Metal Hemming Seaming Machine: A Hydraulic Hemming Press for Sheet Metal is a specialized forming machine designed to fold or roll the edges of sheet metal components with precision and consistency. It uses hydraulic power to apply a controlled force, ensuring accurate hemming operations, especially in automotive, appliance, and metal furniture manufacturing.
Key Features:
- Hydraulic Drive System: Ensures smooth and adjustable force application, ideal for both light and heavy-gauge sheet metals.
- Rigid Frame Construction: Provides structural stability to maintain hemming accuracy over long production cycles.
- Adjustable Stroke and Pressure: Allows operators to fine-tune parameters for different material thicknesses and hemming styles.
- Die Sets or Tooling Options: Equipped with custom hemming dies for open, closed, and teardrop hems.
- Position Sensors and Safety Systems: Includes limit switches and guards for precise control and operator safety.
- PLC or HMI Interface (in advanced models): For programmable operations, repeatability, and integration into automated lines.
Applications:
- Automotive Industry: Used for doors, hoods, tailgates, and trunk lids where edge folding is needed before or after spot welding.
- Appliance Manufacturing: For folded edges on panels, enclosures, and cabinet parts.
- Metal Furniture: Produces clean, rounded, or reinforced edges on table legs, drawers, and body panels.
Advantages:
- Consistent hemming results across high volumes
- Less mechanical wear compared to mechanical presses
- Better force control for delicate or complex profiles
- Reduces need for post-processing (deburring, grinding)
This press is often favored in production lines where precision and material versatility are required, and it’s especially suitable when combined with robotic handling systems for semi- or fully-automated hemming cells.
A hydraulic hemming press for sheet metal operates through the application of hydraulic pressure to fold or roll the edges of metal parts in a controlled and repeatable manner. Unlike mechanical presses, it allows for variable speed and force during the hemming cycle, which is crucial for avoiding deformation, especially on complex or delicate parts. The hemming process typically involves two stages: a pre-hemming operation that partially bends the edge, followed by a final hemming stroke that flattens it completely against the underlying sheet or frame. This method ensures tight and smooth seams, which are essential for structural integrity, aesthetic finish, and corrosion resistance.
These presses can be customized with various dies depending on the desired hem type, such as open hem, closed hem, or teardrop hem, and can accommodate different part geometries and materials including aluminum, mild steel, and coated sheets. The hydraulic system’s ability to control pressure throughout the stroke enhances its suitability for forming layered sheets or irregular profiles. Modern hydraulic hemming presses often feature programmable controls, allowing users to save parameters for different jobs, facilitating rapid changeovers and minimizing setup time in batch production.
The use of hydraulic hemming presses is especially prevalent in the automotive industry where the need for precise, repeatable, and cosmetically clean seams is critical. Door panels, hoods, and trunk lids benefit from hydraulic hemming due to its ability to create strong, uniform edges without visible defects. In industrial manufacturing, these presses support efficient production of enclosures, panels, and assemblies requiring folded edges for safety, reinforcement, or assembly alignment.
Hydraulic hemming presses can be standalone units or integrated into fully automated production lines with robotic feeding systems, sensors, and quality control mechanisms. Their versatility, gentle forming capability, and adaptability make them a preferred solution for manufacturers seeking high-quality edge forming with minimal tooling wear and consistent output.
In addition to their flexibility and precision, hydraulic hemming presses are valued for their relatively quiet operation and lower maintenance requirements compared to mechanical alternatives. The controlled speed and force reduce wear on tooling and components, leading to extended machine lifespan and improved cost efficiency over time. Advanced systems often include real-time monitoring of pressure and stroke position, which ensures consistent quality and enables early detection of deviations or potential failures.
Tooling setup in a hydraulic hemming press is typically designed for quick-change compatibility, which is especially beneficial in operations where multiple part designs are produced on the same line. Magnetic or hydraulic clamping systems may be used to secure dies swiftly and safely, minimizing downtime. The integration of servo-hydraulic technology in newer models allows for even finer control over movement and pressure, enabling more intricate hemming on complex contours and multilayer assemblies without damaging surface coatings or creating micro-cracks.
Another key advantage is the ability to hem pre-painted or pre-coated sheet metals without compromising their finish. This is essential in industries where aesthetics and corrosion resistance are critical, such as in appliance covers or exposed vehicle body parts. The hydraulic press applies pressure gradually, reducing friction and avoiding scuffs or peeling of the protective layers.
Some hydraulic hemming presses are designed with rotating or multi-position tables, allowing operators to load and unload parts while another cycle is in progress. This increases productivity and optimizes workflow, particularly in high-throughput environments. Safety systems, including light curtains, pressure-sensitive mats, and emergency stop circuits, are standard features to protect operators and ensure compliance with industrial safety regulations.
Overall, hydraulic hemming presses represent a combination of precision engineering and adaptable technology. They cater to the growing demand for high-quality, efficient, and sustainable metal forming processes across a range of industries. Whether used in low-volume prototyping or full-scale automated production, these machines provide a reliable solution for achieving perfect hems on diverse metal parts.
High-Speed Hemming Machine for Metal Fabrication

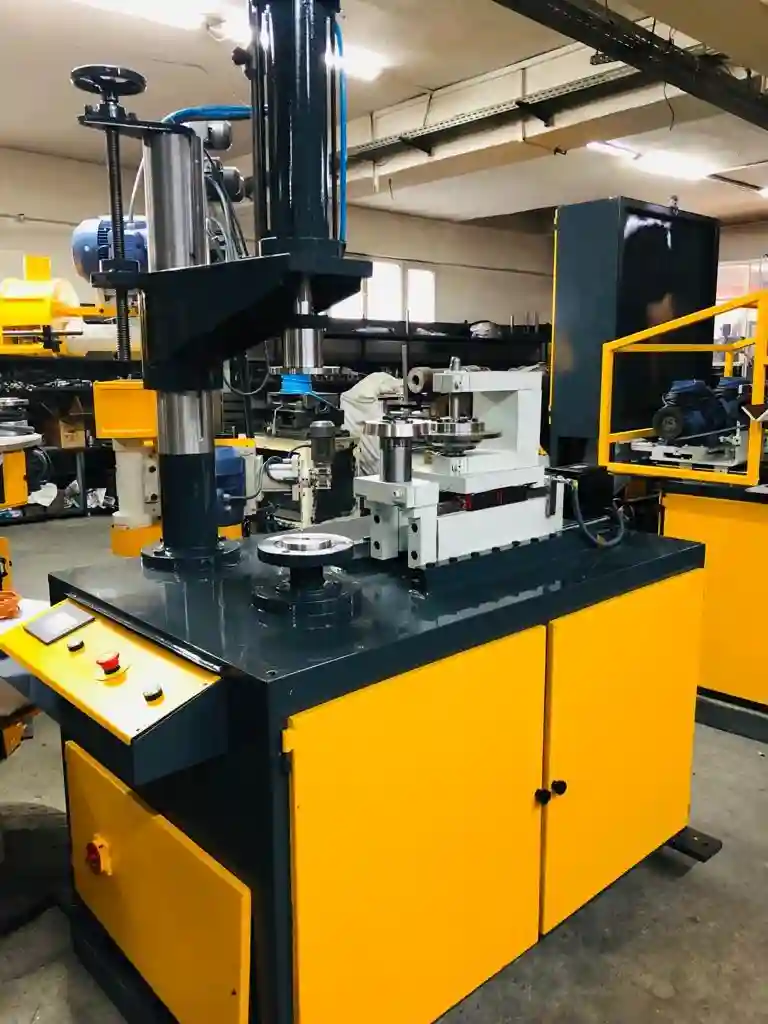
A high-speed hemming machine for metal fabrication is engineered to deliver rapid and precise edge-forming operations in production environments that demand both speed and quality. Unlike traditional hydraulic systems, these machines typically utilize servo-electric or pneumatic actuators, or a hybrid drive combining servo motors with hydraulic assistance, to achieve significantly faster cycle times while maintaining accuracy. This makes them ideal for industries with high production volumes, such as automotive panel manufacturing, appliance housing, or metal furniture components.
The core functionality revolves around folding, tucking, or curling the edge of a sheet metal component onto itself or onto a mating piece, producing a seamless and often structurally reinforced joint. High-speed hemming machines excel in executing these processes quickly, often integrating pre-hemming and final hemming stages in a continuous or synchronized sequence. The motion profile of the hemming tool—carefully controlled in speed, force, and angle—ensures clean edge lines without cracks, wrinkles, or cosmetic defects even at high throughput rates.
These machines are often integrated into robotic cells or transfer lines where automation is crucial. Robotic arms may position parts into fixtures, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or human-machine interfaces (HMIs) coordinate the hemming sequence with real-time feedback for quality assurance. Quick tooling changeovers and recipe memory functions allow operators to switch between product variants efficiently, minimizing downtime during transitions in production batches.
To meet the demands of high-speed operation, the machine frames are constructed with precision-ground and vibration-dampening materials, ensuring stability under dynamic loads. Advanced hemming heads may employ roller mechanisms or segmented tools that adapt to varying geometries, allowing for hemming on both straight and contoured edges. These machines can also accommodate different materials, including aluminum, high-strength steel, and pre-painted or laminated sheets, without compromising cycle time or surface integrity.
In addition to their speed advantage, these machines are designed with a focus on repeatability and zero-defect manufacturing. Integrated vision systems, laser sensors, or force-feedback mechanisms are often included to monitor each hemming cycle, automatically rejecting any part that falls outside specified tolerances. Such systems support lean manufacturing principles and make the equipment suitable for quality-critical applications, particularly in automotive closures and precision panel fabrication.
Overall, high-speed hemming machines represent the cutting edge of edge-forming technology, combining advanced control systems, high-performance drives, and intelligent automation to deliver unmatched productivity and precision in modern metal fabrication settings.
High-speed hemming machines are not only defined by their rapid performance but also by their ability to maintain consistency over long production runs. Their design prioritizes dynamic stability and thermal efficiency, ensuring the hemming quality does not degrade due to heat buildup or mechanical fatigue during continuous operation. Precision ball screws, linear guides, and high-rigidity structures work in concert to suppress vibration and deflection, even under demanding speeds and loads.
These machines are often part of highly automated manufacturing lines where takt time is critical. Their compatibility with robotic handling systems enables seamless integration into synchronized workflows where multiple operations, including stamping, trimming, welding, and hemming, occur in a unified cycle. The hemming unit itself can be either stationary or mounted on a robotic actuator, depending on the complexity of the workpiece geometry. Robotic hemming heads provide the added benefit of flexibility, particularly for components with compound curves or complex edge contours that cannot be processed using fixed dies.
Cycle times on high-speed hemming machines are significantly reduced thanks to multi-axis control, allowing simultaneous vertical and lateral tool movement, which mimics the natural rolling or sweeping motion used in manual edge folding but at a speed and precision level unattainable by human operators. These coordinated motions are controlled by servo drives capable of microsecond-level response, ensuring each stroke adheres strictly to the preprogrammed path and pressure profile.
Tooling design is another area where high-speed hemming machines excel. Modular die systems and rapid-change interfaces are standard features, allowing the machine to switch between different hemming tasks with minimal intervention. This is particularly advantageous for manufacturers producing multiple product lines on a single system. Some advanced models also include self-diagnostic functions, automatically detecting tool wear or misalignment and prompting maintenance before defects occur.
Because speed is only an advantage if quality can be maintained, these machines are equipped with real-time process monitoring technologies. Sensors measure parameters like force, displacement, and tool position throughout the hemming process, and any deviation from the norm triggers automatic adjustments or stops the cycle altogether. In some systems, data from each cycle is logged for traceability and quality assurance, supporting Industry 4.0 standards and predictive maintenance strategies.
Noise and vibration control are also considered in the machine design. Despite operating at high speeds, these hemming systems use damped enclosures, isolated mounting bases, and advanced motion profiles to minimize acoustic impact, ensuring a quieter and more ergonomic working environment. Additionally, safety systems such as light curtains, pressure-sensitive flooring, and interlocked access doors maintain full compliance with international safety standards, allowing high-speed operation without compromising operator security.
In summary, the high-speed hemming machine represents a convergence of performance, precision, and smart automation. It plays a pivotal role in modern metal fabrication, especially where volume, efficiency, and flawless execution are non-negotiable. Whether integrated into a full automotive production line or used in a modular setup for flexible manufacturing, these machines enable the next level of competitive manufacturing in edge-forming applications.
Beyond their mechanical and control sophistication, high-speed hemming machines are increasingly incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms to optimize operation and maintenance. By analyzing vast amounts of sensor data collected during production, these systems can predict tool wear, detect subtle shifts in material behavior, and even suggest optimal hemming parameters for new materials or part geometries. This proactive approach minimizes downtime, reduces scrap rates, and enhances overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
The flexibility of high-speed hemming machines also extends to material compatibility. With advances in drive control and tooling technology, these machines can handle emerging lightweight materials such as advanced high-strength steels (AHSS), aluminum alloys, and composite-metal hybrids without sacrificing cycle time or edge quality. This is especially important as industries push for lighter and stronger components to improve fuel efficiency and performance.
Environmental considerations have also influenced the design of modern hemming machines. Energy-efficient servo drives and hydraulic systems reduce power consumption, while regenerative braking systems can recover and reuse energy during the tool return stroke. Noise reduction and vibration dampening not only improve operator comfort but also contribute to lower overall environmental impact by decreasing the need for additional soundproofing infrastructure.
Maintenance accessibility is a crucial design factor in high-speed hemming machines. Components subject to wear, such as die sets, bearings, and hydraulic seals, are arranged for easy inspection and replacement. Automated lubrication systems ensure consistent servicing of moving parts, reducing manual intervention and extending machine life. Some advanced models also feature remote diagnostics capabilities, allowing service technicians to troubleshoot issues or perform updates without the need for onsite visits.
Integration with manufacturing execution systems (MES) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms enables seamless data exchange, helping manufacturers track production metrics, schedule maintenance, and coordinate supply chains efficiently. Real-time feedback from the hemming machine can be used to adjust upstream or downstream processes, fostering a fully connected smart factory environment.
Looking ahead, the evolution of high-speed hemming machines will likely continue toward increased modularity, enhanced sensor fusion, and greater autonomy. Advances in robotics and additive manufacturing may also influence hemming tooling design, enabling custom or on-demand tool fabrication tailored to specific production needs. As manufacturing moves toward more flexible, adaptive systems, high-speed hemming machines will remain a critical technology, balancing speed, precision, and versatility in metal fabrication.
CNC Sheet Metal Hemming Equipment
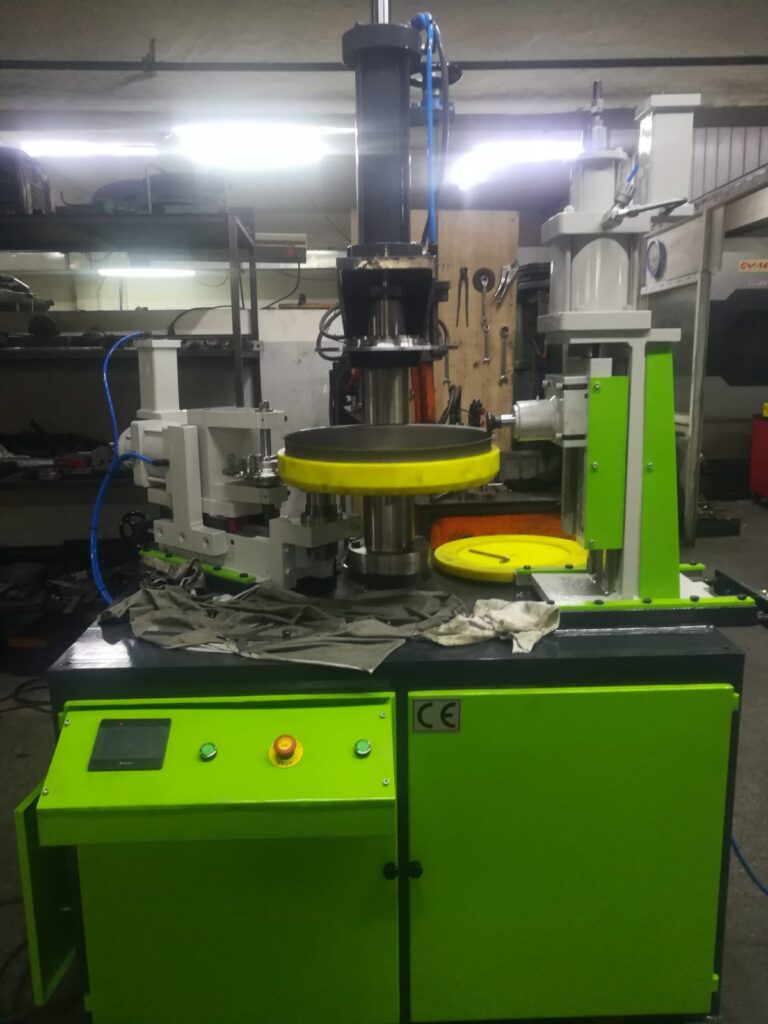

CNC sheet metal hemming equipment is advanced machinery designed to automate the precise folding and rolling of sheet metal edges using computer numerical control (CNC) systems. This equipment combines traditional hemming techniques with modern CNC technology to deliver high accuracy, repeatability, and flexibility in metal fabrication processes.
At its core, CNC sheet metal hemming machines use programmable controls to direct the movement of hemming tools—whether hydraulic, servo-electric, or pneumatic actuators—allowing for exact control over force, speed, and tool path. This precise control enables operators to produce complex hems on a variety of metal parts, including straight, curved, or contoured edges, with minimal manual intervention. The CNC system interprets CAD/CAM data or user input to execute hemming sequences tailored to specific part geometries and materials.
One key advantage of CNC hemming equipment is its ability to store multiple hemming “recipes” or programs. This means operators can quickly switch between different jobs without extensive setup time, significantly improving production efficiency, especially in job shops or facilities with diverse product lines. The automation also reduces human error, enhances consistency, and supports tight tolerances necessary in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and appliance manufacturing.
These machines are typically equipped with a variety of sensors and feedback mechanisms to monitor parameters like tool position, force applied, and cycle timing. The CNC controller uses this data to adjust operations in real time, maintaining optimal hemming conditions and preventing defects such as cracks, wrinkles, or uneven seams. Some systems also include diagnostic tools that alert operators to tooling wear or machine maintenance needs before failures occur.
CNC sheet metal hemming equipment often integrates with robotic handling systems, conveyors, and vision inspection units to form fully automated production lines. This integration allows seamless material flow, precise positioning, and in-line quality control, all coordinated through centralized control systems. Advanced human-machine interfaces (HMIs) provide operators with intuitive control over machine functions, diagnostics, and program management.
Overall, CNC sheet metal hemming equipment enhances productivity, precision, and flexibility in metal fabrication by combining automated control with powerful hemming capabilities. It supports modern manufacturing demands for high-quality parts produced efficiently and consistently across varying product runs.
CNC sheet metal hemming equipment operates by following detailed, pre-programmed instructions that control every aspect of the hemming process. The CNC system precisely manages tool movements along multiple axes, enabling the hemming tool to adapt dynamically to complex part shapes and contours. This multi-axis control is critical for handling the intricate geometries often found in automotive panels, aerospace components, and consumer appliance parts, where consistent edge quality is vital.
The programmability of CNC hemming machines allows for extensive customization of hemming parameters such as tool speed, applied force, dwell time, and tool path trajectory. By fine-tuning these variables, manufacturers can optimize the hemming process for different materials, thicknesses, and surface treatments, minimizing defects like surface scratches or micro-cracks. This adaptability is particularly important when working with advanced materials such as high-strength steels or aluminum alloys, which require careful handling to preserve their structural integrity and finish.
Integration with CAD/CAM software streamlines the programming workflow, allowing engineers to directly convert digital part designs into hemming programs. This reduces the need for manual coding and accelerates the setup time for new jobs. Additionally, simulation tools can verify the hemming process virtually, identifying potential issues before physical production begins, which saves time and material costs.
CNC sheet metal hemming equipment is also designed for high throughput and repeatability. Once a program is loaded, the machine can produce hundreds or thousands of identical parts with minimal variation, ensuring consistent product quality. This level of repeatability is essential for meeting the strict standards of industries such as automotive manufacturing, where parts must fit precisely and perform reliably under stress.
Maintenance and diagnostics are simplified through the CNC interface, which provides real-time feedback on machine status, tooling conditions, and production metrics. This data helps operators and maintenance personnel identify wear patterns and schedule preventative maintenance, reducing unexpected downtime. Some advanced machines also support remote monitoring and troubleshooting, allowing experts to assist with machine health management from off-site locations.
Safety features are integral to CNC hemming machines, with enclosures, light curtains, emergency stops, and interlocks protecting operators from moving parts during operation. Modern CNC systems also incorporate fault detection algorithms that halt the machine if abnormal conditions are detected, preventing damage to the equipment or workpieces.
In production environments, CNC sheet metal hemming equipment can be linked with other manufacturing systems through industrial communication protocols, forming part of an interconnected smart factory. This connectivity facilitates data exchange across various stages of production, enabling comprehensive quality control, production scheduling, and inventory management.
By automating the hemming process with CNC technology, manufacturers gain significant advantages in efficiency, precision, and flexibility. This results in higher-quality finished products, reduced labor costs, and the ability to rapidly respond to changing market demands or design updates. Consequently, CNC sheet metal hemming equipment plays a critical role in modern metal fabrication, supporting both small-batch custom jobs and large-scale industrial production.
Beyond core hemming functions, CNC sheet metal hemming equipment increasingly incorporates advanced features to enhance performance and usability. One such feature is adaptive control, where the machine continuously monitors hemming parameters like force and displacement during operation and automatically adjusts settings to compensate for variations in material thickness, hardness, or surface condition. This adaptive feedback loop helps maintain optimal hemming quality even when raw material properties vary within acceptable tolerances, reducing scrap and rework.
The user interface on modern CNC hemming machines has evolved into highly intuitive touchscreen displays with graphical programming and diagnostics tools. Operators can visualize the hemming path, adjust parameters on the fly, and access step-by-step maintenance guides without needing extensive technical training. Some systems support multilingual options and user-level permissions to streamline operation in multi-shift or multi-operator environments.
Integration with vision systems and in-line quality inspection is another key advancement. Cameras and sensors can inspect the hemmed edges immediately after forming, detecting defects such as incomplete hems, cracks, or surface damage. When linked to the CNC controller, these inspections can trigger automatic rejection of defective parts or initiate corrective actions in real time, helping to maintain a zero-defect production philosophy.
Modular tooling concepts allow CNC hemming machines to accommodate a wide range of part sizes and shapes. Quick-change tooling fixtures and adjustable clamps make it possible to switch between different product lines rapidly, minimizing downtime and increasing overall equipment utilization. In some cases, tooling components are designed to be reconfigurable or adjustable without full replacement, offering cost savings and greater flexibility.
Maintenance routines are also enhanced by embedded sensor networks and predictive analytics. By continuously collecting data on vibration, temperature, and pressure within hydraulic or servo systems, CNC hemming equipment can forecast component wear and schedule maintenance before failures occur. This proactive approach reduces unplanned downtime and extends the lifespan of critical components such as pumps, valves, and bearings.
Environmental considerations are increasingly influencing the design and operation of CNC sheet metal hemming machines. Energy-efficient drives, low-oil hydraulic systems, and regenerative braking mechanisms help reduce power consumption and minimize the carbon footprint of hemming operations. Noise reduction features and ergonomic layouts contribute to improved workplace conditions and operator comfort.
Connectivity to enterprise systems via industrial Ethernet or wireless protocols supports seamless integration into smart manufacturing ecosystems. This enables real-time monitoring of production status, traceability of parts, and detailed reporting for compliance with industry standards such as ISO or automotive quality norms. Data collected from CNC hemming equipment can be analyzed to identify process improvements and optimize throughput.
Looking forward, the evolution of CNC sheet metal hemming equipment is expected to include greater use of artificial intelligence for autonomous process optimization and machine learning to predict material behavior or tool wear. Advances in robotics may further enhance flexibility by enabling hemming of highly complex geometries or custom one-off parts with minimal setup.
In summary, CNC sheet metal hemming equipment represents a sophisticated fusion of precision mechanics, advanced control systems, and smart automation. Its continual development addresses the growing demands of modern manufacturing for speed, quality, flexibility, and sustainability, making it an indispensable asset in competitive metal fabrication operations.
Industrial-Grade Sheet Metal Hemmer
An industrial-grade sheet metal hemmer is a robust, high-capacity machine designed to fold and secure the edges of sheet metal parts with precision, durability, and efficiency suitable for heavy-duty manufacturing environments. Built to withstand continuous operation under demanding conditions, these machines are essential in industries such as automotive, aerospace, appliance manufacturing, HVAC, and metal furniture production.
Industrial-grade hemmers typically feature heavy-duty frames made from high-strength steel or cast iron to minimize deflection and vibration during operation. This structural rigidity ensures consistent hemming quality even when working with thick or high-strength materials. The drive mechanisms are usually hydraulic or servo-electric, offering powerful, adjustable force and precise control over the hemming cycle to handle a wide range of metal gauges and types, including stainless steel, aluminum, and coated steels.
These hemmers accommodate various hemming styles — open hems, closed hems, and double hems — and often come equipped with interchangeable or adjustable tooling systems to support diverse product geometries and production requirements. Tooling is engineered for durability and precision, with quick-change capabilities to minimize downtime during product changeovers.
In addition to raw power, industrial-grade sheet metal hemmers emphasize automation and safety. Many models integrate programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs) to enable flexible operation, precise control of hemming parameters, and repeatable performance. Safety features such as guarding, light curtains, emergency stops, and interlocks are standard to protect operators during high-force operations.
To maximize productivity, industrial hemmers may be integrated with robotic part handling systems, conveyors, or rotary indexing tables, creating automated cells capable of high throughput with minimal manual intervention. Advanced models include sensors and monitoring systems that track process parameters like hemming force and stroke position in real time, enabling quality assurance and early detection of tooling wear or malfunctions.
Maintenance considerations are crucial in industrial settings, so these machines are designed for easy access to wear components, equipped with automated lubrication systems, and support predictive maintenance through embedded sensors and diagnostic software. Energy efficiency is also a focus, with modern hemmers employing servo-driven or optimized hydraulic systems that reduce power consumption without sacrificing performance.
Overall, industrial-grade sheet metal hemmers combine strength, precision, and automation to deliver reliable, high-quality edge forming in demanding manufacturing applications. Their ability to handle tough materials, maintain consistent quality at high volumes, and integrate into automated production lines makes them indispensable in modern industrial metal fabrication.
Industrial-grade sheet metal hemmers are engineered to provide consistent, high-quality hemming results while operating continuously in fast-paced production environments. Their robust construction not only resists wear and tear but also maintains tight tolerances over extended periods, which is critical for parts that must meet stringent dimensional and aesthetic standards. These machines often feature reinforced frames with vibration-dampening foundations to reduce noise and mechanical stress, extending machine life and improving operator comfort.
The hemming process itself in these machines is precisely controlled through advanced hydraulic or servo-electric systems that can deliver substantial force smoothly and accurately. This control is vital when working with advanced materials such as high-strength steels or thick aluminum sheets, where improper force application can lead to cracks or surface defects. The machines’ capability to fine-tune parameters like hemming speed, force, and dwell time allows them to adapt to different materials and part complexities, ensuring optimal results without manual trial-and-error.
In terms of tooling, industrial hemmers use high-grade steels and alloys for durability, with surfaces often hardened or coated to resist abrasion and corrosion. The tooling systems are typically modular, allowing for rapid die changes and adjustments to accommodate different part geometries or production runs. This flexibility is essential for manufacturers handling diverse product lines or frequently updating designs.
Automation integration is a hallmark of industrial-grade hemmers, which often operate as part of larger manufacturing cells. They can be synchronized with upstream and downstream equipment, including stamping presses, robotic feeders, and quality inspection stations. Such integration enables smooth workflow, reduces cycle times, and minimizes human intervention, lowering labor costs and improving safety. Real-time monitoring systems track hemming parameters and machine health, enabling predictive maintenance strategies that reduce downtime and extend tool life.
Safety remains paramount, with multiple layers of protective measures like physical guards, light curtains, and emergency stop systems built into these machines. Operator ergonomics are also considered, with controls positioned for easy access, adjustable platforms for different operators, and clear visual interfaces that provide status updates and alerts.
Energy efficiency is increasingly prioritized, with modern industrial hemmers utilizing servo drives or optimized hydraulic systems that minimize power consumption while delivering the necessary force. Some machines incorporate energy recovery systems that capture and reuse energy during tool retraction or idle phases, contributing to sustainability goals and reducing operational costs.
Overall, industrial-grade sheet metal hemmers represent a synthesis of power, precision, and automation designed to meet the rigorous demands of heavy-duty manufacturing. Their ability to produce high-quality hems consistently on a wide variety of materials and part complexities makes them a critical asset for manufacturers aiming to maintain competitiveness and product excellence in today’s fast-evolving industrial landscape.
In addition to their core hemming capabilities, industrial-grade sheet metal hemmers increasingly feature advanced connectivity options that align with Industry 4.0 principles. By integrating with factory-wide networks through protocols such as OPC UA, Ethernet/IP, or Profinet, these machines enable real-time data exchange and remote monitoring. This connectivity supports detailed production tracking, process optimization, and swift response to any issues, enhancing overall plant efficiency.
The data generated by industrial hemmers can feed into centralized manufacturing execution systems (MES), enabling comprehensive quality control and traceability. For industries with strict regulatory or customer requirements—such as automotive, aerospace, or medical device manufacturing—this traceability ensures that every hemmed part meets predefined standards and that any deviations can be quickly identified and addressed.
Another growing trend is the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms within hemming equipment. These technologies analyze process data to detect subtle patterns indicative of tooling wear, material inconsistencies, or setup errors. By predicting maintenance needs or adjusting hemming parameters autonomously, AI-enhanced hemmers reduce downtime and improve yield, delivering a more efficient and cost-effective operation.
Ergonomics and operator support also continue to evolve. Interactive touchscreens with graphical interfaces simplify machine setup and troubleshooting, while augmented reality (AR) applications can assist maintenance personnel by overlaying instructions or highlighting components in real time. Such tools reduce training time and increase the accuracy of maintenance tasks, further minimizing machine downtime.
In terms of versatility, industrial hemmers are adapting to handle increasingly complex and lightweight materials. Hybrid hemming processes combining mechanical, hydraulic, and servo-electric actions allow the machines to form advanced high-strength steels (AHSS), aluminum alloys, and multi-layer composites without damaging surface coatings or inducing stress cracks. This capability supports manufacturers’ goals of lightweighting and improving product performance without compromising production speed or quality.
Sustainability considerations are also influencing the design of industrial hemming systems. Energy-efficient drives, low-friction bearings, and optimized hydraulic circuits contribute to reduced energy consumption. Additionally, the use of environmentally friendly hydraulic fluids and improved sealing technologies minimize leaks and environmental impact. Some manufacturers also design their hemmers for easier end-of-life recycling, emphasizing circular economy principles.
Looking forward, the future of industrial-grade sheet metal hemmers is likely to include greater modularity and scalability, enabling manufacturers to tailor hemming solutions precisely to their production volumes and part complexities. Enhanced robotics integration will provide even more flexibility, allowing hemming of intricate shapes or one-off custom parts with minimal setup time.
In summary, industrial-grade sheet metal hemmers are evolving from powerful standalone machines into intelligent, connected, and adaptable components of modern manufacturing ecosystems. Their combination of rugged construction, precise control, automation readiness, and smart technologies positions them as essential tools for manufacturers striving to meet the challenges of today’s demanding production environments while preparing for the innovations of tomorrow.
Automated Hemming System for Sheet Metal
An automated hemming system for sheet metal is a sophisticated production solution designed to fold and finish the edges of metal components with minimal human intervention. These systems combine precision hemming machinery with robotic handling, programmable controls, and integrated quality inspection to deliver high-speed, consistent, and repeatable edge-forming processes suitable for mass production environments such as automotive manufacturing, appliance fabrication, and metal furniture assembly.
The heart of an automated hemming system is typically a hemming press or hemming robot equipped with specialized tooling capable of performing various hemming styles—open, closed, teardrop, or double hems—on a wide range of sheet metal thicknesses and materials. The hemming process is fully controlled through programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or CNC systems that manage force, stroke speed, tool path, and dwell time to optimize edge quality and minimize material deformation or surface defects.
Material handling is a key component of automation, often realized through industrial robots, conveyors, and fixtures that load, position, and unload parts with high precision. Robotic arms equipped with vision systems ensure correct part orientation and placement, allowing the hemming tool to follow the programmed path accurately. This reduces setup times and enables quick transitions between different product variants, boosting overall line flexibility.
Quality assurance is integrated into the system via in-line inspection technologies such as laser scanners, cameras, and force sensors. These devices monitor each hemming cycle, verifying parameters like hem dimensions, seam integrity, and surface finish. Real-time feedback enables immediate detection of defects, prompting automatic rejection or adjustment without halting production.
Automated hemming systems are designed with safety and ergonomics in mind, incorporating protective enclosures, light curtains, emergency stops, and interlocks to safeguard operators. The systems often include intuitive human-machine interfaces (HMIs) that provide operators and technicians with easy access to program controls, diagnostic data, and maintenance schedules, streamlining operation and upkeep.
The integration capabilities of automated hemming systems extend beyond the hemming cell itself. They can communicate with upstream and downstream equipment—such as stamping presses, welding stations, and assembly robots—through industrial networks, forming part of a fully coordinated smart manufacturing line. This connectivity supports synchronized workflows, reduces bottlenecks, and enhances production throughput.
Energy efficiency and sustainability are addressed through the use of servo-electric drives or optimized hydraulic systems that minimize power consumption. Some systems also implement energy recovery during tool retraction phases. Maintenance is facilitated by condition monitoring sensors and predictive analytics, enabling proactive service and reducing unplanned downtime.
Overall, automated hemming systems represent a convergence of advanced mechanical engineering, robotics, control technology, and data analytics. They provide manufacturers with a reliable, efficient, and flexible solution for producing high-quality hemmed sheet metal parts at scale, supporting the demands of modern industrial production while improving consistency, safety, and operational efficiency.
Automated hemming systems operate by synchronizing multiple components to achieve a seamless and efficient hemming process. The hemming machine or robot executes programmed sequences that precisely control the application of force and movement to fold the sheet metal edge, ensuring uniformity and structural integrity. Robots or automated handlers manage the loading and unloading of parts, positioning each piece accurately in the hemming station to maintain tight tolerances and reduce cycle times.
These systems often incorporate advanced vision and sensor technologies that verify part placement, measure hemming dimensions, and detect surface imperfections in real time. The data collected not only ensures quality control but also feeds back into the control system to adjust hemming parameters dynamically, compensating for variations in material properties or part geometry. This closed-loop feedback mechanism enhances process robustness and minimizes scrap rates.
Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and CNC systems form the automation backbone, orchestrating the movements of the hemming tool, robots, and auxiliary equipment according to pre-set recipes. Operators can select and modify these recipes via intuitive human-machine interfaces (HMIs), which provide graphical representations of the process, status indicators, and troubleshooting assistance. This interface reduces the need for highly specialized operators and shortens setup and changeover times, increasing overall production flexibility.
The automation of material handling reduces manual labor, lowers the risk of injury, and enhances repeatability. Robotic arms equipped with grippers or vacuum fixtures can manipulate parts of various sizes and shapes, facilitating multi-station operations or continuous flow lines. Integration with conveyors or rotary indexing tables allows for smooth transitions between process steps, optimizing line throughput.
Safety is a critical design consideration; automated hemming systems employ protective guarding, light curtains, and emergency stop systems to prevent operator access during machine operation. Furthermore, the system can perform self-diagnostics and error reporting, automatically halting operation if unsafe conditions or equipment faults are detected, thereby preventing damage and ensuring personnel safety.
Energy consumption is optimized through the use of servo-electric drives and energy-efficient hydraulic components that reduce power usage during operation. Regenerative braking and power recovery systems capture energy during tool retraction phases, contributing to lower operational costs and environmental impact.
Maintenance processes are streamlined by incorporating sensors that monitor critical parameters such as hydraulic pressure, motor load, and tool wear. Predictive maintenance algorithms analyze this data to forecast when servicing or component replacement will be necessary, minimizing unexpected downtime and prolonging equipment life.
In addition to standalone operation, automated hemming systems are designed to integrate with factory-wide digital infrastructures. By connecting with manufacturing execution systems (MES) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, these systems enable real-time tracking of production metrics, traceability of parts, and seamless communication across the production line. This integration supports lean manufacturing principles and continuous improvement initiatives.
The modular nature of many automated hemming systems allows manufacturers to scale capacity or adapt to new product lines without extensive retooling. This adaptability is especially valuable in industries where product variants and customization demands are increasing.
Looking forward, trends such as the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and advanced robotics will further enhance the capabilities of automated hemming systems. These technologies will enable greater process optimization, self-correction, and flexibility, empowering manufacturers to meet evolving quality standards and production requirements with minimal human intervention.
Overall, automated hemming systems for sheet metal represent a vital advancement in modern metal fabrication, delivering superior quality, productivity, and safety while supporting the drive toward smarter, more connected manufacturing environments.
Building on these capabilities, automated hemming systems increasingly leverage digital twin technology—virtual replicas of the physical hemming process and equipment. Digital twins allow engineers to simulate and optimize hemming operations before actual production, identifying potential issues and testing parameter adjustments without wasting materials or downtime. This virtual modeling also supports training operators and maintenance personnel in a risk-free environment, enhancing skill development and reducing the learning curve for new equipment.
The adaptability of automated hemming systems is further enhanced by modular robotic tooling and flexible end-effectors. These tools can quickly switch between different hemming profiles or grip various part geometries, enabling one system to handle multiple product families or custom orders without requiring dedicated machinery. This flexibility significantly lowers capital expenditure and increases the responsiveness of manufacturing lines to changing market demands.
In industries with stringent regulatory requirements, automated hemming systems provide detailed process documentation and traceability. Integrated data logging captures information on each hemming cycle—such as force applied, cycle time, and inspection results—ensuring compliance with quality standards and facilitating audits. This comprehensive data collection also aids in continuous improvement efforts by highlighting trends or anomalies that may affect product quality.
As manufacturers aim to reduce environmental impact, automated hemming systems are being designed with sustainability in mind. Energy-efficient components, optimized cycle times, and reduced scrap rates contribute to lower carbon footprints. Additionally, some systems incorporate environmentally friendly coolants and lubricants, as well as filtration and recycling units that minimize waste generation.
Remote monitoring and support have become standard features, allowing manufacturers to connect with equipment suppliers or service teams worldwide. This connectivity enables rapid troubleshooting, software updates, and process adjustments without the need for onsite visits, reducing downtime and improving responsiveness. Advanced analytics platforms can also process production data from multiple sites to provide benchmarking and predictive insights across global operations.
Ergonomics continues to be a focus, with automated hemming systems designed to minimize operator fatigue and facilitate safe interaction. Adjustable control panels, clear visual feedback, and simplified maintenance access reduce the physical demands on staff and support better overall workplace conditions.
In the future, the convergence of automation, AI, and robotics will likely give rise to fully autonomous hemming cells capable of self-optimization and real-time adaptation to new materials or part designs. Collaborative robots (cobots) may work alongside human operators to provide greater flexibility in low-volume or custom production runs, combining the efficiency of automation with human judgment and dexterity.
In essence, automated hemming systems are not just machines but integral components of smart manufacturing ecosystems. Their evolution reflects broader industry trends toward increased digitalization, connectivity, and sustainability, empowering manufacturers to produce higher quality sheet metal components more efficiently and with greater agility than ever before.
Precision Sheet Metal Hemming Machine
A precision sheet metal hemming machine is a specialized piece of equipment engineered to deliver exceptionally accurate and consistent edge-forming results on sheet metal components. Designed for applications where dimensional accuracy, cosmetic finish, and structural integrity are critical, these machines are widely used in sectors such as automotive body panel manufacturing, aerospace component production, medical equipment fabrication, and high-end appliance manufacturing.
The defining characteristic of a precision hemming machine is its ability to control every aspect of the hemming process with fine granularity. Whether driven by servo-electric, hydraulic, or hybrid actuation systems, these machines offer precise modulation of force, stroke length, and tool path. This ensures smooth, uniform hemming along both straight and complex curved surfaces, eliminating wrinkles, cracks, or distortion in the material—issues that are unacceptable in high-specification applications.
Precision hemmers typically feature rigid, low-vibration frames and high-accuracy guide systems that keep tool movement perfectly aligned even under load. The hemming head, often equipped with roller or segmented tools, follows tightly controlled motion profiles that can be tailored to the specific part geometry and material properties. These machines can process a wide variety of metals, including aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, and coated or pre-painted sheets, without compromising surface finish.
Advanced control systems, often CNC-based, enable operators to program detailed hemming sequences with multiple stages—such as pre-hemming followed by final hemming—while monitoring real-time feedback from position sensors and force gauges. This feedback loop allows the machine to correct for minor inconsistencies automatically, maintaining a high standard of repeatability from part to part.
The user interface is designed for clarity and control, typically incorporating touchscreen panels that display part programs, diagnostics, and live performance metrics. Operators can quickly switch between different part recipes and adjust settings without manual recalibration, significantly reducing setup time and ensuring reliable output in both small-batch and high-volume production.
Precision hemming machines are often integrated into automated production lines or robotic cells, where coordinated handling systems ensure accurate part placement and orientation. This integration supports faster throughput while maintaining tight tolerances and eliminating human error. In quality-critical environments, these machines may be paired with in-line inspection tools—such as laser scanners or machine vision systems—that verify hem quality on every part and trigger corrective actions if deviations are detected.
With growing emphasis on lightweight materials and advanced metal alloys, precision hemming machines are essential for forming delicate or sensitive materials without surface damage or material fatigue. Their ability to accommodate thinner metals and tighter bend radii expands design possibilities while reducing material waste.
In modern manufacturing contexts, these machines contribute to lean production, just-in-time processes, and digital traceability by offering connectivity to MES and ERP systems. Data logging capabilities ensure that each hemming cycle is recorded and traceable, supporting rigorous quality assurance protocols and compliance with industry standards.
Ultimately, precision sheet metal hemming machines combine meticulous mechanical design with intelligent control systems to deliver perfect hems, cycle after cycle. They enable manufacturers to meet the highest expectations in terms of accuracy, aesthetics, and process reliability, making them indispensable wherever flawless edge forming is required.
Precision sheet metal hemming machines are engineered to maintain exacting standards over long production runs, where even the smallest deviation in edge geometry or surface quality can lead to assembly issues, visual imperfections, or product rejection. Their ability to handle tight tolerances makes them a preferred solution for applications involving visible exterior panels, sealed joints, or interfacing components that must fit precisely without additional finishing work. These machines rely on synchronized multi-axis motion to deliver consistent force and positioning throughout the hemming cycle, reducing the risk of inconsistencies even when processing parts with variable curvature or compound geometries.
In many configurations, the hemming heads use roller-based or articulated tooling systems that travel along predefined paths with millimeter-level precision. These tools apply gradual pressure to fold the sheet edge over its mating surface, ensuring that material flow is smooth and controlled. The entire process is orchestrated by a high-resolution feedback system that constantly measures tool position, stroke speed, and material resistance. As the hemming progresses, any slight shift in material thickness or springback is detected in real time, allowing the controller to adapt tool pressure or motion dynamically to prevent defects.
Material compatibility is a key strength of precision hemming machines. They can process delicate surfaces such as painted, anodized, or laminated sheets without damaging the coating. This is made possible through low-friction tool coatings, programmable motion curves that avoid abrupt contact, and optimized clamping systems that stabilize the workpiece without leaving marks. These features are critical in industries where aesthetic quality and corrosion resistance are non-negotiable, such as in car doors, appliance panels, or aircraft fairings.
The machines are also built with modular tooling and fixture setups that enable rapid changeovers between different parts or product versions. This flexibility supports high-mix production environments where manufacturers must adapt quickly to customer demands or design updates. Tool changes can be assisted by automatic or semi-automatic systems that guide the operator through each step using digital prompts or visual indicators, minimizing downtime and setup errors.
In terms of data and connectivity, precision hemming machines support full integration with smart factory infrastructure. Every hemming cycle can be logged with detailed process parameters, such as time, applied force, displacement, and pass/fail inspection outcomes. This data is stored locally or sent to a central server, where it can be analyzed for trend detection, performance optimization, or traceability. In high-regulation industries, this level of documentation supports certification processes and guarantees product accountability.
Maintenance is streamlined through predictive analytics and self-diagnostic routines that monitor the health of critical components like bearings, actuators, and sensors. The machine alerts the operator when servicing is required, helping avoid unexpected breakdowns and extending machine lifespan. Key service points are made easily accessible through hinged panels or removable covers, and many models include built-in maintenance wizards that guide technicians through tasks with visual aids and status checks.
As production speeds continue to increase and quality standards become more rigorous, the demand for precision sheet metal hemming machines is expected to grow. Their combination of force control, motion precision, surface protection, and digital integration makes them a cornerstone of modern metal forming lines. Whether operating as a standalone workstation or as part of an automated robotic cell, these machines deliver the reliability, adaptability, and process visibility that advanced manufacturing requires.
Precision sheet metal hemming machines also excel in process consistency, which is vital when working within tolerance bands as narrow as a few tenths of a millimeter. The tight repeatability is especially important when hemming parts that will later be assembled using automated systems or robots, where any deviation could cascade into larger alignment or sealing problems. This level of consistency is achieved not only through hardware stability but also through software control systems that can interpolate complex motion paths, ensure precise timing between tool engagement and material response, and compensate for thermal expansion or part distortion during the cycle.
Many precision hemming systems are also capable of adaptive cycle control, where the machine responds in real time to live sensor feedback from each part. This means the machine can slightly alter its hemming motion or force if it detects small differences in material behavior, such as springback or localized hardness. These micro-adjustments help reduce scrap and ensure that parts meet spec even when working with variable material batches—a common reality in large-scale production.
Another advantage lies in the way precision hemmers handle thin or difficult-to-control parts. These machines often use vacuum fixtures or intelligent clamping systems to hold components in place without introducing stress or distortion. This not only ensures dimensional accuracy but also eliminates the need for secondary fixtures or additional forming operations, saving time and cost.
In highly aesthetic applications, such as visible outer panels on vehicles or consumer products, hemming must be flawless in both alignment and finish. Precision hemming machines use smooth, progressive forming strokes that eliminate the risk of creating tool marks, ripples, or microfractures. In applications requiring adhesive bonding inside the hem, these machines can accommodate sealant beads without disturbing their uniformity, ensuring proper sealing and corrosion protection.
For complex part geometries—such as double-curved edges or sharp internal radii—customized roller paths or multi-stage hemming programs can be programmed into the CNC controller. These allow the machine to execute precise and repeatable edge forming even on intricate components. For operations where space is constrained, some precision hemmers feature compact designs with integrated control cabinets and vertically oriented motion systems, making them suitable for installation in crowded factory layouts.
In modern manufacturing workflows, these machines are increasingly part of a digitally connected production line where each piece of equipment shares data and status information. Precision hemming machines can communicate with upstream stamping lines and downstream inspection or assembly cells, adjusting their parameters to compensate for variation or to align with production scheduling. This level of synchronization is essential in high-efficiency operations and supports just-in-time manufacturing goals.
In summary, the precision sheet metal hemming machine stands as a critical asset in industries where performance, appearance, and reliability are all mandatory. It combines exacting force control, advanced motion technology, intelligent feedback systems, and full digital integration into one platform. Its ability to process a wide variety of metals and part types without sacrificing accuracy or finish quality makes it indispensable in modern production environments committed to excellence and competitiveness.
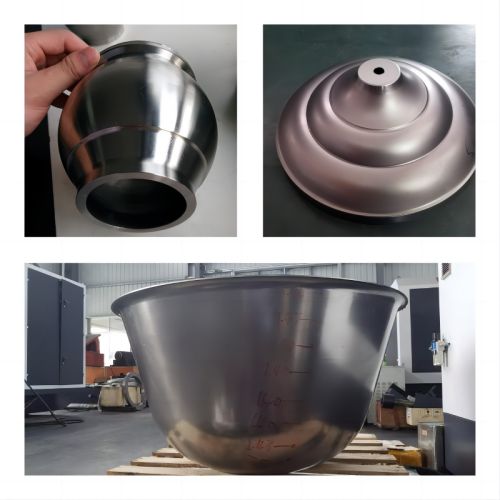
Belt Type Cookware Surface Sander
A belt type cookware surface sander is a specialized machine designed to finish and refine the exterior and sometimes interior surfaces of cookware items such as pots, pans, and lids. Using continuous abrasive belts, this equipment removes imperfections, oxidation layers, welding marks, or casting residues to achieve a uniform surface texture that may be either matte, brushed, or polished, depending on production requirements. It is a critical part of the post-forming or post-welding process in cookware manufacturing, ensuring both functional and aesthetic quality.
The abrasive belt in this machine is tensioned and driven over rollers, typically mounted on a sturdy frame that supports steady and vibration-free operation. Cookware items are either fed manually or automatically into the sanding zone, where controlled pressure is applied to the belt as it moves across the metal surface. The contact pressure, belt speed, and feed rate are adjustable to accommodate different cookware materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, or copper, each of which requires distinct treatment to achieve the desired finish.
Belt type surface sanders are often equipped with one or more heads that can be positioned to sand various zones of the cookware, such as the base, sidewalls, or even the rim. Some machines include multiple sanding stations with varying grit levels, enabling rough sanding, fine sanding, and polishing in a single pass. These multi-stage systems increase efficiency and reduce the need for secondary finishing operations.
To ensure consistent quality, the sanding pressure is often regulated with pneumatic or hydraulic systems, and the sanding belts are kept clean and effective by automatic cleaning brushes or air jets. Dust and particulate collection systems are also integral, especially when processing aluminum or stainless steel, as these materials generate fine metallic dust that must be captured to maintain safety and cleanliness.
More advanced belt sanders include programmable controls, digital interfaces, and memory settings for different product types, which allow for quick changeovers and standardized results across production batches. In high-volume production lines, robotic arms or conveyors may be used to load and unload cookware automatically, reducing labor dependency and increasing throughput.
Overall, a belt type cookware surface sander is an essential tool in the cookware manufacturing process. It ensures that the final product not only meets visual standards but also provides the smoothness required for non-stick coatings or ease of cleaning. Its robust construction, versatility, and high degree of control make it suitable for both mass production and specialized, high-end cookware lines.
Belt type cookware surface sanders are engineered for precision and durability, built to handle repetitive operations while maintaining consistent surface quality across thousands of units. The machine’s abrasive belt, typically made of aluminum oxide, zirconia, or ceramic grain, runs over a tensioned loop that can span horizontal or vertical configurations depending on the type of cookware and the surface area to be processed. The belt’s grit can range from coarse for heavy material removal to fine for delicate finishing, and changing belts for different finishes is designed to be quick to minimize production downtime.
The sanding head applies uniform pressure against the cookware surface, either via a fixed platen or a contact roller system, depending on the specific application. In more advanced machines, the pressure system is dynamically controlled to adapt to subtle changes in surface curvature or part thickness, ensuring even material removal without gouging or heat distortion. This is particularly important when finishing thin-walled stainless steel or aluminum pans, where overheating or aggressive abrasion can warp the product or leave permanent marks.
To ensure ergonomic operation and operator safety, most belt type sanders are equipped with protective covers, emergency stop mechanisms, and dust extraction ports. The generated metal dust is often collected in a central vacuum or filtration system, which is vital not only for safety but also for maintaining surface quality by preventing particles from redepositing on the cookware. In some systems, mist or coolant spray may be introduced to reduce heat buildup and extend belt life, particularly when polishing to a high gloss.
Automated feeding mechanisms enhance production speed and consistency. These may include rotating tables, conveyor belts, or clamping fixtures that hold each cookware item securely while guiding it under the sanding belt. Multi-axis systems allow for simultaneous processing of sidewalls and bottoms in a continuous operation, making it possible to achieve a uniform finish in one pass. For complex shapes or larger items such as deep pots or kettles, articulated arms or adjustable sanding heads may be used to reach all relevant surfaces without repositioning the item manually.
Consistency in finish is a top priority, particularly for high-end cookware brands where the exterior aesthetics reflect product quality. Brushed finishes are commonly achieved using medium-grit belts, giving cookware a uniform linear texture. For a satin or mirror finish, multiple passes are made using increasingly fine belts, sometimes followed by buffing or polishing operations. The ability to control every stage of this surface refinement with repeatable accuracy is one of the main advantages of belt-type systems.
Control panels on modern belt sanders feature digital touchscreens that allow the operator to set belt speed, sanding duration, pressure, and feed rate for different product types. Pre-programmed recipes can be saved and recalled to simplify transitions between product lines. Diagnostic functions alert the operator to belt wear, motor load, or feed misalignment, reducing the chance of damaging the product or halting production unexpectedly.
Maintenance is straightforward, with components such as belt rollers, guides, and contact platens designed for easy access and quick replacement. The belt tracking mechanism ensures that the abrasive remains centered and tensioned, preventing premature wear or uneven sanding. Some machines even include auto-tracking systems that adjust the belt’s alignment in real time.
Ultimately, the belt type cookware surface sander is a cornerstone of quality control in cookware manufacturing. It transforms raw or welded metal forms into finished consumer-ready products by delivering reliable, efficient, and scalable surface treatment. Its flexibility in handling various materials and finishes, combined with automation and precision control, makes it essential for any manufacturer seeking to meet modern standards for durability, hygiene, and aesthetics in cookware production.
Beyond standard finishing tasks, belt type cookware surface sanders are increasingly integrated into fully automated production lines to boost throughput and reduce manual labor. These integrated systems coordinate with upstream processes like stamping, welding, or spinning, ensuring that each cookware piece moves seamlessly from forming to surface finishing without delays or handling errors. Automated sorting and orientation systems guarantee the correct side of the cookware faces the sanding belt, further enhancing precision and repeatability.
Advancements in sensor technology have also enabled real-time monitoring of sanding quality. Optical sensors and laser profilometers can measure surface roughness and detect imperfections immediately after sanding, feeding this data back to the control system. If anomalies are detected—such as scratches, uneven abrasion, or belt contamination—the system can adjust sanding parameters on the fly or flag parts for manual inspection, maintaining consistent product quality throughout the production run.
In addition, some modern belt sanders incorporate adaptive control algorithms that learn from historical data to optimize sanding parameters dynamically. By analyzing variables like belt wear rate, material hardness, and production speed, the system can extend belt life, reduce energy consumption, and minimize scrap rates, contributing to more sustainable and cost-effective manufacturing.
Customization options allow manufacturers to tailor belt sanders to specific product needs. For example, machines can be configured with specialized belts for non-stick coating preparation, ensuring the surface has the right texture and cleanliness to promote adhesion without damaging the substrate. Other setups might include dual-belt configurations to simultaneously treat different parts of complex cookware or add-on polishing stations for final finishing steps.
Operator ergonomics remain a focus in design improvements. Adjustable height controls, easy-to-clean surfaces, and user-friendly interfaces reduce physical strain and simplify training. Safety features continue to evolve with light curtains, interlock switches, and automatic shutdown protocols designed to protect operators without compromising production speed.
As sustainability becomes more critical, manufacturers are exploring environmentally friendly abrasive materials and recycling options for spent belts. Some systems also integrate energy recovery solutions and low-emission dust collection to minimize environmental impact and meet stricter workplace regulations.
Looking ahead, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine vision will likely further transform belt type cookware surface sanding. Predictive maintenance, automated defect detection, and process optimization could become standard, enabling even higher levels of quality control and operational efficiency.
In conclusion, the belt type cookware surface sander is a vital technology in modern cookware manufacturing. Its ability to consistently deliver high-quality surface finishes, combined with increasing automation, intelligent controls, and sustainable design considerations, ensures it remains a key contributor to producing durable, attractive, and consumer-ready cookware products.
Sheet Metal Rotary Embossing Machine

A sheet metal rotary embossing machine is a specialized piece of equipment designed to create decorative or functional raised patterns on sheet metal surfaces by pressing the material between two rotating embossing rolls. This continuous process imparts textures, logos, grooves, or other embossed designs onto metal sheets used in various industries including automotive, appliances, HVAC, and architectural panel manufacturing.
The core of the machine consists of a pair of precisely machined rolls—one typically engraved with the desired pattern and the other acting as a backing roll. As the sheet metal passes through the nip between these rotating rolls, high pressure is applied, causing the metal surface to plastically deform and replicate the pattern. The rotary action allows for high-speed production of embossed sheets with consistent quality and repeatability.
Rotary embossing machines are designed to handle various types of metals such as aluminum, stainless steel, copper, and galvanized steel, with thicknesses ranging from thin foils to heavier gauge sheets. Adjustable roll pressure and gap settings enable the machine to accommodate different material properties and embossing depths, ensuring optimal results without damaging or tearing the sheet.
To support continuous operation, the machine is equipped with robust feeding and guiding systems that maintain proper sheet alignment and tension throughout the embossing process. Automated tension controls and edge guiding help prevent wrinkles, misalignment, or material distortion, which is critical for maintaining pattern uniformity over long production runs.
Some advanced rotary embossing machines incorporate heated rolls or cooling systems to manage metal temperature during embossing, improving pattern definition and reducing material stress. Additionally, interchangeable roll sets allow for quick changes of embossing patterns, providing flexibility for producing different designs or product variants without extensive downtime.
Control systems range from simple manual adjustments to sophisticated CNC interfaces that enable precise control over roll speed, pressure, and embossing parameters. Integration with upstream and downstream equipment such as decoilers, slitters, or recoilers facilitates seamless production flow within metal processing lines.
Maintenance features include quick-access roll housings for cleaning and inspection, lubrication systems to ensure smooth operation, and sensors that monitor roll condition and alignment. These help minimize downtime and extend machine life.
In summary, a sheet metal rotary embossing machine is essential for adding texture, branding, or functional surface features to metal sheets efficiently and consistently. Its combination of speed, precision, and adaptability makes it a valuable asset in industries requiring both aesthetic appeal and performance in metal products.
Rotary embossing machines operate by continuously feeding sheet metal through a pair of rotating embossing rolls, where the upper roll typically contains the engraved or raised pattern, and the lower roll provides counter pressure. This setup allows for high-speed production, often reaching several meters per minute, depending on the material and pattern complexity. The continuous rotary motion contrasts with slower, stroke-based embossing methods, making rotary embossing ideal for large-volume manufacturing.
The quality and clarity of the embossed pattern depend heavily on the precision of the roll engraving and the control of process parameters such as roll pressure, speed, and material feed rate. Advanced machines use servo motors and CNC controls to synchronize these variables accurately, ensuring consistent depth and sharpness of the embossing across the entire sheet length. This precision is vital for applications requiring detailed branding, anti-slip textures, or decorative effects.
Material handling is critical in rotary embossing systems. Automated feeding mechanisms, such as decoilers and straighteners, prepare the sheet before embossing, while recoilers or stackers collect the finished product. Edge guiding systems ensure the metal remains centered between the rolls, preventing pattern misalignment or edge damage. Tension control systems maintain appropriate material stress, reducing defects like wrinkling or stretching.
Some rotary embossing machines incorporate heated rolls to enhance embossing on harder metals or to assist in forming deeper or more intricate patterns by softening the material. Conversely, cooling systems may be employed when working with heat-sensitive materials or to prevent thermal distortion during high-speed operation. The ability to switch between heated and cooled rolls adds versatility and broadens the range of embossable materials.
Roll maintenance is crucial for long-term operation. Rolls are typically manufactured from hardened steel and may be chrome-plated or otherwise surface-treated to resist wear and corrosion. Interchangeable roll sets allow manufacturers to switch embossing patterns quickly, minimizing downtime during product changes. Regular cleaning and inspection ensure the patterns remain crisp and free of debris, which could mar the sheet surface or damage the tooling.
Integration with factory automation systems is increasingly common. Sensors monitor parameters such as roll gap, pressure, and temperature, feeding data to control units for real-time adjustments. This connectivity enables predictive maintenance, quality monitoring, and synchronization with other equipment in the production line, facilitating efficient workflow and reducing waste.
Rotary embossing machines are versatile enough to produce a wide variety of patterns, from simple geometric textures that improve grip or reduce glare, to intricate logos and decorative motifs that enhance product aesthetics. They are used across industries to add value, functionality, or branding to sheet metal products, helping manufacturers meet both practical and marketing requirements.
In conclusion, the sheet metal rotary embossing machine combines robust mechanical design with precise control and automation to deliver high-quality embossed metal sheets at scale. Its ability to efficiently process diverse materials and patterns makes it indispensable for manufacturers seeking to enhance the surface characteristics of metal products while maintaining production speed and consistency.
Further advancements in sheet metal rotary embossing machines include the integration of modular design principles, allowing manufacturers to customize and scale their equipment according to specific production needs. Modular components, such as roll stands, drive units, and control systems, can be added or removed to adapt the machine for different sheet widths, thicknesses, or pattern complexities without requiring a complete system overhaul. This flexibility supports rapid response to changing market demands and product innovations.
The development of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) technologies has significantly enhanced the roll engraving process. High-precision laser engraving and CNC machining enable the creation of highly detailed and repeatable embossing patterns that were previously impossible or economically unfeasible. These advances allow manufacturers to offer customized or limited-edition embossed designs with minimal lead times.
Incorporating environmentally friendly practices is another focus area. Modern embossing systems often employ energy-efficient drives and optimized hydraulic or pneumatic components to reduce power consumption. Noise reduction measures, such as vibration isolation and sound enclosures, improve the workplace environment. Additionally, systems are designed to minimize material waste by optimizing sheet utilization and reducing scrap during embossing.
Safety features continue to evolve, with machines equipped with advanced guarding, emergency stop mechanisms, and light curtains to protect operators without hindering productivity. User-friendly interfaces with touchscreens provide real-time machine status, diagnostics, and maintenance reminders, empowering operators to manage processes proactively.
Emerging trends point toward the adoption of Industry 4.0 capabilities, where rotary embossing machines connect to factory-wide networks for seamless data exchange. This connectivity enables remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and integration with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, enhancing overall production efficiency and traceability.
In sectors such as automotive and aerospace, where stringent quality standards prevail, rotary embossing machines contribute to meeting regulatory requirements by producing consistent, defect-free embossed surfaces that facilitate downstream assembly or bonding processes. Their role in creating functional textures, such as anti-slip or aerodynamic patterns, also supports product performance enhancements.
Looking ahead, innovations such as adaptive embossing—where the machine dynamically adjusts embossing parameters based on real-time material feedback—are under development. Such capabilities will further improve quality and reduce waste, solidifying the rotary embossing machine’s position as a cornerstone technology in advanced metal fabrication.
Ultimately, the sheet metal rotary embossing machine embodies a fusion of mechanical robustness, precision engineering, and intelligent automation. Its continuous evolution ensures it remains a vital tool for manufacturers seeking to combine aesthetics, functionality, and efficiency in their metal products.
Sheet Metal Stamping Embossing Machine
A sheet metal stamping embossing machine is a versatile industrial device designed to imprint raised or recessed patterns, logos, textures, or structural features onto sheet metal surfaces using a stamping press and custom dies. Unlike rotary embossing, which uses rotating rolls, stamping embossing applies force through a stationary or mechanically driven punch and die set to shape the metal in discrete cycles. This process enables highly detailed and complex designs, making it ideal for automotive panels, electrical enclosures, decorative metal parts, and appliance components.
The machine’s core components include a robust press frame, a ram or slide that drives the punch downward, and tooling sets specifically crafted to produce the desired embossing pattern. The sheet metal blank is positioned between the punch and die, and when the press cycles, the punch presses the metal into the die cavity, permanently deforming the sheet to form the embossed feature. The depth, shape, and precision of the embossing depend on the die design, press tonnage, and material characteristics.
Stamping embossing machines are available in various configurations, including mechanical, hydraulic, and servo-driven presses. Mechanical presses are favored for high-speed, high-volume production due to their rapid cycling and energy efficiency, while hydraulic and servo presses offer more precise control over force and speed, which is beneficial for delicate materials or complex embossing patterns.
These machines can handle a wide range of materials, from thin aluminum sheets used in consumer goods to thicker steel plates for structural applications. Adjustable press settings, such as stroke length, speed, and pressure, allow the embossing process to be fine-tuned for different metals and thicknesses, ensuring clean, accurate impressions without tearing or wrinkling.
Automation is commonly integrated into stamping embossing operations to improve throughput and consistency. Automated feeders, robotic part handlers, and positioning systems ensure accurate placement of blanks and rapid cycle times. Sensors and vision systems may be used to verify part orientation and quality immediately after embossing, allowing defective parts to be removed from the production flow.
Tooling design is critical for stamping embossing machines. Dies must be engineered for durability and precision, often constructed from hardened tool steels and sometimes coated to reduce wear and friction. Quick-change die systems facilitate rapid product changeovers, minimizing downtime in multi-product manufacturing environments.
Safety features are an integral part of stamping embossing machines, including safety guards, light curtains, emergency stops, and two-hand control systems that prevent operator injury during machine operation. Ergonomic considerations help reduce operator fatigue and improve workflow.
In summary, the sheet metal stamping embossing machine offers a precise and powerful method for adding functional or decorative embossing to sheet metal components. Its adaptability across materials and designs, combined with automation and safety features, make it a cornerstone of modern metal fabrication processes requiring detailed surface features and high production efficiency.
Sheet metal stamping embossing machines operate through a cyclical process where a metal blank is fed into the press and precisely positioned between the punch and die. Upon activation, the ram drives the punch downward with controlled force, deforming the sheet metal into the die cavity to create the embossed pattern. After the embossing stroke, the ram retracts, and the finished part is removed, either manually or via automated systems, preparing the machine for the next cycle.
The accuracy and quality of the embossed features rely heavily on the synchronization of press speed, stroke length, and applied force. Advanced machines use servo or hydraulic controls to fine-tune these parameters, enabling consistent results even with complex or delicate materials. This level of control also helps minimize wear on tooling and reduces the risk of material defects such as cracking, wrinkling, or distortion.
Material handling systems integrated with stamping embossing machines include feeders, conveyors, and robotic arms that ensure precise blank delivery and part removal. Vision systems and sensors verify part placement and orientation, reducing errors and enhancing overall line efficiency. Automated systems can also track production metrics in real time, allowing operators to monitor throughput, detect anomalies, and adjust parameters proactively.
Tooling plays a pivotal role, with dies designed for longevity and ease of maintenance. They often incorporate features like interchangeable inserts or modular components to facilitate quick repairs and adjustments without full die replacement. Surface treatments and coatings on tooling help resist abrasion and corrosion, extending operational life and maintaining embossing quality over time.
The flexibility of stamping embossing machines allows manufacturers to produce a wide range of patterns, from simple textures that improve grip or aesthetics to intricate logos and structural reinforcements that add strength or functionality. This adaptability makes the process suitable for diverse industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and household appliances.
Safety remains a top priority, with machines equipped with comprehensive guarding, light curtains, and emergency stop functions to protect operators from the high forces involved. Ergonomic design considerations reduce operator fatigue and facilitate easy access for maintenance and die changes.
Moreover, modern stamping embossing presses are increasingly integrated into smart factory environments. Networked control systems enable communication with other machines, MES platforms, and quality management software. This integration supports predictive maintenance, production scheduling, and traceability, helping manufacturers optimize efficiency and ensure product consistency.
Overall, the sheet metal stamping embossing machine combines powerful mechanical action with precise control and automation to deliver high-quality embossed parts efficiently. Its role in shaping metal surfaces with intricate and durable patterns is essential to meeting the demands of contemporary manufacturing for both functional and decorative applications.
Building on these capabilities, sheet metal stamping embossing machines continue to evolve with advancements in automation, materials, and digital control technologies. The adoption of servo-electric presses, for example, offers improved energy efficiency and more precise control over motion profiles compared to traditional mechanical or hydraulic presses. This translates to better embossing quality, reduced cycle times, and lower operational costs.
In addition to traditional flat sheet embossing, many machines now support progressive and transfer stamping operations, where multiple embossing and forming stages are combined into a single continuous process. This integration allows for complex parts to be produced with consistent embossing patterns, dimensional accuracy, and reduced handling between steps. Progressive dies further improve productivity by enabling multiple embossing features and other forming operations to occur sequentially in one press cycle.
Customization and rapid tooling development have also improved, thanks to computer-aided design (CAD) and manufacturing (CAM) software paired with advanced tooling fabrication techniques such as wire EDM and additive manufacturing. These technologies allow for quicker turnaround times when creating or modifying dies, enabling manufacturers to respond faster to market demands or design changes.
Material innovations, including high-strength steels, aluminum alloys, and composite metal laminates, require stamping embossing machines to adapt through more refined control over press parameters and tooling materials. Machines equipped with real-time force and position monitoring can adjust embossing pressure dynamically to accommodate variable material behavior, reducing scrap and improving part consistency.
Furthermore, enhanced sensor integration and machine learning algorithms are increasingly being used to monitor machine health and product quality. Predictive maintenance models can forecast component wear or potential failures, prompting maintenance before unplanned downtime occurs. Quality inspection systems integrated inline can detect embossing defects immediately, enabling corrective actions that maintain high yield rates.
Sustainability considerations also influence the design of modern stamping embossing machines. Energy-efficient drives, regenerative braking systems, and optimized press cycles contribute to lower energy consumption. Moreover, tooling designs that minimize material waste and facilitate easier recycling support environmental responsibility goals.
Safety and ergonomics continue to be refined with innovations such as collaborative robots (cobots) assisting with die changes or material handling, reducing operator risk and fatigue. Advanced control interfaces with augmented reality (AR) guidance are emerging to assist operators and technicians in setup, troubleshooting, and maintenance.
In summary, the sheet metal stamping embossing machine remains a cornerstone of metal fabrication, continuously advancing through integration with smart technologies, enhanced automation, and flexible manufacturing capabilities. These improvements empower manufacturers to produce complex, high-quality embossed components efficiently and sustainably in today’s competitive industrial landscape.
Sheet Metal Roll Forming Seaming Machine

A sheet metal roll forming seaming machine is a specialized industrial device designed to join, shape, and seal metal sheets or profiles by progressively bending and interlocking their edges through a series of precisely engineered rollers. This continuous forming process is widely used in manufacturing industries such as roofing, HVAC ductwork, automotive panels, and metal furniture, where durable, consistent seams are essential for structural integrity, weather resistance, or aesthetic appeal.
The machine operates by feeding flat or pre-formed sheet metal into a sequence of roll stations, each imparting incremental bends to the edges. As the metal progresses through the rollers, the edges are gradually folded and locked together in a controlled seaming operation, producing a strong, leak-proof joint without the need for welding or adhesives. This method ensures high-speed, uniform seam production while maintaining material strength and surface finish.
Roll forming seaming machines accommodate various seam types, including single lock, double lock, snap lock, and standing seam profiles, depending on the application requirements. Adjustable tooling and roll configurations enable manufacturers to switch between different seam styles or material thicknesses efficiently, supporting flexible production runs and custom orders.
Material compatibility is broad, covering metals such as galvanized steel, aluminum, stainless steel, and copper. The machine’s adjustable roll pressure, speed, and gap settings allow for precise control of forming forces to accommodate different metal properties and prevent damage such as cracking, wrinkling, or surface marring.
Automation features commonly integrated into roll forming seaming machines include motorized feeding systems, automated straighteners, and computerized control panels that monitor and regulate parameters like roll speed, seam tightness, and material feed rate. Some systems also incorporate inline inspection devices to verify seam quality, detecting defects like incomplete locks or misalignments and triggering alerts or rejection protocols.
The robust frame and precision bearings in the machine ensure stable, vibration-free operation, essential for maintaining seam accuracy over long production runs. Quick-change roll sets and modular design allow for rapid tooling swaps, reducing downtime when transitioning between different product specifications.
Safety is a priority, with guarding around moving parts, emergency stop functions, and sensors to prevent operation if abnormal conditions are detected. Ergonomic design elements facilitate easier operator interaction, maintenance access, and material handling.
In conclusion, a sheet metal roll forming seaming machine combines continuous roll forming with precise edge interlocking to deliver efficient, high-quality seams essential for a wide range of metal fabrication applications. Its adaptability, automation capabilities, and robust construction make it a vital asset for manufacturers seeking reliable and consistent seam production.
Sheet metal roll forming seaming machines function by progressively bending and folding the edges of metal sheets as they pass through a series of carefully aligned rollers. Each roller station performs a specific part of the forming sequence, gradually shaping the metal edges to create a secure seam. This incremental approach minimizes material stress and deformation, ensuring the seam maintains strength and durability throughout its length.
The machines are designed to handle various seam profiles, from simple single-lock seams to complex double-lock or standing seams used in architectural panels and roofing systems. By adjusting roller geometry and spacing, operators can tailor the seam configuration to match specific design and performance requirements. This flexibility allows manufacturers to produce a wide variety of products on a single machine, improving efficiency and reducing the need for multiple specialized tools.
Material handling systems play a crucial role in maintaining consistent seam quality. Automated feeders and straightening units ensure that the sheet metal enters the roll forming section smoothly and without distortion. Precise control of material feed rate and roll speed synchronization prevents slippage or misalignment that could compromise seam integrity.
The machine’s control systems often incorporate programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or CNC technology, enabling real-time monitoring and adjustments. Sensors track parameters such as roll pressure, seam tightness, and material thickness, allowing the system to compensate for variations in metal properties or thickness. This capability enhances product consistency and reduces scrap rates.
In-line quality inspection is frequently integrated into these machines, using optical or ultrasonic sensors to detect seam defects such as incomplete locks, gaps, or surface irregularities. Early detection allows operators to address issues promptly, maintaining high production standards and minimizing rework.
Maintenance accessibility is an important design consideration. Roll sets and forming stations are often modular and mounted on easily removable frames, allowing quick changeovers for different seam profiles or material types. Lubrication systems and cooling mechanisms help reduce wear on critical components, extending machine life and ensuring reliable operation.
Safety features include guarding around pinch points and moving rollers, emergency stop buttons within easy reach, and interlocks that prevent machine operation during maintenance or roll changes. Ergonomic design elements, such as adjustable control panels and operator-friendly loading areas, reduce fatigue and support efficient workflow.
Overall, sheet metal roll forming seaming machines are integral to producing consistent, high-quality seams essential for structural performance, weatherproofing, and aesthetics in metal products. Their combination of mechanical precision, automation, and adaptability allows manufacturers to meet diverse production demands with speed and reliability.
Advancements in sheet metal roll forming seaming machines continue to focus on increasing automation, precision, and versatility. Modern systems often integrate with broader manufacturing execution systems (MES), enabling real-time data exchange and enhanced process control. This connectivity supports predictive maintenance by monitoring machine conditions and usage patterns to schedule service proactively, reducing unplanned downtime.
Increased use of servo-driven roll forming stations allows for dynamic adjustment of roller speed and pressure during operation. This adaptability enables the machine to handle complex seam profiles or variable material thicknesses without stopping production, improving throughput and reducing waste.
Modular designs are becoming more prevalent, enabling manufacturers to expand or reconfigure machines easily as production needs evolve. For example, additional roll stations can be added to accommodate new seam designs or to enhance forming precision for thicker or more challenging materials.
Energy efficiency is another focus area, with modern machines incorporating regenerative drives that recover braking energy and reduce overall power consumption. Noise reduction measures and improved dust collection systems enhance the workplace environment, ensuring compliance with health and safety standards.
Robotic automation is increasingly applied to material handling before and after the seaming process. Automated loading and unloading systems reduce manual labor, improve safety, and maintain consistent part positioning, which is critical for seam accuracy.
Quality assurance continues to benefit from advancements in non-destructive testing technologies, such as ultrasonic seam inspection and high-resolution optical scanners. These systems detect defects early and enable immediate corrective actions, helping maintain high product standards while minimizing waste.
As manufacturers demand faster changeovers to accommodate shorter production runs and greater product variety, quick-change tooling and flexible roll modules reduce setup times significantly. Some machines feature automated roll swapping mechanisms controlled via the operator interface, allowing rapid transitions between different seam types without extensive manual intervention.
Safety innovations keep pace with machine complexity, incorporating comprehensive guarding systems, light curtains, and interlocks integrated with control logic to ensure operator protection without compromising productivity. Training simulators and augmented reality (AR) tools assist operators and maintenance personnel in learning machine operation and troubleshooting efficiently.
In summary, sheet metal roll forming seaming machines continue to evolve as sophisticated, highly automated solutions that combine precision engineering with smart manufacturing principles. Their ability to produce durable, consistent seams across a range of materials and profiles makes them indispensable in industries demanding quality, efficiency, and flexibility in metal joining processes.
Select Hydraulic Sheet Metal Seaming Machine
A hydraulic sheet metal seaming machine is a heavy-duty industrial device designed to join and seal sheet metal edges by applying controlled hydraulic pressure to fold, crimp, or interlock the material edges precisely. Unlike mechanical or roll forming seaming machines, hydraulic seaming equipment uses a hydraulic system to generate strong, consistent force, allowing it to handle thicker materials, more complex seam profiles, or applications requiring higher seam strength and durability.
These machines are commonly used in industries such as roofing, HVAC duct fabrication, automotive body assembly, and metal container manufacturing, where robust, leak-proof seams are critical. They excel at producing a variety of seam types including single lock, double lock, snap lock, and custom crimped joints, often tailored to specific product or industry requirements.
The hydraulic sheet metal seaming machine typically consists of a rigid frame, hydraulic power unit, precision tooling, and a control system. The hydraulic system delivers adjustable force through cylinders or presses that actuate forming tools, folding the sheet metal edges together under high pressure. The force and speed of the operation can be finely controlled to optimize seam quality and prevent damage to the material.
Machine tooling is designed to accommodate different seam geometries and material thicknesses. Interchangeable dies and rolls enable quick changes between seam profiles, enhancing flexibility in production. The tooling surfaces are often hardened and coated to resist wear and maintain consistent seam quality over extended runs.
Automation features include programmable hydraulic controls, CNC interfaces, and sensor feedback that monitor pressing force, stroke position, and cycle timing. These capabilities enable precise control of the seaming process, repeatable results, and integration with other production line equipment for efficient workflow.
Material handling is facilitated by automated feeding systems, positioning fixtures, and conveyor integration to ensure accurate alignment of sheets before seaming. Some machines incorporate vision systems or laser guides for enhanced precision and quality assurance.
Safety is a critical aspect, with machines equipped with guarding, emergency stops, pressure relief valves, and interlocks to protect operators during high-force operations. Ergonomic designs help reduce operator fatigue and simplify maintenance tasks.
In conclusion, hydraulic sheet metal seaming machines provide powerful, precise, and adaptable solutions for producing strong, reliable seams in a wide range of sheet metal fabrication applications. Their combination of hydraulic force, versatile tooling, and advanced control systems make them essential for manufacturers requiring high seam integrity and production efficiency.
Hydraulic sheet metal seaming machines operate by applying controlled hydraulic pressure through cylinders or rams that drive forming tools to fold or crimp metal sheet edges into secure seams. The hydraulic system allows for adjustable force settings, enabling the machine to handle a variety of material thicknesses and types while maintaining consistent seam quality. This flexibility is especially beneficial for thicker gauges or harder metals that require greater force than mechanical systems typically provide.
The machine’s tooling is carefully engineered to match specific seam profiles and material characteristics. Interchangeable dies and rolls facilitate quick changes between seam types, allowing manufacturers to switch production runs efficiently without extensive downtime. Tooling materials are often hardened and coated to resist wear and ensure long-lasting precision, even under high-pressure operations.
Automation plays a significant role in modern hydraulic seaming machines. Programmable controllers regulate hydraulic pressure, ram speed, and stroke length to optimize seam formation and minimize material stress or distortion. Sensors continuously monitor key parameters such as force, position, and cycle time, providing real-time feedback that enhances process consistency and helps detect potential faults early.
Material handling integration includes motorized feeding systems, alignment fixtures, and conveyors that ensure accurate positioning of sheets before and after seaming. Advanced systems may use vision-based alignment or laser guides to improve precision further, especially when dealing with complex or variable parts.
Safety measures are comprehensive due to the high forces involved. Machines incorporate guards around moving parts, emergency stop mechanisms, pressure relief valves to prevent overloading, and interlocks that disable operation during maintenance or tool changes. Ergonomic considerations in machine design help reduce operator fatigue and facilitate easier access for routine maintenance or troubleshooting.
Hydraulic sheet metal seaming machines are widely used in applications requiring durable, leak-proof joints that can withstand mechanical stress, environmental exposure, or pressure differentials. Industries such as HVAC ductwork, roofing panels, automotive assembly, and industrial containers rely on these machines to produce seams that meet stringent performance and quality standards.
In addition to strength and reliability, these machines offer consistent repeatability, enabling manufacturers to maintain tight tolerances and uniform seam appearance across large production volumes. Their ability to adapt to various seam designs and material specifications makes them a versatile and valuable asset in modern metal fabrication environments.
Maintenance of hydraulic seaming machines involves regular inspection of hydraulic components, seals, and tooling surfaces to ensure optimal performance. Preventive maintenance schedules and built-in diagnostics help avoid unexpected breakdowns and extend machine life. Quick-change tooling systems and modular hydraulic units further simplify upkeep and reduce downtime.
Overall, hydraulic sheet metal seaming machines combine powerful hydraulic actuation with precise tooling and advanced control systems to deliver efficient, high-quality seam production. Their robustness, adaptability, and integration capabilities make them essential equipment for manufacturers demanding strong, reliable sheet metal joints in diverse applications.
Advancements in hydraulic sheet metal seaming machines continue to enhance their precision, efficiency, and versatility. Modern machines increasingly feature servo-hydraulic systems that offer even finer control over force and speed compared to traditional hydraulic setups. This improvement allows for more delicate handling of thin or coated materials while still delivering the robust power needed for thicker metals.
Integration with digital control platforms and Industry 4.0 technologies is becoming standard, enabling remote monitoring, data collection, and predictive maintenance. Sensors embedded throughout the machine track parameters like hydraulic pressure, cycle counts, and tooling condition, feeding information to centralized control systems. This connectivity helps manufacturers optimize machine usage, prevent downtime, and maintain consistent seam quality.
Flexible automation solutions, such as robotic loading and unloading, are often combined with hydraulic seaming machines to further increase throughput and reduce manual labor. Automated part positioning and alignment systems improve seam accuracy and repeatability, particularly important when producing complex or custom-shaped components.
Safety innovations keep pace with increased automation and force levels. Advanced guarding systems, light curtains, and dual-control operations ensure operator protection while maintaining efficient production flow. User-friendly interfaces and augmented reality (AR) support tools assist operators and maintenance personnel in setup, troubleshooting, and training.
Hydraulic sheet metal seaming machines also benefit from ongoing developments in tooling materials and design. New coatings and surface treatments reduce friction and wear, extending tooling life and maintaining seam precision over longer production runs. Modular tooling designs facilitate rapid changeovers, helping manufacturers adapt quickly to shifting product demands.
Sustainability efforts are reflected in energy-efficient hydraulic components, such as variable displacement pumps and energy recovery systems, which lower power consumption and reduce environmental impact. Waste reduction is supported by improved process control and defect detection, minimizing scrap and rework.
In specialized applications, hydraulic seaming machines are capable of producing high-integrity seams that meet demanding industry standards for strength, corrosion resistance, and airtightness. This capability makes them indispensable in sectors like aerospace, automotive, and industrial equipment manufacturing.
In summary, hydraulic sheet metal seaming machines have evolved into highly sophisticated tools that blend powerful hydraulic actuation with precise control, automation, and digital integration. These advancements enable manufacturers to produce strong, consistent seams efficiently while adapting to diverse materials and complex seam designs, ensuring competitiveness in today’s dynamic fabrication landscape.
Sheet metal seaming machines for precision joining are specialized industrial tools engineered to create accurate, reliable seams between sheet metal components. These machines are essential in applications where tight tolerances, consistent seam integrity, and clean finishes are critical, such as in automotive manufacturing, aerospace assemblies, HVAC systems, and high-end appliance production.
Precision seaming machines employ various joining methods—including folding, crimping, hemming, and interlocking—to achieve strong mechanical bonds without compromising material strength or surface quality. Their designs often incorporate fine control mechanisms, such as servo-driven actuators, CNC-controlled tooling, and real-time sensor feedback, to ensure every seam meets exacting specifications.
These machines can handle a broad range of materials—from lightweight aluminum alloys to high-strength steels—and accommodate different sheet thicknesses by adjusting force, speed, and tooling configuration. The tooling itself is crafted with high precision, using hardened and coated components to maintain accuracy and longevity under repetitive use.
Automation is a key feature in precision seaming machines, integrating advanced control systems that monitor parameters like seam width, fold angle, and pressure during operation. Inline quality inspection tools, such as laser scanners and optical sensors, verify seam consistency and detect defects early, allowing immediate adjustments or part rejection to maintain high production standards.
Material handling systems—including automated feeders, alignment guides, and robotic handlers—support seamless workflow integration, reducing manual intervention and enhancing repeatability. Quick-change tooling and modular design further improve flexibility and minimize downtime when switching between product variants.
Safety is carefully addressed through protective enclosures, emergency stops, and interlocks, ensuring operators are safeguarded during high-force operations. Ergonomic considerations enhance usability and reduce operator fatigue, especially in continuous production environments.
Overall, sheet metal seaming machines for precision joining combine robust mechanical design with sophisticated control and inspection technologies to deliver consistently high-quality seams. Their ability to adapt to diverse materials and complex seam profiles makes them indispensable for manufacturers focused on precision, efficiency, and product reliability.
Precision sheet metal seaming machines operate by applying controlled mechanical force to fold, crimp, or interlock metal edges with exact accuracy. The process begins with the precise positioning of sheet components using automated feeders and alignment systems, ensuring that the edges to be joined are correctly oriented. As the machine cycles, servo motors or hydraulic actuators drive the tooling to perform the seam-forming action with tightly controlled speed, pressure, and timing.
Advanced control systems continuously monitor seam parameters such as fold angle, seam width, and applied force. Feedback from sensors allows real-time adjustments, maintaining consistent seam quality even when material properties vary slightly. This adaptability is crucial when working with high-strength or coated metals, where excessive force can cause deformation or surface damage.
Tooling in precision seaming machines is engineered for durability and repeatability, often incorporating hardened steel components with specialized coatings to minimize wear and friction. Modular tooling designs enable quick changes between different seam profiles or product specifications, reducing setup time and increasing production flexibility.
Integration with inline quality inspection equipment allows for immediate detection of seam defects, such as incomplete folds, gaps, or misalignments. Optical scanners, laser measurement devices, and pressure sensors provide detailed data that help operators or automated systems identify issues and take corrective actions promptly, minimizing scrap and rework.
Material handling plays a vital role in overall process efficiency. Automated conveyors, robotic arms, or gantry systems transport parts to and from the seaming station with high precision, reducing manual labor and ensuring repeatable positioning. This automation supports higher throughput and consistent seam results across large production runs.
Safety features are comprehensive and designed to protect operators without impeding productivity. Enclosures, interlock switches, emergency stop buttons, and light curtains prevent accidental contact with moving parts or high-force tooling. Ergonomic design considerations reduce operator fatigue during setup, maintenance, and operation, supporting sustained manufacturing performance.
Maintenance protocols typically involve regular inspection and lubrication of moving components, timely replacement of tooling parts, and calibration of control systems to maintain machine accuracy. Built-in diagnostics and predictive maintenance tools help identify potential issues before they cause downtime, contributing to reliable, continuous operation.
In summary, precision sheet metal seaming machines combine mechanical strength, sophisticated control, and automated quality assurance to deliver highly consistent, strong seams tailored to exacting industrial requirements. Their adaptability and reliability make them fundamental equipment for manufacturers prioritizing product quality and production efficiency.
Continuous improvements in precision sheet metal seaming machines focus on enhancing automation, control accuracy, and adaptability to diverse production needs. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies allows these machines to connect seamlessly with factory-wide systems, enabling real-time data exchange, remote monitoring, and advanced analytics. This connectivity supports predictive maintenance, process optimization, and quality traceability, helping manufacturers reduce downtime and improve overall equipment effectiveness.
Servo-driven actuation systems have become increasingly prevalent, offering finer control over seam formation by precisely regulating force, speed, and position throughout the seaming cycle. This level of control allows for delicate handling of advanced materials, including ultra-high-strength steels and coated metals, minimizing the risk of damage while ensuring seam integrity.
Modular machine designs and quick-change tooling systems facilitate rapid product changeovers, addressing the growing demand for shorter production runs and greater product variety. These features enable manufacturers to maintain high productivity while adapting quickly to new seam profiles or customer specifications.
Advanced in-line inspection technologies continue to evolve, employing high-resolution cameras, laser scanners, and ultrasonic sensors to detect microscopic seam defects in real time. Coupled with machine learning algorithms, these systems can automatically classify defects, trigger process adjustments, and improve overall yield without human intervention.
Material handling automation, including robotic loading and unloading, contributes to consistent part positioning and reduces operator fatigue. Collaborative robots (cobots) are increasingly employed for tasks such as tooling changes and part transfers, enhancing safety and flexibility within the production environment.
Safety systems have been enhanced with multi-level guarding, presence-sensing devices, and interlocks integrated directly into the control logic. User interfaces are designed for intuitive operation, often incorporating touchscreens, graphical diagnostics, and augmented reality (AR) support to guide operators through setup, troubleshooting, and maintenance procedures.
Energy efficiency is addressed through the use of variable frequency drives, energy recovery systems, and optimized hydraulic or electric actuation, lowering operational costs and environmental impact.
In conclusion, precision sheet metal seaming machines are advancing toward smarter, more flexible, and highly automated solutions. These developments empower manufacturers to produce superior seams with greater efficiency, adaptability, and quality assurance, meeting the complex demands of modern industrial production.
Sheet Metal Edge Seaming Machine
A sheet metal edge seaming machine is a specialized industrial device designed to join, fold, or crimp the edges of sheet metal components to create secure, precise seams. These machines are widely used in industries such as HVAC, roofing, automotive, and appliance manufacturing, where strong, leak-proof, and aesthetically consistent edge joints are essential.
The machine works by feeding sheet metal parts into a series of forming stations equipped with rolls, dies, or presses that progressively bend and lock the edges together. This process ensures a tight mechanical interlock without the need for welding or adhesives, preserving material properties and surface finishes.
Sheet metal edge seaming machines accommodate various seam types, including single lock, double lock, snap lock, and specialized custom seams tailored to specific product requirements. Adjustable tooling and roll configurations allow operators to switch between different seam profiles and material thicknesses, offering versatility and production flexibility.
Material handling systems integrated with these machines ensure precise alignment and feeding of sheet metal parts. Automated feeders, straighteners, and positioning guides maintain consistent part orientation and tension, minimizing defects like wrinkles, gaps, or misalignments in the seam.
Control systems typically feature programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or CNC interfaces that regulate seam pressure, roll speed, and forming sequence. Sensors monitor critical parameters such as seam tightness and material thickness in real-time, enabling process adjustments and quality assurance.
Robust construction with precision-machined components and hardened tooling ensures durability and consistent seam quality over long production runs. Quick-change tooling systems reduce setup times when switching between different products or seam types.
Safety features include guarding around moving parts, emergency stop functions, and interlocks to protect operators during high-force forming operations. Ergonomic machine design supports operator comfort and ease of maintenance.
In summary, sheet metal edge seaming machines provide efficient, reliable, and precise edge joining solutions for a wide range of metal fabrication applications. Their adaptability, automation capabilities, and robust construction make them indispensable in producing strong, high-quality seams that meet both functional and aesthetic requirements.
Sheet metal edge seaming machines operate by feeding metal sheets through a sequence of forming rollers or presses that progressively bend and interlock the edges to create a secure seam. The gradual shaping process minimizes stress on the material, reducing the risk of cracks or surface damage, which is especially important for coated or delicate metals. The machine’s feeding and guiding systems ensure that sheets remain properly aligned and under consistent tension to maintain seam uniformity throughout production.
Adjustable tooling and roll configurations enable operators to customize seam profiles for various applications, from simple single-lock seams used in ductwork to complex double-lock or snap-lock seams common in roofing and architectural panels. This flexibility allows manufacturers to quickly switch between product lines or accommodate different material thicknesses without compromising seam quality.
Automation is often incorporated to improve efficiency and consistency. Programmable control systems regulate roll pressure, forming speed, and seam dimensions, while sensors monitor process variables in real-time. These features help detect deviations early, allowing for immediate corrections or automatic machine stoppage to prevent defective output.
Integration with upstream and downstream equipment streamlines workflow. Automated feeders deliver sheets into the seaming machine with precise timing and positioning, and conveyors or robotic arms remove finished parts, reducing manual handling and increasing throughput. Vision systems or laser guides may also be used to verify seam alignment and detect surface defects inline.
Maintenance considerations include easy access to tooling for cleaning and replacement, as well as lubrication systems that prolong the life of moving components. Modular machine designs facilitate rapid tooling changes and minimize downtime during product transitions.
Safety remains a priority, with comprehensive guarding, emergency stops, and interlocks ensuring operator protection during operation and maintenance. Ergonomic controls and adjustable workstations improve operator comfort and reduce fatigue over extended production periods.
Overall, sheet metal edge seaming machines combine mechanical precision, automation, and robust construction to deliver strong, consistent seams essential for a variety of metal fabrication industries. Their adaptability and integration capabilities make them key assets for manufacturers focused on quality, efficiency, and flexibility.
Recent advancements in sheet metal edge seaming machines emphasize increased automation, precision control, and integration with smart manufacturing systems. Modern machines often utilize servo-driven motors and CNC technology to provide highly accurate adjustments of roll pressure, speed, and seam profile during operation. This dynamic control helps accommodate material variations and complex seam designs, improving product consistency and reducing scrap.
Connectivity to Industry 4.0 platforms allows real-time monitoring of machine performance, seam quality, and maintenance needs. Data collected through sensors and control systems enable predictive maintenance scheduling, minimizing unplanned downtime and extending equipment lifespan. Manufacturers can also analyze production data to optimize process parameters and improve overall efficiency.
Flexible tooling systems continue to evolve, with quick-change roll modules and adjustable forming stations reducing setup times and enabling rapid transitions between different seam types or product specifications. This adaptability supports shorter production runs and customized manufacturing without sacrificing throughput.
Enhanced material handling automation—including robotic loading/unloading and automated alignment systems—improves part positioning accuracy and reduces manual labor, further boosting productivity and seam quality. Inline inspection technologies, such as laser scanners and vision systems, provide immediate feedback on seam integrity and surface finish, allowing for quick corrective action.
Safety features have advanced with multi-level guarding, presence detection sensors, and integrated control interlocks, ensuring operator protection even in highly automated environments. User-friendly interfaces with touchscreens and diagnostic tools streamline operation and maintenance tasks.
Energy efficiency improvements, such as variable frequency drives and regenerative power systems, reduce operating costs and environmental impact. Additionally, machine designs increasingly focus on minimizing waste through precise forming and optimized material usage.
In summary, sheet metal edge seaming machines are becoming smarter, more flexible, and highly automated. These innovations enable manufacturers to produce high-quality, reliable seams efficiently while adapting quickly to changing production demands and maintaining stringent quality standards.
Metal Pipe Necking Machine
A metal pipe necking machine is an industrial device designed to reduce the diameter of one end of a metal pipe or tube, creating a tapered or “necked” section. This necking process is commonly used in manufacturing industries such as automotive, aerospace, HVAC, and furniture, where precise pipe ends are required for fitting, joining, or aesthetic purposes.
The machine operates by applying controlled mechanical force through rollers, dies, or hydraulic presses that gradually compress and reshape the pipe end. This deformation reduces the pipe’s outer diameter while maintaining wall thickness and structural integrity. Depending on the design, the necking process can produce various taper angles and lengths to meet specific application requirements.
Metal pipe necking machines can handle a wide range of pipe materials, including steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and other alloys. Adjustable tooling and forming parameters enable the machine to accommodate different pipe diameters, wall thicknesses, and material properties, ensuring consistent and accurate necking results.
Common machine configurations include rotary necking, where rollers rotate around the pipe to form the neck uniformly, and hydraulic or mechanical presses that squeeze the pipe end between shaped dies. Some machines incorporate servo-driven systems for precise control over forming speed and pressure, enhancing product quality and repeatability.
Material feeding and positioning systems help align pipes accurately before necking, often integrating with conveyors, feeders, or robotic handling for automated production lines. Sensors and control systems monitor critical parameters during operation, allowing real-time adjustments and ensuring compliance with dimensional tolerances.
Safety features such as guarding, emergency stops, and interlocks protect operators from moving parts and high-force mechanisms. Ergonomic designs facilitate easy loading, unloading, and maintenance.
In summary, metal pipe necking machines provide a reliable and precise method for shaping pipe ends to specified dimensions. Their adaptability, automation capabilities, and robust construction make them essential equipment for manufacturers requiring high-quality necked pipe components in various industrial applications.
Metal pipe necking machines function by progressively applying force to the pipe end, gradually reducing its diameter while controlling the pipe’s wall thickness to prevent cracking or deformation. The process typically involves multiple forming stages, where each stage incrementally shapes the pipe to achieve the desired neck profile. This staged approach helps maintain material integrity and ensures uniformity around the circumference.
The machines use precision tooling such as rollers, mandrels, or dies, which are often adjustable or interchangeable to accommodate various pipe sizes and necking specifications. In rotary necking systems, rollers rotate around the pipe, exerting radial pressure evenly to produce smooth, consistent necks. Hydraulic or mechanical press systems apply axial or radial force through custom-shaped dies to compress and reshape the pipe end accurately.
Control systems integrated into modern necking machines monitor parameters like forming force, speed, and position, often using servo motors for fine adjustments. Real-time feedback from sensors enables the machine to compensate for material inconsistencies or variations in pipe dimensions, improving repeatability and reducing scrap rates.
Automated material handling is commonly paired with pipe necking machines to increase throughput and reduce manual labor. Feeding mechanisms align and position pipes precisely before forming, while conveyors or robotic arms handle finished parts for further processing or packaging. These integrations facilitate continuous production and minimize operator intervention.
Safety mechanisms are critical due to the high forces and moving components involved. Machines are equipped with protective guarding, emergency stop functions, and safety interlocks to prevent accidental contact and ensure operator protection. Ergonomic considerations also improve accessibility for loading, unloading, and maintenance tasks.
Maintenance routines focus on inspecting and lubricating tooling components, checking hydraulic or mechanical systems, and calibrating control electronics to sustain machine accuracy and reliability. Modular tooling and quick-change features reduce downtime during size or profile changes.
Metal pipe necking machines serve a vital role in industries requiring precise pipe end modifications for joining, assembly, or aesthetic purposes. Their robust design, combined with advanced control and automation features, enables efficient, high-quality production of necked pipe components that meet stringent dimensional and performance standards.
Recent developments in metal pipe necking machines emphasize enhanced automation, precision, and flexibility to meet diverse manufacturing demands. The integration of servo-driven systems allows for precise control over forming speed, pressure, and tool positioning, which is especially beneficial when working with high-strength alloys or thin-walled pipes that require delicate handling to avoid defects.
Modern machines often include programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and touchscreen interfaces that enable easy setup, parameter adjustments, and real-time monitoring of the necking process. This digital control facilitates quick changeovers between different pipe sizes and neck profiles, reducing downtime and increasing production efficiency.
Advanced sensor technology provides continuous feedback on forming force, pipe alignment, and dimensional accuracy, allowing the machine to automatically compensate for material variations or irregularities. This results in consistent, high-quality necked ends with minimal scrap.
Automation extends beyond the necking process itself, with robotic loading and unloading systems improving throughput and minimizing manual handling. Integration with upstream and downstream equipment creates seamless production lines for pipes, enhancing overall workflow and productivity.
Safety enhancements include comprehensive guarding, light curtains, emergency stop systems, and interlocks that ensure operator protection during high-force operations. Ergonomic machine designs facilitate ease of access for maintenance, tooling changes, and part handling.
Materials handled by these machines continue to expand, with capabilities now including exotic alloys and composite pipes used in aerospace and specialized industrial applications. Tooling innovations, such as modular dies and wear-resistant coatings, support longer service life and easier maintenance.
Energy efficiency improvements, such as variable frequency drives and optimized hydraulic systems, reduce power consumption and environmental impact. Furthermore, integration with Industry 4.0 frameworks enables data collection and analytics, supporting predictive maintenance and continuous process optimization.
Overall, metal pipe necking machines have evolved into sophisticated, highly adaptable equipment combining robust mechanical design with advanced control, automation, and safety features. These advancements empower manufacturers to produce precise, reliable necked pipe ends efficiently across a wide range of materials and applications.
Beyond core functionality, metal pipe necking machines increasingly incorporate smart technologies that enhance operational intelligence and production insights. Real-time data analytics track forming parameters, cycle times, and tooling wear, enabling operators and maintenance teams to make informed decisions that optimize machine performance and lifespan.
Predictive maintenance systems analyze sensor data to forecast component fatigue or failure before breakdowns occur, reducing unplanned downtime and maintenance costs. This proactive approach also extends tooling life by preventing overuse or operating outside optimal parameters.
Customization options have expanded, with machines capable of producing complex neck geometries such as stepped or tapered profiles, flanges, or grooved ends. These specialized shapes are essential in applications ranging from automotive exhaust systems to hydraulic cylinders and aerospace tubing.
Hybrid machines combining necking with additional forming processes—like flaring, swaging, or beading—offer integrated solutions that streamline production workflows and minimize handling between steps. Such multifunctional systems reduce equipment footprint and improve overall efficiency.
Environmental considerations drive machine designs that minimize waste through precision forming and reduced scrap. Energy-saving features, including regenerative drives and efficient hydraulic circuits, contribute to greener manufacturing practices.
User interfaces now often support remote access and control, allowing technicians to monitor and adjust machine operations from off-site locations. This capability is particularly valuable for global manufacturing facilities seeking centralized management or rapid troubleshooting.
Training and support tools increasingly leverage augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies to assist operators in setup, maintenance, and troubleshooting, improving safety and reducing errors.
In essence, metal pipe necking machines have transformed from purely mechanical devices into intelligent, connected systems. Their evolution reflects broader trends in manufacturing toward automation, digitalization, and sustainability, enabling producers to meet stringent quality standards while optimizing productivity and operational costs.
Sheet Metal Embossing Machine
A sheet metal embossing machine is an industrial device designed to create raised or recessed patterns, textures, or designs on sheet metal surfaces by pressing the metal between matched male and female dies. This process enhances the aesthetic appeal, structural rigidity, or functional properties of metal sheets and is widely used in industries like automotive, architecture, appliances, and decorative metalwork.
The machine operates by feeding flat sheet metal into the embossing press, where a hydraulic, mechanical, or servo-driven ram forces the sheet between the embossing dies. The dies imprint detailed patterns onto the metal surface by plastic deformation without significantly thinning or damaging the material. Depending on the design, embossing can be shallow or deep, uniform or varied across the sheet.
Sheet metal embossing machines accommodate a variety of metals, including steel, aluminum, copper, and stainless steel, and can handle different thicknesses by adjusting pressure, die design, and press parameters. The dies are typically precision-machined from hardened tool steel to ensure consistent, high-quality embossing over long production runs.
Automation features such as programmable controls, automated feeders, and material straighteners improve production speed and repeatability. Sensors monitor sheet positioning, embossing pressure, and cycle timing to maintain accuracy and reduce scrap. Some machines integrate inline quality inspection systems that detect defects like misalignment or incomplete embossing.
Safety measures include guarding around moving parts, emergency stops, and interlocks to protect operators. Ergonomic designs facilitate easy loading, unloading, and die changes, reducing operator fatigue and downtime.
In summary, sheet metal embossing machines combine precise mechanical force, durable tooling, and advanced controls to produce decorative or functional surface patterns efficiently and consistently. Their versatility and quality make them essential in many metal fabrication processes requiring enhanced surface characteristics.
Sheet metal embossing machines function by progressively feeding metal sheets into a press where matched embossing dies imprint patterns through controlled pressure. The metal undergoes plastic deformation as it conforms to the die contours, creating raised or recessed designs without compromising overall sheet integrity. To ensure uniform embossing, the machines use precise material handling systems, including feeders and straighteners, which maintain sheet alignment and tension during the process.
The dies are engineered to withstand high pressures and repetitive cycles, often crafted from hardened tool steel with specialized coatings to minimize wear and maintain surface quality. Depending on the application, embossing depth and pattern complexity can be adjusted by selecting appropriate die geometries and fine-tuning press force and speed.
Automation enhances production efficiency, with programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and CNC interfaces regulating press operations. Sensors track sheet position, embossing pressure, and cycle timing, enabling real-time adjustments to maintain consistent embossing quality. Inline inspection systems such as cameras or laser scanners may be incorporated to detect defects early and reduce scrap rates.
Material versatility is significant; embossing machines can handle a broad range of metals, from soft aluminum to harder steels, as well as varying thicknesses. This adaptability allows manufacturers to produce embossed sheets for diverse sectors like automotive trim, decorative panels, packaging, and appliance facades.
Maintenance and tooling changeovers are designed to be straightforward, with modular die sets and accessible press components facilitating quick swaps and minimizing downtime. Lubrication systems and cooling mechanisms help prolong die life and prevent overheating during continuous operation.
Operator safety is paramount, with comprehensive guarding, emergency stop functions, and interlocks protecting against accidental contact with moving parts. Ergonomic considerations support efficient workflow and reduce operator fatigue, especially during repetitive tasks.
Overall, sheet metal embossing machines are critical for adding texture, strength, or aesthetic detail to metal sheets efficiently and reliably. Their combination of mechanical precision, durable tooling, and automated controls enables consistent production of high-quality embossed metal components across a wide range of industrial applications.
Recent advancements in sheet metal embossing machines focus on improving precision, flexibility, and integration with smart manufacturing systems. Servo-driven presses have become increasingly common, offering superior control over embossing force, speed, and position compared to traditional mechanical or hydraulic presses. This enhanced control enables delicate handling of thin or coated materials, reducing the risk of damage while achieving complex or finely detailed embossing patterns.
Automation and digital control systems allow operators to program and adjust embossing parameters easily, enabling rapid changeovers between different patterns and materials. Integration with Industry 4.0 platforms facilitates real-time monitoring, data collection, and predictive maintenance, helping manufacturers optimize machine performance, reduce downtime, and maintain consistent product quality.
Material handling automation, including robotic loading and unloading, further streamlines production by minimizing manual intervention and ensuring precise sheet positioning. Inline quality inspection technologies such as high-resolution cameras and laser scanners detect embossing defects instantly, allowing for immediate corrective action and minimizing scrap.
Tooling innovations, such as modular die systems and advanced surface coatings, extend die life and simplify maintenance. Some machines now support hybrid processes that combine embossing with other forming or cutting operations in a single press cycle, enhancing manufacturing efficiency and reducing handling steps.
Energy efficiency improvements, including variable frequency drives and regenerative systems, reduce power consumption and environmental impact. Enhanced safety features with comprehensive guarding, light curtains, and integrated interlocks ensure operator protection without compromising productivity.
Ergonomic design elements improve operator comfort and ease of use, especially important in high-volume production environments. Training tools leveraging augmented reality (AR) assist operators and technicians in setup, troubleshooting, and maintenance tasks, reducing errors and downtime.
In summary, sheet metal embossing machines continue to evolve into highly sophisticated, flexible, and connected equipment. These advancements empower manufacturers to produce complex, high-quality embossed metal products efficiently while adapting quickly to changing market demands and maintaining rigorous quality standards.
Sheet Metal Roll Bending Machine
A sheet metal roll bending machine is an industrial tool designed to bend and shape flat metal sheets into curved or cylindrical forms by passing them through a series of rotating rolls. Commonly used in metal fabrication, manufacturing, and construction industries, this machine enables the production of components such as pipes, tanks, drums, curved panels, and architectural elements with precise radii and smooth surfaces.
The machine typically consists of three or more rollers arranged horizontally: two lower rolls and one or two upper rolls. The metal sheet is fed between these rolls, and by adjusting the position and pressure of the upper rolls, the sheet is gradually bent as it passes through. This rolling action applies controlled deformation, allowing the operator to achieve the desired curvature without causing wrinkles, cracks, or surface damage.
Sheet metal roll bending machines can handle a variety of metals, including steel, aluminum, stainless steel, and copper, across a wide range of thicknesses and widths. The machine’s rolls are made from hardened steel or other durable materials to withstand high pressures and provide consistent bending quality.
Modern roll bending machines often feature hydraulic or servo-driven adjustments for roll positioning and pressure control, allowing precise bending radius settings and repeatability. Some models include CNC controls to automate the bending process, enabling complex shapes and multiple bends with high accuracy and reduced operator intervention.
Material handling systems, such as powered feeders and alignment guides, help ensure accurate sheet feeding and positioning for consistent bends. Additionally, some machines integrate with downstream fabrication equipment for streamlined production workflows.
Safety features include guarding around moving parts, emergency stops, and overload protection systems to safeguard operators during operation. Ergonomic designs facilitate easier loading, adjustment, and maintenance.
In summary, sheet metal roll bending machines provide a versatile and efficient solution for forming curved metal parts with precision and smooth finishes. Their combination of mechanical robustness, control accuracy, and automation capabilities makes them essential equipment in many metalworking industries.
Sheet metal roll bending machines work by feeding flat metal sheets between multiple rollers that apply gradual pressure to bend the material into the desired curvature. The process relies on controlled deformation, where the adjustable rolls—usually arranged with two or three configurations—compress the metal progressively, preventing damage such as cracking or wrinkling. Operators can fine-tune the position and pressure of the rolls to achieve precise bending radii, whether forming simple cylinders, cones, or more complex curved shapes.
The machine’s rolls are precision-engineered and often made from hardened steel or alloy materials to ensure durability and maintain consistent bending quality over prolonged use. Roll surfaces may be coated or polished to protect the metal sheets from scratches or surface imperfections during processing. The roll diameter and spacing are designed to accommodate a range of sheet thicknesses and widths, offering versatility across different material types and project requirements.
Modern roll bending machines incorporate hydraulic or servo-driven systems for adjusting roll positions and pressures with high accuracy. CNC controls are frequently employed to automate the bending process, allowing operators to input desired bend parameters and execute repeatable, complex bending sequences with minimal manual intervention. This automation improves productivity and reduces the risk of errors.
Material handling features such as motorized feeders, alignment guides, and straighteners ensure the metal sheet enters the roll bending section smoothly and accurately positioned. This consistency is critical for producing uniform bends and maintaining dimensional tolerances. Some systems also include back gauges or sensors to monitor bend angles and provide real-time feedback for quality control.
Safety is a key consideration in roll bending machine design. Protective guarding around the moving rolls, emergency stop buttons, and overload sensors help prevent accidents and equipment damage. Ergonomic features, including adjustable controls and accessible maintenance points, contribute to operator comfort and efficient machine servicing.
Maintenance routines typically involve regular inspection and lubrication of rollers, bearings, and drive systems to ensure smooth operation and prolong machine life. Quick-change roll sets or modular components may be available to facilitate setup changes for different bending tasks, minimizing downtime.
Overall, sheet metal roll bending machines combine mechanical strength, precision control, and automation to deliver efficient and reliable metal forming solutions. Their ability to produce smooth, accurate curves on a variety of metals makes them indispensable tools in manufacturing sectors such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and industrial equipment production.
Advancements in sheet metal roll bending machines continue to focus on increasing precision, automation, and versatility. Modern machines often feature multi-roll configurations, such as four or five-roll systems, which provide enhanced control over the bending process, allowing for more complex shapes like conical sections or variable-radius bends. These additional rolls help distribute pressure more evenly and reduce springback, improving dimensional accuracy.
Integration with advanced CNC controls and touchscreen interfaces enables operators to program detailed bending sequences, store multiple job setups, and execute rapid changeovers. This reduces setup times and increases productivity, especially for manufacturers dealing with varied production runs or custom parts.
Servo-hydraulic and electric servo drives replace traditional hydraulic systems in many machines, offering smoother, more energy-efficient operation with greater control over roll movement and pressure. These systems contribute to improved repeatability and reduce maintenance requirements.
Material handling automation, including robotic loading and unloading, conveyors, and automated alignment systems, further streamlines production by minimizing manual labor and ensuring consistent part positioning. Inline sensors and feedback loops monitor bending angles and sheet positioning in real-time, allowing automatic adjustments to maintain quality and reduce scrap.
Safety remains a priority, with modern machines equipped with multi-level guarding, light curtains, emergency stop functions, and integrated safety interlocks. Ergonomic design enhancements, such as adjustable operator stations and simplified control layouts, improve usability and reduce operator fatigue during extended shifts.
Tooling innovations include quick-change rolls and modular components that can be swapped or reconfigured rapidly to accommodate different material types, thicknesses, or bend profiles. Surface treatments and coatings on rolls help extend tooling life by reducing wear and preventing corrosion.
Energy efficiency improvements, like regenerative drives that recover braking energy, lower operational costs and environmental impact. Some roll bending machines are also designed to integrate seamlessly with broader Industry 4.0 systems, enabling data collection, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance.
In summary, sheet metal roll bending machines have evolved into highly sophisticated, flexible, and automated systems. These advancements empower manufacturers to produce precise, complex curved components efficiently while maintaining high quality and adapting quickly to changing production demands.
Sheet Metal Hemming Machine
A sheet metal hemming machine is specialized equipment used in metal fabrication to fold and secure the edges of sheet metal parts by bending the flange over onto itself or another surface. This process creates a smooth, rounded edge or seam that enhances the strength, appearance, and safety of metal components. Hemming is commonly employed in automotive body panels, appliance manufacturing, HVAC ductwork, and various other industries requiring clean, durable edge finishes.
The hemming machine typically operates by clamping the sheet metal part and then using a series of precision dies and rollers or presses to gradually fold the flange over in controlled stages. This multi-step approach minimizes material stress and prevents cracking, wrinkling, or deformation during hemming. Depending on the design, hemming machines can perform different types of hems, including open hems, closed hems, and overlapping hems, to meet specific product requirements.
Modern sheet metal hemming machines incorporate hydraulic or servo-driven systems to provide consistent force and precise control over bending speed and angle. CNC controls allow operators to program hemming sequences, adjust parameters for different part geometries and materials, and ensure repeatable, high-quality results across production runs.
Material handling features such as automated feeders, clamps, and positioning systems improve accuracy and efficiency by ensuring consistent part placement and reducing manual handling. Some hemming machines integrate with robotic arms or conveyor systems for fully automated operation within a production line.
The tooling used in hemming machines consists of interchangeable dies and rollers made from hardened steel or other durable materials, designed to withstand repetitive bending forces while maintaining dimensional accuracy. Quick-change tooling systems enable rapid setup for different part types, supporting flexible manufacturing.
Safety considerations include protective guarding around moving components, emergency stop mechanisms, and interlocks to prevent accidental operation during maintenance. Ergonomic designs assist operators with loading, unloading, and machine controls, reducing fatigue and improving workflow.
In summary, sheet metal hemming machines combine precise mechanical action, advanced control systems, and robust tooling to produce strong, aesthetically pleasing hems efficiently and reliably. Their adaptability and automation capabilities make them essential in industries demanding high-quality edge finishing for sheet metal products.
Sheet metal hemming machines work by securely holding the metal part in place while progressively folding the flange edge through a series of controlled bending operations. The hemming process is often divided into multiple stages—such as pre-bending, final hemming, and sometimes flanging—to ensure the metal flows smoothly without cracking or wrinkling. This staged approach is particularly important when working with high-strength or coated materials, which can be more susceptible to damage if bent too abruptly.
The machine’s clamping system is critical for maintaining precise alignment and preventing part movement during hemming. Hydraulic or servo-driven clamps provide adjustable pressure to accommodate varying part sizes and shapes. Simultaneously, hemming rollers or dies apply consistent bending force along the flange, guided by programmable controls that regulate speed, angle, and pressure for optimal results.
Automation plays a significant role in modern hemming machines. CNC control systems allow operators to set customized hemming profiles and save multiple programs for different parts, improving repeatability and reducing setup time. Integrated sensors monitor parameters such as bend angle, force, and part position, providing real-time feedback that helps maintain seam quality and detect defects early.
Material handling automation, including feeders, conveyors, and robotic arms, facilitates smooth part transfer into and out of the hemming station, increasing throughput and minimizing manual labor. Vision systems or laser alignment tools may be used to ensure exact part placement before hemming begins, which is essential for maintaining dimensional tolerances.
Tooling components are typically made from hardened, wear-resistant materials to withstand repeated bending forces and maintain precise geometries. Quick-change tooling systems enable rapid adaptation to different flange sizes or part designs, reducing downtime and enhancing flexibility in production.
Safety features are incorporated throughout the machine, including guards to shield operators from moving parts, emergency stop buttons, and interlocks that disable operation during tool changes or maintenance. Ergonomic machine layouts help reduce operator fatigue and facilitate easier access for loading, unloading, and servicing.
Regular maintenance involves inspecting and lubricating mechanical components, checking hydraulic or servo systems, and monitoring tooling wear to ensure consistent performance and prevent unexpected downtime. Some machines include built-in diagnostics and alerts to support proactive maintenance practices.
Overall, sheet metal hemming machines provide efficient, precise, and repeatable methods for creating strong, smooth edges on metal parts. Their combination of robust mechanical design, advanced automation, and flexible tooling makes them indispensable in industries where high-quality sheet metal finishing is critical.
Continuous improvements in sheet metal hemming machines focus on increasing automation, precision, and integration within smart manufacturing environments. Servo-electric and servo-hydraulic actuation systems have become more prevalent, offering finer control over hemming speed, force, and positioning compared to traditional hydraulic setups. This allows for gentler handling of advanced high-strength steels and coated materials, reducing defects such as cracking or surface damage.
Advanced CNC controls and user-friendly interfaces enable operators to program complex hemming sequences, store multiple job recipes, and make quick adjustments for different part geometries or materials. This capability supports flexible manufacturing and rapid changeovers, which are essential for meeting diverse customer demands and shorter production runs.
Automation integration extends to robotic loading and unloading systems, automated clamping, and inline inspection tools. Vision-based alignment systems ensure precise part placement before hemming, while real-time sensors monitor bend angle, force, and part deformation to maintain consistent quality. Inline defect detection allows immediate correction or rejection of non-conforming parts, minimizing scrap.
Tooling technology advances include modular hemming dies and rollers with wear-resistant coatings, increasing tooling life and simplifying maintenance. Quick-change tooling systems reduce downtime during product transitions, enhancing overall productivity.
Energy efficiency improvements, such as regenerative drives and optimized hydraulic circuits, reduce power consumption and environmental impact. Safety systems have evolved with multi-level guarding, light curtains, emergency stop features, and operator presence sensors to ensure safe operation without compromising productivity.
Ergonomic considerations support operator comfort and efficiency, incorporating adjustable controls, easy access points for maintenance, and intuitive human-machine interfaces. Training and support tools leveraging augmented reality (AR) help operators with setup, troubleshooting, and routine maintenance.
In summary, modern sheet metal hemming machines have transformed into sophisticated, automated systems that combine precise mechanical action with intelligent controls and safety features. These advancements enable manufacturers to produce high-quality, consistent hems efficiently while adapting quickly to changing production needs and maintaining stringent quality standards.
Small Deep Drawing Press
A small deep drawing press is a compact industrial machine designed to form sheet metal blanks into complex, hollow-shaped components through the deep drawing process. Deep drawing involves pulling a flat metal sheet into a die cavity using a punch, causing the material to stretch and take the shape of the die without fracturing. Small deep drawing presses are commonly used in manufacturing small to medium-sized parts such as kitchenware, automotive components, electrical enclosures, and decorative items.
These presses typically have a lower tonnage capacity compared to larger deep drawing presses but maintain high precision and control suitable for intricate, delicate parts. The press applies a controlled downward force via a punch onto the sheet metal positioned over the die, which shapes the metal by plastic deformation. Blank holders or restrainers are used to control material flow and prevent wrinkling or tearing during the drawing operation.
Small deep drawing presses come in various configurations, including mechanical, hydraulic, and servo-electric models. Mechanical presses are known for their high speed and repeatability, hydraulic presses offer adjustable force and stroke control for versatility, and servo-electric presses provide precise positioning, energy efficiency, and programmability.
Modern small deep drawing presses often feature CNC control systems that allow operators to set parameters such as stroke length, punch speed, and holding force with high accuracy. These controls enable consistent part quality and accommodate different materials, thicknesses, and geometries.
The machines are equipped with tooling sets—including punches, dies, and blank holders—customized for each specific part design. Tooling materials are chosen for durability and precision, often incorporating hardened steel components with coatings to extend life and reduce friction.
Safety measures in small deep drawing presses include protective guards, emergency stops, light curtains, and two-hand control systems to prevent operator injury. Ergonomic design facilitates easy loading, unloading, and maintenance.
In summary, small deep drawing presses provide manufacturers with precise, reliable, and efficient equipment to produce detailed, hollow sheet metal parts in limited spaces or for smaller-scale production needs. Their combination of controlled force application, automation, and flexible tooling makes them valuable in diverse fabrication environments.
Small deep drawing presses operate by applying a controlled downward force through a punch onto a sheet metal blank placed over a die cavity. The metal is drawn into the die as the punch descends, stretching the material into the desired hollow shape without cracking or wrinkling. To control the flow of the metal during forming, blank holders or pressure pads apply force around the sheet’s perimeter, preventing excessive material movement that could cause defects.
The press stroke and speed are carefully controlled to optimize material flow and ensure uniform wall thickness in the drawn part. Mechanical presses provide consistent, high-speed cycles ideal for high-volume production of small parts, while hydraulic and servo-electric presses offer variable speed and force control suited for complex or sensitive materials.
CNC controllers enable precise adjustment of process parameters such as punch position, force, and dwell time, ensuring repeatable results and the flexibility to switch between different part designs quickly. Integration with automated feeding and part handling systems further enhances productivity by reducing manual intervention and improving cycle times.
Tooling plays a crucial role, with punch and die sets custom-designed to match part geometries and material properties. Tool surfaces are often coated or treated to reduce friction and wear, extending service life and maintaining dimensional accuracy. Quick-change tooling systems are common in small deep drawing presses to facilitate rapid transitions between jobs.
Safety features protect operators from high-force moving components. These include light curtains, interlocks, emergency stops, and two-hand operation controls to prevent accidental engagement. Ergonomically designed workstations improve operator comfort and reduce fatigue during repetitive tasks.
Maintenance routines focus on inspecting and lubricating moving parts, checking hydraulic or servo systems, and monitoring tooling condition. Some presses incorporate built-in diagnostics to alert operators to potential issues before they cause downtime.
Overall, small deep drawing presses offer precise and reliable forming solutions for producing detailed, hollow sheet metal components. Their versatility, compact footprint, and advanced controls make them well-suited for industries requiring quality parts in limited production spaces or for smaller batch sizes.
Advancements in small deep drawing presses emphasize enhanced control, automation, and energy efficiency to meet evolving manufacturing demands. Servo-electric drives have gained popularity due to their precise control over stroke speed, position, and force, combined with reduced energy consumption compared to traditional hydraulic or mechanical systems. This precision allows delicate handling of advanced materials such as high-strength steels and aluminum alloys, minimizing defects like cracking or thinning.
Modern presses feature sophisticated CNC controls with intuitive touchscreens, enabling operators to program complex forming sequences, store multiple part recipes, and quickly adjust parameters for different jobs. This flexibility supports shorter production runs and rapid changeovers, essential for customized or just-in-time manufacturing.
Automation integration includes robotic loading and unloading systems, automated blank feeding, and part ejection mechanisms, which improve throughput and reduce manual labor. Inline sensors monitor force, position, and material behavior during forming, providing real-time feedback for quality assurance and early detection of issues such as wrinkles or splits.
Tooling technology continues to evolve with advanced materials, coatings, and modular designs that extend tool life and simplify maintenance. Quick-change tooling systems reduce setup times and enable faster transitions between different part geometries.
Safety is enhanced through multi-level guarding, light curtains, two-hand operation controls, and emergency stop systems that protect operators without hindering productivity. Ergonomic design improvements support operator comfort and accessibility for maintenance and tooling changes.
Energy-saving features such as regenerative braking, optimized drive systems, and intelligent standby modes contribute to lower operating costs and environmental impact. Connectivity to Industry 4.0 platforms allows remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven process optimization.
In summary, small deep drawing presses have transformed into highly adaptable, efficient, and intelligent machines. These advancements enable manufacturers to produce high-quality, complex sheet metal parts reliably while responding quickly to changing production needs and maintaining stringent quality standards.
Sheet Metal Offset Bending Machine
A sheet metal offset bending machine is a specialized piece of equipment designed to create precise bends at multiple angles along a metal sheet, producing offset or stepped bends. This forming process is commonly used in fabrication applications where sheet metal parts require complex profiles, such as in HVAC ducts, electrical enclosures, automotive panels, and architectural components.
The machine operates by clamping the sheet metal and using a ram or punch to press the material against a die, creating a bend at a specific location. For offset bends, the machine performs sequential bends in opposite directions separated by flat sections, forming a step or offset in the sheet. The ability to create these multiple bends in a controlled manner enables the production of parts that fit together or accommodate other components within assemblies.
Sheet metal offset bending machines are typically mechanical, hydraulic, or servo-electric, each offering different advantages in terms of speed, precision, and flexibility. Hydraulic and servo-electric models provide adjustable bending force and stroke control, which are beneficial for handling a variety of material thicknesses and types, including steel, aluminum, and stainless steel.
CNC control systems are often integrated to program complex bending sequences, including precise bend angles, lengths, and offsets. This automation enhances repeatability and reduces setup time, allowing manufacturers to efficiently produce varied or customized parts.
The tooling consists of punches and dies configured for the specific bend radius and offset dimensions required. Tooling materials are chosen for durability and precision, often featuring hardened steel with surface treatments to extend service life.
Material handling systems, such as clamps and back gauges, ensure consistent positioning and alignment of the sheet during bending, improving accuracy and reducing errors. Some machines also incorporate sensors to monitor bending force and position, providing real-time feedback for quality control.
Safety features include guarding around moving parts, emergency stop buttons, and interlocks to protect operators during machine operation. Ergonomic design considerations facilitate easier loading, unloading, and adjustment of tooling.
In summary, sheet metal offset bending machines provide an efficient and precise method for producing stepped bends in sheet metal components. Their combination of robust mechanical design, advanced controls, and versatile tooling makes them essential in industries requiring complex sheet metal profiles.
Sheet metal offset bending machines operate by clamping the metal sheet securely and then applying force through a punch or ram to create a bend at a specific point. For offset bends, the machine performs a series of bends in alternating directions separated by flat sections, effectively forming a stepped profile. This sequential bending process requires precise control over bend angles, distances between bends, and material positioning to ensure consistent and accurate offsets.
The machine’s tooling system plays a crucial role in achieving high-quality bends. Punches and dies are custom-designed based on the desired offset dimensions and bend radii, with materials and surface treatments selected to withstand repetitive forming forces and reduce wear. Adjustable tooling setups allow the machine to accommodate different sheet thicknesses, materials, and bend configurations.
Automation and CNC control systems enhance the machine’s flexibility and precision by enabling operators to program detailed bending sequences, including exact angles, lengths, and offsets. Real-time feedback from sensors monitoring force, position, and material behavior allows for dynamic adjustments during operation, minimizing defects such as cracking, springback, or uneven bends.
Material handling features, such as back gauges, clamps, and alignment guides, ensure the sheet metal is positioned accurately for each bend. This consistency is vital for producing parts that meet tight tolerances and fit precisely in assembly applications. Some machines integrate with upstream feeding and downstream handling equipment to streamline production workflows and improve throughput.
Safety considerations include protective guarding, emergency stop mechanisms, and interlocks that prevent operation during maintenance or tooling changes. Ergonomic design supports easier part loading, tooling adjustments, and operator comfort during extended use.
Maintenance practices focus on regular inspection and lubrication of moving parts, monitoring tooling condition, and calibrating control systems to sustain machine performance and bending accuracy. Modular tooling systems simplify changeovers and reduce downtime when switching between different parts or bend requirements.
Overall, sheet metal offset bending machines provide a reliable and efficient solution for producing complex, stepped bends in sheet metal components. Their combination of mechanical strength, precise control, and automation capabilities makes them indispensable in manufacturing environments demanding consistent, high-quality offset bends.
Recent advancements in sheet metal offset bending machines emphasize greater automation, precision, and integration with digital manufacturing systems. Servo-electric and hydraulic drives offer enhanced control over ram speed, position, and bending force, enabling smoother bends and reducing material stress. This is especially important when working with advanced high-strength materials or thin gauges that require delicate handling to avoid cracking or distortion.
Modern machines incorporate CNC controls with user-friendly interfaces, allowing operators to program complex bending sequences involving multiple offsets, varying angles, and custom dimensions. This flexibility supports quick changeovers and accommodates small batch or customized production runs without sacrificing accuracy or efficiency.
Sensor technology plays a vital role in real-time monitoring of bending parameters such as force, position, and part alignment. Feedback loops enable the machine to automatically adjust during operation, ensuring consistent quality and minimizing scrap rates. Inline inspection systems may also be integrated to detect bending defects early in the process.
Material handling automation, including powered back gauges, motorized clamps, and robotic loading/unloading, streamlines workflow and reduces manual labor. These systems improve part positioning accuracy and boost throughput, especially in high-volume or continuous production environments.
Tooling advancements feature modular, quick-change components with wear-resistant coatings, extending tool life and simplifying maintenance. Some machines offer adaptive tooling systems capable of adjusting to different bend radii or sheet thicknesses without extensive manual intervention.
Safety remains a priority with multi-layer guarding, emergency stops, light curtains, and interlocks to protect operators from high-force moving parts. Ergonomic design enhancements reduce operator fatigue and improve accessibility for tooling changes and maintenance.
Energy-efficient components, such as variable frequency drives and regenerative systems, lower power consumption and reduce environmental impact. Connectivity with Industry 4.0 platforms allows remote monitoring, data analytics, and predictive maintenance, helping manufacturers optimize machine uptime and production quality.
In summary, sheet metal offset bending machines have evolved into highly automated, precise, and flexible equipment. These innovations enable manufacturers to produce complex offset bends efficiently, reliably, and with consistent quality while adapting to diverse production demands and maintaining stringent safety and environmental standards.
Channel Sheet Metal Bending Machine
A channel sheet metal bending machine is specialized equipment designed to bend flat sheet metal into channel-shaped profiles with precise angles and consistent dimensions. These channel bends, often U-shaped or C-shaped, are widely used in structural applications, framing, construction, automotive parts, and various fabrication projects requiring strong, uniform bends.
The machine works by clamping the sheet metal securely while applying force through a bending beam, ram, or punch to form the sheet around a shaped die or former. The metal is plastically deformed to take on the channel shape, with the bending angle and radius controlled through adjustable tooling and press settings.
Channel sheet metal bending machines come in various configurations, including mechanical, hydraulic, and servo-electric presses. Hydraulic and servo-driven systems provide adjustable pressure, stroke control, and precise positioning, enabling accurate bends in a range of materials and thicknesses.
CNC controls are often integrated to program bend sequences, angles, and tooling movements, allowing for repeatable production and quick changeovers between different channel profiles. This automation enhances productivity and consistency, especially in batch or custom manufacturing.
The tooling typically consists of a V-shaped or custom contoured punch and matching die designed for the specific channel dimensions. Tooling materials are hardened and treated for durability and to maintain tight tolerances over prolonged use.
Material handling features such as clamps, back gauges, and automated feeders ensure consistent sheet positioning and alignment during bending. Some machines include sensors for real-time monitoring of bending force and angle, providing quality control feedback and minimizing defects like springback or distortion.
Safety measures include guarding around moving parts, emergency stop functions, and interlocks to protect operators during operation and maintenance. Ergonomic considerations support operator comfort and efficient workflow, with easy access for loading, unloading, and tooling changes.
In summary, channel sheet metal bending machines provide precise, reliable, and efficient forming of channel profiles from flat sheets. Their robust mechanical design, advanced controls, and versatile tooling make them essential for producing consistent channel bends across a variety of industrial applications.
Channel sheet metal bending machines operate by securely clamping the metal sheet before applying controlled force through a punch or bending beam onto a die, shaping the metal into a channel profile. The bending process relies on precise control of the force, stroke length, and positioning to achieve the desired bend angle and radius without causing material cracking, wrinkling, or deformation.
The tooling system is central to the machine’s performance. Punches and dies are custom-designed for specific channel dimensions, with materials and surface treatments chosen to withstand repetitive bending forces and minimize wear. Adjustable tooling setups allow operators to accommodate different sheet thicknesses, materials, and channel sizes, enhancing machine versatility.
Modern machines frequently incorporate CNC controls that enable programming of complex bending sequences, precise control of ram or punch movement, and automated back gauge positioning. These features improve repeatability, reduce setup time, and facilitate quick changeovers, making the machine suitable for both small batch and high-volume production.
Material handling systems, including clamps, back gauges, and alignment guides, ensure the sheet is positioned accurately and held securely during the bending cycle. Some machines include sensors to monitor bending force and position, providing real-time feedback for quality assurance and enabling automatic adjustments to maintain dimensional accuracy.
Safety is addressed through guarding around moving parts, emergency stop buttons, light curtains, and interlocks that prevent machine operation during setup or maintenance. Ergonomic machine designs help reduce operator fatigue and simplify loading, unloading, and tooling changes.
Routine maintenance involves inspecting and lubricating mechanical components, checking hydraulic or servo systems, and monitoring tooling condition to ensure consistent performance. Modular tooling and quick-change features help minimize downtime during production transitions.
Overall, channel sheet metal bending machines combine mechanical strength, precise control, and automation to deliver efficient and reliable formation of channel profiles. Their ability to produce consistent, high-quality bends makes them indispensable in fabrication industries requiring strong, accurately formed sheet metal channels.
Recent developments in channel sheet metal bending machines focus on enhancing precision, automation, and adaptability to meet increasingly complex manufacturing requirements. Servo-electric and advanced hydraulic drive systems offer improved control over bending speed, force, and positioning, enabling the formation of channel profiles with tighter tolerances and smoother bends, even on advanced high-strength materials or thicker sheets.
Integration of sophisticated CNC controls allows operators to program intricate bending sequences with multiple angles and varying channel dimensions. These systems store multiple job setups, facilitating rapid changeovers and supporting flexible production runs. Real-time monitoring through sensors provides feedback on bending force and position, enabling dynamic adjustments to reduce defects such as springback or distortion.
Automation in material handling—including motorized clamps, back gauges, and robotic feeding and unloading—streamlines production and increases throughput by minimizing manual intervention. Inline inspection systems ensure dimensional accuracy and surface quality, allowing early detection and rejection of defective parts.
Tooling advancements include modular dies and punches with wear-resistant coatings, extending tool life and simplifying maintenance. Quick-change tooling systems enable fast transitions between different channel profiles, reducing downtime and improving overall productivity.
Safety remains a top priority, with enhanced guarding, light curtains, emergency stop features, and interlocks integrated into machine designs to protect operators without compromising efficiency. Ergonomic improvements make loading, unloading, and machine operation more comfortable, supporting sustained operator performance.
Energy efficiency is improved through variable frequency drives, regenerative braking, and optimized hydraulic circuits, contributing to reduced operating costs and environmental impact. Connectivity with Industry 4.0 platforms enables remote monitoring, data analysis, and predictive maintenance, allowing manufacturers to optimize uptime and product quality.
In summary, channel sheet metal bending machines have evolved into highly automated, precise, and flexible systems. These advancements empower manufacturers to produce consistent, high-quality channel profiles efficiently while adapting swiftly to diverse production needs and maintaining rigorous safety and environmental standards.
U Bending Machine
A U bending machine is a specialized sheet metal forming machine designed to create precise U-shaped bends in flat metal sheets or strips. This type of bending is widely used in manufacturing structural components, brackets, frames, enclosures, and other parts that require a U-profile for strength, functionality, or assembly purposes.
The machine typically clamps the sheet metal securely while applying force through a punch or bending beam that presses the material into a corresponding U-shaped die. This controlled deformation bends the sheet into the desired U profile with specific dimensions and bend radii, ensuring consistent geometry and strength across produced parts.
U bending machines come in various configurations, including mechanical, hydraulic, and servo-electric types. Hydraulic and servo-electric systems provide adjustable force, stroke control, and precise positioning, allowing for flexibility in handling different sheet thicknesses, materials, and U-bend sizes.
Modern U bending machines often feature CNC controls that enable programming of bend sequences, angles, and dimensions, improving repeatability and reducing setup times. This automation is particularly beneficial for batch production or custom parts requiring frequent changes.
Tooling consists of punches and dies shaped to the exact U-profile specifications, made from hardened steel or other durable materials to withstand repeated bending cycles without wear or deformation. Quick-change tooling options facilitate rapid transitions between different bend profiles or material types.
Material handling features such as clamps, back gauges, and alignment guides ensure accurate positioning and secure holding of the sheet during bending. Sensors may be integrated to monitor bending force and position in real time, providing quality control feedback and minimizing defects like springback or uneven bends.
Safety systems include guarding around moving parts, emergency stops, interlocks, and light curtains to protect operators during machine operation and maintenance. Ergonomic designs improve operator comfort and accessibility, reducing fatigue and enhancing workflow efficiency.
In summary, U bending machines provide efficient, precise, and repeatable methods for forming U-shaped bends in sheet metal components. Their combination of robust mechanical design, advanced controls, and versatile tooling makes them essential in industries requiring strong, accurate U-profile parts.
U bending machines function by firmly clamping the sheet metal while a punch or bending beam presses the material into a matching U-shaped die, gradually forming the metal into the desired profile. The bending process is carefully controlled to achieve the correct bend angle, radius, and dimensions without causing material cracking, wrinkling, or distortion. This control is especially important when working with thicker or high-strength metals.
The tooling system is critical for consistent results; punches and dies are custom-made to match specific U-bend requirements and are typically constructed from hardened steel to endure repetitive use. Adjustable tooling setups allow the machine to accommodate varying sheet thicknesses, materials, and bend sizes, enhancing flexibility across different jobs.
Automation features, such as CNC control, enable operators to program precise bending sequences, adjust parameters, and store multiple job profiles. This capability reduces setup time, ensures repeatability, and supports quick changeovers between parts with different specifications.
Material handling components like clamps, back gauges, and alignment guides position and hold the sheet accurately throughout the bending cycle. Some machines incorporate sensors that monitor bending force and position, providing real-time feedback to maintain quality and detect potential defects early.
Safety is ensured through protective guarding, emergency stop mechanisms, light curtains, and interlocks that prevent accidental operation during maintenance or tooling changes. Ergonomic machine designs facilitate easier loading, unloading, and adjustments, reducing operator fatigue and improving efficiency.
Regular maintenance includes inspecting and lubricating moving parts, checking hydraulic or servo systems, and monitoring tooling wear to sustain performance and prolong machine life. Quick-change tooling systems help minimize downtime during production transitions.
Overall, U bending machines offer reliable, precise, and efficient solutions for producing high-quality U-shaped bends in sheet metal. Their robust construction, advanced controls, and adaptable tooling make them indispensable in manufacturing sectors requiring consistent and accurate metal forming.
Recent innovations in U bending machines emphasize increased precision, automation, and integration with digital manufacturing systems. Servo-electric and advanced hydraulic drives provide enhanced control over bending force, speed, and positioning, enabling smoother bends and reducing the risk of defects, especially when working with high-strength or coated materials.
CNC controls with user-friendly interfaces allow operators to easily program complex bending sequences, adjust parameters, and store multiple job setups for fast changeovers. This flexibility supports both high-volume production and small batch runs with varying specifications.
Automation extends to material handling, with motorized clamps, back gauges, and robotic loading/unloading systems streamlining workflows and improving throughput. Real-time monitoring using sensors tracks bending force and position, allowing dynamic adjustments to maintain quality and reduce scrap.
Tooling advancements include modular, quick-change dies and punches with wear-resistant coatings, increasing tool life and reducing setup times. Some machines feature adaptive tooling capable of handling different bend radii or sheet thicknesses without extensive manual adjustments.
Safety remains a priority, with comprehensive guarding, light curtains, emergency stops, and interlocks ensuring operator protection without hindering productivity. Ergonomic improvements enhance operator comfort and ease of machine operation, particularly during repetitive tasks.
Energy efficiency gains come from variable frequency drives, regenerative braking, and optimized hydraulic circuits, lowering operational costs and environmental impact. Integration with Industry 4.0 platforms allows for remote monitoring, data analytics, and predictive maintenance, helping manufacturers optimize uptime and product quality.
In summary, U bending machines have evolved into highly automated, precise, and flexible systems. These advancements enable manufacturers to produce consistent, high-quality U-shaped bends efficiently while adapting quickly to changing production demands and maintaining strict safety and environmental standards.
V Bending Machine
A V bending machine is a specialized piece of equipment used in sheet metal fabrication to create precise bends by pressing the metal sheet into a V-shaped die using a matching V-shaped punch. This bending method is one of the most common and versatile processes for forming angular bends in metal sheets, suitable for producing parts like brackets, enclosures, frames, and various structural components.
The machine clamps the sheet metal firmly while the punch descends into the V-shaped die, plastically deforming the material to the desired angle and radius. The bend angle can be adjusted by controlling the depth of the punch stroke, allowing for a wide range of angles from shallow to sharp bends.
V bending machines come in mechanical, hydraulic, and servo-electric configurations. Mechanical presses offer fast cycle times and are ideal for high-volume production, hydraulic presses provide adjustable force and stroke for flexibility, and servo-electric models deliver precise control, energy efficiency, and programmability.
CNC controls are commonly integrated to enable operators to program bend sequences, control punch stroke and speed, and store multiple part programs for efficient changeovers. This automation enhances repeatability and consistency, reducing setup times and increasing throughput.
The tooling consists of V-shaped punches and dies made from hardened steel or other durable materials to withstand repeated bending forces and maintain dimensional accuracy. Tooling can be customized for different sheet thicknesses and materials, with options for varying die opening widths to accommodate diverse bend radii.
Material handling features such as clamps, back gauges, and alignment guides ensure accurate sheet positioning and secure holding during bending, which is essential for dimensional precision and consistent quality. Sensors may be used to monitor bending force and angle, providing feedback for quality control.
Safety measures include guarding around moving parts, emergency stops, light curtains, and interlocks to protect operators. Ergonomic machine designs improve accessibility, reduce operator fatigue, and facilitate loading, unloading, and tooling changes.
In summary, V bending machines offer a reliable, efficient, and flexible solution for producing accurate angular bends in sheet metal. Their combination of robust mechanical design, advanced controls, and adaptable tooling makes them vital equipment in diverse metal fabrication industries.
V bending machines function by securely clamping the sheet metal while a V-shaped punch descends into the corresponding V-shaped die, forcing the metal to bend at the desired angle. The depth of the punch stroke determines the bend angle, allowing operators to produce a range of bends from shallow to sharp with precision. The controlled bending process ensures minimal material stress, reducing the risk of cracking or deformation, especially when working with various metals and thicknesses.
The tooling system is fundamental to the machine’s effectiveness. Punches and dies are made from hardened steel or other durable materials to withstand repetitive bending forces and maintain consistent dimensions over time. Different die opening widths are used depending on the sheet thickness and the required bend radius, offering flexibility across a variety of applications.
CNC controls enhance the machine’s capabilities by allowing precise programming of bend sequences, stroke depth, speed, and pressure. Operators can save multiple job profiles for quick changeovers, improving efficiency and repeatability. Real-time feedback from sensors monitoring bending force and position helps maintain quality and detect potential issues early.
Material handling components such as clamps, back gauges, and alignment guides ensure accurate positioning and secure holding of the sheet during bending. Some machines incorporate motorized or automated back gauges to facilitate faster setups and increase throughput, especially in batch production environments.
Safety features are integral, including guarding around moving parts, emergency stop buttons, light curtains, and interlocks to prevent accidental operation during maintenance or tooling changes. Ergonomic design considerations improve operator comfort and reduce fatigue during repetitive tasks.
Routine maintenance involves inspecting and lubricating mechanical components, checking hydraulic or servo systems, and monitoring tooling condition to sustain performance and prolong machine lifespan. Quick-change tooling options help minimize downtime when switching between different parts or bending requirements.
Overall, V bending machines provide a versatile and reliable solution for producing precise angular bends in sheet metal. Their combination of sturdy mechanical design, advanced automation, and adaptable tooling makes them indispensable in many fabrication industries where accuracy and efficiency are essential.
Recent advancements in V bending machines focus on improving precision, automation, and energy efficiency to meet the evolving needs of metal fabrication industries. Servo-electric drives have become increasingly popular due to their ability to offer highly accurate control over punch position, speed, and force, combined with reduced energy consumption compared to traditional hydraulic or mechanical systems. This precise control is essential when working with advanced high-strength materials or delicate metals that require gentle handling.
Modern V bending machines often incorporate sophisticated CNC control systems with touchscreen interfaces, enabling operators to program complex bend sequences, adjust parameters on the fly, and store multiple job profiles for quick changeovers. This flexibility supports both high-volume production and custom, small-batch manufacturing.
Automation extends to material handling, with features such as motorized clamps, automated back gauges, and robotic loading/unloading systems that streamline workflow and improve throughput. Integrated sensors monitor bending force, position, and angle in real time, allowing dynamic adjustments to maintain consistent quality and reduce scrap.
Tooling improvements include modular punches and dies with wear-resistant coatings, which extend tool life and simplify maintenance. Quick-change tooling systems reduce setup times and enable rapid adaptation to different sheet thicknesses and bend radii.
Safety enhancements encompass multi-level guarding, light curtains, emergency stop functions, and interlocks to ensure operator protection without compromising productivity. Ergonomic designs facilitate ease of use and reduce operator fatigue during repetitive operations.
Energy efficiency measures, such as variable frequency drives, regenerative braking, and optimized hydraulic circuits, contribute to lower operating costs and environmental impact. Connectivity with Industry 4.0 platforms enables remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven process optimization.
In summary, V bending machines have evolved into highly automated, precise, and versatile equipment. These advancements empower manufacturers to produce accurate angular bends efficiently while adapting quickly to changing production demands and maintaining rigorous safety and quality standards.
Edge Bending Machine
An edge bending machine is specialized equipment designed to create precise bends along the edges of sheet metal parts. This bending process is essential in forming flanges, lips, or folded edges that add strength, facilitate assembly, or improve the aesthetic finish of metal components. Edge bending is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, appliance manufacturing, HVAC ductwork, and architectural metalwork.
The machine operates by clamping the sheet metal securely while a bending beam or punch applies controlled force to the edge, folding it over a die or anvil to the desired angle. This action produces clean, accurate bends along straight or curved edges, depending on the tooling and machine design.
Edge bending machines come in mechanical, hydraulic, and servo-electric configurations, each offering different benefits in terms of speed, force control, and precision. Hydraulic and servo-electric models provide adjustable bending force and stroke control, which accommodate a variety of materials and thicknesses while minimizing distortion or cracking.
CNC controls are commonly integrated to allow operators to program bend angles, sequences, and tool movements, improving repeatability and reducing setup times. This capability supports both high-volume production and small-batch, customized jobs.
Tooling typically includes bending beams, dies, and anvils designed to match specific edge profiles and bending radii. Tool materials are chosen for durability and precision, often hardened and coated to resist wear and maintain consistent results.
Material handling components such as clamps, back gauges, and alignment guides ensure consistent positioning and secure holding of the sheet during bending. Some machines incorporate sensors to monitor bending force and angle, providing real-time feedback for quality control.
Safety features include guarding around moving parts, emergency stop buttons, light curtains, and interlocks to protect operators during operation and maintenance. Ergonomic machine designs facilitate easier loading, unloading, and adjustments, reducing operator fatigue and enhancing workflow.
In summary, edge bending machines provide efficient, precise, and versatile solutions for forming strong, accurate bends along sheet metal edges. Their robust design, advanced controls, and adaptable tooling make them indispensable in manufacturing processes requiring high-quality edge finishing.
Edge bending machines work by securely clamping the sheet metal while a bending beam or punch applies force to fold the edge over a die or anvil, creating a precise bend at the desired angle. The process requires careful control of bending speed, force, and position to ensure consistent results without causing cracks, wrinkles, or deformation, particularly when working with different materials and thicknesses.
Tooling is a critical component, consisting of bending beams, dies, and anvils shaped to match the required bend radius and profile. These tools are typically made from hardened steel and may have surface coatings to reduce friction and wear, ensuring durability and maintaining dimensional accuracy. Adjustable tooling setups allow the machine to accommodate various edge profiles and material specifications.
Modern edge bending machines often include CNC control systems that enable operators to program bend angles, sequences, and tool paths. This automation improves repeatability, reduces setup times, and facilitates quick changeovers between different part designs or production runs. Real-time sensors may monitor bending force and angle, providing feedback for quality control and enabling dynamic adjustments during the bending cycle.
Material handling features such as clamps, back gauges, and alignment guides ensure precise positioning and secure holding of the sheet metal throughout the bending process. Some machines incorporate automated feeding and unloading systems to increase throughput and reduce manual handling.
Safety considerations are integral to machine design, with guarding around moving parts, emergency stop buttons, light curtains, and interlocks to protect operators during operation and maintenance. Ergonomic features enhance operator comfort and accessibility, helping reduce fatigue and improve productivity.
Maintenance practices typically involve regular inspection and lubrication of mechanical components, checking hydraulic or servo systems, and monitoring tooling condition to sustain performance and prolong machine life. Modular tooling and quick-change systems help minimize downtime during production transitions.
Overall, edge bending machines combine precise mechanical action, advanced automation, and robust tooling to deliver efficient, accurate bending of sheet metal edges. Their versatility and reliability make them essential equipment in industries where strong, clean, and consistent edge profiles are critical for product quality and functionality.
Recent advancements in edge bending machines emphasize enhanced automation, precision, and integration with smart manufacturing technologies. Servo-electric and hydraulic drive systems offer improved control over bending force, speed, and positioning, enabling smoother, more accurate bends even in advanced high-strength or coated materials that require delicate handling to avoid surface damage or cracking.
Sophisticated CNC controls with intuitive interfaces allow operators to program complex bending sequences, adjust parameters on the fly, and store multiple job profiles for rapid changeovers. This flexibility supports both high-volume production and small batch runs with varying specifications, improving efficiency and reducing downtime.
Automation extends to material handling through motorized clamps, automated back gauges, and robotic feeding and unloading systems, streamlining workflows and boosting throughput. Real-time sensors monitor bending force, angle, and position, providing continuous feedback to maintain consistent quality and reduce scrap rates.
Tooling improvements include modular, quick-change bending beams and dies with wear-resistant coatings that extend tool life and simplify maintenance. Adaptive tooling systems enable easy adjustments for different edge profiles and material thicknesses without extensive manual intervention.
Safety remains a priority, with comprehensive guarding, light curtains, emergency stops, and interlocks designed to protect operators without compromising productivity. Ergonomic machine designs improve operator comfort and accessibility, reducing fatigue during repetitive tasks.
Energy efficiency is enhanced through variable frequency drives, regenerative braking, and optimized hydraulic circuits, lowering operational costs and environmental impact. Connectivity with Industry 4.0 platforms facilitates remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven process optimization, helping manufacturers maximize uptime and product quality.
In summary, edge bending machines have evolved into highly automated, precise, and versatile systems. These advancements enable manufacturers to produce strong, clean, and accurate edge bends efficiently while adapting quickly to changing production demands and maintaining stringent safety and quality standards.
Hydraulic Press for Kitchen Sink Manufacturing
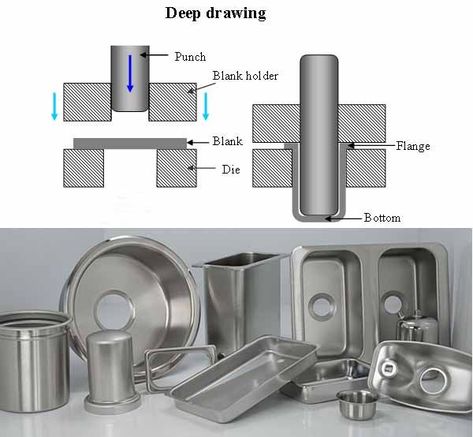
A hydraulic press for kitchen sink manufacturing is a specialized machine designed to shape sheet metal into durable, precise kitchen sink components using hydraulic force. This press applies controlled pressure to form, emboss, or draw metal sheets—commonly stainless steel or composite materials—into sink basins, rims, and other complex shapes with smooth finishes and consistent dimensions.
The hydraulic system generates the necessary force by pressurizing fluid, which moves a piston to apply steady, powerful pressure on the metal blank through custom-designed dies. This allows for deep drawing, bending, and embossing operations required to produce sinks with intricate contours, drain grooves, and mounting flanges.
Hydraulic presses offer advantages such as adjustable force control, consistent pressure application, and smooth operation, which are critical for preventing defects like cracking, wrinkling, or uneven thickness in kitchen sink components. Their versatility enables them to handle various metal gauges and sink designs, from shallow utility sinks to deep, multi-compartment models.
Integration of CNC or programmable logic controllers (PLC) enhances precision and repeatability by controlling ram speed, stroke length, and pressure profiles. Automated controls allow for quick setup adjustments, storage of multiple product programs, and consistent cycle times, improving manufacturing efficiency and quality.
Tooling in hydraulic presses includes durable punches and dies engineered for sink geometries, often made from hardened steel with surface treatments to resist wear and facilitate smooth metal flow. Quick-change tooling systems minimize downtime during product switches.
Material handling features such as clamps, feeders, and positioning guides ensure accurate blank placement and secure holding during pressing. Some systems include robotic loading and unloading to increase throughput and reduce manual labor.
Safety systems encompass guarding around moving parts, emergency stops, light curtains, and interlocks to protect operators. Ergonomic designs support easy access for tool changes and maintenance, improving operator comfort and productivity.
In summary, hydraulic presses for kitchen sink manufacturing combine robust mechanical power, precise control, and versatile tooling to produce high-quality, consistent sink components efficiently. Their design supports diverse sink styles and materials while maintaining tight tolerances and superior surface finishes required in the kitchenware industry.
Hydraulic presses for kitchen sink manufacturing operate by applying controlled pressure through a piston driven by hydraulic fluid onto a metal blank placed over a die. This pressure deforms the sheet metal to the desired shape, whether it’s deep drawing a basin, forming flanges, or embossing decorative patterns. The hydraulic system’s ability to deliver smooth, consistent force throughout the stroke is essential to avoid defects such as wrinkling, cracking, or uneven thickness.
The machine’s hydraulic components—pumps, cylinders, valves, and fluid reservoirs—are engineered to provide adjustable pressure and precise control over ram speed and position. This flexibility allows manufacturers to optimize the forming process for different sink designs, material types, and thicknesses, ensuring high-quality results across a variety of products.
Tooling is customized to the specific kitchen sink design, consisting of punches, dies, and blank holders made from hardened steel with surface treatments to reduce friction and extend tool life. Tooling accuracy and durability are critical to maintaining consistent part dimensions and smooth surface finishes.
Advanced hydraulic presses often incorporate CNC or PLC control systems that enable programming of stroke sequences, pressure profiles, and cycle times. Operators can save multiple production programs, facilitating rapid changeovers and maintaining repeatability. Real-time sensors monitor pressure, position, and speed, providing feedback to ensure process stability and product quality.
Material handling systems, such as clamps, feeders, and positioning guides, secure the metal blank and maintain precise alignment during forming. Automated loading and unloading options improve throughput and reduce manual handling, increasing overall efficiency.
Safety measures include guarding around moving parts, emergency stop buttons, light curtains, and interlocks to protect operators from injury. Ergonomic design elements ease tooling changes, maintenance, and operation, enhancing comfort and productivity.
Regular maintenance involves inspecting hydraulic components for leaks or wear, lubricating moving parts, checking tooling condition, and calibrating control systems to maintain optimal performance.
Overall, hydraulic presses designed for kitchen sink manufacturing provide reliable, precise, and efficient metal forming capabilities. Their combination of robust hydraulic power, programmable control, and specialized tooling makes them well-suited to producing high-quality kitchen sinks that meet strict dimensional and aesthetic standards.
Recent developments in hydraulic presses for kitchen sink manufacturing focus on improving automation, precision, and energy efficiency to meet modern production demands. Enhanced hydraulic systems with servo-assisted valves offer better control over ram speed and pressure, allowing gentler forming of delicate materials and complex sink designs while reducing cycle times.
Integration of advanced CNC or PLC controls with user-friendly touchscreens enables operators to easily program and adjust forming parameters, store multiple product profiles, and monitor machine status in real time. This automation enhances repeatability, reduces setup time, and supports flexible manufacturing for diverse sink styles and batch sizes.
Material handling automation, including robotic loading, unloading, and part transfer systems, streamlines workflows and increases throughput while minimizing manual labor and potential handling errors. Sensors embedded in the press monitor critical variables like pressure, position, and force, providing real-time feedback to optimize the forming process and ensure consistent product quality.
Tooling technology has advanced with the introduction of modular, quick-change dies and punches coated with wear-resistant materials, reducing downtime and extending tool life. Adaptive tooling systems allow rapid adjustments to accommodate different sink geometries and metal thicknesses without extensive manual intervention.
Safety remains paramount, with comprehensive guarding, light curtains, emergency stops, and interlocks integrated seamlessly into machine operation to protect operators while maintaining productivity. Ergonomic design enhancements improve operator comfort, facilitating easier tool changes and maintenance access.
Energy-efficient hydraulic circuits with variable frequency drives and regenerative technologies reduce power consumption and operational costs. Connectivity with Industry 4.0 platforms enables remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven process optimization, helping manufacturers maximize uptime and product quality.
In summary, hydraulic presses for kitchen sink manufacturing have evolved into sophisticated, automated, and energy-efficient machines. These advancements allow manufacturers to produce high-quality, consistent kitchen sinks efficiently while adapting quickly to changing production requirements and maintaining strict safety and quality standards.
High Tonnage Hydraulic Press
A high tonnage hydraulic press is a powerful industrial machine designed to exert very large forces—often thousands to tens of thousands of tons—on materials for forming, shaping, or assembling heavy-duty components. These presses are widely used across industries such as automotive, aerospace, shipbuilding, heavy equipment manufacturing, and metal fabrication, where substantial force is required to deform thick or high-strength materials.
The core of a high tonnage hydraulic press is its hydraulic system, which uses pressurized fluid to move large pistons or rams that deliver immense force to the workpiece. The hydraulic system provides smooth, controllable pressure and stroke, allowing precise shaping operations such as deep drawing, forging, stamping, blanking, and extrusion on large or tough materials.
High tonnage presses typically feature robust frames constructed from heavy-duty steel to withstand extreme loads without deformation, ensuring long-term accuracy and durability. The ram and bed are engineered for rigidity and stability, with surfaces often hardened to resist wear.
Control systems range from simple manual setups to advanced CNC or PLC-based automation, enabling precise regulation of ram speed, stroke length, pressure, and dwell time. Automation improves repeatability, reduces cycle times, and facilitates integration into modern manufacturing lines.
Tooling for high tonnage presses is custom-designed to handle large workpieces and extreme forces, often requiring specialized materials and cooling or lubrication systems to endure the stresses of heavy-duty operations.
Safety is a critical consideration, with comprehensive guarding, light curtains, emergency stop functions, and interlocks to protect operators from hazards associated with high-force equipment.
Maintenance involves regular inspection and servicing of hydraulic components, structural elements, and tooling to ensure safe, reliable operation over the machine’s lifespan.
In summary, high tonnage hydraulic presses provide essential heavy-duty forming and assembly capabilities, combining immense force with precise control and robust construction to meet demanding industrial production requirements.
High tonnage hydraulic presses operate by using a hydraulic pump to pressurize fluid, which then moves a large piston or ram downward with significant force onto the workpiece. This force can be precisely controlled to accommodate various heavy-duty forming processes, including deep drawing, forging, stamping, and metal extrusion. The ability to maintain consistent pressure throughout the stroke ensures high-quality results even when working with thick, hard, or complex materials.
The press frame is typically constructed from heavy-gauge steel or alloy to resist deformation under extreme loads. Reinforcements and stress-relief features are incorporated into the design to maintain structural integrity and alignment over time, which is critical for precision and tool longevity. The bed and ram surfaces are precision-machined and hardened to withstand repetitive impact and wear.
Hydraulic systems in these presses include pumps, valves, accumulators, and cylinders engineered to deliver smooth, reliable force with variable speed and pressure controls. Many high tonnage presses use servo-hydraulic technology to combine the power of hydraulics with the precision of electronic control, improving efficiency and process repeatability.
Advanced control units, often based on CNC or PLC platforms, allow operators to program detailed forming sequences, adjust pressure profiles, stroke speed, and dwell times, and monitor real-time performance data. This level of automation reduces setup time, minimizes operator error, and facilitates integration into larger production workflows.
Tooling used with high tonnage presses is specially designed to endure extreme pressures and large part sizes. Materials such as hardened tool steels or carbide composites are common, often featuring cooling or lubrication systems to extend tool life and ensure consistent forming quality.
Safety systems are paramount due to the immense forces involved. Multi-level guarding, light curtains, emergency stop buttons, and interlocks are standard to prevent accidental access during operation. Operator training and strict safety protocols are essential to safe use.
Routine maintenance includes inspection of hydraulic seals and hoses, fluid condition monitoring, structural integrity checks, and regular calibration of control systems. Proper maintenance ensures optimal performance, extends machine life, and prevents costly downtime.
Overall, high tonnage hydraulic presses are indispensable in industries requiring massive forming forces combined with precise control. Their robust design, advanced hydraulics, and automation capabilities enable efficient, reliable production of large, complex metal components with stringent quality standards.
Recent advancements in high tonnage hydraulic presses emphasize improved efficiency, precision, and integration with smart manufacturing technologies to meet evolving industrial demands. Servo-hydraulic systems have gained traction by combining the high force capability of hydraulics with the precise control and energy savings of servo motors, resulting in smoother operation, faster cycle times, and reduced power consumption.
Modern presses feature sophisticated CNC or PLC-based control units with user-friendly interfaces that allow operators to program complex forming sequences, adjust force and speed dynamically, and monitor system performance in real time. These controls facilitate quick changeovers between jobs and help maintain consistent part quality across large production runs.
Automation integration extends to material handling and tooling change systems, including robotic loading and unloading, automated die clamping, and quick-change tooling setups. These enhancements reduce manual labor, improve safety, and increase overall throughput.
Structural design improvements employ advanced finite element analysis (FEA) during development to optimize frame rigidity while minimizing weight, allowing for better precision and reduced foundation requirements. Surface treatments and coatings on ram and bed components extend wear resistance and reduce maintenance needs.
Energy efficiency measures such as regenerative braking, variable frequency drives, and optimized hydraulic circuits contribute to lower operational costs and environmental impact. Condition monitoring sensors and predictive maintenance software enable early detection of potential issues, reducing unplanned downtime and extending machine life.
Comprehensive safety systems integrate multi-zone guarding, presence-sensing devices, emergency stop networks, and safety-rated control architectures to protect operators and equipment while complying with the latest regulatory standards.
In summary, high tonnage hydraulic presses have evolved into highly advanced, efficient, and flexible machines. Their combination of immense forming power, precise electronic control, automated features, and robust design enables manufacturers to meet increasingly complex production requirements with superior quality, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
Metal Sheet Forming Press

A metal sheet forming press is a versatile and powerful machine used to shape flat metal sheets into desired forms through compressive force. These presses are central to manufacturing processes in industries such as automotive, aerospace, appliances, construction, and cookware. The machine works by forcing a sheet of metal into a die using a punch, a ram, or a combination of tooling components, which creates specific features such as bends, curves, holes, ribs, or entire part geometries.
The core principle involves placing the sheet metal blank onto the die surface, and then applying downward force from the ram or punch to deform the material plastically into the shape of the die cavity. Depending on the forming method, the press may perform operations such as bending, blanking, drawing, embossing, flanging, coining, or stamping. Each operation has different force requirements, tool configurations, and press cycle characteristics, all of which are managed by the machine’s control system.
Metal sheet forming presses can be mechanical, hydraulic, or servo-electric. Mechanical presses use flywheels and cams to generate rapid, repeatable motion with high production speeds, ideal for shallow forming and stamping. Hydraulic presses offer smoother and more adjustable force application over the full stroke, which is especially useful for deep drawing, forming high-strength metals, or producing parts with complex contours. Servo-electric presses provide high energy efficiency and extremely precise motion control, allowing variable speed and dwell times during a single stroke, which improves material flow and surface quality.
Tooling used in these presses includes hardened steel dies and punches that match the desired shape and part dimensions. These tools must be carefully designed to distribute stress evenly, guide metal flow, and minimize defects such as wrinkling, tearing, or springback. In multi-operation setups, progressive or transfer die systems are used to perform several forming operations in sequence as the part advances through the press, improving throughput and part consistency.
Control systems are essential for modern presses. CNC or PLC systems allow the operator to program stroke length, speed, force, and cycle timing. These settings can be fine-tuned for different materials, thicknesses, and part geometries. Advanced systems include sensors that monitor force, position, and tooling temperature in real time, enabling adaptive control that maintains consistent quality even with variable inputs.
Material handling systems such as feeders, straighteners, de-coilers, and robotic arms are often integrated with sheet forming presses to automate loading and unloading, align blanks precisely, and ensure continuous production. These integrations reduce manual labor, enhance safety, and increase production speed.
Safety features include emergency stops, light curtains, interlocks, two-hand control systems, and full perimeter guarding. These are mandatory in most industrial environments to protect workers from the high forces and moving components involved.
In terms of materials, sheet forming presses handle a wide variety including carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, brass, and coated metals. Different materials require specific press force, lubrication, die design, and forming speeds, which are all accounted for in press setup.
Overall, a metal sheet forming press combines raw force with precision engineering and control to deliver high-quality parts at industrial scales. Whether forming simple brackets or intricate automotive panels, these machines are indispensable in transforming flat sheet stock into functional components across nearly every manufacturing sector.
Modern metal sheet forming presses are designed not only for performance but also for flexibility and integration into fully automated production lines. With the growing demand for shorter lead times and frequent product changes, presses are now built with modular tooling systems and quick-change die setups that reduce downtime between production runs. Tool clamping mechanisms are often hydraulic or pneumatic, allowing for automated die exchange that can take place in just a few minutes. This capability significantly boosts productivity and is especially valuable in just-in-time manufacturing environments.
The precision of formed parts depends heavily on the rigidity of the press frame and the accuracy of the ram guidance system. H-frame and C-frame configurations are the most common structural designs, with H-frames preferred for higher tonnage and better load distribution. Frame rigidity minimizes deflection under load, ensuring that tooling remains aligned and parts are consistently formed to tight tolerances. Ram guidance is typically achieved using linear bearings or eight-point gib systems that provide accurate vertical motion and resist lateral forces.
As forming requirements evolve, servo-controlled presses have emerged as the most advanced category. They offer programmable motion profiles that can be optimized for each stage of the forming cycle. For example, a servo press can slow down as the punch approaches the sheet, hold at the bottom dead center to allow metal to settle or stretch uniformly, then return rapidly to reduce overall cycle time. This precision is especially beneficial when working with advanced high-strength steels or lightweight alloys that have limited formability and require exact control to prevent cracking or distortion.
Integrated sensing and monitoring systems are increasingly used to enhance press reliability and product quality. Load cells, displacement sensors, and temperature monitors provide real-time feedback during operation. If any parameter deviates from the preset range, the press can automatically pause, alert the operator, or adjust settings to correct the issue. This level of intelligence reduces scrap, increases uptime, and helps maintain consistent production even in demanding applications.
Sheet forming presses are also designed with energy efficiency in mind. Hydraulic presses now use variable speed pump drives and accumulator systems that reduce energy use when full force is not required. Servo presses consume significantly less energy by eliminating hydraulic circuits entirely, making them ideal for environmentally conscious manufacturers seeking to lower operational costs and carbon emissions.
Noise and vibration control have also improved with better damping materials, isolation mounts, and quieter drive systems. This creates a more comfortable and safer working environment, particularly in high-speed operations where presses cycle hundreds of times per hour.
Customization plays a large role in how presses are configured for specific tasks. Some are equipped with heated platens for warm or hot forming of thick or exotic materials. Others include die cushion systems beneath the press bed to support reverse forming operations or assist with drawing complex shapes. Presses can be fitted with single or multiple rams, depending on the type and number of operations required.
In high-precision industries like electronics or medical device manufacturing, presses may feature micron-level control, temperature-regulated tooling, and vacuum systems to prevent dust contamination. At the other end of the spectrum, heavy-duty presses for shipbuilding or structural steel production may be designed to exert thousands of tons of force and form massive parts from thick plate steel.
Ultimately, metal sheet forming presses represent the convergence of mechanical strength, digital precision, and manufacturing intelligence. They are adaptable to a vast range of materials, part geometries, and production volumes, making them foundational to the modern industrial landscape. Whether producing fine-detailed parts in high volumes or shaping large, structural components with precision, these machines continue to evolve
The adaptability of metal sheet forming presses extends to the materials they can handle and the types of deformation processes they can execute. From soft aluminum alloys used in consumer electronics housings to ultra-high-strength steels required in automotive crash structures, the press must be capable of applying the appropriate force and following material-specific forming speeds and dwell times. Material behavior under stress varies significantly, and presses are often programmed with optimized stroke profiles that reduce work hardening, control springback, and prevent tearing or wrinkling, especially in multi-stage forming operations.
In complex component manufacturing, forming is often combined with piercing, trimming, and even in-die tapping. These additional operations can be integrated directly into the press cycle using specialized tooling and automation, creating finished parts in a single press stroke. This eliminates the need for secondary processes, saving floor space, tooling costs, and labor while boosting overall productivity. For example, automotive body panels can be blanked, formed, trimmed, pierced for fasteners, and lightly embossed in a single press line with progressive dies.
Manufacturers often rely on coil-fed press lines where metal sheets are continuously unrolled, leveled, lubricated, and fed into the forming press at controlled speeds. Advanced feeder systems synchronize with the press cycle, ensuring precise alignment and feed lengths for each stroke. Straighteners remove coil memory and ensure flatness, while lubrication units apply consistent coating to reduce die wear and ensure smooth material flow. Coil-fed lines are ideal for high-speed, high-volume production, minimizing waste and maximizing material usage through nested blank layouts.
As digitalization becomes standard across manufacturing, presses are increasingly connected to factory networks through Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platforms. Data from press sensors, tooling wear monitors, material tracking systems, and output quality scanners are fed into centralized dashboards that help operators and engineers make informed decisions. This connectivity supports predictive maintenance, real-time performance optimization, and root cause analysis of defects or downtime. In smart factories, presses are no longer isolated machines—they are intelligent nodes in a connected production ecosystem.
Training and usability have also evolved with modern HMI (human-machine interface) systems that use graphical touchscreens, diagnostics, and guided workflows to simplify operation and reduce errors. Operators can recall saved settings for different jobs, adjust force or timing parameters, and monitor process conditions through intuitive displays. This accessibility allows less experienced personnel to manage complex press operations safely and effectively, reducing dependence on highly specialized labor.
In the context of sustainability, many metal sheet forming presses are being designed to minimize not just energy usage but also overall material waste. With increasingly expensive metals, scrap minimization is a core design goal. Presses with integrated nesting algorithms and real-time blank optimization can significantly reduce offcuts. In some applications, recycled or previously formed metal can be reshaped or joined with virgin material using advanced forming techniques like mechanical clinching or hybrid deep drawing.
The future of metal sheet forming presses points toward more automation, greater customization, and integration with artificial intelligence. Presses will be able to auto-correct for thermal expansion in tooling, adapt stroke speeds mid-cycle based on part feedback, and even learn over time which die setups produce the highest yield. Modular press systems with reconfigurable tooling will support mass customization, allowing manufacturers to switch between product variants with minimal interruption.
Overall, the metal sheet forming press continues to evolve into a smarter, more efficient, and more capable platform. It is no longer just a source of mechanical force but a fully integrated system that combines precision mechanics, real-time data, adaptive control, and digital connectivity. Whether producing consumer goods, transportation components, or structural elements, the press remains one of the most essential and technologically dynamic tools in modern manufacturing.
Press Ram Double Action
A double action press ram is a specialized configuration used in metal forming presses, particularly in deep drawing and complex sheet metal forming operations. It features two independently controlled rams—an outer ram (also called the blank holder or binder ram) and an inner ram (the main punch ram). These two rams move concentrically and sequentially or simultaneously, providing better control over the forming process, especially when drawing deep or large parts.
In a typical operation, the outer ram descends first to hold the metal blank firmly against the die surface. This blank holding action is crucial for preventing wrinkles and ensuring a controlled material flow during the forming stroke. Once the blank is securely clamped, the inner ram begins to move downward, pressing the blank into the die cavity and forming the part.
The blank holder force applied by the outer ram is adjustable and can be fine-tuned to suit different materials, thicknesses, and part geometries. Too much force can restrict metal flow and cause tearing; too little can allow excess material to enter the die cavity and result in wrinkles or buckling. The ability to adjust the force and timing of both rams independently is a major advantage of the double action system.
Double action presses are especially valuable in forming large, deep, or irregularly shaped parts, such as automotive body panels, kitchen sinks, fuel tanks, and cylindrical vessels. They are also commonly used for reverse drawing, redrawing, or operations that involve flanging after deep drawing.
Hydraulic double action presses allow even more control over the speed and pressure of each ram. Advanced models are equipped with CNC or PLC controls to synchronize the two rams precisely, customize stroke profiles, and adjust forming parameters dynamically during the press cycle.
In summary, a double action press ram system improves control, precision, and quality in demanding forming applications by dividing the functions of blank holding and forming between two independent rams. This separation enables better management of material flow, reduces defects, and enhances flexibility across a wide range of metal forming tasks.
Double action press rams are essential in achieving consistent and defect-free parts when dealing with deep cavities or complex part geometries that cannot be formed reliably using a single ram system. The independent movement of the outer and inner rams allows for staged forming, where the blank is gradually shaped in a controlled environment. This reduces material stress, enhances dimensional stability, and accommodates high-strength or low-ductility materials that are prone to tearing under sudden or uneven pressure.
The outer ram, acting as the blank holder, can also be designed to perform additional shaping operations such as restriking or pre-forming before the inner ram completes the final draw. In some configurations, the outer ram may have variable segments or zones that apply different levels of pressure to different areas of the blank. This is especially useful for irregular parts where uniform binder force may not be optimal. Programmable hydraulic systems allow this zoning capability and enable dynamic pressure adjustment throughout the stroke, responding to material flow in real time.
In practical applications, the inner and outer rams often have different stroke lengths. The outer ram may descend a short distance to clamp the blank, while the inner ram continues downward for a much deeper stroke. Timing control between the two rams is critical—any premature or delayed motion can lead to distortion, uneven wall thickness, or loss of part shape. To address this, modern double action presses include stroke monitoring systems and electronic position feedback that synchronize ram movements with millisecond precision.
Maintenance and tool alignment in double action presses are also more complex compared to single ram systems. The die and punch must be precisely centered relative to both rams to avoid off-axis loading or uneven wear. Tool setup is facilitated by die setting jacks, alignment gauges, and automatic leveling systems. Additionally, the press frame must be exceptionally rigid to handle the distributed loads from both rams operating under high tonnage.
Tooling for double action presses often includes a three-piece setup: the die cavity mounted in the bed, the blank holder ring attached to the outer ram, and the punch affixed to the inner ram. All components must be designed to withstand high contact pressures and repetitive impact, so tool steels are commonly hardened and coated to resist wear. Lubrication is applied to reduce friction and aid in smooth material flow, especially where the sheet is drawn over tight radii or deep into the cavity.
In automated lines, double action presses are often paired with robotic arms or transfer feeders that load blanks and extract finished parts without interrupting the cycle. Sensors monitor every stage of the process, from blank position to ram pressure and part ejection. These systems enable continuous production of high-precision components with minimal operator intervention.
Double action press rams are used in everything from household sink production to automotive floor pans, appliance panels, aerospace skins, and battery enclosures. Their ability to manage material flow with greater finesse makes them a superior solution for forming deep, strong, and cosmetically critical parts. As materials become lighter and stronger, and part geometries more challenging, the flexibility and control of double action presses will continue to be a fundamental asset in modern sheet metal forming.
Double Stroke Hydraulic Press
A double stroke hydraulic press is a type of hydraulic press machine designed to perform two pressing strokes within a single operating cycle. This capability allows it to increase production efficiency by completing multiple forming actions—such as initial shaping and secondary pressing—without requiring the operator to reset or reposition the workpiece between strokes. The two strokes may have different pressures, speeds, or stroke lengths tailored to the specific forming requirements.
In operation, the press ram moves downward through a first stroke applying a predetermined force to the workpiece. Once that stroke is complete, the ram retracts partially or fully and then executes a second stroke, which may apply a different force or reach a different depth. This sequence can be programmed and controlled precisely using hydraulic valves and electronic controls, often governed by a PLC or CNC system.
The hydraulic system powering the double stroke press typically includes pumps, valves, cylinders, and accumulators designed to handle the complex pressure cycles involved. By utilizing hydraulic power, the machine delivers smooth, adjustable force throughout both strokes with the ability to hold pressure at any point, which is essential for processes like deep drawing, molding, or coining that require dwell times.
Double stroke presses often feature adjustable stroke lengths and force settings for each stroke, providing flexibility for a variety of materials and part geometries. The frame and mechanical components are robustly engineered to withstand the stresses of repeated dual strokes without loss of precision or structural integrity.
Control systems coordinate the timing and synchronization of the two strokes, ensuring the ram moves accurately and safely. Sensors monitor position, pressure, and speed, providing feedback to maintain consistency and detect any anomalies during operation. Safety devices such as interlocks and emergency stops are integral to protect operators during the complex motion cycles.
Applications of double stroke hydraulic presses include metal forming tasks requiring sequential deformation steps, such as deep drawing followed by trimming, or forging operations where multiple force applications improve material flow and part quality. By consolidating these steps into one press cycle, manufacturers can reduce cycle time, labor costs, and handling errors.
Maintenance of double stroke hydraulic presses focuses on the hydraulic system’s integrity—checking for leaks, maintaining fluid quality, and inspecting seals and valves—as well as mechanical components like guide systems and ram bearings. Regular calibration ensures that the dual stroke motions remain precise and synchronized.
Overall, double stroke hydraulic presses enhance manufacturing efficiency and versatility by combining multiple forming actions into a single machine cycle, offering precise control over force and stroke parameters to meet diverse industrial forming needs.
Double stroke hydraulic presses are particularly valuable in applications where multiple sequential forming operations are required on the same workpiece, eliminating the need to transfer parts between different machines or reposition tooling. This consolidation not only speeds up production but also reduces the potential for alignment errors and damage that can occur during handling. The ability to program and adjust each stroke independently allows manufacturers to optimize the forming process for complex geometries and different materials, enhancing part quality and consistency.
The hydraulic system in these presses is engineered to provide smooth, controllable motion for both strokes, with precise regulation of pressure and flow rates. Variable displacement pumps and proportional valves often regulate fluid delivery, ensuring that the ram applies the correct force throughout each stroke phase. The capacity to hold pressure during dwell periods is crucial for processes that require material to flow or set under constant load.
Structural design considerations include reinforcing the press frame and guiding systems to handle the repetitive stresses of dual-stroke operation without deformation or loss of alignment. Precision linear guides and robust ram support minimize lateral movement, ensuring that the force is applied evenly across the tooling and workpiece.
Control systems typically feature programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or CNC units that synchronize the timing of the two strokes, monitor sensor feedback, and adjust parameters in real time to maintain process stability. These systems often include user interfaces that allow operators to easily set stroke lengths, forces, speeds, and dwell times for each stroke independently, facilitating quick changeovers between different jobs.
Safety remains paramount, with multiple interlocks, emergency stop functions, and guarding to protect operators from the complex motions of the ram during both strokes. Sensors detect any unexpected conditions or obstructions and can halt the cycle immediately to prevent accidents or equipment damage.
Maintenance routines focus on hydraulic fluid cleanliness and pressure integrity, as well as inspecting seals, valves, and cylinders for wear that could affect stroke performance or cause leaks. Mechanical components such as guide rails and bearings are regularly lubricated and checked to maintain smooth operation and accuracy.
By integrating two forming strokes into one machine cycle, double stroke hydraulic presses deliver improved throughput, reduced cycle times, and enhanced product quality. This makes them especially advantageous in high-volume manufacturing environments where efficiency and precision are critical. Their versatility and programmable control also allow manufacturers to adapt quickly to changing production demands, making these presses a valuable asset in modern industrial operations.
In addition to their core advantages, double stroke hydraulic presses often support integration with automated material handling systems, such as robotic arms or conveyors, which further streamline production lines. By minimizing manual intervention, automation reduces labor costs, improves safety, and ensures consistent part placement for each cycle. This seamless integration enables high-volume manufacturing with minimal downtime and consistent quality.
The flexibility of double stroke presses extends to their tooling configurations as well. Modular tooling systems can be designed to accommodate different stroke requirements or product variants, allowing quick changeovers between jobs without significant machine downtime. This adaptability supports just-in-time manufacturing and reduces inventory costs.
Advancements in sensor technology and data analytics have also enhanced the monitoring capabilities of these presses. Real-time data collection on pressure, stroke position, and cycle timing helps operators optimize process parameters on the fly and identify inefficiencies. Over time, accumulated data can feed into predictive maintenance models, anticipating component wear or hydraulic fluid degradation before failures occur, thereby minimizing unplanned outages.
Environmental considerations have led to the development of energy-efficient hydraulic components used in double stroke presses, such as pumps with variable speed drives and low-friction seals. These features reduce power consumption and heat generation, lowering operational costs and improving machine longevity. The use of biodegradable hydraulic fluids further aligns with sustainability goals without compromising performance.
Training and support are vital to maximizing the benefits of double stroke hydraulic presses. Operators must understand the complex interplay between dual strokes, hydraulic dynamics, and control systems to ensure safe and efficient operation. Manufacturers often provide comprehensive training programs, including simulation tools and troubleshooting guides, to build this expertise.
Looking ahead, ongoing innovations are expected to bring even greater intelligence and connectivity to double stroke hydraulic presses. Integration with factory-wide digital ecosystems will enable more sophisticated process optimization, remote diagnostics, and adaptive control strategies. This evolution will further enhance productivity, reduce waste, and increase the ability to produce complex parts with tighter tolerances.
In essence, double stroke hydraulic presses represent a powerful combination of mechanical robustness, hydraulic precision, and intelligent control that meets the demanding needs of modern manufacturing. Their capacity to consolidate multiple forming operations within a single, controlled cycle makes them indispensable for industries seeking efficiency, flexibility, and high-quality output.
Automated Sheet Metal Forming
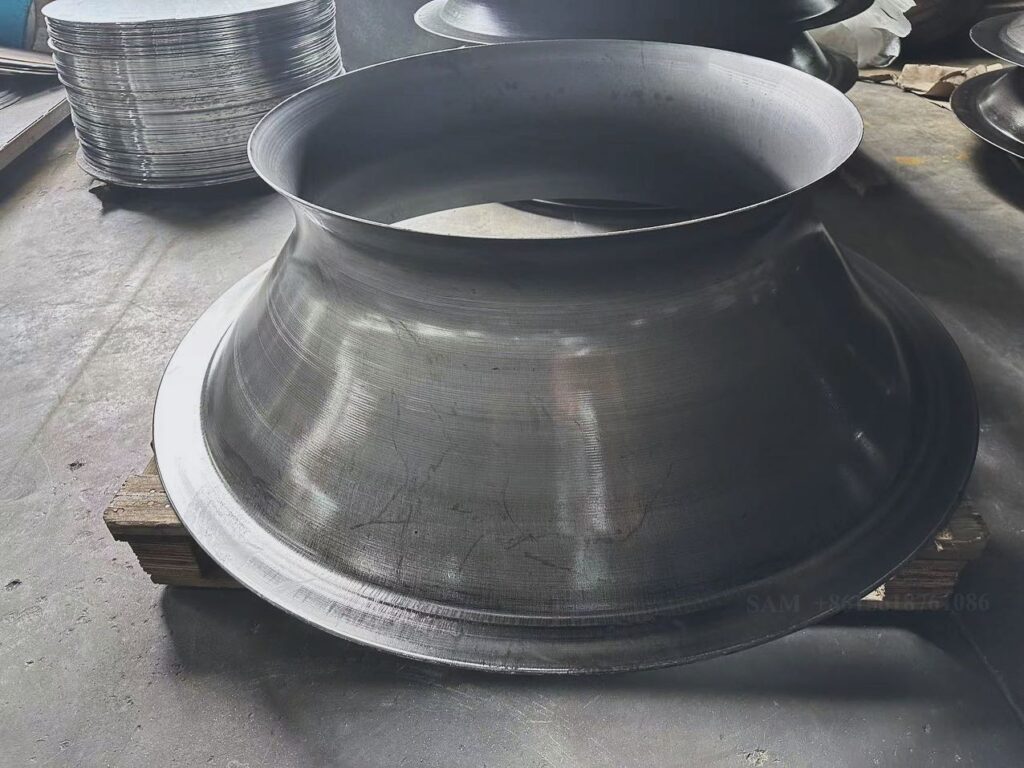

Automated sheet metal forming refers to the use of advanced machinery and control systems to perform sheet metal shaping processes with minimal human intervention. By integrating robotics, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), sensors, and computer numerical control (CNC) technology, these automated systems can efficiently handle tasks such as blanking, deep drawing, bending, stamping, and trimming at high speed and with consistent precision.
Automation enhances productivity by reducing cycle times and enabling continuous operation with fewer errors caused by manual handling. It also improves safety by limiting operator exposure to heavy machinery and repetitive tasks. Automated sheet metal forming systems often include robotic arms or gantry systems for loading and unloading materials, positioning blanks, and transferring parts between forming stations or presses.
Advanced control systems enable precise regulation of process parameters such as force, speed, stroke length, and tool positioning, adapting dynamically to variations in material thickness or part geometry. Sensors monitor critical variables in real time, providing feedback for quality control, fault detection, and process optimization.
In mass production environments like automotive and appliance manufacturing, automated sheet metal forming lines integrate multiple forming operations in sequence, often within press lines or flexible manufacturing cells. These systems support quick changeovers and high repeatability, essential for meeting strict quality standards and production targets.
The use of simulation software and digital twins in automated forming helps design tooling, optimize process parameters, and predict potential defects before production starts. This reduces setup time and scrap rates, contributing to cost savings and sustainability goals.
Overall, automated sheet metal forming represents a key evolution in manufacturing, combining precision, speed, and flexibility to meet the demands of modern industry while enhancing efficiency and safety.
Automated sheet metal forming systems rely heavily on integration between machinery and control software to coordinate complex sequences of operations. Robotics play a crucial role by handling raw material loading, part transfer between presses or forming stations, and finished part stacking or packaging. This reduces manual labor, speeds up production, and minimizes the risk of damage or misalignment during handling. Sensors embedded in the equipment continuously monitor parameters such as force, position, temperature, and vibration, providing data that enables real-time process adjustments and ensures consistent quality.
The flexibility of automated forming lines allows manufacturers to quickly switch between different part designs and production volumes. CNC-controlled presses and servo-driven systems offer precise control over ram speed, stroke length, and pressure, accommodating a wide range of materials and complex geometries. Tool changers and modular tooling systems enable rapid setup changes, supporting just-in-time manufacturing and reducing downtime.
Quality assurance is enhanced through inline inspection technologies such as machine vision, laser scanning, and dimensional gauging. These systems detect defects like wrinkles, cracks, or dimensional deviations immediately, allowing corrective actions to be taken without halting the entire production line. Data collected during forming can be stored and analyzed for traceability and continuous improvement.
Energy efficiency is an important consideration in automated sheet metal forming. Variable speed drives, energy recovery systems, and optimized hydraulic circuits reduce power consumption and heat generation. Environmentally friendly lubricants and fluid management systems further contribute to sustainable manufacturing practices.
Training and workforce development are essential to fully leverage automation’s benefits. Operators and maintenance personnel need skills in programming, troubleshooting, and maintaining integrated systems. Many manufacturers provide simulation-based training and remote support tools to facilitate skill development and reduce downtime.
As Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) continue to evolve, automated sheet metal forming lines become increasingly connected, enabling seamless communication with enterprise systems for production planning, inventory management, and predictive maintenance. This connectivity supports smarter factories with greater responsiveness to market demands and improved operational efficiency.
In summary, automated sheet metal forming combines robotics, advanced controls, real-time monitoring, and data analytics to create highly efficient, flexible, and precise manufacturing systems. These capabilities meet the increasing complexity and volume requirements of modern industry while enhancing quality, safety, and sustainability.
Further advancing automated sheet metal forming, machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) are increasingly integrated into control systems to optimize process parameters and predict maintenance needs. AI algorithms analyze historical and real-time data to detect subtle patterns or anomalies that human operators might miss, enabling adaptive adjustments that improve part quality and reduce scrap. Predictive maintenance powered by AI helps schedule service before breakdowns occur, minimizing costly downtime and extending equipment life.
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are also becoming more common in automated forming environments. Unlike traditional industrial robots that operate in fenced-off areas, cobots safely work alongside human operators, assisting with tasks such as material loading, inspection, or handling complex parts. This synergy enhances flexibility and efficiency, especially for small batch production or frequent changeovers.
Digital twin technology plays a significant role in design and process optimization. By creating a virtual replica of the forming line, engineers can simulate production scenarios, test tooling modifications, and anticipate issues before physical implementation. This reduces setup times, tooling costs, and trial-and-error iterations, accelerating time to market.
Additive manufacturing complements automated sheet metal forming by enabling rapid prototyping and the production of complex tooling components that are lightweight and highly durable. Combining additive and subtractive methods within automated lines can offer new possibilities for product customization and innovation.
Sustainability remains a key driver, with automated forming lines incorporating energy-efficient components, water recycling systems, and eco-friendly lubricants. Closed-loop feedback systems optimize resource usage, reducing waste and environmental impact. Manufacturers are also exploring circular economy principles by integrating automated processes for recycling scrap metal and reintroducing it into the production cycle.
Workforce transformation is critical to support these technological advancements. Upskilling initiatives focus on digital literacy, robotics programming, data analysis, and cybersecurity to prepare workers for increasingly sophisticated manufacturing environments. Remote monitoring and augmented reality (AR) tools facilitate maintenance and troubleshooting, allowing experts to assist onsite staff from anywhere in the world.
In essence, automated sheet metal forming continues to evolve rapidly, driven by digitalization, smart technologies, and sustainability goals. These developments position manufacturers to meet growing demands for complex, high-quality metal parts with greater speed, flexibility, and environmental responsibility.
EMS Metalworking Machines
We design, manufacture and assembly metalworking machinery such as:
- Hydraulic transfer press
- Glass mosaic press
- Hydraulic deep drawing press
- Casting press
- Hydraulic cold forming press
- Hydroforming press
- Composite press
- Silicone rubber moulding press
- Brake pad press
- Melamine press
- SMC & BMC Press
- Labrotaroy press
- Edge cutting trimming machine
- Edge curling machine
- Trimming beading machine
- Trimming joggling machine
- Cookware production line
- Pipe bending machine
- Profile bending machine
- Bandsaw for metal
- Cylindrical welding machine
- Horizontal pres and cookware
- Kitchenware, hotelware
- Bakeware and cuttlery production machinery
as a complete line as well as an individual machine such as:
- Edge cutting trimming beading machines
- Polishing and grinding machines for pot and pans
- Hydraulic drawing presses
- Circle blanking machines
- Riveting machine
- Hole punching machines
- Press feeding machine
You can check our machinery at work at: EMS Metalworking Machinery – YouTube
Applications:
Flange-punching
Beading and ribbing
Flanging
Trimming
Curling
Lock-seaming
Ribbing