during finishing, maintaining a clean working environment and improving operator safety. Cooling or lubrication systems may also be incorporated to reduce heat buildup during the grinding or polishing process, protecting the tank shell surface and extending the life of abrasive materials.
Safety features such as emergency stop buttons, protective guards, and ergonomic controls ensure safe operation in industrial settings. The machine is constructed with durable materials designed to withstand heavy use and exposure to polishing compounds and environmental factors.
By automating and standardizing the surface finishing process, the Tank Shell Finishing Machine improves efficiency, reduces manual labor, and delivers consistent high-quality finishes essential for the longevity, cleanliness, and compliance of industrial tanks.
The Tank Shell Finishing Machine works by applying abrasive or polishing materials through rotating heads, belts, or wheels that move systematically over the curved surface of the tank shell. These components are mounted on adjustable arms or frames that can be positioned to fit tanks of varying diameters and heights, allowing for comprehensive coverage without the need for manual scaffolding or repositioning. Operators control the speed and pressure applied by the polishing elements to tailor the finish according to the material type and surface condition, enabling everything from initial weld seam removal to final high-gloss polishing.
During operation, the machine generates metal dust and debris, which are collected by integrated dust extraction systems to maintain a clean and safe working environment while minimizing contamination risks. Cooling fluids or lubricants may be used to reduce friction and heat buildup, protecting both the tank surface and the abrasives, thus prolonging the life of consumable parts and ensuring a consistent finish.
The design emphasizes safety and ease of use, with features such as emergency stop buttons, protective guards around moving parts, and ergonomic control interfaces that reduce operator fatigue. The machine’s robust construction allows it to endure the harsh conditions of industrial polishing environments, including exposure to polishing compounds and extended operating hours.
Maintenance is straightforward, with quick access to key components such as polishing pads, belts, and motors, facilitating timely replacement and reducing downtime. Some models also offer programmable polishing cycles and memory settings, enabling operators to replicate precise finishes across multiple tanks and improve production consistency.
By automating the finishing process, the Tank Shell Finishing Machine reduces labor intensity and time requirements while improving surface quality, corrosion resistance, and compliance with industry standards. This combination of precision, efficiency, and safety makes it a vital tool for manufacturers and maintenance teams working with large industrial tanks.
The Tank Shell Finishing Machine can often be integrated into larger production workflows, working alongside cleaning, inspection, and passivation equipment to form a complete tank fabrication or maintenance line. This integration minimizes manual handling and transfer times, improving overall productivity and ensuring that each tank meets strict quality standards before moving to the next stage.
Advanced models may include automation features such as robotic arms or CNC-controlled polishing heads, which precisely follow programmed paths around the tank shell. This automation enhances repeatability and surface uniformity, reducing operator dependency and variability in finish quality. It also allows for faster processing speeds, which is critical in high-volume manufacturing environments.
Portability is another key feature for many Tank Shell Finishing Machines, especially those used in on-site maintenance or refurbishment. Portable units with adjustable arms or handheld polishing tools allow technicians to work on tanks that are too large or fixed in place, restoring surface finishes without requiring costly disassembly or transport.
Environmental considerations are addressed through efficient dust and waste collection systems, noise reduction technologies, and the use of eco-friendly polishing compounds when possible. These features contribute to safer, cleaner workplaces and help companies meet regulatory requirements related to workplace health and environmental protection.
Training and user support are essential components of machine operation, with manufacturers often providing comprehensive manuals, tutorials, and sometimes on-site training to ensure operators can safely and effectively use the equipment. Intuitive controls and clear feedback displays help minimize errors and optimize polishing processes.
Overall, the Tank Shell Finishing Machine is a critical asset in industrial tank production and maintenance, offering precise, consistent surface finishes that improve tank performance, appearance, and lifespan. Its combination of adaptability, safety features, and efficiency makes it indispensable for industries where tank quality directly impacts product integrity and regulatory compliance.
Cylindrical Tank Polishing Equipment

Cylindrical Tank Polishing Equipment is specialized machinery designed to polish and finish the curved surfaces of cylindrical tanks used across industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and storage. These tanks require smooth, clean, and defect-free surfaces to meet hygiene standards, improve corrosion resistance, and enhance aesthetic appeal.
This equipment typically consists of rotating polishing heads, abrasive belts, or buffing wheels mounted on adjustable arms or frames that can conform to the cylindrical shape and varying diameters of tanks. The adjustable mechanism ensures full coverage of the tank surface, including edges and weld seams, without the need for manual scaffolding.
Operators can control polishing speed and pressure to accommodate different materials and surface conditions, enabling finishes that range from rough grinding to fine polishing. Some advanced models incorporate automation features such as robotic arms or CNC controls that systematically move polishing heads around the tank surface, providing uniform results and reducing manual labor.
Integrated dust collection and extraction systems help manage debris and maintain a clean, safe work environment. Cooling sprays or lubricants may be applied during polishing to reduce friction and prevent overheating, prolonging the life of polishing tools and protecting the tank surface.
Safety features such as emergency stop controls, protective guards, and ergonomic interfaces ensure operator safety and comfort during use. The equipment’s rugged construction is designed to withstand industrial environments and heavy usage.
Cylindrical Tank Polishing Equipment enhances production efficiency by speeding up the finishing process, improving surface quality, and ensuring compliance with industrial standards. Its versatility, precision, and safety features make it a vital tool in the manufacturing and maintenance of cylindrical tanks.
The Cylindrical Tank Polishing Equipment operates by using rotating polishing heads, abrasive belts, or buffing wheels mounted on adjustable arms or frames that conform to the tank’s curved surface. These components move systematically around the tank’s circumference and height to cover the entire exterior, including weld seams and edges. The adjustable design accommodates tanks of varying diameters and sizes, ensuring consistent polishing without the need for manual repositioning or scaffolding.
Operators control the speed and pressure of the polishing elements, tailoring the process to different tank materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, or carbon steel, as well as the desired finish—from coarse grinding to fine polishing. In more advanced setups, robotic arms or CNC controls automate the movement of polishing tools, enhancing precision and repeatability while reducing operator fatigue and labor costs.
During operation, the equipment generates metal dust and polishing debris, which are captured by integrated dust extraction systems to maintain a clean working environment and improve operator safety. Cooling sprays or lubricants are often applied to reduce heat buildup caused by friction, which helps protect the tank surface and extend the lifespan of abrasive components.
The design prioritizes operator safety and comfort, including emergency stop mechanisms, protective guards around moving parts, and ergonomic control panels that simplify machine operation. The equipment’s construction is durable and suited to withstand the demanding conditions of industrial polishing, including exposure to polishing compounds and extended use.
Maintenance is straightforward, with easy access to replaceable polishing pads, belts, and filters, as well as diagnostic features that alert operators when service is needed to minimize downtime. The equipment may also offer programmable settings or memory functions to quickly reproduce polishing cycles for tanks with similar specifications, improving consistency and efficiency.
By automating and standardizing the polishing process for cylindrical tanks, this equipment reduces manual labor, enhances surface quality, and ensures compliance with hygiene and corrosion resistance standards. Its combination of precision, adaptability, and safety makes it an essential tool in tank manufacturing and maintenance operations across various industries.
The Cylindrical Tank Polishing Equipment can be integrated into larger production workflows to streamline tank finishing processes. When combined with cleaning, inspection, and passivation systems, it helps create a seamless fabrication or refurbishment line that reduces handling time and improves overall throughput. This integration allows manufacturers to maintain consistent quality standards and shorten production cycles.
Automation capabilities in advanced models include robotic arms or computer-controlled polishing heads that follow pre-programmed paths around the tank. This reduces operator involvement and human error, delivering highly uniform finishes while increasing processing speed. Such automation is particularly beneficial for large-scale production or tanks with complex surface geometries.
Portability is another key feature, with some equipment designed as mobile units or including handheld polishing tools mounted on adjustable arms. This flexibility enables on-site polishing and maintenance of tanks that are too large or fixed in place, avoiding costly disassembly or relocation. Portable units are valuable for field servicing in industries like oil and gas, water treatment, and manufacturing plants.
Environmental and worker safety considerations are addressed through efficient dust collection systems, noise reduction measures, and the use of non-toxic polishing compounds where possible. These features help meet regulatory requirements and improve working conditions, fostering safer and more sustainable operations.
Training and user support are critical, with manufacturers often providing detailed manuals, operator training, and customer service to ensure effective and safe equipment use. Intuitive controls and real-time feedback systems make operation straightforward, even for less experienced users.
Overall, Cylindrical Tank Polishing Equipment offers a reliable, efficient solution for achieving high-quality finishes on cylindrical tanks. Its adaptability, automation options, and safety features make it indispensable for industries where tank surface quality directly impacts product integrity, regulatory compliance, and operational longevity.
Tank Wall Surface Refining System
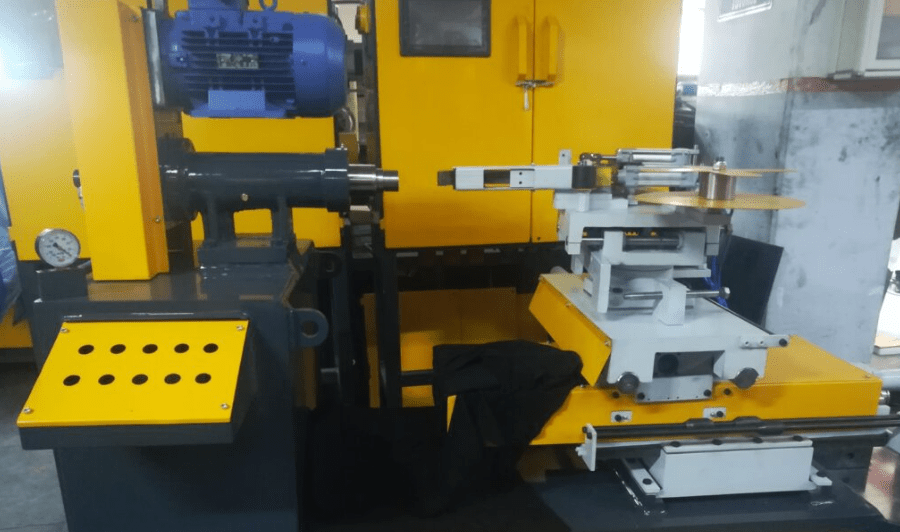
A Tank Wall Surface Refining System is specialized equipment designed to enhance the surface quality of tank walls, particularly those used in industrial applications such as chemical processing, food and beverage storage, pharmaceuticals, and water treatment. The system’s primary function is to refine, smooth, and polish the interior and/or exterior surfaces of tank walls to remove imperfections, weld marks, corrosion, and surface roughness, thereby improving durability, hygiene, and appearance.
Typically, the system uses a combination of mechanical polishing, grinding, and buffing tools mounted on adjustable arms, robotic manipulators, or frames that can conform to the tank wall’s shape and size. These tools apply controlled abrasive action to the surface, resulting in a uniform finish that can range from matte to mirror-like gloss depending on process requirements.
The refining system often includes variable speed controls, allowing operators to adjust the polishing intensity and speed to match different tank materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or aluminum. Integrated dust and debris extraction systems help maintain a clean working environment by capturing particles generated during the process, which also enhances operator safety.
Some advanced systems feature automated or CNC-controlled polishing heads that follow programmed paths to ensure consistent and repeatable surface refinement, reducing manual labor and improving efficiency. Cooling and lubrication mechanisms are sometimes incorporated to reduce heat buildup and extend the lifespan of abrasives and equipment components.
Safety features such as emergency stop buttons, protective covers, and ergonomic controls are standard to protect operators during operation. The system’s design emphasizes durability and reliability to withstand continuous industrial use.
By providing precise and consistent surface finishing, the Tank Wall Surface Refining System helps manufacturers meet stringent quality and regulatory standards, improve corrosion resistance, facilitate easier cleaning, and extend tank service life. It is an essential tool in tank fabrication and maintenance operations focused on quality and efficiency.
The Tank Wall Surface Refining System functions by utilizing mechanical polishing, grinding, or buffing tools mounted on adjustable arms, robotic manipulators, or frames that conform to the tank wall’s shape. These tools apply controlled abrasive action over the surface to remove weld marks, roughness, corrosion, and other imperfections, delivering a smooth and uniform finish. The adjustable setup accommodates different tank sizes and shapes, ensuring comprehensive coverage without requiring manual repositioning or scaffolding.
Operators control the polishing speed and pressure to suit various materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or aluminum, tailoring the finish from coarse grinding to fine polishing as needed. More advanced systems feature automated or CNC-controlled polishing heads that follow programmed paths, enhancing precision and repeatability while reducing manual labor and operator fatigue.
During operation, dust and debris generated by the abrasive process are captured by integrated extraction systems, maintaining a clean environment and protecting operator health. Cooling and lubrication mechanisms may be employed to reduce frictional heat, protecting both the tank surface and polishing tools, and extending consumable life.
The design includes essential safety features such as emergency stops, protective guards, and ergonomic controls to ensure safe and user-friendly operation. The robust construction allows the system to withstand the demanding conditions of industrial environments, including long operating hours and exposure to polishing compounds.
Maintenance is made straightforward by easy access to polishing components and filters, along with diagnostic features that signal when service or replacement is required, minimizing downtime. Programmable settings or memory functions allow operators to replicate polishing cycles for similar tanks, improving efficiency and consistency.
By automating and standardizing the surface refining process, this system reduces labor intensity, shortens finishing times, and improves surface quality, corrosion resistance, and hygiene. Its precision, adaptability, and safety features make the Tank Wall Surface Refining System a vital tool in the manufacturing and maintenance of industrial tanks across various sectors.
The Tank Wall Surface Refining System can be integrated into broader production and maintenance workflows, working alongside cleaning, inspection, and passivation equipment to create streamlined tank finishing lines. This integration reduces manual handling and transfer times, improving throughput and ensuring consistent quality standards across multiple tanks.
Automation capabilities, such as robotic arms or CNC-controlled polishing heads, allow the system to follow precise, repeatable polishing paths, enhancing surface uniformity and reducing dependence on operator skill. This leads to faster processing times and consistent finishes, which are particularly beneficial in large-scale manufacturing or refurbishment operations.
Portability is often a key feature in refining systems designed for on-site maintenance or repairs. Mobile units or handheld polishing tools with adjustable arms enable technicians to work on tanks that cannot be moved or disassembled, minimizing downtime and costs associated with tank relocation.
Environmental and worker safety concerns are addressed through efficient dust extraction, noise reduction, and the use of environmentally friendly polishing compounds where possible. These features help facilities comply with occupational health and safety regulations and reduce environmental impact.
Comprehensive training and user support, including manuals, tutorials, and sometimes on-site instruction, are provided to ensure operators can safely and effectively use the system. Intuitive controls and feedback mechanisms facilitate ease of use and process optimization.
Overall, the Tank Wall Surface Refining System delivers precise, efficient, and safe surface finishing solutions that enhance tank performance, extend service life, and ensure regulatory compliance. Its combination of adaptability, automation, and user-friendly design makes it essential for industries reliant on high-quality tank fabrication and maintenance.
Stainless Steel Tank Polishing Machine
A Stainless Steel Tank Polishing Machine is specialized equipment designed to polish and finish the surfaces of stainless steel tanks used in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and cosmetics. Stainless steel tanks require smooth, clean, and defect-free surfaces to meet strict hygiene standards, prevent corrosion, and maintain product purity.
This machine typically features rotating polishing heads, abrasive belts, or buffing wheels mounted on adjustable arms or frames that conform to the tank’s shape and size. It can polish both the interior and exterior surfaces of tanks, ensuring uniform coverage including weld seams, edges, and hard-to-reach areas. The adjustable design allows the machine to accommodate tanks of varying diameters and heights.
Operators can control polishing speed, pressure, and abrasive grade to suit different stainless steel grades and desired surface finishes, ranging from matte to mirror polish. Advanced models may incorporate automation technologies such as robotic arms or CNC controls to follow programmed polishing paths, enhancing precision, consistency, and efficiency while reducing manual labor.
Integrated dust and debris extraction systems help maintain a clean working environment by capturing polishing residues and metal particles. Cooling or lubrication systems may also be included to prevent overheating and extend the life of polishing tools.
Safety features such as emergency stops, protective guards, and ergonomic controls ensure operator safety and comfort. The machine’s robust construction enables it to withstand the demanding conditions of industrial polishing environments.
By automating the stainless steel tank finishing process, this machine improves productivity, ensures consistent high-quality finishes, and helps manufacturers comply with stringent regulatory and hygiene requirements.
The Stainless Steel Tank Polishing Machine operates by using rotating polishing heads, abrasive belts, or buffing wheels that are mounted on adjustable arms or frames designed to fit the tank’s shape and size. These components move systematically over the tank’s interior and exterior surfaces, covering weld seams, edges, and hard-to-reach areas to ensure a uniform polish. The adjustable setup accommodates tanks of various diameters and heights, eliminating the need for manual repositioning or scaffolding.
Operators control the polishing speed, pressure, and abrasive grade to match different stainless steel types and achieve finishes ranging from matte to mirror-like shine. Some advanced machines feature robotic arms or CNC-controlled polishing heads that follow programmed paths, enhancing precision, repeatability, and efficiency while reducing operator fatigue and labor costs.
During operation, the machine generates metal dust and polishing debris, which are collected by integrated extraction systems to maintain a clean, safe working environment and protect operator health. Cooling or lubrication systems help reduce frictional heat, protecting both the stainless steel surface and polishing tools, thereby extending tool life and preserving surface integrity.
Safety is prioritized with features such as emergency stop buttons, protective guards around moving parts, and ergonomic controls designed for ease of use and operator comfort. The machine’s durable construction ensures reliability in industrial environments, enduring long hours of operation and exposure to polishing compounds.
Maintenance is straightforward, with easy access to polishing pads, belts, and dust filters, alongside diagnostic indicators that notify when service or replacement is needed, minimizing downtime. Programmable settings enable operators to save and reproduce polishing cycles for tanks of similar specifications, improving consistency and throughput.
By automating and standardizing the polishing process, the Stainless Steel Tank Polishing Machine reduces manual labor, shortens finishing times, and delivers high-quality surface finishes that meet hygiene and corrosion resistance standards. Its precision, adaptability, and safety features make it an essential tool in the manufacturing and maintenance of stainless steel tanks across various industries.
The Stainless Steel Tank Polishing Machine can be seamlessly integrated into larger production and maintenance workflows to enhance operational efficiency. When combined with cleaning, inspection, and passivation systems, it forms a comprehensive finishing line that minimizes manual handling and accelerates the overall tank fabrication or refurbishment process.
Automation capabilities such as robotic arms or CNC-controlled polishing heads allow for highly precise, repeatable polishing cycles, reducing reliance on operator skill and minimizing inconsistencies in surface finish. This leads to faster processing times and higher throughput, which is particularly advantageous in high-volume manufacturing or stringent regulatory environments.
Portability and flexibility are important features, especially for on-site polishing or maintenance. Mobile units or handheld polishing attachments mounted on adjustable arms enable technicians to work on tanks that cannot be moved or disassembled, reducing downtime and logistical challenges.
Environmental and workplace safety are addressed through efficient dust extraction systems, noise reduction technologies, and the use of eco-friendly polishing compounds where feasible. These measures help facilities comply with health, safety, and environmental regulations while maintaining a comfortable and safe working environment.
Training and user support are key components, with manufacturers providing detailed manuals, operator training sessions, and customer service to ensure safe, efficient operation. User-friendly interfaces and real-time feedback systems help optimize polishing parameters and reduce the risk of errors.
In summary, the Stainless Steel Tank Polishing Machine is a vital asset in industries requiring impeccable tank surface finishes. Its blend of automation, precision, safety, and adaptability makes it indispensable for achieving consistent, high-quality results that enhance product integrity, comply with regulations, and extend tank lifespan.
Tank Outer Surface Polisher
A Tank Outer Surface Polisher is a specialized machine designed to polish and finish the external surfaces of industrial tanks used in sectors like chemical processing, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and storage. Its primary function is to enhance the tank’s exterior surface by removing imperfections such as weld marks, scratches, corrosion, and surface roughness, resulting in a smooth, uniform, and aesthetically pleasing finish.
The machine typically features rotating polishing heads, abrasive belts, or buffing wheels mounted on adjustable arms or frames that can be tailored to the tank’s size and shape. This adaptability ensures full coverage of the curved tank surfaces, including edges and weld seams, without the need for manual repositioning or scaffolding.
Operators can control polishing parameters such as speed, pressure, and abrasive grade to suit different tank materials—commonly stainless steel, carbon steel, or aluminum—and achieve finishes ranging from matte to mirror polish. Advanced models may offer automation through robotic arms or CNC controls, which enable precise, repeatable polishing motions, improving efficiency and surface quality while reducing labor intensity.
Dust and debris generated during polishing are managed through integrated extraction systems, maintaining a clean working environment and protecting operator health. Cooling sprays or lubricants may be applied during operation to reduce heat buildup and prolong the life of polishing tools.
Safety features include emergency stop buttons, protective guards, and ergonomic controls, ensuring operator safety and comfort during use. The equipment is constructed from durable materials to withstand the rigors of industrial environments and continuous use.
By automating and standardizing the finishing process, the Tank Outer Surface Polisher improves productivity, enhances corrosion resistance, and helps manufacturers meet regulatory and aesthetic standards, making it an essential tool in tank fabrication and maintenance.
The Tank Outer Surface Polisher works by employing rotating polishing heads, abrasive belts, or buffing wheels attached to adjustable arms or frames designed to fit the tank’s exterior contours. These polishing components move systematically over the tank’s curved surface, including weld seams and edges, to deliver a consistent and uniform finish. The adjustable setup allows the machine to accommodate tanks of various diameters and heights, eliminating the need for manual repositioning or scaffolding.
Operators control polishing speed, pressure, and abrasive type to suit different materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or aluminum, and to achieve finishes ranging from matte to high gloss. Advanced versions may incorporate robotic arms or CNC-controlled polishing tools that follow programmed paths, enhancing precision, consistency, and efficiency while reducing manual labor and operator fatigue.
During operation, dust, metal particles, and polishing debris are generated; integrated dust extraction systems capture and remove these byproducts to maintain a clean and safe working environment. Cooling or lubrication sprays may be used to reduce frictional heat, protecting both the tank surface and polishing tools, and prolonging tool life.
Safety is ensured through features like emergency stop buttons, protective guards around moving parts, and ergonomic controls that improve operator comfort and usability. The machine’s sturdy construction enables it to endure the demanding conditions of industrial polishing, including extended hours of operation and exposure to polishing compounds.
Maintenance is simplified with easy access to replaceable polishing pads, belts, and dust filters, as well as diagnostic alerts that notify operators when servicing is required, minimizing downtime. Programmable settings enable operators to save and replicate polishing routines for tanks with similar specifications, improving workflow efficiency.
By automating and standardizing the tank exterior finishing process, the Tank Outer Surface Polisher reduces manual effort, shortens processing times, and produces high-quality surface finishes that enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. This equipment is indispensable for manufacturers and maintenance teams aiming for consistent, efficient, and safe polishing of industrial tanks.
The Tank Outer Surface Polisher can be integrated into comprehensive tank fabrication or refurbishment workflows, working in conjunction with cleaning, inspection, and protective coating systems to streamline the entire finishing process. This integration minimizes manual handling, reduces turnaround times, and helps maintain consistent quality standards across batches.
Automation features, such as robotic polishing arms or CNC-guided polishing heads, enable the system to follow precise, repeatable polishing patterns, reducing operator dependency and variability. This consistency is crucial for meeting industry regulations and customer specifications, especially in sectors demanding high hygiene or aesthetic standards.
Portability and flexibility are key considerations for many applications. Some polishers are designed as mobile units or include handheld attachments mounted on adjustable arms, allowing technicians to perform on-site polishing of tanks that are too large or fixed in place. This capability minimizes downtime and avoids costly tank relocation or disassembly.
Environmental and safety factors are addressed through efficient dust extraction, noise suppression, and the use of environmentally friendly polishing compounds when possible. These measures help organizations comply with occupational health and environmental regulations, enhancing workplace safety and sustainability.
Manufacturers typically provide comprehensive user support, including detailed operation manuals, training programs, and responsive customer service, to ensure safe and effective use of the equipment. Intuitive controls, real-time feedback, and programmable settings make operation accessible to users with varying levels of experience, optimizing productivity and finish quality.
Overall, the Tank Outer Surface Polisher delivers precise, efficient, and reliable polishing solutions that improve tank appearance, corrosion resistance, and longevity. Its combination of adaptability, automation, and safety makes it an essential tool for industries requiring high-quality tank surface finishing.
Tank Body Buffing Machine

A Tank Body Buffing Machine is a specialized piece of equipment designed to buff and polish the cylindrical or curved surfaces of industrial tanks, enhancing their surface smoothness, shine, and overall finish. It is commonly used in industries such as chemical processing, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and storage tank manufacturing, where tank surface quality impacts durability, hygiene, and appearance.
The machine typically consists of rotating buffing wheels or pads mounted on adjustable arms or fixtures that conform to the tank’s shape and size. These buffing elements apply controlled pressure and motion to the tank body surface, removing minor imperfections like scratches, weld marks, oxidation, or surface roughness, and imparting a polished, uniform finish.
Operators can adjust parameters such as buffing speed, pressure, and pad type to suit various materials—including stainless steel, carbon steel, or aluminum—and to achieve finishes ranging from satin matte to mirror polish. Some advanced buffing machines incorporate automated or CNC-controlled systems that guide the buffing heads along precise, repeatable paths, improving consistency and reducing manual labor.
Dust and buffing residues are managed by integrated extraction systems, ensuring a clean work environment and protecting operator health. Cooling or lubrication systems may also be used to prevent heat buildup during the buffing process, which protects both the tank surface and the buffing tools.
Safety features include emergency stop functions, protective guards, and ergonomic controls to ensure operator safety and comfort. The machine’s sturdy construction allows it to withstand the rigors of industrial use, including extended operation hours and exposure to polishing compounds.
By automating the buffing process, the Tank Body Buffing Machine improves productivity, delivers high-quality finishes, enhances corrosion resistance, and helps manufacturers meet stringent quality and hygiene standards. It is an essential tool in tank fabrication and maintenance operations aiming for precise and consistent surface finishing.
The Tank Body Buffing Machine operates by utilizing rotating buffing wheels or pads mounted on adjustable arms or fixtures designed to conform to the tank’s cylindrical or curved surface. These buffing components move systematically along the tank body, applying controlled pressure and motion to remove surface imperfections such as scratches, weld marks, oxidation, and roughness, resulting in a smooth, uniform, and polished finish. The adjustable setup accommodates tanks of various sizes and diameters, allowing for efficient and thorough buffing without the need for manual repositioning.
Operators have control over key parameters including buffing speed, pressure, and the type of buffing pad or wheel used, enabling customization according to the material of the tank—commonly stainless steel, carbon steel, or aluminum—and the desired surface finish, ranging from a satin matte look to a high-gloss mirror polish. Advanced models may include automated or CNC-controlled buffing heads that follow programmed paths, ensuring precision, repeatability, and reduced manual labor and operator fatigue.
During the buffing process, dust, metal particles, and polishing residues are generated. Integrated extraction and dust collection systems capture these byproducts to maintain a clean and safe working environment and to protect operator health. Cooling or lubrication systems may be applied simultaneously to minimize heat buildup caused by friction, preserving both the integrity of the tank surface and the lifespan of buffing tools.
Safety features are incorporated throughout the design, including emergency stop mechanisms, protective guards around moving parts, and ergonomic controls that improve ease of use and operator comfort. The machine’s robust construction enables it to endure the demands of industrial environments, including prolonged operation and exposure to various polishing compounds.
Maintenance is facilitated by easy access to buffing pads, wheels, and dust filters, along with diagnostic systems that alert operators when servicing or component replacement is necessary, thereby minimizing downtime. Programmable settings allow operators to save and replicate buffing routines for tanks with similar specifications, enhancing workflow efficiency and consistency.
By automating and standardizing the buffing process, the Tank Body Buffing Machine reduces manual effort, accelerates finishing times, and produces high-quality surface finishes that improve corrosion resistance and overall tank aesthetics. This machine is vital for manufacturers and maintenance teams focused on achieving precise, reliable, and safe buffing of industrial tank bodies.
The Tank Body Buffing Machine can be integrated into broader tank manufacturing and maintenance workflows, working alongside surface cleaning, inspection, and protective coating systems to create efficient finishing lines. This integration reduces manual handling and turnaround times, ensuring tanks are polished to consistent quality standards before delivery or redeployment.
Automation plays a significant role in enhancing the machine’s efficiency and precision. Robotic arms or CNC-guided buffing heads enable the machine to follow exact polishing paths, reducing variability caused by manual operation and improving surface uniformity. This level of control is especially important in industries with stringent regulatory and aesthetic requirements.
Portability and flexibility are important for on-site maintenance and repairs, where tanks cannot be easily moved or disassembled. Some buffing machines are designed as mobile units or include handheld attachments mounted on adjustable arms, allowing technicians to access hard-to-reach areas and perform polishing without dismantling the tank. This capability reduces downtime and lowers maintenance costs.
Workplace safety and environmental concerns are addressed through built-in dust extraction systems, noise reduction features, and the use of environmentally friendly polishing compounds when possible. These aspects help companies comply with health, safety, and environmental regulations, contributing to a safer work environment.
Comprehensive operator training and support are often provided by manufacturers to ensure proper and safe use of the machine. Intuitive control interfaces, real-time feedback, and programmable settings make the equipment accessible to operators of varying skill levels, optimizing productivity and quality.
Overall, the Tank Body Buffing Machine offers a reliable, efficient, and precise solution for achieving high-quality surface finishes on industrial tanks. Its combination of automation, adaptability, and safety features makes it an indispensable tool for industries focused on durability, hygiene, and visual appeal in tank fabrication and maintenance.
Tank Mirror Finishing Machine

A Tank Mirror Finishing Machine is a specialized polishing system designed to produce a high-gloss, mirror-like finish on the surfaces of industrial tanks, typically made from stainless steel or other metals. This type of finish not only enhances the aesthetic appeal but also improves corrosion resistance and hygiene by creating a smooth, reflective surface that is easy to clean and less prone to bacterial buildup, making it essential in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and beverages.
The machine uses a combination of fine abrasive polishing wheels, buffing pads, and sometimes polishing compounds, all mounted on adjustable arms or robotic polishing heads. These components rotate at controlled speeds and apply precise pressure to the tank surface, progressively smoothing out microscopic surface irregularities until the desired mirror finish is achieved.
Operators can adjust polishing parameters—including speed, pressure, and abrasive grade—to match the specific tank material and size, ensuring optimal results. Advanced models often feature CNC or robotic automation, enabling the machine to follow programmed polishing paths for consistent, repeatable finishes while reducing manual labor and operator fatigue.
During the mirror finishing process, the machine employs integrated dust and debris extraction systems to maintain a clean work environment and protect operator health. Cooling sprays or lubrication may be used to prevent heat buildup, which could damage the surface or polishing tools.
Safety features such as emergency stop buttons, protective guards, and ergonomic controls are standard to protect operators and ensure ease of use. The machine’s durable construction withstands demanding industrial conditions, including extended operation and exposure to polishing compounds.
By automating the polishing process, the Tank Mirror Finishing Machine enhances productivity, reduces finishing times, and delivers superior surface quality that meets strict industry standards for cleanliness and appearance. It is a critical tool for manufacturers and maintenance teams aiming for flawless, mirror-like finishes on tank exteriors and interiors.
The Tank Mirror Finishing Machine operates by using a series of fine abrasive polishing wheels, buffing pads, and sometimes polishing compounds mounted on adjustable arms or robotic heads that rotate at controlled speeds. These components apply precise and consistent pressure to the tank’s surface, progressively eliminating microscopic irregularities, scratches, and surface roughness until a smooth, mirror-like finish is achieved. The adjustable design allows the machine to accommodate tanks of various sizes and shapes, ensuring even polishing across curved and flat areas alike.
Operators control key parameters such as polishing speed, pressure, and abrasive grade to match the specific tank material—typically stainless steel or other metals—and the desired finish quality. Advanced models feature CNC or robotic automation that follows programmed polishing paths, providing repeatability, precision, and uniformity while minimizing manual labor and reducing operator fatigue.
Throughout the polishing process, dust, metal particles, and polishing residues are produced. Integrated extraction systems capture and remove these byproducts, maintaining a clean and safe working environment and protecting operator health. Cooling sprays or lubricants are often used to reduce heat buildup caused by friction, protecting both the tank surface and the polishing tools from damage.
Safety is a key consideration, with features like emergency stop buttons, protective guards around moving parts, and ergonomic controls to enhance operator comfort and safety. The machine’s robust construction ensures durability under continuous industrial use, including resistance to polishing compounds and long operation hours.
Maintenance is straightforward, with easy access to polishing wheels and pads for replacement or cleaning, as well as monitoring systems that alert operators when service is required, reducing downtime. Programmable settings allow operators to save polishing routines for tanks with similar specifications, enhancing efficiency and consistency.
By automating and standardizing the mirror finishing process, the Tank Mirror Finishing Machine delivers superior surface quality, improved corrosion resistance, and an aesthetically appealing reflective finish. This makes it an essential tool in industries where high standards of hygiene, appearance, and durability are critical for tank performance and compliance.
The Tank Mirror Finishing Machine can be seamlessly integrated into broader tank fabrication and maintenance workflows, complementing cleaning, inspection, and protective coating processes to create efficient production lines. This integration helps reduce handling time and ensures that tanks consistently meet stringent surface quality requirements before being shipped or put into service.
Automation capabilities such as robotic polishing arms or CNC-controlled heads significantly enhance the machine’s efficiency and precision. These systems follow exact programmed polishing paths, minimizing human error and ensuring consistent, repeatable mirror finishes even on complex curved surfaces. This level of control is especially valuable in industries with strict regulatory standards and aesthetic demands, such as pharmaceuticals and food processing.
Portability and flexibility are also important, especially for on-site polishing of large or fixed tanks that cannot be easily moved. Some machines are designed with mobile bases or include handheld polishing tools mounted on adjustable arms, allowing technicians to access difficult areas and perform mirror finishing without disassembling or relocating the tank. This reduces downtime and maintenance costs.
Workplace safety and environmental concerns are addressed through features like dust extraction, noise reduction, and the use of environmentally friendly polishing compounds when feasible. These measures help companies comply with health and safety regulations, creating a safer and more sustainable work environment.
Manufacturers often provide comprehensive support, including training programs, detailed manuals, and responsive technical assistance to ensure users operate the machine safely and effectively. User-friendly controls, real-time feedback, and programmable settings make it accessible for operators with varying levels of experience, optimizing both productivity and finish quality.
Overall, the Tank Mirror Finishing Machine is a critical asset for achieving flawless, reflective surfaces on industrial tanks. Its combination of precision, automation, safety, and adaptability makes it indispensable for industries demanding high standards of surface finish, durability, and hygiene.
Tank Surface Smoothing Equipment

A Tank Surface Smoothing Equipment is designed to prepare and refine the exterior or interior surfaces of industrial tanks by removing roughness, weld marks, minor dents, and other surface imperfections. This smoothing process is crucial before further finishing steps like polishing or coating, ensuring a uniform and defect-free base surface that enhances durability, appearance, and corrosion resistance.
The equipment typically employs rotating abrasive pads, sanding belts, or grinding wheels mounted on adjustable arms or robotic systems that conform to the tank’s shape and size. These abrasive components move methodically over the tank surface, applying controlled pressure and motion to gradually even out irregularities.
Operators can adjust parameters such as speed, pressure, and abrasive grit level based on the tank material—commonly stainless steel, carbon steel, or aluminum—and the extent of surface smoothing required. Advanced machines may feature CNC or robotic automation, allowing precise, repeatable smoothing patterns and reducing manual effort.
Integrated dust extraction systems capture particles generated during the smoothing process, maintaining a clean workspace and protecting operator health. Cooling or lubrication sprays are often applied to reduce frictional heat, preventing damage to both the tank surface and abrasive tools.
Safety features like emergency stops, protective guards, and ergonomic controls ensure operator protection and ease of use. The machine’s robust build enables it to withstand continuous industrial use, exposure to abrasives, and extended operation periods.
Maintenance is simplified through easy access to replaceable abrasives and dust filters, along with diagnostic alerts for timely servicing. Programmable settings allow operators to save and replicate smoothing routines for tanks with similar specifications, improving workflow efficiency.
By automating and standardizing surface smoothing, this equipment reduces manual labor, shortens preparation time, and produces consistent, high-quality surfaces ideal for subsequent finishing processes. It is essential for manufacturers and maintenance teams aiming to achieve reliable, smooth tank surfaces that enhance overall product quality and lifespan.
The Tank Surface Smoothing Equipment functions by employing rotating abrasives such as pads, belts, or grinding wheels to methodically remove weld marks, scale, oxidation, and other surface inconsistencies from the body of industrial tanks. These abrasives are typically mounted on movable arms or robotic platforms that can adjust to the shape and size of the tank, allowing them to maintain consistent pressure and coverage across curved or cylindrical surfaces. As the equipment moves along the tank’s surface, it progressively smooths out irregularities, creating a uniform and clean foundation that is essential for further finishing steps such as polishing, coating, or painting.
The machine is equipped with adjustable settings for abrasive speed, contact pressure, and grit type, enabling operators to customize the smoothing process according to the tank material and the desired level of refinement. Materials like stainless steel, carbon steel, and aluminum each require specific abrasives and techniques to avoid over-grinding or damaging the surface. CNC or automated systems may be integrated to control the movement of the abrasives precisely, allowing for programmable routines that can be repeated consistently across multiple tanks, thus reducing human error and operator fatigue.
Dust and debris generated by the smoothing process are controlled by built-in extraction and filtration systems, which help maintain a safe and clean working environment while also extending the life of the machine and abrasives. In cases where heat generation is significant, the equipment may apply cooling agents or lubricants directly to the surface, reducing thermal stress and preserving the integrity of both the tank and the tools in use.
Safety is a core consideration in the design, with features such as enclosed grinding areas, emergency stop systems, and intuitive operator interfaces that minimize risk and enhance usability. The construction of the machine is typically heavy-duty to withstand the vibrations, abrasive exposure, and continuous use associated with industrial manufacturing environments.
Routine maintenance is made efficient with accessible abrasive mounts and tool change systems, along with diagnostic features that alert users when components are worn or need service. For production lines that handle tanks of similar size and material, operators can store and recall smoothing programs to maintain consistency and streamline operations.
The Tank Surface Smoothing Equipment ultimately serves to reduce manual labor, shorten tank finishing timelines, and increase surface quality. It is essential in any application where a clean, uniform tank surface is critical to functionality, longevity, or appearance—such as in the food and beverage, pharmaceutical, chemical, or water storage industries. Its precision, adaptability, and efficiency make it a foundational machine for modern tank production and refurbishment processes.
The Tank Surface Smoothing Equipment is also highly valuable for improving downstream process performance. A properly smoothed tank surface facilitates better adhesion of protective coatings and reduces the risk of coating failures such as blistering or delamination. In hygienic industries like dairy or pharmaceuticals, a smoother surface significantly lowers the risk of bacterial contamination by eliminating micro-crevices where residues and microbes could accumulate. This contributes directly to improved product quality and regulatory compliance.
Another benefit is the reduction in the amount of polishing or finishing required afterward. A well-smoothed tank may require fewer polishing passes, less compound, and less energy consumption to reach a mirror or satin finish, which translates into cost and time savings. In high-throughput environments, this can make a noticeable difference in production cycle times.
In terms of machine configuration, many units are modular and can be adapted for horizontal or vertical tank positioning. This flexibility allows the same machine to be used across different tank types—stationary, mobile, pressure-rated, or non-pressure vessels—without needing to invest in multiple dedicated systems. Custom fixtures or tank holders can also be added to keep the workpiece stable during processing.
For large-scale operations, the equipment can be integrated with conveyor systems or robotic handling arms, enabling continuous or semi-automatic workflows. Tanks can be loaded, smoothed, and then transferred directly to polishing or inspection stations with minimal manual intervention. This integration improves workplace ergonomics, reduces handling errors, and allows for better scheduling of work in progress.
Data monitoring and digital control systems are increasingly being incorporated, enabling operators and plant managers to log surface smoothing parameters, track performance, and even analyze wear on consumables. This information can be used to fine-tune operations, predict maintenance needs, and reduce waste. Some systems also allow remote diagnostics and updates, which support uptime and reduce the need for on-site technical interventions.
In summary, the Tank Surface Smoothing Equipment is not just a machine for surface preparation—it is a productivity tool that enhances the quality, hygiene, and efficiency of tank production and maintenance. Its ability to automate a traditionally labor-intensive process while delivering repeatable, high-quality results makes it a strategic investment for manufacturers seeking consistent standards and operational scalability.
Rotary Tank Polishing Machine

A Rotary Tank Polishing Machine is engineered for high-efficiency, automated surface finishing of cylindrical or round industrial tanks, typically made of stainless steel or similar metals. The machine uses a rotating polishing mechanism—often equipped with abrasive wheels, buffing pads, or flap brushes—that moves uniformly over the tank’s surface to eliminate scratches, weld marks, discoloration, and other surface imperfections. The end result is a smooth, visually refined surface that may range from matte to high-gloss, depending on the polishing stage and media used.
This system typically features a rotating base or fixture to securely hold the tank, allowing the polishing head to apply pressure consistently while rotating around or along the surface. The synchronization between the tank’s rotation and the polishing tool’s movement ensures complete, even coverage, particularly on round or elliptical surfaces. The polishing head may be manually guided or automated using CNC or servo-controlled arms that follow preset polishing paths, improving repeatability and surface uniformity.
The operator can control variables such as rotation speed, polishing pressure, abrasive type, and feed rate through an intuitive control panel or touch-screen interface. Depending on the application, different polishing compounds or abrasives can be used in successive stages—from coarse grit for initial smoothing to fine compounds for mirror finishing.
Cooling systems or mist sprays are often integrated to dissipate heat generated during high-friction polishing, which helps prevent warping or surface burn marks. Dust extraction and filtration systems are standard to maintain cleanliness and operator safety, capturing fine particulate matter and spent polishing compounds.
Rotary tank polishing machines are designed with durability in mind, capable of handling the mechanical stress of polishing heavy industrial tanks across multiple shifts. Their frames are typically built from reinforced steel, and wear components like polishing heads and belts are easily replaceable to minimize downtime.
These machines are indispensable in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, chemical manufacturing, and beverage production, where the surface finish of storage tanks plays a vital role in product hygiene, corrosion resistance, and visual standards. By significantly reducing manual labor and polishing time, rotary tank polishing machines increase productivity while ensuring consistent, high-quality surface finishes that meet industry regulations and customer expectations.
A Rotary Tank Polishing Machine operates by using a combination of rotational motion and abrasive tools to refine the surface of cylindrical or round tanks, typically composed of stainless steel or similar corrosion-resistant metals. The machine includes a rotating mechanism that either spins the tank itself or allows a polishing head to revolve around the stationary tank. This synchronized rotary action ensures consistent contact and pressure across the tank’s outer surface, enabling the uniform removal of oxidation, weld discoloration, scratches, and minor surface defects.
The polishing head is generally mounted on an adjustable arm, which can be controlled manually or via an automated system such as CNC or servo drive. These arms allow for vertical and horizontal movement, enabling the machine to follow the tank’s contour precisely. Depending on the finishing requirement, the operator can mount a range of abrasives onto the polishing head—from coarse grit wheels for initial smoothing to soft buffing pads with fine polishing compounds for mirror finishing. This adaptability allows the same machine to handle multiple stages of the polishing process in sequence.
Speed and pressure can be precisely adjusted to match the material and polishing goal. Higher speeds are generally used during the fine finishing stages, while slower, more forceful passes may be applied during the initial grinding or smoothing phase. Integrated cooling sprays or misting systems are often employed to keep temperatures down during prolonged contact, reducing the risk of thermal deformation or discoloration of the metal surface. These cooling systems also help flush away spent abrasive and prevent clogging of the polishing head.
Safety features are built into the system, such as emergency shutoffs, safety enclosures, and dust extraction units. The dust collection system is especially important because polishing operations generate fine metal particles and residual polishing compound, which can pose both health and fire risks if not properly managed. These particles are captured and filtered to maintain a clean and safe workspace.
Modern versions of the Rotary Tank Polishing Machine are equipped with programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or touchscreen interfaces that allow operators to store and recall polishing parameters for different tank sizes and materials. This is particularly useful in production settings where a variety of tanks must be processed with consistent results. Some machines are designed to be mobile or adaptable to accommodate horizontal or vertical tank orientations, increasing their usability across different production lines or maintenance environments.
The robust construction of these machines ensures long-term durability, even in heavy industrial use. Frame structures are typically made from powder-coated or stainless steel to resist vibration, wear, and corrosion. Maintenance tasks such as replacing polishing media, lubricating moving parts, or adjusting calibration points are made accessible through modular design elements and diagnostic interfaces.
Rotary Tank Polishing Machines are widely used in the manufacturing and maintenance of tanks for the pharmaceutical, food and beverage, chemical, and cosmetic industries—sectors where tank cleanliness, corrosion resistance, and surface hygiene are paramount. The smooth, reflective finishes achieved with this equipment not only enhance aesthetic appeal but also reduce the risk of bacterial buildup and make cleaning easier. By automating a traditionally labor-intensive process, these machines increase throughput, reduce operator fatigue, and improve the consistency and quality of tank surface finishes, making them an essential part of modern tank production and refurbishing operations.
The versatility of a Rotary Tank Polishing Machine also extends to its compatibility with tanks of varying diameters, lengths, and surface conditions. Whether used in the fabrication of new tanks or the refurbishing of older units, the machine can be adapted to suit both light and heavy-duty tasks. In large-scale production facilities, it’s common for the machine to be part of an integrated finishing line, where tanks are moved sequentially through grinding, polishing, inspection, and packaging stations. This streamlined approach not only boosts productivity but also standardizes surface finish quality across batches.
In many applications, especially those involving hygienic or high-purity environments, the target finish is a mirror-like surface with minimal surface roughness, often measured in Ra (roughness average) micrometers. The Rotary Tank Polishing Machine excels in achieving such finishes through controlled, progressive passes with increasingly finer abrasives. Operators can select from various polishing pastes or compounds depending on the end-use—be it food-grade, pharmaceutical-grade, or decorative finish requirements.
Another key benefit lies in the reduction of human error. Manual polishing of large tanks is physically demanding and difficult to control uniformly, often resulting in inconsistent results and operator fatigue. With the rotary system, consistent pressure and motion are applied throughout the tank’s entire circumference, minimizing the likelihood of over-polishing or missed areas. This automation not only improves quality control but also enhances worker safety by limiting prolonged exposure to dust and repetitive strain.
These machines are also designed for energy efficiency, with motors and drives optimized to deliver torque and speed only as needed, reducing unnecessary power consumption. The use of variable frequency drives (VFDs) allows precise control of motor speed and reduces mechanical stress on components, prolonging machine life and lowering maintenance frequency.
From an investment perspective, a Rotary Tank Polishing Machine offers long-term returns through reduced labor costs, increased throughput, and minimized rework due to surface defects. Spare parts such as polishing belts, wheels, or pads are often standardized and easily available, and many machines come with remote support or diagnostic systems to aid in quick troubleshooting and minimal downtime.
In operations where traceability is essential—such as pharmaceutical or food-grade tank production—modern systems can log polishing cycles, abrasive types used, and surface finish readings, creating digital records that support quality assurance and compliance reporting.
Ultimately, the Rotary Tank Polishing Machine is a critical asset for any facility aiming to deliver high-quality, consistent, and hygienically finished tanks. It bridges the gap between craftsmanship and automation, combining the precision of machine-driven control with the adaptability needed to handle diverse tank configurations and finish standards.
Automated Tank Polishing System

An Automated Tank Polishing System is a high-precision, industrial-grade solution designed to streamline and standardize the surface finishing of cylindrical, conical, or elliptical tanks made primarily from stainless steel or other polishable metals. This system is fully automated, reducing the need for manual labor while ensuring consistent, repeatable results across batches. It combines mechanical, electrical, and software components to deliver a programmable polishing process that meets stringent industry standards in sectors such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, cosmetics, and high-end metal fabrication.
At the core of the system is a computer-controlled mechanism—typically driven by servo motors or stepper motors—that maneuvers polishing heads over the tank surface with precision. These heads may include abrasive wheels, sanding belts, or buffing pads, depending on the required level of material removal or surface finish. The system can accommodate multiple polishing stages in a single operation, such as rough grinding, intermediate smoothing, and final finishing or mirror polishing. Tool heads are often interchangeable or modular, making it possible to adapt the system for various tank sizes, shapes, and finish grades.
A tank positioning mechanism, such as a powered rotary chuck or a rolling bed, keeps the tank rotating or shifting as required during polishing. This motion is synchronized with the polishing head movement to ensure uniform coverage and consistent surface pressure. In larger systems, automatic tank loading and unloading are integrated using conveyors or robotic arms, further enhancing productivity and reducing handling time.
Advanced Automated Tank Polishing Systems include real-time monitoring sensors that track polishing pressure, temperature, and abrasive wear. These sensors feed data to a central controller or PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), allowing the machine to adjust parameters on the fly to maintain optimal polishing conditions. If the system detects deviations—such as excessive force, temperature spikes, or irregular tank rotation—it can automatically halt operation or trigger alerts to prevent damage to the tank or tooling.
Safety and environmental controls are integral to the system. Enclosures, interlocks, and emergency stops protect operators from moving parts, while high-efficiency dust extraction systems remove fine particulates and abrasive residue from the air. Cooling sprays or lubricant misting units help control surface temperature during intensive polishing, which is essential to prevent metal warping or discoloration.
User interfaces on these machines are typically intuitive touchscreen panels that allow operators to select tank profiles, adjust polishing parameters, and monitor performance in real-time. Many systems support recipe storage—saving the settings for specific tank types—so they can be recalled instantly for repeat jobs. Some are even network-connected, allowing for remote diagnostics, software updates, and integration into larger production management systems for full traceability and production analytics.
An Automated Tank Polishing System not only enhances finish quality and consistency but also dramatically reduces the labor and time involved in tank finishing operations. It improves safety, lowers operational costs, minimizes the risk of contamination in hygienic industries, and ensures compliance with industry-specific surface roughness standards. As a result, this system has become a cornerstone in modern tank manufacturing facilities, ensuring faster throughput without compromising on quality or finish.
An Automated Tank Polishing System is a fully integrated industrial solution designed to perform the surface finishing of metal tanks with minimal human intervention. It combines mechanical precision, sensor feedback, and programmable controls to deliver consistent and repeatable polishing results across various tank sizes and shapes, particularly cylindrical or elliptical stainless steel vessels used in hygienic or industrial environments. The core function of the system revolves around synchronized motion between a rotating tank support mechanism and an automated polishing head. The tank may either rotate on powered rollers or be held stationary while the polishing head traverses its surface in a controlled path, ensuring that every part of the outer wall receives uniform treatment.
The polishing head is mounted on a multi-axis arm—often servo- or CNC-controlled—which can be programmed to move vertically, horizontally, or circumferentially based on the geometry of the tank. This automated movement allows precise control over polishing pressure, feed rate, and coverage. Different tooling can be mounted on the polishing head, including abrasive wheels, flap brushes, belt heads, or soft buffing pads, depending on whether the goal is rough grinding, satin finishing, or mirror polishing. The system is capable of progressing through multiple polishing stages in a single automated cycle without stopping for tool changes, significantly improving throughput.
Sensors integrated into the system continuously monitor polishing force, temperature, and tool wear. These inputs are processed in real-time by a programmable logic controller (PLC) that adjusts speed, pressure, and motion path to ensure consistent performance. If any anomaly is detected—such as surface irregularities, excessive heat, or tool failure—the system can automatically pause operation or trigger maintenance alerts. Cooling systems, often using mist or fluid spray, are activated during high-friction polishing stages to prevent overheating and maintain the metallurgical integrity of the tank surface.
Dust and debris generated during the process are managed by a dedicated extraction and filtration system that keeps the work area clean and compliant with health and safety regulations. The user interface is typically a touchscreen HMI (human-machine interface) where operators can select tank profiles, input surface finish requirements, and monitor the process status. Recipes can be saved for repeated use, allowing quick setup when polishing identical tank models.
In large-scale production environments, the Automated Tank Polishing System may be integrated with robotic loaders, conveyors, or overhead cranes to allow seamless loading and unloading, further minimizing manual handling. The robust frame of the machine is usually built from reinforced steel and features shock-absorbing mounts to reduce vibration and ensure long-term precision. Electrical components are housed in sealed, dustproof enclosures to prevent contamination and ensure reliable operation even under continuous duty cycles.
This type of system is particularly beneficial for industries that require strict surface hygiene and finish consistency, such as food processing, dairy, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and brewing. By eliminating the variability of manual polishing and significantly reducing labor costs, it enhances productivity, product appearance, and regulatory compliance. With options for data logging, remote diagnostics, and integration into plant-wide automation systems, the Automated Tank Polishing System represents a leap forward in both efficiency and quality assurance for tank manufacturers and refurbishers.
The Automated Tank Polishing System also offers a high degree of customization, allowing manufacturers to tailor the system to specific production needs. For instance, different abrasive media can be used based on the tank’s material and the desired finish—ranging from coarse grit for weld removal to fine compounds for mirror-like surfaces. The pressure exerted by the polishing heads can be dynamically adjusted through servo feedback, which is particularly useful when dealing with tanks of uneven surface thickness or those with pre-existing dents or welds.
Some systems are equipped with vision cameras or laser profiling tools that scan the tank’s surface before and during polishing. These tools generate a topographic map, enabling the system to identify high or low points and compensate automatically. This adaptive polishing not only improves surface uniformity but also reduces waste and the need for rework.
For operations with stringent documentation and compliance requirements, such as pharmaceutical or bioprocessing tank production, the system can generate detailed polishing logs. These logs may include cycle duration, polishing pressure, abrasive type, tool change intervals, and final surface roughness values. This data can be stored locally or on a networked server for quality control audits or regulatory inspections.
In terms of operator safety, the system often includes light curtains, safety interlocks, and emergency stop zones. This makes it compliant with industrial safety standards while still allowing for efficient operation. Sound insulation and dust containment measures reduce environmental impact, ensuring a safer and cleaner working environment.
Maintenance requirements are relatively low due to the robust construction and modular design. Tooling and wear parts can be quickly replaced thanks to quick-release mechanisms, and predictive maintenance schedules are often built into the software interface. The system can also be integrated with enterprise-level MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems), enabling centralized control, real-time monitoring, and production scheduling.
Energy efficiency is another area where modern Automated Tank Polishing Systems excel. High-efficiency motors, smart power management, and the ability to run only the necessary axes or tools at any given time contribute to lower operating costs and reduced environmental impact. This aligns with the growing demand for sustainable manufacturing practices.
Overall, an Automated Tank Polishing System represents a significant upgrade over manual or semi-automated processes. It offers superior precision, repeatability, and throughput, all while reducing human error and operational fatigue. As a long-term investment, it not only increases output capacity but also elevates product quality and consistency—making it an essential asset in competitive industrial environments focused on high-performance metal finishing.
Horizontal Tank Polishing Machine

A Horizontal Tank Polishing Machine is a specialized piece of equipment engineered to polish the outer surfaces of cylindrical tanks positioned horizontally on support rollers or a cradle. These machines are widely used in industries that manufacture stainless steel or metal tanks for food processing, dairy, brewing, pharmaceutical, and chemical applications. The primary purpose is to achieve a uniform surface finish—ranging from brushed to mirror-like—on horizontally oriented tanks with minimal manual intervention and high consistency.
The core structure of the machine typically includes a heavy-duty frame that supports the rotation of the tank and a mobile polishing head that travels along the tank’s length. The tank is mounted horizontally on powered rollers that rotate it slowly during polishing. This rotation allows the polishing head, which usually contains abrasive belts, pads, or flap wheels, to work consistently around the entire circumference of the tank. The polishing head moves longitudinally—typically via a motorized carriage or rail system—ensuring full coverage from one end of the tank to the other.
Advanced models include multiple axes of movement for the polishing head, allowing it to adjust position in real-time for tanks with variable diameters or slight misalignments. Some systems come equipped with digital controllers and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) that let operators set parameters such as polishing speed, pressure, abrasive type, and number of passes. This makes it easy to repeat polishing cycles for identical tanks and maintain uniform surface quality.
Horizontal tank polishing machines often integrate a dust extraction unit and coolant spray system. These not only keep the working area clean but also extend the life of polishing abrasives and prevent overheating or discoloration of the metal surface. Depending on the production scale, the system may be semi-automatic—requiring manual loading and unloading—or fully automated with integrated tank handling.
These machines provide substantial labor savings and eliminate the inconsistencies associated with manual polishing. Their ability to handle tanks of various sizes—typically with adjustable supports and adaptable polishing heads—makes them highly versatile for both small batch and mass production environments. In applications requiring hygienic or decorative finishes, a horizontal tank polishing machine is a critical asset that ensures surface smoothness, removes weld seams, and enhances the aesthetic and functional qualities of the finished product.
A Horizontal Tank Polishing Machine is a robust and efficient industrial system designed to polish cylindrical tanks that are placed in a horizontal orientation. These machines are widely used for polishing stainless steel tanks utilized in sectors such as dairy, brewing, chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food manufacturing. The primary function of this equipment is to ensure a consistent and high-quality surface finish—typically from matte to mirror grade—on the outer shell of horizontally positioned tanks. The tanks are supported on powered rollers that rotate them steadily, while a motorized polishing head travels longitudinally along the length of the tank. This synchronized motion allows for complete surface coverage around the circumference as well as from one end of the tank to the other, ensuring no area is left untreated.
The polishing head may be equipped with a variety of abrasive tools, including sanding belts, flap wheels, abrasive brushes, or buffing pads, depending on the stage of finishing. The head is mounted on a movable carriage that can adjust vertically and horizontally to follow the curvature and profile of the tank. High-end systems feature servo-driven axes and PLC control that allow for programmable polishing paths, adjustable pressure, and variable speed control to match different tank sizes, materials, and finish requirements. This adaptability makes the machine suitable for both standardized production and custom tank polishing tasks.
A key feature of horizontal tank polishing machines is their ability to deliver repeatable, high-quality finishes while minimizing manual effort. Operators can input polishing recipes via a touchscreen interface, select tank dimensions, and monitor real-time parameters such as speed, load, and abrasive wear. These settings can be saved and reused, greatly increasing productivity and consistency in repeat jobs. Safety mechanisms including emergency stop functions, protective guards, and automatic shutoff features are built into the system to ensure safe operation.
Dust collection and cooling systems are typically integrated to manage heat and airborne particles generated during polishing. Misting units or coolant spray nozzles are positioned near the contact point to reduce frictional heat and extend the life of consumables. Dust extractors remove fine metal particles and abrasive residues, maintaining a clean work environment and preventing equipment fouling. These machines are constructed from heavy-duty materials and built for continuous operation, with reinforced frames and vibration-resistant mounts ensuring long-term durability and precision.
The machine’s modular design often allows for optional attachments such as automatic loading and unloading systems, multiple polishing stations, or additional heads for multi-step finishing in a single pass. In environments with high throughput demands, the entire polishing line can be integrated into an automated workflow with conveyors, robotic handlers, and central control systems. This enhances not only efficiency but also traceability and quality control.
A Horizontal Tank Polishing Machine delivers a significant return on investment through reduced labor costs, faster turnaround times, improved surface quality, and compliance with surface roughness specifications critical to industries that demand hygienic or decorative finishes. As manufacturing standards continue to evolve, this machine remains a vital tool in modern fabrication facilities, enabling scalable, consistent, and high-performance tank surface preparation.
The versatility of a Horizontal Tank Polishing Machine makes it well-suited for a wide range of tank diameters and lengths. Adjustable roller supports can accommodate tanks from small vessels a few feet long to large industrial tanks several meters in length and diameter. The polishing heads are often designed to be interchangeable, allowing quick swaps between rough grinding tools for weld seam removal and finer polishing pads for achieving mirror finishes.
In addition to standard cylindrical tanks, some horizontal polishing machines are equipped with custom fixtures or adaptable tooling to handle tanks with complex geometries, such as those with welded nozzles, flanges, or manways. These features allow for targeted polishing around difficult-to-reach areas without requiring manual intervention, improving both safety and finish quality.
Because these machines operate continuously and precisely, they help manufacturers meet strict regulatory standards that apply to hygienic tanks used in food and pharmaceutical production. For example, surface roughness specifications such as Ra values must often fall below a certain threshold to prevent bacterial growth and ensure cleanability. Automated polishing systems help achieve these finishes more reliably than manual methods.
Maintenance of the horizontal tank polishing machine is typically straightforward due to modular components and easy access to wear parts. Polishing belts, pads, and brushes can be replaced quickly to minimize downtime. Regular lubrication and inspection of rollers, motors, and guide rails ensure smooth operation and long service life.
The adoption of advanced control software also enables predictive maintenance, where the system alerts operators when tooling is nearing the end of its service life or when mechanical components require servicing. This proactive approach reduces unplanned downtime and helps maintain consistent output quality.
From an operational perspective, the horizontal tank polishing machine reduces ergonomic risks associated with manual polishing, such as repetitive strain injuries and prolonged exposure to dust and noise. Automation improves workplace safety by limiting operator interaction with moving parts and abrasive surfaces.
Overall, the Horizontal Tank Polishing Machine streamlines tank surface finishing, enhances consistency, and boosts throughput in metal fabrication facilities. By integrating automation, precision motion control, and advanced tooling, it delivers superior surface quality efficiently and safely, making it indispensable for modern tank manufacturing and finishing operations.
Tank External Polisher

A Tank External Polisher is a specialized machine designed specifically for finishing the outer surface of large metal tanks. These polishers focus on refining the tank’s exterior, enhancing its aesthetic appeal, improving corrosion resistance, and ensuring compliance with hygienic or industrial standards. Used predominantly in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and cosmetics, the tank external polisher delivers a smooth, uniform surface by removing imperfections, weld marks, and oxidation through controlled abrasive action.
The machine typically consists of a robust framework that supports the tank or allows it to remain stationary while a polishing unit moves over its surface. Depending on the design, the tank can be rotated on powered rollers, or the polishing head may be maneuvered around a fixed tank. The polishing unit includes abrasive tools such as belts, pads, brushes, or buffing wheels, which are driven by electric motors with adjustable speed and pressure settings to accommodate different materials and desired finishes.
Advanced tank external polishers feature automated controls with programmable paths and polishing cycles. These systems allow precise control over the polishing parameters, ensuring consistent coverage and finish quality. The polishing heads often have multi-axis movement capabilities—such as vertical, horizontal, and rotational adjustments—to follow the tank’s curvature and reach all external surfaces effectively.
Safety and operational efficiency are key considerations in tank external polishers. Integrated dust extraction systems capture airborne metal particles and debris generated during polishing, while coolant sprays or misting systems help regulate surface temperature and prolong tool life. Emergency stop mechanisms, protective guards, and user-friendly interfaces contribute to safe, intuitive operation.
Tank external polishers may also be modular, allowing customization with different tooling or additional polishing stations to meet specific production demands. These machines reduce manual labor, increase throughput, and improve surface finish uniformity, ultimately enhancing product quality and lifespan. Through automation and precision control, tank external polishers have become essential in modern manufacturing environments where high-quality surface finishing of large tanks is required.
A Tank External Polisher is an industrial machine designed to efficiently and uniformly polish the outer surface of large metal tanks used across various industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and cosmetics. Its primary function is to smooth out surface imperfections, remove weld marks, oxidation, and minor scratches, and deliver a consistent finish that improves both the tank’s appearance and resistance to corrosion. This enhances the tank’s longevity and ensures it meets industry-specific surface finish standards, particularly in hygienic applications where smooth surfaces are critical for cleanliness and contamination prevention.
The design of a tank external polisher generally revolves around either rotating the tank itself on powered rollers or moving the polishing head around a stationary tank. In the rotating tank approach, the tank is supported on a set of motorized rollers that slowly turn the vessel while the polishing heads—mounted on adjustable arms or carriages—apply controlled abrasive action around the circumference and along the length of the tank. Alternatively, the polishing heads may move circumferentially and longitudinally around a fixed tank using robotic arms or CNC-controlled rails, especially useful for very large or heavy tanks that are difficult to rotate.
The polishing units are equipped with interchangeable abrasive tools such as sanding belts, flap wheels, buffing pads, or brushes, allowing operators to select the appropriate tool for each stage of finishing—from rough grinding to fine polishing or mirror finishing. Motor speeds and polishing pressures are adjustable and often controlled via programmable logic controllers (PLCs), ensuring precise and repeatable surface treatment tailored to the tank’s material, size, and finish requirements.
Modern tank external polishers incorporate integrated dust extraction and cooling systems. Dust collectors capture airborne metal particles and polishing debris, maintaining a clean and safe working environment and protecting sensitive machine components from abrasive contamination. Cooling sprays or misting systems help manage the temperature generated during polishing, preventing heat-induced damage such as discoloration or warping of the tank surface and extending the life of abrasive media.
Operator safety is ensured through the inclusion of emergency stop functions, safety interlocks, protective shields, and automated monitoring systems that halt operations in the event of anomalies like excessive vibration or tool failure. User interfaces with touchscreens enable operators to set polishing parameters, monitor real-time process data, and store repeatable polishing programs, reducing the risk of human error and improving production efficiency.
Tank external polishers are often modular in design, allowing customization to fit specific production workflows and tank dimensions. Multiple polishing heads or stations can be installed for simultaneous multi-stage finishing, reducing cycle times and increasing throughput. Integration with automated loading and unloading systems or robotic material handlers further enhances operational efficiency in large-scale manufacturing settings.
By automating the polishing process, these machines significantly reduce labor costs, minimize ergonomic risks associated with manual polishing, and improve finish quality and consistency. This leads to better product aesthetics, higher compliance with industry surface finish standards, and longer equipment service life. As manufacturing demands grow for precision, speed, and repeatability, tank external polishers have become indispensable tools in the production and maintenance of metal tanks, offering a cost-effective and reliable solution for achieving superior external surface finishes.
Tank external polishers are designed to handle a variety of tank sizes and shapes, from small vessels used in laboratory or pharmaceutical settings to large industrial tanks employed in food processing or chemical storage. The machines are engineered with adjustable fixtures, supports, and polishing heads that can accommodate different diameters and lengths. This adaptability ensures that a wide range of tanks can be processed with minimal setup time, increasing overall productivity.
In addition to polishing flat cylindrical surfaces, these machines often feature specialized tooling or attachments to address more complex tank features, such as welded seams, flanges, nozzles, and manways. These critical areas are prone to surface irregularities that can harbor contaminants or cause stress concentrations. Automated polishing of these sections helps ensure the entire tank exterior meets stringent quality and hygiene standards.
Maintenance and ease of operation are key factors in the design of tank external polishers. Modular components such as replaceable abrasive belts and pads, quick-change tool mounts, and accessible lubrication points help minimize downtime. Operators benefit from intuitive control panels that guide them through setup and operation, while advanced machines may include diagnostics and predictive maintenance alerts to prevent unexpected failures.
With an emphasis on automation, many tank external polishers integrate seamlessly into broader manufacturing lines. They can be combined with robotic handling systems for loading and unloading, conveyor systems for transport, and quality inspection stations for surface finish verification. This integration facilitates continuous, high-volume production with consistent output quality.
Environmental and safety considerations are also paramount. The polishing process generates metal dust and particles that must be effectively managed to protect worker health and prevent environmental contamination. High-efficiency dust collection systems capture these particles at the source, while proper ventilation and filtration ensure clean air quality. Noise reduction features and ergonomic designs help create a safer and more comfortable work environment.
Ultimately, tank external polishers enable manufacturers to deliver products that not only meet functional requirements but also exhibit superior aesthetics and surface integrity. By automating what was traditionally a labor-intensive, skill-dependent process, these machines reduce costs, improve turnaround times, and elevate the overall quality of finished tanks. As industries continue to demand higher precision and consistency, the role of advanced tank external polishing equipment will only grow in importance, supporting innovation and excellence in metal tank fabrication and finishing.
Pressure Vessel Polishing Machine

A Pressure Vessel Polishing Machine is a specialized industrial system designed to polish the external and sometimes internal surfaces of pressure vessels—heavy-duty containers engineered to hold gases or liquids at high pressures. These vessels are critical components in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, pharmaceuticals, and food production, where safety, durability, and surface integrity are paramount. The polishing machine ensures the pressure vessel’s surfaces are smooth, free from defects like weld marks or corrosion, and meet stringent quality and safety standards.
Typically, a pressure vessel polishing machine accommodates the vessel either horizontally or vertically, depending on the size and shape of the vessel, and the polishing process requirements. The vessel is mounted on heavy-duty rollers or cradles that allow slow, controlled rotation, providing even exposure to the polishing tools. Alternatively, in cases where rotation is not feasible, the polishing heads move around or inside the vessel using automated carriage systems, robotic arms, or CNC-controlled mechanisms.
The polishing heads are equipped with various abrasive elements such as sanding belts, flap discs, buffing pads, or wire brushes, selected based on the polishing stage and the vessel material—often stainless steel, carbon steel, or specialized alloys. These tools are powered by variable-speed motors, allowing precise control over the polishing pressure and speed to avoid surface damage while achieving the desired finish, from a matte texture to a mirror-like shine.
Advanced pressure vessel polishing machines integrate programmable controls and automation to optimize the polishing cycle, ensuring uniform surface treatment and repeatability. Operators can set parameters such as rotation speed, tool pressure, polishing path, and number of passes through a user-friendly interface. Some machines incorporate sensors to monitor surface conditions in real time, adjusting the process dynamically for consistent quality.
Because pressure vessels operate under high stress and often in regulated environments, surface finish is critical to prevent corrosion, fatigue cracking, and contamination. Polishing reduces surface roughness, eliminates micro-cracks and crevices, and enhances the vessel’s resistance to environmental factors. It also facilitates better inspection and coating adherence, improving the vessel’s lifespan and safety.
The machines often include dust extraction and cooling systems to manage metal particles and heat generated during polishing. Safety features such as emergency stops, protective guards, and automated shutoffs safeguard operators from hazards associated with rotating equipment and abrasive tools.
Overall, a pressure vessel polishing machine is a vital tool in manufacturing and maintenance processes, improving the quality, safety, and durability of pressure vessels while reducing manual labor and increasing operational efficiency. Its precision and automation capabilities make it indispensable for meeting the rigorous standards demanded by modern industrial applications.
A Pressure Vessel Polishing Machine is engineered to deliver high-quality surface finishing on the exterior and sometimes interior surfaces of pressure vessels, which are designed to safely contain gases or liquids at high pressures. The machine’s purpose is to remove surface imperfections such as weld seams, scratches, oxidation, and corrosion, resulting in a smooth, uniform finish that enhances the vessel’s durability, corrosion resistance, and compliance with industry regulations.
Typically, the vessel is mounted horizontally or vertically on robust supports or rollers that allow controlled rotation. This rotation enables even exposure of the vessel’s surface to the polishing tools, which may include abrasive belts, flap wheels, buffing pads, or wire brushes driven by adjustable-speed motors. In some configurations, the polishing heads move along tracks or robotic arms to reach different areas without rotating the vessel, especially useful for larger or more complex shapes.
The machine’s automation systems use programmable logic controllers to regulate variables such as polishing speed, pressure, and tool paths, ensuring consistent and repeatable results. Operators can select different polishing programs tailored to the vessel’s material—commonly stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloys—and desired surface finish, whether it is a rough grit removal or a fine mirror polish.
Dust extraction systems are integral to the design, capturing metal particulates generated during polishing to maintain a safe working environment and protect machinery components. Cooling sprays or mists help reduce heat buildup that can damage the surface or tooling. Safety features such as emergency stops, protective shields, and sensors to detect abnormal vibrations or tool wear protect operators and equipment.
The polished surface minimizes the risk of corrosion and fatigue failure by eliminating stress concentrators like micro-cracks and weld irregularities. It also improves the vessel’s compatibility with coatings or linings used for further protection or compliance with hygiene standards, especially in food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries.
By automating the polishing process, the machine reduces manual labor, enhances operator safety, and increases throughput and consistency. This leads to better product quality and longer service life for pressure vessels, which is critical given their role in high-pressure and often hazardous environments.
Overall, the Pressure Vessel Polishing Machine plays a crucial role in the fabrication and maintenance of pressure vessels, ensuring they meet stringent safety and quality standards through precise, efficient surface finishing.
Pressure vessel polishing machines are designed to handle a wide range of vessel sizes, from small, specialized reactors to large industrial tanks used in power plants or chemical processing. The machines often feature adjustable supports, allowing them to accommodate different diameters and lengths while maintaining stability during polishing. For very large vessels, modular or sectional polishing units can be used, which move along the vessel’s length to cover the entire surface area systematically.
In addition to standard cylindrical shapes, these machines can be adapted for vessels with complex geometries such as dished ends, nozzles, flanges, or manways. Specialized polishing heads with flexible or articulating mounts enable access to these challenging areas, ensuring a uniform finish throughout the vessel’s exterior. Some advanced systems incorporate 3D scanning or laser-guided positioning to map the vessel’s surface and tailor the polishing path accordingly.
Maintenance and operational efficiency are key considerations in pressure vessel polishing machines. Quick-change abrasive tools and easily accessible components minimize downtime, while integrated diagnostics alert operators to tool wear, motor performance, or other issues that could affect finish quality. Automated lubrication systems and dust collectors help extend machine life and maintain a clean working environment.
Integration with other fabrication processes is common, with polishing machines linked to robotic welders, inspection systems, or coating stations, forming part of a fully automated production line. This integration reduces manual handling, improves throughput, and ensures consistent quality from welding through final surface finishing.
Environmental and safety measures are essential, as polishing generates metal dust and fine particulates. High-efficiency dust extraction, ventilation, and filtration systems protect workers and comply with environmental regulations. Noise reduction features and ergonomic controls also contribute to a safer workplace.
By automating the surface finishing of pressure vessels, these machines reduce labor costs, enhance safety, and ensure compliance with industry standards such as ASME, PED, or ISO, which specify surface finish requirements for pressure-retaining equipment. The result is a high-quality, durable product that meets both functional and aesthetic criteria, essential for critical applications where failure is not an option.
As technology advances, pressure vessel polishing machines continue to incorporate smarter controls, real-time monitoring, and adaptive polishing strategies that further improve efficiency and finish consistency. This ongoing innovation supports manufacturers in meeting growing demands for precision, safety, and productivity in the fabrication of pressure vessels.
Large Tank Surface Finisher

A Large Tank Surface Finisher is an industrial machine designed to polish, grind, or smooth the external surfaces of large storage tanks, reactors, or vessels. These tanks are commonly used in industries like oil and gas, chemical processing, water treatment, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals. The finisher ensures that the tank’s outer surface is free from imperfections such as weld seams, rough patches, corrosion spots, or oxidation, improving both the tank’s aesthetic appeal and functional longevity.
This equipment typically accommodates tanks of substantial diameter and length, often employing heavy-duty supports or rollers to either rotate the tank or hold it steady while polishing heads move around the surface. In some designs, the tank remains stationary and the polishing mechanism moves circumferentially and longitudinally along the tank’s surface using automated rails, robotic arms, or CNC-controlled systems.
The polishing units use a variety of abrasive tools like sanding belts, flap discs, buffing pads, or wire brushes depending on the stage of finishing and the tank material, which is frequently stainless steel, carbon steel, or specialized alloys. These tools are powered by variable-speed motors to control polishing pressure and speed precisely, ensuring uniform surface treatment without causing damage.
Automation plays a key role in large tank surface finishers, with programmable logic controllers (PLCs) managing polishing parameters such as speed, pressure, and tool path. This automation guarantees consistent results across the entire tank surface, minimizes human error, and reduces manual labor.
Dust extraction systems integrated into the machine capture metal particles and debris generated during finishing, maintaining a clean and safe work environment. Cooling sprays or misting systems help regulate the temperature of the tank surface and the abrasive tools, preventing overheating and discoloration.
Safety features such as emergency stops, protective barriers, and sensor-based monitoring ensure operator protection and machine reliability. The machine’s design often includes modular components for easy maintenance, quick replacement of consumables, and adaptability to various tank sizes and shapes.
Large tank surface finishers enhance tank durability by reducing surface roughness that can promote corrosion and bacterial growth, which is especially critical in sanitary applications. They also prepare surfaces for subsequent coating or painting processes, improving adhesion and overall finish quality.
By automating and standardizing the finishing process, these machines reduce production times, labor costs, and variability in surface quality, ultimately contributing to higher product reliability and longer service life. As manufacturing demands grow for precision and efficiency, large tank surface finishers have become essential equipment in the fabrication and maintenance of industrial tanks.
A Large Tank Surface Finisher is designed to provide consistent and high-quality surface treatment for tanks that are too large for conventional polishing methods. These machines are capable of handling tanks with large diameters and lengths, often supported by heavy-duty rollers or cradles that allow the tank to rotate slowly, enabling the polishing tools to access the entire surface evenly. Alternatively, the tank can remain stationary while polishing heads move along its length and circumference using automated carriages or robotic arms.
The polishing tools include abrasive belts, flap wheels, buffing pads, and wire brushes, which can be swapped out or adjusted depending on the required finish and the material of the tank—typically stainless steel, carbon steel, or other alloys. Variable-speed motors control the pressure and speed of the polishing action to avoid damaging the tank surface while achieving a uniform finish, whether it’s a coarse grind to remove weld marks or a fine polish for aesthetic and protective purposes.
Automation and programmable controls are crucial features, allowing operators to set specific polishing patterns, speeds, and pressures that ensure repeatability and reduce human error. These controls often integrate sensors that monitor tool wear, surface conditions, and motor performance to dynamically adjust the process in real time. This level of precision ensures that the surface finish meets industry standards for corrosion resistance, cleanliness, and visual quality.
Dust and particulate matter generated during polishing are managed through high-efficiency extraction systems, which maintain a clean environment and protect both workers and machinery. Cooling systems may also be incorporated to dissipate heat buildup, preventing discoloration or warping of the tank surface. Safety measures such as emergency stop buttons, protective enclosures, and vibration detection enhance operator safety and machine reliability.
Large Tank Surface Finishers also accommodate tanks with complex shapes, including curved ends, flanges, and welded joints, by using specialized flexible or articulating polishing heads. These features ensure that every part of the tank exterior receives adequate surface treatment, improving the overall integrity and lifespan of the tank.
By automating the surface finishing of large tanks, manufacturers benefit from increased throughput, reduced labor costs, and consistent quality. The machines prepare tanks for further processing, such as coating or inspection, by producing smooth, defect-free surfaces that meet stringent regulatory requirements. This results in tanks that are safer, more durable, and visually appealing, which is critical in industries where performance and compliance are non-negotiable.
As industrial demands evolve, large tank surface finishers continue to integrate advanced technologies such as real-time monitoring, adaptive polishing algorithms, and robotic automation, driving efficiency and precision to new levels. This progression ensures that large tanks meet the highest standards for both functionality and appearance while optimizing manufacturing workflows.
Large Tank Surface Finishers are engineered to accommodate a variety of tank sizes and materials, offering versatility to industries with diverse processing needs. Their modular design allows for easy scaling and customization, enabling manufacturers to tailor the machine’s capabilities to specific tank dimensions or surface finish requirements. This flexibility is especially important when dealing with custom-built tanks or those requiring specialized finishes for unique applications.
The finishing process typically begins with more aggressive abrasive tools to remove major surface irregularities, weld beads, and scale, followed by progressively finer abrasives to achieve a smooth, uniform finish. Some machines offer multiple polishing heads that can work simultaneously or sequentially, speeding up the finishing process while maintaining high precision. The ability to switch between different polishing stages without manual intervention enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime.
In addition to surface smoothing, these machines can help improve corrosion resistance by eliminating surface imperfections where rust or contaminants might accumulate. This is particularly critical for tanks used in chemical storage, food processing, or pharmaceutical production, where surface integrity directly affects product safety and quality. The polished surface also facilitates cleaning and maintenance, contributing to longer tank service life and reduced operational costs.
Integration with digital control systems enables operators to program and monitor the finishing process remotely, allowing for data collection, process optimization, and quality assurance. Real-time feedback from sensors measuring parameters like surface roughness, tool pressure, and vibration ensures the finishing process adapts dynamically, maintaining consistent quality even as tool wear occurs.
Maintenance considerations are integral to the design of large tank surface finishers. Features such as quick-change abrasive modules, accessible tool mounts, and automated lubrication systems simplify routine upkeep and extend machine longevity. These aspects minimize downtime and help maintain production schedules, which is crucial in industries where tank fabrication and turnaround times directly impact operational efficiency.
Environmental controls, including dust extraction and filtration systems, address workplace safety and regulatory compliance by capturing airborne particulates generated during polishing. Noise reduction measures and ergonomic controls improve operator comfort and safety, supporting sustainable and responsible manufacturing practices.
Overall, large tank surface finishers are vital for ensuring that industrial tanks meet stringent quality standards, offering a blend of precision, efficiency, and adaptability. Their advanced automation, robust construction, and comprehensive safety features make them indispensable tools in modern tank fabrication and maintenance workflows, contributing to higher-quality products and safer, more reliable industrial operations.
Tank Abrasive Polishing Equipment

Tank Abrasive Polishing Equipment is specialized machinery designed to perform abrasive finishing on the surfaces of industrial tanks, often made of stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloy materials. This equipment uses abrasive media such as sanding belts, discs, or pads to remove surface imperfections like weld seams, oxidation, rust, scale, and scratches, resulting in a smoother, more uniform finish that enhances the tank’s durability and aesthetic appeal.
The system typically includes a heavy-duty frame that supports the tank either horizontally or vertically, allowing controlled rotation or stable positioning during the polishing process. Abrasive polishing heads are mounted on adjustable arms or automated carriages that move along the tank’s surface, enabling consistent contact and pressure over the entire area.
Powered by variable-speed motors, these polishing heads can be fitted with different abrasive grades depending on the required surface finish—from coarse grinding to fine polishing. This adaptability allows for multiple finishing stages within a single machine, improving efficiency and minimizing manual intervention.
Automation features often include programmable logic controllers (PLCs) that regulate polishing speed, pressure, and tool path, ensuring uniformity and repeatability. Sensors monitor tool wear and surface conditions, providing real-time feedback to adjust the process dynamically for optimal results.
Dust extraction and filtration systems are integral to the design, capturing metal particles and dust generated during abrasive polishing to maintain a safe working environment and protect machinery components. Cooling mechanisms may also be incorporated to reduce heat buildup, preventing surface discoloration and preserving material integrity.
Safety features such as emergency stop controls, protective guards, and vibration sensors ensure operator protection and machine reliability. Easy access for maintenance and quick-change abrasive modules reduce downtime and enhance operational efficiency.
Tank abrasive polishing equipment is essential in industries where surface quality directly affects performance and safety, such as chemical processing, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and petrochemical storage. By delivering consistent and high-quality finishes, this equipment extends tank lifespan, improves corrosion resistance, and prepares surfaces for subsequent coating or inspection processes.
With ongoing advancements in automation, sensor integration, and adaptive polishing techniques, tank abrasive polishing equipment continues to evolve, providing manufacturers with efficient, precise, and reliable solutions for large-scale tank surface finishing.
Tank Abrasive Polishing Equipment is designed to efficiently and uniformly finish the surfaces of industrial tanks by using abrasive materials such as sanding belts, discs, or pads to remove surface defects like weld marks, rust, scale, and scratches. These machines accommodate large tanks by supporting them on robust frames or rollers that allow controlled rotation or keep the tank steady while polishing heads move along the surface. The abrasive heads, powered by variable-speed motors, can be adjusted to apply different grades of abrasives depending on whether a rough grind or fine polish is required. Automation plays a key role in these systems, with programmable controllers managing the speed, pressure, and movement of polishing tools to ensure consistent, repeatable results and reduce manual labor. Real-time sensor feedback helps adjust the polishing process dynamically, compensating for tool wear or surface variations. Dust extraction and filtration systems capture the metal particulates generated during polishing, maintaining a clean and safe work environment while protecting equipment from contamination. Cooling mechanisms prevent overheating, which can cause discoloration or damage to the tank’s surface. Safety features such as emergency stops, guards, and vibration detection safeguard operators and machinery. Maintenance is streamlined with quick-change abrasive modules and accessible components, minimizing downtime. This equipment is critical in industries like chemical processing, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and petrochemicals, where surface finish impacts corrosion resistance, cleanliness, and compliance with standards. By automating abrasive polishing, manufacturers achieve high-quality finishes that extend tank life, improve product safety, and prepare surfaces for further treatments or inspections. Continuous technological advancements in sensor integration, automation, and adaptive polishing strategies enhance the efficiency and precision of tank abrasive polishing equipment, meeting the growing demand for reliable and consistent large-scale surface finishing solutions.
Tank abrasive polishing equipment often features modular designs to accommodate a wide range of tank sizes and shapes, including cylindrical bodies, domed ends, and complex welded joints. This flexibility allows manufacturers to polish new tanks during fabrication or refurbish older tanks to extend their service life. The equipment may include multiple polishing heads operating simultaneously or in sequence, which improves throughput and ensures comprehensive coverage without operator fatigue.
The polishing tools themselves can be customized with various abrasive materials—such as aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, or diamond-coated pads—depending on the tank material and desired finish quality. These abrasives can be configured for wet or dry polishing, with wet polishing using coolant sprays to reduce dust and heat, further protecting the tank surface and polishing equipment.
Integrated control systems often allow operators to program specific polishing cycles, adjusting parameters like speed, pressure, and tool path based on the tank’s surface condition and finish requirements. Advanced machines may incorporate 3D scanning or surface mapping technologies to detect irregularities and guide the polishing heads precisely, ensuring an even finish even on complex geometries.
Maintenance-friendly features, such as easily accessible tool mounts and quick-change abrasive cartridges, minimize downtime and keep production schedules on track. Automated lubrication systems and self-cleaning dust filters help maintain optimal machine performance over time.
Environmental considerations are addressed through dust and waste management systems that capture and contain metal particles and abrasive residues. These systems help companies comply with workplace safety regulations and reduce environmental impact. Additionally, noise reduction technologies are often employed to create a safer and more comfortable working environment.
Overall, tank abrasive polishing equipment plays a vital role in producing tanks that meet strict industry standards for surface finish, which is essential for preventing corrosion, facilitating cleaning, and ensuring safe operation in critical applications. As demand for higher-quality finishes and more efficient production methods increases, the development of smarter, more adaptable polishing equipment continues, helping manufacturers deliver superior tanks with reduced labor and improved consistency.
Metal Fabrication Surface Polisher

A Metal Fabrication Surface Polisher is a specialized machine designed to smooth, clean, and enhance the surface finish of metal components produced through fabrication processes such as cutting, welding, bending, and assembling. These polishers are widely used across industries like automotive, aerospace, construction, and manufacturing, where high-quality surface finishes are essential for both functional performance and aesthetic appeal.
The machine employs abrasive tools—such as belts, discs, brushes, or pads—that rotate or oscillate at controlled speeds to remove imperfections like burrs, weld splatter, scratches, oxidation, and scale from metal surfaces. Depending on the application, polishers can handle a range of metals including stainless steel, aluminum, carbon steel, brass, and other alloys.
Metal fabrication surface polishers vary in design, from handheld units and bench-mounted machines to large automated systems with multiple polishing heads. Advanced models often incorporate variable speed controls, allowing operators to adjust the abrasion intensity according to the metal type and desired finish level. Some systems feature oscillating or reciprocating motions to achieve uniform polishing without leaving swirl marks or uneven patches.
Automation is increasingly integrated into these machines, with programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and robotic arms enabling consistent, repeatable polishing operations on complex or high-volume parts. This reduces manual labor, increases throughput, and improves quality control.
Dust extraction and filtration systems are critical components that capture metal particles and polishing debris, maintaining a clean work environment and protecting worker health. Cooling mechanisms may also be used to prevent overheating, which can damage metal surfaces or affect material properties.
Safety features such as emergency stops, protective guards, and vibration dampening are standard to ensure operator protection and machine longevity. Easy access to wear parts and modular abrasive tool attachments facilitate maintenance and reduce downtime.
Metal fabrication surface polishers enhance product durability by removing surface defects that could lead to corrosion or mechanical failure. They also prepare surfaces for further finishing steps such as painting, coating, or plating by creating a clean, smooth base.
Overall, these polishers are essential equipment in metal fabrication shops, delivering consistent, high-quality surface finishes that meet industry standards while improving efficiency, safety, and operator comfort. As technology advances, surface polishers continue to evolve with smarter controls, adaptive polishing strategies, and integration into fully automated production lines.
A Metal Fabrication Surface Polisher is designed to improve and refine the surface quality of metal parts created through fabrication processes such as cutting, welding, and forming. It uses abrasive tools like belts, discs, brushes, or pads that rotate or move to remove imperfections including burrs, weld spatter, scratches, oxidation, and scale. These polishers accommodate various metals like stainless steel, aluminum, carbon steel, and alloys, adjusting speed and pressure to suit each material and achieve the desired finish. They come in different formats—from handheld and bench-mounted machines to large automated systems with multiple polishing heads—allowing for flexibility depending on part size and production volume. Automation through PLCs and robotic arms ensures consistent, repeatable results, reducing manual labor and increasing throughput. Dust extraction and filtration systems are essential to capture metal particles and debris, maintaining a safe and clean environment. Cooling systems prevent overheating that could damage metal surfaces. Safety features such as emergency stops, guards, and vibration control protect operators and enhance machine durability. Maintenance is simplified with modular abrasive attachments and accessible wear parts to minimize downtime. By removing surface defects, these polishers help improve corrosion resistance, prepare parts for coatings or plating, and enhance overall product durability and appearance. Continual technological advancements bring smarter controls and adaptive polishing capabilities, integrating these machines seamlessly into automated production lines to boost efficiency and quality in metal fabrication workflows.
Metal Fabrication Surface Polishers are integral in ensuring that fabricated metal parts meet both functional and aesthetic standards required in various industries. They help achieve uniform surface finishes that not only improve the visual appeal but also enhance resistance to corrosion, wear, and fatigue. By eliminating rough edges and surface irregularities, these machines contribute to safer handling and assembly of components, reducing the risk of injury or malfunction.
In many fabrication settings, surface polishers are used after welding to smooth weld beads and remove discoloration caused by heat, ensuring that joints are both strong and visually consistent. For complex parts with intricate geometries, advanced polishing systems with adjustable heads and multi-axis movements allow thorough finishing even in hard-to-reach areas. This capability is crucial for aerospace and medical device manufacturing where precision and surface integrity are critical.
Integration with digital control systems enables operators to create and save polishing programs tailored to specific parts or materials, enhancing repeatability and quality control. Sensors and feedback mechanisms monitor polishing pressure, tool condition, and surface finish in real time, allowing dynamic adjustments to maintain optimal results throughout production runs.
Ergonomics and safety are also key considerations, with many machines designed to minimize operator fatigue and exposure to dust or noise. Features such as adjustable work heights, vibration dampening, and enclosed polishing zones contribute to a healthier workplace environment.
Maintenance protocols are streamlined through modular design, enabling quick replacement of worn abrasives and components, which reduces machine downtime and keeps production schedules on track. The use of durable materials and robust construction ensures long service life, even under demanding industrial conditions.
Overall, metal fabrication surface polishers are essential tools that enhance product quality, operational efficiency, and workplace safety. They enable manufacturers to meet stringent industry standards and customer expectations, supporting innovation and competitiveness across metalworking sectors.
Sheet Metal Polishing Equipment

Sheet Metal Polishing Equipment is specialized machinery designed to refine the surface of flat or curved sheet metal panels, enhancing their appearance, smoothness, and durability. This equipment is widely used in industries such as automotive, appliance manufacturing, aerospace, and construction, where polished sheet metal surfaces contribute to both functional performance and aesthetic quality.
The polishing process involves abrasive tools like belts, pads, brushes, or rollers that move across the sheet metal surface to remove imperfections such as scratches, scale, oxidation, and minor dents. Depending on the material and desired finish, the equipment can apply varying levels of pressure and speed, ranging from aggressive grinding to fine polishing.
Sheet metal polishing machines come in several forms, including belt polishers, roller polishers, and flatbed polishing systems. Belt polishers use abrasive belts that run continuously over rollers, allowing quick and uniform finishing of large metal sheets. Roller polishers press rotating polishing wheels or brushes against the metal surface, suitable for smoothing and shining curved or flat panels. Flatbed polishers provide a stationary polishing surface where sheets are moved across abrasive pads or brushes, often used for high-precision finishing.
Automation and programmable controls are common in modern sheet metal polishing equipment, enabling consistent operation, adjustable polishing parameters, and integration with production lines. Features such as variable speed drives and adjustable pressure systems allow operators to customize the process for different metal types and thicknesses.
Dust extraction and filtration systems are essential to capture metal particles and abrasive debris, ensuring a clean work environment and protecting operator health. Cooling mechanisms may be included to prevent overheating and surface damage during intensive polishing cycles.
Safety features like emergency stops, protective guards, and ergonomic designs help minimize operator risk and fatigue. Maintenance is simplified by modular abrasive tool systems and easy access to wear parts, reducing downtime and improving productivity.
Overall, sheet metal polishing equipment plays a critical role in producing high-quality metal panels with smooth, reflective surfaces that meet industry standards. By combining precision, efficiency, and safety, these machines help manufacturers deliver superior products in competitive markets.
Sheet Metal Polishing Equipment is designed to improve the surface finish of flat or curved metal sheets by removing imperfections such as scratches, oxidation, scale, and minor dents. It uses abrasive elements like belts, pads, brushes, or rollers that move over the sheet metal to achieve smoothness and shine. Depending on the specific machine and application, polishing intensity, speed, and pressure can be adjusted to suit different metals and desired finishes, from coarse grinding to fine polishing. Common types include belt polishers that run abrasive belts over rollers for uniform finishing, roller polishers that use rotating wheels or brushes for both flat and curved surfaces, and flatbed polishers where sheets are moved across a stationary abrasive surface for precision work. Many modern machines feature automation and programmable controls to maintain consistent results, adjust parameters for various materials, and integrate seamlessly into production lines. Dust extraction systems capture metal particles and debris to ensure a clean, safe working environment, while cooling mechanisms prevent heat buildup that could damage the metal surface. Safety features such as emergency stops, guards, and ergonomic designs protect operators and reduce fatigue. Maintenance is streamlined with modular abrasive tools and accessible components, minimizing downtime. By delivering efficient and consistent surface finishing, sheet metal polishing equipment plays a vital role in producing high-quality metal panels used across automotive, aerospace, appliance manufacturing, and construction industries, helping manufacturers meet strict quality standards and market demands.
Sheet metal polishing equipment often incorporates adjustable polishing heads or multiple abrasive stations to handle various finishing stages in a single pass, from initial rough grinding to final mirror-like polishing. This multi-stage capability improves efficiency by reducing the need to move sheets between different machines. Some systems use oscillating or reciprocating motions in addition to rotational movement, which helps achieve uniform surface finishes without swirl marks or uneven textures.
Advanced versions of this equipment may include sensors and feedback controls that monitor surface quality in real time, enabling dynamic adjustments to pressure, speed, or abrasive type to maintain optimal polishing conditions. This technology helps reduce material waste and ensures consistent output, especially important in high-volume manufacturing environments.
The machines are designed to handle a wide range of sheet metal materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, galvanized steel, and copper alloys. Polishing parameters can be fine-tuned to accommodate the hardness, thickness, and corrosion resistance requirements of each material. For example, softer metals might require gentler polishing to avoid surface deformation, while harder metals may need more aggressive abrasion to remove surface flaws.
Integration with other fabrication equipment, such as cutting, stamping, or forming machines, is common, enabling seamless workflow and reducing handling time. Conveyor systems often feed sheets automatically into polishing units, improving throughput and minimizing manual labor.
Dust and particulate collection systems use high-efficiency filters and cyclones to capture fine metal dust generated during polishing, protecting both the operator and machinery from contamination. Noise reduction features and vibration damping systems contribute to a safer and more comfortable work environment.
Regular maintenance is facilitated through quick-change abrasive components and accessible service points. Some machines are equipped with diagnostic tools that alert operators to tool wear or maintenance needs, helping prevent unexpected downtime.
Overall, sheet metal polishing equipment enhances product quality, operational efficiency, and workplace safety, making it an indispensable tool in modern metal fabrication industries where surface finish and precision are critical.
Multi-Metal Surface Finishing Unit

A Multi-Metal Surface Finishing Unit is a versatile machine designed to polish, buff, grind, and finish a variety of metal types within a single system. It is engineered to handle different materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, brass, copper, carbon steel, and various alloys, making it ideal for fabrication shops and manufacturing environments that work with diverse metal components.
This unit typically features adjustable settings—such as variable speed controls, pressure regulation, and interchangeable abrasive tools—that allow operators to tailor the finishing process to the specific metal’s hardness, thickness, and surface condition. This flexibility ensures optimal results, whether the task involves removing surface imperfections, smoothing welds, achieving a satin finish, or creating a mirror-like shine.
The machine may incorporate multiple polishing stations, each equipped with different abrasives or brushes suited for various metals and finishing stages. Automation and programmable controls allow for consistent processing, repeatable quality, and increased throughput, reducing manual labor and minimizing operator error.
To accommodate the different dust and debris produced by various metals, the unit includes advanced dust extraction and filtration systems designed to safely capture and contain fine metal particles, enhancing workplace safety and compliance with environmental regulations.
Safety features such as protective guards, emergency stops, vibration reduction, and ergonomic designs ensure operator comfort and reduce the risk of accidents during extended use. Maintenance is simplified with modular components and quick-change abrasive attachments, helping minimize downtime.
Multi-metal surface finishing units are essential for industries requiring high-quality finishes on mixed-metal assemblies or products, such as automotive parts, aerospace components, decorative metalwork, and electronics enclosures. Their adaptability and efficiency help manufacturers meet stringent surface quality standards while optimizing production workflows.
A Multi-Metal Surface Finishing Unit is designed to provide versatile finishing capabilities for a wide range of metals including stainless steel, aluminum, brass, copper, carbon steel, and various alloys. The machine features adjustable settings such as variable speed controls, pressure adjustments, and interchangeable abrasive tools to tailor the finishing process to the specific characteristics of each metal type, ensuring optimal removal of surface imperfections, smoothing of welds, and achieving finishes ranging from matte to mirror-like shine. It often includes multiple polishing stations with different abrasives or brushes to accommodate various metals and stages of finishing within a single operation. Automation and programmable controls help maintain consistent results, improve throughput, and reduce manual labor and operator errors. Advanced dust extraction and filtration systems safely capture metal dust and debris, enhancing operator safety and environmental compliance. Safety features like guards, emergency stops, vibration dampening, and ergonomic design promote comfortable and secure operation. Maintenance is streamlined through modular components and quick-change abrasive attachments, minimizing downtime. This unit is essential in industries where high-quality finishes are required on assemblies made from mixed metals, such as automotive, aerospace, decorative metalwork, and electronics manufacturing, helping manufacturers meet stringent quality standards efficiently.
The Multi-Metal Surface Finishing Unit is often equipped with advanced sensor technology and feedback systems that monitor polishing pressure, surface texture, and tool wear in real time. This allows the machine to automatically adjust parameters during operation, ensuring consistent finish quality across different metal types and reducing material waste. Such adaptive control is especially valuable in production environments handling complex or custom metal parts.
To accommodate the diversity of metal shapes and sizes, these units may offer flexible tooling arrangements, including adjustable polishing heads, multi-axis movement, and customizable work holding fixtures. This versatility allows operators to efficiently process flat sheets, curved panels, tubes, or irregularly shaped components without extensive setup changes.
Integration with other fabrication processes is common, with conveyors, robotic arms, or loading/unloading systems facilitating seamless material flow through the finishing line. This connectivity supports higher production speeds and reduces manual handling risks.
The unit’s robust construction ensures durability and stability under heavy workloads, while noise reduction and vibration control features contribute to a safer, more comfortable work environment. Cooling systems prevent overheating during intensive polishing cycles, protecting both the workpiece and abrasive tools.
Routine maintenance is made easier with diagnostic alerts for component wear and quick access to service points. Modular design allows abrasive pads, belts, brushes, or wheels to be swapped out swiftly, keeping downtime to a minimum.
Overall, the Multi-Metal Surface Finishing Unit enhances manufacturing efficiency by delivering high-quality, consistent finishes on a wide range of metals. Its adaptability and automation capabilities help meet stringent industry standards while optimizing production workflows and reducing labor costs.
Inner Pot Belt Grinder

An Inner Pot Belt Grinder is a specialized machine designed to grind and finish the interior surfaces of pots, pans, and similar cylindrical or bowl-shaped cookware. It uses an abrasive belt system that moves continuously to remove surface imperfections such as weld marks, rough edges, scale, or oxidation inside the pot, ensuring a smooth, uniform finish.
The machine typically features a rotating mechanism to hold and slowly turn the pot, allowing the abrasive belt to contact the inner surface evenly. Adjustable pressure controls enable precise grinding to avoid damaging the pot’s material while achieving the desired level of smoothness. The belt speed can also be varied to accommodate different metals and thicknesses.
Inner Pot Belt Grinders are often equipped with dust extraction systems to capture metal particles generated during grinding, maintaining a clean work environment and protecting operator health. Safety features like guards and emergency stops enhance operator safety during the grinding process.
These grinders are essential in cookware manufacturing where the inner surface finish impacts both the product’s aesthetics and functional performance, such as heat distribution and ease of cleaning. They improve production efficiency by automating a task that would otherwise require manual labor and help maintain consistent quality across large production batches.
Modular abrasive belts and easy-to-access service points simplify maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs. Suitable for materials like stainless steel, aluminum, and other metals commonly used in cookware, Inner Pot Belt Grinders ensure a high-quality finish that meets industry standards and customer expectations.
An Inner Pot Belt Grinder is a machine designed specifically for grinding and finishing the inside surfaces of pots, pans, and similar cookware with cylindrical or bowl-shaped interiors. It uses a continuously moving abrasive belt that comes into contact with the inner surface as the pot is rotated or held steadily, allowing for even removal of imperfections like weld seams, rough edges, scale, and oxidation. The machine offers adjustable pressure and variable belt speed controls to suit different metal types and thicknesses, ensuring precise grinding without damaging the material. Dust extraction systems are commonly integrated to capture metal particles, maintaining a clean workspace and protecting operator health. Safety features such as protective guards and emergency stop buttons are standard to ensure safe operation. This equipment is critical in cookware manufacturing for producing smooth, uniform inner surfaces that improve heat distribution and ease of cleaning. By automating a process that would otherwise be manual and labor-intensive, the Inner Pot Belt Grinder enhances production efficiency and ensures consistent product quality. Its modular design allows for easy replacement of abrasive belts and simple maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs. It is suitable for finishing various metals including stainless steel and aluminum, meeting industry standards and customer expectations for high-quality cookware.
Inner Pot Belt Grinders often feature adjustable fixtures or customizable chucks to securely hold different pot sizes and shapes during grinding. This flexibility allows manufacturers to process a range of cookware designs without extensive setup changes, enhancing production versatility. Some machines incorporate automated loading and unloading systems to further streamline workflow and reduce manual handling, which improves both efficiency and operator safety.
The abrasive belts used are available in various grit sizes and materials, allowing operators to select the appropriate level of abrasiveness for the stage of grinding—coarse belts for initial material removal and finer belts for finishing touches. Cooling systems may be integrated to prevent overheating of both the workpiece and abrasive belt, extending tool life and preserving surface integrity.
In addition to standard cylindrical pots, some Inner Pot Belt Grinders are adapted to handle more complex shapes, including tapered or flared interiors, through multi-axis movement and programmable controls. This capability supports the production of modern cookware designs with intricate inner profiles.
Maintenance is simplified with quick-change belt mechanisms and accessible service panels, enabling rapid replacement of worn abrasives and routine machine servicing. Dust extraction units often use high-efficiency filters to trap fine metal dust and maintain air quality in the manufacturing environment.
Overall, Inner Pot Belt Grinders contribute significantly to consistent, high-quality finishing of cookware interiors, ensuring products meet aesthetic and functional requirements while optimizing manufacturing speed and safety.
Belt Grinding Unit for Cookware

A Belt Grinding Unit for Cookware is a specialized machine designed to grind, smooth, and finish the surfaces of various cookware items such as pots, pans, lids, and other kitchen utensils. It utilizes an abrasive belt that moves continuously over rollers or drums to remove surface imperfections, weld marks, scale, and roughness, resulting in a uniform and refined finish.
This unit typically supports adjustable belt speed and pressure controls, allowing operators to customize the grinding process to suit different cookware materials like stainless steel, aluminum, or non-stick coated metals. The belt’s abrasive grit can also be varied depending on whether rough grinding or fine finishing is required.
Cookware items are held securely during grinding, often using rotary or fixed fixtures that ensure consistent contact between the abrasive belt and the surface. For interior surfaces, specialized attachments or configurations allow grinding of curved or cylindrical shapes, while flat or outer surfaces are handled with suitable setups to maintain efficiency and precision.
Dust extraction systems are integrated to capture metal particles and debris generated during grinding, promoting a clean working environment and protecting operators from inhaling harmful dust. Safety features like guards, emergency stop buttons, and ergonomic design are standard to ensure safe and comfortable operation.
The Belt Grinding Unit for Cookware enhances manufacturing productivity by automating surface finishing processes that would otherwise be time-consuming if done manually. It ensures consistent quality, reduces labor costs, and helps cookware manufacturers meet strict industry standards for surface finish, durability, and aesthetics.
Maintenance is simplified with quick-change abrasive belts and accessible machine components, minimizing downtime and extending the life of the equipment. This machine is an essential asset in cookware production lines, contributing to high-quality, visually appealing, and functional kitchen products.
A Belt Grinding Unit for Cookware is designed to grind, smooth, and finish various cookware surfaces such as pots, pans, lids, and utensils using a continuously moving abrasive belt. It removes surface imperfections, weld marks, and roughness to produce a uniform, refined finish. The machine features adjustable belt speed and pressure controls to accommodate different materials like stainless steel, aluminum, or coated metals, and the abrasive grit can be selected based on whether rough or fine finishing is needed. Cookware is securely held during grinding with rotary or fixed fixtures to ensure consistent contact between the belt and surface, including configurations for both interior curved surfaces and flat or outer surfaces. Integrated dust extraction systems capture metal particles and debris, maintaining a clean environment and operator safety, while safety features such as guards and emergency stops protect users. This unit automates surface finishing processes, increasing manufacturing efficiency, reducing manual labor, and ensuring consistent quality that meets industry standards. Maintenance is streamlined through quick-change abrasive belts and accessible components, minimizing downtime and extending equipment lifespan, making it a vital part of cookware production lines focused on delivering high-quality, durable, and visually appealing kitchen products.
The Belt Grinding Unit for Cookware often includes modular design elements that allow for easy customization and upgrades depending on production needs. Operators can switch between different belt widths, abrasive materials, and grit sizes to handle various finishing stages—from heavy material removal to polishing—without requiring a full machine change. This flexibility supports a wide range of cookware types and materials in a single production environment.
To improve efficiency, some units incorporate automated loading and unloading systems, robotic arms, or conveyor integration, enabling continuous operation with minimal manual intervention. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and touchscreen interfaces allow operators to set and monitor grinding parameters precisely, ensuring repeatable quality and reducing the risk of errors.
The machine’s construction is typically rugged and designed to withstand the demands of industrial environments, with corrosion-resistant materials used in areas exposed to metal dust and coolant fluids. Cooling and lubrication systems may be built-in to enhance abrasive belt life and maintain consistent surface quality.
Safety and ergonomics are prioritized, with adjustable workstations, noise reduction measures, and vibration dampening features to improve operator comfort during extended use. Dust extraction units often employ high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters or cyclone separators to maintain air quality and comply with workplace safety regulations.
Regular maintenance is facilitated through easy access panels and diagnostic software that alerts users to belt wear or mechanical issues before they lead to downtime. This proactive approach helps maximize machine uptime and ensures consistent product quality throughout production runs.
Overall, the Belt Grinding Unit for Cookware is essential for modern cookware manufacturing, offering adaptability, precision, and automation to meet high standards for surface finish, durability, and aesthetic appeal while optimizing production efficiency and worker safety.
Pots Surface Belt Abrasive Machine

A Pots Surface Belt Abrasive Machine is a specialized industrial device designed to grind, smooth, and finish the external surfaces of pots and similar cookware using an abrasive belt system. This machine employs a continuous abrasive belt that moves over rollers or drums to remove surface imperfections such as weld seams, scale, scratches, and oxidation from the pot’s exterior, producing a consistent, polished finish.
The machine usually offers adjustable belt speed and pressure controls, enabling operators to customize the grinding intensity based on the pot’s material—commonly stainless steel, aluminum, or other metals—and the desired finish quality. Different abrasive belt grits can be used to perform everything from coarse material removal to fine polishing.
Pots are securely held during the process, often with rotary fixtures that allow the pot to spin while the abrasive belt presses against its outer surface evenly. This rotation ensures uniform abrasion around the entire circumference, preventing uneven wear or finish defects.
Dust extraction and collection systems are integrated to capture metal particles and debris generated during abrasive grinding, maintaining a cleaner work environment and protecting worker health. Safety features such as protective guards, emergency stops, and ergonomic designs enhance operator safety and comfort during use.
The Pots Surface Belt Abrasive Machine automates what would otherwise be labor-intensive manual finishing, improving production efficiency, ensuring consistent surface quality, and helping manufacturers meet industry standards for durability and appearance. Its modular design allows quick replacement of abrasive belts and easy maintenance, minimizing downtime and extending the machine’s operational life.
Overall, this machine is a crucial asset in cookware manufacturing, delivering high-quality surface finishes that contribute to product performance and aesthetic appeal.
A Pots Surface Belt Abrasive Machine is designed to grind, smooth, and finish the outer surfaces of pots and similar cookware using a continuous abrasive belt system. The belt moves over rollers or drums to remove imperfections like weld seams, scale, scratches, and oxidation, resulting in a uniform polished finish. Operators can adjust the belt speed and pressure to suit different materials such as stainless steel or aluminum, and select various abrasive grit sizes for coarse grinding or fine polishing. Pots are typically held securely in rotary fixtures that spin them, allowing even contact between the belt and the entire outer surface for consistent abrasion. Integrated dust extraction systems capture metal particles and debris to maintain a clean workspace and protect worker health. Safety features including guards, emergency stop buttons, and ergonomic designs ensure operator safety and comfort. This machine automates the finishing process, improving production efficiency, reducing manual labor, and ensuring consistent surface quality that meets industry standards for durability and appearance. Its modular design facilitates quick abrasive belt replacement and easy maintenance, minimizing downtime and extending equipment life. The Pots Surface Belt Abrasive Machine is essential in cookware manufacturing for producing high-quality, durable, and visually appealing products.
The Pots Surface Belt Abrasive Machine often incorporates features such as adjustable fixtures to accommodate pots of various sizes and shapes, enhancing its versatility for different production requirements. Some models include programmable controls and digital displays that allow precise setting of grinding parameters, ensuring repeatability and consistent quality across batches.
To further boost productivity, these machines can be integrated with automated loading and unloading systems or conveyors, reducing manual handling and speeding up the finishing process. The abrasive belts themselves come in a variety of materials and grit options, allowing operators to tailor the machine’s performance from aggressive material removal to delicate surface polishing.
Robust construction with corrosion-resistant components ensures durability in demanding manufacturing environments, while vibration dampening and noise reduction features improve operator comfort and workplace safety. Cooling or lubrication systems may be included to prolong belt life and prevent overheating of both the belt and the pot surface during extended grinding cycles.
Maintenance is simplified with easy-access panels and quick-change belt mechanisms, enabling fast replacement of worn abrasives and reducing downtime. Advanced machines may also offer diagnostic systems that alert users to mechanical issues or belt wear before they affect production.
Overall, the Pots Surface Belt Abrasive Machine is a critical tool in modern cookware production, combining precision, efficiency, and safety to deliver high-quality surface finishes that meet industry standards and customer expectations.
Belt-Type Grinder for Utensils

A Belt-Type Grinder for Utensils is an industrial machine designed to grind, smooth, and finish the surfaces of various kitchen utensils such as spoons, ladles, spatulas, and small cookware components. It uses a continuous abrasive belt that moves over rollers or drums to remove surface imperfections like burrs, weld marks, rough edges, and oxidation, resulting in a clean and polished finish.
The machine typically features adjustable belt speed and pressure controls, allowing operators to tailor the grinding intensity based on the utensil’s material—commonly stainless steel, aluminum, or other metals—and the desired finish quality. Different abrasive belts with varying grit sizes can be used to perform rough grinding or fine polishing, depending on production needs.
Utensils are held securely during grinding, either manually or with fixtures that ensure consistent contact between the abrasive belt and the surface. The design often accommodates both flat and contoured shapes, allowing versatile finishing of diverse utensil profiles.
Dust extraction systems are integrated to capture metal particles generated during grinding, maintaining a clean work environment and protecting operator health. Safety features such as protective guards, emergency stop buttons, and ergonomic designs are standard to ensure safe and comfortable operation.
The Belt-Type Grinder for Utensils automates the surface finishing process, increasing manufacturing efficiency, reducing labor costs, and ensuring consistent quality. Maintenance is simplified through quick-change abrasive belts and accessible machine components, minimizing downtime and extending equipment lifespan.
Overall, this machine is essential in utensil manufacturing and finishing, delivering smooth, durable, and visually appealing products that meet industry standards and customer expectations.
A Belt-Type Grinder for Utensils is an industrial machine designed to grind, smooth, and finish surfaces of kitchen utensils like spoons, ladles, spatulas, and small cookware parts using a continuous abrasive belt. The belt moves over rollers to remove imperfections such as burrs, weld marks, rough edges, and oxidation, producing a clean, polished finish. Operators can adjust belt speed and pressure to match different materials—typically stainless steel or aluminum—and select abrasive belts with varying grit sizes for rough grinding or fine polishing. Utensils are securely held, either manually or with fixtures, ensuring consistent contact between the belt and the surface, and the machine accommodates both flat and contoured shapes for versatile finishing. Integrated dust extraction captures metal particles, maintaining a clean workspace and protecting worker health. Safety features including guards, emergency stops, and ergonomic design ensure operator safety and comfort. The machine automates finishing processes, boosting manufacturing efficiency, reducing labor costs, and delivering consistent quality. Maintenance is easy with quick-change abrasive belts and accessible components, minimizing downtime and extending machine life. This grinder is vital for producing smooth, durable, and visually appealing utensils that meet industry standards and customer expectations.
Advanced models of the Belt-Type Grinder for Utensils may include programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and digital interfaces that allow precise control over grinding parameters, ensuring repeatable quality across production batches. These systems enable users to save specific settings for different utensil types, reducing setup time when switching between products. Some machines are also compatible with robotic arms or conveyor systems for automated feeding and retrieval, further increasing throughput and reducing manual handling.
The abrasive belts used in these grinders are available in a variety of materials such as aluminum oxide, zirconia alumina, or ceramic, each suited to different levels of material hardness and finishing requirements. This allows manufacturers to tailor the grinding process to achieve everything from aggressive stock removal to high-gloss surface polishing.
The grinder’s frame is typically constructed from heavy-duty steel or corrosion-resistant alloys to ensure stability and long-term durability in industrial environments. Vibration damping components and noise insulation features contribute to a safer, more comfortable workspace, especially during prolonged operation.
To extend belt life and improve surface finish consistency, some units are equipped with cooling or misting systems that reduce friction heat buildup. The inclusion of monitoring sensors can also alert operators to issues like belt misalignment, excessive wear, or mechanical faults before they result in product defects or machine damage.
Overall, the Belt-Type Grinder for Utensils is a high-precision, high-efficiency solution designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern utensil production. Its combination of mechanical robustness, operational flexibility, and user-focused features makes it indispensable in facilities where quality, consistency, and productivity are critical.
Stainless Steel Pot Belt Finishing Machine

A Stainless Steel Pot Belt Finishing Machine is a specialized industrial system designed to deliver high-quality surface finishing to stainless steel pots using an abrasive belt mechanism. This machine operates by guiding a moving abrasive belt over the pot’s surface, efficiently removing weld lines, scratches, oxidation, and other imperfections to produce a smooth, uniform, and visually appealing finish. It is especially suitable for cookware manufacturers seeking consistent quality in mass production.
The machine typically includes a rotating fixture or holding system that securely grips the pot while it spins, ensuring all sides are evenly exposed to the abrasive belt. Adjustable settings allow the operator to control belt speed, tension, and grinding pressure to suit various pot sizes, contours, and finishing requirements—from coarse grinding to fine polishing. The abrasive belts are available in different grits and materials, such as aluminum oxide or ceramic, enabling a tailored approach for different surface treatment needs.
To support operator safety and product quality, the system often integrates dust extraction units that remove fine metal particles and debris generated during the process. This not only ensures a cleaner working environment but also extends the service life of machine components. Additional safety features like emergency stop buttons, protective covers, and thermal overload protection are standard.
Durably constructed from corrosion-resistant materials, the Stainless Steel Pot Belt Finishing Machine is built for long-term, heavy-duty operation in high-volume manufacturing settings. It is often designed with easy-access panels and quick-change belt systems to reduce maintenance time and downtime. Some advanced models include digital interfaces and programmable controls for enhanced process repeatability and production efficiency.
Overall, this machine plays a critical role in the cookware production line by delivering consistent, high-grade finishes that meet industry standards for aesthetics, hygiene, and durability in stainless steel pots.
A Stainless Steel Pot Belt Finishing Machine is an industrial device engineered to provide a smooth, polished surface on stainless steel pots by means of a continuous abrasive belt. The machine functions by securing the pot—typically through a rotating fixture or clamping system—and applying an abrasive belt that moves at high speed across the pot’s outer surface. As the pot rotates, the belt systematically grinds away imperfections such as weld lines, scratches, discoloration, and oxidation, resulting in a uniform, refined finish suitable for cookware that meets both functional and aesthetic standards. Belt speed, pressure, and angle can be adjusted to accommodate different pot sizes, shapes, and desired surface finishes, from coarse texture removal to mirror-like polishing. Abrasive belts come in various grit levels and materials like aluminum oxide or ceramic to suit specific finishing tasks. The machine’s structure is generally composed of corrosion-resistant materials to ensure durability in demanding production environments. Integrated features such as dust extraction units help maintain a clean workspace and protect operator health by capturing fine metal particles generated during grinding. Safety is supported by elements like emergency stop functions, protective guards, and thermal overload protection. Many models feature easy-to-access maintenance panels and quick-change belt systems to reduce downtime. Advanced systems may offer programmable controls or digital interfaces for precise setting adjustments and production consistency. This machine significantly enhances productivity and quality control in cookware manufacturing by automating and standardizing the finishing process, delivering stainless steel pots that are not only visually appealing but also smooth, hygienic, and ready for market.
In more advanced configurations, the Stainless Steel Pot Belt Finishing Machine may incorporate CNC or PLC-based automation systems that allow operators to pre-program finishing parameters such as belt speed, rotation speed, contact pressure, and polishing duration. These programmable settings ensure uniformity across multiple units, significantly reducing variability and human error. For manufacturers handling different sizes or designs of pots, memory functions allow quick switching between saved configurations, optimizing both changeover time and production efficiency.
Some machines are equipped with servo-driven or pneumatic mechanisms that automatically adjust the position of the abrasive belt relative to the pot’s surface contours, maintaining consistent contact and pressure. This adaptive control is especially beneficial when processing pots with tapered or curved profiles, as it eliminates the need for manual repositioning and ensures even finishing across all geometries.
To further enhance surface quality and process reliability, the system may include a belt tensioning and tracking mechanism that continuously maintains optimal alignment of the abrasive belt, reducing wear and improving lifespan. Integrated cooling systems, such as mist spray or air jet nozzles, may also be used to dissipate heat generated during grinding, which not only protects the surface of the stainless steel from thermal discoloration but also improves belt performance and reduces the risk of warping the workpiece.
In large-scale operations, the Stainless Steel Pot Belt Finishing Machine can be integrated into an automated production line alongside forming, welding, and inspection stations, enabling seamless workflow and real-time quality control. Sensors can detect anomalies in belt condition or workpiece position, triggering automatic alerts or system shutoffs to prevent defective output and minimize downtime.
Ultimately, the machine’s ability to combine high throughput, surface uniformity, and operator safety makes it indispensable in cookware and kitchenware manufacturing. Its role in consistently producing durable, hygienic, and attractive stainless steel pots contributes directly to product value and brand reputation in competitive markets.
Cookware Belt Grinding System

A Cookware Belt Grinding System is a robust and precision-engineered machine used for surface preparation, defect removal, and aesthetic finishing of cookware items such as pots, pans, and lids. It utilizes an abrasive belt, which travels continuously over a set of rollers, to grind and smooth metal surfaces, typically stainless steel or aluminum. Cookware is held against or moved along the abrasive belt, allowing for uniform material removal that eliminates welding seams, surface imperfections, and oxidation marks, leaving a clean and even surface ready for polishing or final use.
This system is commonly configured with either a flat grinding table or rotary fixtures that can rotate the cookware during the process, ensuring full 360-degree surface coverage. Adjustable parameters such as belt speed, grinding pressure, and contact angle enable customization for different cookware shapes, wall thicknesses, and finishing requirements—ranging from heavy stock removal to light deburring or fine surface conditioning.
The belts themselves come in various grit levels and materials (e.g., aluminum oxide, zirconia, ceramic) and can be quickly swapped to suit different finishing stages. For curved or contoured surfaces, the grinding head may be mounted on a flexible arm or spring-loaded platen that adapts to the cookware’s profile, ensuring consistent contact and surface uniformity.
To maintain process cleanliness and extend machine life, most systems include an integrated dust and debris extraction unit that removes fine particles and metal shavings. Safety is ensured through emergency stop buttons, belt guards, thermal overload protection, and operator-friendly controls. In high-volume environments, the belt grinding system can be combined with automated loading arms, conveyors, or robotic handlers to reduce manual labor and improve throughput.
Whether used as a standalone finishing tool or as part of a fully automated cookware production line, the Cookware Belt Grinding System plays a vital role in delivering a precise, high-quality finish that enhances both the appearance and functionality of the end product.
A Cookware Belt Grinding System is a continuous abrasive finishing solution designed to refine the surface of cookware items such as stainless steel or aluminum pots and pans. The system operates using an abrasive belt mounted on motor-driven rollers that run at variable speeds, enabling efficient material removal and surface conditioning. Cookware is either manually or automatically held against the moving belt, and as it rotates or moves along the belt’s length, surface imperfections like weld seams, oxidation, scale, or rough textures are removed uniformly. The result is a smoother, more consistent finish suitable for further polishing or direct use, depending on the desired final appearance.
The grinding process can be fine-tuned with adjustments to belt tension, speed, and angle of contact, making it adaptable for different shapes and sizes of cookware. Some systems include rotary fixtures or flexible grinding heads that conform to the cookware’s curves, ensuring uniform coverage even on contoured or tapered surfaces. Abrasive belts are available in multiple grit sizes, allowing operators to switch between aggressive grinding and finer finishing by simply changing the belt.
Built with industrial-grade steel frames and vibration-reducing structures, these machines are engineered for stability and long operational life. Integrated dust extraction units help maintain a clean working environment by removing fine metal particles produced during grinding, which also contributes to longer belt life and improved machine performance. Operator safety features such as emergency stop mechanisms, thermal protection, and belt guards are standard, ensuring safe usage even in continuous operation.
Some models incorporate programmable controls or digital interfaces to store grinding parameters for different cookware types, making repeat production fast and accurate. In high-throughput settings, the system may be integrated with conveyors or robotic loading units for automated, hands-free operation. This reduces labor intensity and increases production speed while ensuring consistent surface quality.
The Cookware Belt Grinding System is a core component in modern cookware manufacturing, delivering smooth, uniform finishes that enhance product durability, hygiene, and market appeal. It plays a critical role in achieving production efficiency, surface integrity, and the high visual standards expected in consumer kitchenware.
In advanced manufacturing environments, the Cookware Belt Grinding System may also feature servo-controlled movement of the grinding head or workpiece, ensuring precision across complex geometries and minimizing manual adjustment. These automated functions allow the system to adapt to various cookware profiles in real-time, optimizing both material removal and belt wear. Sensors can be incorporated to monitor belt condition, workpiece positioning, and surface contact pressure, providing feedback to a central control unit that can make immediate adjustments, thereby maintaining quality standards and reducing scrap rates.
The choice of abrasive material on the belt—such as ceramic for aggressive grinding or Trizact for fine surface finishing—further tailors the system to the specific requirements of the cookware being processed. Some operations combine dry and wet grinding techniques, where coolant is sprayed directly onto the belt or work surface to reduce heat buildup, improve finish quality, and extend the lifespan of both the belt and the cookware piece.
To streamline workflows, these systems are often part of a larger finishing line that includes deburring, polishing, ultrasonic cleaning, and drying stations. Integration with conveyors or gantry robots ensures continuous movement from one process to the next, reducing handling time and operator fatigue. This automation enables higher throughput and consistency, particularly beneficial in large-scale cookware production where time, uniformity, and surface quality are critical to competitiveness.
The system is not only applicable to standard round pots and pans but can also be configured or accessorized to handle lids, handles, and non-standard or multi-material cookware items, increasing its versatility across different product lines. Maintenance is generally minimal, thanks to modular designs, easy belt replacement mechanisms, and diagnostics that alert users to wear or faults before they cause downtime.
Overall, the Cookware Belt Grinding System represents a scalable and customizable solution for high-performance surface finishing, combining power, precision, and flexibility to meet the demands of modern cookware manufacturing.
Belt Surface Grinder for Pots

A Belt Surface Grinder for Pots is a specialized machine designed to perform precision grinding and surface finishing on the outer bodies of cookware, particularly pots made of stainless steel or aluminum. It utilizes a continuous abrasive belt that runs over rollers, providing a high-friction surface against which the pot is pressed to remove material evenly. This process eliminates surface defects such as welding seams, oxidation marks, scratches, and uneven textures, preparing the pot either for final polishing or direct market-ready finish depending on the required surface grade.
The machine typically features a robust frame with adjustable guides or fixtures to hold pots of various sizes securely in position during grinding. Depending on the configuration, the pot may be rotated automatically as it contacts the belt, ensuring 360-degree uniformity in surface treatment. Variable speed controls allow operators to fine-tune belt movement to match the hardness of the material and the aggressiveness of the grind needed, whether for rough sanding or fine finishing.
Advanced versions may be equipped with servo-driven arms or floating contact wheels that maintain consistent pressure along the pot’s contours. These floating systems automatically adapt to variations in shape and wall thickness, which is crucial for maintaining even finishes on curved or tapered cookware bodies. Abrasive belts in different grit sizes—from coarse to ultrafine—can be quickly swapped to shift from grinding to smoothing operations.
To protect the workpiece and optimize grinding performance, the system often includes integrated cooling mechanisms such as air blowers or coolant spray nozzles that dissipate heat generated by friction. An onboard dust extraction or vacuum system keeps the working area clean, prevents airborne particle buildup, and extends the life of the abrasive components.
Safety features like emergency stop buttons, overload protection, and guarded enclosures are standard to ensure safe operation. The user interface typically includes intuitive controls or touchscreens that allow for real-time adjustment and monitoring. In mass production settings, this grinder can be linked with automated feeders and conveyors for continuous, unattended operation.
The Belt Surface Grinder for Pots is a key asset in cookware production lines, delivering consistent quality, improved production speed, and an attractive, functional surface finish that enhances the appearance and usability of the final product.
A Belt Surface Grinder for Pots is an industrial machine used to achieve uniform grinding and surface finishing on the outer bodies of cooking pots, particularly those made from stainless steel or aluminum. The system employs a continuously moving abrasive belt that runs over powered rollers, creating a consistent grinding surface against which the pot is pressed. As the pot comes into contact with the abrasive belt, surface imperfections such as weld seams, oxidation, discoloration, and fabrication marks are efficiently removed, producing a smooth, uniform surface texture suitable for further polishing or direct sale depending on the finish requirement.
The machine typically includes a durable frame and adjustable holding mechanisms to accommodate various pot sizes and shapes. Some models incorporate rotating fixtures or workpiece holders that spin the pot during grinding, allowing the abrasive belt to act on the entire circumference without manual repositioning. The speed of the belt and the rotational movement of the pot can usually be adjusted independently to achieve the desired removal rate and surface quality. The grinder’s structure is designed to absorb vibration and maintain stability, ensuring even contact between the abrasive belt and the cookware surface.
For pots with curved or tapered profiles, the machine may feature a floating contact wheel or spring-mounted platen that automatically adjusts to the surface contour, maintaining even pressure and contact area. This adaptive design prevents excessive material removal in any one area and ensures consistent surface treatment. The abrasive belts used in the grinder vary in grit size and composition depending on the stage of processing. Coarser grits are used for initial grinding and defect removal, while finer grits are employed for finishing and smoothing operations.
To enhance operational efficiency and prolong machine life, many systems include built-in cooling features such as water mist or air jets that prevent overheating of the cookware and the belt. Additionally, dust collection systems are integrated to extract fine metal particles generated during grinding, maintaining a clean workspace and reducing airborne contaminants. Operator safety is supported through standard features like emergency stop switches, protective enclosures, and automatic shut-off systems triggered by belt overload or jamming.
In high-volume production environments, the belt surface grinder may be integrated with automated loading arms, robotic handlers, or conveyor systems to allow for continuous, hands-free operation. This significantly increases throughput and consistency while reducing manual labor and the possibility of handling errors. The control interface of the machine often includes digital displays or programmable logic controls that allow operators to store and recall process settings for different pot sizes and material types, streamlining production changeovers.
Overall, the Belt Surface Grinder for Pots is a high-precision, industrial-grade solution essential for cookware manufacturing. It delivers superior surface preparation, dimensional accuracy, and aesthetic quality, playing a vital role in ensuring that each cookware piece meets modern standards for appearance, performance, and durability.
These grinders are particularly valued in modern cookware production lines for their repeatability and reduced reliance on manual intervention. Their modular construction allows for easy upgrades or replacement of wear components, such as contact wheels, tensioning assemblies, and abrasive belts. Operators can quickly switch belts with different grit levels or abrasive materials—ranging from zirconia alumina for aggressive grinding to silicon carbide for finer surface finishing—depending on the type of metal and desired outcome. This adaptability helps manufacturers meet diverse finish requirements, from matte brushed effects to surfaces prepped for mirror polishing.
In production cells designed for high throughput, multiple belt grinders can be arranged in sequence, where each unit performs a different stage of surface refinement. The first grinder may focus on heavy material removal, the next on mid-level smoothing, and the final one on fine finishing. This sequential arrangement is often synchronized through centralized controls, ensuring smooth transitions and optimal utilization of abrasives while keeping cycle times low.
More advanced Belt Surface Grinder systems can be paired with vision systems or laser profiling tools that scan the pot’s dimensions in real time and adjust grinding parameters accordingly. These technologies enhance quality control by identifying inconsistencies in workpiece geometry and automatically compensating to maintain uniform surface treatment. The use of servo motors in critical axes can provide high-resolution control over movement and pressure, allowing for delicate treatment of thin-walled cookware without risking deformation.
Some models are equipped with multi-station heads that enable the grinding of both the side and base of a pot without needing to reposition the workpiece manually. This not only increases efficiency but also ensures alignment and consistency across different surfaces. Additionally, integration with manufacturing execution systems (MES) allows for tracking of workpiece data, tool life management, and production analytics, supporting lean manufacturing initiatives and predictive maintenance planning.
As environmental and safety regulations become more stringent, many manufacturers choose belt grinders with enclosed designs and active filtration systems to capture fine particulates, reduce noise, and minimize coolant spillage. These closed-loop systems make the equipment more sustainable and suitable for operation in clean or high-sensitivity production environments.
In summary, the Belt Surface Grinder for Pots is a scalable and technologically adaptable machine that addresses the surface preparation needs of cookware production. Its robust design, precision controls, and potential for full automation make it a critical asset in achieving high-quality, consistent finishes across large production volumes. Whether used as a standalone unit or part of an integrated finishing line, it contributes significantly to the aesthetic and functional value of modern cooking vessels.
Utensil Belt Sanding Machine

An Utensil Belt Sanding Machine is an industrial device designed specifically for sanding and surface finishing kitchen utensils such as spoons, ladles, spatulas, and small cookware components. This machine employs a continuous abrasive belt that moves over a set of rollers, providing a high-speed sanding surface that smooths, removes burrs, and prepares the utensil’s metal surface for subsequent polishing or coating.
The machine is built to accommodate the varied shapes and sizes of utensils, often featuring adjustable fixtures or jigs to securely hold items during sanding. Depending on the model, utensils can be manually fed or automatically positioned on conveyor systems for high-volume production. The abrasive belt’s speed and grit type are selectable to match the material and desired finish—ranging from coarse belts that remove rough edges and scale to fine belts that create a smooth, uniform texture.
Utensil Belt Sanding Machines often incorporate adjustable sanding heads or floating platen assemblies that maintain consistent pressure and conform to the utensil’s contours, ensuring even material removal without damaging delicate shapes. This is especially important for curved or hollow parts, where maintaining the integrity of edges and profiles is critical.
To optimize performance and protect the workpieces, many machines include dust extraction systems that capture metal particles and prevent debris accumulation, which enhances operator safety and reduces maintenance needs. Cooling mechanisms like air jets or mist sprays may also be integrated to control heat buildup during extended sanding operations.
Safety features typically include emergency stop buttons, guarded belts, and overload protection to prevent damage or injury during operation. User-friendly control panels allow operators to adjust belt speed, pressure, and feed rate, ensuring flexibility and precision for different utensil types and production requirements.
In automated production settings, the Utensil Belt Sanding Machine can be part of a larger finishing line, seamlessly integrated with polishing, buffing, and inspection stations. This integration helps maintain consistent quality standards and boosts overall throughput by reducing manual handling and setup time.
Overall, the Utensil Belt Sanding Machine is a vital tool in the manufacture and finishing of metal kitchen utensils, providing efficient, reliable, and uniform sanding that improves the surface quality, appearance, and safety of the final products.
An Utensil Belt Sanding Machine is an essential industrial tool designed to efficiently sand and finish metal kitchen utensils such as spoons, spatulas, ladles, and other small cookware parts. The machine operates using a continuous abrasive belt stretched over rollers, which moves at adjustable speeds to provide a consistent sanding surface. Utensils are either manually fed or positioned using automated conveyors or robotic arms, depending on the production scale, ensuring a steady flow of components through the sanding process.
To accommodate the varied shapes and sizes of utensils, the machine often includes adjustable jigs or fixtures that securely hold each piece during sanding. Some machines employ floating sanding heads or spring-loaded platens that adapt to the contours of the utensil, applying uniform pressure and preventing excessive material removal or distortion, especially on delicate or curved surfaces. The abrasive belts come in different grit sizes and materials, from coarse belts designed to remove burrs and rough edges, to finer grits that create smooth, uniform finishes, tailored to the type of metal and desired surface quality.
Heat generation from continuous sanding is mitigated through integrated cooling systems, such as air jets or fine mist sprays, protecting both the workpieces and abrasive belts from damage. Dust extraction units are typically built into the system to collect metal particles and airborne debris, maintaining a clean and safe working environment while reducing maintenance frequency. Safety features include enclosed sanding zones, emergency stop mechanisms, and belt guards to protect operators from moving parts and accidental contact.
The control interface generally allows operators to adjust belt speed, sanding pressure, and feed rate, enabling precise customization for different utensil materials and finishing requirements. In high-volume manufacturing, these machines can be integrated into automated production lines with upstream feeding systems and downstream polishing or inspection stations, facilitating continuous, hands-free operation that boosts throughput and consistency.
Overall, the Utensil Belt Sanding Machine offers a reliable, adaptable, and efficient solution for the initial surface finishing stages of kitchen utensil production. By removing imperfections, smoothing edges, and preparing surfaces for subsequent polishing, it plays a critical role in enhancing both the aesthetic appeal and functional quality of the finished products.
These machines are often designed with modular components to allow quick replacement or adjustment of belts, sanding heads, and fixtures, minimizing downtime during production shifts. The ability to rapidly change abrasive belts—from coarse grits for heavy stock removal to fine grits for finishing—provides manufacturers with flexibility to handle a wide variety of utensil materials and thicknesses, including stainless steel, aluminum, and sometimes even coated metals.
In more advanced models, servo motors and programmable controls enable automated adjustment of sanding parameters in real time, based on feedback from sensors monitoring belt tension, workpiece dimensions, or sanding pressure. This automation improves consistency across batches, reduces operator error, and optimizes abrasive belt life. Some machines include vision or laser scanning systems to inspect utensils before and after sanding, ensuring surface defects are fully addressed and quality standards are met.
The integration of dust collection and filtration systems is critical not only for environmental compliance but also for operator health and machinery longevity. Fine metal dust generated during sanding can pose respiratory risks and accelerate wear on mechanical components if not properly managed. Therefore, many Utensil Belt Sanding Machines are equipped with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters or cyclonic separators to capture the dust effectively.
Safety is a paramount consideration, with machines featuring protective enclosures, interlocks that prevent belt operation when guards are open, and emergency stop buttons strategically placed for quick access. Noise reduction measures, such as sound-dampening panels or insulated enclosures, are also common to create a more comfortable workplace environment.
In modern manufacturing setups, these machines are integrated into larger automated production cells where robotic arms handle loading and unloading of utensils, conveyor belts transfer items between stations, and sensors provide data for monitoring machine health and production metrics. This level of integration supports lean manufacturing principles, reduces manual labor costs, and increases throughput while maintaining high quality.
Overall, the Utensil Belt Sanding Machine is a vital part of the cookware and kitchenware production process, delivering efficient, consistent, and high-quality surface preparation. It lays the foundation for subsequent polishing or finishing operations that ultimately result in attractive, durable, and safe utensils for consumer use.
Rotary Pot Belt Grinding Equipment

Rotary Pot Belt Grinding Equipment is specialized machinery designed for the efficient surface grinding and finishing of pots, pans, and similar cookware items. This equipment combines the rotary motion of the pot with the continuous abrasive action of a belt grinder, enabling uniform material removal, smoothing, and preparation of the pot’s surface for further polishing or coating.
The core principle involves mounting the pot on a rotating fixture or chuck that turns the workpiece at a controlled speed. Simultaneously, a sanding or grinding belt, mounted on a set of rollers, moves continuously over a platen or contact wheel. The belt is pressed gently but firmly against the pot’s surface, grinding away imperfections such as weld marks, scale, or rough edges, while maintaining the shape and structural integrity of the pot.
Adjustability is a key feature: the rotational speed of the pot, belt speed, belt grit, and contact pressure can all be precisely controlled to match the material type and desired finish. Some machines feature automated feed mechanisms that move the grinding belt along the pot’s height or circumference, ensuring complete and consistent surface coverage. This automation reduces manual labor and improves repeatability across large production runs.
Rotary Pot Belt Grinding Equipment typically incorporates floating sanding heads or spring-loaded contact wheels that adapt to the pot’s curved surfaces, delivering even pressure and conforming to the contours. This flexibility is essential for avoiding localized over-grinding or surface distortion, especially on thin-walled cookware.
To maintain high-quality finishes and protect machine components, cooling systems such as air jets or misting units may be integrated to dissipate heat generated during grinding. Dust extraction systems are also commonly included to remove metal particles and abrasive debris, keeping the workspace clean and safe.
Safety measures include guards around moving belts and rotating pots, emergency stop controls, and sensors to detect belt wear or abnormal operating conditions. The machines often have user-friendly control panels or touchscreens that allow operators to quickly set parameters, monitor process variables, and execute routine maintenance tasks.
In production environments, Rotary Pot Belt Grinding Equipment can be integrated into automated finishing lines, working in concert with polishing, buffing, and inspection stations. This integration enhances throughput and quality consistency while reducing human intervention.
In summary, Rotary Pot Belt Grinding Equipment is an essential solution in modern cookware manufacturing, providing precise, efficient, and adaptable grinding of pots’ surfaces to improve their appearance, functionality, and readiness for final finishing stages.
Rotary Pot Belt Grinding Equipment is designed to efficiently grind and finish the surfaces of pots and similar cookware by combining the rotation of the pot with the continuous abrasive action of a belt grinder. The pot is mounted on a rotating fixture or chuck, which turns it at a controlled speed to expose the entire surface evenly to the abrasive belt. Meanwhile, the grinding belt runs continuously over rollers and is pressed against the pot’s surface, removing imperfections such as weld seams, rough edges, and scale while maintaining the pot’s shape and structural integrity.
Key adjustable parameters include the rotational speed of the pot, belt speed, grit size of the abrasive belt, and the pressure applied between the belt and the pot. These controls allow the machine to handle various materials and achieve different surface finishes, from coarse grinding to fine smoothing. Some models have automated feed systems that move the belt vertically or circumferentially along the pot, ensuring uniform coverage without manual repositioning, which enhances efficiency and repeatability.
The equipment often features floating sanding heads or spring-loaded contact wheels that adapt to the curved surfaces of pots, providing consistent pressure and preventing over-grinding or surface damage, especially important for thin-walled or delicate cookware. Cooling systems such as air jets or mist sprays are commonly integrated to dissipate heat generated during grinding, protecting both the workpiece and the abrasive belts.
Dust extraction systems are standard to capture metal dust and abrasive particles, maintaining a clean work environment and safeguarding operator health. Safety features include enclosed belts and rotating parts, emergency stop buttons, and sensors to monitor belt wear or detect abnormal operating conditions, minimizing risk during operation.
User interfaces are typically designed to be intuitive, often incorporating digital displays or touchscreens for easy adjustment of grinding parameters, monitoring of operational status, and maintenance alerts. In automated production lines, rotary pot belt grinders can be linked with robotic loading/unloading systems and subsequent polishing or inspection stations to streamline the finishing process and improve throughput.
Overall, Rotary Pot Belt Grinding Equipment is a versatile, precise, and efficient tool in cookware manufacturing, enabling consistent surface finishing that enhances both the aesthetic appeal and functional quality of pots before they proceed to final polishing or coating stages.
These machines are engineered for durability and high throughput, often constructed with heavy-duty frames and precision components to withstand continuous industrial use. The rotating fixture or chuck is designed to securely hold pots of various sizes and shapes, sometimes featuring quick-change mechanisms to speed up setup times between different product runs. This flexibility is critical in manufacturing environments that produce a wide range of cookware dimensions.
The abrasive belts used in rotary pot belt grinding machines come in multiple grades and materials, such as aluminum oxide or zirconia alumina, chosen based on the metal type and desired surface finish. Changing belts is streamlined to minimize downtime, and some systems include belt tracking adjustments to maintain optimal alignment and prevent premature wear.
Advanced models may incorporate servo-controlled drives for both pot rotation and belt movement, allowing precise synchronization and adjustment of speeds to optimize grinding efficiency and finish quality. Sensors can monitor belt tension and grinding force in real-time, feeding data back to control systems that automatically fine-tune operational parameters or alert operators to potential issues.
Environmental considerations are addressed through integrated dust extraction units equipped with filters capable of capturing fine metal particles generated during grinding. This not only keeps the workspace cleaner but also extends the life of the abrasive belts and mechanical parts by preventing dust accumulation.
Operator safety is further enhanced through machine enclosures, interlocks that disable operation if safety covers are opened, and ergonomic design features that reduce strain during loading and unloading of heavy pots. Noise dampening materials and sound enclosures are sometimes incorporated to reduce workplace noise levels.
In modern production lines, rotary pot belt grinding equipment often functions as part of a coordinated finishing system. Automated handling equipment, such as robotic arms or conveyors, may load pots onto the grinding machine and transfer them to downstream polishing or inspection stations without manual intervention. This integration supports lean manufacturing practices, increasing output while maintaining consistent product quality.
Maintenance accessibility is also a key design factor, with machines engineered for easy access to wear components like belts, rollers, and drive motors. Regular maintenance schedules, supported by machine diagnostics and alerts, help ensure reliable operation and minimize unplanned downtime.
In summary, rotary pot belt grinding equipment combines precision engineering, automation, and robust construction to deliver efficient, consistent, and high-quality surface grinding tailored to the cookware industry’s demanding production requirements. It plays a pivotal role in preparing pot surfaces for finishing processes that enhance appearance, durability, and consumer safety.
Belt-Driven Polisher for Pots

A Belt-Driven Polisher for Pots is a specialized machine designed to polish the surfaces of pots, pans, and similar cookware using a continuous abrasive or polishing belt. This equipment focuses on enhancing the aesthetic finish and surface smoothness of metal cookware, typically made from stainless steel, aluminum, or other alloys, by removing minor scratches, oxidation, and surface imperfections.
The machine operates by moving a polishing belt at high speeds over a contact surface, while the pot is either held stationary or rotated slowly to expose different areas of its surface to the belt. The belt is tensioned and guided over a series of rollers, and it can be made from various materials and grit sizes depending on the level of polishing required—from coarse belts for initial surface preparation to fine belts or cloth belts impregnated with polishing compounds for final finishing.
In many designs, the pot is mounted on a rotary fixture or jig, allowing uniform exposure to the polishing belt. Some machines feature adjustable rotation speeds and tilt mechanisms to ensure even contact with curved surfaces and complex pot geometries. Alternatively, in simpler setups, operators manually hold and guide the pot against the moving belt, although automated systems provide higher consistency and throughput in industrial settings.
The polisher often incorporates pressure adjustment systems, either manual or automated, to control the force exerted between the belt and the pot’s surface. This prevents over-polishing or damage, especially on thinner materials. Cooling features such as air jets or water mist sprays are sometimes integrated to reduce heat buildup from friction, protecting both the pot’s finish and the polishing belt.
To maintain a clean working environment and protect operator health, these machines typically include dust extraction or vacuum systems that capture metal particles and polishing residues generated during the process. Safety guards surround moving belts and rotating fixtures to prevent accidental contact, and emergency stop buttons are standard.
Control panels allow operators to set and monitor belt speed, rotation speed, and polishing pressure, facilitating customization for different pot sizes and materials. In advanced models, programmable logic controllers (PLCs) automate process parameters, improve repeatability, and reduce operator fatigue.
Belt-driven polishers are often integrated into larger finishing lines, combined with grinding, buffing, and inspection stations to produce cookware with high-quality, mirror-like finishes. Their role is crucial in enhancing not only the appearance but also the corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning of finished pots.
In summary, a Belt-Driven Polisher for Pots is an effective and versatile tool in cookware manufacturing, providing controlled, uniform polishing that improves product quality, durability, and consumer appeal.
A Belt-Driven Polisher for Pots is designed to deliver smooth, uniform polishing on cookware surfaces by utilizing a continuously moving abrasive or polishing belt. The pot is either fixed on a rotary fixture or moved manually to ensure consistent contact with the belt. The polishing belt, made from various materials and grit levels, is tensioned and runs over rollers to provide the necessary abrasive action. Adjustable speed controls for both the belt and pot rotation allow operators to tailor the polishing process to different materials and desired finishes. Pressure applied between the belt and pot can be controlled to avoid surface damage, and cooling systems such as air jets or misting help dissipate heat generated by friction. Integrated dust extraction systems capture metal particles and polishing residues, maintaining a clean environment and safeguarding operator health. Safety features include guards around moving parts and emergency stop controls. Control panels or PLC systems enable fine-tuning of process parameters and automation in industrial setups. These machines are often part of finishing lines where they contribute to enhancing the cookware’s appearance, corrosion resistance, and surface cleanliness. The belt-driven polisher’s efficient and consistent operation makes it indispensable for producing high-quality pots with mirror-like finishes.
The construction of a Belt-Driven Polisher for Pots typically involves a sturdy frame made from heavy-duty steel or aluminum to withstand continuous industrial use and vibrations during operation. The polishing belt is mounted on a series of precision-engineered rollers, often coated or designed to reduce friction and wear, ensuring smooth movement and consistent contact with the pot surface. The drive system usually consists of an electric motor connected to the belt rollers via pulleys or direct drives, allowing adjustable speed control for varying polishing requirements.
The rotary fixture or chuck holding the pot can be motorized or manual, with some machines featuring quick-release mechanisms for fast changeovers between different pot sizes or types. For more advanced setups, servo motors provide precise control over rotation speed and positioning, enabling complex polishing patterns and improved uniformity.
The belt material selection is critical: abrasive belts such as those made from zirconia alumina or ceramic grains provide aggressive material removal during initial polishing phases, while finer grit or non-woven abrasive belts impregnated with polishing compounds deliver high-gloss finishes. Operators can quickly switch belts to match the current stage of the finishing process.
To ensure operator safety and product quality, many machines include sensors that monitor belt tension, wear, and alignment. These sensors can trigger alerts or automatic shutdowns to prevent damage or inconsistent polishing. Additionally, built-in lighting systems may be incorporated to help operators visually inspect the polishing quality during operation.
The dust extraction system is typically connected to an external vacuum or filtration unit, removing metal dust and fine abrasive particles from the workspace. This not only improves air quality but also helps maintain the longevity of machine components by preventing abrasive buildup.
Maintenance accessibility is designed into these machines, with easy access panels for belt replacement, roller cleaning, and motor servicing. Regular maintenance schedules and diagnostic feedback help reduce downtime and keep production running smoothly.
Overall, Belt-Driven Polishers for Pots combine robust mechanical design, precise control, and effective safety and environmental measures to provide reliable and high-quality polishing solutions tailored for cookware manufacturing environments.
Outer Surface Belt Grinder for Cookware

An Outer Surface Belt Grinder for Cookware is a specialized machine designed to grind and finish the external surfaces of pots, pans, and other kitchenware. It uses a continuous abrasive belt that moves over rollers to smooth, shape, and remove surface imperfections such as weld seams, burrs, and scale from the cookware’s outer shell.
The cookware piece is typically mounted on a fixture or held manually to expose its outer surface uniformly to the moving abrasive belt. In many industrial models, the cookware is rotated or manipulated mechanically to ensure consistent contact and even grinding across curved or irregular surfaces.
The grinding belt, available in various grit sizes and abrasive materials like aluminum oxide or zirconia alumina, can be selected based on the desired finish—ranging from rough grinding for initial material removal to fine grinding for surface preparation before polishing.
The machine usually offers adjustable parameters such as belt speed, grinding pressure, and rotation speed or positioning of the cookware, allowing customization according to the type of metal and thickness of the cookware. Some systems incorporate floating sanding heads or spring-loaded rollers that adapt to the cookware’s contours, improving surface uniformity while minimizing the risk of over-grinding.
Integrated cooling methods, like air jets or mist sprays, help control heat buildup during grinding, preventing damage to both the cookware and abrasive belts. Dust extraction systems are commonly included to capture metal particles and grinding debris, maintaining a clean and safe work environment.
Safety features such as protective guards around moving belts, emergency stops, and interlocks ensure operator protection during use. Control interfaces range from simple manual controls to computerized panels with programmable settings for repeatability and process optimization.
Outer Surface Belt Grinders for Cookware are essential in manufacturing lines, providing efficient and consistent grinding that prepares the cookware’s external surfaces for subsequent polishing, coating, or finishing processes. Their robust design and precise control contribute to producing high-quality kitchenware with smooth, defect-free outer surfaces.
An Outer Surface Belt Grinder for Cookware is designed to efficiently grind and smooth the external surfaces of pots, pans, and similar kitchenware using a continuously moving abrasive belt. The cookware is held securely—either manually or on a fixture—and rotated or moved to ensure even exposure to the grinding belt. The belt, made from various abrasive materials and grits, runs over rollers and can be adjusted in speed and tension to match the specific grinding requirements. This setup removes weld seams, burrs, and surface imperfections, preparing the cookware for further finishing stages. Features such as floating sanding heads or spring-loaded rollers help the belt conform to curved surfaces, ensuring uniform grinding without damaging the metal. Cooling mechanisms, including air jets or mist sprays, reduce heat generated during grinding to protect both the cookware and the abrasive belt. Integrated dust extraction systems capture metal particles and debris, maintaining a clean workspace and enhancing operator safety. Protective guards and emergency stop controls are standard to prevent accidents. Control panels allow adjustment of belt speed, grinding pressure, and rotation parameters, often with programmable options for consistent production. These machines are crucial in cookware manufacturing, delivering smooth, defect-free outer surfaces that improve product quality and aesthetics.
The machine frame is typically constructed from heavy-duty steel to provide stability and minimize vibrations during operation, which ensures precision in grinding. The abrasive belt is mounted on a series of rollers, often coated or designed to reduce friction and wear, enhancing belt life and consistency of contact with the cookware surface. An electric motor drives the belt, with variable speed control allowing operators to tailor the grinding aggressiveness to different materials and finishes.
In automated versions, the cookware is held by a rotary chuck or fixture that can be programmed to rotate at specific speeds and angles, enabling even grinding across complex shapes. Manual machines rely on operator skill to maintain consistent pressure and movement, whereas automated models improve repeatability and throughput.
Belt selection is key: coarser belts remove material quickly for initial grinding, while finer grits prepare the surface for polishing. Some machines allow quick belt changes to optimize workflow. To protect the cookware from heat damage caused by friction, cooling systems like air blasts or mist sprays are integrated, reducing thermal stress and preventing discoloration.
Dust and debris generated during grinding are removed by integrated extraction systems connected to external vacuum or filtration units. This keeps the working area clean and protects workers from inhaling metal dust. Safety features such as transparent shields, interlocks that stop the machine if guards are opened, and emergency stop buttons are standard.
Maintenance access points allow for easy belt replacement, roller cleaning, and motor servicing, minimizing downtime. Control panels may feature digital displays and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to allow operators to save grinding recipes for different cookware types.
Overall, Outer Surface Belt Grinders for Cookware combine durability, precision, and safety, making them essential in producing high-quality kitchenware with smooth, flawless external finishes ready for further processing or packaging.
Belt Grinding Machine for Metal Pots

A Belt Grinding Machine for Metal Pots is a specialized piece of equipment designed to grind, smooth, and finish the surfaces of metal cookware such as pots and pans. Using a continuous abrasive belt, this machine removes surface defects like weld marks, burrs, scratches, and uneven areas, preparing the pots for polishing or coating.
The machine operates by moving an abrasive belt over rollers powered by an electric motor, with adjustable speed controls to match the grinding intensity required for different metals and thicknesses. The metal pot is either fixed on a rotating fixture or manually fed against the belt to ensure uniform grinding of curved and complex surfaces.
The abrasive belts come in various grit sizes and materials—such as aluminum oxide or zirconia alumina—to suit different stages of grinding, from coarse stock removal to fine finishing. Many machines feature spring-loaded or floating sanding heads that conform to the pot’s contours, allowing consistent pressure and contact for a smooth finish without causing damage.
To prevent overheating and material discoloration caused by friction, integrated cooling systems using air jets or mist sprays are often included. Dust extraction systems remove metal particles and debris from the workspace, maintaining cleanliness and improving operator safety.
Safety measures like protective guards around moving parts, emergency stop buttons, and interlocks are standard. Control panels offer manual or programmable operation, enabling precise control over belt speed, grinding pressure, and rotation speed or positioning of the pot for consistent results.
Belt Grinding Machines for Metal Pots are essential in cookware manufacturing lines, delivering efficient and uniform surface preparation that enhances the durability, appearance, and quality of the finished product.
A Belt Grinding Machine for Metal Pots uses a continuously moving abrasive belt to grind and finish the surfaces of metal cookware. The metal pot is held either manually or on a rotating fixture that moves it against the abrasive belt, ensuring consistent and uniform surface contact. The belt runs over rollers driven by an electric motor with adjustable speed controls to accommodate different grinding requirements based on the metal type and thickness. Abrasive belts come in various grit sizes and materials, such as aluminum oxide or zirconia alumina, allowing the machine to perform everything from rough grinding to fine finishing. Floating sanding heads or spring-loaded rollers conform to the curved surfaces of pots, providing even pressure and reducing the risk of surface damage. Cooling systems like air jets or mist sprays prevent overheating and discoloration caused by friction. Integrated dust extraction removes metal particles and grinding debris to keep the workspace clean and safe for operators. Safety features include guards, emergency stops, and interlocks to protect users from moving parts. Control panels, which may include programmable logic controllers, enable precise adjustments of belt speed, grinding pressure, and pot rotation speed, ensuring repeatable, high-quality finishes. This machine is crucial in manufacturing lines for preparing metal pots’ surfaces, improving their aesthetic appeal and functional durability before final polishing or coating stages.
Kitchenware Belt Finishing Unit

A Kitchenware Belt Finishing Unit is an industrial machine designed to provide precise surface finishing to various kitchenware items such as pots, pans, and utensils. This unit utilizes a continuous abrasive belt to grind, smooth, and refine the outer and sometimes inner surfaces of metal kitchenware, preparing them for polishing or other finishing processes.
The unit typically features a robust frame to support high-speed operations with minimal vibration, ensuring consistent contact between the abrasive belt and the kitchenware surface. The abrasive belt is mounted on rollers powered by an electric motor, with adjustable speed settings that allow operators to select appropriate grinding speeds for different materials and surface conditions.
Kitchenware pieces are positioned manually or mechanically, often on rotating fixtures, to expose all required surfaces evenly to the moving belt. Some units include spring-loaded or floating sanding heads that adapt to curved or irregular shapes, improving uniformity in surface finishing while minimizing the risk of over-grinding.
The abrasive belts vary in grit size and type, from coarse belts for initial material removal to finer belts for smooth finishing. Quick-change mechanisms enable rapid swapping of belts to optimize workflow and accommodate different finishing stages.
Integrated cooling systems such as air jets or mist sprays help dissipate heat generated by friction during grinding, preventing surface damage or discoloration. Dust extraction systems capture airborne metal particles and abrasive debris, maintaining a clean and safe working environment.
Safety features like protective guards, emergency stop buttons, and interlock systems protect operators during use. Control interfaces may range from simple manual controls to advanced programmable panels, offering precision and repeatability in finishing operations.
Overall, a Kitchenware Belt Finishing Unit enhances the quality and appearance of kitchenware by providing efficient, controlled surface finishing, making it an essential component in cookware manufacturing and finishing lines.
A Kitchenware Belt Finishing Unit operates by continuously moving an abrasive belt over rollers driven by an electric motor with adjustable speeds to match different finishing needs. The kitchenware, such as pots or pans, is held manually or fixed on a rotating fixture, allowing the belt to uniformly contact and smooth the surface. The abrasive belts come in a range of grit sizes and materials, which can be quickly changed to suit various stages of finishing—from heavy material removal to fine surface refinement. Floating sanding heads or spring-loaded rollers help the belt conform to the curved and irregular shapes typical of kitchenware, ensuring consistent pressure and even finishing without damaging the metal. Cooling systems like air or mist sprays prevent heat buildup caused by friction, protecting both the kitchenware and abrasive belts from damage. Dust extraction systems remove grinding debris and metal particles, keeping the work environment clean and safe. The machine includes protective guards and emergency stop features for operator safety. Control panels provide manual or programmable options for adjusting belt speed, grinding pressure, and fixture rotation, allowing precise and repeatable finishing processes. This unit is essential in industrial kitchenware production for producing smooth, uniform surfaces that enhance both the functionality and aesthetics of finished cookware.
Design and Construction
A Kitchenware Belt Finishing Unit is engineered for durability and precision. The machine’s frame is typically made from heavy-gauge steel or cast iron to provide a rigid, vibration-free structure, which is essential for consistent grinding and finishing. The abrasive belt runs on a set of precision-engineered rollers designed to maintain proper belt tension and tracking, which are crucial for uniform surface contact. These rollers are often coated with low-friction materials or equipped with bearings to ensure smooth operation and long service life. The belt drive system is powered by an electric motor, commonly fitted with variable frequency drives (VFDs) or similar controls, allowing operators to adjust the belt speed to match different materials, thicknesses, and finishing requirements.
Operation and Functionality
The unit is designed to handle various types of kitchenware such as metal pots, pans, trays, and utensils. Depending on the model and level of automation, the workpieces may be manually positioned or held in place by mechanical fixtures that can rotate or oscillate the kitchenware to expose all surfaces evenly to the abrasive belt. Floating sanding heads or spring-loaded rollers conform to the contours of irregular or curved shapes, enabling uniform pressure distribution and reducing the risk of gouging or uneven finishing. The abrasive belts are available in multiple grit sizes and compositions — from coarse belts for removing weld seams and heavy burrs to fine belts for producing a smooth, ready-to-polish surface. Quick-change belt mechanisms facilitate swift switching between different abrasives, enhancing productivity.
Cooling and Dust Management
During the grinding process, friction generates heat, which can lead to discoloration, warping, or other surface damage on sensitive kitchenware materials. To prevent this, the machine incorporates cooling systems such as air jets or mist spray nozzles that apply a fine cooling medium directly at the belt-workpiece interface. This cooling helps maintain the integrity of the kitchenware and prolongs abrasive belt life. Additionally, dust and metal particles generated by grinding are captured by integrated dust extraction systems, which may include hoods, ducting, and filters connected to external vacuum units. This not only keeps the work environment clean but also improves operator safety by minimizing exposure to airborne particulates.
Safety and Controls
Safety is a critical aspect of the Kitchenware Belt Finishing Unit. The machine is equipped with transparent protective guards that prevent accidental contact with moving belts and rollers while allowing operators to monitor the process. Emergency stop buttons and interlocks ensure that the machine halts immediately if safety doors or guards are opened during operation. Control panels range from basic manual switches to advanced programmable logic controllers (PLCs), offering operators the ability to precisely adjust belt speed, grinding pressure, rotation speed, and other parameters. Programmable settings enable repeatability and consistency across production batches, reducing human error and enhancing quality control.
Applications and Benefits
This finishing unit is integral to industrial kitchenware manufacturing lines where surface quality directly impacts product performance and aesthetics. By providing an efficient, automated method of surface grinding and finishing, it reduces labor costs and production times while delivering superior and uniform finishes. The versatility of the machine allows it to work with a range of metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and copper alloys, making it suitable for diverse kitchenware products. Ultimately, the Kitchenware Belt Finishing Unit enhances product durability, corrosion resistance, and visual appeal, which are key factors in market competitiveness and customer satisfaction.
Pot Edge Belt Grinding Machine
A Pot Edge Belt Grinding Machine is a specialized industrial machine designed specifically to grind, smooth, and finish the edges of metal pots and similar cookware. The machine’s primary function is to remove sharp burrs, weld seams, and roughness along the rim or edge of pots, ensuring safety, structural integrity, and a clean, polished appearance.
Design and Construction
The machine features a compact yet sturdy frame, often constructed from heavy-duty steel, to provide a stable and vibration-free platform during grinding operations. At the core of the machine is a high-speed abrasive belt mounted on precision rollers. The belt typically runs horizontally or at an adjustable angle to optimize contact with the pot’s edge. The abrasive belt material and grit size are chosen based on the metal type and the finishing requirements, ranging from coarse belts for heavy material removal to fine belts for smooth finishing.
A key design feature is a specialized fixture or jig that holds the pot securely in place and positions the edge precisely against the moving abrasive belt. This fixture may include clamps or adjustable guides to accommodate pots of different diameters and shapes, ensuring consistent edge treatment. Some machines incorporate rotating or oscillating mechanisms to feed the pot edge evenly against the belt, resulting in uniform grinding around the entire circumference.
Operation and Functionality
The operator or automated system places the pot on the fixture, aligns the edge, and initiates the grinding process. The abrasive belt moves continuously, and the pot’s edge is brought into contact either manually or automatically through the fixture’s controlled movement. The machine’s speed controls allow for adjustment of the belt speed to optimize grinding efficiency and finish quality without overheating or damaging the metal.
Floating sanding heads or pressure control mechanisms can be integrated to maintain consistent contact pressure between the pot edge and the abrasive belt. This ensures smooth, burr-free edges without gouging or deformation. Cooling systems such as air jets or mist sprays may be used to prevent heat buildup during grinding, protecting the pot material and the abrasive belt.
Safety and Maintenance
Safety features include protective shields covering moving parts and emergency stop buttons for immediate shutdown in case of an emergency. The design typically incorporates dust extraction ports to remove metal dust and grinding debris, maintaining a clean working environment and reducing health risks.
Routine maintenance involves checking and replacing abrasive belts, inspecting the fixture and rollers for wear, and lubricating moving parts to ensure smooth operation. Regular cleaning of dust extraction systems is essential to maintain suction efficiency.
Applications and Benefits
This machine is essential in cookware manufacturing lines focused on high-quality production where edge finishing is critical for product safety and aesthetics. By automating and standardizing edge grinding, the Pot Edge Belt Grinding Machine reduces manual labor, enhances precision, and increases throughput. It produces safe, smooth, and visually appealing pot edges that improve user comfort and product longevity.
Overall, the Pot Edge Belt Grinding Machine is a vital tool for ensuring that metal pots meet stringent quality and safety standards before proceeding to further finishing or packaging stages.
A Pot Edge Belt Grinding Machine is designed to smooth and finish the edges of metal pots. It uses an abrasive belt running on rollers to grind away roughness, burrs, and weld seams from the pot’s rim. The pot is held securely by a fixture that can adjust for different sizes, ensuring the edge is evenly ground all around. The belt speed is adjustable to suit different metals and finishing needs. Cooling systems like air or mist sprays prevent heat damage during grinding, and dust extraction keeps the work area clean. Safety features include guards and emergency stops. This machine increases efficiency, improves edge quality, and ensures the final product is safe and visually appealing. Maintenance mainly involves belt replacement, cleaning, and lubrication. It’s widely used in cookware manufacturing to standardize and speed up the edge finishing process.
The Pot Edge Belt Grinding Machine plays a crucial role in the cookware manufacturing process by focusing specifically on the precise finishing of pot edges, which is essential both for user safety and the overall quality of the product. This machine is engineered to provide consistent, high-quality grinding of the pot rims, removing any sharp burrs, welding residues, or surface imperfections that can result from fabrication processes. The heart of the machine is its abrasive belt system, which runs continuously over a series of carefully engineered rollers designed to maintain proper tension and alignment for optimal contact with the pot edge. The abrasive belts themselves come in a variety of materials and grit sizes to cater to different stages of grinding—from initial heavy material removal to final smooth finishing—allowing manufacturers to tailor the process according to the specific metal type, thickness, and surface finish required. The pot is secured in a fixture that can be adjusted or customized to fit a wide range of pot sizes and shapes, ensuring the grinding action is uniform around the entire circumference of the edge. Some advanced models feature rotary or oscillatory movement mechanisms that automatically feed the pot edge against the belt with precise control, which enhances consistency and reduces operator fatigue. Belt speed and pressure can be finely tuned to avoid overheating and damage to the metal while maximizing grinding efficiency. To prevent thermal damage and extend both the belt and pot life, the machine often incorporates cooling systems such as air jets or mist sprays that target the contact zone between the belt and pot edge, effectively dissipating heat generated by friction. Additionally, integrated dust extraction systems capture metal particles and grinding debris, which keeps the workspace clean, reduces health risks from airborne particulates, and prolongs the lifespan of mechanical components. Safety is paramount, so machines are equipped with protective guards to shield operators from moving parts and abrasive belts, and emergency stop buttons enable immediate shutdown in case of any hazards. Maintenance routines focus on timely abrasive belt replacement, inspection of rollers and fixtures for wear, lubrication of moving parts, and ensuring dust extraction systems remain unblocked and functional. The benefits of utilizing a Pot Edge Belt Grinding Machine are multifold: it dramatically improves the safety of cookware by eliminating sharp edges, enhances the aesthetic appeal of the product with smooth and polished rims, reduces manual labor and human error, and accelerates production cycles with automated or semi-automated operation. This machine is indispensable in modern cookware manufacturing where consistent quality, operator safety, and high throughput are critical factors.
Abrasive Belt Machine for Pots

An Abrasive Belt Machine for Pots is a specialized grinding and finishing device designed to improve the surface quality of pots by removing imperfections such as rough spots, weld seams, and burrs. It uses a continuous abrasive belt mounted on rollers that rotate at controlled speeds, allowing the belt to polish or grind the pot’s surface efficiently. The pots are positioned so their surfaces, edges, or curved areas come into contact with the moving belt, either manually or using fixtures that ensure consistent pressure and angle. The machine allows for adjustment of belt speed and pressure to suit different metal types and desired finishes, ranging from coarse grinding for heavy material removal to fine polishing for smooth, shiny surfaces. Cooling systems like air or mist sprays help prevent overheating during operation, protecting both the pot and abrasive belt. Dust and debris generated are extracted through built-in suction systems to maintain cleanliness and operator safety. The machine is widely used in cookware manufacturing for batch or continuous processing, increasing productivity while ensuring uniform surface quality and a professional finish. Maintenance involves regular belt replacement, cleaning, and lubrication of mechanical parts. This machine streamlines pot finishing by automating grinding tasks that would otherwise be labor-intensive and inconsistent.
The Abrasive Belt Machine for Pots is essential in metal cookware production, providing a reliable and efficient method to enhance the surface quality of pots by systematically removing surface imperfections such as weld marks, rough patches, and burrs that naturally occur during manufacturing. The machine operates by driving an abrasive belt over rollers at variable speeds, allowing for precise control over the grinding or polishing process. Pots are positioned to make consistent contact with the belt, either manually or through fixtures that maintain the correct pressure and angle, ensuring an even finish around edges and curved surfaces. The versatility of the abrasive belts, available in various grit sizes and materials, allows the machine to handle different metals and thicknesses, enabling everything from aggressive material removal to delicate polishing to achieve a high-quality finish. To prevent damage from heat generated during friction, many machines integrate cooling mechanisms such as air jets or mist sprays, which help preserve both the pot’s integrity and the lifespan of the abrasive belt. Dust and metal particles produced during grinding are managed through built-in extraction systems, maintaining a safe and clean working environment. The machine enhances productivity by reducing the time and labor required for manual finishing, while ensuring consistent and repeatable results across batches. Routine maintenance includes monitoring belt wear and replacing it as necessary, cleaning the dust collection components, and lubricating moving parts to sustain smooth operation. By automating the abrasive finishing process, this machine plays a vital role in producing cookware that meets strict quality, safety, and aesthetic standards efficiently.
The abrasive belt machine’s design often includes adjustable tensioners and tracking systems to keep the belt aligned and taut during operation, which is critical for uniform grinding and to prevent belt slippage or damage. Operators can fine-tune variables such as belt speed, pressure applied to the pot surface, and feed rate to match different pot sizes and materials, allowing flexibility across production lines. Some advanced versions offer automation features like programmable cycles, robotic loading and unloading, or sensors that monitor belt wear and surface finish quality in real time, further increasing efficiency and reducing the need for manual intervention. The machine’s frame is built for durability, frequently constructed from heavy-gauge steel to withstand continuous industrial use while minimizing vibrations that could affect finish quality. Additionally, safety measures such as emergency stop buttons, protective guards around moving parts, and integrated dust extraction not only protect operators but also ensure compliance with workplace safety regulations. This type of machine is widely used in industries producing stainless steel, aluminum, or other metal cookware, where a polished, burr-free finish is essential for both functional and aesthetic reasons. By improving surface smoothness and removing defects, the abrasive belt machine helps extend the life of the pots, improves their corrosion resistance, and enhances their market appeal. Overall, it is a critical piece of equipment for manufacturers seeking to optimize production speed, quality control, and worker safety during the finishing stages of pot manufacturing.
Belt Type Cookware Surface aSander

A Belt Type Cookware Surface Sander is a specialized machine designed to sand and smooth the surfaces of cookware items such as pots, pans, and other metal utensils. It employs a continuous abrasive belt that moves over a set of rollers, creating a consistent sanding surface. The cookware is either manually fed or placed on fixtures that hold it steady against the moving belt, allowing the abrasive surface to remove imperfections like scratches, weld marks, and unevenness from the metal surface. The machine allows adjustment of belt speed, sanding pressure, and sometimes belt grit type to accommodate various metals and desired surface finishes, ranging from rough sanding for initial shaping to fine sanding for a smooth, polished appearance. Cooling systems such as air or mist sprays are often incorporated to prevent overheating caused by friction, which can damage both the cookware and the sanding belt. Dust extraction systems collect sanding debris to maintain a clean work environment and protect operators from inhaling metal dust. This sander enhances manufacturing efficiency by automating the surface preparation stage, providing uniform sanding results that improve cookware quality and appearance. Regular maintenance includes belt replacement, cleaning, and lubrication of moving parts to ensure consistent performance and longevity of the machine. It is widely used in cookware production lines where consistent surface finishing is critical.
The Belt Type Cookware Surface Sander is engineered to deliver precise and consistent sanding performance, essential for preparing cookware surfaces before further finishing steps such as polishing or coating. The abrasive belt system runs continuously over rollers designed to maintain proper tension and alignment, ensuring even contact with the cookware surfaces. The machine can accommodate various shapes and sizes of cookware by using adjustable fixtures or manual positioning, allowing operators to effectively sand flat, curved, or contoured surfaces. Adjustable speed controls enable the operator to select optimal belt speeds depending on the metal type and the stage of sanding, whether it requires aggressive material removal or gentle surface smoothing. Pressure applied during sanding is carefully controlled to avoid deformation or damage to delicate cookware while still achieving a uniform finish. Integrated cooling mechanisms such as mist sprays or forced air help dissipate the heat generated by friction, preventing discoloration, warping, or weakening of the metal. The dust extraction system is designed to capture fine sanding particles, improving air quality in the workplace and reducing the risk of machinery clogging or abrasive belt wear. This equipment not only increases throughput by automating the sanding process but also reduces operator fatigue compared to manual sanding methods, while consistently producing high-quality surfaces that meet strict manufacturing standards. Routine maintenance is straightforward, focusing on timely abrasive belt replacement, inspection and cleaning of dust extraction components, and lubrication of moving parts to prevent wear. The Belt Type Cookware Surface Sander is widely valued in the cookware manufacturing industry as it streamlines the finishing process, improves product aesthetics and durability, and enhances overall production efficiency.
The Belt Type Cookware Surface Sander is often integrated into larger production lines, allowing for continuous processing of cookware pieces, which is vital for meeting high-volume manufacturing demands. Its robust construction ensures durability under heavy usage, with frames typically made of reinforced steel and components designed to withstand the mechanical stresses of sanding metal surfaces. The versatility of this machine makes it suitable for a wide range of cookware materials including stainless steel, aluminum, and other alloys, by simply changing the abrasive belt grit or adjusting the operational parameters. Operators benefit from ergonomic designs that reduce physical strain, with controls placed conveniently for easy access and adjustments during operation. Safety features such as emergency stop buttons, protective shields around moving belts, and proper ventilation systems protect workers from injury and exposure to metal dust. The machine also allows for quick belt changes, minimizing downtime and maintaining production flow. By ensuring a smooth and consistent surface finish, the Belt Type Cookware Surface Sander helps improve the adhesion of coatings or paints if applied later, and enhances the cookware’s resistance to corrosion and wear. This results in higher quality products with longer lifespans, which is crucial for customer satisfaction and brand reputation. Overall, this machine is an indispensable tool in modern cookware manufacturing, combining efficiency, precision, and safety to meet industry standards and consumer expectations.
Pots Outer Wall Belt Grinding Machine
A Pots Outer Wall Belt Grinding Machine is a specialized industrial device designed to grind, smooth, and finish the external surfaces of pots and similar cookware. This machine uses a continuous abrasive belt that moves over rollers at controlled speeds, enabling efficient removal of surface defects such as weld seams, rough spots, and oxidation from the pot’s outer wall. The pots are typically mounted on fixtures or held by operators so their curved outer surfaces consistently contact the moving abrasive belt. The machine’s adjustable settings allow operators to control belt speed, grinding pressure, and belt grit to suit various metals and desired finishes, ranging from heavy grinding to prepare the surface to fine smoothing for a polished look. To prevent overheating and damage, cooling systems like air jets or mist sprays are often integrated. Dust extraction units collect metal particles and debris, keeping the work environment clean and safe. The machine improves production efficiency by automating a critical finishing step that would be time-consuming and inconsistent if done manually. Regular maintenance includes replacing worn abrasive belts, cleaning dust collectors, and lubricating moving parts. This equipment is essential for cookware manufacturers aiming to deliver high-quality, visually appealing pots with smooth, defect-free outer surfaces that meet industry standards.
The Pots Outer Wall Belt Grinding Machine is engineered to handle the unique challenges of working with curved, often irregular surfaces typical of pot exteriors. Its design ensures consistent contact between the abrasive belt and the pot’s outer wall by using adjustable fixtures or rotating mechanisms that can hold the pot steadily and rotate it against the grinding belt. This enables even material removal across the entire surface, avoiding uneven patches or missed spots. Operators can fine-tune the grinding parameters, such as belt speed and pressure, to optimize the process for different metals like stainless steel or aluminum, and to transition smoothly from aggressive grinding for weld seam removal to fine finishing for surface smoothness. The machine’s sturdy frame and precision-engineered rollers maintain belt tension and alignment, critical for effective grinding and prolonging belt life. Integrated cooling systems protect both the pot and the abrasive belt from heat damage generated by friction during operation. Efficient dust extraction prevents accumulation of metal particles, reducing wear on the machinery and maintaining a clean workspace that complies with safety standards. By automating the outer wall finishing process, this machine significantly speeds up production times, reduces manual labor, and improves product uniformity and aesthetic appeal. Maintenance routines are straightforward, focusing on timely abrasive belt changes, dust collector cleaning, and routine lubrication, ensuring long-term reliable operation. This machine is a vital component in modern cookware manufacturing lines, delivering high-quality, smooth, and visually appealing pot exteriors ready for packaging or further finishing steps.
High-Gloss Polisher for Metal Utensils

A High-Gloss Polisher for Metal Utensils is a precision machine designed to produce a mirror-like, reflective finish on metal kitchenware such as spoons, forks, knives, and other utensils. This polisher uses a combination of rotating buffing wheels, polishing pads, and specially formulated polishing compounds to remove fine scratches, oxidation, and surface imperfections that remain after grinding or initial sanding processes. The machine often features multiple buffing heads operating simultaneously or sequentially, enabling efficient and uniform polishing on various utensil shapes and sizes. Operators place the utensils in holders or manually guide them against the rotating polishing surfaces, which spin at controlled speeds to ensure optimal contact and friction for achieving a brilliant shine without damaging delicate details or edges. Adjustable speed controls and interchangeable polishing materials allow customization of the finish, from satin to high-gloss mirror polish, depending on product requirements. Cooling systems, such as air jets, prevent overheating and potential discoloration of the metal surface. Dust and polishing residue are collected through built-in extraction systems, maintaining a clean work environment and reducing health hazards for operators. This machine enhances production efficiency by automating the polishing step, delivering consistent, high-quality finishes that improve the aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance of metal utensils. Regular maintenance involves cleaning polishing wheels, replacing worn pads, and ensuring lubrication of moving parts to sustain performance. High-Gloss Polishers are essential in metal utensil manufacturing, enabling brands to meet consumer expectations for premium appearance and durability.
The High-Gloss Polisher for Metal Utensils is built to handle a wide variety of utensil shapes, including flatware, ladles, and serving spoons, ensuring each piece receives an even and flawless polish. Its design often incorporates multiple buffing stations arranged either horizontally or vertically, allowing for continuous processing and reducing handling time. Polishing compounds used with the machine are specially formulated to gradually refine the metal surface, progressively eliminating micro-scratches and producing a deep, reflective shine that enhances both visual appeal and surface protection. Operators benefit from ergonomic fixtures or jigs that securely hold utensils during polishing, minimizing manual effort and ensuring consistent results. The polisher’s speed controls allow precise adjustments to accommodate different metals such as stainless steel, brass, or aluminum, as well as varying thicknesses and finishes desired by customers. Cooling features prevent the heat generated by friction from altering the metal’s structural integrity or causing discoloration, which is critical for maintaining the utensil’s quality. Dust extraction and filtration systems capture fine polishing residues and airborne particles, improving workplace safety and equipment longevity. This machine not only boosts throughput but also helps manufacturers maintain high standards by delivering uniform surface finishes that enhance the utensils’ corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning. Maintenance involves routine replacement of polishing pads or wheels, cleaning of dust collectors, and lubrication of mechanical components to ensure smooth and reliable operation. Overall, the High-Gloss Polisher for Metal Utensils is an indispensable tool in the production line, elevating product quality and consumer satisfaction through superior finishing capabilities.
The High-Gloss Polisher for Metal Utensils is frequently integrated into automated or semi-automated production lines, where it works in tandem with other finishing equipment such as grinders, sanders, and washers. This seamless integration allows for streamlined workflows and minimizes manual intervention, which reduces labor costs and the potential for human error. The machine’s adaptability extends to various utensil sizes and designs, including those with intricate patterns or delicate handles, thanks to interchangeable polishing heads and adjustable fixture settings. This flexibility enables manufacturers to cater to diverse market demands, from everyday cutlery to premium, decorative sets. Additionally, the polisher’s robust construction and use of high-quality materials ensure durability and consistent performance even under heavy production schedules. Safety features such as emergency stops, protective covers, and noise reduction components are standard, safeguarding operators while maintaining a comfortable working environment. Advanced models may include digital controls and monitoring systems that track polishing cycles, machine health, and consumable wear, facilitating predictive maintenance and minimizing downtime. By delivering a flawless high-gloss finish, this machine significantly enhances the perceived value of metal utensils, helping brands to differentiate themselves in competitive markets. It also contributes to longer-lasting products by smoothing surface imperfections that could harbor corrosion or bacteria, thus improving hygiene and durability. Ultimately, the High-Gloss Polisher for Metal Utensils is a critical investment for manufacturers aiming to achieve excellence in finish quality, operational efficiency, and product appeal.
EMS Metalworking Machines
We design, manufacture and assembly metalworking machinery such as:
- Hydraulic transfer press
- Glass mosaic press
- Hydraulic deep drawing press
- Casting press
- Hydraulic cold forming press
- Hydroforming press
- Composite press
- Silicone rubber moulding press
- Brake pad press
- Melamine press
- SMC & BMC Press
- Labrotaroy press
- Edge cutting trimming machine
- Edge curling machine
- Trimming beading machine
- Trimming joggling machine
- Cookware production line
- Pipe bending machine
- Profile bending machine
- Bandsaw for metal
- Cylindrical welding machine
- Horizontal pres and cookware
- Kitchenware, hotelware
- Bakeware and cuttlery production machinery
as a complete line as well as an individual machine such as:
- Edge cutting trimming beading machines
- Polishing and grinding machines for pot and pans
- Hydraulic drawing presses
- Circle blanking machines
- Riveting machine
- Hole punching machines
- Press feeding machine
You can check our machinery at work at: EMS Metalworking Machinery – YouTube
Applications:
Flange-punching
Beading and ribbing
Flanging
Trimming
Curling
Lock-seaming
Ribbing
